Abstract
There has been an insurgence of allergic respiratory diseases such as asthma and rhinitis in industrialized countries in the last few decades as a result of the interaction between air pollutants and pollen, which has become a global and dramatic health problem. Air pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ozone, and carbon dioxide affect the physical, chemical and biological properties of pollen such as the pollen content, production, and allergenicity, exacerbating symptoms in vulnerable subjects. When investigating these interactions and their effects, the environmental impact of climate change, weather variables and urbanization should be taken into account as well as the pollen species, type of pollutant, conditions of exposure, and individual susceptibility. Up to 25% of asthma adult cases are work-related, because several categories of workers in different sectors are exposed to aeroallergens and outdoor air pollutants. Thus, in this study, we evaluated the significant impacts of occupational allergies on worker’s health and quality of life. In summary, to assess the effect of interactions between air pollutants and pollen on public and occupational health, all the factors that play a role in this context will be investigated, including environmental factors, individual susceptibility in relation to pollen species, type of pollutants, and conditions of exposure.
1. Introduction
In the atmosphere, there are several outdoor pollutants of different origin that especially in high concentrations may cause adverse impacts on human health and the environment, particularly the development of respiratory diseases [1,2]. The main air pollutants derived by anthropogenic activities are carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PMx), which includes bioaerosols (i.e., pollen, fungal spore, bacteria, viruses, etc.) and chemical particles such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and ozone (O3). The high concentrations of bioaerosols in the atmosphere, especially airborne allergens derived from plant pollen, may increase and exacerbate allergic respiratory symptoms and diseases [3,4]. During the last few decades, allergic and respiratory diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis have increased rapidly and globally in adults and children, which is probably also due to rapid industrial development and traffic emissions [4,5,6,7,8,9]. The development of allergies is a complex multifactorial process that involves various factors influencing the individual susceptibility and immune response, and the development of allergic diseases depends on exposure to allergens, environmental and lifestyle factors [10]. A relevant issue to consider is the rising trend in sensitization to pollen and respiratory symptoms/disorders in people living in urban areas than in rural environments [6,11,12]. Therefore, atmospheric concentration and human exposure to bioaerosol and aeroallergens are affected by climate change and meteorological conditions that influence vegetation patterns and plant physiology through spatial and temporal changes in air temperature, humidity, rainfall and wind speed [10,13,14,15,16]. Meteorological factors such as air temperature, humidity, wind speed, and rainfall may influence significantly the concentration, release, distribution, long-range transport and seasonality of pollen in the atmosphere [13,16]. Airborne pollen of different plants has been shown to be a sensitive bio-indicator of climate change and environmental variations [17,18]. Many authors proposed pollen grains as good indicators of the state of the environment, as they have been found to be sensitive to air pollutants [19,20]. Different studies nowadays advise to take into account both pollen types and specific air pollutants for the epidemiological assessment of environmental factors in respiratory allergies [21,22,23]. In this regard, cumulative research data indicate that pollen grains and air pollution reciprocally interact, and environmental pollution may cause morphological, ultrastructural, biochemical, and physiological changes on pollen [14,24]. The direct effect of air pollution on pollen and on its allergenic potential is currently a critical scientific area of interest. Air pollutants increase the allergen content of pollen and damage its surface, releasing more allergens [25]. In fact, air pollutants can act as adjuvants and alter the immunogenicity of allergenic proteins, exacerbating symptoms in sensitized subjects and the incidence of pollen allergy [25,26,27,28,29]. Atmospheric pollutants interact with pollen, causing changes in its fertility and affecting the reproductive cycle of seed plants [30]. At the cellular level, air pollutants provoke damage of the membrane structures and interfere with cellular mechanisms as well as the gene expression. The adverse effects of air pollutants on the biological properties of pollen such as viability and fertility are usually detected during pollen germination. At the molecular level, air pollutants have a relatively strong oxidative role that affects biomolecules such as proteins (consisting of their nitration and oxidation), lipids (change in content, composition and quantitative properties) and nucleic acids (mutation in the genetic material), interfering with pollen germination and elongation of the pollen tube [31,32,33]. In the literature, several studies highlight that each plant species may have a different susceptibility/tolerance to the atmosphere’s pollution levels such as NO2 and O3, and each species (i.e., Betula, Ambrosia, Birch, Quercus) shows different reactions depending on the pollutant type and concentration [4,24,34,35,36]. However, these effects of air pollutants on pollen species must also be considered in the context of vegetation and the influence of meteorological conditions [14,34]; therefore, the sensitivity of people in different areas changes with pollen species [13,37]. To this purpose, in this work, we have investigated, with attention especially on the most recent studies, the effects of air pollutants on pollen grains to understand how the interactions between pollen and air pollutants affect public and occupational health in relation to the factors (i.e., climate change, urbanization, pollens species) that play a role in this context. Therefore, the impact of climate change on pollen concentrations and air pollutants levels that significantly affect air quality deserves particular attention.
2. Interaction between Air Pollutants and Pollen
2.1. Effects of Air Pollutants on Physical and Chemical Properties of Pollen
Because of the specific sculpture of the pollen wall and exine lipophilicity, different types of pollutants, including gaseous compounds and fractions of particulate matter, may adhere to the pollen surface (Figure 1) [16].

Figure 1.
Examples of Poaceae pollen grains, with particulate matter adhered to the external surface: (a) integer pollen grain, (b) deformed pollen grain with attached fungal spores. Pollen grains have been stained with basic fuchsine.
Atmospheric pollutants such as PMx, NO2, SO2, and CO have a direct effect on the physical and chemical properties of pollen grains, modifying the characteristics of the pollen surface, its allergenic potential, allergens/proteins release from pollen and the molecular structure of proteins [3,38,39,40,41,42]. To this purpose, morphological analysis of the pollen grains is very important. Several studies showed changes in the morphological structure of the cell wall such as shrinkage, thinning, rupture of exine, dilatation of the intine wall and in the pollen wall’s constituents such as sporopollenin that can be determinant in the resistance of pollen grains to environmental pollution [34,43,44,45] (Figure 2).
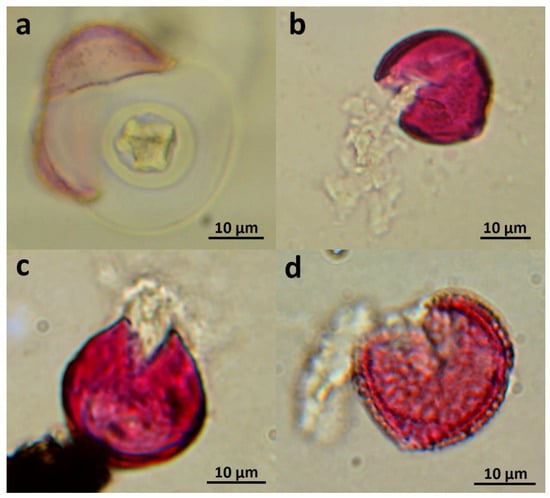
Figure 2.
Examples of damaged, cracked or ruptured pollen grains: (a) Cupressus sempervirens, (b) Ailanthus altissima, (c) Vitis vinifera, (d) Olea europaea. Pollen grains have been stained with basic fuchsine.
In an interesting study, the researchers demonstrated the shrinkage of exine of many species of pollen (Cyperus rotundus, Syzygium cumini, Hyptis suaveolens, Cocos nucifera, Acacia nilotica, Eucalyptus tereticornis, Azadirachta indica and Zea mays) that had been exposed to high concentrations of some pollutants of anthropogenic origin (PMx particles, SO2 and NOx) [46]. In this regard, as suggested by some papers, pollen with thinner exine may result in higher susceptibility to deformation, fragility or rupture [47,48]. The fragility of exine varies significantly among pollen species/families; for instance, Cupressaceae pollen exine, which is rather thin, is clearly more easily fragilized than other pollen types [38,49], and Platanus orientalis pollen became swollen after several hours of fumigation with NO2, or SO2 [14,40]. Therefore, the exine rupture seems to be faster and higher in polluted pollen grains [49], resulting in an increased number of allergens or sub-pollen particles containing allergens released into the environment [50]. Such particles of small size (~2.5 microns or less) may be easily inhaled and then penetrate more deeply into the lower respiratory system, contributing to enhance pollen spreading and allergenicity, causing an exacerbation of symptoms in sensitized individuals [24,38]. To this purpose, the particulate matter is a mixture of solid and liquid particles suspended in air, and it can differ in sizes, shapes and composition. The particle size influences significantly the ability of the particulate to pervade deeply in the lung [22]. Ultrafine particles (PM < 0.1 mm) can access the alveolar region, resulting in more aggressive and dangerous effects than other breathable fractions of larger size both at the respiratory level (especially in vulnerable subjects) and at the molecular level. Different studies demonstrated that particulate matter can act as a carrier of allergens and could bind with airborne pollen through micrometer-sized aggregates, modifying their allergen content and composition [16]. In some research studies, pollen of a non-polluted area was observed with normal size and structure [44]. Nevertheless, other papers found no significant variations between polluted and non-polluted pollen, which may be due to differences in the pollen grain species and the conditions of exposure to gas pollutants [38,51]. Therefore, chemical modification by air pollution may influence the biochemical composition and content of pollen [32,34] and promote alterations in the structure of proteins in the pollen cell wall (i.e., amino acid oxidation, conformational changes, crosslinking, oligomerization, degradation of protein), affecting protein stability, the polypeptide profile and some properties such as hydrophobicity and the acidity of binding sites [10,31,52]. Many studies detected a general decreasing trend of protein content in pollen (i.e., Birch pollen) exposed to O3, SO2 [31,47,53], and the pollen collected from a polluted area contained a lower content of soluble proteins [54]. On the contrary, according to other authors [55], atmospheric pollutants may increase the total protein content of pollen under stress conditions as a mechanism of the plant’s defense system [56]. In a specific research study, the results highlighted that the protein content of Acer negundo was lower in SO2-exposed pollen samples and slightly higher in NO2-exposed pollen compared to the control sample [55]. Therefore, the same pollutant gas may interact with each specific allergen and cause various effects (more or less relevant) due to differences in pollutants (NO2 and O3) and pollen interspecies variations [14,57]. Previous results confirm that the pollen species present different behavior in terms of the total soluble protein (TSP) concentration when exposed to pollutant gases, and the reaction is not always positively correlated with concentration [34]. The more common post-translational modifications of proteins include their nitration and oxidation, which may alter the allergenic potency of the pollen and molecular structure of their protein, such as Pla a 3 [25,58,59,60]. Gases like ozone and NO2 are oxidant compounds, which can activate and increase reactive oxygen species (ROS) production by the pollen grain in response to stress conditions, affecting the structural and conformational changes of proteins [61,62]. Some authors evidenced that the defense mechanism reaction toward the oxidative stress and its efficiency can change between different pollen species much like the pollen size or cell wall. In one study, B. pendula and C. avellana pollen behave in a similar way, where the pollutants seemed to activate less ROS production than in the case of A. negundo and Q. robur [34]. For instance, ROS attack proteins to form carbonyls and can react with nitrogen species then to form nitrotyrosine with tyrosine and with lipids to generate ethane and isoprostanes. These reactions could have an impact on membrane organization. The ROS such as hydroxyl-free radical (neutral form of hydroxide ion OH−), superoxide anion (O2−), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are highly toxic and can damage proteins, resulting in their dysfunction [38] (Figure 3).
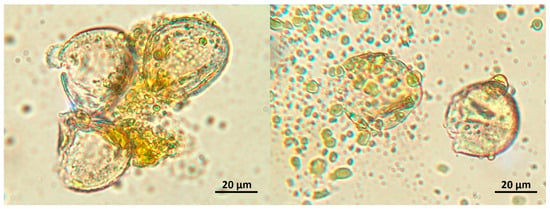
Figure 3.
Pollen grains of Chamaerops humilis damaged due to exposure to an oxidative agent (hydrogen peroxide) with spillage of the cellular content.
The reaction of nitration resulting from some gases such as NO2 and O3 at atmospheric concentrations, with the addition of nitro groups to the aromatic rings of tyrosine residues in the polypeptide chain, can increase the allergic potential of many proteins and cause differences in recognition by changing protein activity and function [52,59]. Other fundamental components such as pollen lipids play also an important role in the development and in the biochemistry of allergies [63,64,65,66]. Some authors observed a modification of lipid content (reduction in fatty acids and phospholipids) in pine pollen (Pinus sylvestris) of industrial areas and a significant reduction in the degree of unsaturation of fatty acids [54]. Other papers showed that in conditions of elevated levels of ozone, the lipid composition of birch pollen was altered (decrease in the glycerolipids concentrations), inducing a modulated immune response [27,51,67,68] and modifications of other constituents such as unsaturated fatty acids, which have important binding activities with the allergenic protein Bet v 1 [64,69,70]. Modification of the lipidic fraction of Pinus halepensis pollen has been evidenced in experimental condition of exposure to ozone [71]. The pollen can act as a carrier of lipids with adjuvant effects on the immune response to allergenic proteins [65]. To better understand the influence of lipids with the immune system in allergy development, it is important to investigate by experimentation the modifications of pollen lipidomes induced by air pollutants [64].
2.2. Effects of Air Pollutants on Biological Properties of Pollen
Numerous atmospheric pollutants interact with pollen and may cause biological effects on the pollen viability, germination rate and fertility, as shown in several studies on a wide variety of pollen exposed to different levels of some gases such as CO, CO2, O3, and SO2 [31,38,72,73]. Pollen viability and germination rate are critical factors directly influencing plant reproductive function. These parameters are the simplest and most widely used biological parameters to evidence the effect on pollen exposed to air pollutants [38]. The evaluation of pollen viability after exposure to pollutants, in vivo or in experimental conditions, has been investigated by many studies to highlight the direct effects of pollution on pollen [74,75,76]. In a study performed under controlled conditions, the Betula pendula pollen after exposure to elevated levels of some pollutants (CO, O3, SO2) showed a significant lowering in viability (about 14%) and germination rate (about 36%), while a minor effect was revealed at the lowest pollutants concentration [31]. Other in vitro and in vivo studies evidenced a significant decrease in germination rate and/or viability (up to 50%) in Iridaceae pollen species exposed to different concentrations of O3 and CO in Lepidium virginicum, Pinus nigra and Pinus pinea exposed to SO2 [72,77,78]. Another research tested the pollen viability of different species in a fumigation chamber, and the highest decrease in pollen viability was evidenced for C. avellana (average of 15% when exposed to O3 and 11% to NO2) followed by B. pendula (average of 9% when exposed to O3 and 13% when exposed to NO2), Q. robur (average of 5% when exposed to O3 and 7% when exposed to NO2) and finally A. negundo (average of 8% when exposed to NO2). The more evident effect on viability was detected for C. avellana when exposed to both and Q. robur when exposed to NO2, while A. negundo was more tolerant to pollutants compared to the other tested species. The percentage loss varied depending on pollen species, type and concentration of pollutants tested [34]. Therefore, pollen tolerance to pollutants seems to be higher when the grains are exposed in vivo compared to experimental conditions, which is due to the protective role of the anther [74] (Figure 4).
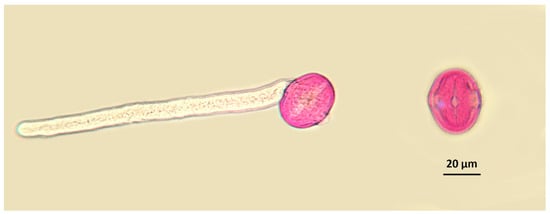
Figure 4.
Examples of vital (left) and non-vital (right) pollen grains (Melilotus italicus). Note that the vital pollen grain has a well-developed pollen tube, while the non-vital one has no visible cellular content. Pollen grains have been stained with basic fuchsine.
The seeds’ development and composition change in relation to the pollutant concentrations; in conditions of elevated O3, the seeds had far less stored carbohydrate, lipids, and proteins, which are fundamental for pollen germination, elongation of the pollen tube and growth rate. In this regard, the reduction in lipids content and the change in their composition due also to metabolic process resulted in germination pollen decline [73,79,80]. On the contrary, according to the results of other studies, the presence of elevated CO2 levels affects chemical pollen composition and seed development (increase in carbohydrate, lipids, and proteins content in seed), and it may enhance significantly the germination rate, favoring pollen production [81,82]. At the cellular level, air pollutants, due to their oxidative properties, may damage the cell structures, provoke organelle disconnection and the release of pollen cytoplasmic granules, and interfere with cellular mechanisms as well as with the gene sequence and expression [83,84,85,86]. In this regard, the higher frequency of discrete and point mutations in pollen grains collected in urban polluted areas caused changes in the gene sequences’ expression, influencing the proteins’ function and their allergen content and potential [23,41,87]. The oxidative properties of air pollutants may damage biomolecules such as proteins, lipids and nucleic acids that constitute the main material pollen reservoir, affecting pollen germination and elongation of the pollen tube [88,89]. Air pollutants can interact indirectly with epithelial surfaces, inducing inflammations and increasing epithelial permeability, and they can also act directly as adjuvants, promoting the production of some cytokines in airway epithelial cells and pro-allergic immune reactions such as IgE-mediated responses, enhancing the expression of allergenic proteins in pollen grains [6,10,90].
Therefore, oxidative degradation of the protein and the formation of amide and carbonyl groups decrease the recognition of allergenic proteins; otherwise, other chemical modifications, such as nitration or crosslinking, may enhance the allergenic potential of molecules, as shown in several studies that examine the nitration of the Bet v 1 allergen of birch pollen [59,60]. These post-translational allergens modifications may induce adverse effects on their stability, affecting the immune reactions in several processes such as the duration of exposure times to cellular receptors and the process of antigen presentation via major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II [10]. Some of the mentioned mechanisms, including an increased deposition of allergen in the airways due to carriage by air pollutants, may increase sensitization to allergens, which in a genetically predisposed individual could cause and exacerbate clinical manifestations such as asthma [91].
3. Air Pollutants, Pollen and Human Health
3.1. Air Pollutants, Pollen and Public Health
The prevalence of allergic disorders such as asthma and rhinitis, especially in developed and industrialized countries, has become a dramatic health problem in the last few decades, increasing considerably over time [92,93,94] (approximately 10% to 30% of the global population and 30% to 40% of the European population) [1,95,96]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), several million people around the world suffer from rhinitis, and over 260 million suffer from asthma [95,97].
Some studies show that this percentage is higher in industrialized countries, although the diffusion represents a critical health problem also in developing countries because of the interaction between air pollution and pollen that may exacerbate asthma and other allergic manifestations [93,98,99,100]. Other studies agree that the prevalence and incidence of allergic diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis increased worldwide, especially in high-income countries, and the temporal trend variation of their burden depends on numerous factors (geographical, social, individual, environmental) [93,95]. Therefore, in contrast, few studies showed a reduction in the incidence of allergic diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis, which can be due to an improvement in air quality of the urban area where the participants lived [96]. In this complex context, the advent and the rise of green technologies based on renewable energy such as wind, solar, and geothermal may produce positive effects in reducing pollution and allergic diseases, improving people’s quality of life in different parts of the world. Different studies highlighted that combined exposure to allergens like pollen and outdoor air pollutants like NO2 and O3 amplify allergenic airway disease and enhance inflammatory response with the recruitment of inflammatory cells, cytokines and interleukins for those predisposed, vulnerable populations [101,102].
Children are vulnerable subjects because of differences in their breathing rates and patterns. They inhale a volume of air containing a higher level of pollen and other pollutants per body weight than adults; therefore, they are more affected by pollutant environments [100].
There is clear evidence in the literature that asthma is the most common respiratory chronic disease in children, which is often characterized by underlying inflammation [103].
The rising trend of air pollutants due to industrial activities and motor vehicles depends on global warming and influences each individual’s response to changes in living environments [104].
Climate change (i.e., the presence of elevated levels of CO2, heatwaves) and weather variables significantly influence the production, concentration, diffusion, and bioavailability of allergens as well as the timing, intensity and duration of the pollen season, affecting health outcomes such as aeroallergen sensitization prevalence, hospitalizations and recovery for asthma attacks [18,26,105,106]. Global warming modifies the onset, duration, and intensity of the pollen season as well as the allergenicity of the pollen. In conditions of high atmospheric levels of CO2, plants exhibit enhanced reproductive effects and increased pollen production [107]. Climate change causes extreme events such as heatwaves and drought that can provoke adverse effects such as stress and respiratory diseases [92]. In the literature, there is clear evidence of interactions between aeroallergens and extreme meteorological events such as thunderstorms. During the pollen season, rapid changes in the weather factors such as rain, humidity, temperature may favor the hydration of pollen grains and also their fragmentation after rupture by osmotic shock, which generates atmospheric biological aerosols carrying elevated levels of allergens such as pollen, [108,109], including inhalable allergen-carrying cytoplasmic starch granules (<5 μm) or other paucimicronic components. Such small particles may penetrate into the lower respiratory system and provoke asthma in vulnerable subjects [110].
Thunderstorms can induce epidemic thunderstorm asthma (ETSA), and it sometimes can also induce severe asthma crises and deaths in patients that are sensitized and more vulnerable. Due to constant climate change, future thunderstorm asthma (TA) events are likely to become more common and more unpredictable; as a consequence, it is fundamental to investigate this topic to prevent and/or reduce asthma attacks [109].
In the same way, weather variables such as air temperature, sunlight, and rainfall together with CO2 are among the main factors modifying the dynamics of pollen release and production by plant [111,112]. Temperature and air humidity impact the amount of pollen released during flowering; air temperature is the most important meteorological factor that correlated positively to daily pollen concentration, and the effect of temperature is stronger on the spring and early summer flowering plants [16,113,114]. In conditions of air humidity, in particular, some types of pollen absorb water and increase in weight until they burst. On the contrary, dry air favors anther dehiscence in several anemophilous species [115]. An important factor that affects flowering intensity and pollen concentrations is rainfall; in conditions of abundant precipitation, the pollen content decreases [116,117]. In addition, also the wind speed influences the movement, release and dispersion of all aeroallergens in the atmosphere [118].
In combination with climate change and extreme weather conditions, industrialized and developed countries are facing an increased frequency of respiratory allergic diseases and asthma, as urbanization is associated with poorer air quality as well as high levels of pollutants and aeroallergens [119]. By 2050, it is predicted that 68% of the world’s population will be living in urban centers [102], and currently, 80% of people living in urban areas are exposed to air pollution levels that exceed WHO guidelines [92].
Some studies have shown that people of many countries living in urban areas are more sensitive to respiratory allergies, and as a consequence, the prevalence of pollinosis is increasing, especially in polluted cities [120,121,122]. Pollen taxa may differ in urban and rural environments [12]. As suggested by the hygiene hypothesis, increased urbanization in industrialized countries has reduced microbial exposure in early life, which resulted in the increased prevalence of allergic sensitization and disease [123,124].
In the same way, urban children have a higher prevalence of allergic diseases and atopy than children living in rural areas, which is probably due to the effect of air pollution on the onset and development of allergic disorders [96,125]. Evidence suggests that 13% of global incidence of asthma in children could be attributable to traffic-related air pollution, and air pollution has a negative effect on asthma outcomes in both adult and pediatric populations [90]. As described previously, children are more vulnerable than adults, and a study conducted in an urban population evidenced that the association between asthma morbidity and air pollution was stronger in children than in adolescents and adults [126]. Another study evidenced that approximately 40% of children in Poland suffer from allergies, and children aged 6–7 who live in cities have a 5-fold increase in the risk of allergic diseases compared to children of the same age group living in rural environments [127]. The urban heat island (UHI) is a well-investigated phenomenon in the literature, which is characterized by elevated ambient temperatures, reduced levels of relative air humidity and specific thermal winds, and increased levels of different air pollutants such as NO2, SO2, CO2, and O3, all of which are responsible for an increase in allergen content and production [5,128,129]. Therefore, the urbanization affects pollen season timing, which starts earlier and ends later compared to corresponding rural areas [130,131].
Therefore, the results of different studies highlighted that airborne pollen concentrations are higher in rural areas than in urban areas [12,132]. In fact, in urban environments, the vegetal biomass and floral biodiversity are reduced, and pollen sources may be relatively small, although some pollen species may be more numerous [131]. The qualitative and quantitative composition of airborne pollen grains differs in rural and urban areas and depends on many critical aspects such as the degree of urbanization, size and cover of vegetation areas, distance to pollen source in relation to pollen transport and diffusion, presence of ornamental vegetation, climate, weather factors and geographical conditions. A further and critical factor to consider is the sensitization of the individuals that, especially for vulnerable subjects, may exacerbate the pollinosis [12,132].
Although peaks may be less elevated in urban areas than in rural areas, the dynamic of hourly variations shows that the number of hours in the day that sensitized people are exposed to pollen levels is still higher in urban areas [130,132]. The overexposure to high levels of pollen during the day in the urban area could potentially lower the quality of life of allergic people [133].
3.2. Air Pollutants, Pollen and Occupational Health
Numerous categories of workers may be exposed to different biological, chemical, and physical agents that may trigger and/or exacerbate allergic disorders in sensitized subjects [134,135,136]. Occupational immune diseases are among the most common illnesses that affect workers; they can cause adverse effects on worker’s health and impacts on quality and capacity of work, resulting in economics losses [137].
Occupational asthma is the most common occupational respiratory disorder in industrialized countries; up to 25% of adult asthma cases are work-related, which represents a significant issue worldwide [138,139,140]. Work-related asthma (WRA) is used to define both asthma caused by the presence of a specific agent in the workplace, i.e., occupational asthma (OA), and pre-existing asthma that is worsened by exposure to non-specific stimuli at work but not caused by it, i.e., work-exacerbated asthma (WEA) [139,141]. Therefore, worldwide, asthma exacerbations provoke a large proportion of asthmatic individuals to miss work each year: 17% in western Europe, 23% in central and eastern Europe, 27% in the Asia-Pacific region and 30% in Japan [142]. WEA is known to be more prevalent in particular among specific working categories such as healthcare, education and service workers [143].
In the literature, there are still a few studies concerning occupational allergies that may potentially have a negative impact on occupational health related to polluted urban environments. Some authors have investigated potential exposure to agents responsible for allergic diseases such as asthma, allergic contact dermatitis, urticaria, and allergic rhinitis in different working sectors (i.e., construction, agriculture, fishing, hunting, park maintenance, farming, and operators in urban and suburban environments) in association with outdoor environmental pollutants [144,145]. Some studies evidenced a higher prevalence of allergic respiratory symptoms and allergic sensitization in specific groups of workers (traffic wardens, traffic policemen) exposed, for a big part of their working time, to outdoor pollutants in areas with high traffic intensity. The results of clinical and allergological tests of these studies showed a prevalence of positive results (~60%) in the exposed workers compared to the controls. These results highlight that allergological tests should be included in the health surveillance protocols for workers exposed to outdoor pollutants [145,146].
Another interesting multicenter study highlighted that workers employed in 13 different occupations (i.e., office staff, attendants, blue-collar workers, drivers, businessmen, farmers, school members) and different regions of China that were screened for common allergens, including weed pollen mix and tree pollen mix, showed distinctive sensitization patterns of asthma. The workers with the highest positive rates to pollen occurred among blue-collar workers employed in different sectors (i.e., construction workers, railway workers, coal mine workers) and drivers (taxi and bus drivers). In this regard, some occupations such as drivers may have a higher exposure to air pollutants such as traffic emissions during their outdoor activities. Therefore, the combined effect of smoking and air pollution may be a worsening factor of asthma and other allergic diseases. The study evidenced that the pattern of asthma distribution depends on many factors including geographical features, cover of vegetation, meteorological factors, and the habits of daily living in the different regions. To this purpose, subjects recruited from regions in the northeast of China with no history of smoking had the highest rate of sensitization to tree pollen and weed pollen due to climatic regional conditions (dry and windy, with less precipitation in springs and falls, and hot and humid in summers) and higher pollen content in these areas, which could promote the diffusion and inhalation of allergens. Then, in the same paper, the researchers underlined that several factors such as air pollutants, allergens, and smoking, especially combined, are important causes of severe asthma [147].
Therefore, the synergic effects due to environmental and occupational exposure to allergens, air pollutants, climate change and individual sensitization should be taken into account in the management of these diseases [144,148]. To this purpose, strategies for control and prevention should be applied in relation to conditions of exposure, especially the characteristics of occupational settings, to identify and protect workers in high-risk categories.
4. Conclusions
The prevalence of allergic disorders such as asthma and rhinitis, also because of the interaction between air pollution and pollen, has become a critical health problem in the last few decades. Cumulative data in the literature indicate that airborne allergens such as pollen grains interact significantly with many air pollutants (i.e., O3, PM, NO2, SO2), resulting in different effects on pollen content, production, and allergenicity [149,150]. Air pollutants affect the morphological and physical properties of the pollen surface (i.e., deformation, rupture of pollen wall), resulting in an increased bioavailability of allergen or sub-pollen particles containing allergens released into the environment. The oxidative properties of air pollutants may modify the composition and chemical properties of macromolecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, affecting the germination and elongation of the pollen tube as well as the modulation of immune response in many cellular and molecular processes. The exposure to air pollutants also influences the biological properties of pollen such as the viability and germination rate (i.e., reduction in viability and germination rate), which are critical factors for plant reproductive function [73]. All effects of air pollutants on pollen species depend on environmental factors such as climate change, meteorological conditions, and urbanization as well as individual factors such as sensitization to allergens in relation to conditions of exposure, pollen and pollutants types [4]. Climate change and weather factors influence significantly the production, concentration, diffusion, bioavailability of allergens and pollen seasonality, affecting aeroallergen sensitization prevalence and respiratory diseases. Moreover, the effect of urbanization has to be taken into account in this context. In fact, as shown in the literature, the urban heat island (UHI) effect may affect levels of chemical air pollutants and be responsible for an increase in allergen content and production. Furthermore, pollen species may be different in urban and rural environments [120,148]. Although there are still few studies regarding occupational allergies in relation to air pollutants, they may have a negative and significant impact on worker’s health and quality of life in different categories of workers in many sectors (i.e., construction, agriculture, farming, health care), resulting in economic losses and a high prevalence of allergic respiratory diseases [145,147]. In summary, in this work, we have investigated the effects of interactions between air pollutants and pollen grains to understand the outcomes on public and occupational health in relation to all the factors (i.e., climate change, weather variables, urbanization, individual sensitization) that play a role in this context. More studies will be promoted to investigate the role of several factors and biochemical mechanisms involved in the responses to different environmental exposures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: P.C. and M.C.D.; Methodology: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Formal analysis, P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Investigation: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Data curation: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Writing—original draft preparation: P.C.; Writing—review and editing: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Visualization: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Supervision: P.C., A.L. and M.C.D.; Project administration: P.C. and M.C.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kolek, F.; Plaza, M.D.P.; Leier-Wirtz, V.; Friedmann, A.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Damialis, A. Earlier Flowering of Betula pendula Roth in Augsburg, Germany, Due to Higher Temperature, NO2 and Urbanity, and Relationship with Betula spp. Pollen Season. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalve, F.; Tomás, C.; Fraile, R. Influence of meteorological parameters and air pollutants onto the morbidity due to respiratory diseases in Castilla-La Mancha, Spain. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduber, F.; Calvo, A.I.; Blanco-Alegre, C.; Castro, A.; Vega-Maray, A.M.; Valencia-Barrera, R.M.; Fernández-González, D.; Fraile, R. Links between recent trends in airborne pollen concentration, meteorological parameters and air pollutants. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisler, A. Allergies in urban areas on the rise: The combined effect of air pollution and pollen. Int. J. Public Health 2021, 66, 1604022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowska-Korzeniowska, M.; Jerzyńska, J.; Polańska, K.; Kaleta, D.; Stelmach, I.; Kunert, A.; Stelmach, W. The effect of air pollution on the respiratory system in preschool children with contribution of urban heat islands and geographic data–the aim of the study and methodological assumptions. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2021, 34, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedghy, F.; Varasteh, A.R.; Sankian, M.; Moghadam, M. Interaction between air pollutants and pollen grains: The role on the rising trend in allergy. Rep. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 6, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Madaniyazi, L.; Xerxes, S. Outdoor air pollution and the onset and exacerbation of asthma. Chronic Dis. Transl. Med. 2021, 7, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luschkova, D.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Ludwig, A. Climate change and allergies. Allergo J. Int. 2022, 31, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weger, L.A.; Bruffaerts, N.; Koenders, M.M.J.F.; Verstraeten, W.W.; Delcloo, A.W.; Hentges, P.; Hentges, F. Long-term pollen monitoring in the Benelux: Evaluation of allergenic pollen levels and temporal variations of pollen seasons. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 676176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth-Selzle, K.; Kampf, C.J.; Lucas, K.; Lang-Yona, N.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Shiraiwa, M.; Lakey, P.S.J.; Lai, S.; Liu, F.; Kunert, A.T.; et al. Air pollution and climate change effects on allergies in the anthropocene: Abundance, interaction, and modification of allergens and adjuvants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4119–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puc, M. Influence of meteorological parameters and air pollution on hourly fluctuation of birch (Betula L.) and ash (Fraxinus L.) airborne pollen. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2012, 19, 660–665. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch-Cano, F.; Bernard, N.; Sudre, B.; Gillet, F.; Thibaudon, M.; Richard, H.; Badot, P.M.; Ruffaldi, P. Human exposure to allergenic pollens: A comparison between urban and rural areas. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Yan, A. Correlation of pollen concentration and meteorological factors with medical condition of allergic rhinitis in Shenyang area. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 4619693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, M.P.; Alcázar, P.; Oteros, J.; Galán, C. Atmospheric pollutants and their association with olive and grass aeroallergen concentrations in Córdoba (Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 45447–45459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Haines, S.; Wang, E.; Nassikas, N.; Kinney, P.L. Synergistic health effects of air pollution, temperature, and pollen exposure: A systematic review of epidemiological evidence. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, N.Č.; Popović, A.; Dordević, D. Air pollution by pollen grains of anemophilous species: Influence of chemical and meteorological parameters. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska-Weryszko, K.; Weryszko-Chmielewska, E.; Sulborska, A.; Konarska, A.; Dmitruk, M.; Kaszewski, B.M. Amaranthaceae pollen grains as indicator of climate change in Lublin (Poland). Environ. Res. 2021, 193, 110542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams-Groom, B.; Selby, K.; Derrett, S.; Frisk, C.A.; Pashley, C.H.; Satchwell, J.; King, D.; McKenzie, G.; Neilson, R. Pollen season trends as markers of climate change impact: Betula, Quercus and Poaceae. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batos, B.; Veselinović, M.; Rakonjac, L.; Miljković, D. Morphological properties of pollen as bioindicators of deciduous woody species in Belgrade Parks (Serbia). Topola 2019, 203, 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Nagpal, A.K. Effect of vehicular traffic on pollen size and viability of Apocynaceous plant species. Trop. Plant Res. 2017, 4, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjøth, C.A.; Kurganskiy, A.; Grundström, M.; Werner, M.; Adams-Groom, B. Air pollution affecting pollen concentrations through radiative feedback in the atmosphere. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldacci, S.; Maio, S.; Cerrai, S.; Sarno, G.; Baïz, N.; Simoni, M.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Viegi, G. Allergy and asthma: Effects of the exposure to particulate matter and biological allergens. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavoni, G.; D’Amato, G.; Afferni, C. The dangerous liaison between pollens and pollution in respiratory allergy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017, 118, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilevskaya, N. Pollution of the environment and pollen: A review. Stresses 2022, 2, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Yao, C.; Zhang, L.; Rao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; et al. Characterization of allergenicity of Platanus pollen allergen a 3 (Pla a 3) after exposure to NO2 and O3. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggs, P.J. Climate change, aeroallergens, and the aeroexposome. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Elkelish, A.; Durner, J.; Lindermayr, C.; Winkler, J.B.; Ruёff, F.; Behrendt, H.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Holzinger, A.; Kofler, W.; et al. Common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.): Allergenicity and molecular characterization of pollen after plant exposure to elevated NO2. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, H.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, S.; Li, S.; et al. Allergenicity of recombinant Humulus japonicus pollen allergen 1 after combined exposure to ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundström, M.; Dahl, Å.; Ou, T.; Chen, D.; Pleijel, H. The relationship between birch pollen, air pollution and weather types and their effect on antihistamine purchase in two Swedish cities. Aerobiologia 2017, 33, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elagoz, W.; Manning, W.J. Responses of sensitive and tolerant bush beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to ozone in open-top chambers are influenced by phenotypic differences, morphological characteristics, and the chamber environment. Environ. Pollut. 2005, 136, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuinica, L.G.; Abreu, I.; Gomes, C.R.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. Exposure of Betula pendula Roth pollen to atmospheric pollutants 2013. CO, O3 and SO2. Grana 2013, 52, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depciuch, J.; Kasprzyk, I.; Roga, E.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. Analysis of morphological and molecular composition changes in allergenic Artemisia vulgaris L. pollen under traffic pollution using SEM and FTIR spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 23203–23214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewling, L.; Frątczak, A.; Kostecki, L.; Nowak, M.; Szymańska, A.; Bogawski, P. Biological and chemical air pollutants in an urban area of central Europe: Co-exposure assessment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Fernández-González, M.; Guedes, A.; Abreu, I.; Ribeiro, H. The strong and the stronger: The effects of increasing ozone and nitrogen dioxide concentrations in pollen of different forest species. Forests 2021, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Kampf, C.J.; Weber, B.; Huffman, J.A.; Pöhlker, C.; Andreae, M.O.; Lang-Yona, N.; Burrows, S.M.; Gunthe, S.S.; Elbert, W.; et al. Bioaerosols in the Earth System: Climate, Health, and Ecosystem Interactions. Atmos. Res. 2016, 182, 346–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malayeri, B.E.; Noori, M.; Jafari, M. Using the pollen viability and morphology for fluoride pollution biomonitoring. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahillon, V.; Saussez, S.; Michel, O. High incidence of sensitization to ornamental plants in allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2006, 61, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sénéchal, H.; Visez, N.; Charpin, D.; Shahali, Y.; Peltre, G.; Biolley, J.P.; Lhuissier, F.; Couderc, R.; Yamada, O.; Malrat-Domenge, A.; et al. A review of the effects of major atmospheric pollutants on pollen grains, pollen content, and allergenicity. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 940243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehregani, A.; Majde, A.; Moin, M.; Gholami, M.; Shariatzadeh, M.A.; Nassiri, H. Increasing allergy potency of Zinnia pollen grains in polluted areas. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 58, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Ren, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.; Wu, M.; Yi, F.; Lin, J.; Shinich, Y.; Wag, Q. Characterisation of proteins expression of Platanus pollen following exposure to gaseous pollutants and vehicle exhaust particles. Aerobiologia 2014, 30, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, F.; Youcef, S.; Pourpak, Z.; Majd, A.; Ghahremaninejad, F. Year-to-year variation of the elemental and allergenic contents of Ailanthus altissima pollen grains: An allergomic study. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visez, N.; Ivanovsky, A.; Roose, A.; Gosselin, S.; Senechal, H.; Poncet, P.; Choël, M. Atmospheric particulate matter adhesion onto pollen: A review. Aerobiologia 2020, 36, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanejad, F.; Ahmad, M.; Seyed, M.; Mostafa, M.; Masoud, A.; Maryam, M. Effect of air pollution on soluble proteins, structure and cellular material release in pollen of Lagerstroemia indica L. (Lytraceae). Acta Biol. Cracoviensia Ser. Bot. 2003, 45, 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- Azzazy, M.F. Environmental impacts of industrial pollution on pollen morphology of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. (Myrtaceae). J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galveias, A.; Costa, A.R.; Bortoli, D.; Alpizar-Jara, R.; Salgado, R.; Costa, M.J.; Antunes, C.M. Cupressaceae pollen in the city of Évora, South of Portugal: Disruption of the pollen during air transport facilitates allergen exposure. Forests 2021, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga Kailas, J.; Ramakrishna, H.; Seva, B. Pollution effect on pollen morphology in industrial areas of Hyderabad, Telangana state, India. J. Ind. Pollut. Control 2015, 31, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Majd, A.; Chehregani, A.; Moin, M.; Gholami, M.; Kohno, S.; Nabe, T.; Shariatzade, M.A. The effects of air pollution on structures, proteins and allergenicity of pollen grains. Aerobiologia 2004, 20, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanejad, F. Air pollution effects on structure, proteins and flavonoids in pollen grains of Thuja orientalis L. (Cupressaceae). Grana 2009, 48, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahali, Y.; Pourpak, Z.; Moin, M.; Mari, A.; Majd, A. Instability of the structure and allergenic protein content in Arizona cypress pollen. Allergy 2009, 64, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.C.; Marliere, M.; Peltre, G.; Sterenberg, P.A.; Lacroix, G. Traffic-related air pollutants induce the release of allergen containing cytoplasmic granules from grass pollen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 139, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanter, U.; Heller, W.; Durner, J.; Winkler, J.B.; Engel, M.; Behrendt, H.; Holzinger, A.; Braun, P.; Hauser, M.; Ferreira, F.; et al. Molecular and immunological characterization of ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia L.) pollen after exposure of the plants to elevated ozone over a whole growing season. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franze, T.; Weller, M.G.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Protein nitration by polluted air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Farah, J.; Choel, M.; Gosselin, S.; Baroudi, M.; Petitprez, D.; Visez, N. Uptake of ozone and modification of lipids in Betula Pendula pollen. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukacki, P.M.; Chałupka, W. Environmental pollution changes in membrane lipids, antioxidants and vitality of scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) pollen. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2003, 72, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Duque, L.; Duarte, A.J.; Gomes, C.R.; Ribeiro, H.; Cruz, A.; Silva, J.C.G.E.; Abreu, I. In vitro exposure of Acer negundo pollen to atmospheric levels of SO2 and NO2: Effects on allergenicity and germination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2406–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Singh, R.P.; Kushwaha, G.S.; Iqbal, N.; Singh, A.; Kaushink, S.; Kaur, P.; Sharma, S.; Sigh, T.P. Current overview of allergens of plant pathogenesis related protein families. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 543195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, H.; Costa, C.; Abreu, I.; da Silva, J.C.E. Effect of O3 and NO2 atmospheric pollutants on Platanus x acerifolia pollen: Immunochemical and spectroscopic analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alscher, R.G.; Donahue, J.L.; Cramer, C.L. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants: Relationships in green cells. Physiol. Plant 1997, 100, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackaert, C.; Kofler, S.; Horejs-Hoeck, J.; Zulehner, N.; Asam, C.; von Grafenstein, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Briza, P.; Liedl, K.R.; Bohle, B.; et al. The impact of nitration on the structure and immunogenicity of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1.0101. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karle, A.C.; Oostingh, G.J.; Mutschlechner, S.; Ferreira, F.; Lackner, P.; Bohle, B.; Fischer, G.F.; Vogt, A.B.; Dusch, A. Nitration of the pollen allergen bet v10101 enhances the presentation of bet v1-derived peptides by HLA-DR onhuman dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, I.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Hansson, A. Oxidative Modifications to Cellular Components in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Uhm, S.J.; Lee, H.T. Effect of vitrification and beta-mercaptoethanol on reactive oxygen species activity and in vitro development of oocytes vitrified before or after in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 2010, 93, 2602–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risse, U.; Tomczok, J.; Huss-Marp, J.; Darsow, U.; Behrendt, H. Health relevant interaction between airborne particulate matter and aeroallergens pollen. J. Aerosol Sci. 2000, 31, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.E.H.; Lui, J.H.; Palnivelu, R.; Naclerio, R.M.; Preuss, D. Pollen lipidomics: Lipid profiling exposes a notable diversity in 22 allergenic pollen and potential biomarkers of the allergic immune response. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Kasche, A.; Menzel, A.; Jakob, T.; Thiel, M.; Ring, J.; Behrendt, H. Impact of pollen on human health: More than allergen carriers? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilles-Stein, S.; Beck, I.; Chaker, A.; Bas, M.; McIntyre, M.; Cifuentes, L.; Petersen, A.; Gutermuth, J.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Behrendt, H.; et al. Pollen derived low molecular compounds enhance the human allergen specific immune response in vivo. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1355–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, I.; Jochner, S.; Gilles, S.; McIntyre, M.; Buters, J.T.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Behrendt, H.; Ring, J.; Menzel, A.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C. High environmental ozone levels lead to enhanced allergenicity of birch pollen. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, U.; Ernst, D. Effects of NO2 and ozone on pollen allergenicity. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, J.E.; Wimmer, R.; Larsen, J.N.; Spangfort, M.D.; Otzen, D.E. The major birch allergen, Bet v 1, shows affinity for a broad spectrum of physiological ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23684–23692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henricsson, S.; Westerholm, R.; Nilsson, S.; Berggren, B. Chemical characterisation of extractable compounds found in the coating of birch (betula) pollen. Grana 1996, 35, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, O.; Mendez, M.; Quijada, M.; Gosselin, S.; Farah, J.; Choukri, A.; Visez, N. Chemical modification of coating of Pinus halepensis pollen by ozone exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chichiriccò, G.; Picozzi, P. Reversible inhibition of the pollen germination and the stigma penetration in Crocus vernus ssp. vernus (Iridaceae) following fumigations with NO2, CO, and O3 gases. Plant Biol. 2007, 9, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbah, J.N.; Kubiske, M.E.; Nelson, N.; Oksanen, E.; Vaapavuori, E.; Karnosky, D.F. Impacts of elevated atmospheric CO2 and O3 on paper birch (Betula papyrifera): Reproductive fitness. Sci.World J. 2007, 7, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolters, J.H.B.; Martens, M.J.M. Effects of air pollutants on pollen. Bot. Rev. 1987, 53, 372–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, S.; Tedeschini, E.; Frenguelli, G.; Wopfner, N.; Ferreira, F.; D’Amato, G.; Ederli, L. Ozone affects pollen viability and NAD(P)H oxidase release from Ambrosia artemisiifolia pollen. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2823–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, S.K.; Saeed, S.; Asrar, M.; Ahmed, A.; Tariq, I.; Marri, A.A.; Sadiq, N.; Baloch, A.; Latif, A.; Shawani, N.A. Response of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) pollen grains to vehicular exhaust pollution at quetta, balochistan, pakistan. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 4387–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Bay, D.T.; Murdy, W.H. The impact of sulfur dioxide on plant sexual reproduction: In vivo and in vitro effects compared. J. Environ. Qual. 1983, 12, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardini, E.; Cristofolini, F.; Paoletti, E.; Lazzeri, P.; Pepponi, G. Pollen viability for air pollution bio-monitoring. J. Atmos. Chem. 2004, 49, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, V.J.; Black, C.R.; Roberts, J.A.; Stewart, C.A. Impact of the ozone on the reproductive development of plants. New Phytol. 2000, 147, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, S.L.; Gifford, D.J. Structural and biochemical changes in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) seeds during germination and early seedling growth. II. Storage triacylglycerols and carbohydrates. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1999, 160, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Kubiske, M.E.; Connor, K.F. Germination of CO2 enriched Pinus taeda L. seeds and subsequent seedling growth responses to CO2 enrichment. Funct. Ecol. 2001, 15, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeau, S.L.; Clark, J.S. Elevated CO2 and tree fecundity: The role of tree size, interannual variability, and population heterogeneity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemianin, M.; Waga, J.; Czarnobilska, E.; Myszkowska, D. Changes in qualitative and quantitative traits of birch (Betula pendula) pollen allergenic proteins in relation to the pollution contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 39952–39965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Fan, E.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Effect of nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide on viability and morphology of oak pollen. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashpulatov, A.S.; Clement, P.; Akimcheva, S.A.; Belogradova, K.A.; Barinova, I.; Rakhmawaty, F.D.; Heberle-Bors, E.; Touraev, A. A model system to study the environment-dependent expression of the Bet v 1a gene encoding the major birch pollen allergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2004, 134, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overmyer, K.; Brosché, M.; Pellinen, R.; Kuittinen, T.; Tuominen, H.; Ahlfors, R.; Keinänen, M.; Saarma, M.; Scheel, D.; Kangasjärvi, J. Ozone-induced programmed cell death in the Arabidopsis radical-induced cell death1 mutant. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryce, M.; Drews, O.; Schenk, M.; Menzel, A.; Estrella, N.; Wiechenmeier, I.; Smulders, M.J.M.; Buters, J.; Ring, J.; Gorg, A.; et al. Impact of urbanization on the proteome of birch pollen and its chemotactic activity on human granulocytes. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 151, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chichiriccò, G. Viability-germinability of Crocus (Iridaceae) pollen in relation to cyto- and ecophysiological factors. Flora 2000, 195, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshchina, V.V.; Mel’nikova, E.V. Pollen chemosensitivity to ozone and peroxides. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 48, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiotiu, A.I.; Novakova, P.; Nedeva, D.; Chong-Neto, H.J.; Novakova, S.; Steiropoulos, P.; Kowal, K. Impact of air pollution on asthma outcomes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Pereira, M.; Guidos-Fogelbach, G.; Solé, D. Climate changes, air pollution and allergic diseases in childhood and adolescence. J. Pediatr. 2022, 98 (Suppl. S1), S47–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldakheel, F.M. Allergic diseases: A comprehensive review on risk factors, immunological mechanisms, link with COVID-19, potential treatments, and role of allergen bioinformatics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartra, J.; Mullol, J.; del Cuvillo, A.; Dávila, I.; Ferrer, M.; Jáuregui, I.; Montoro, J.; Sastre, J.; Valero, A. Air pollution and allergens. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2007, 17, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.H.; Hwang, J.; Kwon, R.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, J.I.; Yon, D.K.; GBD 2019 Allergic Disorders Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of allergic disorders and their risk factors in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Allergy 2023, 78, 2232–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, M.; Czarnobilska, M.; Dyga, W.; Czarnobilska, E. Trends in the epidemiology of allergic diseases of the airways in children growing up in an urban agglomeration. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Díaz, S.N.; Arias-Cruz, A.; Macouzet-Sánchez, C.; Partida-Ortega, A.B. Impact of air pollution in respiratory allergic diseases. Med. Univ. 2016, 18, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Bergmann, K.C.; Cecchi, L.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Sanduzzi, A.; Liccardi, G.; Vitale, C.; Stanziola, A.; D’Amato, M. Climate change and air pollution: Effects on pollen allergy and other allergic respiratory diseases. Allergo J. Int. 2014, 23, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, H. Impact of air pollution on allergic diseases. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2011, 26, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, J.A.; Bielory, L.; Fagliano, J.A. Associations between ozone, PM2.5, and four pollen types on emergency department pediatric asthma events during the warm season in New Jersey: A case-crossover study. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Duhl, T.; Salam, M.T.; House, J.M.; Flagan, R.C.; Avol, E.L.; Gilliland, F.D.; Guenther, A.; Chung, S.H.; Lamb, B.K.; et al. Development of a regional-scale pollen emission and transport modeling framework for investigating the impact of climate change on allergic airway disease. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 3977–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Sayeau, K.; Ellis, A.K. Air pollution and allergic rhinitis: Role in symptom exacerbation and strategies for management. J. Asthma Allergy 2020, 13, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licari, A.; Castagnoli, R.; Brambilla, I.; Marseglia, A.; Tosca, M.A.; Marseglia, G.L.; Ciprandi, G. Asthma endotyping and biomarkers in childhood asthma. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2018, 31, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Holgate, S.T.; Pawankar, R.; Ledford, D.K.; Cecchi, L.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Al-Enezi, F.; Al-Muhsen, S.; Ansotegui, I.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; et al. Meteorological conditions, climate change, new emerging factors, and asthma and related allergic disorders. A statement of the World Allergy Organization. World Allergy Organ J. 2015, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrig, R.; Clot, B. 50 years of pollen monitoring in Basel (Switzerland) demonstrate the influence of climate change on airborne pollen. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 677159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Orozco, R.; García-Mozo, H.; Oteros, J.; Galan, C. Long-term trends in atmospheric quercus pollen related to climate change in southern Spain: A 25-year perspective. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 262, 118637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoflich, C.; Balakirski, G.; Hajdu, Z.; Baron, J.M.; Kaiser, L.; Czaja, K.; Merk, H.F.; Gerdsen, S.; Strassen, U.; Bas, M.; et al. Potential health risk of allergenic pollen with climate change associated spreading capacity: Ragweed and olive sensitization in two German federal states. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2016, 219, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Price, D.; Hughes, K.M.; Thien, F.; Suphioglu, C. Epidemic Thunderstorm Asthma: Lessons learned from the storm down-under. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1510–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Urrutia-Pereira, M.; Del Giacco, S.; Rosario Filho, N.A.; Chong-Neto, H.J.; Solé, D.; Ansotegui, I.; Cecchi, L.; Sanduzzi Zamparelli, A.; et al. Thunderstorm allergy and asthma: State of the art. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2021, 16, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, R.B. Grass pollen, thunderstorms and asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1993, 23, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępalska, D.; Myszkowska, D.; Piotrowicz, K.; Kasprzyk, I. The phenological phases of flowering and pollen seasons of spring flowering tree taxa against a background of meteorological conditions in Kraków, Poland. Acta Agrobot. 2016, 65, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puc, M.; Kasprzyk, I. The patterns of Corylus and Alnus pollen seasons and pollination periods in two Polish cities located in different climatic regions. Aerobiologia 2013, 29, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdziewicz, M.; Fernandez-Martinez, M.; Bonal, R.; Belmonte, J.; Espelta, J.M. The moran effect and environmental vetoes: Phenological synchrony and drought drive seed production in a mediterranean oak. Proc. R. Soc. B 2017, 284, 20171784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levetin, E.; Van de Water, P. Changing pollen types/concentrations/distribution in the United States: Fact or fiction? Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2008, 8, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemmer, F.; Dahl, Å.; Galán, C. The duration and severity of the allergenic pollen season in Istanbul, and the role of meteorological factors. Aerobiologia 2022, 38, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, C.; Alcazar, P.; Oteros, J.; Garcia-Mozo, H.; Aira, M.J.; Belmonte, J.; Diaz de la Guardia, C.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, D.; Gutierrez-Bustillo, M.; Moreno-Grau, S.; et al. Airborne pollen trends in the Iberian Peninsula. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboulaich, N.; Achmakh, L.; Bouziane, H.; Trigo, M.M.; Recio, M.; Kadiri, M.; Cabezudo, B.; Riadi, H.; Kazzaz, M. Effect of meteorological parameters on Poaceae pollen in the atmosphere of Tetouan (NW Morocco). Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 57, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ślusarczyk, J.; Kopacz-Bednarska, A.; Posłowska, J. Influence of meteorological factors on the dynamics of hazel, alder, birch and poplar pollen in the 2021 season in Kielce, Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2022, 29, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makra, L.; Csepe, Z.; Matyasovszky, I.; Deak, A.J.; Sumeghy, Z.; Tusnady, G. The effects of the current and past meteorological elements influencing the current pollen concentrations for different taxa. Bot. Stud. 2014, 55, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ščevková, J.; Dušička, J.; Zahradníková, E.; Sepšiová, R.; Kováč, J.; Vašková, Z. Impact of meteorological parameters and air pollutants on airborne concentration of Betula pollen and Bet v 1 allergen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 95438–95448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, J.; Wichmann, H.E. Traffic related pollutants in Europe and their effect on allergic disease. Curr. Opinion Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 4, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalo-Garijo, M.A.; Tormo-Molina, R.; Muńoz-Rodrìguez, A.F.; Silva-Palacios, I. Differences in the spatial distribution of airborne pollen concentrations at different urban locations within a city. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 16, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Platts-Mills, T.A.; Erwin, E.; Heymann, P.; Woodfolk, J. Is the hygiene hypothesis still a viable explanation for the increased prevalence of asthma? Allergy 2005, 60, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, N.; Siddique, N.; Custovic, A. Allergic disease in urban and rural populations: Increasing prevalence with increasing urbanization. Allergy 2005, 60, 1357–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarnobilska, E.; Bulanda, M.; Bulanda, D.; Mazur, M. The Influence of air pollution on the development of allergic inflammation in the airways in Krakow’s atopic and Non-atopic residents. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veremchuk, L.V.; Tsarouhas, K.; Vitkina, T.I.; Mineeva, E.E.; Gvozdenko, T.A.; Antonyuk, M.V.; Rakitskii, V.N.; Sidletskaya, K.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Golokhvast, K.S. Impact evaluation of environmental factors on respiratory function of asthma patients living in urban territory. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stróżek, J.; Samoliński, B.K.; Kłak, A.; Gawińska-Drużba, E.; Izdebski, R.; Krzych-Fałta, E.; Raciborski, F. The indirect costs of allergic diseases. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health. 2019, 32, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimet, A.; Pellsier, V.; Quènol, H.; Aguejdad, R.; Dubreuil, V.; Roze, H. Urbanisation induces early flowering: Evidence from Platanus acerifolia and Prunus cerasus. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2009, 53, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Ribeiro, H.; Delgado, J.L.; Abreu, I. Seasonal and intradiurnal variation of allergenic fungal spores in urban and rural areas of the North of Portugal. Aerobiologia 2009, 25, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carińanos, P.; Sànchez-Mesa, J.A.; Prieto-Baena, J.C.; López, A.; Guerra, F.; Moreno, C.; Dominguez, E.; Galan, C. Pollen allergy related to the area of residence in the city of Còrdoba, south-west Spain. J. Environ. Monit. 2002, 4, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, I. Comparative study of seasonal and intradiurnal variation of airborne herbaceous pollen in urban and rural areas. Aerobiologia 2006, 22, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rajo, F.J.; Fdez-Sevilla, D.; Stach, A.; Jato, V. Assessment between pollen seasons in areas with different urbanization level related to local vegetation sources and differences in allergen exposure. Aerobiologia 2010, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, J.; Kramer, U.; Schafer, T.; Behrendt, H. Why are allergies increasing? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2001, 13, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Ravindra, K.; Mor, S. Occupational exposure to airborne pollen and associated health risks among gardeners: A perception-based survey. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 70084–70098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, H.C.; Ronsmans, S.; Hoet, P.H.M.; Nemery, B.; Vanoirbeek, J.A.J. Occupational asthma caused by low-molecular-weight chemicals associated with contact dermatitis: A retrospective study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2346–2354.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, J.; Gill, N.; Ramanathan, M., Jr.; Patadia, M. Unified airway disease: Environmental factors. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 56, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.E.; Long, C.; Dotson, G.S. Occupational Allergy. Eur. Med. J. 2017, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, D.; Reed, C.E. Environmental and occupational allergies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125 (Suppl. S2), S150–S160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiotiu, A.I.; Novakova, S.; Labor, M.; Emelyanov, A.; Mihaicuta, S.; Novakova, P.; Nedeva, D. Progress in occupational asthma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsonk, E.L. Work-related asthma and implications for the general public. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, M.; Lemière, C. Occupational asthma. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Adachi, M.; Lai, C.K.W.; Soriano, J.B.; Vermeire, P.A.; Weiss, K.B.; Weiss, S.T. Worldwide severity and control of asthma in children and adults: The global asthma insights and reality surveys. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.; Liss, G.M.; Vernich, L.; Buyantseva, L.; Tarlo, S.M. Work-exacerbated asthma in a workers’ compensation population. Occup. Med. 2014, 64, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ovidio, M.C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L. Climate change and occupational allergies: An overview on biological pollution, exposure and prevention. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanità 2016, 52, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimercati, L.; Gatti, M.F.; Baldassarre, A.; Nettis, E.; Favia, N.; Palma, M.; Martina, G.L.; Di Leo, E.; Musti, M. Occupational exposure to urban air pollution and allergic diseases. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 12977–12987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimercati, L.; Carrus, A.; Bisceglia, L.; Tato, I.; Bellotta, M.R.; Russo, A.; Martina, G.; Daprile, C.; di Leo, E.; Nettis, E.; et al. Biological monitoring and allergic sensitization in traffic police officers exposed to urban air pollution. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2006, 19, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Xue, M.; Wei, N.; Zheng, P.; Wu, G.; An, N.; Huang, H.; Sun, B. Sensitisation of severe asthma in different occupations: A multicentre study in China. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, G.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Biagioni, B.; Lancia, A.; Cecchi, L.; D’Ovidio, M.C.; D’Amato, M. New Developments in climate change, air pollution, pollen allergy, and interaction with SARS-CoV-2. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelliccioni, A.; Ciardini, V.; Lancia, A.; Di Renzi, S.; Brighetti, M.A.; Travaglini, A.; Capone, P.; D’Ovidio, M.C. Intercomparison of indoor and outdoor pollen concentrations in rural and suburban research workplaces. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, E.; Zhang, L. Associations among air pollutants, grass pollens, and daily number of grass pollen allergen-positive patients: A longitudinal study from 2012 to 2016. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).