Effect of the Interaction between Excreta Type and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions in Pastures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Area
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Collection of Bovine Feces and Urine
2.4. N2O, CH4, and CO2 Flux Measurements and Emission Factors
2.5. Evaluation of N Losses by Ammonia Volatilization
2.6. Soil and Meteorological Parameters
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
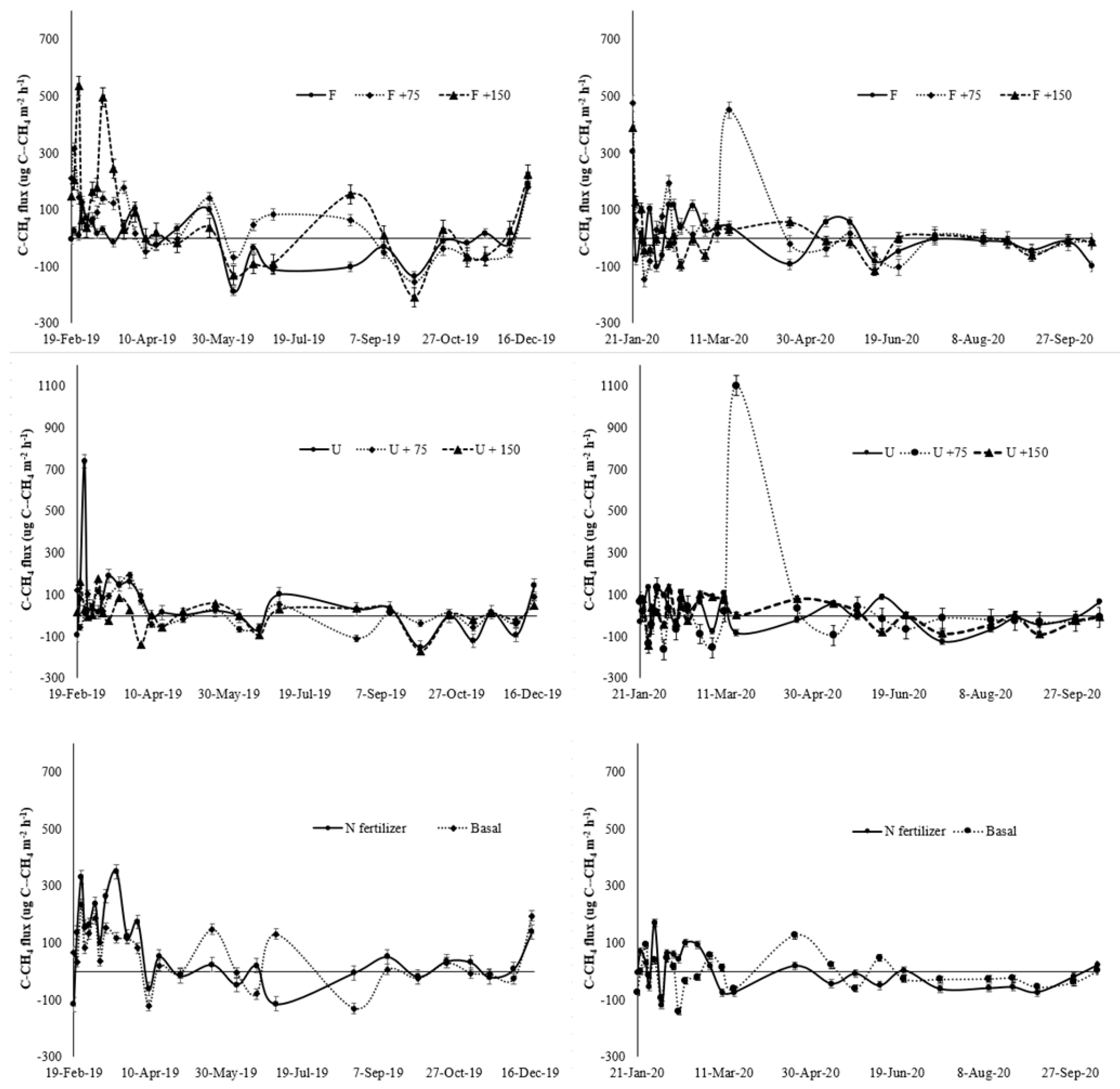
3.1. Seasonal Variation of N2O, CH4 and CO2 Fluxes
3.2. Effect of N Source on Accumulated Emissions of N2O, CH4, and CO2
3.3. Effect of Excreta Type Combined with Doses of N Fertilizer on Accumulated Emission of N2O, CH4 and CO2
3.4. Ammonia Volatilization
3.5. The Emission Factor of N2O and CH4
4. Discussion
4.1. Seasonal Variation of N2O, CH4, and CO2 Fluxes
4.2. Effect of N Source on Accumulated Emissions of N2O, CH4 and CO2
4.3. Effect of Excreta Type Combined with Doses of N Fertilizer on Accumulated Emission of N2O, CH4 and CO2
4.4. Ammonia Volatilization
4.5. The Emission Factor of N2O and CH4
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanderson, M.A.; Liebig, M.A. Forages and the Environment. In Forages: The Science of Grassland Agriculture; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 249–259. ISBN 9781119436669. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, A.S.; Mosnier, A.; Havlik, P.; Valin, H.; Herrero, M.; Schmid, E.; O’Hare, M.; Obersteiner, M. Cattle Ranching Intensification in Brazil Can Reduce Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Sparing Land from Deforestation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7236–7241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, R.P.; Malheiros, E.B.; Araújo, T.L.R.; Nave, R.L.G.; Mulliniks, J.T.; Berchielli, T.T.; Ruggieri, A.C.; Reis, R.A. Combining Marandu Grass Grazing Height and Supplementation Level to Optimize Growth and Productivity of Yearling Bulls. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 209, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, T.J.; de Medeiros Florindo, G.I.B.; Talamini, E.; da Costa, J.S.; Ruviaro, C.F. Carbon Footprint and Life Cycle Costing of Beef Cattle in the Brazilian Midwest. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.D.; Barbero, R.P.; Romanzini, E.P.; Teobaldo, R.W.; Ongaratto, F.; da Rocha Fernandes, M.H.M.; Ruggieri, A.C.; Reis, R.A. Intensification: A Key Strategy to Achieve Great Animal and Environmental Beef Cattle Production Sustainability in Brachiaria Grasslands. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; Eggleston, H.S., Buendia, L., Miwa, K., Ngara, T., Tanabe, K., Eds.; Publishing Institute of Global Environmental Strategy (IGES): Hayama, Japan, 2006; ISBN 4-88788-032-4. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Bartram, D.M., Cai, B., Buendia, E.C., Dong, H., Garg, A., Guendehou, G.H.S., Limmeechokchai, B., MacDonald, J.D., Ogle, S.M., Ottinger, D.A., et al., Eds.; Task Force on National Greenhouse Gas Inventories (TFB): Hayama, Japan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, P.L.; Dieckow, J.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Zanatta, J.A.; van der Weerden, T.J.; Ramalho, B.; Bayer, C. Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors from Cattle Urine and Dung, and Dicyandiamide (DCD) as a Mitigation Strategy in Subtropical Pastures. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 267, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.D.; Oliveira, S.C.; Janusckiewicz, E.R.; Brito, L.F.; da Morgado, E.S.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. Seasonal Effects on Ammonia, Nitrous Oxide, and Methane Emissions for Beef Cattle Excreta and Urea Fertilizer Applied to a Tropical Pasture. Soil. Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piva, J.T.; Sartor, L.R.; Sandini, I.E.; de Moraes, A.; Dieckow, J.; Bayer, C.; Rosa, C.M. Da Emissions of Nitrous Oxide and Methane in a Subtropical Ferralsol Subjected to Nitrogen Fertilization and Sheep Grazing in Integrated Crop-Livestock System. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2019, 43, e0180140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, D.C.D.; Cardoso, A.S.; Ferreira, M.R.; Siniscalchi, D.; Toniello, A.D.; Lima, G.C.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. CH4, CO2 and N2O Emissions from Soil Are Affected by the Sources and Doses of N in Tropical Pastures. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Corrêa, D.C.C.; da Cardoso, A.S.; Ferreira, M.R.; Siniscalchi, D.; de Gonçalves, P.H.A.; Lumasini, R.N.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. Ammonia Volatilization, Forage Accumulation, and Nutritive Value of Marandu Palisade Grass Pastures in Different N Sources and Doses. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, B.; Forrestal, P.J.; Jahangir, M.M.R.; Ryan, M.; Fanning, A.; Carton, O.T.; Lanigan, G.; Richards, K.G. The Interactive Effects of Fertiliser Nitrogen with Dung and Urine on Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Grassland. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2016, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.R.; Cardenas, L.M.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Donovan, N.; Misselbrook, T.; Williams, J.R.; Thorman, R.E.; McGeough, K.L.; Watson, C.J.; Bell, M.; et al. The Contribution of Cattle Urine and Dung to Nitrous Oxide Emissions: Quantification of Country Specific Emission Factors and Implications for National Inventories. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, J.; Krol, D.; Pasquier, D.; Cowan, N.; Skiba, U.; Rees, R.M.; Reay, D.; Lanigan, G.J.; Richards, K.G. Nitrogen Fertiliser Interactions with Urine Deposit Affect Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Grazed Grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 290, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Merbold, L.; Leitner, S.; Wolf, B.; Pelster, D.; Goopy, J.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Interactive Effects of Dung Deposited onto Urine Patches on Greenhouse Gas Fluxes from Tropical Pastures in Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staff, K.S.S. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- da Araújo, E.S.; Marsola, T.; Miyazawa, M.; de Soares, L.H.B.; Urquiaga, S.; Boddey, R.M.; Alves, B.J.R. Calibração de Câmara Semiaberta Estática Para Quantificação de Amônia Volatilizada Do Solo. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2009, 44, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC Internationa, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists International: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An Examination of the Degtjareff Method for Determining Soil Organic Matter, and a Proposed Modification of the Chromic Acid Titration Method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, A.C.R.; Madari, B.E.; Paredes, D.S.; Boddey, R.M.; Urquiaga, S.; Jantalia, C.P.; Alves, B.J.R. Bovine Urine and Dung Deposited on Brazilian Savannah Pastures Contribute Differently to Direct and Indirect Soil Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, B.J.R.; Smith, K.A.; Flores, R.A.; Cardoso, A.S.; Oliveira, W.R.D.; Jantalia, C.P.; Urquiaga, S.; Boddey, R.M. Selection of the Most Suitable Sampling Time for Static Chambers for the Estimation of Daily Mean N2O Flux from Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 46, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.S.; Alves, B.J.R.; Urquiaga, S.; Boddey, R.M. Effect of Volume of Urine and Mass of Faeces on N2O and CH4 Emissions of Dairy-Cow Excreta in a Tropical Pasture. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Weerden, T.J.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Podolyan, A.; Phillips, R.L.; Saggar, S.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Cox, N.; Ettema, P.; Rys, G. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Urea Fertiliser and Effluent with and without Inhibitors Applied to Pasture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 219, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doane, T.A.; Horwáth, W.R. Spectrophotometric Determination of Nitrate with a Single Reagent. Anal. Lett. 2003, 36, 2713–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordi, A.; Dieckow, J.; Bayer, C.; Alburquerque, M.A.; Piva, J.T.; Zanatta, J.A.; Tomazi, M.; da Rosa, C.M.; de Moraes, A. Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors for Urine and Dung Patches in a Subtropical Brazilian Pastureland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.; Giovani, B.; Rosseto, E.; de Figueiredo, L.; Morgado, S.; Andrade, R.; Claudia, A. N2O Emissions from Urine-Treated Tropical Soil: Effects of Soil Moisture and Compaction, Urine Composition, and Dung Addition. Catena 2017, 157, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, S.J.; Jantalia, C.P.; Aita, C.; Urquiaga, S.S.; Alves, B.J.R. Emissão de Óxido Nitroso Com a Aplicação de Dejetos Líquidos de Suínos Em Solo Sob Plantio Direto. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2006, 41, 1653–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cardoso, A.S.; da Brito, L.F.; Janusckiewicz, E.R.; da Morgado, E.S.; Barbero, R.P.; Koscheck, J.F.W.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. Impact of Grazing Intensity and Seasons on Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Tropical Grassland. Ecosystems 2017, 20, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetto, A.M.; Barneze, A.S.; Feigl, B.J.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Oenema, O.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Cerri, C.C. Use of the Nitrification Inhibitor Dicyandiamide (DCD) Does Not Mitigate N2O Emission from Bovine Urine Patches under Oxisol in Northwest Brazil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 101, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cardoso, A.S.; Quintana, B.G.; Janusckiewicz, E.R.; de Figueiredo Brito, L.; da Silva Morgado, E.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. How Do Methane Rates Vary with Soil Moisture and Compaction, N Compound and Rate, and Dung Addition in a Tropical Soil? Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggar, S.; Bolan, N.S.; Bhandral, R.; Hedley, C.B.; Luo, J. A Review of Emissions of Methane, Ammonia, and Nitrous Oxide from Animal Excreta Deposition and Farm Effluent Application in Grazed Pastures. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2004, 47, 513–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédard, C.; Knowles, R. Physiology, Biochemistry, and Specific Inhibitors of CH4, NH4+, and CO Oxidation by Methanotrophs and Nitrifiers. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Hernández, M.; Guan, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Y.; Di, H.; Xu, J. Impact of Grazing on Shaping Abundance and Composition of Active Methanotrophs and Methane Oxidation Activity in a Grassland Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.F.; Azenha, M.V.; Janusckiewicz, E.R.; Cardoso, A.S.; Morgado, E.S.; Malheiros, E.B.; la Scala, N.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C. Seasonal Fluctuation of Soil Carbon Dioxide Emission in Differently Managed Pastures. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of Ammonium and Nitrate Nutrition on Some Physiological Processes in Higher Plants—Growth, Photosynthesis, Photorespiration, and Water Relations. Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Weerden, T.J.; Luo, J.; de Klein, C.A.M.; Hoogendoorn, C.J.; Littlejohn, R.P.; Rys, G.J. Disaggregating Nitrous Oxide Emission Factors for Ruminant Urine and Dung Deposited onto Pastoral Soils. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemedtsson, L.; von Arnold, K.; Weslien, P.; Gundersen, P. Soil CN Ratio as a Scalar Parameter to Predict Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.J.; Costello, A.; Lidstrom, M.E.; Murrell, J.C. Evidence That Participate Methane Monooxygenase and Ammonia Monooxygenase May Be Evolutionarily Related. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 132, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hütsch, B.W. Methane Oxidation in Arable Soil as Inhibited by Ammonium, Nitrite, and Organic Manure with Respect to Soil PH. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 28, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, I.; Boeckx, P.; Galchenko, V.; van Cleemput, O. Short- and Medium-Term Effects of NH4+ on CH4 and N2O Fluxes in Arable Soils with a Different Texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, E.; Brito, L.F.; Janusckiewicz, E.R.; Oliveira, L.F.; Versuti, J.; Assumpção, F.M.; Cardoso, A.S.; Siniscalchi, D.; Delevatti, L.M.; Malheiros, E.B.; et al. Greenhouse Gases Emissions from Tropical Grasslands Affected by Nitrogen Fertilizer Management. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 4666–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M. Partitioning the Components of Soil Respiration: A Research Challenge. Plant Soil 2006, 284, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojeremane, W.; Rees, R.M.; Mencuccini, M. The Effects of Site Preparation Practices on Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Nitrous Oxide Fluxes from a Peaty Gley Soil. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2012, 85, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.S.K.; Parkin, T.B. Effect of Land Use on Methane Flux from Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluvione, F.; Halvorson, A.D.; del Grosso, S.J. Nitrogen, Tillage, and Crop Rotation Effects on Carbon Dioxide and Methane Fluxes from Irrigated Cropping Systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubbers, I.M.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Fonte, S.J.; Six, J.; Brussaard, L.; van Groenigen, J.W. Greenhouse-Gas Emissions from Soils Increased by Earthworms. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, E.B.; Jayasundara, S.; de Oliveira Bordonal, R.; Berchielli, T.T.; Reis, R.A.; Wagner-Riddle, C.; la Scala, N. Greenhouse Gas Balance and Carbon Footprint of Beef Cattle in Three Contrasting Pasture-Management Systems in Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godde, C.M.; de Boer, I.J.M.; Ermgassen, E.Z.; Herrero, M.; van Middelaar, C.E.; Muller, A.; Röös, E.; Schader, C.; Smith, P.; van Zanten, H.H.E.; et al. Soil Carbon Sequestration in Grazing Systems: Managing Expectations. Clim. Chang. 2020, 161, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, D.R.; Whitehead, D.C. Volatilization of Ammonia from Cattle Urine Applied to Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.O.; Sommer, S.G.; Aaes, O.; Søegaard, K. Ammonia Losses from Urine and Dung of Grazing Cattle: Effect of N Intake. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvaney, M.J.; Cummins, K.A.; Wood, C.W.; Wood, B.H.; Tyler, P.J. Ammonia Emissions from Field-Simulated Cattle Defecation and Urination. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- das Chagas, P.H.M.; Gouveia, G.C.C.; da Costa, G.G.S.; Barbosa, W.F.S.; Alves, A.C. Volatilização de Amônia Em Pastagem Adubada Com Fontes Nitrogenadas. Rev. Agric. Neotrop. 2017, 4, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, R.; Petersen, S.O.; Christofides, C.; Dittert, K.; Hansen, M.N. Short-Term N2O, CO2, NH3 Fluxes, and N/C Transfers in a Danish Grass-Clover Pasture after Simulated Urine Deposition in Autumn. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Angers, D.A.; Chantigny, M.H.; Gasser, M.-O.; MacDonald, J.D.; Pelster, D.E.; Bertrand, N. NH3 Volatilization, Soil Concentration and Soil PH Following Subsurface Banding of Urea at Increasing Rates. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, D.J.; Carolan, R.; Minet, E.; McGeough, K.L.; Watson, C.J.; Forrestal, P.J.; Lanigan, G.J.; Richards, K.G. Improving and Disaggregating N2O Emission Factors for Ruminant Excreta on Temperate Pasture Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaghan, R.M.; Barraclough, D. Some Chemical and Physical Factors Affecting the Rate and Dunamics of Nitrification in Urine-Affected Soil. Plant Soil. 1992, 143, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggar, S.; Hedley, C.B.; Giltrap, D.L.; Lambie, S.M. Measured and Modelled Estimates of Nitrous Oxide Emission and Methane Consumption from a Sheep-Grazed Pasture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 122, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Ongaratto, F.; Fernandes, M.; Cardoso, A.; Lage, J.; Silva, L.; Reis, R.; Malheiros, E. Response of Pasture Nitrogen Fertilization on Greenhouse Gas Emission and Net Protein Contribution of Nellore Young Bulls. Animals 2022, 12, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Variables a | Doses of N Fertilization in Pastures (kg N ha−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 75 | 150 | |
| DM (%) | 15.5 ± 0.24 | 15.5 ± 0.19 | 14.8 ± 0.26 |
| Carbon in feces (% of DM) | 43.8 ± 0.81 | 45.1 ± 2.22 | 43.2 ± 0.67 |
| N in feces (% of DM) | 1.09 ± 0.04 | 1.18 ± 0.06 | 1.26 ± 0.07 |
| N in urine (g L−1) | 1.6 ± 0.83 | 1.8 ± 0.37 | 0.7 ± 0.38 |
| pH—urine | 7.7 ± 0.07 | 8.1 ± 0.01 | 8.2 ± 0.02 |
| C/N | 34.9 | 33.1 | 32.1 |
| Treatment 1 | N2O (mg N2O m−2) | CH4 (mg CH4 m−2) | CO2 (kg CO2 m−2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of N source | ||||
| F | 7.5 | 19.2 | 8.47 ab | |
| U | 4.9 | 60.7 | 10.42 ab | |
| N fertilizer | 0.40 | 71.4 | 11.51 a | |
| Basal | −8.05 | 38.4 | 7.15 b | |
| SEM | 5.47 | 0.19 | 0.47 | |
| p | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.008 | |
| Effect of feces and doses of N fertilizer | ||||
| F | 7.5 | 19.2 | 8.47 | |
| Feces | F + 75 | 17.0 | 65.9 | 10.65 |
| F + 150 | 74.2 | 65.7 | 13.38 | |
| SEM | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.252 | |
| Effect | linear | NS | linear | |
| p | 0.016 | 0.08 | 0.005 | |
| Effect of urine and doses of N fertilizer | ||||
| U | 4.9 | 60.7 | 10.42 | |
| Urine | U + 75 | 47.2 | 42.4 | 10.18 |
| U + 150 | 75.2 | 28.45 | 9.38 | |
| SEM | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.252 | |
| Effect | linear | NS | NS | |
| p | 0.003 | 0.37 | 0.74 | |
| Treatment 1 | NH3 (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Effect of feces and doses of N fertilizer | ||
| F | 6.75 | |
| Feces | F + 75 | 5.32 |
| F + 150 | 2.28 | |
| SEM | 0.018 | |
| Effect | linear | |
| p | 0.0003 | |
| Effect of urine and doses of N fertilizer | ||
| U | 14.1 | |
| Urine | U + 75 | 5.00 |
| U + 150 | 3.27 | |
| SEM | 0.018 | |
| Effect | linear | |
| p | <0.0001 | |
| Treatment 1 | EF (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Effect of N source | ||
| F | 0.11 | |
| U | 0.19 | |
| N fertilizer | 0.17 | |
| SEM | 0.0.086 | |
| p | 0.35 | |
| Effect of feces and doses of N fertilizer | ||
| F | 0.11 | |
| Feces | F + 75 | 0.13 |
| F + 150 | 0.42 | |
| SEM | 0.09 | |
| Effect | linear | |
| p | 0.010 | |
| Effect of urine and doses of N fertilizer | ||
| U | 0.19 | |
| Urine | U + 75 | 0.58 |
| U + 150 | 1.03 | |
| SEM | 0.09 | |
| Effect | linear | |
| p | 0.0006 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ongaratto, F.; Fernandes, M.H.M.d.R.; Dallantonia, E.E.; Lima, L.d.O.; Val, G.A.d.; Cardoso, A.d.S.; Rigobello, I.L.; Gomes, L.M.; Reis, R.A.; Ruggieri, A.C.; et al. Effect of the Interaction between Excreta Type and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions in Pastures. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030492
Ongaratto F, Fernandes MHMdR, Dallantonia EE, Lima LdO, Val GAd, Cardoso AdS, Rigobello IL, Gomes LM, Reis RA, Ruggieri AC, et al. Effect of the Interaction between Excreta Type and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions in Pastures. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030492
Chicago/Turabian StyleOngaratto, Fernando, Marcia Helena Machado da Rocha Fernandes, Erick Escobar Dallantonia, Lais de Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Alves do Val, Abmael da Silva Cardoso, Izabela Larosa Rigobello, Laís Mayumi Gomes, Ricardo Andrade Reis, Ana Claudia Ruggieri, and et al. 2023. "Effect of the Interaction between Excreta Type and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions in Pastures" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030492
APA StyleOngaratto, F., Fernandes, M. H. M. d. R., Dallantonia, E. E., Lima, L. d. O., Val, G. A. d., Cardoso, A. d. S., Rigobello, I. L., Gomes, L. M., Reis, R. A., Ruggieri, A. C., & Malheiros, E. B. (2023). Effect of the Interaction between Excreta Type and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Greenhouse Gas and Ammonia Emissions in Pastures. Atmosphere, 14(3), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030492










