Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
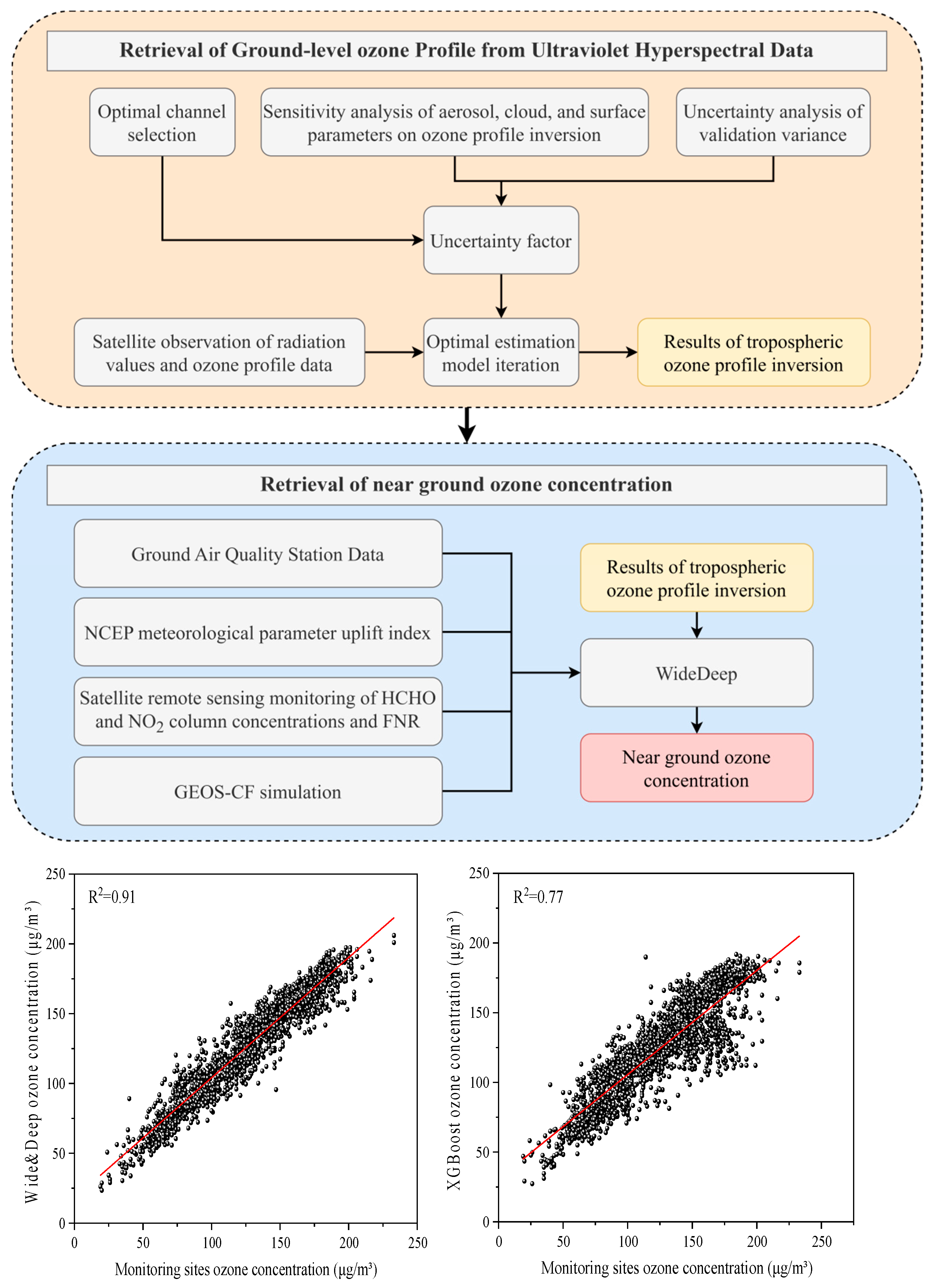
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.1.1. TROPOMI HCHO/NO2
2.1.2. Surface Ozone Data
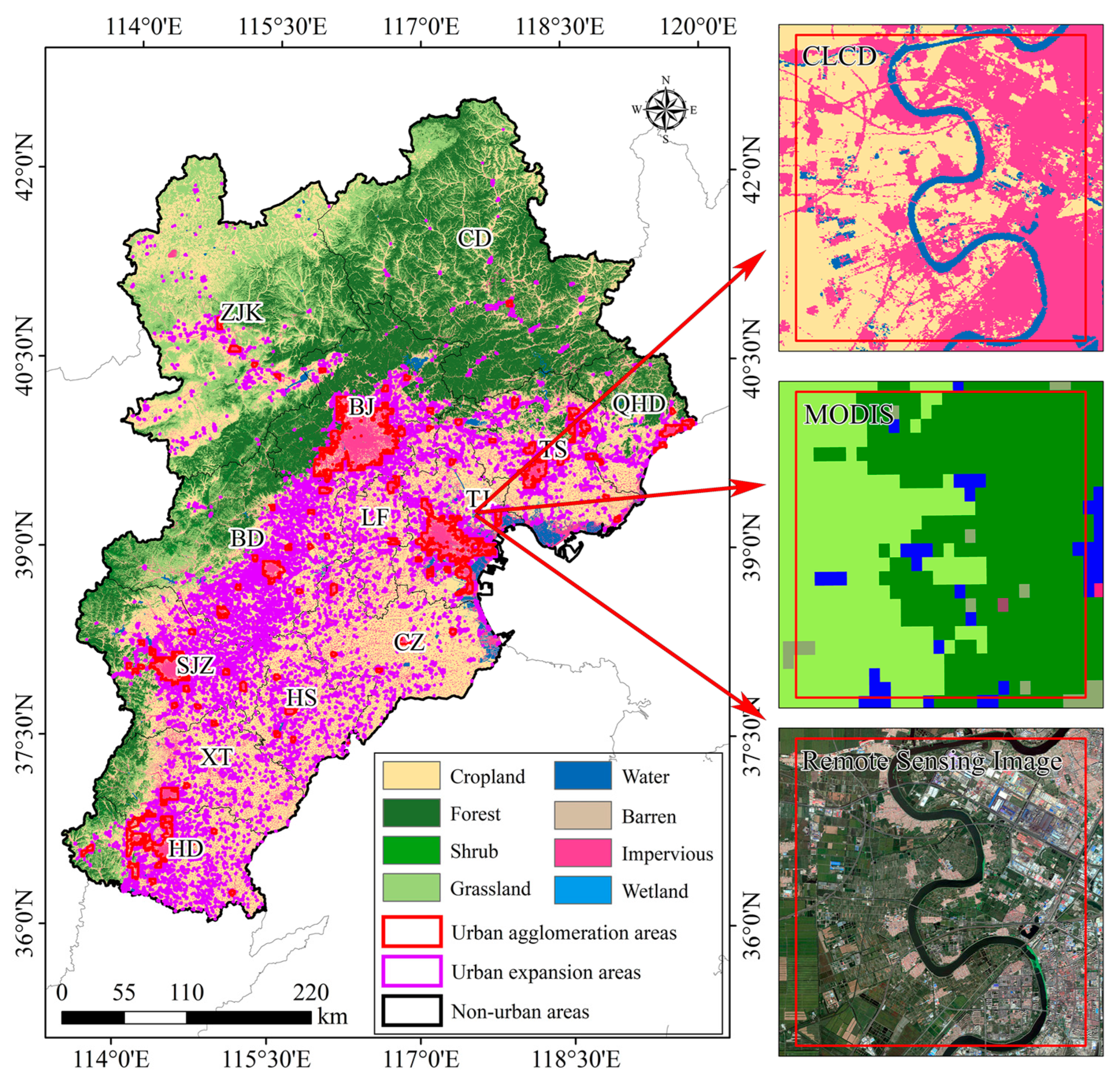
2.1.3. CLCD Land Cover Product
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Comparison of the Ozone Formation Regime between Urban and Non-Urban Areas
2.2.2. The Third-Order Polynomial Fitting Model
3. Results
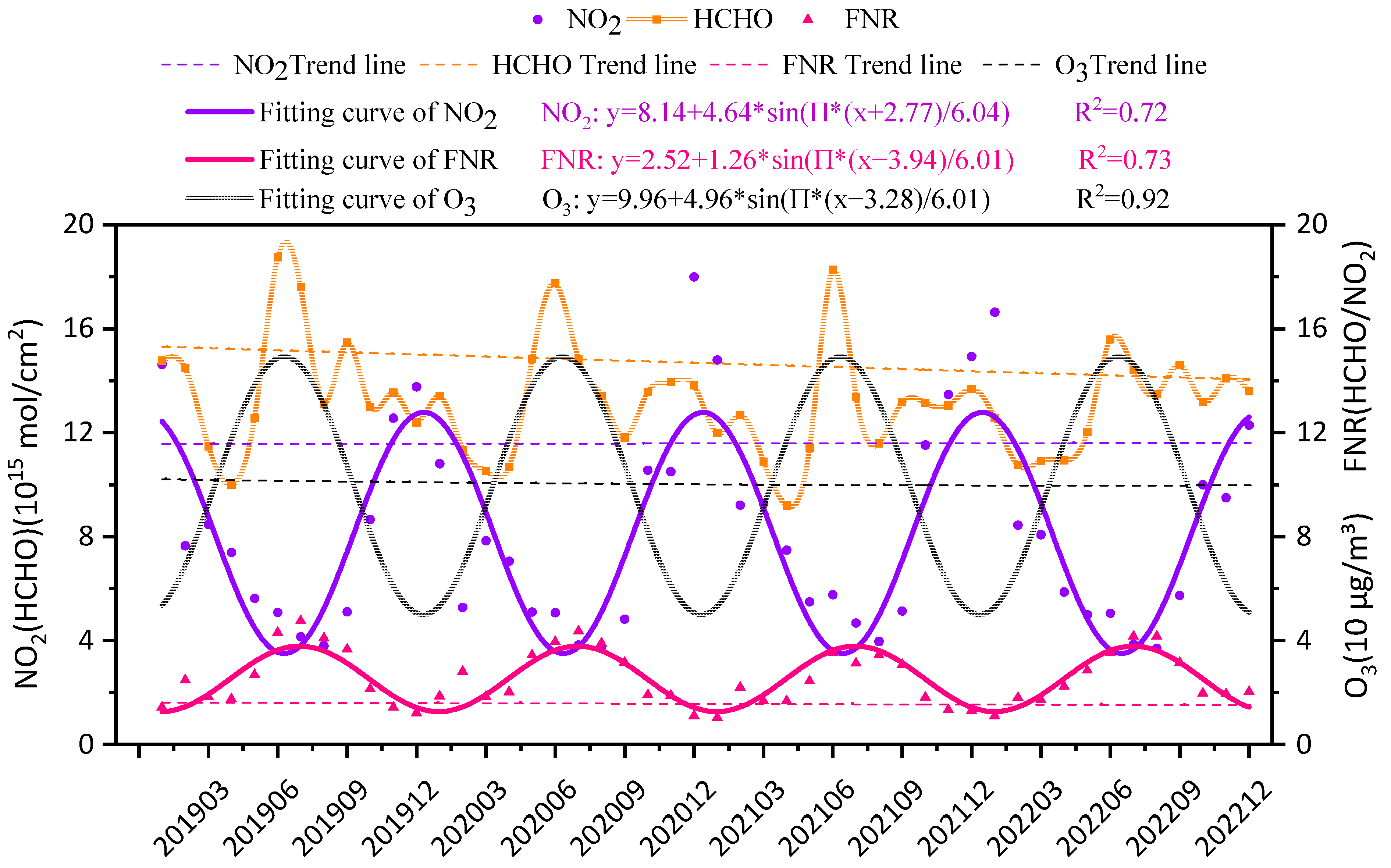
3.1. Time Trends of Ozone Precursors and FNR
3.2. Interannual Variations in HCHO and NO2 Column Concentrations under Different Ground Features
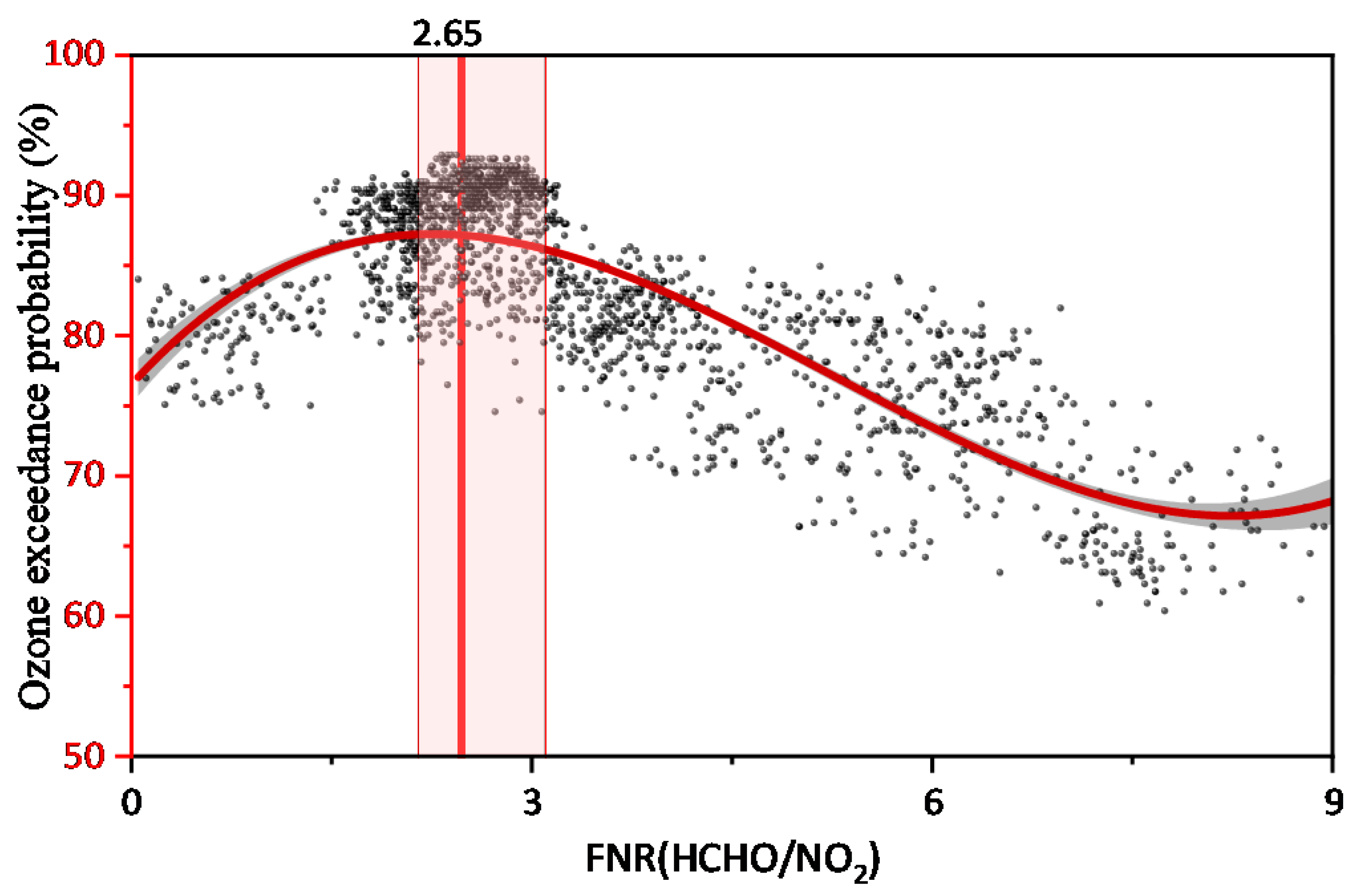
3.3. Estimation of Transition Range of Ozone Formation Regime in the BTH Region
3.4. Spatial Distribution of O3 Formation Regimes
3.5. Change in the Ozone Generation Sensitivity Regime in the BTH Region
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Gao, M.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Y.H. Rapid Increases in warmseason surface ozone and resulting health impact in China Since 2013. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.X.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xu, X.D.; Wang, J.N.; He, H.; Liu, W.Q.; et al. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.J. A Study on the Evolution of Ozone Pollution in China and Regional Management Methods; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Aneja, V.P.; Li, Z. Characterization of ozone at high elevation in the eastern United States: Trends, seasonal variations, and exposure. J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 9873–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, W.S.; Shamoo, D.A.; Anderson, K.R.; Peng, R.C.; Avol, E.L.; Hackney, J.D. Effects of prolonged, repeated exposure to ozone, sulfuric acid, and their combination in healthy and asthmatic volunteers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Comparison of health and economic impacts of PM2.5 and ozone pollution in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Xue, B.; Lv, Z.; Meng, Z.; Yang, X.; Xue, T.; Yu, Q.; He, K. Ground-level ozone pollution and its health impacts in China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xie, S.D.; Tang, X.Y. Ozone source attribution during a severe photochemical smog episode in Beijing, China. Sci. Sin. 2009, 39, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Su, H.; Zhong, L.J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zeng, L.M.; Wang, X.S.; Xiang, Y.R.; Wang, J.L.; Gao, D.F.; Shao, M. Regional ozone pollution and observation-based approach for analyzing ozone-precursor relationship during the PRIDE-PRD2004 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6203–6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, C.H.; Li, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, H.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Streets, D.G.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, G.F.; Chen, Y.R. Emission inventory of anthropogenic air pollutants and VOC species in the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4105–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; Olson, J.R.; Sillman, S.; Martin, R.V.; Lamsal, L.; Hu, Y.; Pickering, K.E.; Retscher, C.; Allen, D.J.; et al. Application of OMI observations to a space-based indicator of NOx and VOC controls on surface ozone formation. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2213–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Wang, Z.R.; Ding, A.J.; Heue, K.P.; Shen, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Shi, Y.N.; Hao, N.; Wenig, M. MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO in Nanjing and a comparison to ozone monitoring instrument observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 10051–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Su, H.; Zhao, S.M.; Zeng, L.M.; Zhong, L.J.; Xiang, Y.R.; Chang, C.C.; Chou, C.K.; Andreas, W. Regional ozone pollution and key controlling factors of photochemical ozone production in Pearl River Delta during summer time. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2010, 40, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Fan, L.Y.; Ye, D.Q. Study on the ozone formation sensitivity in the Pearl River Delta based on OMI satellite data and MODIS land cover type products. Acta Sci. Circum. 2019, 39, 3581–3592. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, L.Y. Ground Level Ozone Concentration Characteristics and Formation Sensitivity in China’s Three Agglomerations; South China University of Technology: Guangzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Cheng, S.; Han, L. Sensitivity of summer ozone to precursor emission change over Beijing during 2010–2015: A WRF-Chem modeling study. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 218, 116984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Attribution of tropospheric ozone to NOx and VOC emissions: Considering ozone formation in the transition regime. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.J.; Wang, S.A.; Gong, Z.Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. Spatial and seasonal variation and regionalization of ozone concentrations in China. China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 4003–4012. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=E0103&zb=A0202®=110000&sj=2022 (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Hu, L.M.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, N.F. Spatiotemporal change characteristics of ozone concentration in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, W.; Hou, M.; Li, Y.S.; Gao, P.; Xia, Q.; Meng, X.Y.; Fan, L.Y.; Ye, D.Q. Sources and control area division of ozone pollution in cities at prefacture level and above in China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 5215–5224. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, Q.P.; Ding, Y.H. Characteristics of ozone and its relationship with meteorological factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.J.; Meng, X.Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yu, H.X. Driving factors of the significant increase in surface ozone in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China, during 2013~2018. Environ. Sci 2020, 41, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Ma, Z.Q.; Hao, T.Y.; Fan, W.Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.X.; Cai, Z.Y.; Han, S.Q. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and background concentration estimation of ozone in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 4999–5008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Chen, Z. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of ground-level nitrogen dioxide and ozone across China during 2015–2020. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L. Satellite Data to Freshman. Total Ozone Column Daily Product. 2022. Available online: http://www.satdatafresh.com (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/missions/sentinel-5p (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/web/sentinel/user-guides/sentinel-5p-tropomi (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusede, S.E.; Cohen, R.C. On the observed response of ozone to NOx and VOC reactivity reductions in San Joaquin valley California 1995-present. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8323–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Fiore, A.; Boersma, K.F.; Smedt, I.; Valin, L. Inferring changes in summertime surface ozone-NOx-VOC chemistry over U.S. urban areas from two decades of satellite and ground-based observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 6518–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Yan, H.; Yao, Y.J.; Zeng, C.L.; Gao, P.; Zhuang, L.Y.; Fan, L.Y.; Ye, D.Q. Relationships of ozone formation sensitivity with precursors emissions, meteorology and land use types, in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 94, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xu, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Gao, B.; Zhao, N.; Yao, Q. Identifying the spatiotemporal variations of ozone formation regimes across China from 2005 to 2019 based on polynomial simulation and causality analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 21, 15631–15646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Guo, F.; Xie, S. Diagnosing ozone–NOx–VOC sensitivity and revealing causes of ozone increases in China based on 2013–2021 satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15035–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.R.; Crawford, J.H.; Fried, A.; Walega, J.; Weinheimer, A.; Wisthaler, A.; Müller, M.; Mikoviny, T.; Chen, G.; Shook, M.; et al. New insights into the column CH2O/NO2 ratio as an indicator of near-surface ozone sensitivity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8885–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Fiore, A.M.; Murray, L.T.; Valin, L.C.; Lamsal, L.N.; Duncan, B.; Boersma, K.F.; De Smedt, I.; Abad, G.G.; Chance, K.; et al. Evaluating a space-based indicator of surface ozone-NOxVOC sensitivity over midlatitude source regions and application to decadal trends. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 10–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.X.; Li, L.J.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhao, W.H. Spatial and temporal characteristics of atmospheric NO2 in the Beijing Tianjin-Hebei region. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Crutzen, P.J. The role of NO and NO2 in the chemistry of the troposphere and stratosphere. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1979, 7, 443–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.T.; Zheng, T.F.; Wan, Q.L.; Tan, H.B.; Deng, X.J.; Fei, L.I.; Deng, T. Spatiotemporal characteristics of NO2 in concentrated PRD urban districts and analysis of anthropogenic influences based on OMI remote sensing data. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2015, 31, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Miao, J. Spatiotemporal variations in satellite based formaldehyde (HCHO) in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China from 2005 to 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, N.F.; Zhao, L.N.; Wu, J.R.; Li, X.; Feng, T.; Li, G.H. Impacts of sea-land and mountain-valley circulations on the air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH): A case study. J. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Li, R.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Meng, F.; Cheng, B.; Ma, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; He, B.; et al. Ground ozone variations at an urban and a rural station in Beijing from 2006 to 2017: Trend, meteorological influences and formation regimes. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 235, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Hou, W.; Chen, L.; Ma, P. Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111637
Song H, Zhao W, Yang X, Hou W, Chen L, Ma P. Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(11):1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111637
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Hanyang, Wenji Zhao, Xingchuan Yang, Wenxing Hou, Linhan Chen, and Pengfei Ma. 2023. "Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data" Atmosphere 14, no. 11: 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111637
APA StyleSong, H., Zhao, W., Yang, X., Hou, W., Chen, L., & Ma, P. (2023). Ozone Sensitivity Analysis and Ozone Formation Regimes Division in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region Based on Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Atmosphere, 14(11), 1637. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111637








