Abstract
Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) events have a strong impact on the tropospheric weather and climate. Past researchers have carried out extensive studies investigating the theories of interactions between the stratosphere and the troposphere. However, detailed studies on the influences of the global tropopause are rarely shown. This study uses Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Radio Occultation (RO) data from the years 2007 to 2013 to investigate the influences of different types of SSW events on the tropopause over latitude bands from 30° S to 90° N. It was found that SSW events have strong influences on the tropopause over 60° N–90° N and over 20° N–30° N regions. In 60° N–90° N, SSW events cause a tropopause temperature increase and, therefore, a tropopause height decrease. The increment in the tropopause temperature are more than 10 K and the decrement in the tropopause height is about to 2 km during strong events. Such influences last for about 1.5 months for strong split events and about 10 days for weaker and/or displacement type events. The influences of SSW events on 20° N–30° N are weaker. Only the January 2009 SSW event shows a visible influence on the tropopause layer with a tropopause temperature decrease of about 4 K and a tropopause height increase of about 1 km. Other SSW events share no common characteristics on the tropical tropopause. This is mainly because SSW events are not strong enough to dominate the tropopause variations and other factors, especially the planetary waves in the troposphere, have stronger impacts on the tropopause layer.
1. Introduction
The stratosphere has been recognized, over a long period, as a stable atmospheric layer. However, with the advancements in observation techniques, it has been found that the stratosphere in the polar region of the northern hemisphere is frequently warmed up in winter seasons [1,2]. Such warming usually occurs in the polar middle stratosphere around 10 hPa. The temperature increases rapidly by several tens of degrees over a couple of days. Regular westerly winds in the polar stratosphere are often found to be decelerated or reversed and the polar vortex split or displaced [3]. Such phenomena are regarded as a Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) event [3,4].
Sudden Stratospheric Warming events change the circulations of the Earth’s atmosphere. The troposphere, mesosphere and ionosphere are all found to be influenced by SSW. Atmospheric pressure, winds, distribution of water vapor, etc. are found to be changed during SSW [5,6,7,8]. Therefore, it is important to monitor, analyze and understand the influences of SSW on the Earth’s atmosphere. In this study, the dynamic coupling between the stratosphere and the troposphere is analyzed.
The troposphere is closely coupled with the stratosphere during all stages of an SSW event. The tropospheric planetary waves in extratropical regions are believed to be the main triggers of SSW events [9,10]. In an Arctic winter, strong westerly winds usually circle around the pole in the stratosphere, which is regarded as the stratospheric polar vortex. If the westerly jet is not too strong, tropospheric planetary waves propagate upwards into the stratosphere where they break and dissipate [11]. The winds in the polar vortex are either weakened or even reversed and, subsequently, cause the polar stratospheric temperature to increase by more than tens of degrees in a few days [12]. Some studies found that surface wave forcing prior to the stratospheric event is not a necessary condition for all SSWs but that they also depend on the stratospheric state prior to an event [13,14,15,16]. However, tropospheric forcing is still believed to be one of the main causes of SSW.
After the occurrence of an SSW event, warming propagates downwards and influences the troposphere in return [17,18]. The downward propagation depth depends on the degree of warming and also the state of the atmosphere [19]. Most strong warmings cause the tropopause height of a high-latitude region to decrease, with a compressed tropospheric column below associated with high pressure [17,20]. Some SSW events have influences on the deep troposphere and change pressure patterns over the extratropical region; subsequently, they change the phase of northern arctic oscillation (NAO). Therefore, arctic cold air propagates downwards to the middle-latitude regions and causes extreme cold weather over the surface [21,22,23,24].
In addition to the influences on the high- and middle-latitude regions, SSW events have been found to have influences on the tropical troposphere through atmospheric meridional circulation [25,26]. The equatorial lower stratosphere is found to be cooled. Such cooling influences the tropical tropopause through atmospheric circulation [27,28,29]. Dhaka et al. (2015) showed that the tropical tropopause temperature changed by 4 K and the tropopause height changed by about 0.5 km for the typical strong SSW event in January 2009 [30]. Research has also shown that some SSW events similarly change the distribution of tropical water vapor [29,31] and may increase the possibility of the occurrence of tropical cyclones [32,33,34].
The above information suggests that the stratosphere has a close coupling with the troposphere. Understanding the dynamic coupling between the stratosphere and the troposphere will provide us with helpful insights into the causes of SSW and the subsequent extreme cold weather over Eurasian regions. The tropopause is a critical layer in studying the interactions between the stratosphere and the troposphere. Planetary waves near the tropopause play an important role in the development of SSWs [18]. Therefore, the tropopause was selected as the main study target in this study to analyze the dynamic coupling between the stratosphere and the troposphere.
Past research mainly focused on investigating the mechanism of the interactions between the stratosphere and the troposphere by studying the dynamics of planetary waves [35,36,37]. Several studies have presented tropopause variations in terms of tropopause height and temperature. However, most of these studies are either based on a single event or centered on large-ensemble mean results. The influences of the different types of SSW events on the tropopause are rarely shown.
In this study, the influences of SSW on the global tropopause are investigated. Several SSW events, including split and displacement types, are selected to investigate influences of the different types of events in the tropopause. The following key questions are addressed: (1) What are the magnitudes of tropopause variations during split and displacement types of events. (2) What are the characteristics of tropopause variations with latitude. (3) How is the tropopause coupling with SSW during different temporal stages? In order to answer these questions, this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces the data and methodology of the paper. Section 3 introduces the dynamic coupling between the tropopause and SSW. Section 4 discusses the results in Section 3, and Section 5 presents the conclusion.
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
In this study, Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Radio Occultation (RO) data were used for analysis. The GNSS RO technique has been used for sensing the Earth’s atmosphere since the 1990s [38]. RO receivers are set on Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites to receive GNSS signals. When the signals penetrate through Earth’s limb atmosphere, they are bent due to the atmospheric refractivity gradient [39]. The formulated bending angles can be calculated based on a Geometric Optic (GO) method using the orbits information of both GNSS and LEO satellites. In the middle and lower troposphere, a wave optic (WO) method is often used for bending angle calculation. Utilizing the obtained bending angle profile, an Abel transform is then used to calculate the refractivity profile. Based on refractivity, other atmospheric profiles including temperature, density and pressure atmospheric parameters can be calculated. In the lower troposphere, where large amounts of water vapor exist, an additional temperature or humidity profile has to be used for resolving these parameters though a 1D-Var process [40].
RO data have been proved to have several important advantages in terms of global availability, high vertical resolution and high accuracy in the lower stratosphere and upper troposphere. Therefore, RO data have been widely used in climate monitoring and weather prediction [41,42]. In addition, many meteorology organizations, such as the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), use RO data in their numerical weather prediction system. Therefore, RO data are rather suitable for studying the influences of SSW events on the tropopause.
Currently, there are several data centers, including the German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ), the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR), the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change (WEGC), the Radio Occultation Meteorology Satellite Application Facility (ROM SAF), etc. Data from these centers have been proved to be consistent in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere regions [43]. In this study, data from ROM SAF were selected.
ROM SAF provides several types of data records in terms of near-real-time (NRT) products, offline and non-time-critical (NTC) products, climate data records (CDRs) and Interim Climate Data Records (ICDRS). Among these types of data, the NRT products provide near-real products of refractivity, dry temperature and 1D-Var products (temperature, humidity and pressure) of the Meteorological Operational (MetOp) satellite only. The NTC products provide non-time-critical products with higher accuracy. In addition to the conventional atmospheric products provided by NRC, NTC products also provide tropopause height and gridded monthly mean parameters. The NTC products are mainly based on the MetOp and the Sentinel-6 satellites, which are operated by ROM SAF. For satellites operated by other organizations, data records are provided by the CDR products. In addition to the MetOp satellites, data from the Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate (COSMIC); the Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE); and the CHAllenging Mini-Satellite Payload (CHAMP) are also provided by the CDRs. The ICDRS products provide climatology data based on the MetOp satellite covering the time period from January 2017 onward. Therefore, the data records of the CDR products were used in this study.
In the RO data processing, ROM SAF uses a typical Geometric Optic method in retrieving atmospheric profiles in dry atmospheric condition [44]. In moist air conditions, a 1D-Var process is used to retrieve atmospheric profiles [45]. Background profiles used in the data retrieval are obtained from ECMWF Reanalysis Archive–Interim (ERA-I) or ERA version 5 (ERA5). In addition to the commonly used atmospheric parameters, ROM SAF also provides tropopause height and temperature parameters. The algorithm to derive tropopause height (TPH) is based on the World Meteorology Organization’s (WMO) definition [46]. TPH is defined as the “the lowest level at which the lapse-rate decreases to 2 °C/km or less”. The detail on the processing steps and also the quality control issues can be referred to in Algorithm theoretical baseline Documents: level 2C tropopause height [46].
In this paper, RO data of the years from 2007 to 2013 were used since data from this period are the densest so far. RO missions that are available during this time period at ROM SAF include CHAMP, COSMIC, GRACE and MetOp. Figure 1 illustrates the numbers of RO events for each single satellite and the total numbers of all available RO events during our observation time. Among all satellites, RO events from a single MetOp satellite are greatest in quantity, with values of around 600 each day. RO events from the CHAMP and GRACE satellites are much less frequent, with numbers varying from 150 to 200, and CHAMP data are only available until the end of 2008 due to the deactivation of the CHAMP satellite. RO events of the COSMIC satellites vary in number from 200 to 400. The bottom panel shows that the total numbers of RO events are larger than 2500 most of the time. The numbers show a decrease during the years of 2011 and 2012 due to the deactivation of two COSMIC satellites. However, since 2013, the launch of the MetOp-B satellite has increased the total number of RO events again.
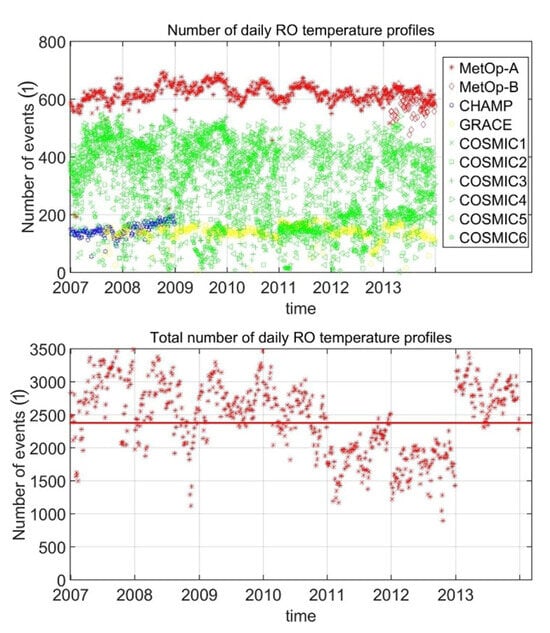
Figure 1.
Upper panel: daily number of available RO profiles of different missions during our observation time from 2007 to 2013. Bottom panel: total number of RO profiles used.
2.2. Determination of SSW Onset Date
In studying the influences of SSW events, the first step is to determine SSW onset dates. However, we found that there is currently no standard definition of an SSW event. Onset dates detected based on different definitions may vary a lot. A commonly used definition is the one from Charlton and Polvani (2007) [3]. They defined that an SSW event is detected if the mean zonal wind at 60° N and 10 hPa is reversed to easterly [3]. This definition is widely used in evaluating the influences of SSW on the atmosphere. According to the differences in detail implementations, e.g., latitude and altitude, several similar approaches have been proposed, e.g., Hu et al. (2015), and Butler and Gerber et al. (2018) [2,47]; multiple decades of SSW climatology data have been developed in their researches [2,47].
However, research has also shown that SSW onset dates determined by wind reversal definitions may differ substantially with those determined by other definitions, such as vortex geometry, geopotential height anomalies, etc. [48,49]. Hitchcock and Simpson (2014) [4] analyzed the times of tropospheric responses to SSW events. They found that the most relevant aspect of stratospheric variability on the troposphere is not the wind reversal in the middle stratosphere but the anomalies in the lower stratosphere, i.e., immediately above the tropopause. Therefore, many studies decided to use temperature increase or other alternative definitions to determine SSW onset date in their studies to study the influences of SSW events.
In this research, two approaches were used to determine SSW onset dates. First of all, the SSW climatology developed by Hu et al. (2015) [47] was used to determine SSW onset dates. As briefly described above, Hu et al. (2015) [47] defined SSW onset dates based on wind reversal at 65° N. They also provided types of SSW events based on the geometry of polar vortices. Since the climatology is only available until the year 2012, the onset date of winter 2013 was obtained from Butler and Gerber (2018) [2]; this event is recognized as a split event in various studies [50]. Secondly, a simplified approach based on temperature increase was used to define the occurrence of SSW events. The onset date of an SSW event was defined as the first day when polar-mean (60–90° N) temperature increases by more than 30 K within two days.
Table 1 shows the exact onset dates determined by the two approaches. Figure 2 shows temporal series of mean polar-cap temperatures during the first three months of each year. The solid vertical blue lines represent onset dates of the SSW events determined by the simplified temperature increase definition, and the dashed lines represent dates determined based on wind reversal definitions. Results of January to March are shown since all events are detected during these three months of the selected years.

Table 1.
SSW onset dates estimated by wind reversal definition and polar mean temperature increase in this study. The types of events are also indicated in the table.
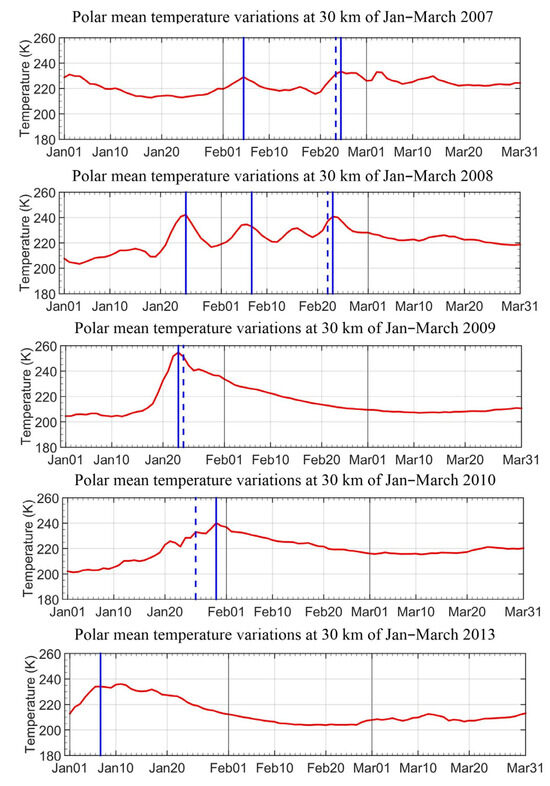
Figure 2.
Temporal series of polar cap mean temperature anomalies at 30 km of January–March for years of 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010 and 2013. Blue solid vertical lines represent dates detected by our method based on temperature increases, while dashed vertical lines represent dates detected by wind reversal definition.
Based on the wind reversal definition, a displacement-type SSW event was detected in each year of 2007 and 2008, and a split SSW event was detected in each year of 2009, 2010 and 2013. Based on the temperature increase definition, multiple warming pulses were detected for the years 2007 and 2008, while the wind reversal definition detected only one event for both years. This is mainly because the wind reversal definition requires at least 20 consecutive days of circumpolar westerlies to exist between two independent major SSW events. However, SSW onset dates detected by the wind reversal definition will always be consistent with one of the onset dates determined by the temperature increase definition. For the years of 2009, 2010 and 2013, both approaches detected only one SSW event. For the years of 2009 and 2013, the onset dates detected by both approaches are very close, with discrepancies within ±1 day. However, for 2010, the onset date determined by the temperature increase definition is four days after the date determined by the wind reversal definition. For the years of 2011 and 2012, no events were detected by both definitions.
2.3. Analysis Methodology
The first step is to understand variations in temperature anomalies during different stages of SSW events. A simplified method was used to estimate temperature anomalies. First of all, a mean temperature profile of each 10° latitudinal band was estimated over our complete observation time from January to March. Secondly, each individual RO temperature profile was subtracted by the mean temperature profile to obtain an anomaly profile. For each day, all available anomaly profiles within a 10° band were averaged to obtain a mean anomaly profile, based on which temporal and spatial variations of temperature anomalies were analyzed. Temperature anomalies and also subsequent tropopause anomalies were analyzed from 90° N to 30° S. Researches show that the influences of SSW on the southern hemisphere regions (30° S–60° S) are minor; therefore, they are not discussed in this study.
Based on the understanding of temperature variations over the tropopause layer, variations in tropopause height and temperature were analyzed during different stages. The first step was to estimate the tropopause height (TPH) and temperature (TPT) anomalies in a similar way as for temperature anomalies. Then, variations in TPH and TPT anomalies in terms of time and latitude were discussed. Finally, variations in tropopause anomalies during four stages of an SSW event—i.e., emerge, occurrence, decay1 and decay2—were analyzed. Each stage has a duration of 7 days. The occurrence stage is defined as the period of 3 days before the onset date until 3 days after the onset date. The emerge stage is defined as the period of 7 days until the occurrence stage. The decay1 and decay2 stages are defined as the periods 1 and 2 weeks after the occurrence stage, respectively. Based on this division, a mean tropopause anomaly of each stage was calculated and the trends of tropopause anomalies during each stage were analyzed.
3. Responses of Global Tropopause to SSW
3.1. Temperature Variations over Latitudinal Bands
Figure 3 shows temporal series of temperature anomalies in selected 10° latitude bands from January to March of the years 2008 and 2009 illustrating displacement- and split-type events, respectively. In order to maintain the simplicity of this paper, results are only shown for every 10° band from 90° N to 30° S. Results of neighboring bands are similar overall. The horizontal black lines indicate the mean tropopause height from January to March of the bands.
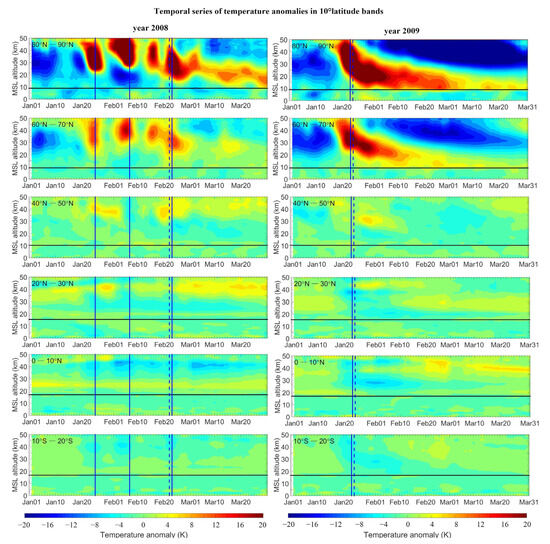
Figure 3.
Temporal series of latitude mean temperature anomaly profiles from January to March for the latitude bands of 80° N–90° N, 60° N–70° N, 40° N–50° N, 20° N–30° N, 0° N–10° N and 10° S–20° S; left panels are results of 2008 and right panels are results of 2009.
For the year 2008, temperature anomalies in the bands of 80° N–90° N and 60° N–70° N show four warming pulses during the three months. For the first two warming pulses (counted by time from 1 January), the largest anomalies are found at a relatively higher altitude than the latter two. The third warming pulse is weaker (smaller anomalies) and, therefore, does not pass our detection criteria (c.f., Table 1). The fourth warming pulse occurs on 23 February, and this one is also detected by the wind reversal definition (c.f., Table 1). It is the only one among the four warming pulses that has visible downward propagation effects. At the mean tropopause layer (indicated by the horizontal black line), temperature anomalies are within ±4 K. In other latitude bands from 50° N to 30° S, temperature anomalies are smaller than 2 K from 30 km below.
For the well-known January 2009 strong SSW event, temperature anomalies of the bands 80° N–90° N and 60° N–70° N at 30 km are more than 20 K on the onset date, 23 January. The warming propagates downward to the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) region with temperature anomalies at the mean tropopause level of more than 8 K. The duration of UTLS warming lasts for about 1.5 months from the end of January to the middle of March. In the 20° N–30° N band, visible cooling is detected in the middle stratosphere with temperature anomalies of more than −8 K. Such cooling is mainly caused by the changes in meridional circulation that induce upwelling, which is caused by wave forcing in the extratropical stratosphere [51,52]. Temperature anomalies in other latitude bands are minor overall, with values varying within ±2 K.
For the other years of 2007, 2010 and 2013, temperature anomalies of two representative bands, i.e., 80° N–90° N and 20° N–30° N, are shown in Figure 4. In the band of 80° N–90° N, all years reveal stratospheric warmings. For the year 2007, several warming pulses are detected and two of them pass our criteria, i.e., the 5 and 24 February ones. The latter one, i.e., the 24 February event, has strong downward influences on the mean tropopause level with temperature anomalies larger than 2 K. The SSW events occur in the years 2010 and 2013; they are both split events and have larger temperature anomalies, with values varying from 4 to 8 K and lasting for about 1.5 months. In the band 20° N–30° N, however, no visible cooling (temperature anomalies larger than −4 K) is detected below 30 km for all the three events.
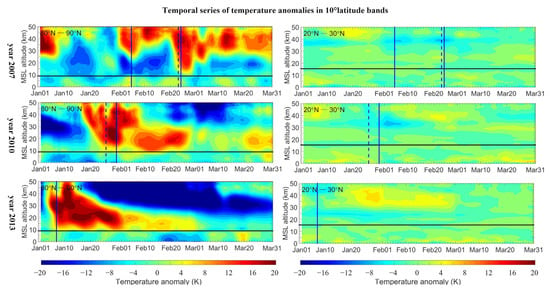
Figure 4.
Temporal series of latitude mean temperature anomalies from January to March for two representative bands of 80° N–90° N (left) and 20° N–30° N (right) in the year 2007 (first row), 2010 (second row) and 2013 (third row).
3.2. Temporal Series of Tropopause Height and Temperature Anomalies
For the year 2008, TPH anomalies reveal a visible increasing trend prior to the first and second SSW onset dates and reveal a decreasing trend after the onset dates. Such trends that occurred around the onset date are defined as a positive peak hereafter. For the first SSW event, such trends are not visible. This could be related to the close occurrence of the second SSW in that the upwelling may limit the downward influences of the first SSW on the tropopause [5]. However, further researches are required to study the detailed dynamical movement of planetary waves in the stratosphere and the troposphere when multiple warming pulses occur.
The second row of Figure 5 shows latitude mean TPH anomalies in the extratropical region. TPH anomalies in the band 50° N–60° N also show a positive trend prior to the first SSW event. This is mainly related to the upwelling of extratropical planetary waves, elevating the tropopause height [5]. However, for the other SSW events of the year, no visible trends are shown. This may suggest that the first SSW event is mainly caused by the upwelling in the band 50° N–60° N. The other warming pulses may be caused by the complicated stratospheric circulations. For the other two bands, 40° N–50° N and 30° N–40° N, variations in TPH anomalies are within ±0.5 km overall.
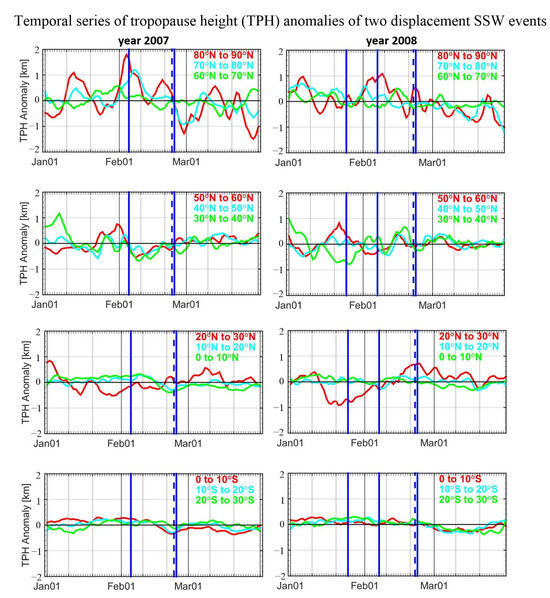
Figure 5.
Temporal evolution of tropopause height anomalies every 10° in latitudinal bands from January to March for the years 2007 (left) and 2008 (right). From the top to the bottom panels, results from polar, extratropical, northern hemisphere tropical and southern hemisphere tropical regions are shown, respectively. The definitions of these regions can be seen in figure panels.
The third and the fourth rows show latitude mean TPH anomalies in the tropical areas of the northern and southern hemisphere, respectively. Variations in TPH anomalies are opposite to that in the polar region. For the year 2008, TPH anomalies of the 20° N–30° N band keep increasing after the first and second SSW events. The increases in TPH anomalies are mainly related to the propagation of equatorial planetary waves, which induces upwelling and cooling [53,54]. The cooling then penetrates further down into the tropical troposphere through the modification and deepening of convective activity in the tropical tropopause layer, subsequently increasing the TPH [5,51]. For the year 2007, TPH anomalies of the band 20° N–30° N also reveal larger variations than the rest of the sub-bands in the tropical region, while no visible trends can be seen related to the occurrence of SSW. This is because not all SSWs produce cooling in the equatorial stratosphere [55]. The responses of the tropical atmosphere to SSW events depends on the duration of planetary waves, the state of prior tropical atmosphere, etc. TPH anomalies in the other bands in the area from 30° N to 30° S are within ±0.2 km overall.
Figure 6 shows the same results as Figure 5 but for the three split SSW events that occurred in 2009, 2010 and 2013. The first row shows that characteristics of anomalies in these three bands are similar overall. For all three split events, TPH anomalies reveal a visible decreasing trend after the occurrence of SSW events. For the strong January 2009 SSW event, TPH anomalies increase to maximum prior to the onset date. After reaching maximum, TPH anomalies decrease until the end of February with a variation of 2 km during 1.5 month.
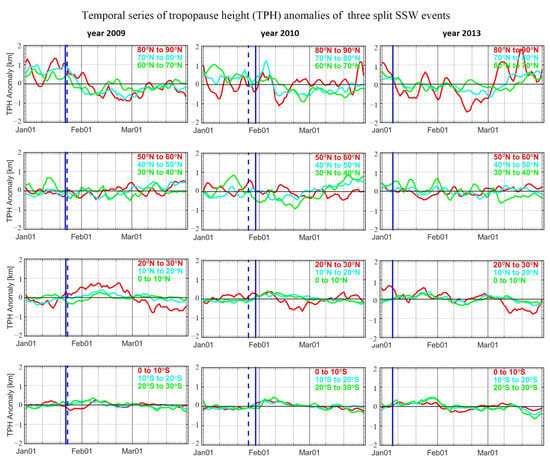
Figure 6.
Temporal evolution of tropopause height variations every 10° latitudinal bands during the 2009, 2010 and 2013 event. From the top to the bottom panel, results from polar, extratropical, northern hemisphere tropical and southern hemisphere tropical regions are shown, respectively. The definitions of these regions can be seen in figure panels.
For the January 2010 event, TPH anomalies also reveal a visible decreasing trend after the occurrence of SSW. The decreasing duration is 1 week and the decrement is 1.5 km. However, the date that the TPH anomaly reached maximum is 5 February, which is after the onset date. This can be related to several reasons. First of all, the onset date of this event detected by different definitions has discrepancies. The onset dates from BG18 and HU15 definitions and the simple temperature increase definition used in this work are 9 February, 26 January and 30 January, respectively. This is mainly attributed to the differences in definitions. In the case of 9 February, TPH anomalies can also reach maximum prior to the onset date. Furthermore, the downward propagation speed and the state of the atmosphere also have influences on the response date of the stratospheric warming.
For the January 2013 event, TPH anomalies also reveal a decreasing trend from early January to 20 January with a duration of about half a month. Since 20 January, TPH anomalies reveal several increasing and decreasing peaks with the evolution of time. This is mainly due to the variations of several increasing and decreasing peaks of temperature at the tropopause layer (c.f., Figure 4). The complicated atmospheric circulation of planetary waves make the tropopause “warm” several times.
Another visible variation in TPH anomalies can be seen in the tropical bands (the third and the fourth row). For the January 2009 SSW event, TPH anomalies of the band 20° N–30° N reveal visible variations compared with that in the other sub-bands. Due to the stratospheric cooling in the tropical region, TPH anomalies increase from −0.5 to 0.8 km with a variation of 1.3 km within 1 month. After reaching maximum, TPH anomalies decrease to −0.8 km due to the downward propagated warming that occurs following tropical stratospheric cooling. TPH anomalies of 10° N–20° N and 0° N–10° N bands also reveal similar trends as those in the 20° N–30° N band but with smaller variations. For the January 2010 and 2013 events, the decrements of TPH anomalies of 20° N–30° N are minor compared with the January 2009 event, with variations generally within 1 km.
Figure 7 illustrates variations in the tropopause temperature anomalies during the three months of years 2008 and 2009, representing the displacement and split types of events. Overall, results of the other years are similar to results of the same types of events that occurred in these two years. Due to the downward propagation of the stratospheric warming, the tropopause layer of high-latitude bands (60° N–90° N, first row) also reveal that warming with TPT anomalies increases with the occurrence of SSW events. For the year 2009, TPT anomalies are about −8 K prior to the onset date and then increase to 6 K with a variation of 14 K during a month. After reaching maximum, TPT anomalies then gradually decrease until the end of March. For the year 2008, when multiple warmings occur, TPT anomalies are found to be increasing after the second and third events. For the first event, however, no increments in TPT anomalies are found. This may be related to the reason that the stratospheric warming of the first event did not propagate down to the troposphere. The increments in TPT anomalies are found to be largest after the second event, with a variation of about 10 K within half a month.
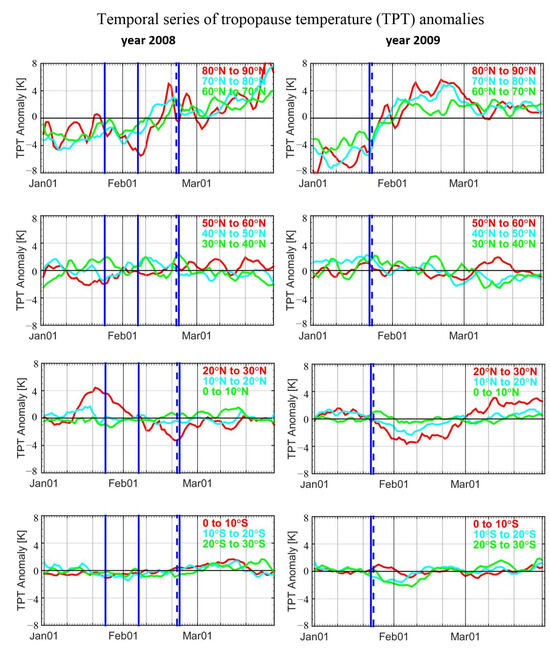
Figure 7.
Temporal evolution of tropopause temperature variations every 10° latitudinal band during the years of 2008 and 2009. From the top to the bottom panel, results from polar, extratropical, northern hemisphere tropical and southern hemisphere tropical regions are shown, respectively. The definitions of these regions can be seen in figure panels.
The second row shows TPT anomalies of the bands 50° N–60° N, 40° N–50° N and 30° N–40° N. Variations in anomalies in these bands are within ±2 K overall, and no visible trends are observed. The third and fourth rows show TPT anomalies in the tropical bands (30° N–30° S). In principle, if tropical stratospheric cooling occurs and propagates down to the tropopause layer, the temperature and TPT anomalies will decrease. However, this is only the case for the very strong January 2009 event. TPT anomalies of 20° N–30° N decrease after the occurrence of the SSW event with a variation of 4 K during half a month. For the multiple events that occurred in 2008, however, the trends are less regular compared with those in 2009. This is mainly due to the reason that no visible stratospheric cooling is detected; therefore, variations in TPT anomalies are mainly dominated by atmospheric planetary waves.
3.3. Tropopause Variations during Different Stages of SSW
In order to better understand the responses of the tropopause to SSW in different temporal stages, mean TPH anomalies in selected temporal periods are calculated and the results are shown in this section. Four temporal periods are formulated including emerge, occur, decay1 and dacay2. Definitions of each period can be referred to in Section 2.3. In order to divide temporal stages, one onset date should be selected. Therefore, for winters that have multiple onset dates, we select the onset date of the event that has the strongest impacts on the polar tropopause. Therefore, 5 February and 7 February are selected for the years 2007 and 2008, respectively.
Figure 8 shows TPH and TPT anomalies during the four stages of all SSW events. Two representative bands 60° N–90° N and 20° N–30° N are selected. Results show that after the occurrence of the SSW events (from the occur to the decay1 stage), TPH anomalies of 60° N–90° N band show a visible decreasing trend for all selected SSW events, while TPT anomalies show an increasing trend. The duration and variations of the decreasing/increasing depend on the strength of each event and also the prior state of the atmosphere. Split events, which generally have stronger warming, can have stronger influences on the tropopause than the displacement events. For the year 2009, TPH anomalies keep decreasing during all four stages with a variation of about 1.0 km. TPT anomalies, in contrast, keep increasing during all stages with a variation of about 7 K. For the years 2013 and 2010, the durations of decreasing/increasing are shorter, with TPH anomalies being generally less than 1 km and TPT anomalies less than 4 K.
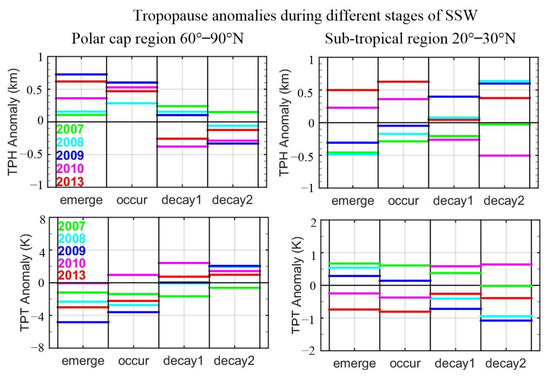
Figure 8.
Latitude mean tropopause height (TPH) anomalies and tropopause temperature (TPT) anomalies during emerge, occur, decay1 and decay2 stages of SSW events. Left panel: results of polar cap region 60° N–90° N. Right panel: results of latitude band 20° N–30° N.
For anomalies in the band of 20° N–30° N, only visible trends are detected for the January 2009 SSW event. From the first emerge stage to the final decay 2 stage, TPH anomalies increase from −0.3 km to 0.6 km with a variation of about 1.0 km. TPT anomalies decrease from 0.2 K to −1.1 K with a variation of about 1.3 K. For the other years, variations in TPH and TPT anomalies reveal larger uncertainties, and no visible trends can be determined. This is because the equatorial cooling in these other years is weaker and, subsequently, has less impact on the tropopause.
4. Discussion
The above results show that SSW events have obvious influences on the tropopause. The stratospheric warming propagates downward to warm the polar tropopause and, subsequently, decreases the tropopause height. Generally, the stronger the SSW events are, the larger the influences on the tropopause. However, in reality, when the stratospheric warming is not strong enough, the prior state of the atmospheric and also tropospheric waves also has influences on the tropopause layer. It is difficult to tell which one is the dominate factor. When multiple warmings occur, the situation is even complicated. The duration of the influences on the tropopause can be limited by the next warming. If a warming pulse occurs following another warming pulse, the decreasing TPH anomalies will quickly increase again due to the upwelling, which causes the next warming. Further studies are required to analyze atmospheric circulations of the tropopause level during SSW events case by case.
Some SSW events are also found to have influences on the tropical region, which is consistent with existing findings. We found visible tropical stratospheric cooling for the January 2009 event. For other years, however, stratospheric cooling is generally minor or not visible. Therefore, TPH and TPT variations in the tropical tropopause are mainly determined by the state of the tropical atmosphere at the time.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the influences of SSW events on the global tropopause are investigated using RO data from 2007 to 2013 provided by ROM SAF. During the selected 7-year period, SSW events are detected to have occurred in five of those years—i.e., 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010 and 2013. For the years 2007 and 2008, displacement-type events are detected and multiple warming pulses are also found. For the years of 2009, 2010 and 2013, a split event was detected in each year. During the occurrence of the SSW events, the tropopause height and temperature anomalies are calculated and analyzed. Consistent with existing findings, the tropopause height decreases after the occurrence of SSW. The influence time and also the magnitudes of tropopause variations depend on the types/strength of each SSW event. For the strong January 2009 split SSW event, TPH anomalies decrease by about 2 km within 1.5 months and TPT anomalies increase by more than 10 K. For the other two splits SSW events, i.e., those in 2010 and 2013, which are of smaller temperature variation, the decrements in TPH anomalies are generally within 1.5 km and the increment in TPT anomalies are within 10 K overall. For the years of 2007 and 2008, when multiple warming pluses are detected, variations in the tropopause anomalies could be influenced by neighboring warmings, and the magnitudes of variations are also smaller.
In addition to the influences on the polar tropopause, SSW events are also found to have influences on the tropical tropopause. For the strongest January 2009 event, visible stratospheric cooling can be found in the tropical regions; TPH anomalies increase and TPT anomalies decrease. The largest tropopause variations are found in the band 20° N–30° N with a variation of 1.3 km during 1 month. TPH and TPT anomalies in other sub-bands are overall similar to those in the band 20° N–30° N but with smaller magnitudes. For the years 2010 and 2013, the stratospheric cooling in the tropical regions is weaker, with variations mostly within ±0.5 km. For the years of 2007 and 2008, when multiple warming pulses occur and the events are overall weaker, no visible stratospheric cooling is detected.
The outcomes of this research suggest that SSW events generally decrease the tropopause height in the polar regions. The magnitudes and the influence time depend on the strength of each event and also the prior atmospheric state. The stronger the event is, the larger the influences of SSW events on the tropopause layer are. For the years that have multiple SSW events, variations in tropopause height and temperature are limited by the adjacent warming. With the influences of SSW on the tropical atmosphere, only strong/split events may have influences on the tropical atmosphere. Displacement-type events, which are generally considered weaker, have limited impacts on the tropical tropopause region.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and Y.L.; data curation, Y.W. and G.W.; formal analysis, Y.W.; funding acquisition, Y.W. and Y.Y.; investigation, Y.W.; methodology, Y.W. and Y.L.; project administration, Y.Y.; resources, G.W.; software, Y.W.; supervision, Y.L. and Y.Y.; validation, Y.W. and H.G.; visualization, Y.W.; writing—original draft, Y.W. and Y.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.W. and Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant NO. 2021MD703896) and supported by Yunnan Fundamental Research Projects (grant NO. 202301AU070101).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The RO data were downloaded from the ROM SAF website. The (numeric) data underlying the results of this study are available from the corresponding author upon qualified request.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge ROM SAF for providing RO data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McInturff, R.M. Stratospheric Warmings: Synoptic, Dynamic and General-Circulation Aspects; NASA-RP-1017; NASA Reference Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 174, pp. 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, A.H.; Seidel, D.J.; Hardiman, S.C.; Butchart, N.; Birner, T.; Match, A. Defining sudden stratospheric warmings. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, A.J.; Polvani, L.M. A new look at stratospheric sudden warmings. Part I: Climatology and modeling benchmarks. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 449–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, P.; Simpson, I.R. The downward influence of stratospheric sudden warmings. J. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 71, 3856–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, N.; Kodera, K.; Nasuno, T. A global non-hydrostatic model study of a downward coupling through the tropical tropopause layers during a stratospheric sudden warming. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, E.; Mitchell, D.M. The stratopause evolution during types of sudden stratospheric warming event. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 3323–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, L.A.; Randall, C.E.; Peck, E.D.; Marsh, D.R.; Smith, A.K.; Harvey, V.L. The influence of major sudden stratospheric warming and elevated stratopause events on the effects of energetic particle precipitation in WACCM. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2013, 118, 11636–11646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flury, T.; Hocke, K.; Haefele, A.; Kämpfer, N.; Lehmann, R. Ozone depletion, water vapor increase, and PSC generation at midlatitudes by the 2008 major stratospheric warming. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D18302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoti, G.; Kalita, B.R.; Bhuyan, P.K.; Baruah, S.; Wang, K. Longitudinal and interhemispheric ionospheric response to 2009 and 2013 SSW events in the African-European and Indian-East Asian sectors. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2020, 125, e2020JA028570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Huang, W.; Shen, H.; Aa, E.; Li, M.; Liu, S.; Luo, B. Ionospheric response to the 2018 sudden stratospheric warming event at middle- and low-latitude stations over China sector. Space Weather. 2019, 17, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttippurath, J.; Nikulin, G. A comparative study of the major sudden stratospheric warmings in the Arctic winters 2003/2004–2009/2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8115–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.G.; Holton, J.G.; Leovy, C.B. Middle Atmospheres Dynamics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Schoeberl, M.R. Stratospheric warmings: Observations and theory. Rev. Geophys. 1978, 16, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.P.; Dunkerton, T.J. Propagation of the Arctic Oscillation from the stratosphere to the troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 4, 30937–30946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaum, M.H.P.; Hoskins, B.J. The NAO troposphere stratosphere connection. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Ren, R.-C. Meridional and downward propagation of atmospheric circulation anomalies. Part I: Northern Hemisphere cold season variability. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 1880–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.K.; Polvani, L.M. Stratospheric control of upward wave flux near the tropopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.K.; Polvani, L.M. Internal Variability of the Winter Stratosphere. Part I: Time-Independent Forcing. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2758–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthewman, N.J.; Esler, J.G. Stratospheric Sudden Warmings as Self-Tuning Resonances. Part I: Vortex Splitting Events. J. Atmos. Sci 2011, 68, 2481–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, E.A.; Sheshadri, A. The role of wave–wave interactions in sudden stratospheric warming formation. Weather. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 1, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, E.A.; Sheshadri, A.; Plumb, R.A. Sudden Stratospheric Warming Formation in an Idealized General Circulation Model Using Three Types of Tropospheric Forcing. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2018, 123, 10125–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, T.; Thompson, D.W.J.; Shepherd, T.G. Up-gradient eddy fluxes of potential vorticity near the subtropical jet. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5988–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn-Sigouin, E.; Shaw, T. Dynamics of anomalous stratospheric eddy heat flux events in an idealized model. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 77, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Garfinkel, C.; Chen, H.; White, I. The 2019 new year stratospheric sudden warming and its real-time predictions in multiple S2S models. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2019, 124, 11155–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Ren, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y. Predictability of stratospheric sudden warmings in the Beijing Climate Center forecast system with statistical error corrections. J. Geophys. Res.—Atmos. 2019, 124, 5385–8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Gerber, E.P.; Jucker, M.; Aquila, V.; Oman, L.D. The downward influence of sudden stratospheric warmings: Association with tropospheric precursors. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.X.; McDaniel, B.A. Diagnostic case studies of the Northern Annular Mode. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3990–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boljka, L.; Birner, T. Tropopause-level planetary wave source and its role in two-way troposphere-stratosphere coupling. Weather. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 1, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumb, A.; Eluszkiewic, J. The Brewer–Dobson circulation: Dynamics of the tropical upwelling. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 868–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, D.E.; Villarin, J.T.; Black, R.X.; Davis, C.A. A new perspective on the dynamical link between the stratosphere and troposphere. Nature 1998, 391, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R.X. Stratospheric forcing of surface climate in the Arctic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R.; Tan, H.-C. The influence of the equatorial quasi-biennial oscillation on the global circulation at 50 mb. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, P.H.; Marks, C.J.; McIntyre, M.E.; Shepherd, T.G.; Shine, K.P. On the ‘‘downward control’’ of extratropical diabetic circulations by eddy-induced mean zonal forces. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 651–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Robinson, W.A. Dynamical mechanisms for stratospheric influences on the troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.R.; Blackburn, M.; Haigh, J.D. The role of eddies in driving the tropospheric response to stratospheric heating perturbations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 66, 1347–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassini, L.; Gerber, E.P.; Baldwin, M.P.; Bunzel, F.; Giorgetta, M. The role of stratosphere-troposphere coupling in the occurrence of extreme winter cold spells over northern Europe. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2012, 4, M00A03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resmi, E.A.; Mohanakumar, K.; Appu, K.S. Effect of polar sudden stratospheric warming on the tropical stratosphere and troposphere and its surface signatures over the Indian region. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 105, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Schofield, J.T.; Linfield, R.P.; Hardy, K.R. Observing Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, G.A.; Kursinski, E.R.; Romans, L.J.; Bertiger, W.I.; Leroy, S.S. A technical description of atmospheric sounding by GPS occultation. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.B.; Eyre, J.R. Retrieving temperature, water vapour and surface pressure information from refractive-index profiles derived by radio occultation: A simulation study. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.K.; Lackner, B.C.; Ladstädter, F.; Scherllin-Pirscher, B.; Foelsche, U.; Kirchengast, G. GPS radio occultation for climate monitoring and change detection. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, RS0D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; Haser, A. Variability of the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere observed with GPS radio occultation bending angles and temperatures. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.-P.; Hunt, D.; Steiner, A.K.; Mannucci, A.J.; Kirchengast, G.; Gleisner, H.; Heise, S.; von Engeln, A.; Marquardt, C.; Sokolovskiy, S.; et al. Reproducibility of GPS radio occultation data for climate monitoring: Profile-to-profile inter-comparison of CHAMP climate records 2002 to 2008 from six data centers. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D18111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROM-SAF. Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document: Level 2A Refractivity Profiles Version 1.6. 2018. Available online: http://www.romsaf.org/product_documents.php (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- ROM-SAF. Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document: Level 2B and 2C 1DVar Products Version 3.1. 2018. Available online: http://www.romsaf.org/product_documents.php (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- ROM-SAF. Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document Version 2.3. 2021. Available online: http://www.romsaf.org/product_documents.php (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Hu, J.; Ren, R.; Xu, H. Occurrence of winter stratospheric sudden warming events and the seasonal timing of spring stratospheric final warming. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 71, 2319–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.M.; Gray, L.J.; Anstey, J.; Baldwin, M.P.; Charlton-Perez, A.J. The influence of stratospheric vortex displacements and splits on surface climate. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2668–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kirchengast, G.; Schwaerz, M.; Ladstädter, F.; Yuan, Y.-B. Monitoring Sudden Stratospheric Warmings using radio occultation: A new approach demonstrated based on the 2009 event. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 2327–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manney, G.L.; Lawrence, Z.D.; Santee, M.L.; Read, W.G.; Livesey, N.J.; Lambert, A.; Froidevaux, L.; Pumphrey, H.C.; Schwartz, M.J. A minor sudden stratospheric warming with a major impact: Transport and polar processing in the 2014/2015 Arctic winter. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 7808–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, K. Influence of stratospheric sudden warming on the equatorial troposphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Yamazaki, K. Tropical cooling in the case of stratospheric sudden warming in January 2009: Focus on the tropical tropopause layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6325–6336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueyama, R.; Gerber, E.P.; Wallace, J.M.; Frierson, D.M.W. The role of high-latitude waves in the intraseasonal to seasonal variability of tropical upwelling in the Brewer–Dobson circulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 70, 1631–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Escolar, M.; Calvo, N.; Barriopedro, D.; Fueglistaler, S. Tropical response to stratospheric sudden warmings and its modulation by the QBO. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7382–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, M. Latitudinal extension of cooling and upwelling signals associated with stratospheric sudden warmings. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 89, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).