Impacts of Multi-Source Microwave Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of Typhoon Ampil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Satellite Observations and WRFDA System
2.1. AMSUA, MHS and MWHS2 Radiance
2.2. WRFDA System
3. Experimental Setup
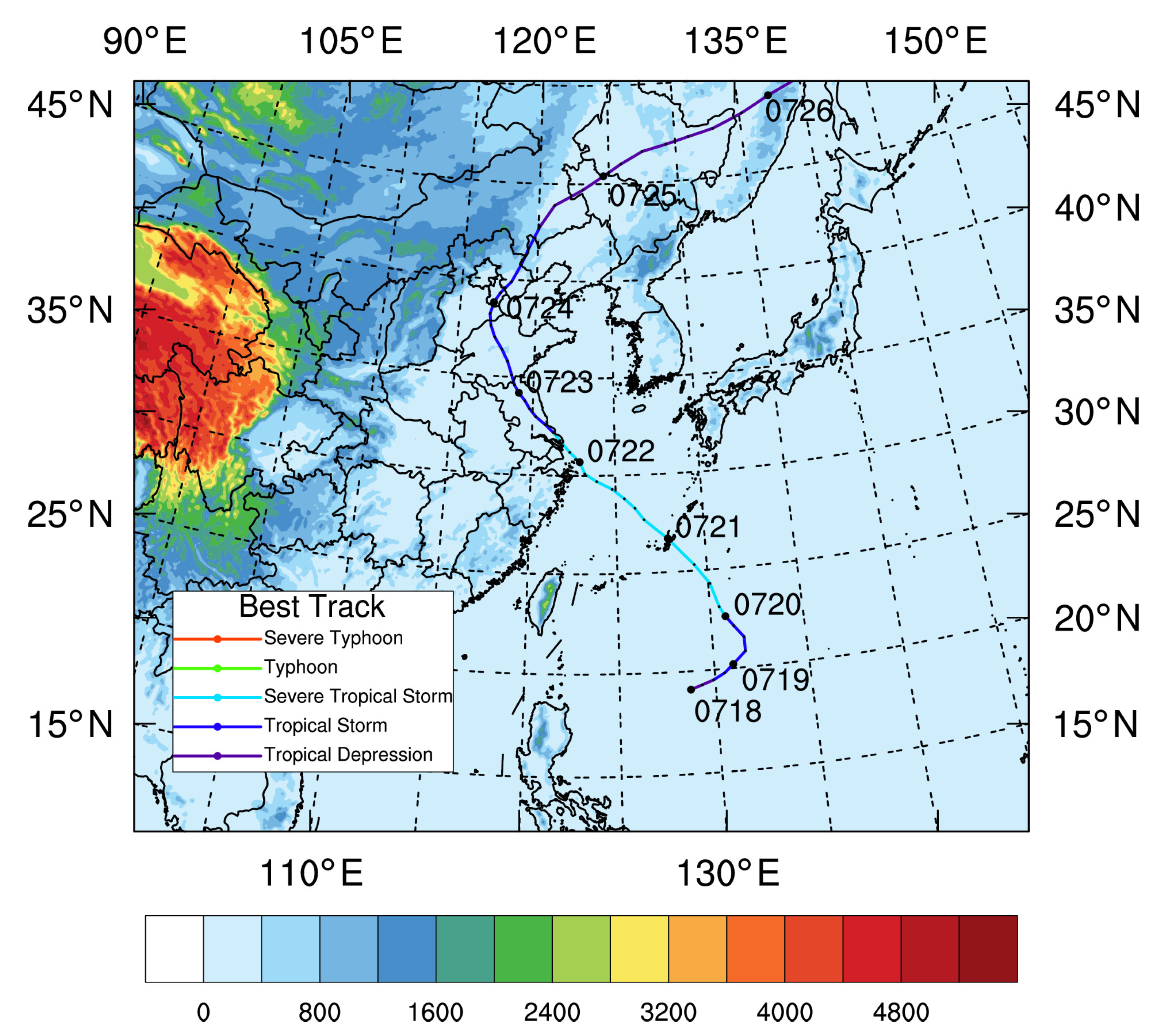
3.1. Typhoon Ampil Case
3.2. Experimental Design
4. Results
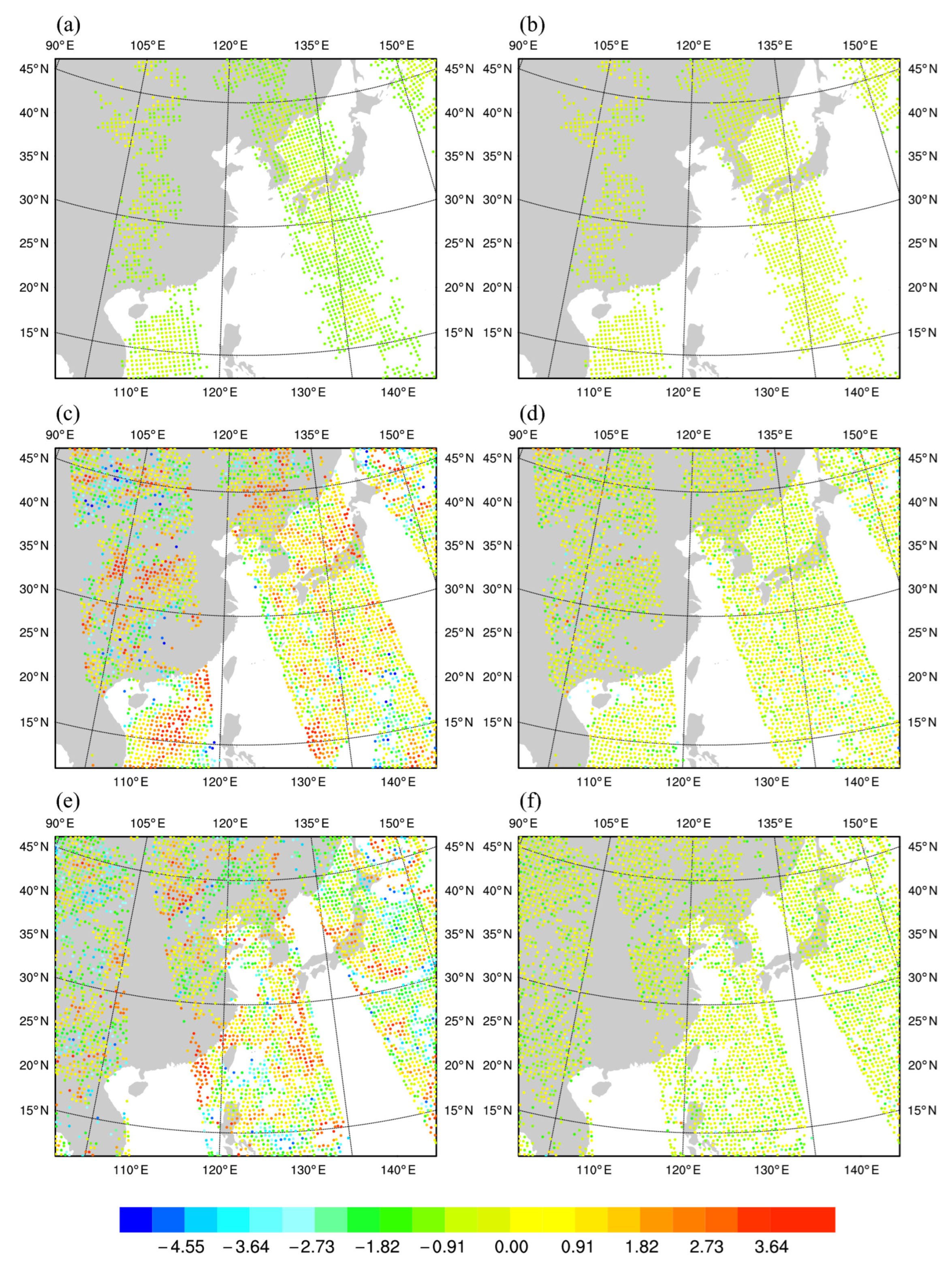
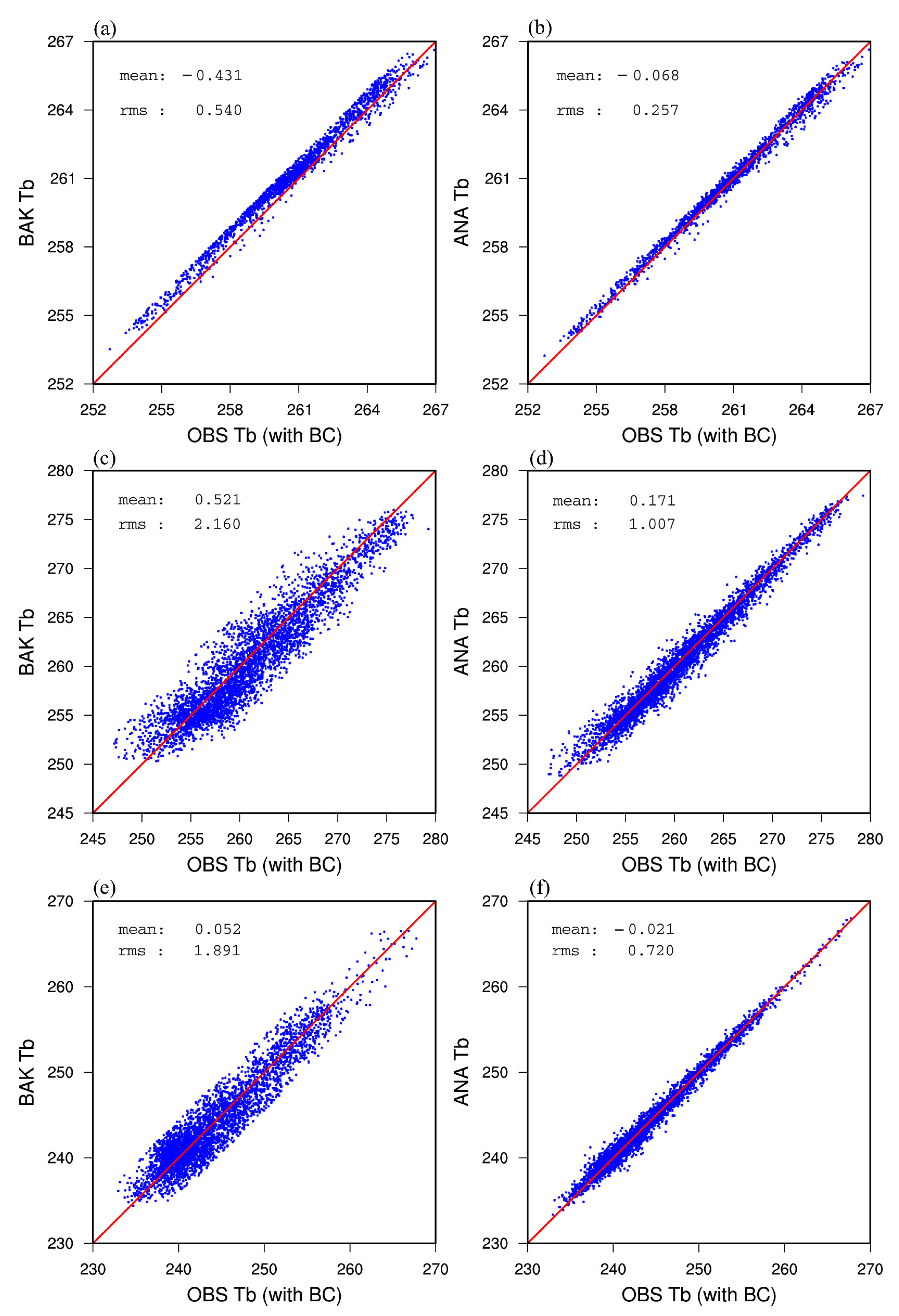
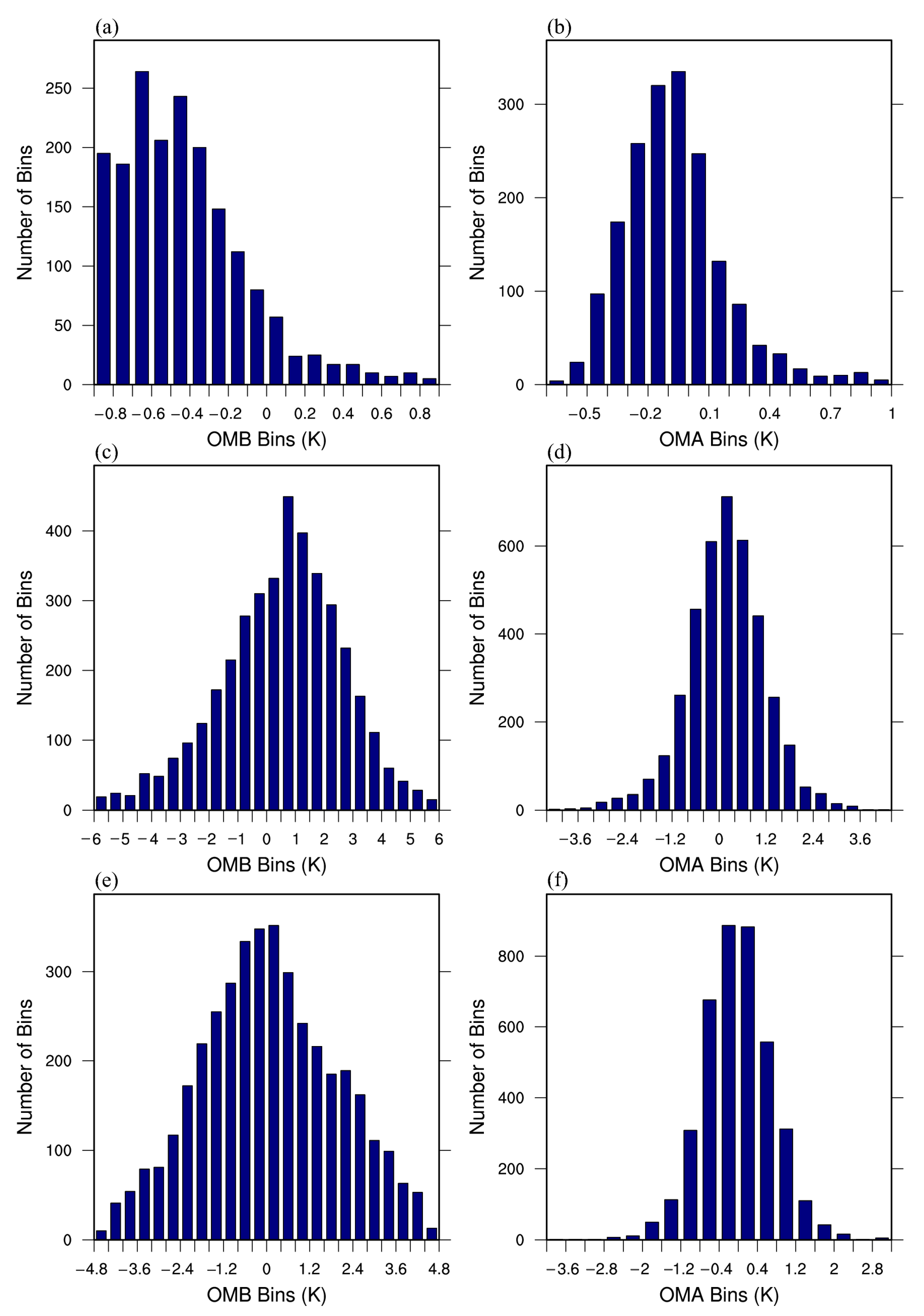
4.1. Radiance Simulation
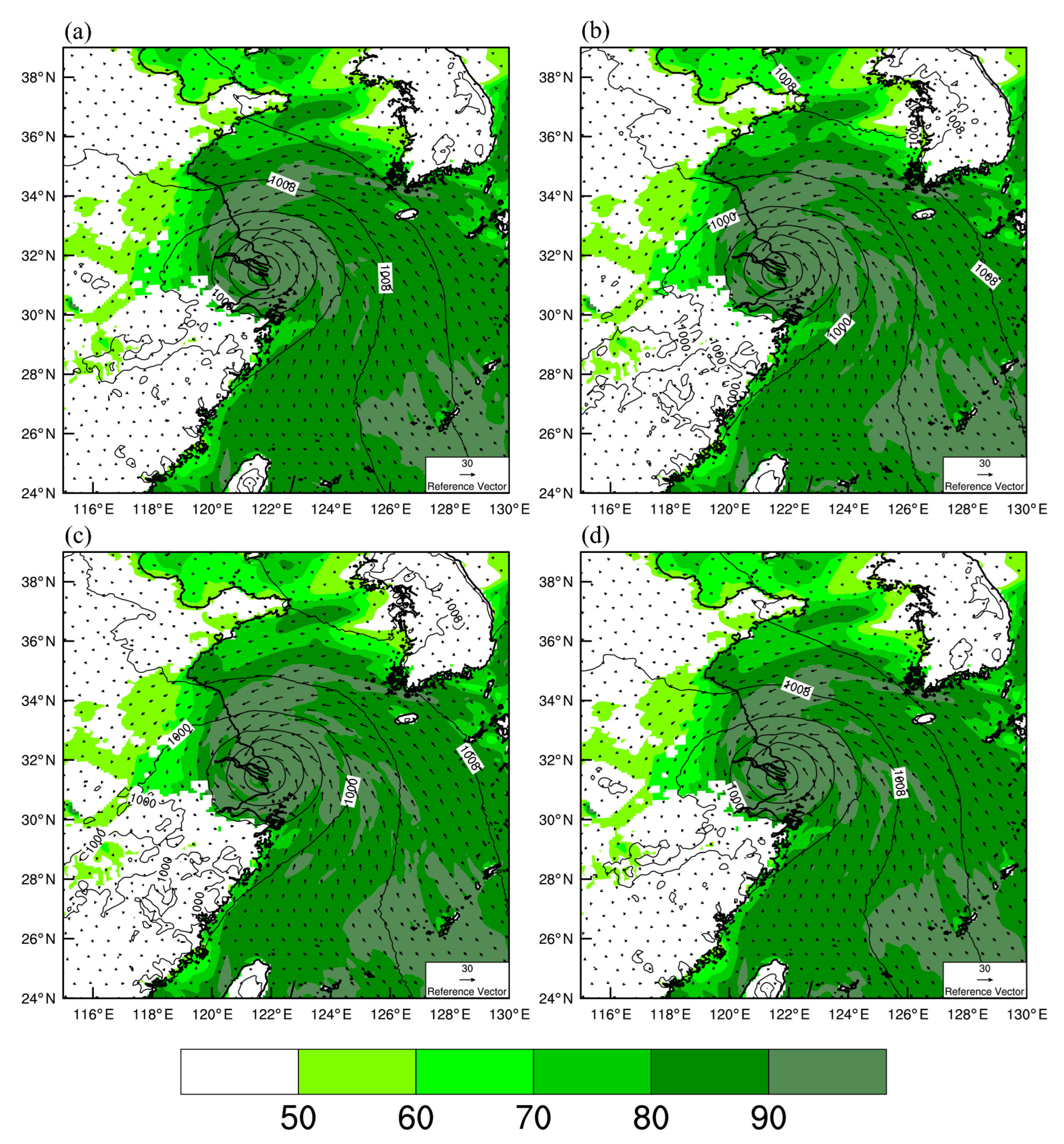
4.2. TC Structure
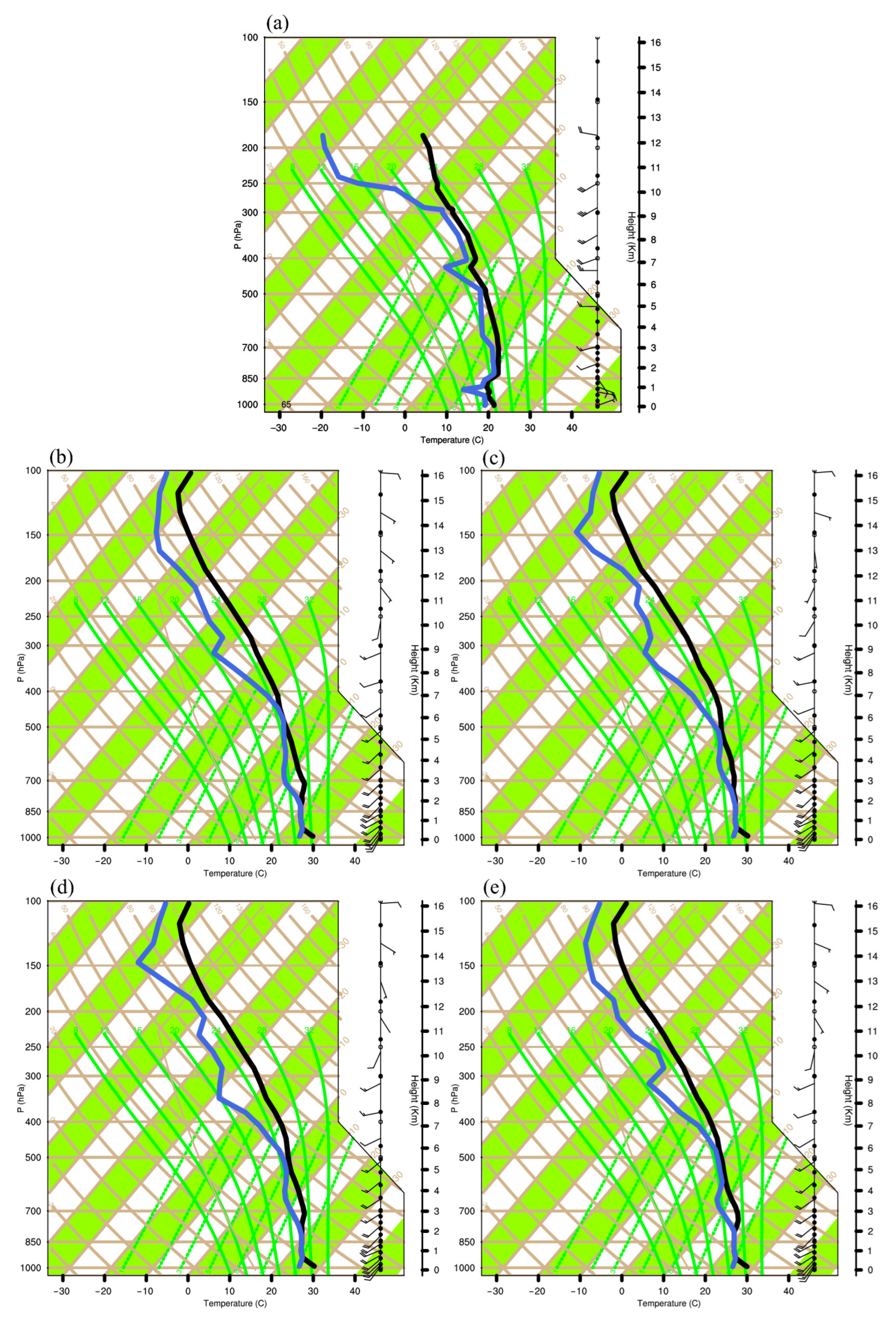
4.3. Skew-T Plot Analysis
4.4. Root-Mean-Square Error of Forecast Fields
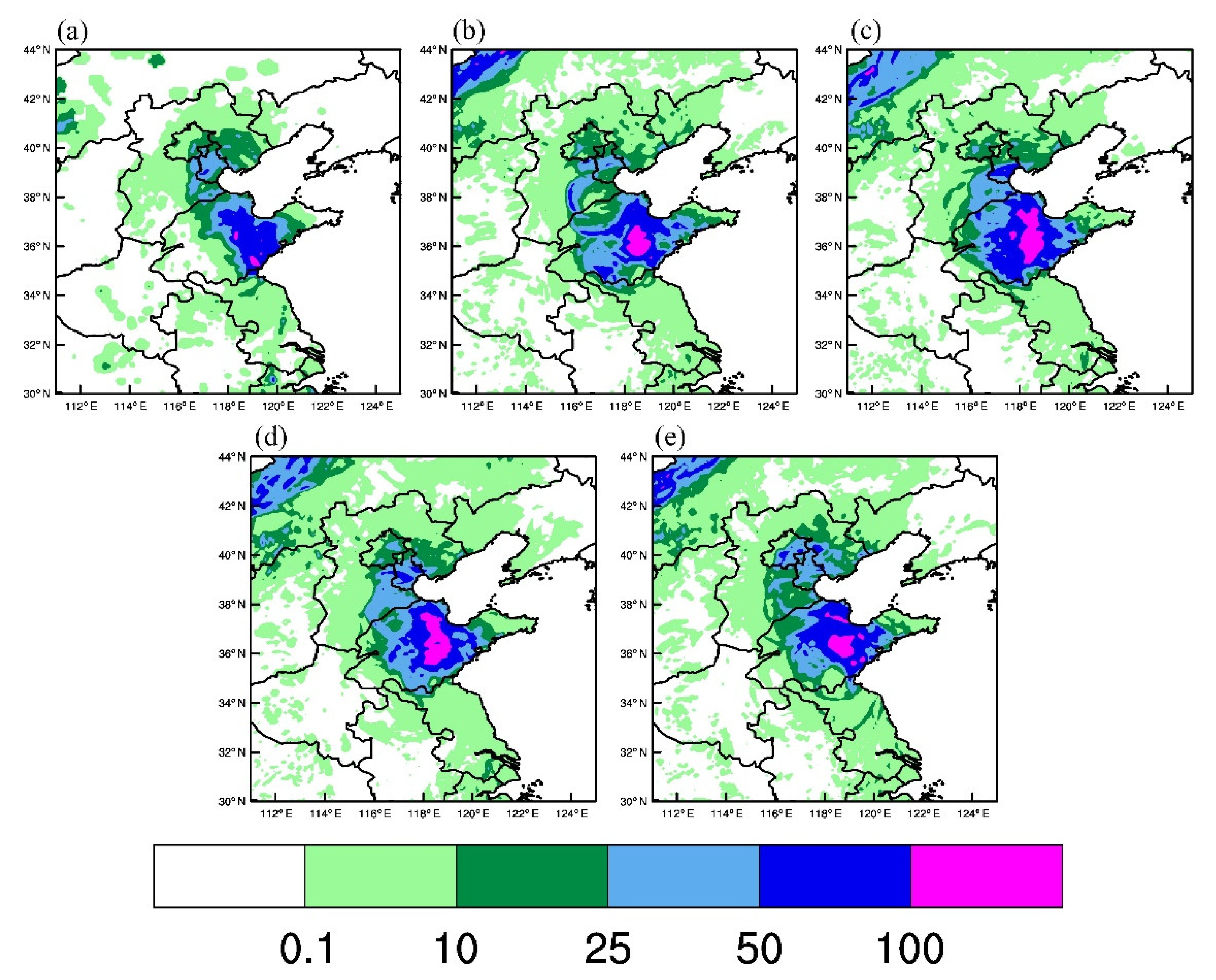
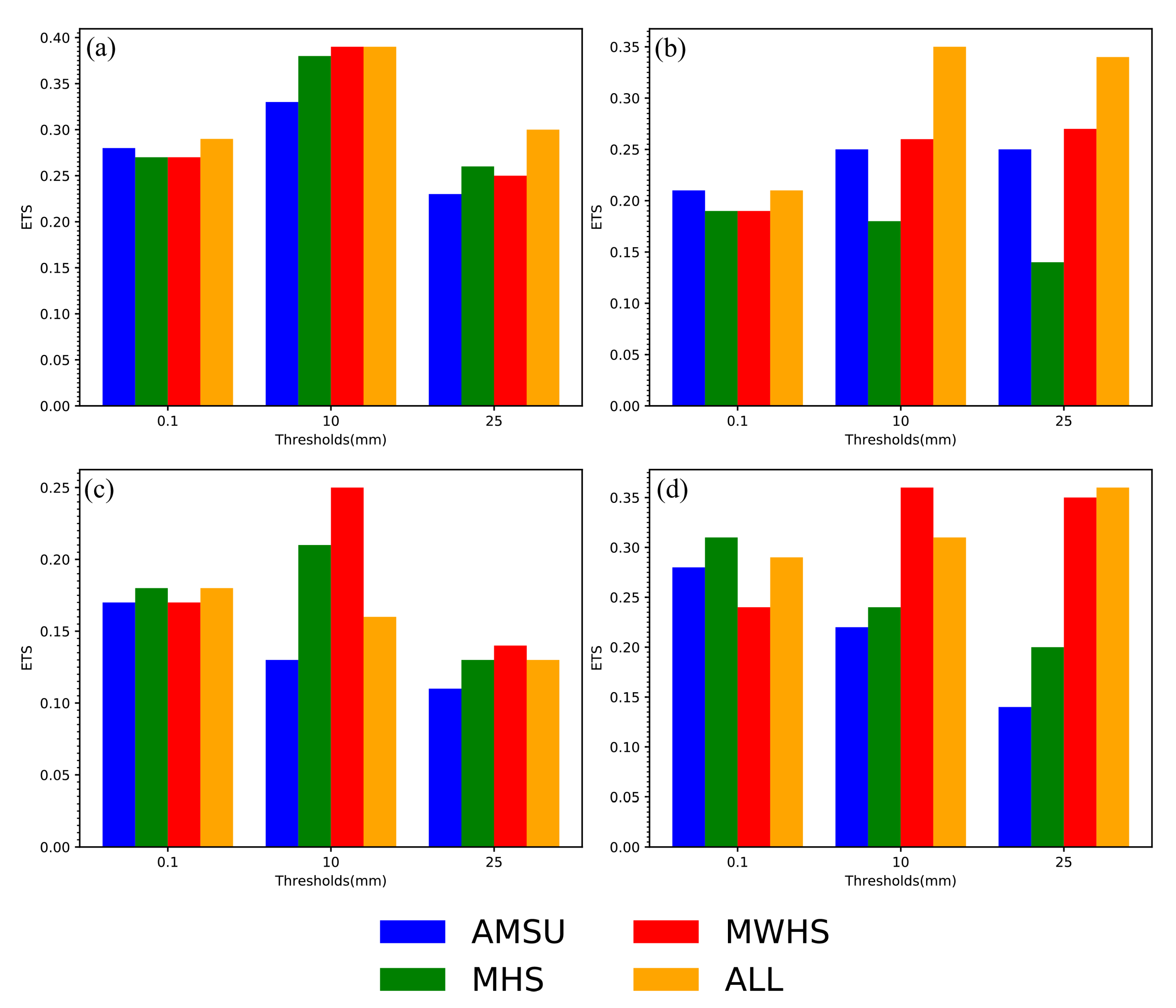
4.5. Precipitation Forecasts
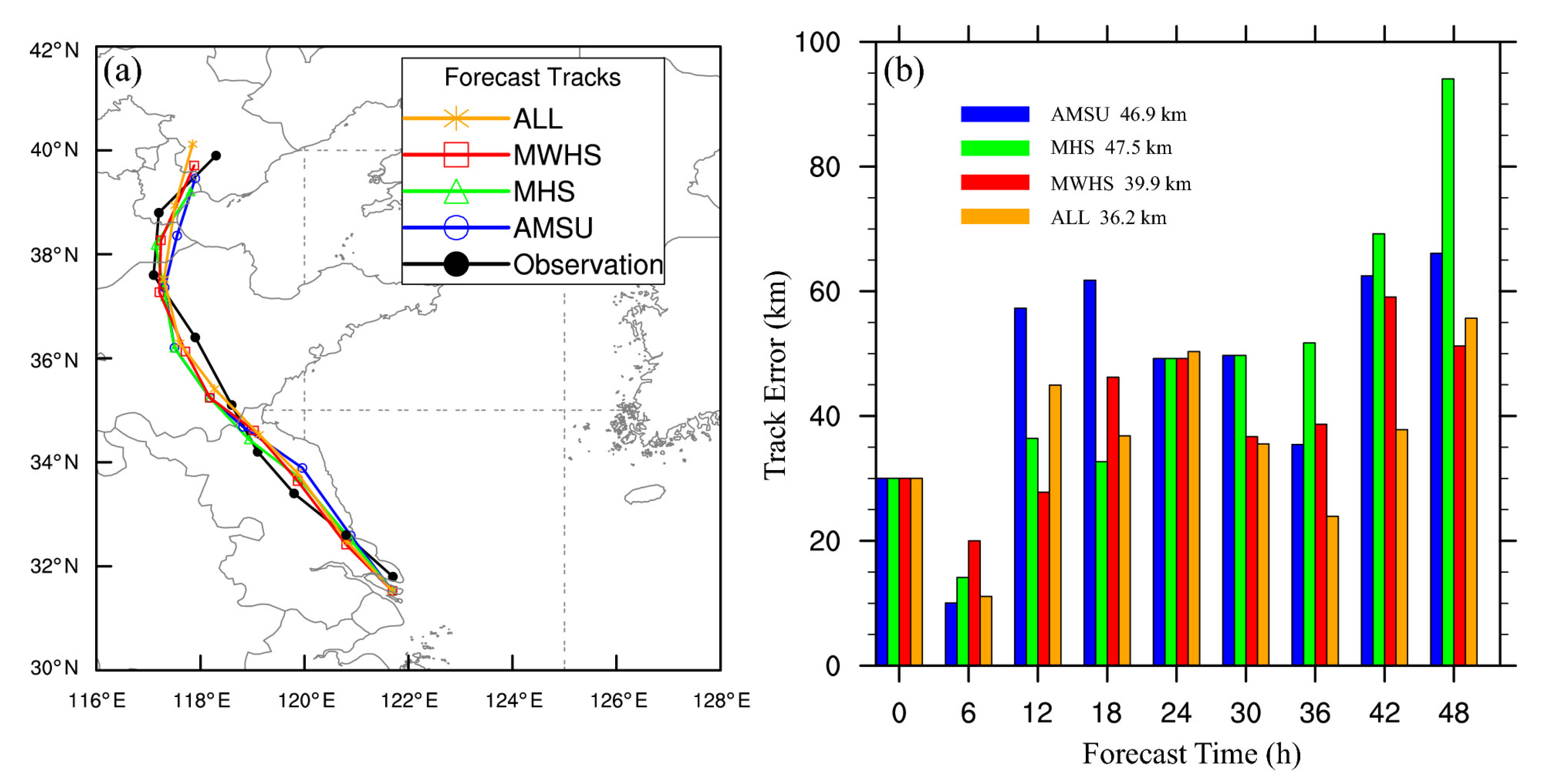
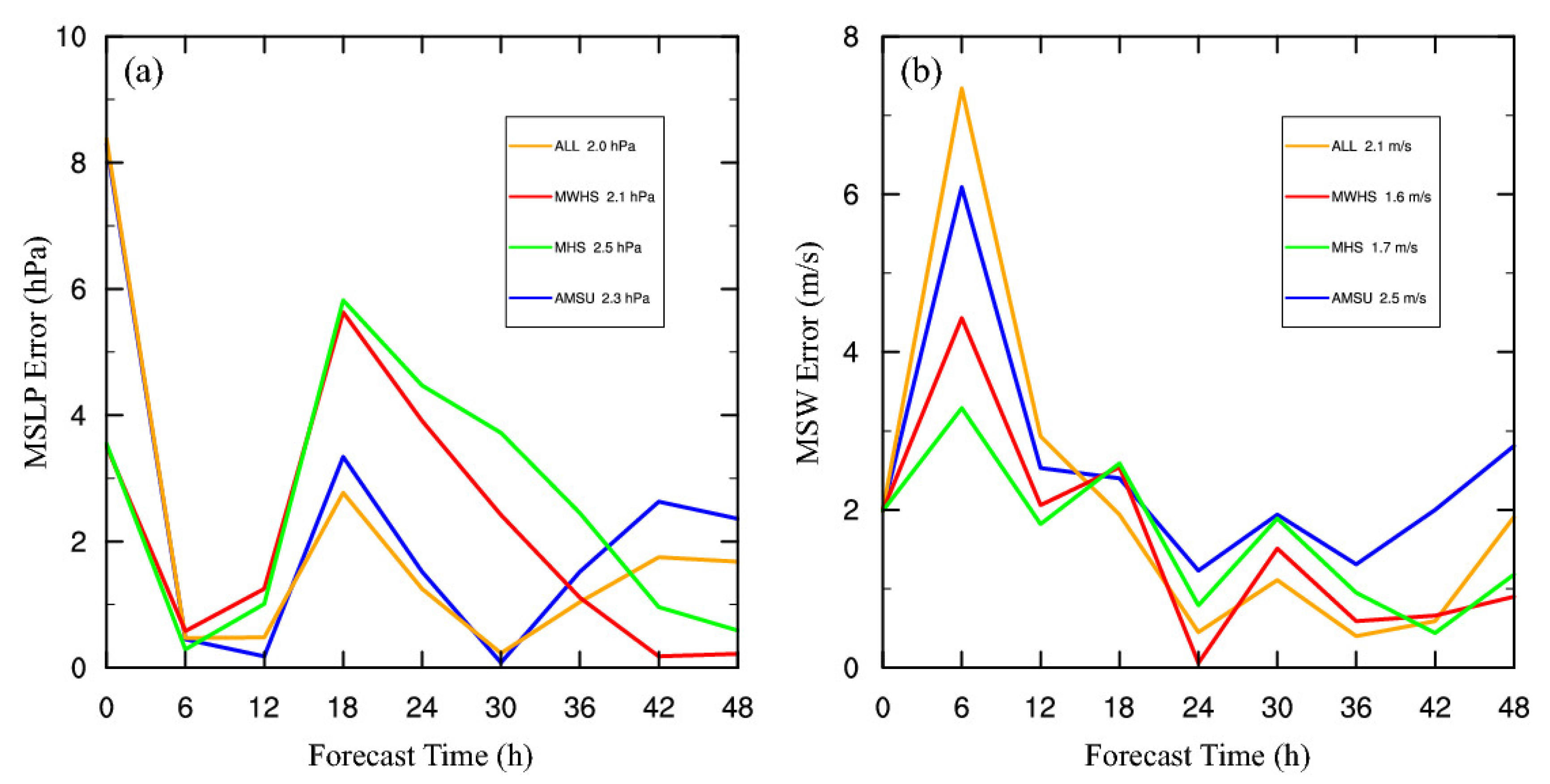
4.6. The Track and Intensity
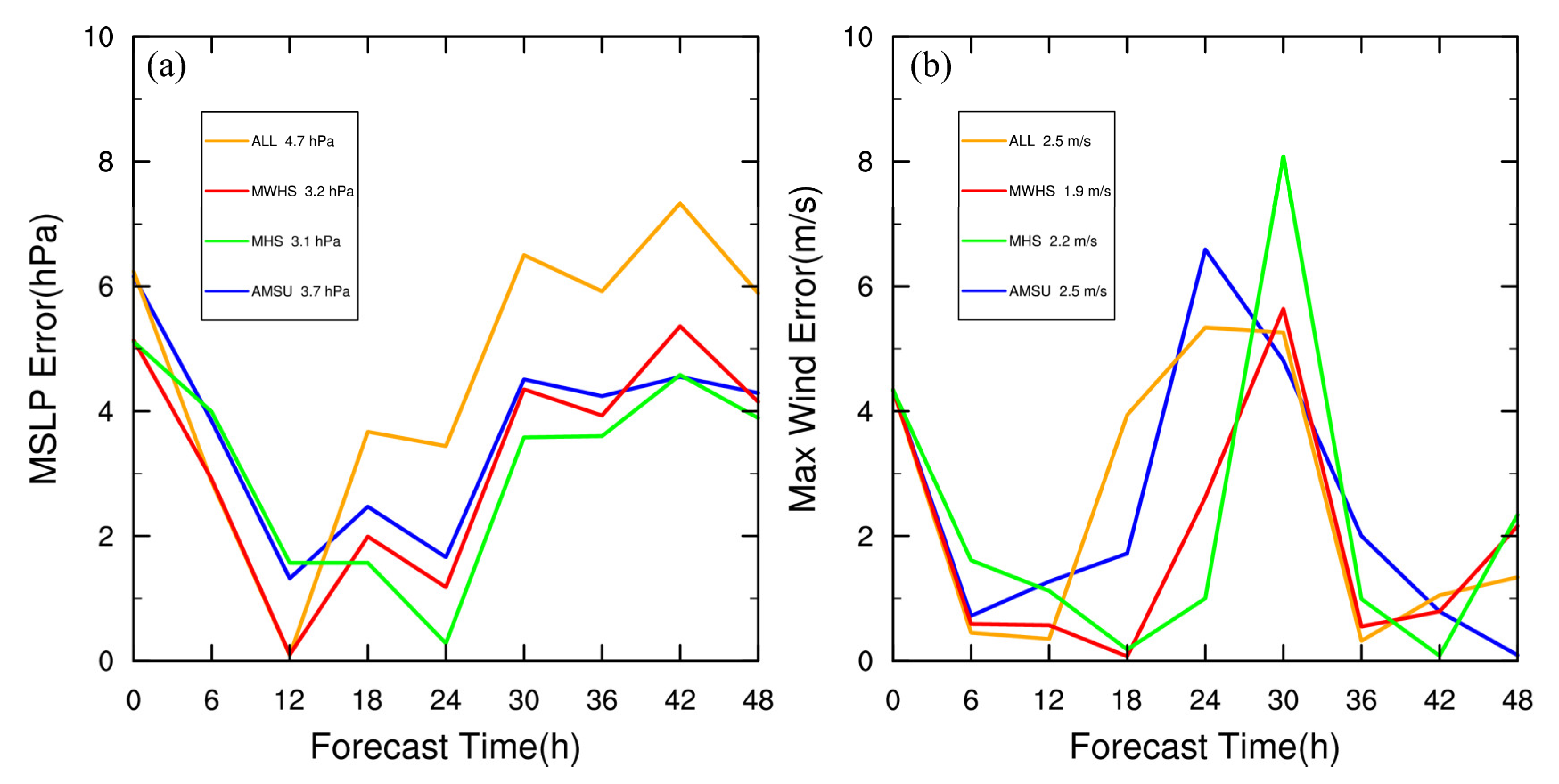
4.7. Results with Another Initialization Time
5. Conclusions and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McNally, A.P.; Derber, J.C.; Wu, W.; Katz, B.B. The use of TOVS level-1b radiances in the NCEP SSI analysis system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 689–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapotocny, T.H.; Jung, J.A.; Marshall, J.F.L.; Treadon, R.E. A two-season impact study of four satellite data types and rawinsondedata in the NCEP Global Data Assimilation System. Weather Forecast. 2008, 23, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.-Y.; Min, J.; Wang, H. Impact of assimilating IASI radiance observations on forecasts of two tropical cyclones. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 122, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.L.; Woolf, H.M.; Hayden, C.M.; Wark, D.Q.; McMillin, L.M. The TIROS-N operational vertical sounder. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1979, 60, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrum, G.; Kidwell, K.B.; Winston, W. (Eds.) NOAA KLM User’s Guide; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Liu, H. Improved hurricane track and intensity forecast using single field-of-view advanced IR sounding measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L11813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Schwartz, C.S.; Snyder, C.; Ha, S.-Y. Impact of assimilating AMSUA radiances on forecasts of 2008 Atlantic tropical cyclones initialized with a limited-area ensemble Kalman filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 4017–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.-Y. Impact of assimilating microwave radiances with a limited-area ensemble data assimilation system on forecasts of Typhoon Morakot. Weather Forecast. 2012, 27, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, K.M.; Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Shao, H.; Huang, X.-Y. Evaluating forecast impact of assimilating microwave humidity sounder (MHS) radiances with a regional ensemble Kalman filter data assimilation system. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 964–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Min, J. Assimilating AMSUA radiance data with the WRF Hybrid En3DVAR system for track predictions of Typhoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collard, A.; Derber, J.; Treadon, R.; Atkinson, N.; Jung, J.; Garrett, K. Toward assimilation of CrIS and ATMS in the NCEP Global Model. In Proceedings of the 18th International TOVS Study Conference, International Atovs Working Group, Toulouse, France, 21–27 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, E.; Mahajan, R. All-Sky Microwave Radiance Assimilation in the NCEP’s GSI Analysis System. Mon. Weather Rev. 2016, 144, 4709–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Wang, X.; Weng, F.; Li, G. Assessments of Chinese Fengyun Microwave Temperature Sounder (MWTS) measurements for weather and climate applications. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 1206–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; English, S.; Bormann, N.; Zhu, J. Assessment of FY-3A and FY-3B MWHS Observations. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; He, J.; Gu, S.; Lu, N. Calibration and validation of Feng Yun-3-D microwave humidity sounder II. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Lawrence, H.; Bormann, N.; English, S.; Lean, K.; Atkinson, N.; Bell, W.; Carminati, F. An evaluation of FY-3C satellite data quality at ECMWF and the Met Office. ECMWF Tech. Memo. 2015, 767, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Carminati, F.; Candy, B.; Bell, W.; Atkinson, N. Assessment and assimilation of FY-3 humidity sounders and imager in the UK Met Office global model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 35, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Min, J.; Shen, F.; Ban, J.; Chen, P. Assimilation of MWHS radiance data from the FY-3B satellite with the WRF Hybrid-3DVAR system for the forecasting of binary typhoons. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2016, 8, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D. Effects of Assimilating Clear-Sky FY-3D MWHS2 Radiance on the Numerical Simulation of Tropical Storm Ampil. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, Y. Assimilation of FY-3D MWHS2 Radiances with WRF Hybrid-3DVAR System for the Forecast of Heavy Rainfall Evolution Associated with Typhoon Ampil. Mon. Weather Rev. 2021, 149, 1419–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, J. Progress achieved on assimilation of satellite data in numerical weather prediction over the last 30 years. In Proceedings of the ECMWF Seminar Proceedings: Recent Developments in Use of Satellite Observations in Numerical Weather Prediction, Shinfield Park, Reading, UK, 3–7 September 2007; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.P.; Shi, C.X.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Y.; Yao, S. Evaluation of Assimilating FY-3C MWHS-2 Radiances Using the GSI Global Analysis System. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaes, K.D.; Cohen, M.; Buhler, Y.; Schlüssel, P.; Munro, R.; Luntama, J.; von Engeln, A.; Clérigh, E.Ó.; Bonekamp, H.; Ackermann, J.; et al. An Introduction to the EUMETSAT Polar system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T. Postlaunch calibration of the NOAA-19 Advanced Microwave Sounding Unit-A. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignori, R. The Microwave Humidity Sounder (MHS): In-orbit performance assessment. In Sensors, Systems, and Next-Generation Satellites XI, Proceedings of the SPIE Remote Sensing, Florence, Italy, 17–20 September 2017; SPIE: Munich, Germany, 2007; Volume 6744, p. 6744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Xian, D.; Xu, Z. Recent progress of Fengyun meteorology satellites. Chin. J. Space Sci. 2018, 38, 788–796. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, D.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, Z.; Auligné, T.; Zhang, X.; Rugg, S.; Ajjaji, R.; Bourgeois, A.; Bray, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. The weather research and forecasting model’s community variational/ensemble data assimilation system: WRFDA. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C. The national meteorological center’s spectral statistical interpolation analysis system. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 120, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, A.C.; Ballard, S.P.; Bell, R.S.; Ingleby, N.B.; Andrews PL, F.; Barker, D.M.; Bray, J.R.; Clayton, A.M.; Dalby, T.; Li, D.; et al. The Met Office global three-dimensional variational data assimilation scheme. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 2991–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, H.; Ying, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Bai, L.; Wan, R. Western North Pacific tropical cyclone database created by the China Meteorological Administration. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.R.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Hall, W.D. Explicit Forecasts of Winter Precipitation Using an Improved Bulk Microphysics Scheme. Part II: Implementation of a New Snow Parameterization. Mon. Weather Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.D.; Suarez, M.J. An Efficient Thermal Infrared Radiation Parameterization for Use in General Circulation Models; NASA Technical Memorandum; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 3, p. 104606. [Google Scholar]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5233–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rabier, F. The interaction between model resolution, observation resolution and observation density in data assimilation: A one-dimensional study. Q. J. Roy Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 128, 1367–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xing, J.; Shi, J.; Dou, Y.; Lei, Y. Impacts of radiance data assimilation on the Beijing 7.21 heavy rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment Name | Used Data |
|---|---|
| AMSU | GTS conventional data and AMSUA/NOAA-19 radiance |
| MHS | GTS conventional data and MHS/NOAA-19 radiance |
| MWHS | GTS conventional data and MWHS2/FY-3D radiance |
| ALL | GTS conventional data and the three types of radiance mentioned above |
| Metric | AMSU | MHS | MWHS | ALL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean RMSE | U: 3.46 | U: 3.54 | U: 3.64 | U: 3.42 |
| V: 3.55 | V: 3.31 | V: 3.71 | V: 3.17 | |
| T: 0.89 | T: 0.85 | T: 0.96 | T: 0.84 | |
| Q: 1.31 | Q: 1.26 | Q: 1.31 | Q: 1.26 | |
| Mean Bias | U: 0.71 | U: 0.63 | U: 0.74 | U: 0.66 |
| V: 0.68 | V: 0.64 | V: 0.79 | V: 0.57 | |
| T: 0.13 | T: −0.09 | T: −0.10 | T: −0.06 | |
| Q: −0.33 | Q: 0.31 | Q: 0.29 | Q: 0.24 | |
| Mean Correlation | U: 0.55 | U: 0.53 | U: 0.49 | U: 0.56 |
| V: 0.58 | V: 0.62 | V: 0.56 | V: 0.63 | |
| T: 0.74 | T: 0.77 | T: 0.72 | T: 0.77 | |
| Q: 0.69 | Q: 0.73 | Q: 0.70 | Q: 0.72 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, A.; Xu, D.; Zhang, S.; Shen, F.; Zhang, X.; Song, L. Impacts of Multi-Source Microwave Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of Typhoon Ampil. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091427
Shu A, Xu D, Zhang S, Shen F, Zhang X, Song L. Impacts of Multi-Source Microwave Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of Typhoon Ampil. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(9):1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091427
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Aiqing, Dongmei Xu, Shiyu Zhang, Feifei Shen, Xuewei Zhang, and Lixin Song. 2022. "Impacts of Multi-Source Microwave Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of Typhoon Ampil" Atmosphere 13, no. 9: 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091427
APA StyleShu, A., Xu, D., Zhang, S., Shen, F., Zhang, X., & Song, L. (2022). Impacts of Multi-Source Microwave Satellite Radiance Data Assimilation on the Forecast of Typhoon Ampil. Atmosphere, 13(9), 1427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13091427








