The Interrelated Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Ningbo, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
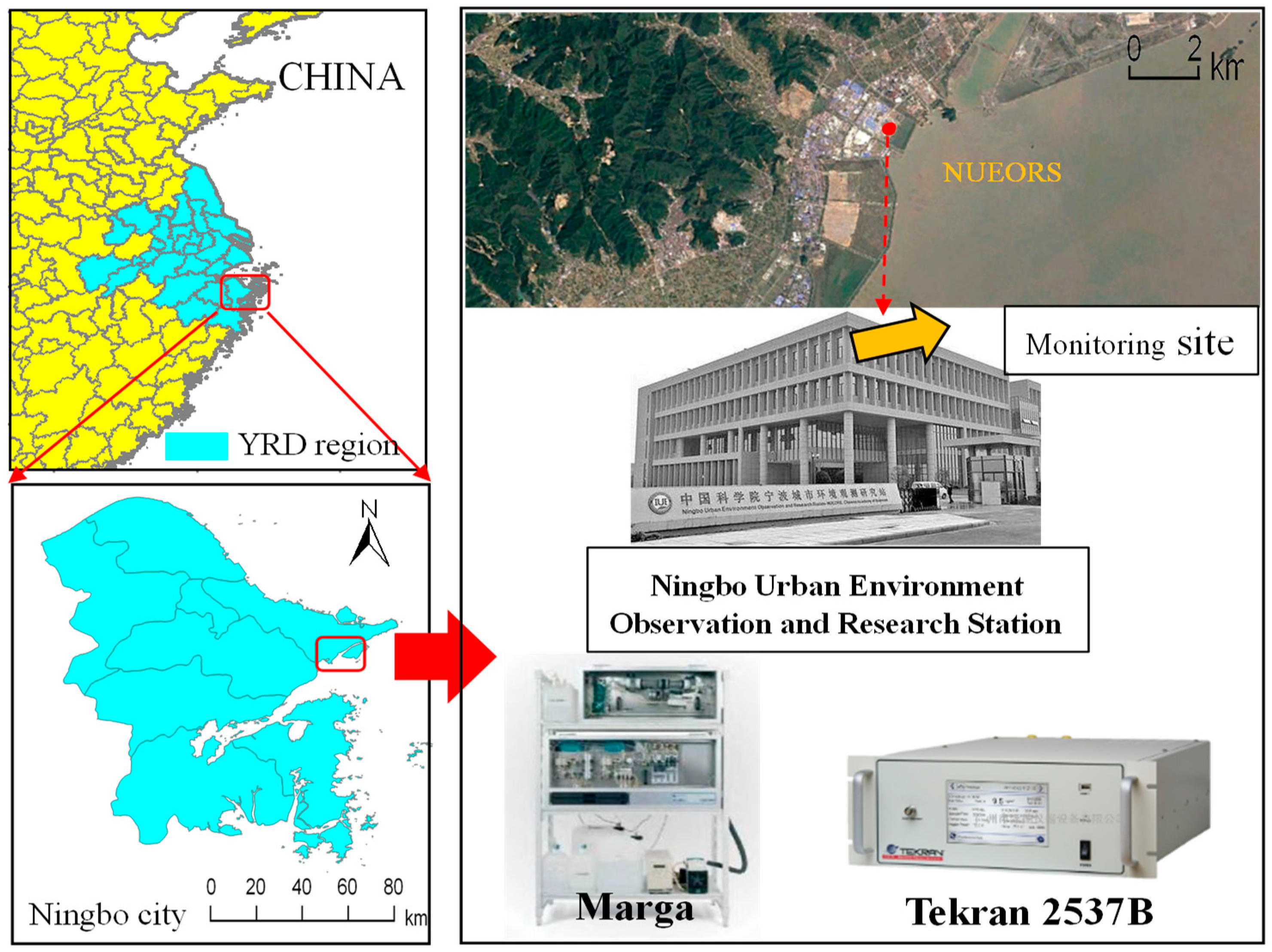
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Measurement of Atmospheric Mercury Species, WSIIs in PM2.5 and Other Parameters
2.3. Piper Diagram Analysis
2.4. Backward Trajectory and Potential Source Contribution Function (PSCF) Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Model Construction Processes
3. Results and Discussion
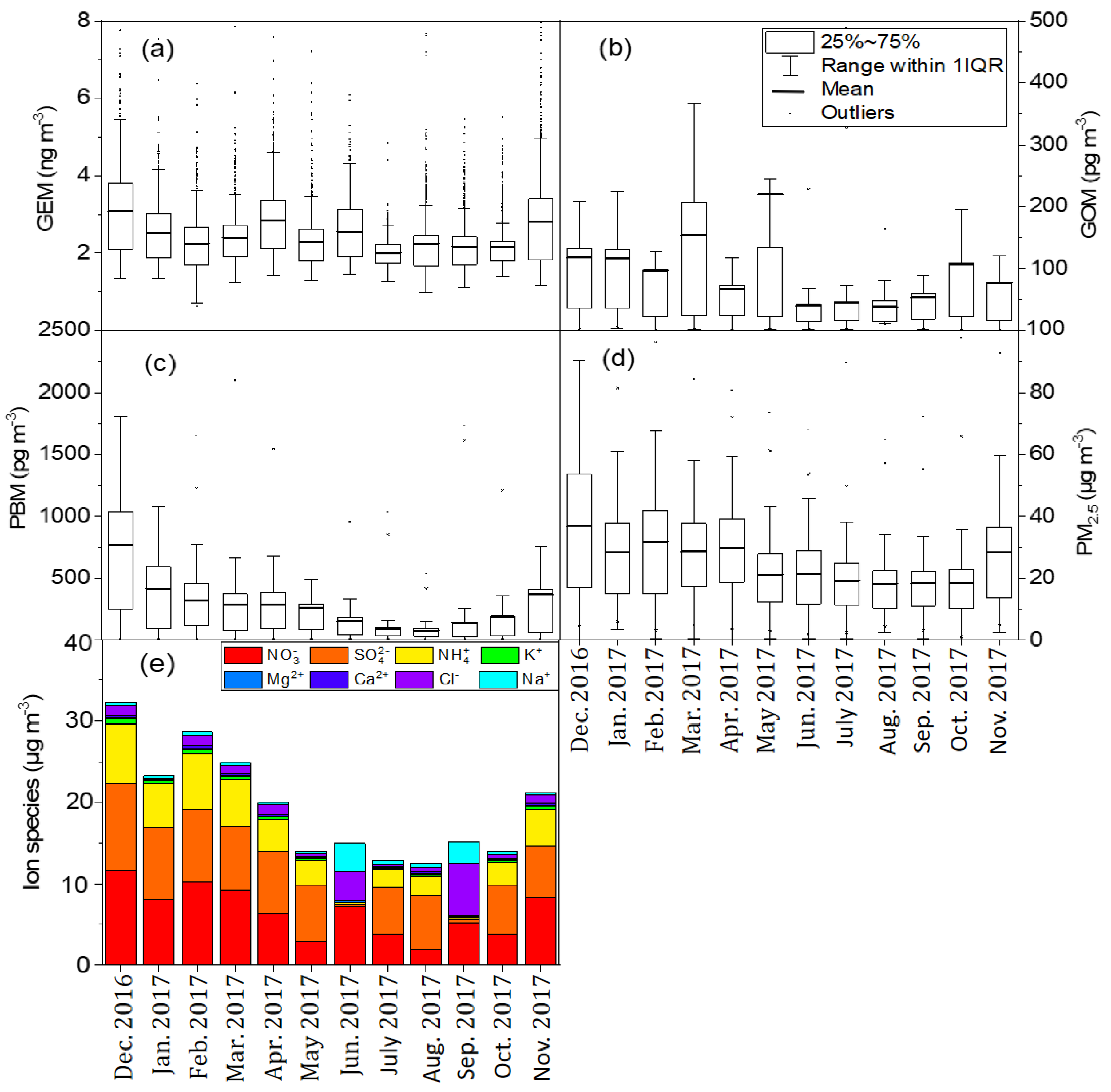
3.1. Temporal Variations of Speciated Hg, PM2.5 and WSIIs
3.2. Correlation Analyses
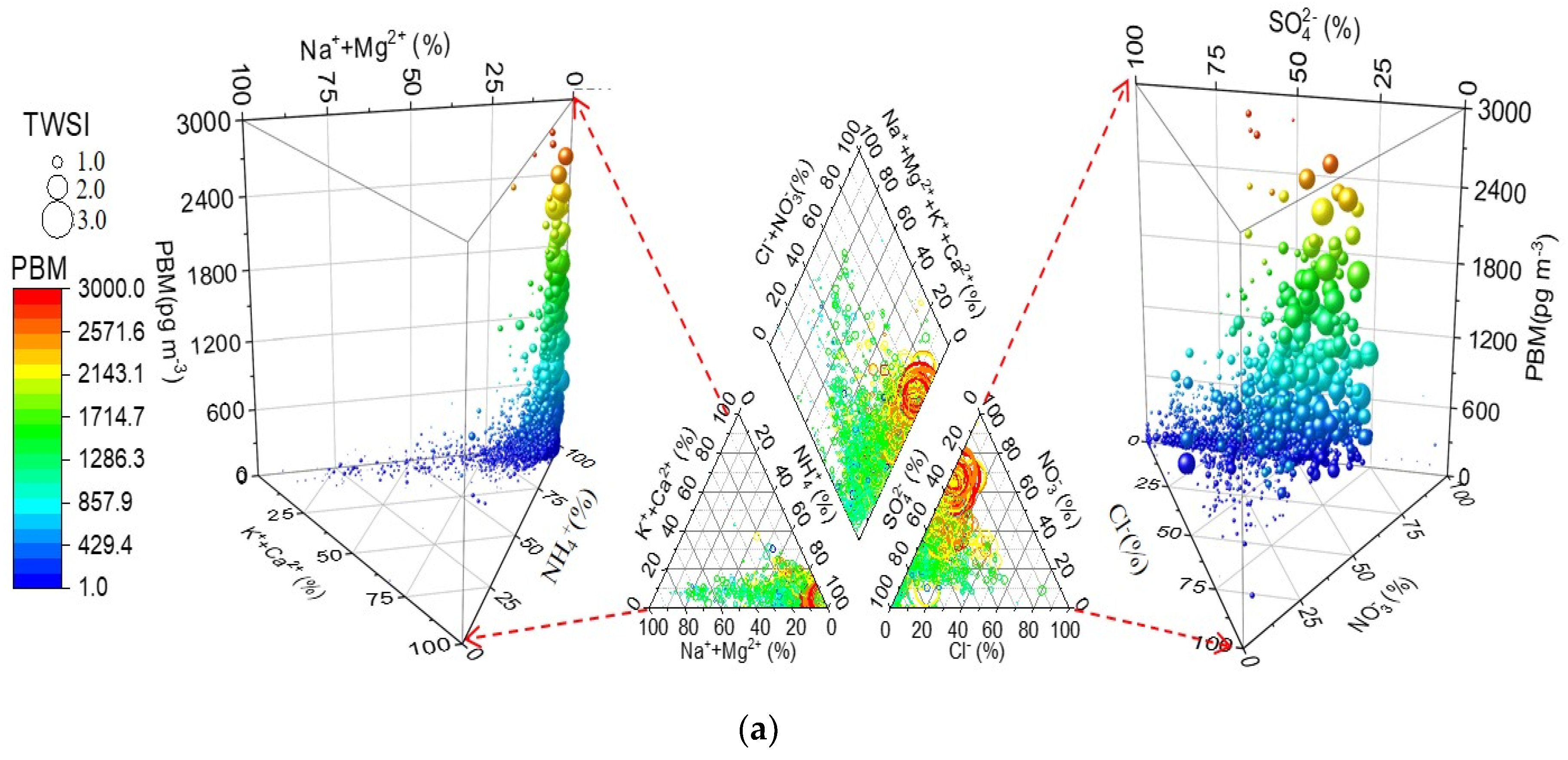
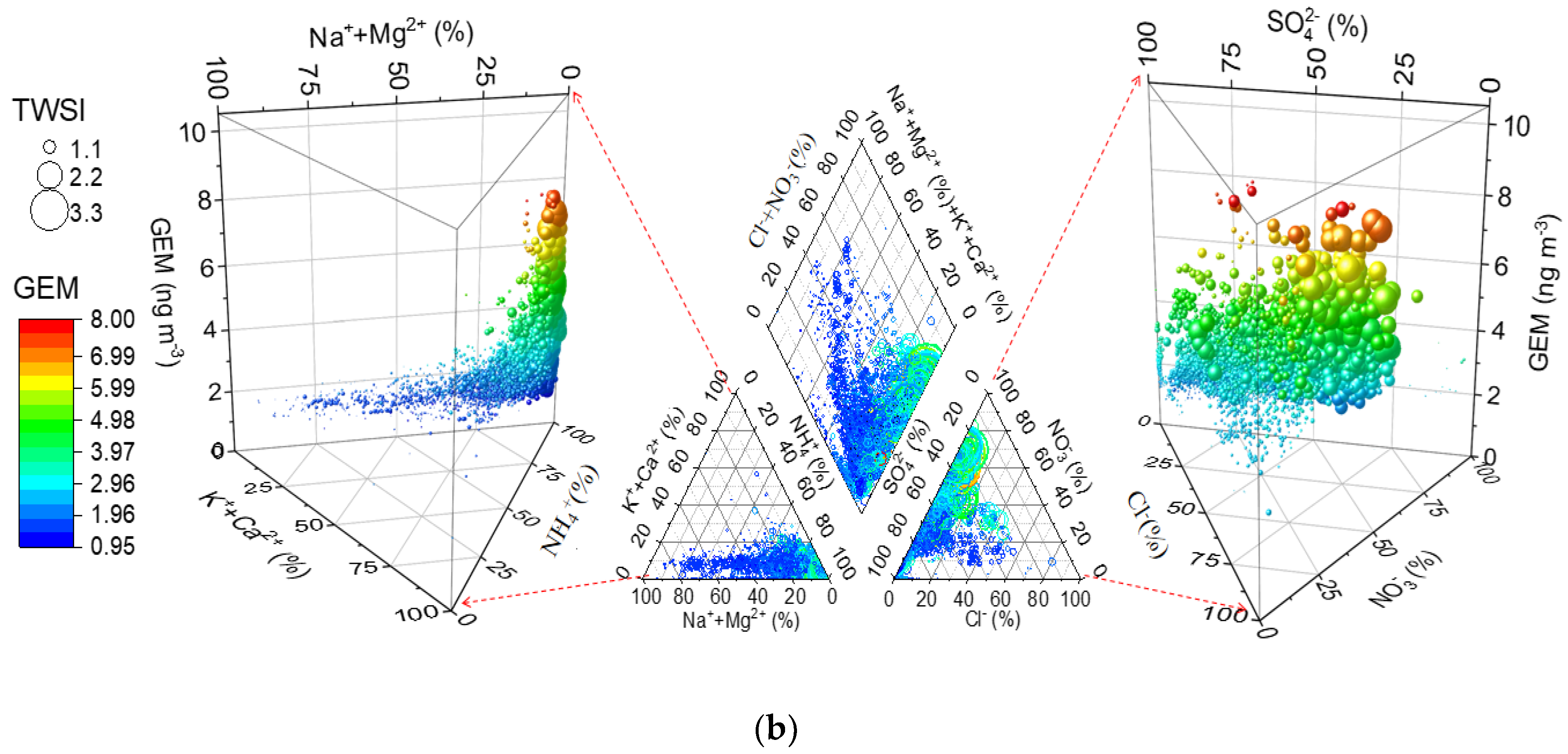
3.3. Piper Diagram Analysis
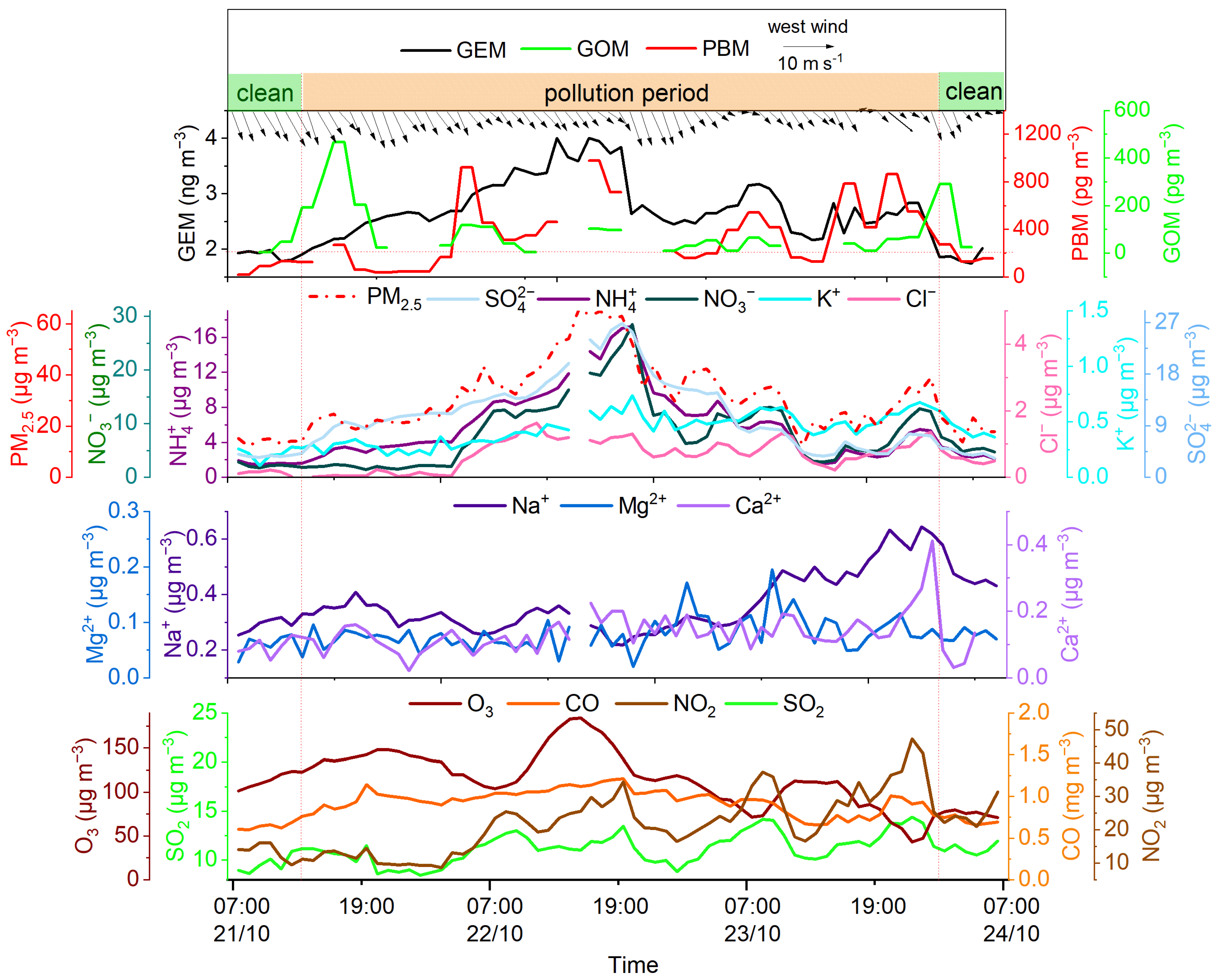
3.4. Pollution Episode Analysis
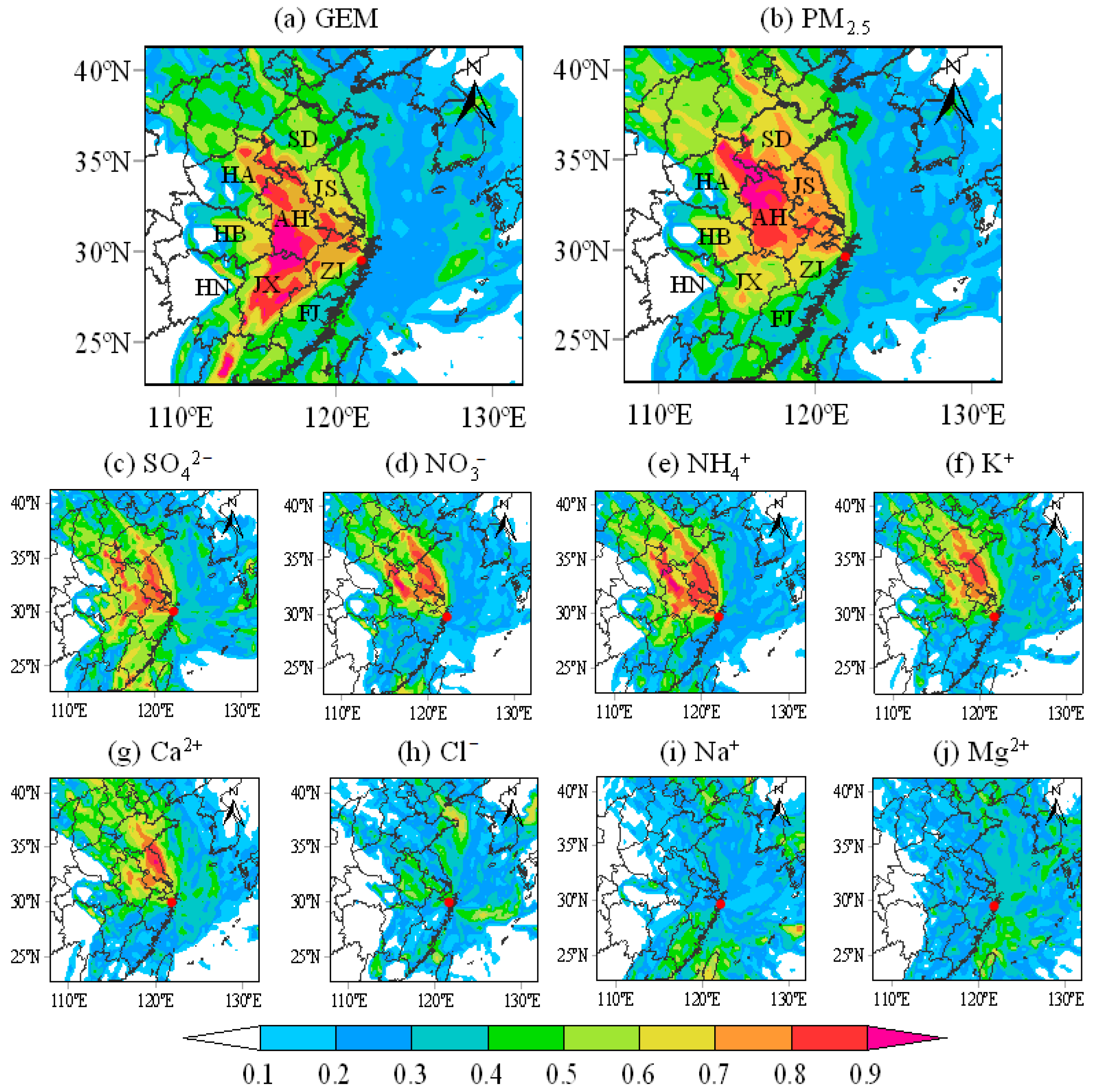
3.5. Potential Source Contribution Function Analysis (PSCF)
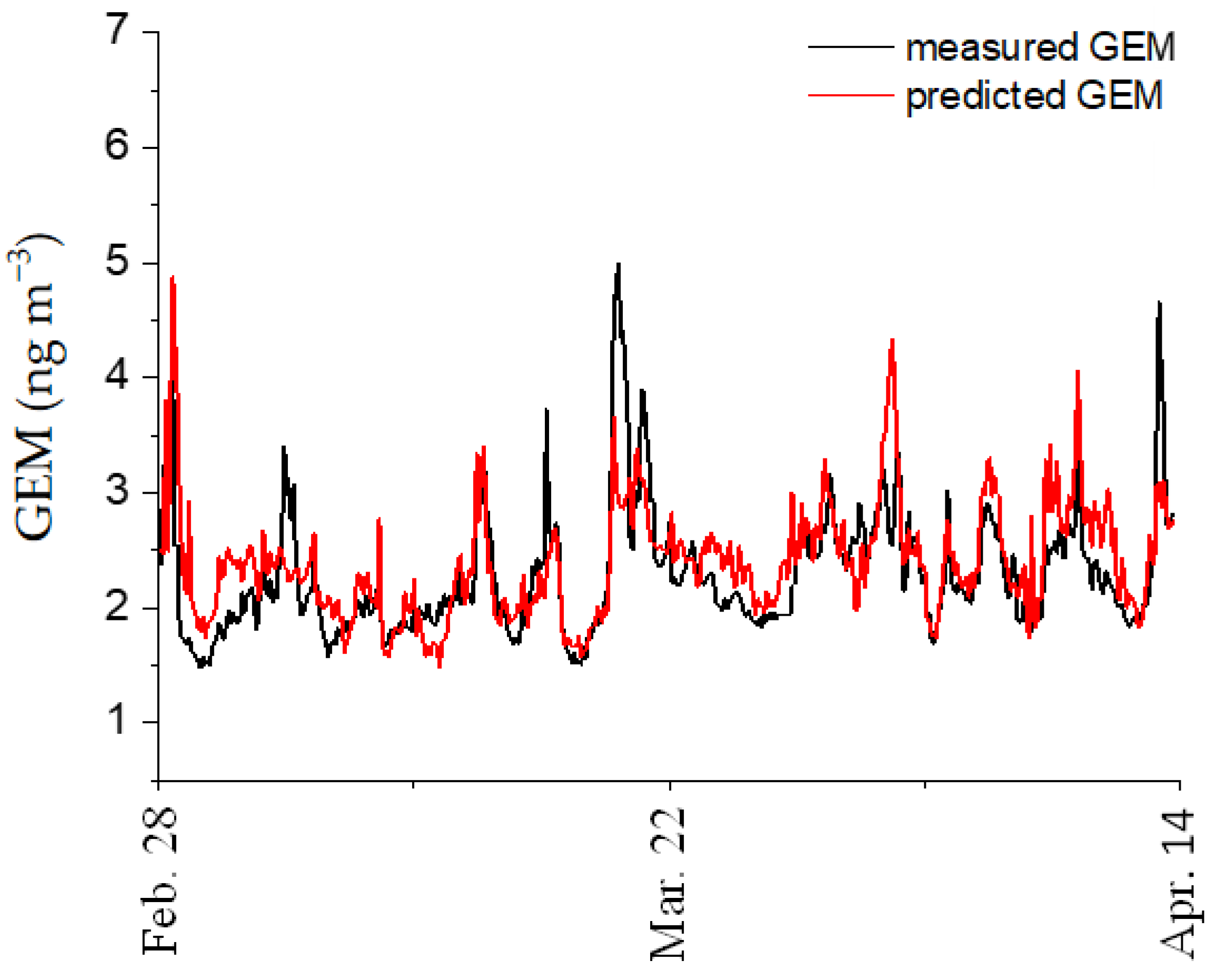
3.6. Empirical Algorithms for Mercury Species Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Guan, D.B.; Su, X.; Zhao, H.Y.; He, K.B. Examining Air Pollution in China Using Production- And Consumption-Based Emissions Accounting Approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14139–14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocci, A.; Rovito, N.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Genchi, G. Mercury Toxicity and Neurodegenerative Effects. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 229, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Talbot, R.; Hegarty, J.; Koermer, J. Speciated Mercury at Marine, Coastal, and Inland Sites in New England–Part 2: Relationships with Atmospheric Physical Parameters. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 4181–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Nelson, P.F.; Edwards, G.C.; Morrison, A.L.; Fisher, J.A.; Ward, J.; Harnwell, J.; van der Schoot, M.; Atkinson, B.; Chambers, S.D.; et al. Atmospheric Mercury in the Southern Hemisphere Tropics: Seasonal and Diurnal Variations and Influence of Inter-Hemispheric Transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11623–11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, N.E.; Jacob, D.J.; Park, R.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Strode, S.; Jaegle, L.; Jaffe, D. Chemical Cycling and Deposition of Atmospheric Mercury: Global Constraints from Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D02308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergan, T.; Rodhe, H. Oxidation of Elemental Mercury in the Atmosphere; Constraints Imposed by Global Scale Modelling. J. Atmos. Chem. 2001, 40, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, D.F.; Duan, Y.S.; Cheng, N.; Xiu, G.L. Atmospheric Mercury Speciation in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongprueksa, P.; Lin, C.J.; Lindberg, S.E.; Jang, C.; Braverman, T.; Bullock, O.R.; Ho, T.C.; Chu, H.W. Scientific Uncertainties in Atmospheric Mercury Models III: Boundary and Initial Conditions, Model Grid Resolution, and Hg(II) Reduction Mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1828–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Ariya, P.A. Reduction of Oxidized Mercury Species by Dicarboxylic Acids (C(2)–C(4)): Kinetic and Product Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5150–5155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, A.P.; Schauer, J.J. The Impact of Aerosol Composition on the Particle to Gas Partitioning of Reactive Mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3934–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subir, M.; Ariya, P.A.; Dastoor, A.P. A Review of the Sources of Uncertainties in Atmospheric Mercury Modeling II. Mercury Surface and Heterogeneous Chemistry—A Missing Link. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baya, A.P.; Van Heyst, B. Assessing the Trends and Effects of Environmental Parameters on the Behaviour of Mercury in the Lower Atmosphere over Cropped Land Over Four Seasons. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8617–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.; Moore, C.; Lew, D.; Lefer, B.; Huey, G.; Tanner, D. Temperature and Sunlight Controls of Mercury Oxidation and Deposition Atop the Greenland Ice Sheet. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8295–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, D.; Jaffe, D.; Prestbo, E.; Swartzendruber, P.C.; Hafner, W.; Weiss-Penzias, P.; Kato, S.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kajii, Y.Z. Reactive and Particulate Mercury in the Asian Marine Boundary Layer. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7988–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Keeler, G.J.; Dvonch, J.T.; Barres, J.A.; Lynam, M.M.; Marsik, F.J.; Morgan, J.T. Urban-Rural Differences in Atmospheric Mercury Speciation. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, G.R.; Lin, N.H.; Wang, J.L.; Lee, C.T.; Yang, C.F.O.; Wang, S.H. Temporal Distribution and Potential Sources of Atmospheric Mercury Measured at A High-Elevation Background Station in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, A.O.; Berg, T.; Dastoor, A.P.; Durnford, D.A.; Engelsen, O.; Hole, L.R.; Pfaffhuber, K.A. Natural and Anthropogenic Atmospheric Mercury in the European Arctic: A Fractionation Study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6273–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.W.; Feng, X.B.; Qiu, G.L.; Shang, L.H.; Zhang, H. Speciated Atmospheric Mercury and its Potential Source in Guiyang, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Han, Y.J.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.M. Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury Concentrations (TGM, Hg(II) and Hg(P)) in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3267–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Chen, J.S.; Yang, L.M.; Niu, Z.C.; Tong, L.; Yin, L.Q.; Chen, Y.T. Characteristics and Sources of Atmospheric Mercury Speciation in a Coastal City, Xiamen, China. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Cinnirella, S.; Pirrone, N. Atmospheric Mercury Footprints of Nations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Talbot, R.; Laine, P.; Torres, A.; Lefer, B.; Flynn, J. Atmospheric Mercury in the Barnett Shale Area, Texas: Implications for Emissions from Oil and Gas Processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10692–10700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, S.N.; Gustin, M.S. Determinants of Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations in Reno, Nevada, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, L.F.; Friedli, H.R.; Heikes, B.G. Atmospheric Mercury over the NE Pacific During Spring 2002: Gradients, Residence Time, Upper Troposphere Lower Stratosphere Loss, and Long-Range Transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Mao, H.; Li, P.; Li, T.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhen, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Total Gaseous Mercury in A Coastal City (Qingdao, China): Influence of Sea-Land Breeze and Regional Transport. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Tong, L.; Lin, J.; Cai, Q. Temporal Variation and Long–Range Transport of Gaseous Elemental Mercury (GEM) over A Coastal Site of East China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 233, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastoor, A.; Ryzhkov, A.; Dumford, D.; Lehnherr, I.; Steffen, A.; Morrison, H. Atmospheric Mercury in the Canadian Arctic. Part II: Insight from Modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Recent Decrease Trend of Atmospheric Mercury Concentrations in East China: The Influence of Anthropogenic Emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 8279–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Xing, J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Hao, J. Emission Inventory of Primary Pollutants and Chemical Speciation in 2010 for the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L. Uncertainty Assessment of Gaseous Oxidized Mercury Measurements Collected by Atmospheric Mercury Network. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodelas, R.R.; Perdrix, E.; Herbin, B.; Riffault, V. Characterization and Variability of Inorganic Aerosols and Their Gaseous Precursors at A Suburban Site in Northern France over One Year (2015–2016). Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumsey, I.C.; Cowen, K.A.; Walker, J.T.; Kelly, T.J.; Hanft, E.A.; Mishoe, K.; Rogers, C.; Proost, R.; Beachley, G.M.; Lear, G.; et al. An Assessment of the Performance of the Monitor for Aerosols and Gases in Ambient Air (MARGA): A Semi-Continuous Method for Soluble Compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5639–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.L.; Dai, X.R.; Li, J.R.; Tong, L.; Hui, Y.; Cao, M.Y.; Li, M.; Xiao, H. The Characteristics and Mixing States of PM2.5 during A Winter Dust Storm in Ningbo of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based Software that Uses Various Trajectory Statistical Analysis Methods to Identify Potential Sources from Long-Term Air Pollution Measurement Data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Liu, C.K.; Huang, C.S.; Fang, G.C. Atmospheric Mercury Pollution at An Urban Site in Central Taiwan: Mercury Emission Sources at Ground Level. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.D.; Jacob, D.J.; Mason, R.P.; Jaffe, D.A. Sources and Deposition of Reactive Gaseous Mercury in the Marine Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2278–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Yu, J.; He, M.M.; Xu, N.B.; Zhang, J.J.; Qian, F.Z.; Feng, J.Y.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of Surface Ozone and Nitrogen Oxides at Urban, Suburban and Rural Sites in Ningbo, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, U.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Walters, J.; Jansen, J.; Edgerton, E.S. Diurnal and Seasonal Variation of Mercury Species at Coastal-Suburban, Urban, and Rural Sites in the Southeastern United States. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Huang, J.Y.; Mondal, S.; Holsen, T.M. Variation in Concentrations of Three Mercury (Hg) Forms at A Rural and A Suburban Site in New York State. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 448, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Choi, H.D.; Laing, J.R.; Cui, H.L.E.; Zananski, T.J.; Chandrasekaran, S.R.; Rattigan, O.V.; Holsen, T.M. Mercury (Hg) Emissions from Domestic Biomass Combustion for Space Heating. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1694–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, S.; Mochida, M.; Kawamura, K. Growth of Organic Aerosols by Biogenic Semi-Volatile Carbonyls in the Forestal Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, A.P.; Schauer, J.J. The Effect of Temperature on the Gas-Particle Partitioning of Reactive Mercury in Atmospheric Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8647–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, A.; Douglas, T.; Amyot, M.; Ariya, P.; Aspmo, K.; Berg, T.; Bottenheim, J.; Brooks, S.; Cobbett, F.; Dastoor, A.; et al. A Synthesis of Atmospheric Mercury Depletion Event Chemistry in the Atmosphere and Snow. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1445–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Huang, J.Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Rattigan, O.V.; Chalupa, D.C.; Utell, M.J.; Holsen, T.M. Effect of the Shutdown of a Large Coal-Fired Power Plant on Ambient Mercury Species. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.; Tong, L.; Huang, Z.W.; Zhang, H.L.; He, M.M.; Dai, X.R.; Zheng, J.; Xiao, H. Seasonal Variation and Size Distributions of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions and Carbonaceous Aerosols at A Coastal Site in Ningbo, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T.; Fjeld, E.; Steinnes, E. Atmospheric Mercury in Norway: Contributions from Different Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 368, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.J.; Kellö, V.; Cernušák, I.; Dibble, T.S. Together, not Separately, OH and O3 Oxidize Hg(0) to Hg(II) in the Atmosphere. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 8266–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.I.; Han, Y.J.; Kim, P.R. Factors Influencing Concentrations of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury Measured at the Farthest Island West of South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Balasubramanian, R.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Behera, S.N.; Bo, D.D.; Huang, X.; Xie, H.Y.; Cheng, J.P. Characteristics of Atmospheric Particulate Mercury in Size-Fractionated Particles during Haze Days in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.J.; Pehkonen, S.O. The Chemistry of Atmospheric Mercury: A Review. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariya, P.A.; Amyot, M.; Dastoor, A.; Deeds, D.; Feinberg, A.; Kos, G.; Poulain, A.; Ryjkov, A.; Semeniuk, K.; Subir, M.; et al. Mercury Physicochemical and Biogeochemical Transformation in the Atmosphere and at Atmospheric Interfaces: A Review and Future Directions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3760–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, D.K.; Deb, M.K.; Verma, D.; Nirmalkar, J. Seasonal Air Quality Profile of Size-Segregated Aerosols in the Ambient Air of A Central Indian Region. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 91, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obrist, D.; Tas, E.; Peleg, M.; Matveev, V.; Fain, X.; Asaf, D.; Luria, M. Bromine-Induced Oxidation of Mercury in the Mid-Latitude Atmosphere. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.J.; Hu, D.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, W.; Deng, C.Y.; Wang, X.J. Atmospheric Mercury Emissions from China’s Primary Nonferrous Metal (Zn, Pb and Cu) Smelting during 1949–2010. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 103, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Mariani, M.; Saunders, K.M.; Maher, W.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Fletcher, M.S.; Zawadzki, A.; Heijnis, H.; Haberle, S.G. How Significant is Atmospheric Metal Contamination from Mining Activity Adjacent to the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area? A Spatial Analysis of Metal Concentrations Using Air Trajectories Models. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Landis, M.S.; Stevens, R.K. Atmospheric Mercury Behavior at Different Altitudes at Ny Alesund During Spring 2003. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7646–7656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Feng, X.B.; Qiu, G.L.; Shang, L.H.; Wang, S.F.; Meng, B. Atmospheric Mercury Emission from Artisanal Mercury Mining in Guizhou Province, Southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2247–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.R.; Xie, Y.Z.; Hu, B.; Wen, T.X.; Xin, J.Y.; Li, X.R.; Wang, Y.S. Size-Resolved Aerosol Water-Soluble Ions during the Summer and Winter Seasons in Beijing: Formation Mechanisms of Secondary Inorganic Aerosols. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Location | Classification | GEM (ng m−3) | GOM (pg m−3) | PBM (pg m−3) | PM2.5 (μg m−3) | Time Period | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ningbo, China | Coastal | 2.4 | 99.3 | 286.5 | 25.1 | December 2016~November 2017 | This study |
| Shanghai, China | Suburban | 4.2 | 21.1 | 197.8 | - | 2014 | [7] |
| Xiamen, China | Suburban | 3.5 | 61.1 | 174.4 | - | March 2012~March 2013 | [20] |
| Guiyang, China | Urban/Mining area | 9.7 | 35.7 | 368 | - | August 2009~December 2009 | [18] |
| Lulin, Taiwan | Background and high elevation | 1.7 | 12.1 | 2.3 | - | April 2006~December 2007 | [16] |
| Taichuang, Taiwan | Urban/Industrial | 6.1 | 332.0 | 71.1 | - | March 2010~February 2011 | [35] |
| Seoul, Korea | Urban | 3.2 | 27.2 | 23.9 | 37.7 | February 2005~February 2006 | [19] |
| Cape Hedo, Japan | Remote | 2.0 | 4.5 | 3.0 | - | March 2004~May 2004 | [14] |
| Spitsbergen, European Arctic | Rural | 1.6 | 8.0 | 8.0 | - | April 2007~December 2008 | [17] |
| Summit, Greenland | Remote | 1.1 | 41.6 | 37.2 | May 2007~June 2007 | [13] | |
| Nova Scotia, Canada | Rural/Coastal | 1.2 | 15.1 | 16.4 | - | November 2006~August 2007 | [12] |
| Detroit, USA | Urban/Industrial | 2.5 | 15.5 | 18.1 | - | 2004 | [15] |
| Dexter, USA | Rural | 1.6 | 3.8 | 6.1 | - | 2004 | [15] |
| Atlanta, USA | Rural | 1.4 | 8.6 | 4.4 | - | 2005~2008 | [38] |
| New York, USA | Suburban | 1.6 | 11.0 | 5.3 | - | December 2007~December 2009 | [39] |
| Average of above cities | 2.92 ± 2.31 | 46.44 ± 83.05 | 81.5 ± 118.07 | 31.4 ± 8.91 | |||
| GEM | GOM | PBM | TGM | Kp | PBM/TGM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | 0.26 ** | 0.18 ** | 0.46 ** | 0.41 ** | - | 0.39 ** |
| NO | 0.25 ** | - | 0.15 ** | 0.21 ** | - | - |
| NO2 | 0.53 ** | - | 0.49 ** | 0.55 ** | - | 0.36 ** |
| NOx | 0.53 ** | - | 0.48 ** | 0.55 ** | - | 0.36 ** |
| CO | 0.53 ** | - | 0.32 ** | 0.53 ** | - | 0.17 ** |
| O3 | −0.20 ** | 0.10 ** | −0.17 ** | −0.14 ** | −0.17 ** | - |
| PM10 | 0.49 ** | - | 0.48 ** | 0.55 ** | - | 0.40 ** |
| PM2.5 | 0.66 ** | 0.11 ** | 0.54 * | 0.69 ** | - | 0.42 ** |
| Cl− | 0.29 ** | - | 0.36 ** | 0.40 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.36 ** |
| NO3− | 0.60 ** | - | 0.49 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.13 ** | 0.42 ** |
| SO42− | 0.51 ** | - | 0.40 ** | 0.58 ** | - | 0.42 ** |
| Na+ | −0.16 ** | - | −0.12 ** | −0.12 ** | - | 0.19 ** |
| NH4+ | 0.66 ** | - | 0.51 ** | 0.70 ** | - | 0.46 ** |
| K+ | 0.51 ** | 0.14 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.53 ** | 0.15 ** | 0.56 ** |
| Mg2+ | −0.19 ** | - | - | −0.14 ** | - | - |
| Ca2+ | 0.25 ** | - | - | 0.36 ** | 0.16 ** | 0.44 ** |
| TWSI | 0.62 ** | - | 0.66 ** | 0.66 ** | - | 0.47 ** |
| T | −0.15 ** | −0.19 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.27 ** | - | −0.44 ** |
| RH | - | −0.16 ** | −0.24 ** | - | - | −0.29 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, H.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Tong, L. The Interrelated Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Ningbo, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111594
Yi H, Li D, Li J, Xu L, Huang Z, Xiao H, Tong L. The Interrelated Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Ningbo, China. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(11):1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111594
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Hui, Dan Li, Jianrong Li, Lingling Xu, Zhongwen Huang, Hang Xiao, and Lei Tong. 2023. "The Interrelated Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Ningbo, China" Atmosphere 14, no. 11: 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111594
APA StyleYi, H., Li, D., Li, J., Xu, L., Huang, Z., Xiao, H., & Tong, L. (2023). The Interrelated Pollution Characteristics of Atmospheric Speciated Mercury and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Ningbo, China. Atmosphere, 14(11), 1594. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14111594






