A Fuzzy-Based Analysis of Air Particle Pollution Data: An Index IMC for Magnetic Biomonitoring
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
2.2. The Magnetic Index of Pollution
2.2.1. Fuzzy Inference System in a Nutshell
2.2.2. The Model
Input Variables—Selection
Input Variables—Construction of Membership Functions. Fuzzy c-Means and Membership Functions
Fuzzy Number as the Response of the IMC Model
The Base Rules
- Low perturbation of concentration χ (C1, i.e., the first row).
- Medium perturbation of ferromagnetic concentration SIRM” (C2, i.e., the second row).
- Low perturbation of coercivity Hcr” (C1, the third row).
- Medium perturbation of particle size SIRM/χ (C2, the fourth row).
2.3. An Indicator of the Accuracy of the Model
2.4. Model Selection
3. Results
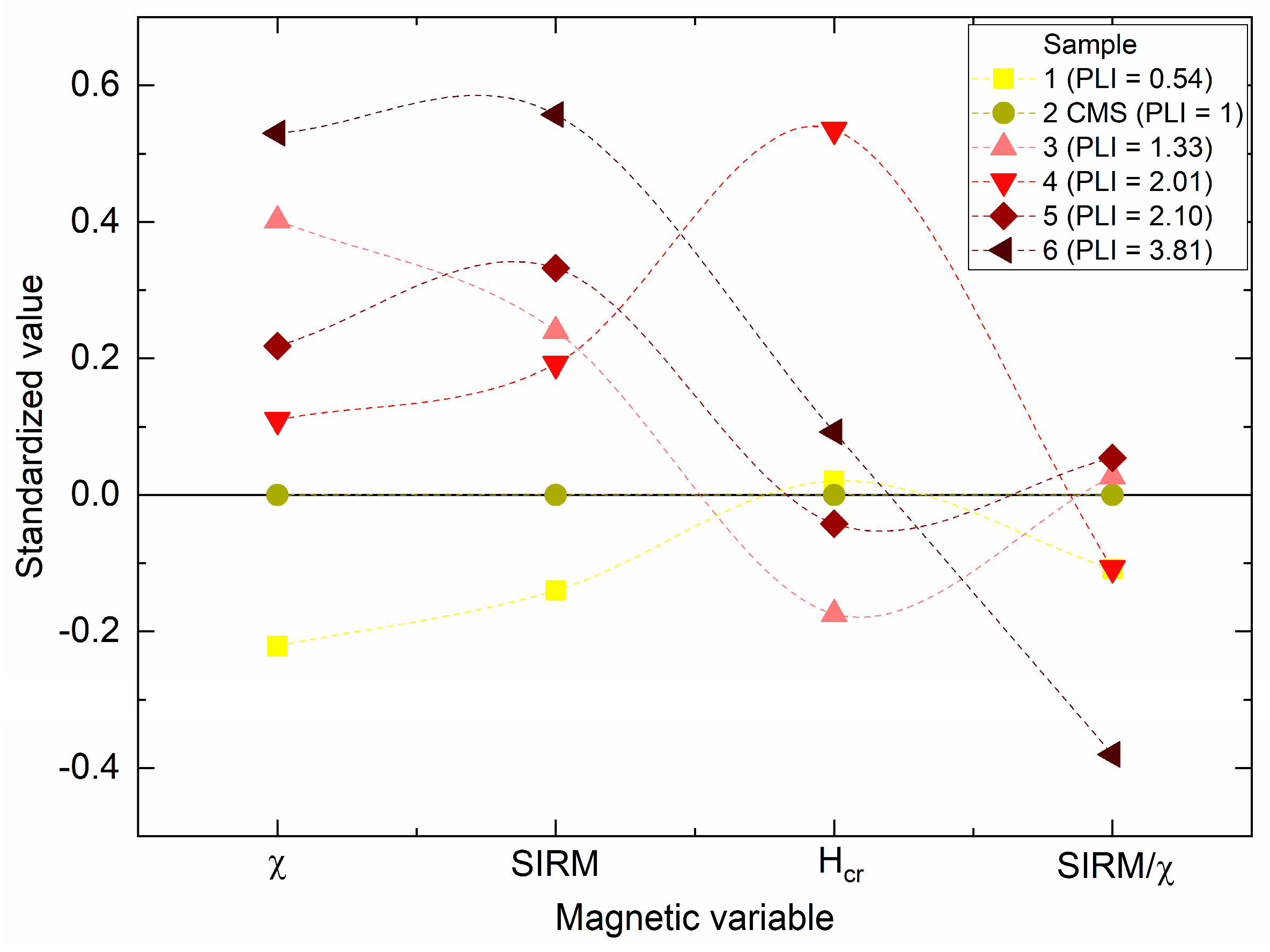
3.1. The Selected Model
3.2. Rules Base
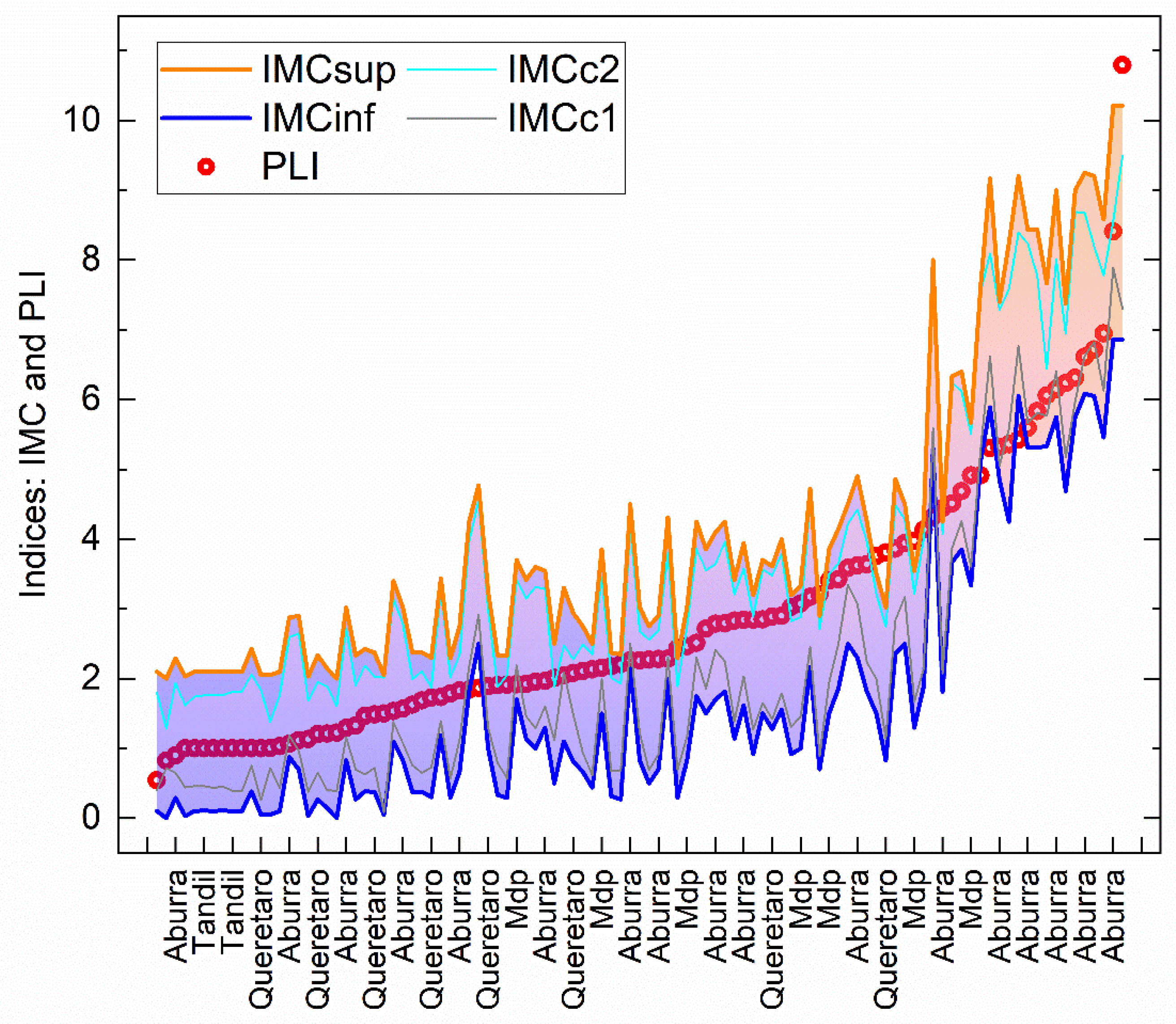
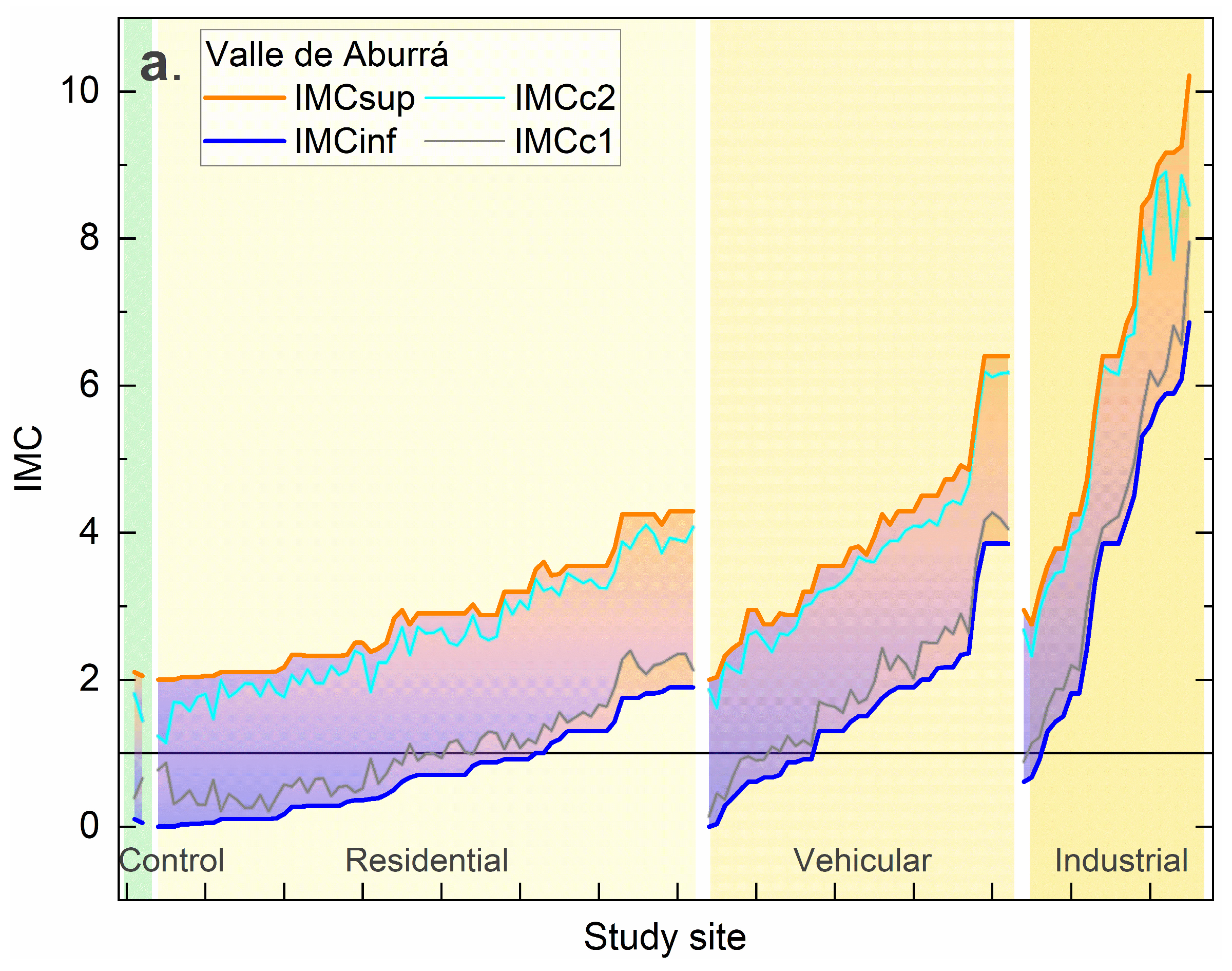
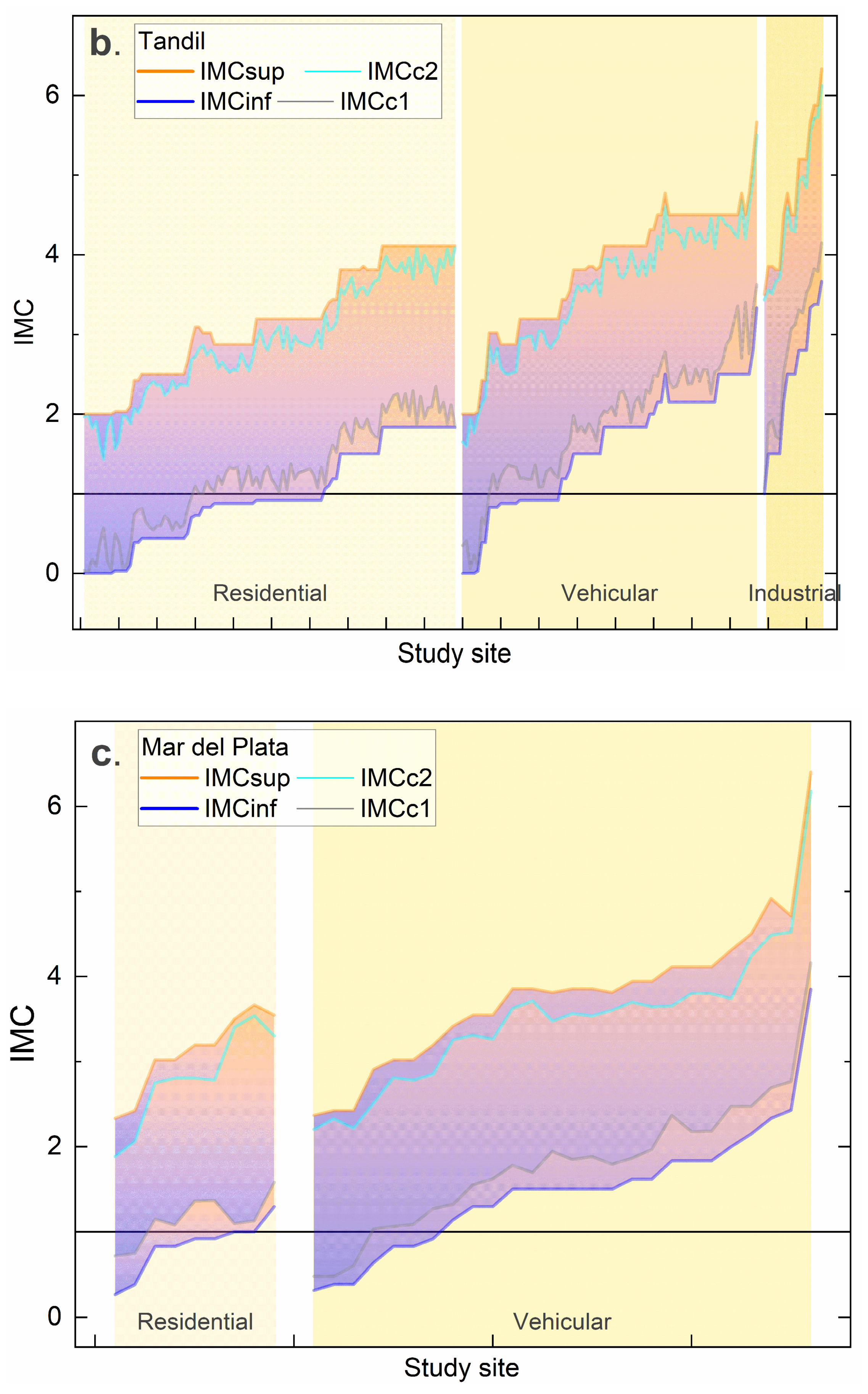
3.3. Study Sites and Simulations
3.3.1. Dataset with PLI of Reference
3.3.2. Estimation of Value IMC without PLI of Reference
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate matter (PM 2.5 and PM 10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 290.
- Schiavo, B.; Meza-Figueroa, D.; Vizuete-Jaramillo, E.; Robles-Morua, A.; Angulo-Molina, A.; Reyes-Castro, P.A.; Inguaggiato, C.; Gonzalez-Grijalva, B.; Pedroza-Montero, M. Oxidative Potential of Metal-Polluted Urbsan Dust as a Potential Environmental Stressor for Chronic Diseases. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 3229–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton-Bermea, O.; Hernández-Alvarez, E.; Almorín-Ávila, M.A.; Ordoñez-Godínez, S.; Bermendi-Orosco, L.; Retama, A. Historical Trends of Metals Concentration in PM10 Collected in the Mexico City Metropolitan Area between 2004 and 2014. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2781–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanfi, M.Y.; Mostafa, M.Y.A.; Zhukovsky, M.V. Heavy Metal Contamination in Urban Surface Sediments: Sources, Distribution, Contamination Control, and Remediation. Environ. Monit. Assess 2020, 192, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E. Airborne Particle Accumulation and Loss in Pollution-Tolerant Lichens and Its Magnetic Quantification. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Airborne Magnetite- and Iron-Rich Pollution Nanoparticles: Potential Neurotoxicants and Environmental Risk Factors for Neurodegenerative Disease, Including Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 71, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; González-Maciel, A.; Mukherjee, P.S.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Pérez-Guillé, B.; Gayosso-Chávez, C.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Cross, J.V.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.V.; et al. Combustion and Friction-Derived Magnetic Air Pollution Nanoparticles in Human Hearts. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.M.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D.A.; Foulds, P.G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D.M.A.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Magnetite Pollution Nanoparticles in the Human Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad.Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10797–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiera, T.; Górka-Kostrubiec, B.; Szumiata, T.; Wawer, M. Technogenic Magnetic Particles from Steel Metallurgy and Iron Mining in Topsoil: Indicative Characteristic by Magnetic Parameters and Mössbauer Spectra. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgeaud, V.M.; Rochette, P.; Ambrosi, J.P.; Vandamme, D.; Williamson, D. Relationship between Heavy Metals and Magnetic Properties in a Large Polluted Catchment: The Etang de Berre (South of France). Phys. Chem. Earth 1997, 22, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Ramírez-Ramírez, M.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Miranda-Avilés, R.; Puy-Alquiza, M.J.; Böhnel, H.N.; Zanor, G.A. Magnetic Parameters as Proxies for Anthropogenic Pollution in Water Reservoir Sediments from Mexico: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordanova, D.; Petrov, P.; Hoffmann, V.; Gocht, T.; Panaiotu, C.; Tsacheva, T.; Jordanova, N. Magnetic Signature of Different Vegetation Species in Polluted Environment. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2010, 54, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Lavornia, J.M.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Sinito, A.M. Biomonitors of Urban Air Pollution: Magnetic Studies and SEM Observations of Corticolous Foliose and Microfoliose Lichens and Their Suitability for Magnetic Monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuković, G.; Urošević, M.A.; Tomašević, M.; Samson, R.; Popović, A. Biomagnetic Monitoring of Urban Air Pollution Using Moss Bags (Sphagnum Girgensohnii). Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnotti, L.; Taddeucci, J.; Winkler, A.; Cavallo, A. Compositional, Morphological, and Hysteresis Characterization of Magnetic Airborne Particulate Matter in Rome, Italy. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovský, E.; Zbořil, R.; Grygar, T.M.; Kotlík, B.; Novák, J.; Kapička, A.; Grison, H. Magnetic Particles in Atmospheric Particulate Matter Collected at Sites with Different Level of Air Pollution. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2013, 57, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovský, E.; Kapička, A.; Grison, H.; Kotlík, B.; Miturová, H. Negative Correlation between Concentration of Iron Oxides and Particulate Matter in Atmospheric Dust: Case Study at Industrial Site during Smoggy Period. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapička, A.; Petrovský, E.; Ustjak, S.; Macháčková, K. Proxy Mapping of Fly-Ash Pollution of Soils around a Coal-Burning Power Plant: A Case Study in the Czech Republic. J. Geochem. Explor. 1999, 66, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marié, D.C.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Gogorza, C.S.G.; Navas, A.; Sinito, A.M. Vehicle-Derived Emissions and Pollution on the Road Autovia 2 Investigated by Rock-Magnetic Parameters: A Case Study from Argentina. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2010, 54, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirő-Kósa, I.; Ahmad, F.; Hoffer, A.; Pósfai, M. Nanoscale Physical and Chemical Properties of Individual Airborne Magnetic Particles from Vehicle Emissions. Atmos. Environ. X 2022, 15, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, P.J. Collection, Measurement, and Analysis of Airborne Magnetic Particulates from Pollution in the Environment. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 5931–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, H.; Paturi, P.; Mäkinen, J. Moss Bag (Sphagnum Papillosum) Magnetic and Elemental Properties for Characterising Seasonal and Spatial Variation in Urban Pollution. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marié, D.C.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Irurzun, M.A.; Lavornia, J.M.; Marinelli, C.; Cepeda, R.; Böhnel, H.N.; Castañeda Miranda, A.G.; Sinito, A.M. Magnetic Mapping of Air Pollution in Tandil City (Argentina) Using the Lichen Parmotrema Pilosum as Biomonitor. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehndorff, E.; Urbat, M.; Schwark, L. Accumulation Histories of Magnetic Particles on Pine Needles as Function of Air Quality. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7082–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, G.; Gómez-Paccard, M.; Osete, M.L. The Magnetic Properties of Particles Deposited on Platanus x hispanica Leaves in Madrid, Spain, and their Temporal and Spatial Variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.; Maher, B.A.; Kinnersley, R. Rates of Particulate Pollution Deposition onto Leaf Surfaces: Temporal and Inter-Species Magnetic Analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzola, L.C.; Muttoni, G.; Merlini, M.; Rotiroti, N.; Pagliardini, L.; Hirt, A.M.; Pelfini, M. Investigating Distribution Patterns of Airborne Magnetic Grains Trapped in Tree Barks in Milan, Italy: Insights for Pollution Mitigation Strategies. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Castañeda-Miranda, A.G.; Marié, D.C.; Gargiulo, J.D.; Lavornia, J.M.; Natal, M.; Böhnel, H.N. Fine Air Pollution Particles Trapped by Street Tree Barks: In Situ Magnetic Biomonitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, A.; Caricchi, C.; Guidotti, M.; Owczarek, M.; Macrì, P.; Nazzari, M.; Amoroso, A.; Di Giosa, A.; Listrani, S. Combined Magnetic, Chemical and Morphoscopic Analyses on Lichens from a Complex Anthropic Context in Rome, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, A.; Contardo, T.; Vannini, A.; Sorbo, S.; Basile, A.; Loppi, S. Magnetic Emissions from Brake Wear Are the Major Source of Airborne Particulate Matter Bioaccumulated by Lichens Exposed in Milan (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Miranda, A.G.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Böhnel, H.N. Magnetic Properties of Tillandsia Recurvata L. and Its Use for Biomonitoring a Mexican Metropolitan Area. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Echeverry, D.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Duque-Trujillo, J.F.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Castañeda Miranda, A.G. Magnetic Biomonitoring as a Tool for Assessment of Air Pollution Patterns in a Tropical Valley Using Tillandsia sp. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Buitrago Posada, D.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Molinari, D.; Chiavarino, L.; Alba, B.; Marié, D.C.; Natal, M.; Böhnel, H.N.; Vaira, M. Urban and suburban’s airborne magnetic particles accumulated on Tillandsia capillaris. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Castañeda Miranda, A.G.; Böhnel, H.N.; Sinito, A.M. An Interval Fuzzy Model for Magnetic Biomonitoring Using the Specie Tillandsia recurvata L. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 54, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Gurgatz, B.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Canavese de Oliveira, D.; Joucoski, E.; Antoniaconi, G.; Hilário do Nascimento Saldiva, P.; Arantes Reis, R. Atmospheric metal pollutants and environmental injustice: A methodological approach to environmental risk analysis using fuzzy logic and tree bark. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 71, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy-Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klir, G.J.; Yuan, B. Fuzzy Sets and Fuzzy Logic: Theory and Applications; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Walden, J.; Oldfield, F.; Smith, J.P. (Eds.) Environmental Magnetism: A Practical Guide; Quaternary Research Association: London, UK, 1999; Volume Technical Guide, No. 6; p. 243. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, C.; Dekkers, M.J. Selected Room Temperature Magnetic Parameters as a Function of Mineralogy, Concentration and Grain Size. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts 2003, 28, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Characterisation of Soils by Mineral Magnetic Measurements. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 1986, 42, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
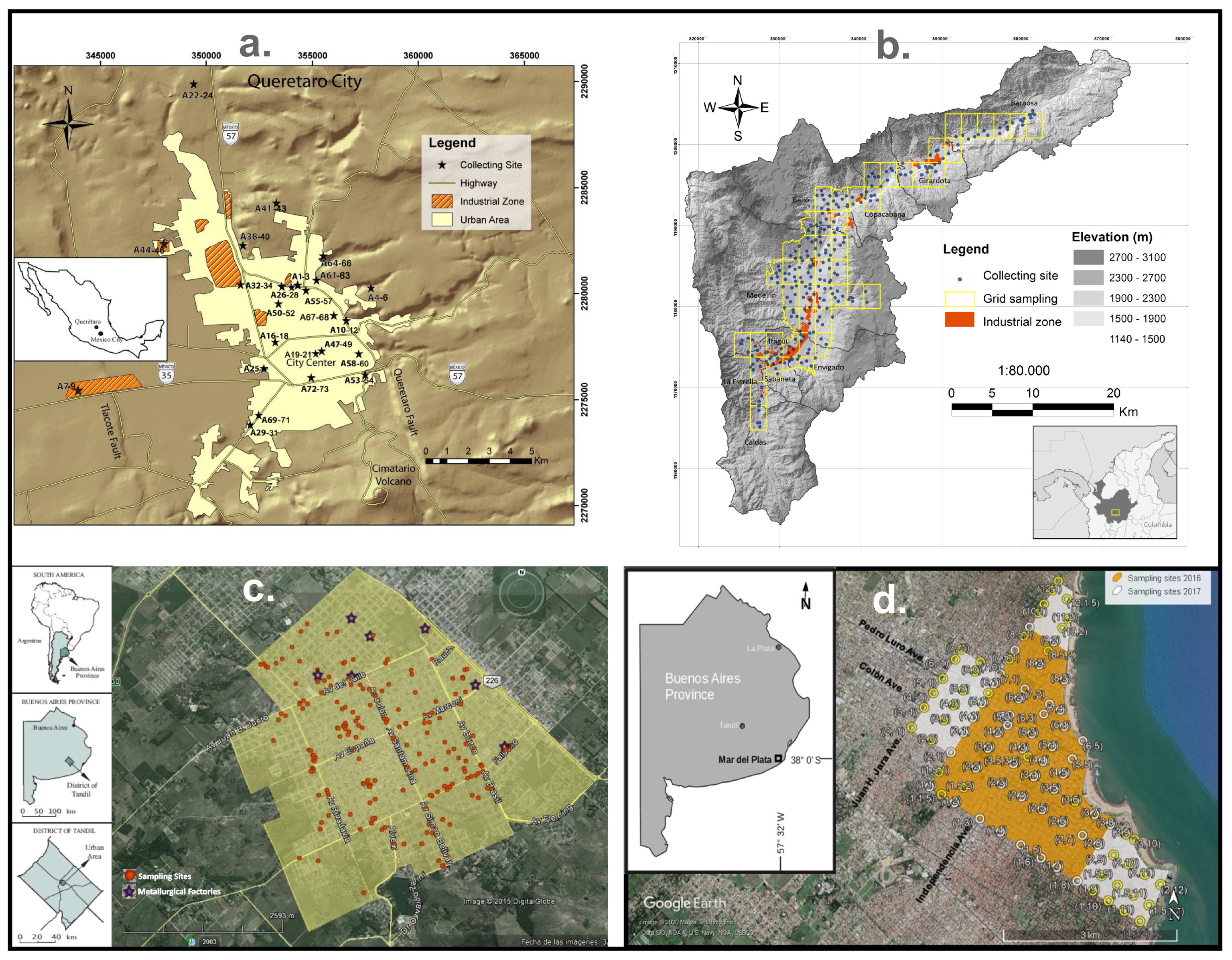


| Dataset | Area km2 | n | Biomonitor and Species | χ 10−8 m3 kg−1 | SIRM 10−3 Am2 kg−1 | Hcr mT | SIRM/χ kA m−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valle de Aburrá [32] | 290 | 185 | Tillandsia sp.: T. recurvata | 4.3 | 0.7 | 33.8 | 17.7 |
| Mar del Plata [28] | 11 | 54 | Tree barks: Cordyline australis, Fraxinus excelsior L., F. pensylvanica | 18.4 | 2.5 | 37.4 | 13.6 |
| Santiago de Querétaro [31] | 25 | 25 | Tillandsia sp.: T. recurvata | 5.5 | 1.4 | 39.7 | 25.7 |
| Tandil [13,23] | 17 | 208 | Lichens: Parmotrema pilosum, Punctelia hipoleucites, Dirinaria picta | 23.9 | 4.0 | 38.2 | 17.1 |
| Variable | χ | SIRM | Hcr | SIRM/χ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF1 | L | −2.000 | −0.800 | −1.000 | −1.000 |
| center | −0.250 | −0.202 | −0.082 | −0.284 | |
| U | 0.210 | 0.106 | −0.005 | −0.120 | |
| MF2 | L | −0.250 | −0.202 | −0.082 | −0.284 |
| center | 0.210 | 0.106 | −0.005 | −0.120 | |
| U | 0.690 | 0.332 | 0.028 | 0.018 | |
| MF3 | L | 0.210 | 0.106 | −0.005 | −0.120 |
| center | 0.690 | 0.332 | 0.028 | 0.018 | |
| U | 1.260 | 0.575 | 0.067 | 1.000 | |
| MF4 | L | 0.690 | 0.332 | 0.028 | |
| center | 1.260 | 0.575 | 0.067 | ||
| U | 3.000 | 0.812 | 1.000 | ||
| MF5 | L | 0.575 | |||
| center | 0.812 | ||||
| U | 1.148 | ||||
| MF6 | L | 0.812 | |||
| center | 1.148 | ||||
| U | 3.000 |
| Rule | IMC | Rule | IMC | Rule | IMC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1112 | 1 | 2333 | 1 ∩ 2 ∩ 4 | 4541 | 4 ∩ 6 |
| 1133 | 1 | 3431 | 3 | 4642 | 5 ∩ 7 |
| 1233 | 1 | 3433 | 3 | 4622 | 6 ∩ 7 |
| 2212 | 1 | 3423 | 2 ∩ 4 | 4532 | 7 |
| 2222 | 1 | 2211 | 4 | 4631 | 5 ∩ 9 |
| 2311 | 1 | 3311 | 4 | 4611 | 7 ∩ 8 |
| 1113 | 1 ∩ 2 | 3341 | 4 | 4641 | 8 ∩ 10 |
| 2213 | 1 ∩ 2 | 3543 | 4 | ||
| 2233 | 1 ∩ 2 | 3411 | 2 ∩ 4 ∩ 5 | ||
| 2312 | 1 ∩ 2 | 3412 | 2 ∩ 4 ∩ 5 | ||
| 1142 | 2 | 3332 | 2 ∩ 5 | ||
| 1143 | 2 | 3523 | 2 ∩ 5 | ||
| 2243 | 2 | 3533 | 2 ∩ 5 | ||
| 2313 | 2 | 3432 | 4 ∩ 5 | ||
| 2332 | 2 | 3441 | 4 ∩ 5 | ||
| 3241 | 2 | 3522 | 5 | ||
| 3442 | 2 | 4632 | 5 | ||
| 3443 | 2 | 4633 | 5 | ||
| 3531 | 2 | 4511 | 6 | ||
| 3532 | 2 | 4512 | 6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Molinari, D.A. A Fuzzy-Based Analysis of Air Particle Pollution Data: An Index IMC for Magnetic Biomonitoring. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040435
Chaparro MAE, Chaparro MAE, Molinari DA. A Fuzzy-Based Analysis of Air Particle Pollution Data: An Index IMC for Magnetic Biomonitoring. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040435
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaparro, Mauro A. E., Marcos A. E. Chaparro, and Daniela A. Molinari. 2024. "A Fuzzy-Based Analysis of Air Particle Pollution Data: An Index IMC for Magnetic Biomonitoring" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040435
APA StyleChaparro, M. A. E., Chaparro, M. A. E., & Molinari, D. A. (2024). A Fuzzy-Based Analysis of Air Particle Pollution Data: An Index IMC for Magnetic Biomonitoring. Atmosphere, 15(4), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040435







