Effect of Source Emission Control Measures on Source of Atmospheric PM2.5 during “Parade Blue” Period
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
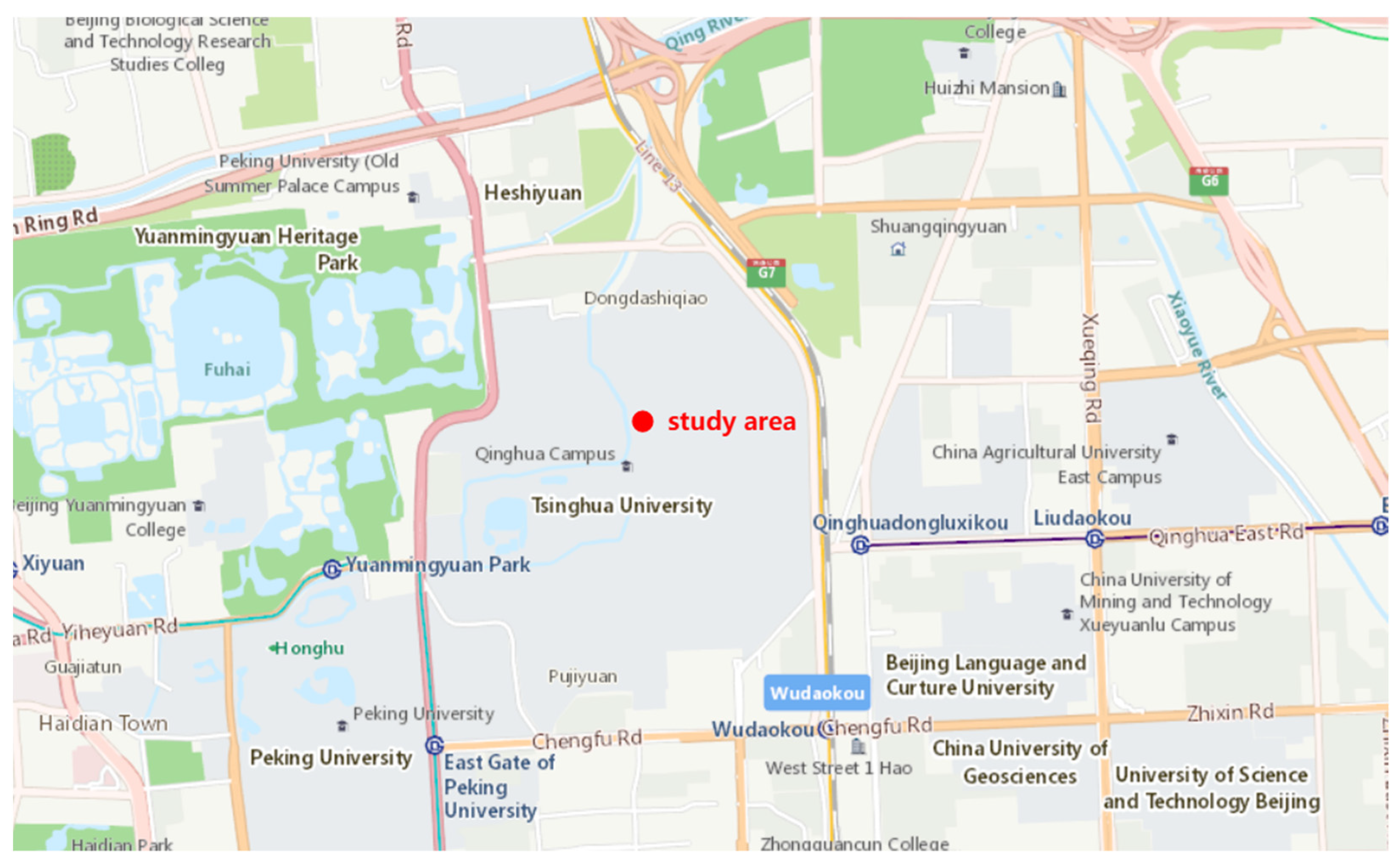
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Component Analysis
2.3. CMB Receptor Model
2.4. Uncertainty Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
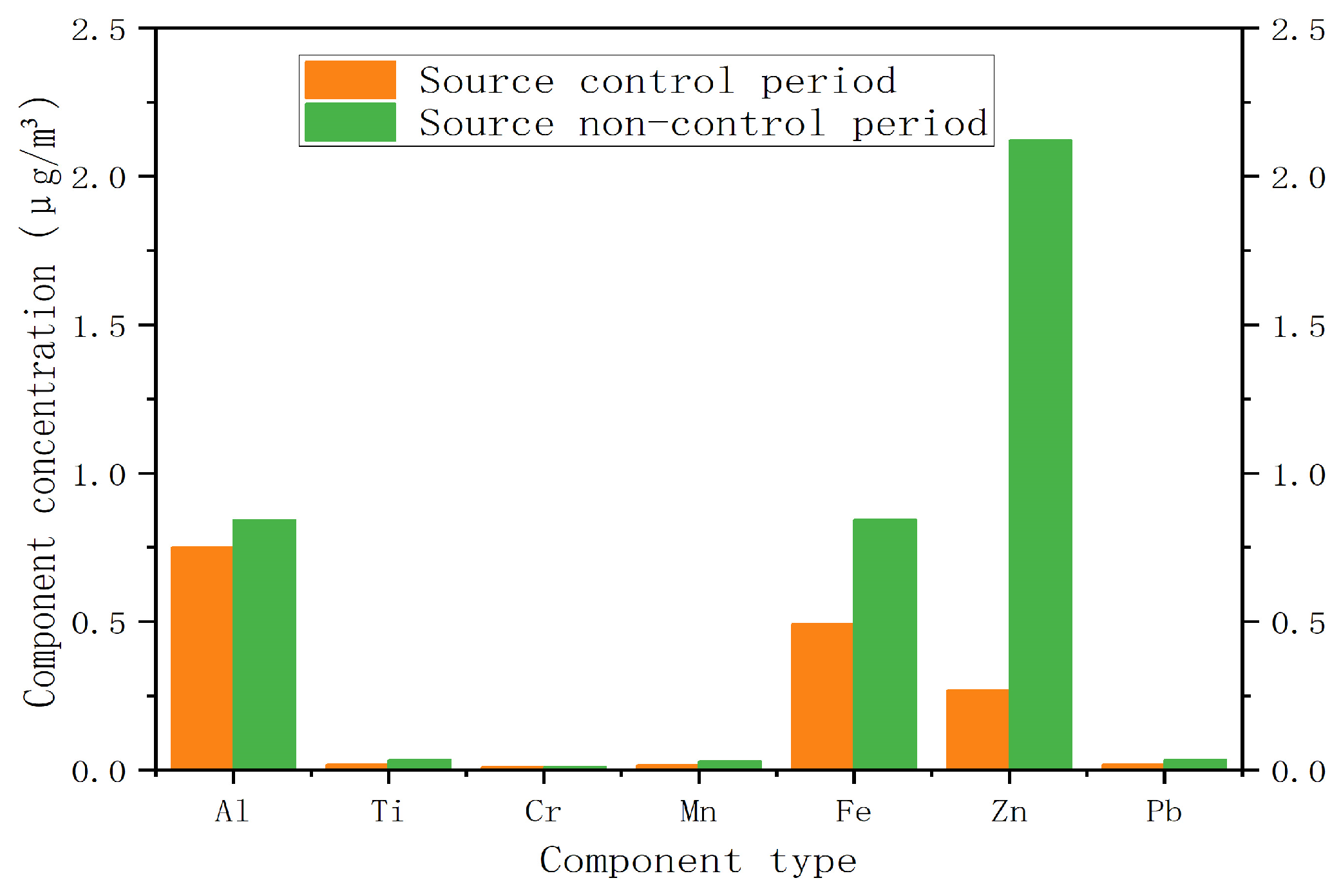
3.1. Concentrations of PM2.5 and Its Components in the Source Control Period/Source Non-Control Period
3.2. Comparison of EPACMB8.2 and NKCMB1.0 Receptor Models
3.2.1. Source Control Period Comparison Results
3.2.2. Source Non-Control Period Comparison Result
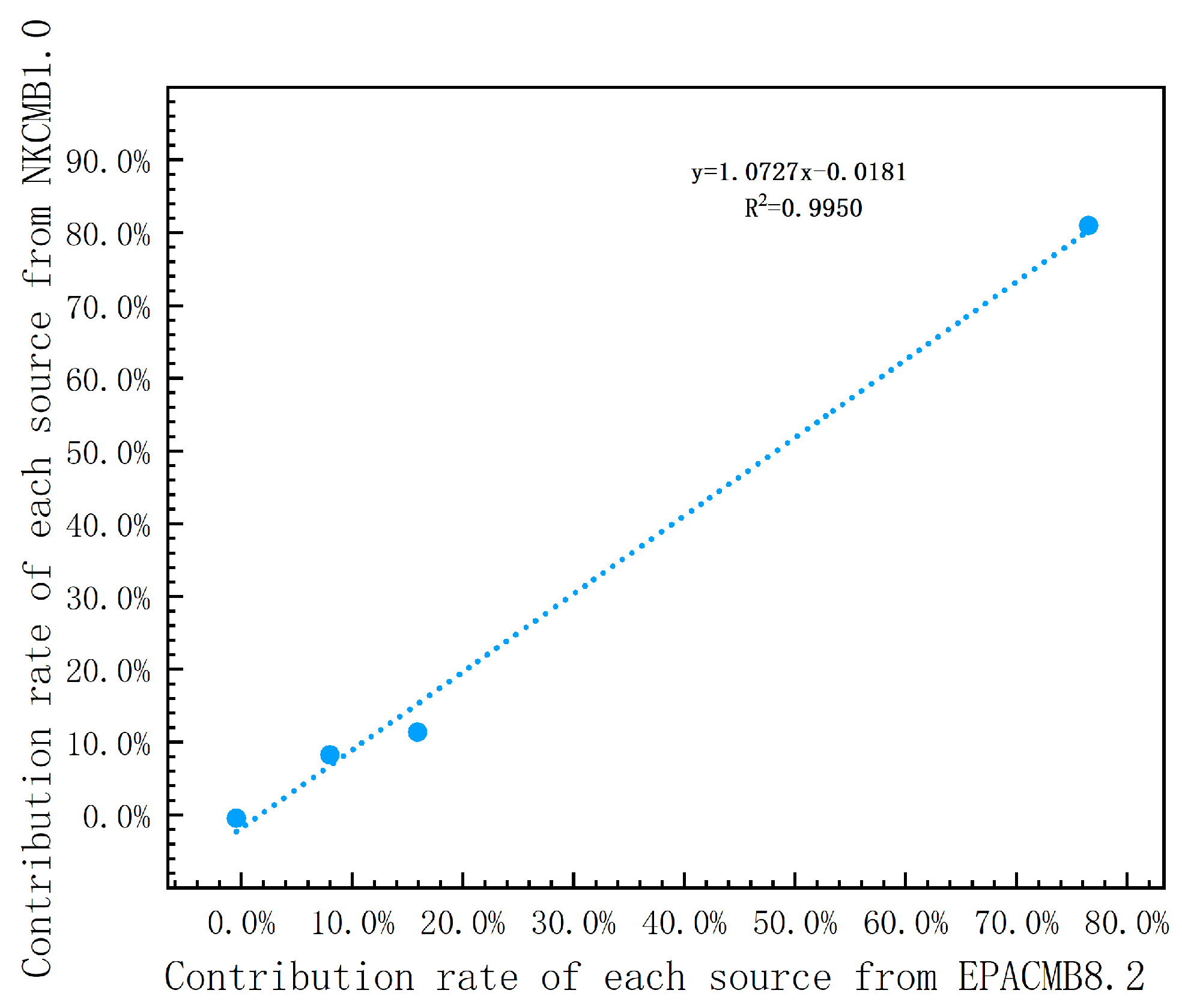
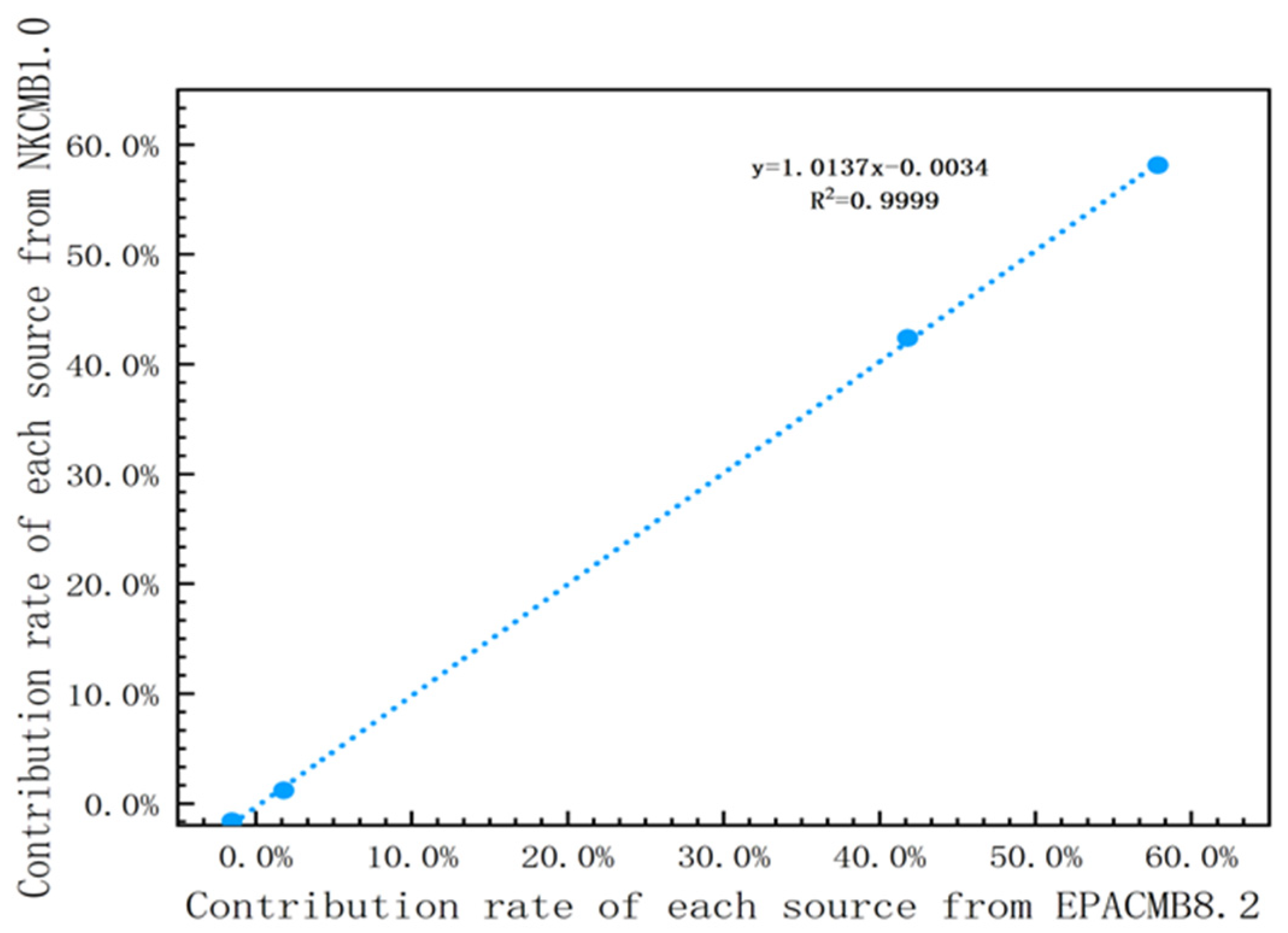
3.2.3. Comparison Results and Discussion
3.3. Limitations and Prospects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, T.T.; Tang, M. Biological effects of airborne fine particulate matter (PM2.5) exposure on pulmonary immune system. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.T.; Xue, B.; Zhou, Q.F.; Su, R.J.; Li, Z.Y. Mitochondrial damage mediated by ROS incurs bronchial epithelial cell apoptosis upon ambient PM2.5 exposure. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 43, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Avila, I.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; Riojas-Rodríguez, H.; Kloog, I.; Just, A.C.; Rothenberg, S.J. Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Mortality Associated With Acute Exposure to PM2.5 in Mexico City. Stroke 2018, 49, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.F.; Xu, Y.H.; Shi, M.H.; Lian, Y.X. The impact of PM2.5 on the human respiratory system. J. Thorac Dis. 2016, 8, E69–E74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Gu, B.J.; Erisman, J.W.; Reis, S.; Fang, Y.Y.; Lu, X.H.; Zhang, X.M. PM2.5 pollution is substantially affected by ammonia emissions in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Fang, D.L.; Chen, B. Human health impact and economic effect for PM2.5 exposure in typical cities. Appl. Energy 2019, 249, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncoro, C.B.D.; Adristi, C.; Asyikin, M.B.Z. Smart Wireless Particulate Matter Sensor Node for IoT-Based Strategic Monitoring Tool of Indoor COVID-19 Infection Risk via Airborne Transmission. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruinong, L. Column: Air Quality Assurance for Commemorating the 70th Anniversary of the Victory of the Chinese People’s War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression and the World Anti-Fascist War; Ministry of Foreign Affairs: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Yin, L.R.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.Z.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W.F. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Haze in Beijing Based on the Multi-Convolution Model. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, J.W.; Zheng, W.F.; Yin, L.R. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of haze and pollution particles in China based on spatial statistics. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Z.X.; Yin, Z.T.; Liu, X.; Li, X.L.; Yin, L.R.; Zheng, W.F. Predict the effect of meteorological factors on haze using BP neural network. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.R.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.Z.; Tian, J.W.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W.F. Haze Grading Using the Convolutional Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Xu, S.C.; Shan, M.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Du, Z.H.; Liu, D.T.; Xu, D.; et al. Variation in Concentration and Sources of Black Carbon in a Megacity of China During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL090444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Song, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, D.Y.; Tang, A.H.; Yang, D.W.; Wang, D.D.; et al. Air quality improvement in a megacity: Implications from 2015 Beijing Parade Blue pollution control actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, Z.Q.; de Foy, B.; Schauer, J.J.; Zhang, Y.X. “Military Parade Blue Skies” in Beijing: Decisive Influence of Meteorological Factors on Transport Channel and Atmospheric Pollutant Concentration Level. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.F.; Tian, H.Z.; Nie, L.; Wu, X.Q.; Zhou, J.R.; Zhou, Z. Multi-dimension apportionment of clean air “parade blue” phenomenon in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 65, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Lang, J.L.; Wang, G. Characterization of Chemical Composition in PM2.5 in Beijing before, during, and after a Large-Scale International Event. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.F.; Zhang, S.H.; Nie, T.; Cao, X.Z.; Shi, A.J. Environmental Effective Assessment of Control Measures Implemented by Clean Air Action Plan (2013-2017) in Beijing, China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, P.F.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.D.; Chen, X.Y. A clustering algorithm for sample data based on environmental pollution characteristics. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridi, S.; Yousefian, F.; Roostaei, V.; Harrison, R.M.; Azimi, F.; Niazi, S.; Naddafi, K.; Momeniha, F.; Malkawi, M.; Safi, H.A.M.; et al. Source apportionment, identification and characterization, and emission inventory of ambient particulate matter in 22 Eastern Mediterranean Region countries: A systematic review and recommendations for good practice. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.X.; Feng, Y.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Cai, J.J.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.M. Source apportionment of PM2.5 during haze episodes in Shanghai by the PMF model with PAHs. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zhang, H.F.; Chen, J.M.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, Q.Z.; Xue, L.K.; Ding, A.J.; Mellouki, A. Six sources mainly contributing to the haze episodes and health risk assessment of PM2.5 at Beijing suburb in winter 2016. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Vijayan, N.; Mandal, T.K. Seasonal characteristics of aerosols (PM2.5 and PM10) and their source apportionment using PMF: A four year study over Delhi, India. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, K.; Yu, X.; Su, F.C.; Yin, S.S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, R.Q. Chemical Characteristics and Source Apportionment by Two Receptor Models of Size-segregated Aerosols in an Emerging Megacity in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Kojima, T.; Amato, F.; Lucarelli, F.; de la Rosa, J.; Calzolai, G.; Nava, S.; Chiari, M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; et al. Daily and hourly chemical impact of springtime transboundary aerosols on Japanese air quality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojgaard, J.K.; Peker, L.; Pernov, J.B.; Johnson, M.S.; Bossi, R.; Massling, A.; Lange, R.; Nielsen, I.E.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Eriksson, A.C.; et al. A local marine source of atmospheric particles in the High Arctic. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 285, 119241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dadashazar, H.; Braun, R.A.; MacDonald, A.B.; Aghdam, M.A.; Maudlin, L.C.; Sorooshian, A. Size-resolved characteristics of water-soluble particulate elements in a coastal area: Source identification, influence of wildfires, and diurnal variability. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 206, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Singh, G.; Yadav, P. Identification and elucidation of anthropogenic source contribution in PM10 pollutant: Insight gain from dispersion and receptor models. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.L.; Yuan, C.S.; Wong, K.W.; Lin, C. Chemical fingerprints and source resolution of atmospheric fine particles in an industrial harbor based on one-year intermittent field sampling data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D. Attributing Atmospheric Methane to Anthropogenic Emission Sources. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1344–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Cumberland, S.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Allan, J.; Young, D.E.; Williams, P.I.; Coe, H. Receptor modelling of fine particles in southern England using CMB including comparison with AMS-PMF factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2139–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Chemical Mass Balance (CMB) Model. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/scram/chemical-mass-balance-cmb-model (accessed on 10 June 2023).
- The State Environment Protection Key Laboratory of Urban Particulate Air Pollution Protection. NKCMB1.0. Available online: https://env.nankai.edu.cn/air/ (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- Friedlander, S.K. Chemical element balances and identification of air pollution sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1973, 7, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, J.G. Chemical Element Balance Receptor Model Methodology for Assessing the Sources of Fine and Total Suspended Particulate Matter in Portland, Oregon; Oregon Graduate Institute of Science and Technology: Portland, OR, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, C.C. EPA-CMB8.2Users Manual [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2020-10/documents/epa-cmb82manual.pdf (accessed on 29 July 2023).
- Wang, T.; Hua, Y.; Xu, Q.-C.; Wang, S.-X. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Suburban Area of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in Autumn and Winter. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2019, 40, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Feng, Y.C. Source Analysis of Atmospheric Particulate Matter: Principle, Technology and Application; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]


| Emission Source | Al | Ti | Cr | Mn | Fe | Zn | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban dust | 0.0547 | 0.0055 | 0 | 0.0003 | 0.0266 | 0.0005 | 0 |
| Tianjin Iron and Steel | 0.0281 | 0.0047 | 0.0010 | 0.0098 | 0.2346 | 0.0183 | 0.0182 |
| Industrial combustion | 0.0038 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0142 | 0.0169 | 0.0001 |
| Gasoline car | 0.0024 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0040 | 0.0027 | 0.0005 |
| Diesel car | 0.0024 | 0.0013 | 0.0010 | 0.0008 | 0.0054 | 0.0008 | 0 |
| Period | Date | PM2.5 | Al | Ti | Cr | Mn | Fe | Zn | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source control | 21 August 2015–4 September 2015 | 26.31 | 0.750 | 0.019 | 0.010 | 0.017 | 0.493 | 0.269 | 0.020 |
| Non-source control | 17 August 2015–20 August 2015 5 September 2015–7 September 2015 | 40.08 | 0.842 | 0.033 | 0.011 | 0.030 | 0.844 | 2.122 | 0.035 |
| Period | Date | Number | Al | Ti | Cr | Mn | Fe | Zn | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-source control | 17 August 2015 | T21 | 2.2886 | 0.0826 | 0.0174 | 0.0561 | 1.5697 | 0.3992 | 0.0545 |
| 19 August 2015 | T04 | 0.8636 | 0.0333 | 0.0106 | 0.0273 | 0.7121 | 0.3136 | 0.0311 | |
| 19 August 2015 | T22 | 0.7597 | 0.0299 | 0.0083 | 0.0229 | 0.6375 | 0.2576 | 0.0201 | |
| Source control | 21 August 2015 | T23 | 1.0606 | 0.0348 | 0.0121 | 0.0273 | 0.8045 | 0.2674 | 0.0159 |
| 22 August 2015 | T03 | 0.7515 | 0.0402 | 0.0121 | 0.0311 | 0.9523 | 0.3023 | 0.0591 | |
| 23 August 2015 | T19 | 0.4555 | 0.0173 | 0.0110 | 0.0155 | 0.5330 | 0.3021 | 0.0110 | |
| 24 August 2015 | T25 | 4.6399 | 0.0190 | 0.0091 | 0.0190 | 0.6441 | 0.2551 | 0.0099 | |
| 25 August 2015 | T11 | 0.4893 | 0.0193 | 0.0108 | 0.0131 | 0.4538 | 0.2474 | 0.0085 | |
| 26 August 2015 | T10 | 0.4173 | 0.0160 | 0.0107 | 0.0122 | 0.3876 | 0.2556 | 0.0076 | |
| 27 August 2015 | T18 | 0.3900 | 0.0180 | 0.0120 | 0.0143 | 0.3848 | 0.2535 | 0.0135 | |
| 28 August 2015 | T24 | 0.7260 | 0.0276 | 0.0103 | 0.0253 | 0.6787 | 0.2904 | 0.0229 | |
| 29 August 2015 | T07 | 0.3507 | 0.0226 | 0.0078 | 0.0187 | 0.5006 | 0.2694 | 0.0320 | |
| 30 August 2015 | T12 | 0.2257 | 0.0130 | 0.0115 | 0.0122 | 0.3053 | 0.2609 | 0.0191 | |
| 31 August 2015 | T17 | 0.1203 | 0.0055 | 0.0086 | 0.0055 | 0.1476 | 0.2413 | 0.0062 | |
| 1 September 2015 | T05 | 0.2095 | 0.0089 | 0.0105 | 0.0081 | 0.2579 | 0.2434 | 0.0097 | |
| 2 September 2015 | T08 | 0.3078 | 0.0103 | 0.0087 | 0.0079 | 0.2833 | 0.2596 | 0.0071 | |
| 3 September 2015 | T13 | 0.3559 | 0.0197 | 0.0087 | 0.0339 | 0.5650 | 0.3149 | 0.0537 | |
| 4 September 2015 | T09 | 0.1647 | 0.0093 | 0.0077 | 0.0077 | 0.1832 | 0.2350 | 0.0186 | |
| Non-source control | 5 September 2015 | T20 | 0.4901 | 0.0178 | 0.0085 | 0.0271 | 0.9021 | 12.936 | 0.0433 |
| 6 September 2015 | T16 | 0.6662 | 0.0313 | 0.0107 | 0.0305 | 1.0565 | 0.3335 | 0.0247 | |
| 7 September 2015 | T15 | 0.6579 | 0.0255 | 0.0108 | 0.0356 | 0.8434 | 0.3765 | 0.0495 |
| Emission Source | EPACMB8.2 | NKCMB1.0 |
|---|---|---|
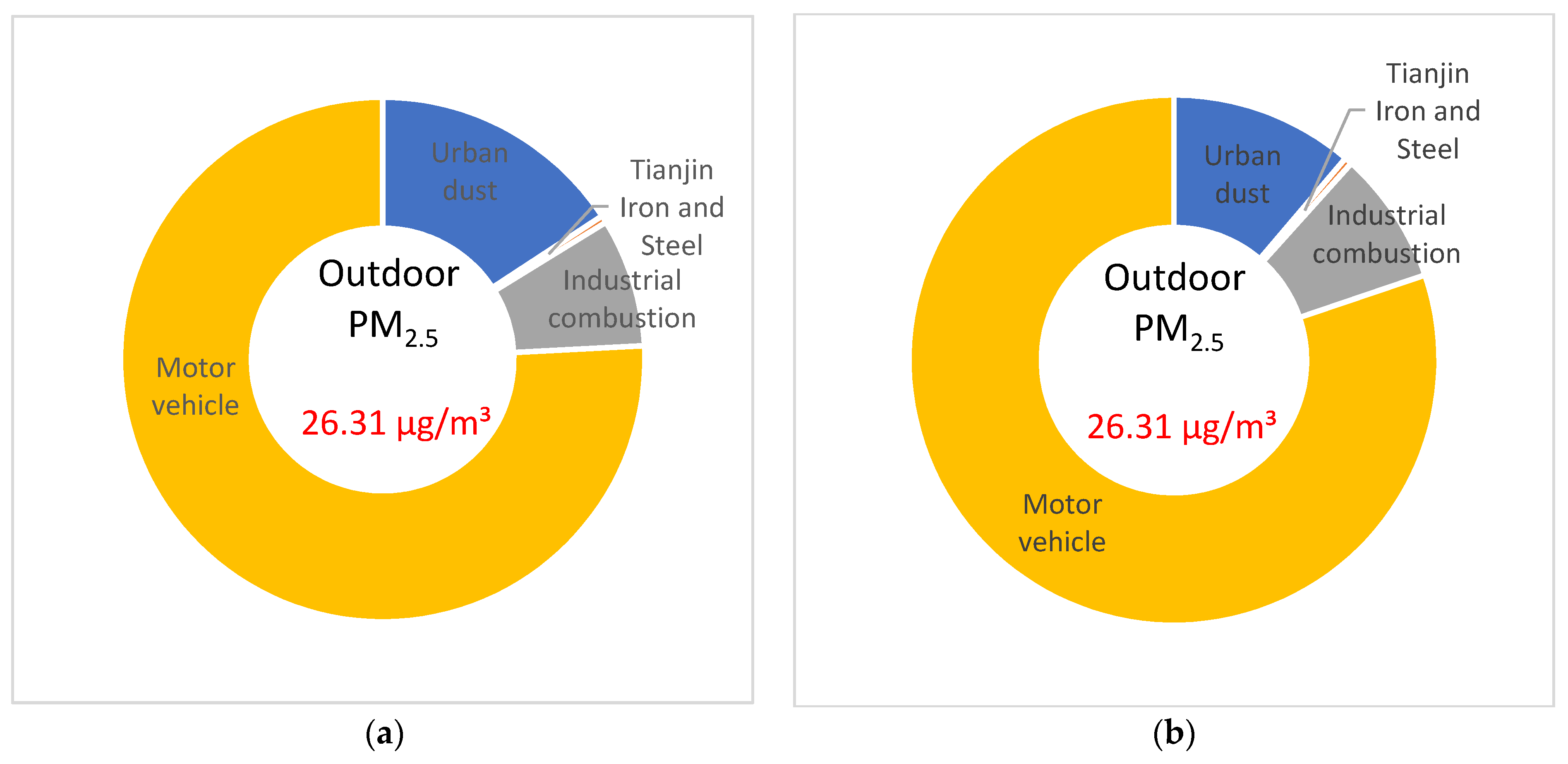
| Urban dust | 15.92% | 11.32% |
| Tianjin Iron and Steel | −0.45% | −0.46% |
| Industrial combustion | 8.01% | 8.20% |
| Motor vehicle | 76.52% | 80.95% |
| Emission Source | EPACMB8.2 | NKCMB1.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Urban dust | 1.81% | 1.16% |
| Tianjin Iron and Steel | −1.50% | −1.62% |
| Industrial combustion | 41.82% | 42.36% |
| Motor vehicle | 57.86% | 58.11% |
| Emission Source | Source Control EPACMB8.2 | Source Control NKCMB1.0 | Non-Source Control EPACMB8.2 | Non-Source Control NKCMB1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban dust | 15.92% | 11.32% | 1.81% | 1.16% |
| Tianjin Iron and Steel | −0.45% | −0.46% | −1.50% | −1.62% |
| Industrial combustion | 8.01% | 8.20% | 41.82% | 42.36% |
| Motor vehicle | 76.52% | 80.95% | 57.86% | 58.11% |
| Period | Receptor Model Software | df (Degrees of Freedom) | PM (%) | χ2 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source control | EPACMB8.2 | 2 | 265.5 | 0.06 | 1.00 |
| NKCMB1.0 | 2 | 196.9 | 0.06 | 0.99 | |
| Non-source control | EPACMB8.2 | 2 | 542.9 | 0.07 | 0.99 |
| NKCMB1.0 | 2 | 215.7 | 0.08 | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ge, A. Effect of Source Emission Control Measures on Source of Atmospheric PM2.5 during “Parade Blue” Period. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111639
Xie Y, Gao Y, Ge A. Effect of Source Emission Control Measures on Source of Atmospheric PM2.5 during “Parade Blue” Period. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(11):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111639
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Yangyang, Yan Gao, and Antong Ge. 2023. "Effect of Source Emission Control Measures on Source of Atmospheric PM2.5 during “Parade Blue” Period" Atmosphere 14, no. 11: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111639
APA StyleXie, Y., Gao, Y., & Ge, A. (2023). Effect of Source Emission Control Measures on Source of Atmospheric PM2.5 during “Parade Blue” Period. Atmosphere, 14(11), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111639





