Characteristics of Vehicle Tire and Road Wear Particles’ Size Distribution and Influencing Factors Examined via Laboratory Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Information
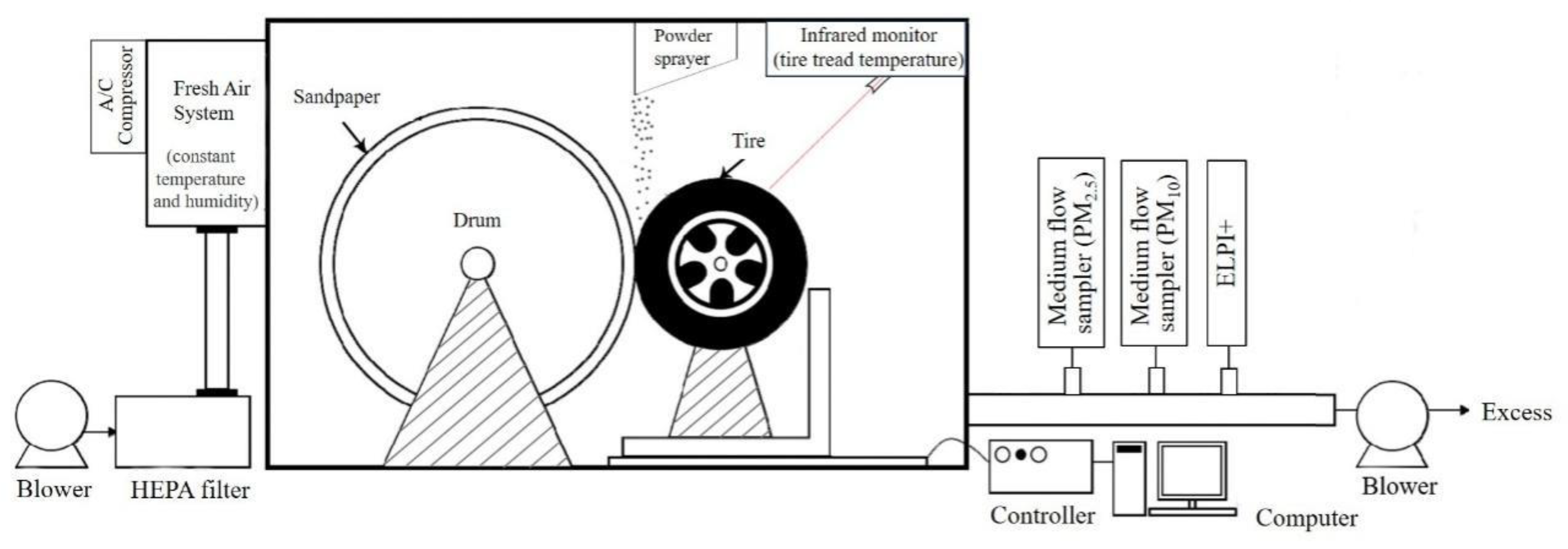
2.2. Sampling Method
2.3. Tire Wear Test Conditions
3. Results and Discussion
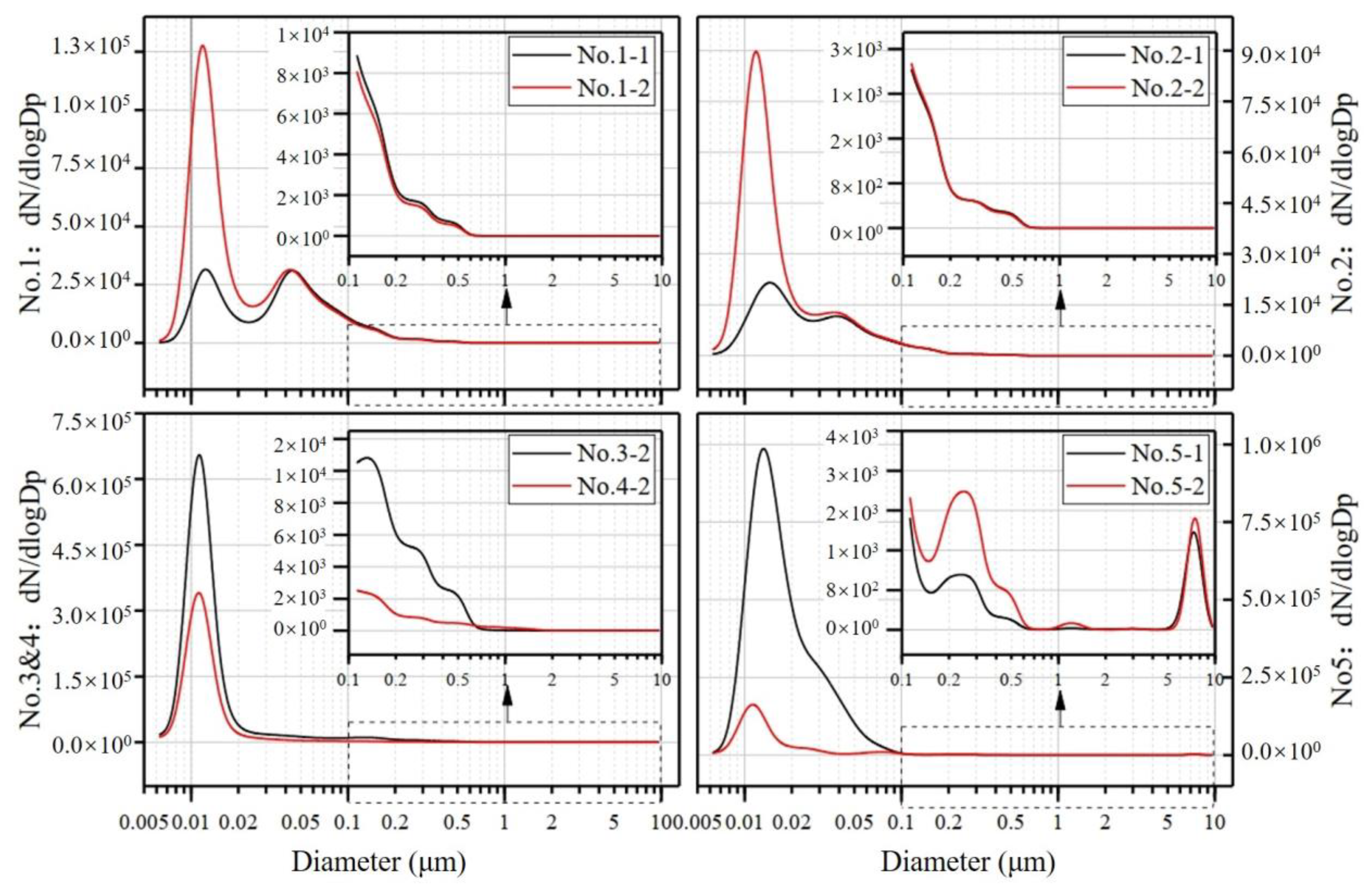
3.1. Number Distribution of TWPs
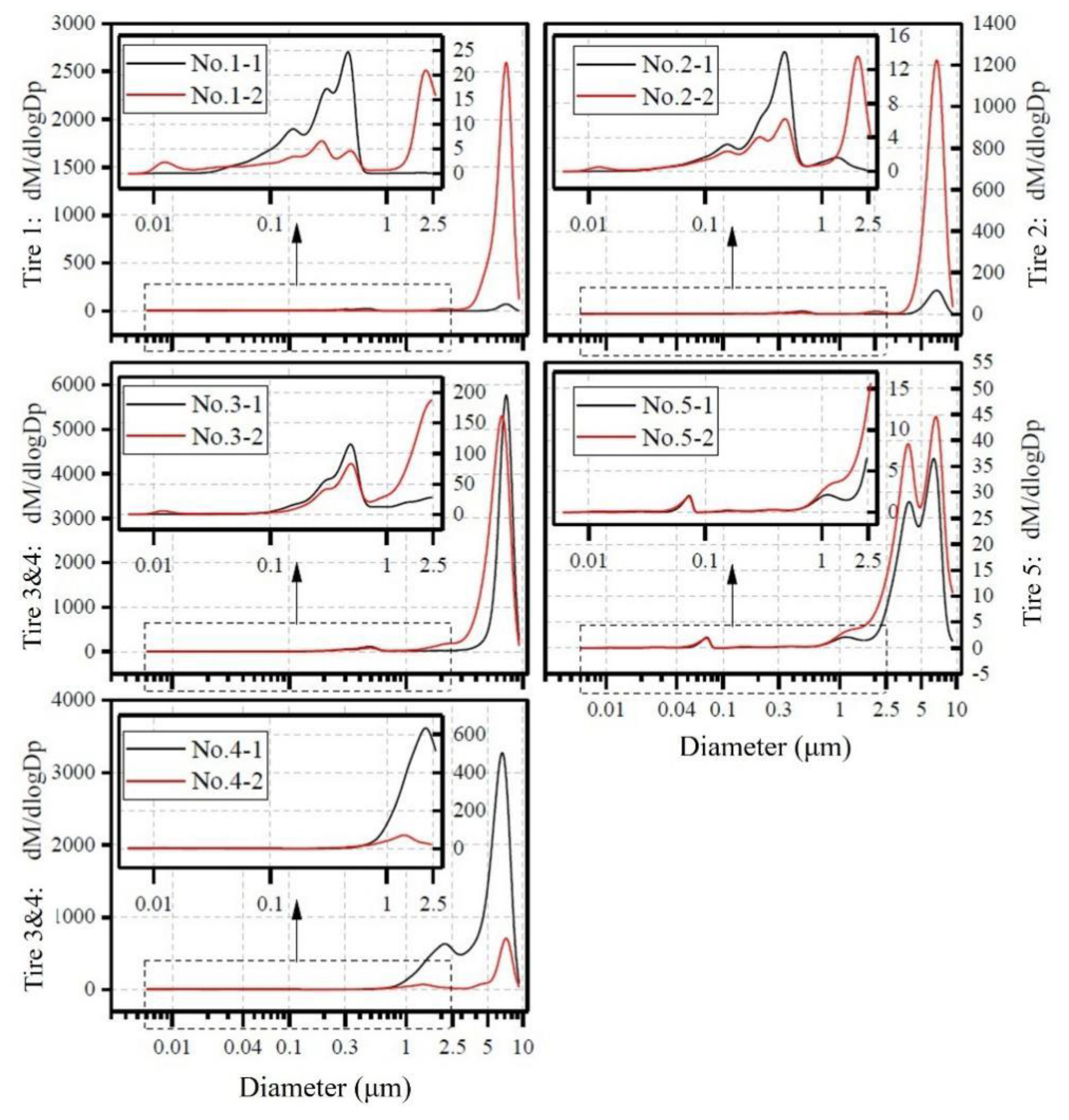
3.2. Mass Distribution of TWPs
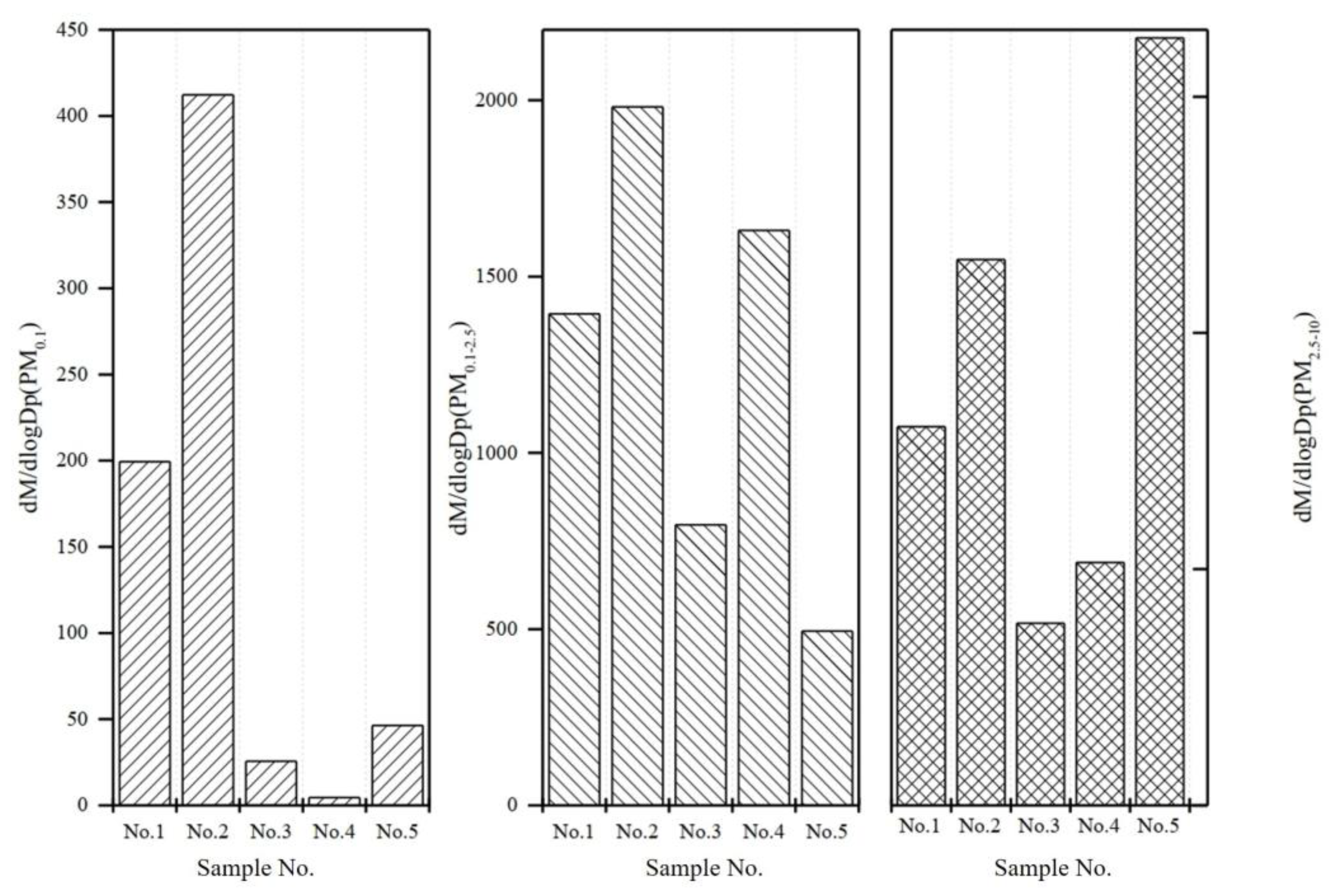
3.3. Emissions Intensity
3.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full name |
| TWPs | Tire wear particles |
| dM/dlogDp | Normalized mass concentration |
| dN/dlogDp | Normalized number concentration |
References
- Winkler, S.L.; Anderson, J.E.; Garza, L.; Ruona, W.C.; Vogt, R.; Wallington, T.J. Vehicle criteria pollutant (PM, NOx, CO, HCs) emissions: How low should we go? Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Allan, J.; Carruthers, D.; Heal, M.R.; Lewis, A.C.; Marner, B.; Murrells, T.; Williams, A. Non-exhaust vehicle emissions of particulate matter and VOC from road traffic: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S.; Peng, J.; Yun, U.; Zhang, Q.; Mao, H. Impacts of methanol fuel on vehicular emissions: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.T.; Naas, I.d.A.; da Silva Lima, N.D. Estimating the urban environmental impact of gasoline-ethanol blended fuels in a passenger vehicle engine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63977–63988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.H. On-road chasing and laboratory measurements of exhaust particle emissions of diesel vehicles equipped with aftertreatment technologies (DPF, urea-SCR). Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2015, 16, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panko, J.; Kreider, M.; Unice, K. Review of Tire Wear Emissions. In Non-Exhaust Emissions; Amato, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Cassee, F.R.; van der Gon, H.A.C.D.; Gehrig, R.; Gustafsson, M.; Hafner, W.; Harrison, R.M.; Jozwicka, M.; Kelly, F.J.; Moreno, T.; et al. Urban air quality: The challenge of traffic non-exhaust emissions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keuken, M.; van der Gon, H.D.; van der Valk, K. Non-exhaust emissions of PM and the efficiency of emission reduction by road sweeping and washing in the Netherlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4591–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowiecki, N.; Lienemann, P.; Hill, M.; Furger, M.; Richard, A.; Amato, F.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Baltensperger, U.; Buchmann, B.; Gehrig, R. PM10 emission factors for non-exhaust particles generated by road traffic in an urban street canyon and along a freeway in Switzerland. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2330–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpure, A.S.; Gurjar, B.R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, P. Estimation of exhaust and non-exhaust gaseous, particulate matter and air toxics emissions from on-road vehicles in Delhi. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 127, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M. PM10 and PM2.5 emission factors for non-exhaust particles from road vehicles: Dependence upon vehicle mass and implications for battery electric vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Commission Proposes New Euro 7 Standards to Reduce Pollutant Emissions from Vehicles and Improve Air Quality; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, A.; Harrison, R.M. Sources and properties of non-exhaust particulate matter from road traffic: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauert, C.; Rødland, E.S.; Okoffo, E.D.; Reid, M.J.; Meland, S.; Thomas, K.V. Challenges with Quantifying Tire Road Wear Particles: Recognizing the Need for Further Refinement of the ISO Technical Specification. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Perseguers, S.; Schnidrig, N.; Grobety, B.; Yajan, P. Automated identification and quantification of tire wear particles (TWP) in airborne dust: SEM/EDX single particle analysis coupled to a machine learning classifier. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarlskog, I.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Rausch, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Stromvall, A.M.; Andersson-Skold, Y. Concentrations of tire wear microplastics and other traffic-derived non-exhaust particles in the road environment. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannessen, C.; Liggio, J.; Zhang, X.; Saini, A.; Harner, T. Composition and transformation chemistry of tire-wear derived organic chemicals and implications for air pollution. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallamach, A. A Theory of Dynamic Rubber Friction. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1966, 39, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Zheng, D.; Schmerwitz, F.; Wriggers, P. An advanced abrasion model for tire wear. Wear 2018, 396–397, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foitzik, M.-J.; Unrau, H.-J.; Gauterin, F.; Dörnhöfer, J.; Koch, T. Investigation of ultra fine particulate matter emission of rubber tires. Wear 2018, 394–395, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Wen, S. Investigation of the external conditions and material compositions affecting the formation mechanism and size distribution of tire wear particles. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 118018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S. Characteristics of Tire Wear Particles Generated by a Tire Simulator under Various Driving Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12153–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kole, P.J.; Lohr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Huffer, T.; Klockner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Air Quality Expert Group. Non-Exhaust Emissions from Road Traffic; Air Quality Expert Group: London, UK, 2019. Available online: https://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/assets/documents/reports/cat09/1907101151_20190709_Non_Exhaust_Emissions_typeset_Final.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Camatini, M.; Crosta, G.F.; Dolukhanyan, T.; Sung, C.; Giuliani, G.; Corbetta, G.M.; Cencetti, S.; Regazzoni, C. Microcharacterization and identification of tire debris in heterogeneous laboratory and environmental specimens. Mater. Charact. 2001, 46, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauser, P.; Tjell, J.C.; Mosbaek, H.; Pilegaard, K. Tire-tread and bitumen particle concentrations in aerosol and soil samples. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2002, 20, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, F. Review of Tires Wear Particles Emission Research Status. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 555, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beji, A.; Deboudt, K.; Khardi, S.; Muresan, B.; Flament, P.; Fourmentin, M.; Lumière, L. Non-exhaust particle emissions under various driving conditions: Implications for sustainable mobility. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 81, 102290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, A.; Gharibi, A.; Swietlicki, E.; Gudmundsson, A.; Bohgard, M.; Ljungman, A.; Blomqvist, G.; Gustafsson, M. Traffic-generated emissions of ultrafine particles from pavement-tire interface. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1314–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathissen, M.; Scheer, V.; Vogt, R.; Benter, T. Investigation on the potential generation of ultrafine particles from the tire–road interface. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6172–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Gietl, J.K.; Olatunbosun, O.A.; Yang, X.; Harrison, R.M. Characteristics of tyre dust in polluted air: Studies by single particle mass spectrometry (ATOFMS). Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. On-road and laboratory investigations on non-exhaust ultrafine particles from the interaction between the tire and road pavement under braking conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagino, H.; Oyama, M.; Sasaki, S. Airborne brake wear particle emission due to braking and accelerating. Wear 2015, 334–335, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEKATI. High Resolution ELPI®+. 2019. Available online: https://dekati.com/products/high-resolution-elpi/ (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Kwak, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, S. Characterization of non-exhaust coarse and fine particles from on-road driving and laboratory measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]


| Sample No. | Country of Brand | Rated Load (kg) | Specification Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tire 1 | South Korea | 690 | 215/55 R18 95H |
| Tire 2 | Germany | 340 | 195/55 R16 91H |
| Tire 3 | China | 690 | 205/65 R16 95H |
| Tire 4 | Germany | 615 | 195/55 R16 95H |
| Tire 5 | South Korea | 500 | 195/60 R15 88H |
| No. | Speed (km/h) | Load (%) | Slip Angle (°) | Roll Angle (°) | Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 75 | 2 | 0 | Speed |
| 0-1 | 60 | 75 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-2 | 80 | 75 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-3 | 100 | 75 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-4 | 120 | 75 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-5 | 60 | 75 | 2 | 0 | Load |
| 0-6 | 60 | 80 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-7 | 60 | 90 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-8 | 60 | 100 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-9 | 40 | 75 | 1 | 0 | Slip angle |
| 0-10 | 40 | 75 | 2 | 0 | |
| 0-11 | 40 | 75 | 3 | 0 | |
| 0-12 | 40 | 75 | 5 | 0 | |
| 0-13 | 60 | 75 | 0 | 1 | Roll angle |
| 0-14 | 60 | 75 | 0 | 2 | |
| 0-15 | 60 | 75 | 0 | 3 | |
| 2 | 40 | 80 | 1 | 1 | Orthogonal test |
| 3 | 40 | 90 | 2 | 2 | |
| 4 | 40 | 100 | 3 | 3 | |
| 5 | 40 | 100 | 5 | 3 | |
| 6 | 60 | 75 | 1 | 2 | |
| 7 | 60 | 80 | 2 | 3 | |
| 8 | 60 | 90 | 3 | 3 | |
| 9 | 60 | 100 | 5 | 0 | |
| 10 | 60 | 100 | 0 | 1 | |
| 11 | 80 | 75 | 2 | 3 | |
| 12 | 80 | 80 | 3 | 0 | |
| 13 | 80 | 90 | 5 | 1 | |
| 14 | 80 | 100 | 0 | 2 | |
| 15 | 80 | 100 | 1 | 3 | |
| 16 | 100 | 75 | 3 | 1 | |
| 17 | 100 | 80 | 5 | 2 | |
| 18 | 100 | 90 | 0 | 3 | |
| 19 | 100 | 100 | 1 | 3 | |
| 20 | 100 | 100 | 2 | 0 | |
| 21 | 120 | 75 | 5 | 3 | |
| 22 | 120 | 80 | 0 | 3 | |
| 23 | 120 | 90 | 1 | 0 | |
| 24 | 120 | 100 | 2 | 1 | |
| 25 | 120 | 100 | 3 | 2 |
| Reference | Country | Method | Instrument | Measured Size Range | Size Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This study | China | Tire simulator | ELPI | 6 nm~10 μm | Bimodal (10~13 nm, 23~41 nm) |
| Dall’Osto et al., 2014 [34] | Spain | Tire simulator | APS + SMPS/CPC | APS: 523 nm~20 μm SMPS TSI3071/CPC 3022: 15~800 nm SMPS TSI3085/CPC 3025: 5~160 nm | Bimodal (35 nm, 85 nm) (35 nm, 85 nm) |
| Mathissen et al., 2011 [33] | Germany | Test site | EEPS | 5.6~562.3 nm | Low speed: unimodal (70~90 nm) High speed: bimodal (<10 nm, 30~60 nm) |
| Dahl et al., 2006 [32] | Denmark | Road simulation | SMPS + CPC | 15~700 nm | 15–50 nm a |
| Kreider et al., 2010 [28] | U.S. | Road vacuum cleaning | TOM | 0.3~100 μm | Unimodal (50~75μm) |
| Tire 3 | Tire 4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Load | Roll Angle | Slip Angle | Speed | Load | Roll Angle | Slip Angle | |
| Range (R) | 40,400 | 37,867 | 22,355 | 94,772 | 181,105 | 156,567 | 86,886 | 266,692 |
| Converted range (R′) | 36,135 | 33,869 | 22,494 | 84,767 | 161,985 | 157,543 | 87,427 | 238,537 |
| Ranking | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 |
| Speed | Roll Angle | Load | Slip Angle | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y = C + B1 × x + B2 × x2 | y = A1 × exp(−x/t1) + y0 | ||||||||
| Tire 3 | Tire 4 | Tire 3 | Tire 4 | Tire 3 | Tire 3 | Tire 4 | Tire 5 | ||
| C | 0.873 | 0.109 | 0.973 | 0.951 | 1.582 | y0 | 0.05525 | 1.04 × 10−2 | 1.17 × 10−2 |
| B1 | −2.14 × 102 | −4.28 × 10−3 | −1.67 × 10−2 | 3.97 × 10−2 | −3.84 × 10−2 | A1 | 5.72 × 10−4 | 1.0 × 10−4 | 3.84 × 10−5 |
| B2 | 1.84 × 104 | 9.73 × 10−5 | 8.63 × 10−3 | −7.79 × 10−3 | 3.25 × 10−4 | t1 | −0.67483 | −0.54625 | −0.49228 |
| R2 | 0.923 | 0.999 | 0.986 | 0.999 | 0.998 | R2 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Fang, T.; Liang, X.; Yin, J.; Peng, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Characteristics of Vehicle Tire and Road Wear Particles’ Size Distribution and Influencing Factors Examined via Laboratory Test. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040423
Zhong C, Sun J, Zhang J, Liu Z, Fang T, Liang X, Yin J, Peng J, Wu L, Zhang Q, et al. Characteristics of Vehicle Tire and Road Wear Particles’ Size Distribution and Influencing Factors Examined via Laboratory Test. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(4):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040423
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Chongzhi, Jiaxing Sun, Jing Zhang, Zishu Liu, Tiange Fang, Xiaoyu Liang, Jiawei Yin, Jianfei Peng, Lin Wu, Qijun Zhang, and et al. 2024. "Characteristics of Vehicle Tire and Road Wear Particles’ Size Distribution and Influencing Factors Examined via Laboratory Test" Atmosphere 15, no. 4: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040423
APA StyleZhong, C., Sun, J., Zhang, J., Liu, Z., Fang, T., Liang, X., Yin, J., Peng, J., Wu, L., Zhang, Q., & Mao, H. (2024). Characteristics of Vehicle Tire and Road Wear Particles’ Size Distribution and Influencing Factors Examined via Laboratory Test. Atmosphere, 15(4), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15040423





