Influence of Saharan Dust on the Composition of Urban Aerosols in Palermo City (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Analysis
2.2. Enrichment Factor (EF)
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Caravaca, A.; Castañer, R.; Clemente, A.; Yubero, E.; Galindo, N.; Crespo, J.; Nicolás, J.F. The Impact of IntenseWinter Saharan Dust Events on PM and Optical Properties at Urban Sites in the Southeast of the Iberian Peninsula. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabatas, B.; Unal, A.; Pierce, R.B.; Kindap, T.; Pozzoli, L. The contribution of Saharan dust in PM10 concentration levels in Anatolian Peninsula of Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logothetis, S.A.; Salamalikis, V.; Gkikas, A.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Kazantzidis, A. 15-year variability of desert dust optical depth on global and regional scales. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16499–16529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkikas, A.; Proestakis, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Di Tomaso, E.; Marinou, E.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Kok, J.F.; Pérez García-Pando, C. Quantification of the dust optical depth across spatiotemporal scales with the MIDAS global dataset (2003–2017). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 3553–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Nicolas, J.F.; Varea, M.; Gil-Molto, J.; Crespo, C. Regional and long-range transport of aerosols at Mt. Aitana, Southeastern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaios, V.N.; Triantafyllou, A.G.; Koutrakis, P. PM10 episodes in Greece: Local sources versus long-range transport observations and model simulations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Becagli, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Prati, P.; Traversi, R.; Udisti, R.; Valli, G.; Vecchi, R. Saharan dust impact in central Italy: An overview on three years elemental data records. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 60, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Perez, N.; Reche, C.; Ealo, M.; Ripoll, A.; Tur, J.; Pandolfi, M.; Pey, J.; Salvador, P.; Moreno, T.; et al. African dust and air quality over Spain: Is it only dust that matters? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.S.; Middleton, N.J. Saharan dust storms: Nature and consequences. Earth Sci. Rev. 2001, 56, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallone, S.; Stafoggia, M.; Faustini, A.; Gobbi, G.P.; Marconi, A.; Forastiere, F. Saharan dust and associations between particulate matter and daily mortality in Rome, Italy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, O.M.; Mokgobu, M.I.; Mukhola, M.S.; Hunter, R.P. Health outcomes of exposure to biological and chemical components of inhalable and respirable particulate matter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A.; Lelieveld, J. Modeled global effects of airborne desert dust on air quality and premature mortality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Cuevas, E.; Rodríguez, S. Influence of African dust on the levels of atmospheric particulates in the Canary Islands air quality network. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5861–5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Kloster, S.; Engelstaedter, S.; Moore, J.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; McConnell, J.R.; Albani, S.; Doney, S.C.; Bhattacharya, A.; Curran, M.A.J.; et al. Observed 20th century desert dust variability: Impact on climate and biogeochemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10875–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, M.G.; Varrica, D. Recognition of Trace Element Contamination Using Ficus macrophylla Leaves in Urban Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 50, 10875–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Basart, S.; Kazadzis, S.; Votsis, A.; Gkikas, A.; Vandenbussche, S.; Tobias, A.; Gama, C.; Terradellas, E.; Nickovic, S.; et al. Multi-sectoral impact assessment of an extreme African dust episode in the Eastern Mediterranean in March 2018. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Clemente, A.; Nicolas, J.F.; Varea, M.; Crespo, J. PM events and changes in the chemical composition of urban aerosols: A case study in the western Mediterranean. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Kazadzis, S.; Taylor, M.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Raptis, P.I.; Marinou, E.; Proestakis, E.; Solomos, S.; Kontoes, C.; et al. Dust impact on surface solar irradiance assessed with model simulations, satellite observations and ground-based measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2435–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachristopoulou, K.; Fountoulakis, I.; Gkikas, A.; Kosmopoulos, P.G.; Nastos, P.T.; Hatzaki, M.; Kazadzis, S. 15-Year Analysis of Direct Effects of Total and Dust Aerosols in Solar Radiation/Energy over the Mediterranean Basin. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaimo, R.; Ferla, P. Presenza di paligorskite nella polvere trasportata dallo scirocco in Sicilia. In Implicazioni Geologiche ed Ambientali; Ist Min Petr Geoch: 1979; Quad 4; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolás, J.F.; Lucarelli, F.; Galindo, N.; Yubero, E.; Crespo, J.; Calzolai, G.; Nava, S. Impact of traffic flows and meteorological events on the hourly elemental composition of fine and coarse particles at an urban site. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grousset, F.E.; Biscaye, P.E. Tracing dust sources and transport patterns using Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozlaker, A.; Prospero, J.M.; Price, J.; Chellam, S. Linking Barbados mineral dust aerosols to North African sources using elemental composition and radiogenic Sr, Nd, and Pb isotope signatures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2018, 123, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Spyrou, C.; Barreto, A.; Rodríguez, S.; González, Y.; Neophytou, M.K.A.; Mouzourides, P.; Bartsotas, N.S.; Kalogeri, C.; Nickovic, S.; et al. The development of METAL-WRF Regional Model for the Description of Dust Mineralogy in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU-Commission. Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Milford, C.; Cuevas, E.; Marrero, C.L.; Bustos, J.J.; Gallo, V.; Rodríguez, S.; Romero-Campos, P.M.; Torres, C. Impacts of Desert Dust Outbreaks on Air Quality in Urban Areas. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, M.; Tobias, A.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; Schwartz, J.; Lorente, J.; Pey, J.; Querol, X. Effect of atmospheric mixing layer depth variations on urban air quality and daily mortality during Saharan dust outbreaks. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 494–495, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Camacho, R.; de la Rosa, J.; Sánchez de la Campa, A. Trends and sources vs air mass origins in a major city in South-western Europe: Implications for air quality management. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, L.; Tobias, A.; Querol, X.; Künzli, N.; Pey, J.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.; Valero, N.; González-Cabré, M.; Sunyer, J. Coarse particles from Saharan dust and daily mortality. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-4-151135-3.
- Stafoggia, M.; Zauli-Sajani, S.; Pey, J.; Samoli, E.; Alessandrini, E.; Basagaña, X.; Cernigliaro, A.; Chiusolo, M.; Demaria, M.; The MED-PARTICLES Study Group. Desert dust outbreaks in Southern Europe: Contribution to Daily PM10 concentrations and short-term associations with mortality and hospital admissions. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negral, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Moreno, J.; Querol, X.; Viana, M.; Alastuey, A. Natural and anthropogenic contributions to PM10 and PM2.5 in an urban area in the Western Mediterranean Coast. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 192, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Satsangi, P. Characterization of particulate matter and its related metal toxicity in an urban location in South West India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7365–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varrica, D.; Dongarrà, G.; Sabatino, G.; Monna, F. Inorganic geochemistry of roadway dust from the metropolitan area of Palermo (Italy). Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources of atmospheric aerosol from long-term measurements (5 years) of chemical composition in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerzoni, S.; Molinaroli, E.; Rossini, P.; Rampazzo, G.; Quarantotto, G.; Cristini, S. Role of desert aerosol in metal fluxes in the Mediterranean area. Chemosphere 1999, 39, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencharif-Madani, F.; Ali-Khodja, H.; Kemmouche, A.; Terrouche, A.; Lokorai, K.; Naidja, L.; Bouziane, M. Mass concentrations, seasonal variations, chemical compositions and element sources of PM10 at an urban site in Constantine, northeast Algeria. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 206, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Viana, M.; Salvador, P.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.; Artiñano, B.; de la Rosa, J.; Gibbons, W. Variations in atmospheric PM trace metal content in Spanish towns: Illustrating the chemical complexity of the inorganic urban aerosol cocktail. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6791–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandropoulou, V.; Torseth, K.; Lazaridis, M. Contribution of natural sources to PM emissions over the Metropolitan areas of Athens and Thessaloniki. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megido, L.; Negral, L.; Castrillón, L.; Suárez-Peña, B.; Fernández-Nava, Y.; Marañón, E. Enrichment factors to assess the anthropogenic influence on PM10in Gijón (Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Grivas, G.; Borge, R.; Lumbreras, J. Study of PM10 and PM2.5 Levels in three European Cities: Analysis of Intra and Inter Urban Variations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Ballester, F.; Llop, S.; Esplugues, A.; Fernández-Patier, R.; García dos Santos, S.; Herce, M.D. Characterising exposure to PM aerosols for an epidemiological study. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1552–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salma, I.; Maenhaut, W. Changes in elemental composition and mass of atmospheric aerosol pollution between 1996 and 2002 in a central European city. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 143, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adgate, J.L.; Mongin, S.J.; Pratt, G.C.; Zhang, J.; Field, M.P.; Ramachandran, G.; Sexton, K. Relationships between personal, indoor, and outdoor exposures to trace elements in PM2.5. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 386, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Tang, Y.; Arimoto, R.; Shen, Z.; Wu, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Elemental profiles and signatures of fugitive dusts from Chinese deserts. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Godoi, R.; Tauler, R.; André, P.; Saldiva, P.; Grieken, R.; Rodriguez de Marchi, M.R. Elemental composition of PM2.5 in Araraquara City (Southeast Brazil) during seasons with and without sugar cane burning. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abate, B.; Catalano, R.; Renda, P.M. Schema geologico dei Monti di Palermo. Boll. Della Soc. Geol. Ital. 1978, 97, 807–819. [Google Scholar]
- Alaimo, M.G.; Dongarrà, G.; Melati, M.R.; Monna, F.; Varrica, D. Recognition of environmental trace metal contamination using pine needles as bioindicators: The urban area of Palermo (Italy). Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrica, D.; Tamburo, E.; Vultaggio, M.; Di Carlo, I. ATR–FTIR spectral analysis and soluble components of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter over the urban area of Palermo (Italy) during normal days and saharan events. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Elert, K. Mineralogy and physicochemical features of Saharan dust wet deposited in the Iberian Peninsula during an extreme red rain event. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10089–10122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokorai, K.; Ali-Khodja, H.; Khardi, S.; Bencharif-Madani, F.; Naidja, L.; Bouziane, M. Influence of mineral dust on the concentration and composition of PM10 in the city of Constantine. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarrà, G.; Manno, E.; Varrica, D.; Vultaggio, M.; Lombardo, M. Study on ambient concentrations of PM10, PM10-2.5, PM2.5 and gaseous pollutants. Trace elements and chemical speciation of atmospheric particulates. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5244–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauskopf, K.B.; Bird, D.K. Introduction to Geochemistry, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Marconi, M.; Sferlazzo, D.M.; Becagli, S.; Bommarito, C.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; di Sarra, A.; Ghedini, C.; G’omez-Amo, J.L.; Lucarelli, F.; et al. Saharan dust aerosol over the central Mediterranean Sea: PM10 chemical composition and concentration versus optical columnar measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuvens, D.; Schütz, L.; Kandler, K.; Ebert, M.; Weinbruch, S. Bulk composition of northern African dust and its source sediments—A compilation. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 170–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Dee Tomasi, F.; Filippo, E.; Manno, D.; Perrone, M.R.; Serra, A.; Tafuro, M.; Tepore, A. Characterization of African dust over southern Italy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiapello, I.; Bergametti, G.; Chatenet, B.; Bousquet, P.; Dulac, F.; Soares, E.S. Origins of African dust transported over the northeastern tropical Atlantic. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 13701–13709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongarrà, G.; Varrica, D. The presence of heavy metals in air particulate at Vulcano island (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 212, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarenzelli, J.; Aspler, L.; Dunnet, L. Multi-element and rare earth element composition of lichens, mosses and vascular plants from the central Barrenlands, Nunavut, Canada. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereini, F.; Alt, F. Anthropogenic Platinum-Group-Element Emissions and Their Impact on Man and Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guinoiseau, D.; Singh, S.P.; Galer, S.J.G.; Abouchami, W.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Kandler, K.; Bristow, C.; Andreae, M.O. Characterization of Saharan and Sahelian dust sources based on geochemical and radiogenic isotope signatures. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2022, 293, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Querol, X.; Castillo, S.; Alastuey, A.; Cuevas, E.; Herrmann, L.; Mounkaila, M.; Elvira, J.; Gibbons, W. Geochemical variations in aeolian mineral particles from the Sahara–Sahel Dust Corridor. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C.; Haustein, K.; Janjic, Z.; Jorba, O.; Huneeus, N.; Baldasano, J.M.; Black, T.; Basart, S.; Nickovic, S.; Miller, R.L.; et al. Atmospheric dust modeling from meso to global scales with the online NMMB/BSC-Dust model—Part 1: Model description, annual simulations and evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13001–13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, M.; Jorba, O.; Gonçalves Ageitos, M.; Escribano, J.; Dawson, M.L.; Obiso, V.; Di Tomaso, E.; Basart, S.; Montané Pinto, G.; Macchia, F.; et al. Mineral dust cycle in the Multiscale Online Nonhydrostatic AtmospheRe CHemistry model (MONARCH) Version 2.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 6403–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; de Caritat, P. Intrinsic Flaws of Element Enrichment Factors (EFs) in Environmental Geochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5084–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, R.; Nimmo, M.; Keyse, S. The influence of Saharan and Middle Eastern desert-derived dust on the trace metal composition of Mediterranean aerosols and rainwaters: An overview. In The Impact of Desert Dust across the Mediterranean; Guerzoni, S., Chester, R., Eds.; Kluver: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 253–273. [Google Scholar]
- Remoundaki, E.; Papayannis, A.; Kassomenos, P.; Mantas, E.; Kokkalis, P.; Tsezos, M. Influence of Saharan Dust Transport Events on PM2.5 Concentrations and Composition over Athens. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1373–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lianou, M.; Chalbot, M.C.; Kavouras, I.G.; Kotronarou, A.; Karakatsani, A.; Analytis, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Puustinen, A.; Hameri, K.; Vallius, M.; et al. Temporal variations of atmospheric aerosol in four European urban areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1202–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

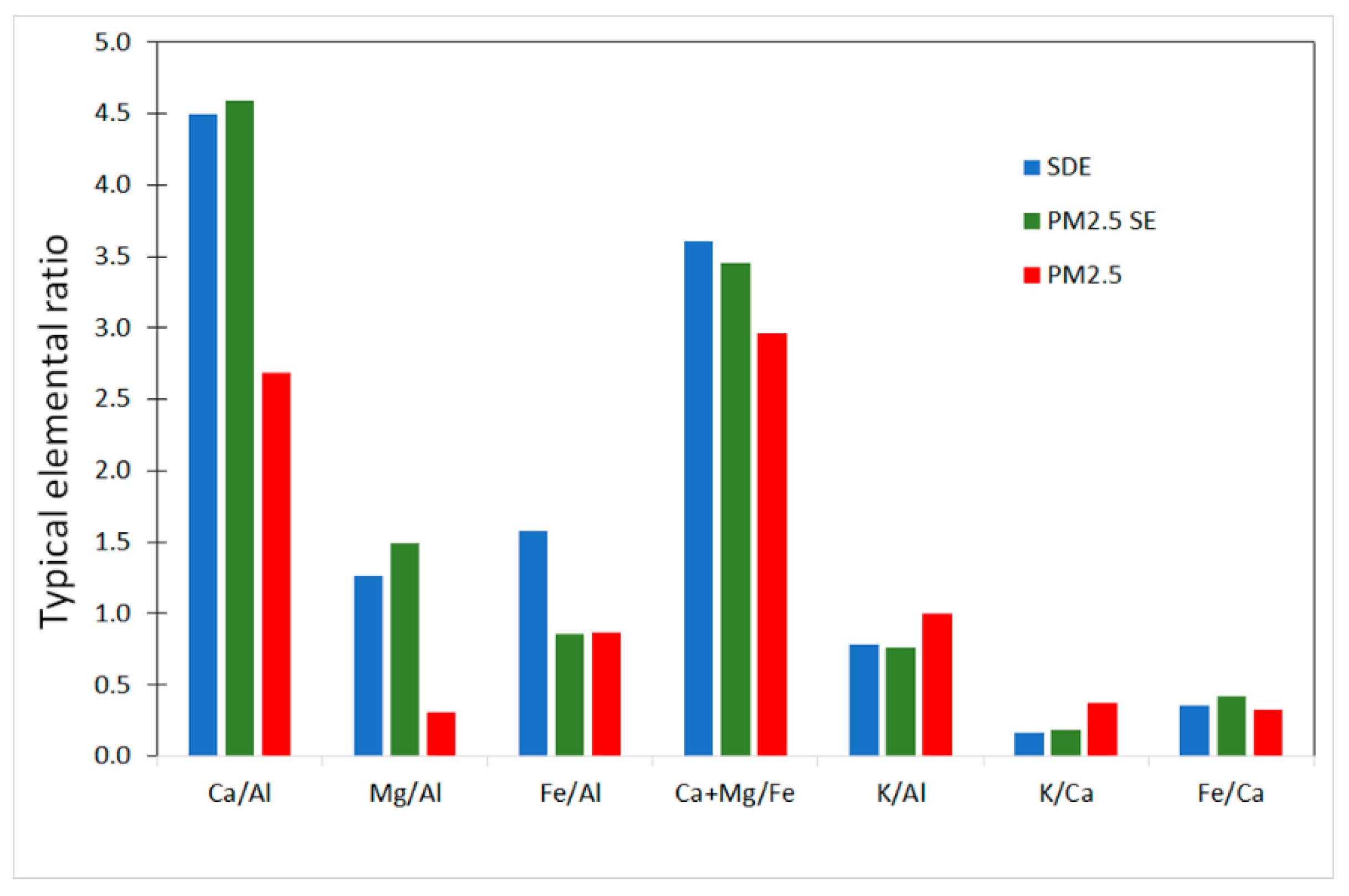
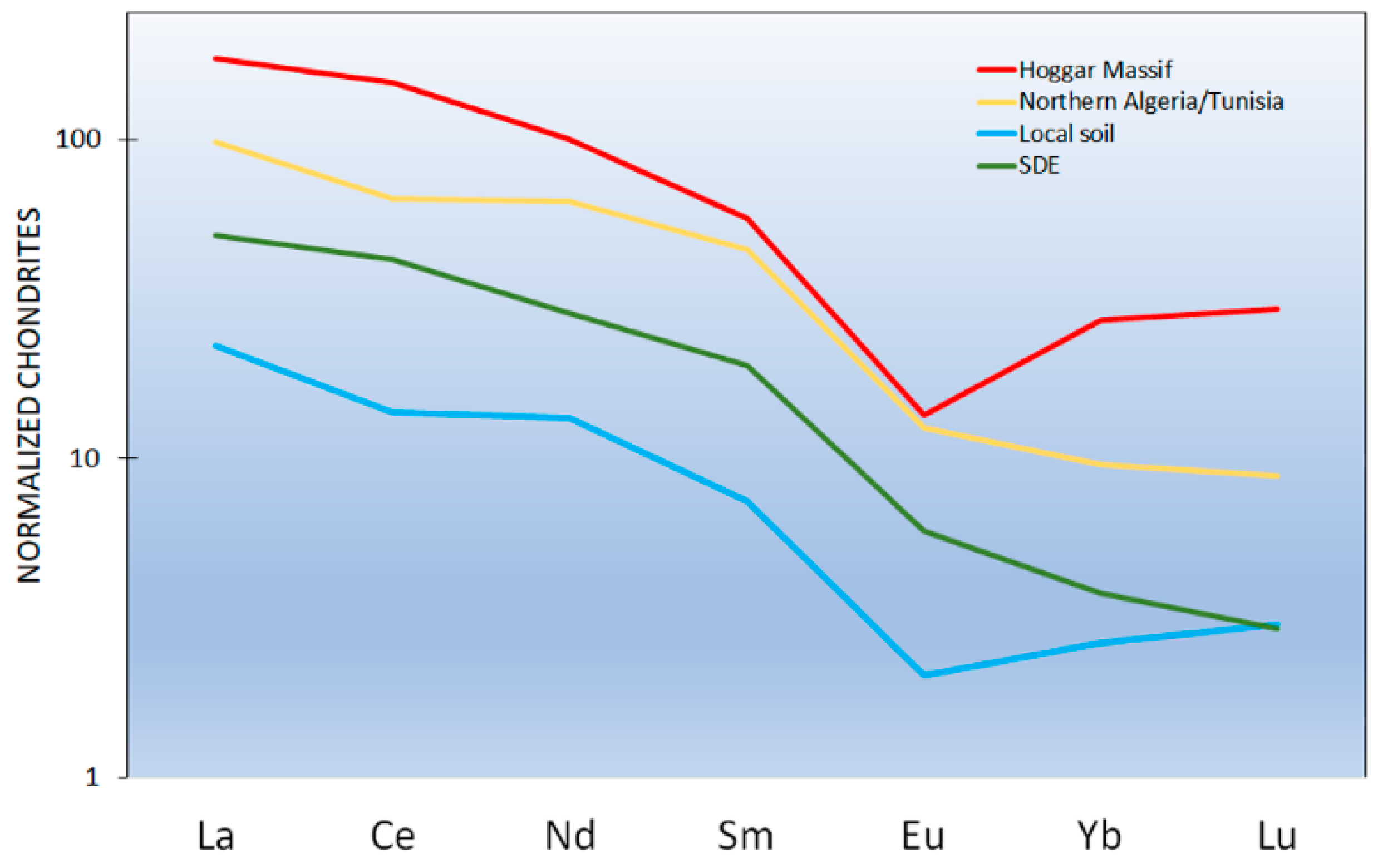
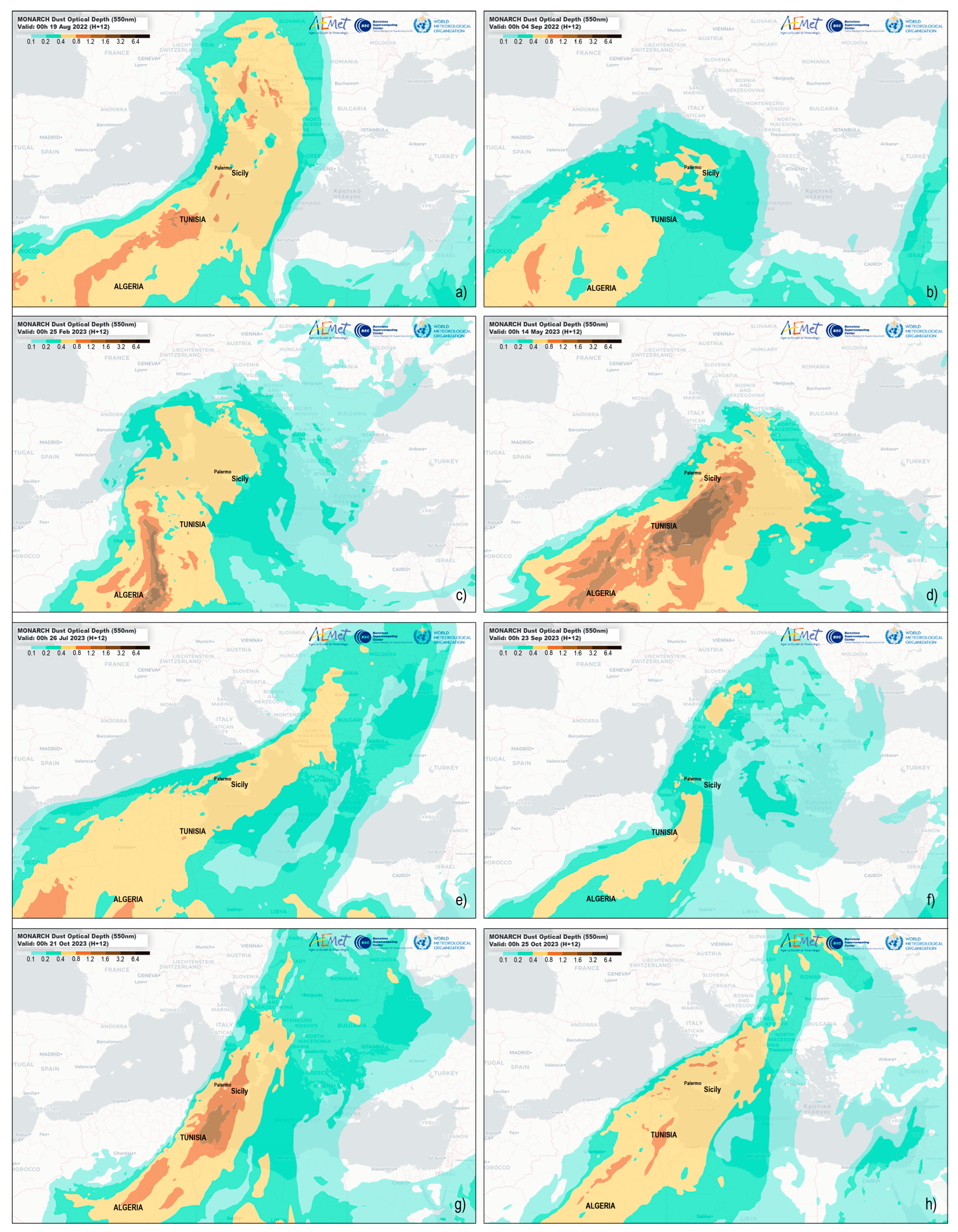
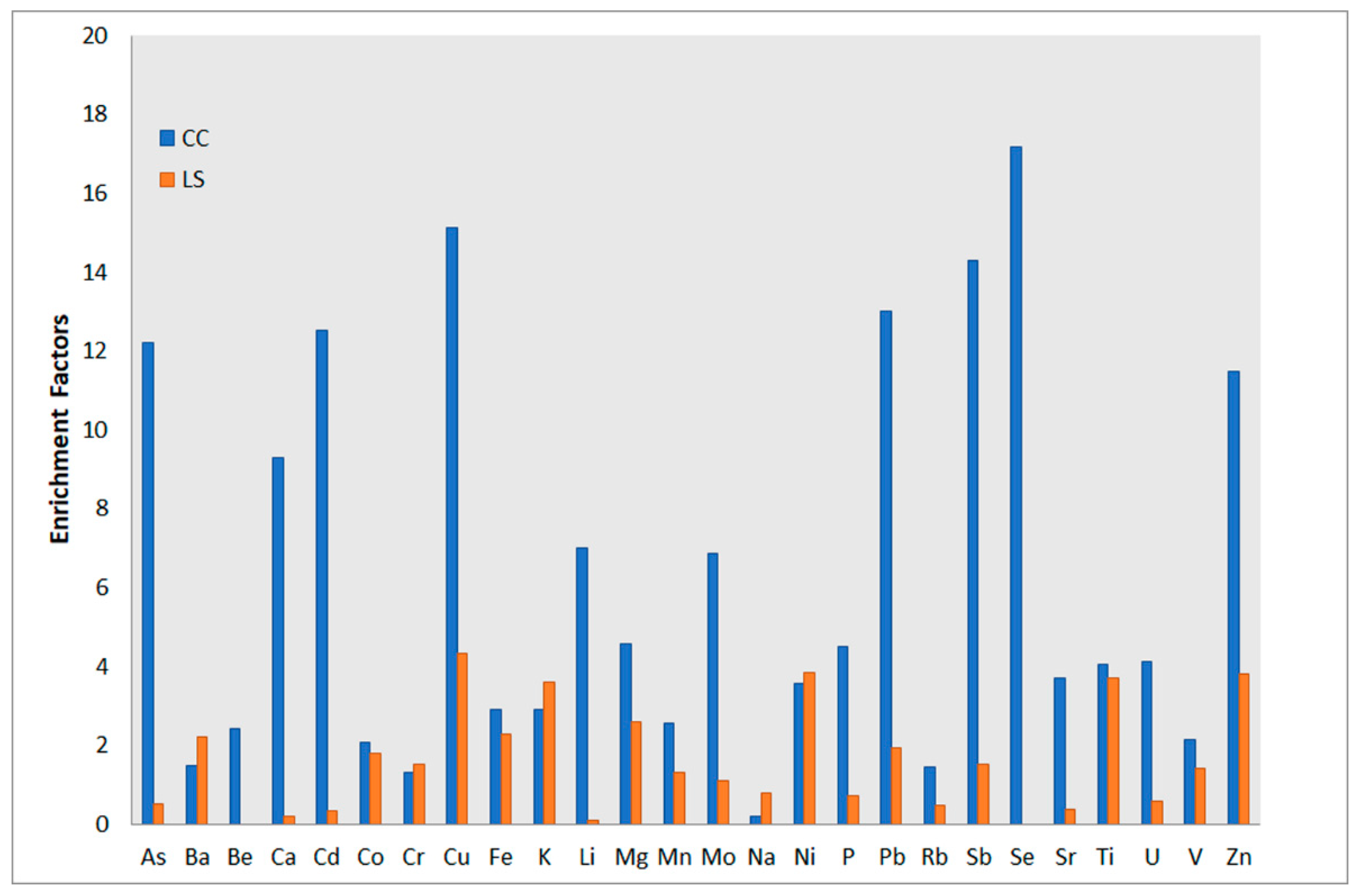

| Al | Ca | K | Fe | Mg | Na | Si | Ti | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Mean | 1.88 | 7.42 | 1.22 | 2.67 | 2.04 | 0.10 | 6.40 | 0.37 |
| Median | 2.03 | 7.58 | 0.50 | 2.71 | 1.93 | 0.09 | 6.91 | 0.40 |
| Min | 0.84 | 7.00 | 0.43 | 2.15 | 1.61 | 0.07 | 2.86 | 0.20 |
| Max | 2.75 | 7.73 | 2.71 | 3.53 | 2.71 | 0.16 | 9.38 | 0.45 |
| As | Ba | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Li | Mn | |
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| Mean | 4.23 | 176 | 0.24 | 11 | 34 | 75 | 26 | 406 |
| Median | 4.46 | 176 | 0.23 | 10 | 37 | 68 | 24 | 397 |
| Min | 3.15 | 129 | 0.06 | 8 | 21 | 35 | 20 | 291 |
| Max | 4.80 | 232 | 0.49 | 15 | 41 | 126 | 33 | 582 |
| Mo | Ni | Pb | Rb | Sb | Se | Sr | U | |
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |
| Mean | 1.56 | 39 | 36 | 25 | 0.82 | 0.37 | 257 | 1.54 |
| Median | 1.49 | 34 | 33 | 24 | 0.79 | 0.30 | 229 | 1.47 |
| Min | 0.78 | 24 | 17 | 16 | 0.27 | 0.18 | 192 | 1.01 |
| Max | 2.66 | 70 | 66 | 33 | 1.78 | 0.74 | 555 | 2.40 |
| V | Zn | |||||||
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||||
| Mean | 43 | 153 | ||||||
| Median | 46 | 168 | ||||||
| Min | 11 | 57 | ||||||
| Max | 60 | 199 | ||||||
| La | Ce | Nd | Sm | Eu | Yb | Lu | ||
| mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||
| Mean | 17 | 38 | 18 | 3.83 | 0.73 | 0.83 | 0.11 |
| PA 1 | PA2 | PA3 | PA4 | PA5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| suburban | medium-high traffic | medium traffic | medium-high traffic | suburban | |
| During Saharan event | |||||
| PM10 | 75.9 | 58.4 | 61.0 | 66.2 | 55.0 |
| PM2.5 | 22.4 | 24.2 | 20.6 | ||
| PM2.5/PM10 | 0.38 | 0.40 | 0.38 | ||
| Normal condition | |||||
| PM10 | 20.5 | 23.1 | 25.4 | 28.8 | 19.6 |
| PM2.5 | 13.4 | 13.5 | 10.2 | ||
| PM2.5/PM10 | 0.58 | 0.53 | 0.52 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varrica, D.; Alaimo, M.G. Influence of Saharan Dust on the Composition of Urban Aerosols in Palermo City (Italy). Atmosphere 2024, 15, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030254
Varrica D, Alaimo MG. Influence of Saharan Dust on the Composition of Urban Aerosols in Palermo City (Italy). Atmosphere. 2024; 15(3):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030254
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarrica, Daniela, and Maria Grazia Alaimo. 2024. "Influence of Saharan Dust on the Composition of Urban Aerosols in Palermo City (Italy)" Atmosphere 15, no. 3: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030254
APA StyleVarrica, D., & Alaimo, M. G. (2024). Influence of Saharan Dust on the Composition of Urban Aerosols in Palermo City (Italy). Atmosphere, 15(3), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15030254









