Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring of Air Quality Indicators during Outdoor Renovation Activities around a Dwelling House
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
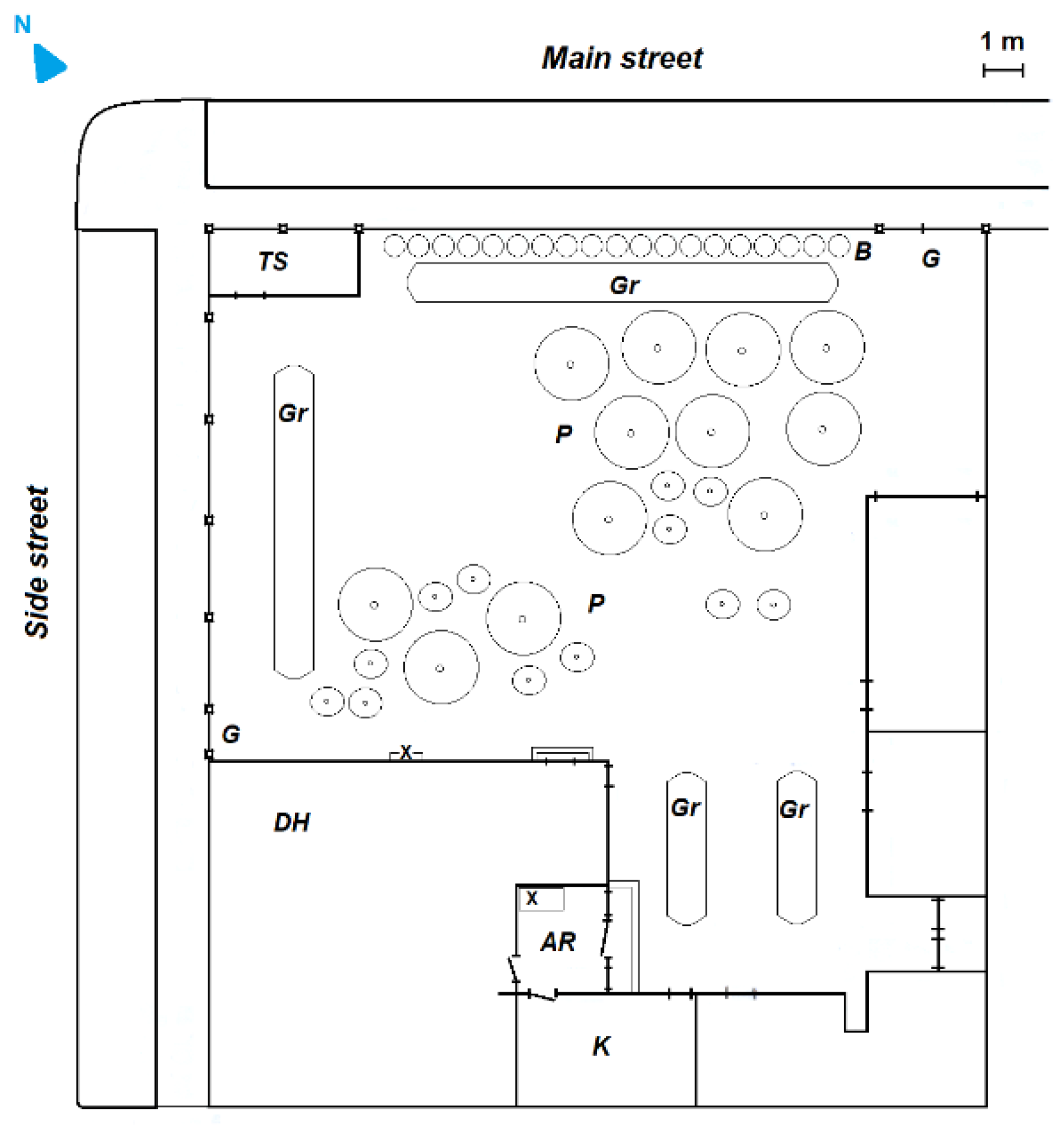
2.1. Description of the Sampling Site and Related Refurbishment Activities
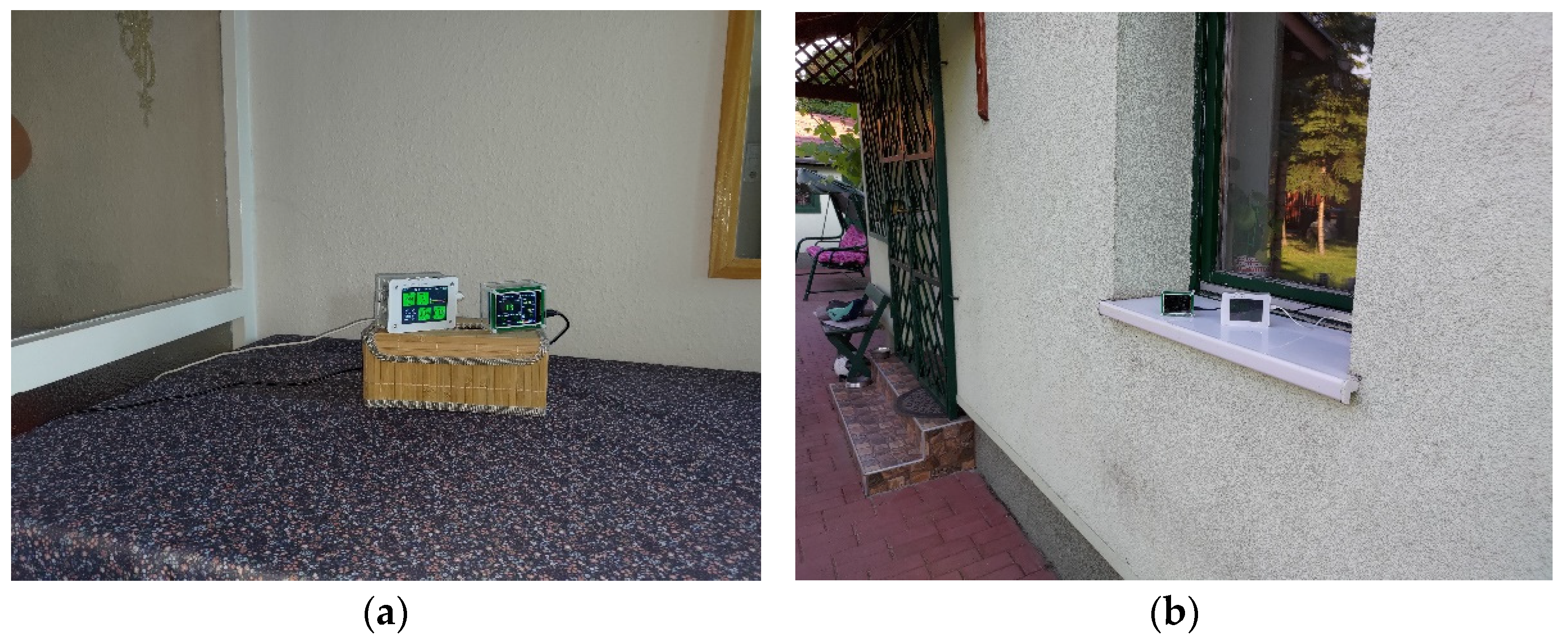
2.2. Instrumentation and Methods
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Indoor and Outdoor Aerosols, Microclimatic Variables and Their Ratios
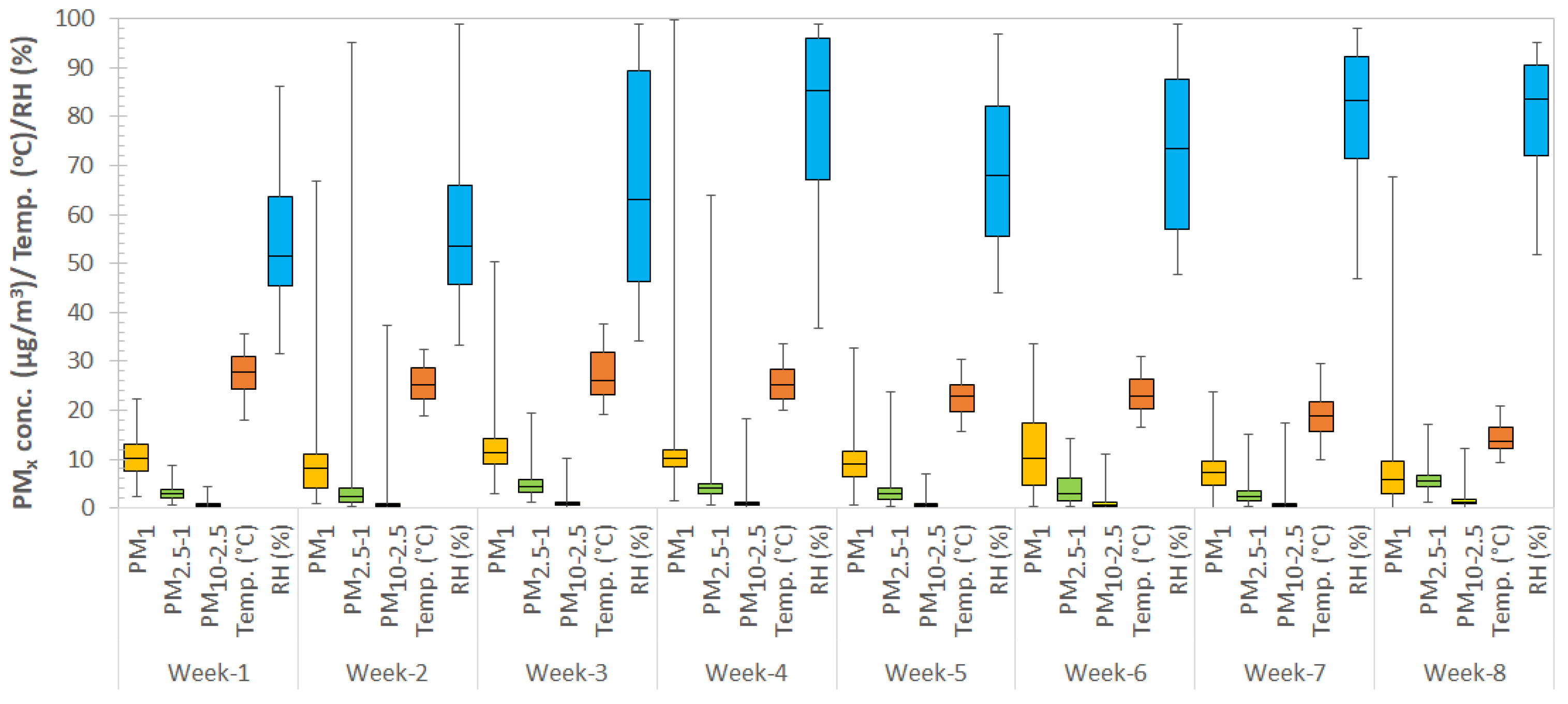
3.1.1. Weekly Outdoor Aerosols and Microclimatic Variations
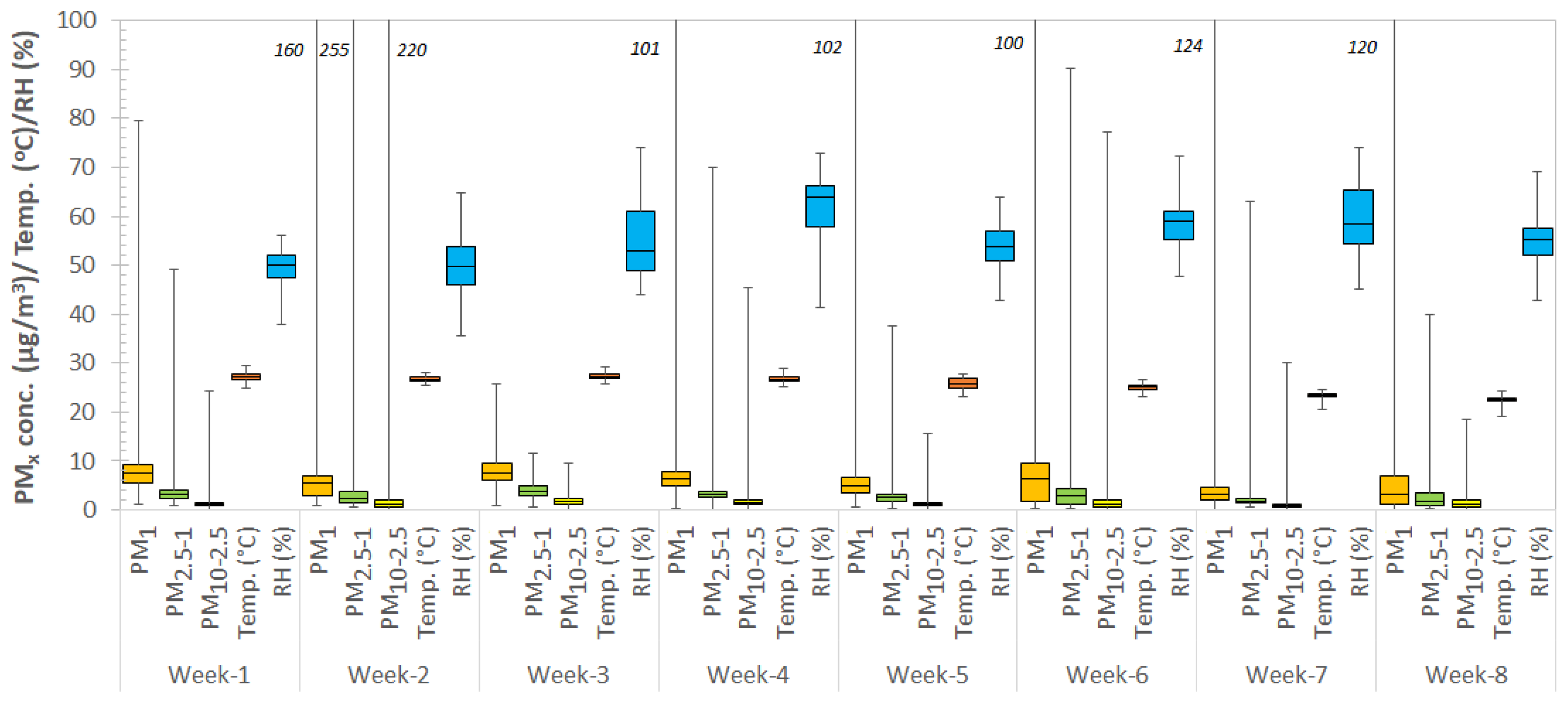
3.1.2. Weekly Indoor Aerosols and Microclimatic Parameters
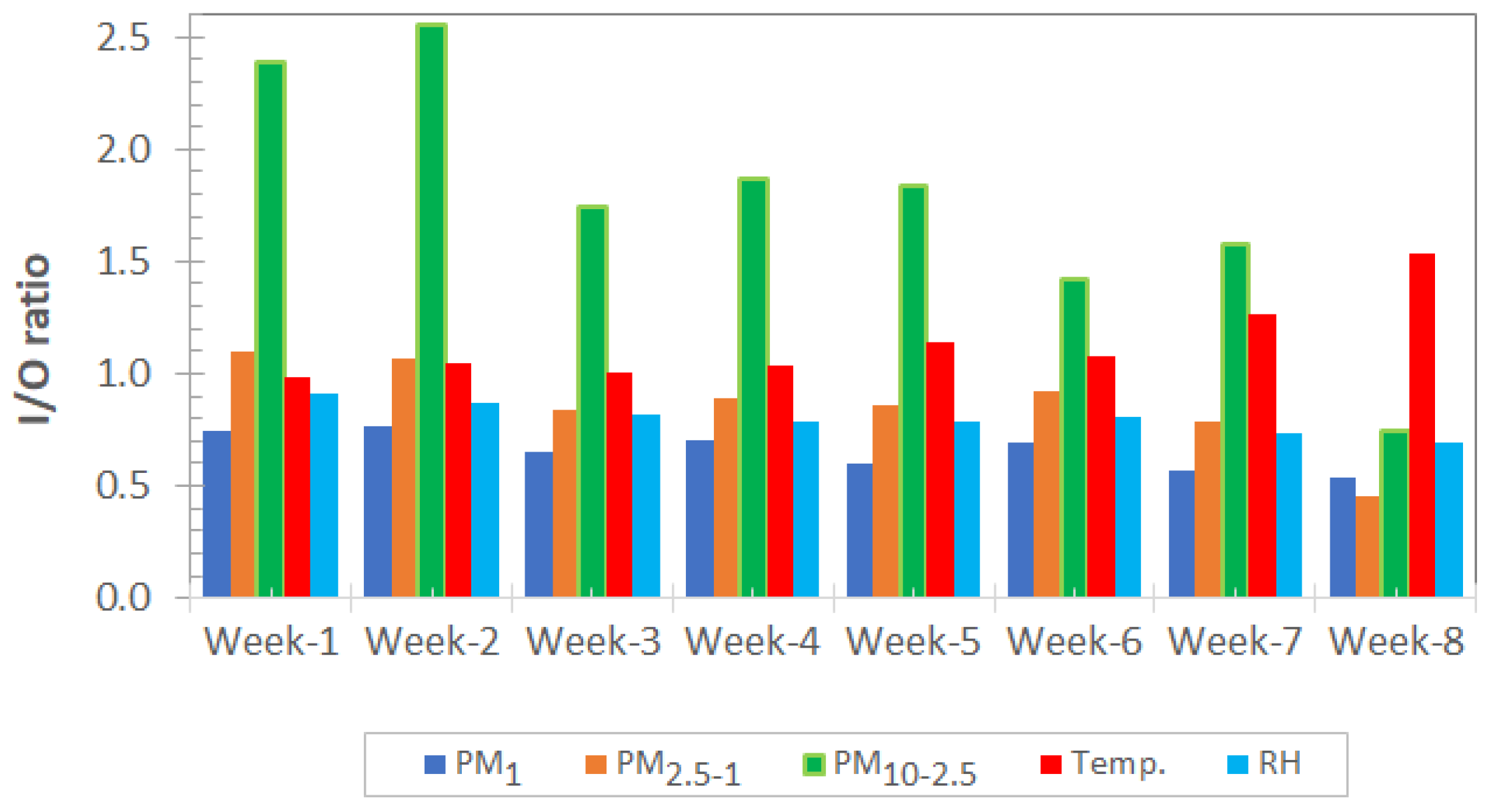
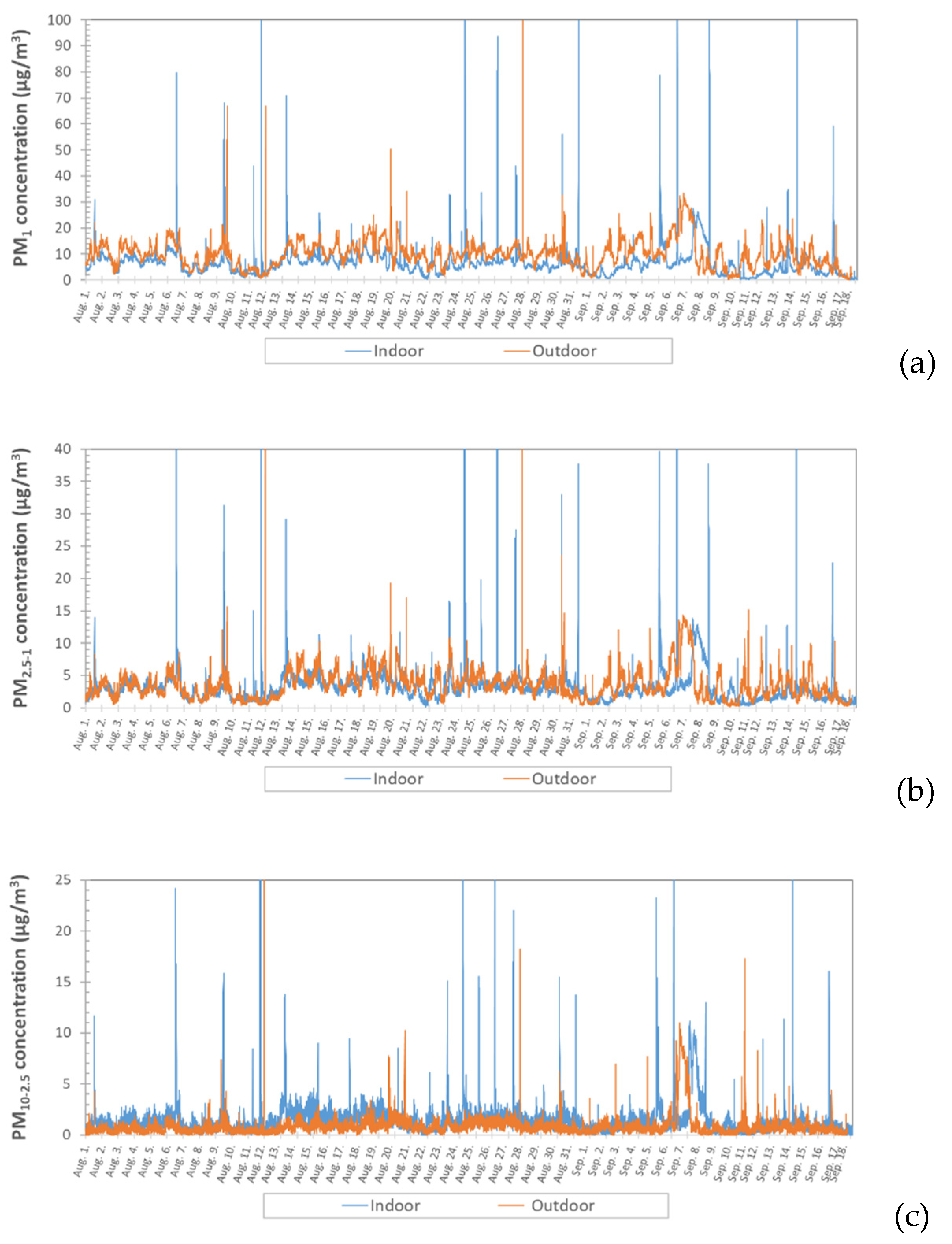
3.1.3. Weekly Trends of Indoor–Outdoor PMx Ratios
3.1.4. Weekly Outdoor Levels of Gaseous Components
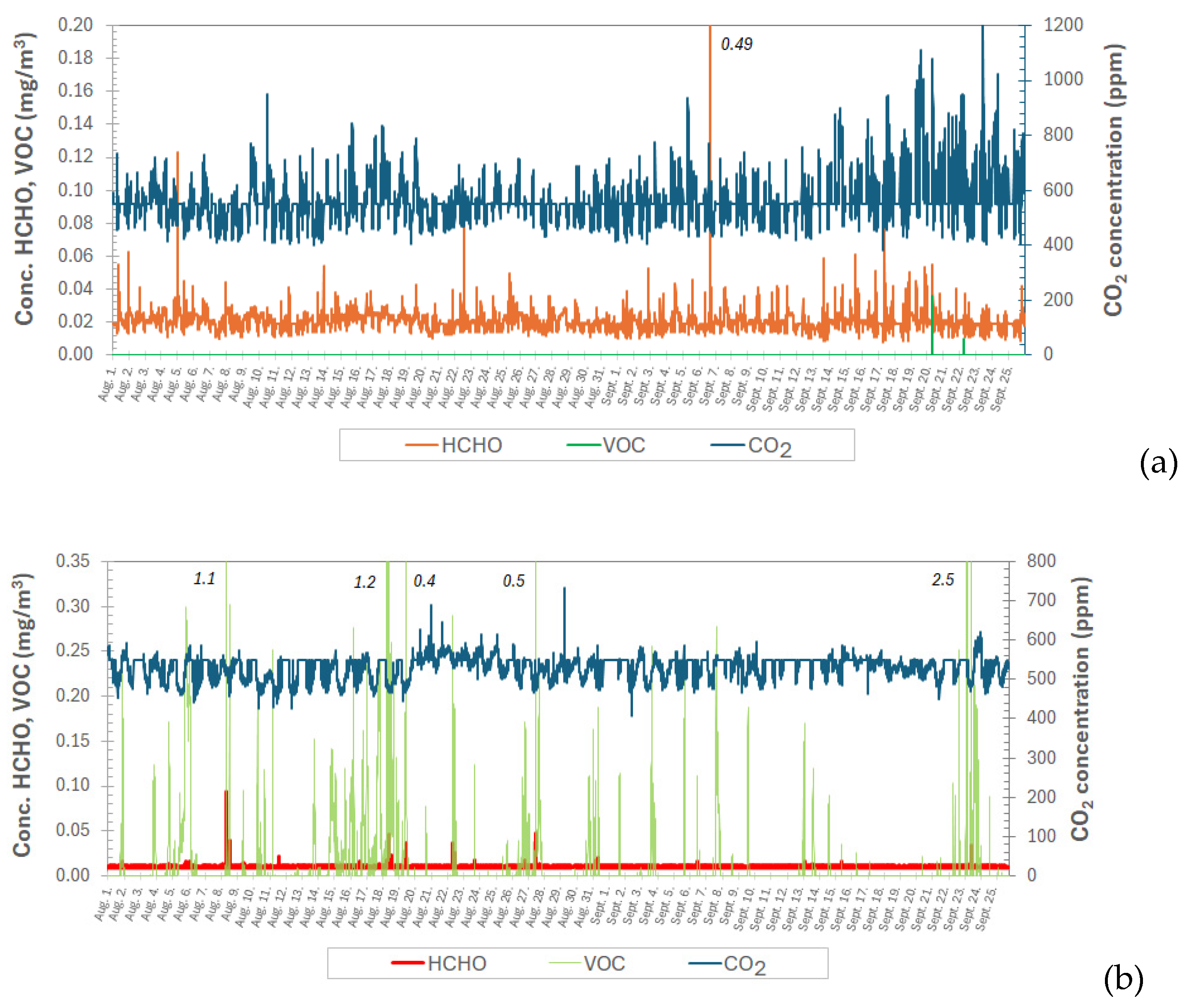
3.1.5. Weekly Indoor Levels of Gaseous Components
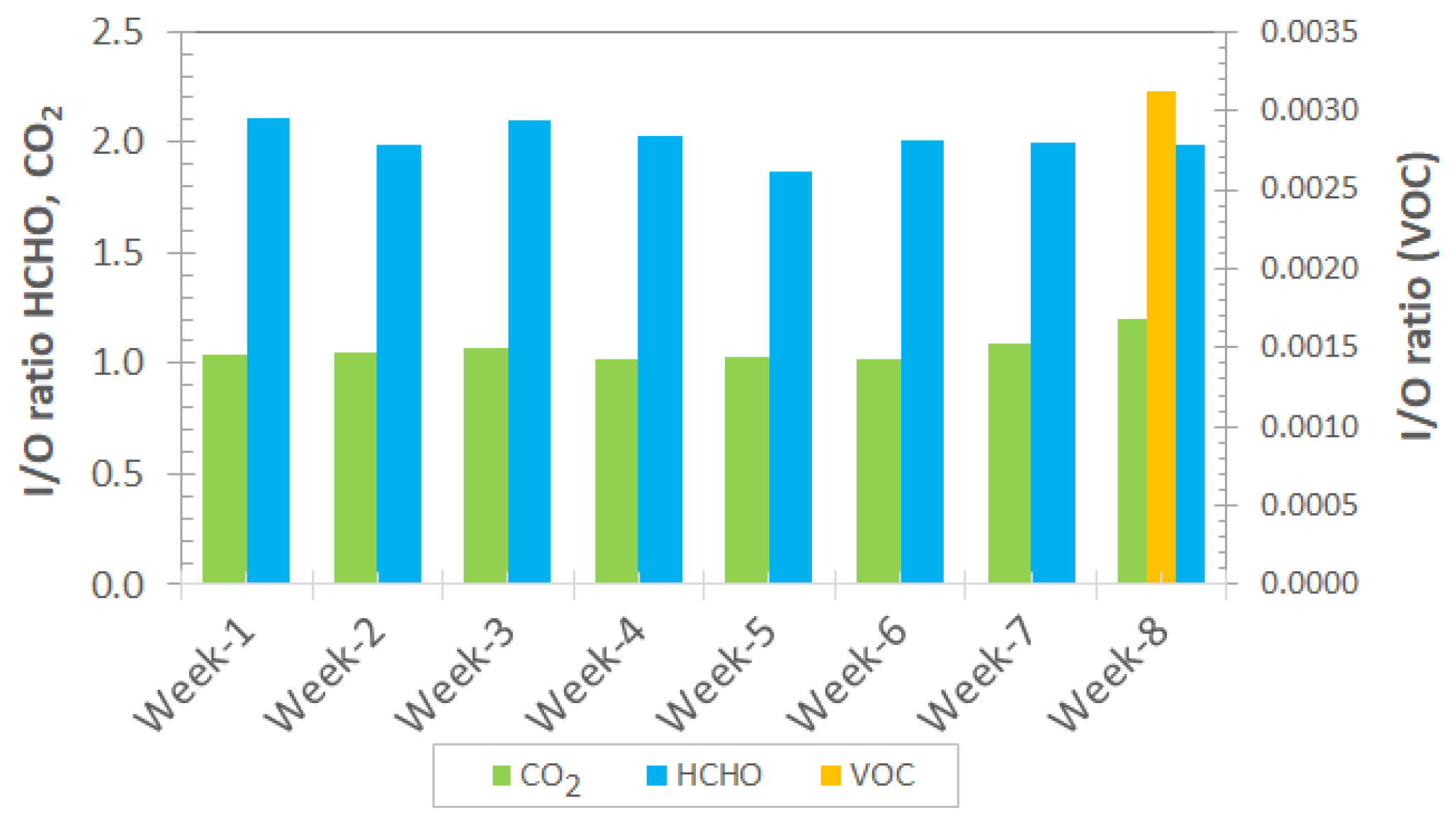
3.1.6. Weekly Indoor-to-Outdoor Ratios for Gaseous Air Pollutants
3.2. Over-Campaign Temporal Evolution of PMx and Gaseous Pollutants
3.2.1. Trends of Indoor and Outdoor PMx
3.2.2. Temporal Evolution of Gaseous Pollutants
3.3. Correlation of Indoor and Outdoor PMx and Gaseous Pollutants
3.4. Temporal Changes in Pollutants at a Nearby Air Quality Station
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis, Sixth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dockery, D.W.; Speizer, F.E.; Stram, D.O.; Ware, J.H.; Spengler, J.D.; Ferris, B.G., Jr. Effects of inhalable particles on respiratory health of children. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolnik, Z.; Bencs, L.; Worobiec, A.; Kontozova, V.; Van Grieken, R. Application of EDXRF and thin window EPMA for the investigation of the influence of hot air heating on the generation and deposition of particulate matter. Microchim. Acta 2005, 149, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stranger, M.; Krata, A.; Kontozova-Deutsch, V.; Bencs, L.; Deutsch, F.; Worobiec, A.; Naveau, I.; Roekens, E.; Van Grieken, R. Monitoring of NO2 in the ambient air with passive samplers before and after a road reconstruction event. Microchem. J. 2008, 90, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencs, L.; Ravindra, K.; de Hoog, J.; Spolnik, Z.; Bleux, N.; Berghmans, P.; Deutsch, F.; Roekens, E.; Van Grieken, R. Appraisal of measurement methods, chemical composition and sources of fine atmospheric particles over six different areas of Northern Belgium. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3421–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaeh, S.E.; Koehler, K.; Eakin, M.N.; Wohn, C.; Diibor, I.; Eckmann, T.; Wu, T.D.; Clemons-Erby, D.; Gummerson, C.E.; Green, T.; et al. Indoor air quality prior to and following school building renovation in a Mid-Atlantic school district. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Sohn, J.; Kim, J.; Son, B.; Park, J. Indoor air quality investigation according to age of the school buildings in Korea. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaeel, W.S.E.; Alamoudy, F.O.; Sameh, R. How renovation activities may jeopardise indoor air quality: Accounting for short and long-term symptoms of sick building syndrome in educational buildings. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2023, 19, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Baharudin, N.H.; Velayutham, P.; Awang, N.; Hamdan, H.; Mohamed, R.; Mokhtar, M.B. Composition of heavy metals and airborne fibers in the indoor environment of a building during renovation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, M.T.; Na, T.S.; Baharudin, N.H.; Srithawirat, T.; Mohamad, N.; Khan, M.F.; Sulaiman, F.R. Composition of trace metals in indoor dust during and after building renovation. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2018, 17, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzig, M.; Mohr, S.; Heinzow, B.; Knoppel, H. VOC emissions after building renovations: Traditional and less common indoor air contaminants, potential sources, and reported health complaints. Indoor Air 1998, 8, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.; Blahout, B.; Benner, D.; Popp, W. Environmental sampling of particulate matter and fungal spores during demolition of a building on a hospital area. J. Hosp. Infect. 2008, 70, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánka, I.; Földváry, V. Indoor air quality of residential building before and after renovation. Slovak J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dodson, R.E.; Udesky, J.O.; Colton, M.D.; McCauley, M.; Camann, D.E.; Yau, A.Y.; Adamkiewicz, G.; Rudel, R.A. Chemical exposures in recently renovated low-income housing: Influence of building materials and occupant activities. Environ. Int. 2017, 109, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozielska, B.; Mainka, A.; Zak, M.; Kaleta, D.; Mucha, W. Indoor air quality in residential buildings in Upper Silesia, Poland. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derbez, M.; Wyart, G.; Le Ponner, E.; Ramalho, O.; Riberon, J.; Mandin, C. Indoor air quality in energy-efficient dwellings: Levels and sources of pollutants. Indoor Air 2018, 28, 318–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilčekova, S.; Apostoloski, I.Z.; Mečiarová, Ľ.; Burdová, E.K.; Kiseľák, J. Investigation of indoor air quality in houses of Macedonia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omelekhina, Y.; Nordquist, B.; Alce, G.; Caltenco, H.; Wallenten, P.; Borell, J.; Wierzbicka, A. Effect of energy renovation and occupants’ activities on airborne particle concentrations in Swedish rental apartments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 149995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, J.; Jung, C. Evaluating the indoor air quality after renovation at the greens in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Buildings 2021, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.A.A.; Yasser, I.H.; Khoder, I.M. Indoor air quality during renovation actions: A case study. J. Envion. Monit. 2004, 6, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, J.L.; Sun, C.J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, B.Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Deng, Q.H.; Zhang, X.; Qian, H.; et al. Associations between household renovation and rhinitis among preschool children in China: A cross-sectional study. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Lu, C.; Miao, Y.F.; Xiang, Y.G.; Chen, L.; Deng, Q.H. Outdoor particulate air pollution and indoor renovation associated with childhood pneumonia in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.H.; Lu, C.; Ou, C.Y.; Liu, W.W. Effects of early life exposure to outdoor air pollution and indoor renovation on childhood asthma in China. Build. Environ. 2015, 93, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejc, T.; Kukec, A.; Bizjak, M.; Godič-Torkar, K. Microbiological and chemical quality of indoor air in kindergartens in Slovenia. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 30, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Giagloglou, E.; Steinle, S.; Davis, A.; Sleeuwenhoek, A.; Galea, K.S.; Dixon, K.; Crawford, J.O. Indoor Exposure to Selected Air Pollutants in the Home Environment: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, B.; Barretta, L.; Del Giudice, A.; De Vito, S.; Di Francia, G.; Esposito, E.; Formisano, F.; Massera, E.; Miglietta, M.L.; Polichetti, T. A review of low-cost particulate matter sensors from the developers’ perspectives. Sensors 2020, 20, 6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.R.; Malings, C.; Pandis, S.N.; Presto, A.A.; McNeill, V.F.; Westervelt, D.M.; Beekmann, M.; Subramanian, R. From low-cost sensors to high-quality data: A summary of challenges and best practices for effectively calibrating low-cost particulate matter sensors. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 158, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.C.; Kumar, P.; Pilla, F.; Skouloudis, A.N.; Di Sabatino, S.; Ratti, C.; Yasar, A.; Rickerby, D. End-user perspective of low-cost sensors for outdoor air pollution monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencs, L.; Plósz, B.; Mmari, A.G.; Szoboszlai, N. Comparative Study on the Use of Some Low-Cost Optical Particulate Sensors for Rapid Assessment of Local Air Quality Changes. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencs, L.; Nagy, A. A Smoke Chamber Study on Some Low-Cost Sensors for Monitoring Size-Segregated Aerosol and Microclimatic Parameters. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Cohen, M.; Stabat, P.; Marchio, D. CO2 tracer gas concentration decay method for measuring air-exchange rate. Build. Environ. 2015, 84, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, R.A.G.; Hernández, L.E.M.; Schalm, O.; Rodríguez, E.H.; Sánchez, D.A.; Pérez, M.C.M.; Caraballo, V.N.; Jacobs, W.; Laguardia, A.M. A Low-Cost Calibration Method for Temperature, Relative Humidity, and Carbon Dioxide Sensors Used in Air Quality Monitoring Systems. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2007; Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality. Addendum q to ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2007; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010.
- Neumann, M.; Dlamini, W.N.; Sallah-Ud-Din, R.; Berekute, A.K.; Siregar, S.; Getnet, M.E.; Maulana, M.; Pan, W.C.; Lung, S.C.C.; Yu, K.P. Assessment of air pollution emitted during cooking using biomass and cleaner fuels in the Shiselweni region of Eswatini (Swaziland). Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO (World Health Organization). WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants, 1st ed.; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789289002134 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Hutter, H.P.; Moshammer, H.; Wallner, P.; Tappler, P.; Kundi, M. Volatile organic compounds: Guidelines from the Austrian working group on indoor air. In Indoor Air 2005, Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Indoor Air Quality and Climate, 4–9 September 2005, Beijing, China; Yang, X., Zhao, B., Zhao, R., Eds.; Volume 1–5, pp. 3519–3522.
- Gordon, S.M.; Callahan, P.J.; Nishioka, M.G.; Brinkman, M.C.; O’Rourke, M.K.; Lebowitz, M.D.; Moschandreas, D.J. Residential environmental measurements in the National Human Exposure Assessment Survey (NHEXAS) pilot study in Arizona: Preliminary results for pesticides and VOCs. J. Exposure Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1999, 9, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N.L.; Gauvin, D.; Guay, M.; Héroux, M.E.; Dupuis, G.; Legris, M.; Chan, C.C.; Dietz, R.N.; Lévesque, B. Housing characteristics and indoor concentrations of nitrogen dioxide and formaldehyde in Quebec City, Canada. Environ. Res. 2006, 102, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurvelin, J.; Vartiainen, M.; Jantunen, M.; Pasanen, P. Personal Exposure Levels and Microenvironmental Concentrations of Formaldehyde and Acetaldehyde in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area, Finland. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Allen, J.; Bahnfleth, W.; Bennett, B.; Bluyssen, P.M.; Boerstra, A.; Buonanno, G.; Cao, J.J.; Dancer, S.J.; Floto, A.; et al. Mandating indoor air quality for public buildings. Science 2024, 383, 1418–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Indoor Parameter | Outdoor Variable | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM1 | PM2.5-1 | PM10-2.5 | CO2 | HCHO | VOC | T | RH | |
| PM1 | 0.37 | 0.34 | 0.16 | −0.13 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.31 | −0.12 |
| PM2.5-1 | 0.40 | 0.43 | 0.13 | −0.04 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.30 | −0.06 |
| PM10-2.5 | 0.22 | 0.14 | 0.15 | −0.20 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.26 | −0.15 |
| CO2 | −0.05 | 0.13 | −0.19 | −0.19 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.32 | −0.22 |
| HCHO | 0.07 | 0.25 | −0.20 | −0.20 | −0.01 | 0.08 | 0.32 | −0.15 |
| VOC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| T | 0.01 | 0.10 | −0.18 | −0.67 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.85 | −0.66 |
| RH | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.11 | −0.15 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bencs, L. Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring of Air Quality Indicators during Outdoor Renovation Activities around a Dwelling House. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070790
Bencs L. Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring of Air Quality Indicators during Outdoor Renovation Activities around a Dwelling House. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(7):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070790
Chicago/Turabian StyleBencs, László. 2024. "Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring of Air Quality Indicators during Outdoor Renovation Activities around a Dwelling House" Atmosphere 15, no. 7: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070790
APA StyleBencs, L. (2024). Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring of Air Quality Indicators during Outdoor Renovation Activities around a Dwelling House. Atmosphere, 15(7), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15070790






