Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Heavy Metal Exposure on Blood Pressure: A Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Measurement of Blood Heavy Metal Concentrations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Considerations
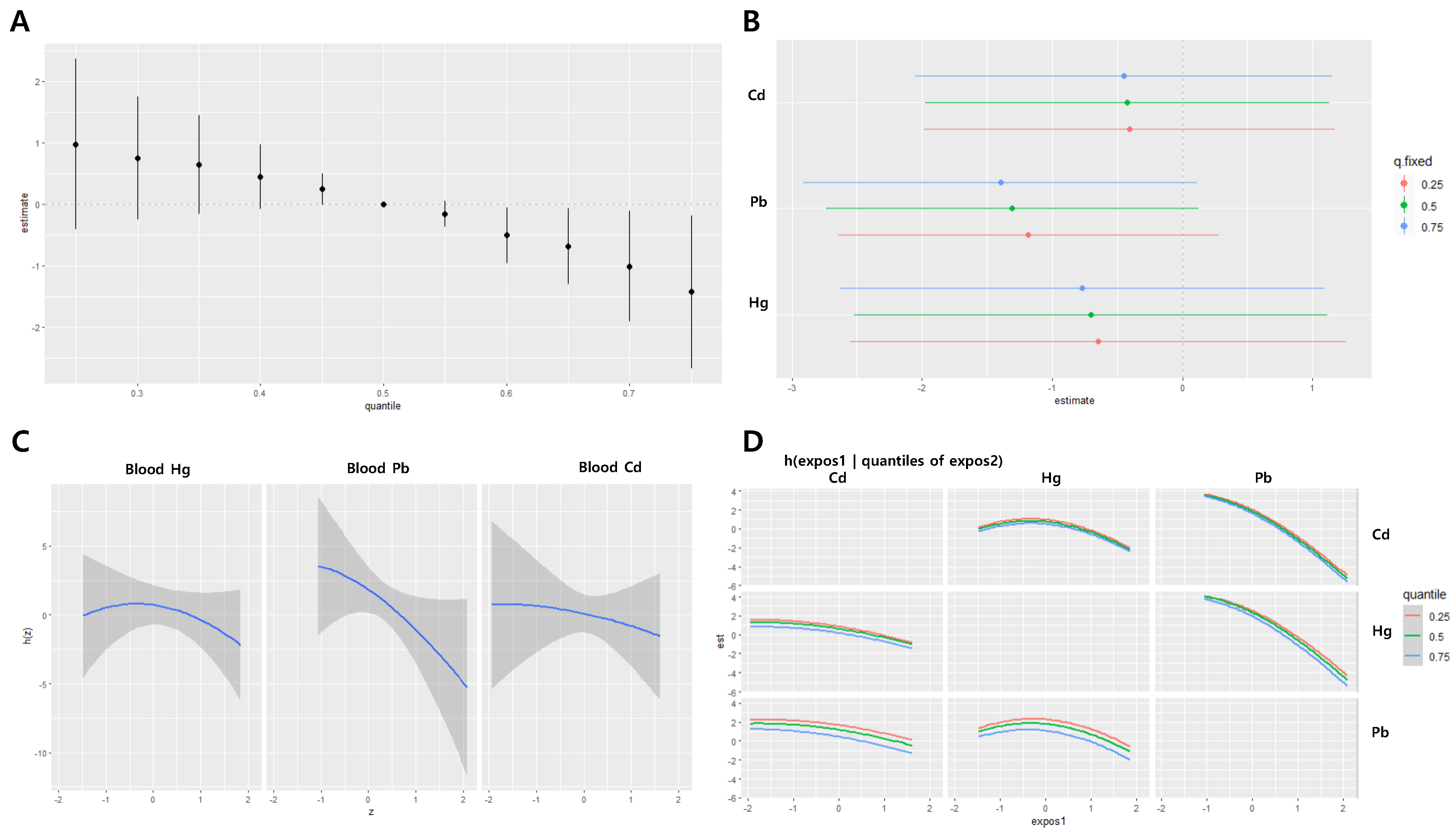
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navas-Acien, A.; Guallar, E.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Rothenberg, S.J. Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease—A systematic review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, L.; Primatesta, P.; Dong, W.; Poulter, N. Blood lead and blood pressure: Evidence from the Health Survey for England 1995. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1999, 13, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Bai, Y. Cadmium Exposure and Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 257. [Google Scholar]
- Barregard, L.; Bergström, G.; Fagerberg, B. Cadmium Exposure in Relation to Myocardial Infarction and Stroke: A Longitudinal Population-Based Study. Epidemiology 2001, 12, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ke, W.; Feng, B.; Lin, H.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, W.; Li, X.; Tao, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. Associations of Short-Term and Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants with Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hypertension 2016, 68, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, Y.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, K.; Lee, C.; Yu, S.D.; Yoo, J. A Study on Heavy Metals Exposure and Major Sociodemographic Influence Factors among Korean Adults—Korean National Environmental Health Survey (2009–2017). J. Environ. Health Sci. 2019, 45, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). 10 Chemicals of Public Health Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/photo-story/photo-story-detail/10-chemicals-of-public-health-concern (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Cai, K.; Li, C.; Na, S. Spatial Distribution, Pollution Source, and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Atmospheric Depositions: A Case Study from the Sustainable City of Shijiazhuang, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.; Al-Shahwani, D.; Al-Thani, H.; Isaifan, R.J. Risk Assessment of the Impact of Heavy Metals in Urban Traffic Dust on Human Health. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarapu, L.N.; Baek, S.O. Determination of heavy metals in the ambient atmosphere. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2017, 33, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Seok, K.J.; Ryu, J.Y.; Jung, W.S.; Park, J.B.; Shin, K.H.; Jang, S.J. Association between Heavy Metal Exposure and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults of South Korea. Korean J. Fam. Pract. 2017, 7, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration fly ash as an important source of heavy metal pollution in China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.T.; Stefanescu, A.; He, J. The global epidemiology of hypertension. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, S.; Newton-Cheh, C.; Dominiczak, A.F. Genetic basis of blood pressure and hypertension. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ji, S.; Ding, L.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Effect of exposures to mixtures of lead and various metals on hypertension, pre-hypertension, and blood pressure: A cross-sectional study from the China National Human Biomonitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.F.; Singh, K.; Chan, H.M. Mercury Exposure, Blood Pressure, and Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 076002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liao, Q.; Chillrud, S.N.; Yang, Q.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Yan, B. Environmental Exposure to Cadmium: Health Risk Assessment and its Associations with Hypertension and Impaired Kidney Function. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Lee, S.J. Association of Blood Heavy Metal Levels and Renal Function in Korean Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Lopes, A.C.B.; Silbergeld, E.K.; Navas-Acien, A.; Zamoiski, R.; Martins, A.D.C., Jr.; Camargo, A.E.I.; Urbano, M.R.; Mesas, A.E.; Paoliello, M.M.B. Association between blood lead and blood pressure: A population-based study in Brazilian adults. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.Y.; Yim, D.H.; Huang, M.; Park, C.H.; Kim, G.B.; Yu, S.D.; Choi, B.S.; Park, J.D.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, H. Copper-zinc imbalance induces kidney tubule damage and oxidative stress in a population exposed to chronic environmental cadmium. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2020, 93, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, C.H.; Eom, S.Y.; Kang, T.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, H. Effects of the exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons or toluene on thiobarbituric acid reactive substance level in elementary school children and the elderly in a rural area. J. Prev. Med. Public Health 2008, 41, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, N.Y.; Bae, H.S.; Yu, S.D.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, H.; Choi, B.S.; Yu, I.J.; et al. Evaluation of factors associated with cadmium exposure and kidney function in the general population. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, A.P.; Buckley, J.P.; O‘Brien, K.M.; Ferguson, K.K.; Zhao, S.; White, A.J. A Quantile-Based g-Computation Approach to Addressing the Effects of Exposure Mixtures. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 47004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobb, J.F.; Valeri, L.; Claus Henn, B.; Christiani, D.C.; Wright, R.O.; Mazumdar, M.; Godleski, J.J.; Coull, B.A. Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 2015, 16, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, C.; Gennings, C.; Wheeler, D.C.; Factor-Litvak, P. Characterization of Weighted Quantile Sum Regression for Highly Correlated Data in a Risk Analysis Setting. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2015, 20, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Park, C.; Sakong, J.; Ye, S.; Son, S.Y.; Baek, K. Association of heavy metal complex exposure and neurobehavioral function of children. Ann. Occup. Environ. Med. 2023, 35, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Min, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Mo, X.; Lin, Y.; Tang, X.; et al. Associations between multiple heavy metals exposure and glycated hemoglobin in a Chinese population. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.I.; Yim, D.H.; Choi, K.; Eom, S.Y.; Choi, B.S.; Park, J.D.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.D. Association Between Multiple Heavy Metal Exposures and Cholesterol Levels in Residents Living Near a Smelter Plant in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2024, 39, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Haque, A.; Fatima, M. Gender Difference in Heavy Metal Toxicity and the Role of Sex Hormones. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 48, 710–721. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.D. Cadmium, lead, and mercury interactions on obstructive lung function in pre- and postmenopausal women. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 73485–73496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Akesson, A.; Liden, C.; Ceccatelli, S.; Berglund, M. Gender differences in the disposition and toxicity of metals. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.L.; Johnson, A.B.; Jones, K.L. Gender Differences in Susceptibility to Heavy Metal-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: The Role of Sex Hormones. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 037001. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.; Johnson, A. Gender Differences in Heavy Metal Metabolism and Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress. Environ. Toxicol. Health 2021, 45, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Idowu, O.; Oyedele, O.; Olaniyan, S.D.; Lawan, E.; Hannah, A. A Review of Sex Differences in Vulnerability to Heavy Metals. Glob. Sci. J. 2023, 11, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Navas-Acien, A.; Selvin, E.; Sharrett, A.R.; Calderon-Aranda, E.; Silbergeld, E.; Guallar, E. Lead, cadmium, smoking, and increased risk of peripheral arterial disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Dong, G. Sex-Specific Associations of Mercury Exposure with Risk of Hypertension: Results from NHANES 2011–2014. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Kromhout, D.; Menotti, A.; Chrysohoou, C.; Dontas, A.; Pitsavos, C.; Adachi, H.; Blackburn, H.; Nedeljkovic, S.; Nissinen, A. The Relation Between Pulse Pressure and Cardiovascular Mortality in 12 763 Middle-aged Men from Various Parts of the World: A 25-Year Follow-up of the Seven Countries Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 2142–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.-Y.; Baek, Y.-W.; Jeon, H.-L.; Kwon, Y.-M.; Lee, N.-Y.; Han, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-J.; Yu, S.-D.; Choi, K.-H. Korean National Environmental Health Survey(KoNEHS)—Annual Report on Third Stage, 2nd Year (2016); National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-D.; Kang, Y.-S. A Report of Survey on Environmental Pollution and Residents’ Health in Bugi-myeon, Cheongju, Chungcheongbuk-do; National Institute of Environmental Research: Incheon, Republic of Korea, 2020. [Google Scholar]



| Characteristics | Total (n = 561) | Men (n = 253) | Women (n = 308) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking status | ||||
| Non-smoker | 367 (65.42) | 67 (26.48) | 300 (97.40) | <0.001 |
| Smoker | 194 (34.58) | 186 (73.52) | 8 (2.60) | |
| Drinking status | ||||
| Non-drinker | 249 (44.39) | 172 (67.98) | 77 (25.00) | <0.001 |
| Drinker | 312 (55.61) | 81 (32.02) | 231 (75.00) | |
| Monthly income | ||||
| <2 million won | 312 (55.61) | 140 (55.34) | 172 (55.84) | 0.372 |
| 2–6 million won | 146 (26.02) | 72 (28.46) | 74 (24.03) | |
| >6 million won | 7 (1.25) | 4 (1.58) | 3 (0.97) | |
| Unknown | 96 (17.11) | 37 (14.62) | 59 (19.16) | |
| Age (years) | 66.38 ± 12.13 | 65.83 ± 11.29 | 66.83 ± 12.78 | 0.295 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.19 ± 3.59 | 23.73 ± 3.33 | 24.57 ± 3.76 | <0.05 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 129.31 ± 14.58 | 130.02 ± 14.80 | 128.73 ± 14.40 | 0.313 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 76.47 ± 9.39 | 76.91 ± 9.73 | 76.11 ± 9.11 | 0.199 |
| Blood Hg (µg/L) | 1.59 (1.91) | 2.04 (1.81) | 1.30 (1.86) | <0.001 |
| Blood Pb (µg/dL) | 1.56 (1.54) | 1.80 (1.48) | 1.38 (1.53) | <0.001 |
| Blood Cd (µg/L) | 0.98 (1.61) | 0.84 (1.61) | 1.10 (1.55) | <0.001 |
| β (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| SBP | DBP | |
| Total | ||
| Blood Hg | –0.250 (–2.388, 1.887) | 0.425 (–0.922, 1.772) |
| Blood Pb | –0.752 (–3.737, 2.233) | 1.720 (–0.161, 3.602) |
| Blood Cd | 0.917 (–1.842, 3.675) | 1.903 (0.165, 3.641) |
| Men | ||
| Blood Hg | 0.899 (–2.329, 4.127) | 1.465 (–0.525, 3.456) |
| Blood Pb | 1.125 (–3.637, 5.887) | 3.298 (0.362, 6.235) |
| Blood Cd | 0.990 (–3.007, 4.988) | 1.457 (–1.008, 3.922) |
| Women | ||
| Blood Hg | –1.087 (–3.925, 1.750) | –0.309 (–2.129, 1.510) |
| Blood Pb | –2.231 (–6.075, 1.614) | 0.612 (–1.853, 3.077) |
| Blood Cd | 1.805 (–2.070, 5.679) | 2.628 (0.143, 5.113) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.-G.; Hong, S.; Yim, S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Choi, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Hong, Y.-S.; Eom, S.-Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.-D. Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Heavy Metal Exposure on Blood Pressure: A Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression Analysis. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101157
Kim I-G, Hong S, Yim S, Jeong J-H, Choi K, Lee J-H, Hong Y-S, Eom S-Y, Kim H, Kim Y-D. Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Heavy Metal Exposure on Blood Pressure: A Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression Analysis. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(10):1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101157
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, In-Gwon, Seonmi Hong, Sojeong Yim, Jang-Hun Jeong, Kyunghi Choi, Ju-Hee Lee, Young-Seoub Hong, Sang-Yong Eom, Heon Kim, and Yong-Dae Kim. 2024. "Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Heavy Metal Exposure on Blood Pressure: A Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression Analysis" Atmosphere 15, no. 10: 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101157
APA StyleKim, I.-G., Hong, S., Yim, S., Jeong, J.-H., Choi, K., Lee, J.-H., Hong, Y.-S., Eom, S.-Y., Kim, H., & Kim, Y.-D. (2024). Sex-Specific Effects of Combined Heavy Metal Exposure on Blood Pressure: A Bayesian Kernel Machine Regression Analysis. Atmosphere, 15(10), 1157. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15101157








