Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Surface Temperature in Recent 20 Years and Analysis of the Effect of Land Use in Jiangxi Province, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
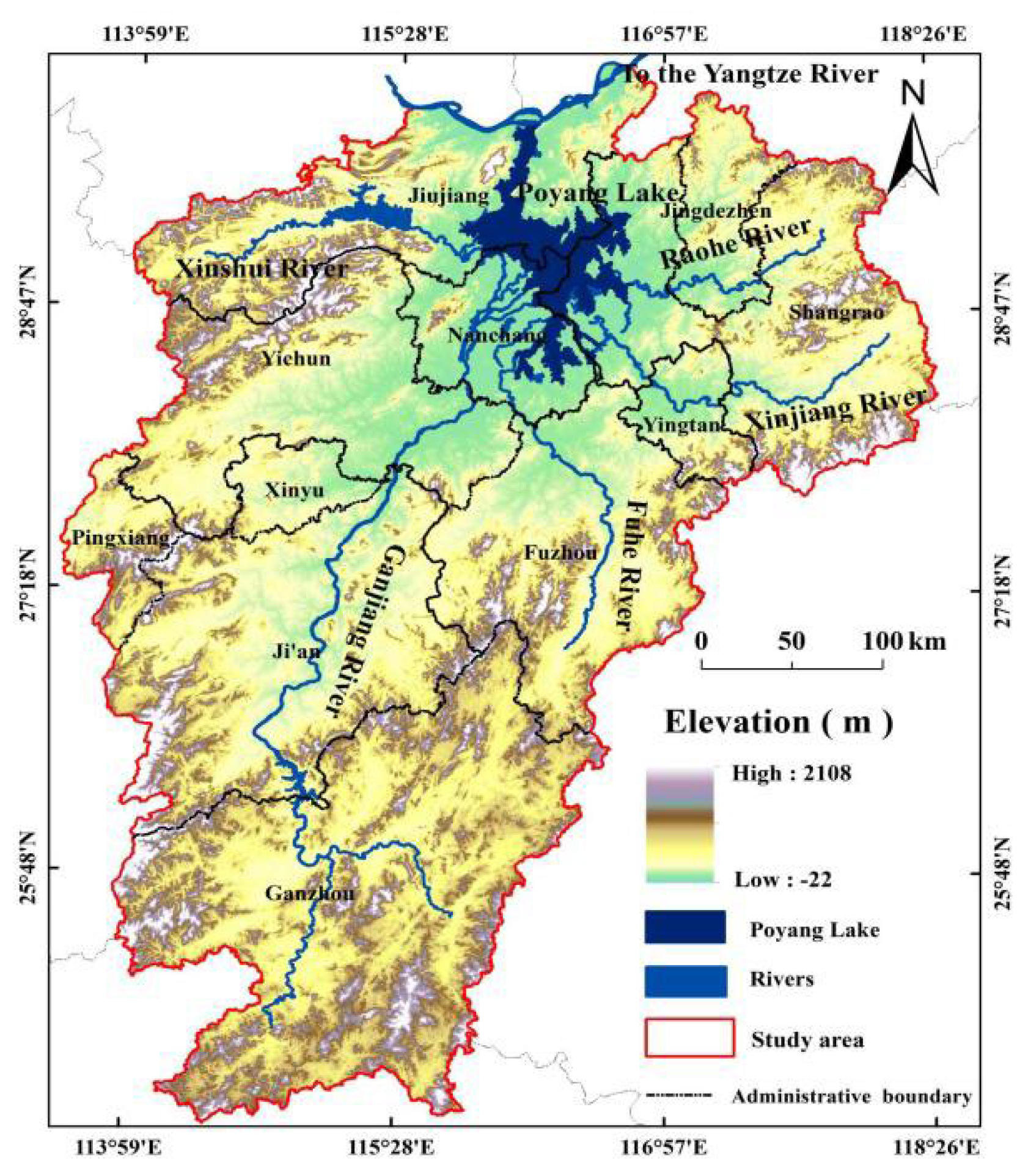
2.1. Research Area
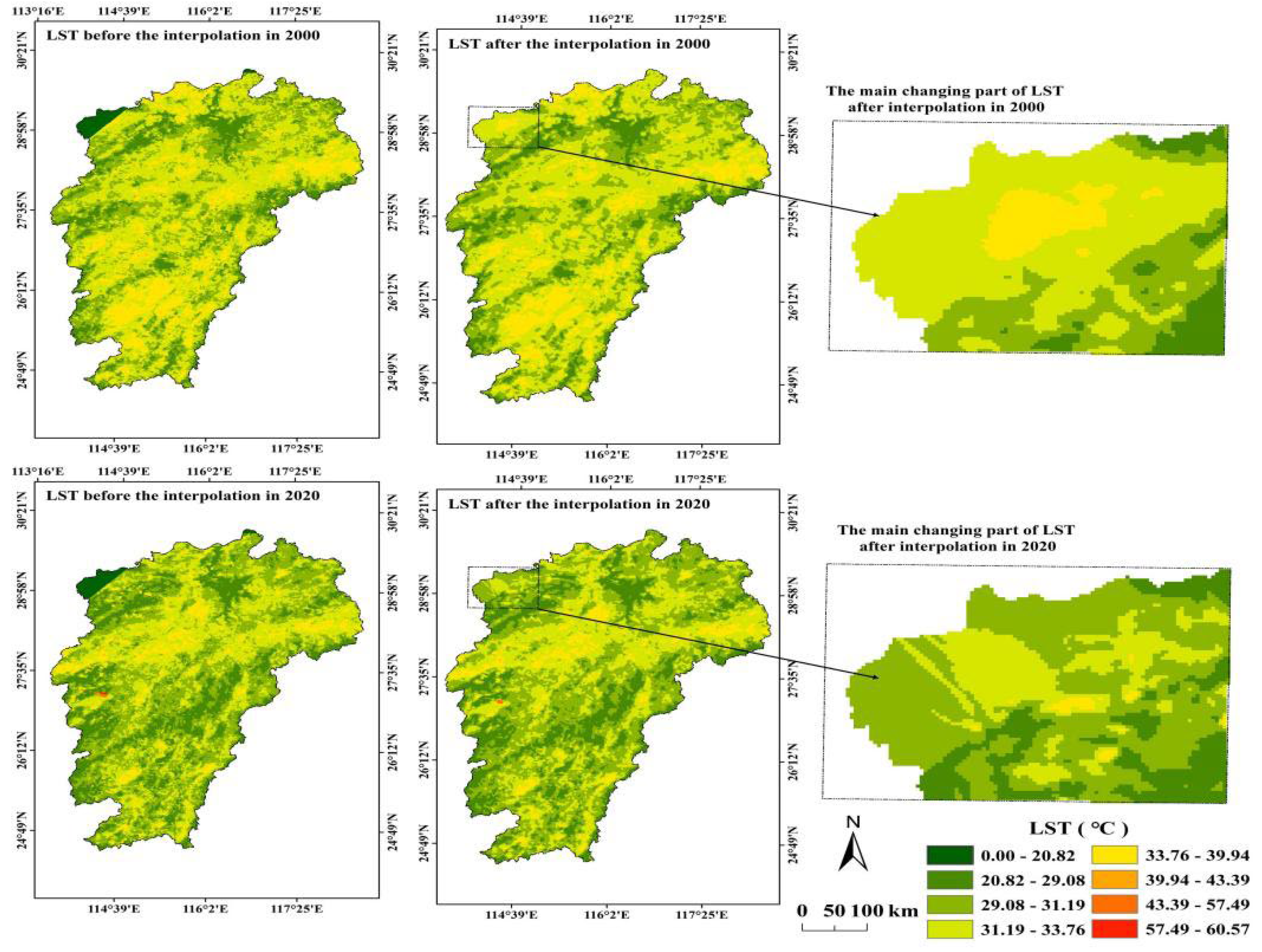
2.2. Data Source and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Theil-Sen + Mann-Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.2. Coefficient of Variation Analysis
2.3.3. Hurst Index Analysis
2.3.4. Contribution Index Analysis
2.3.5. Diversity Index Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Spatiotemporal Evolution of Pixel-wise LST
3.1.1. Variation Characteristics
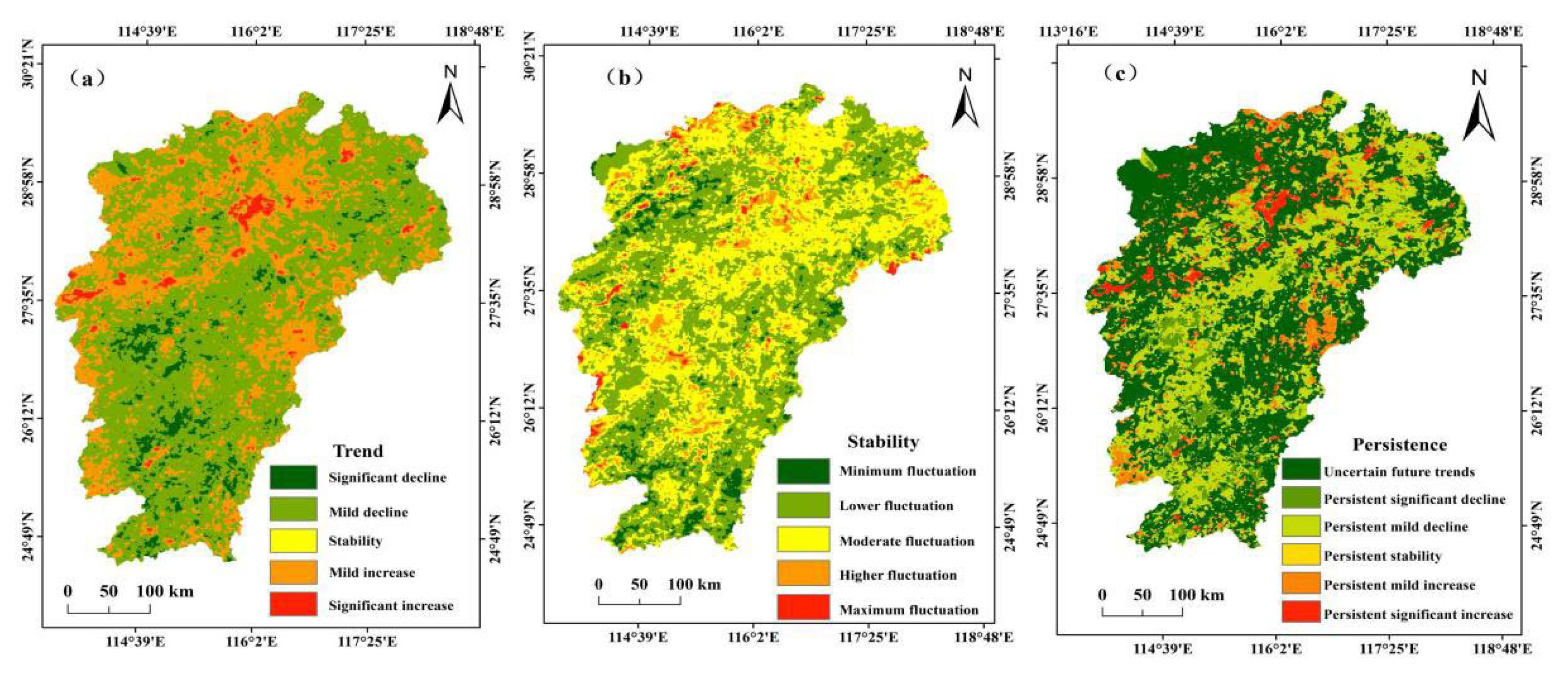
3.1.2. Trend Characteristics
3.1.3. Stability Characteristics
3.1.4. Persistent Characteristics
3.2. Land Use Impact Analysis
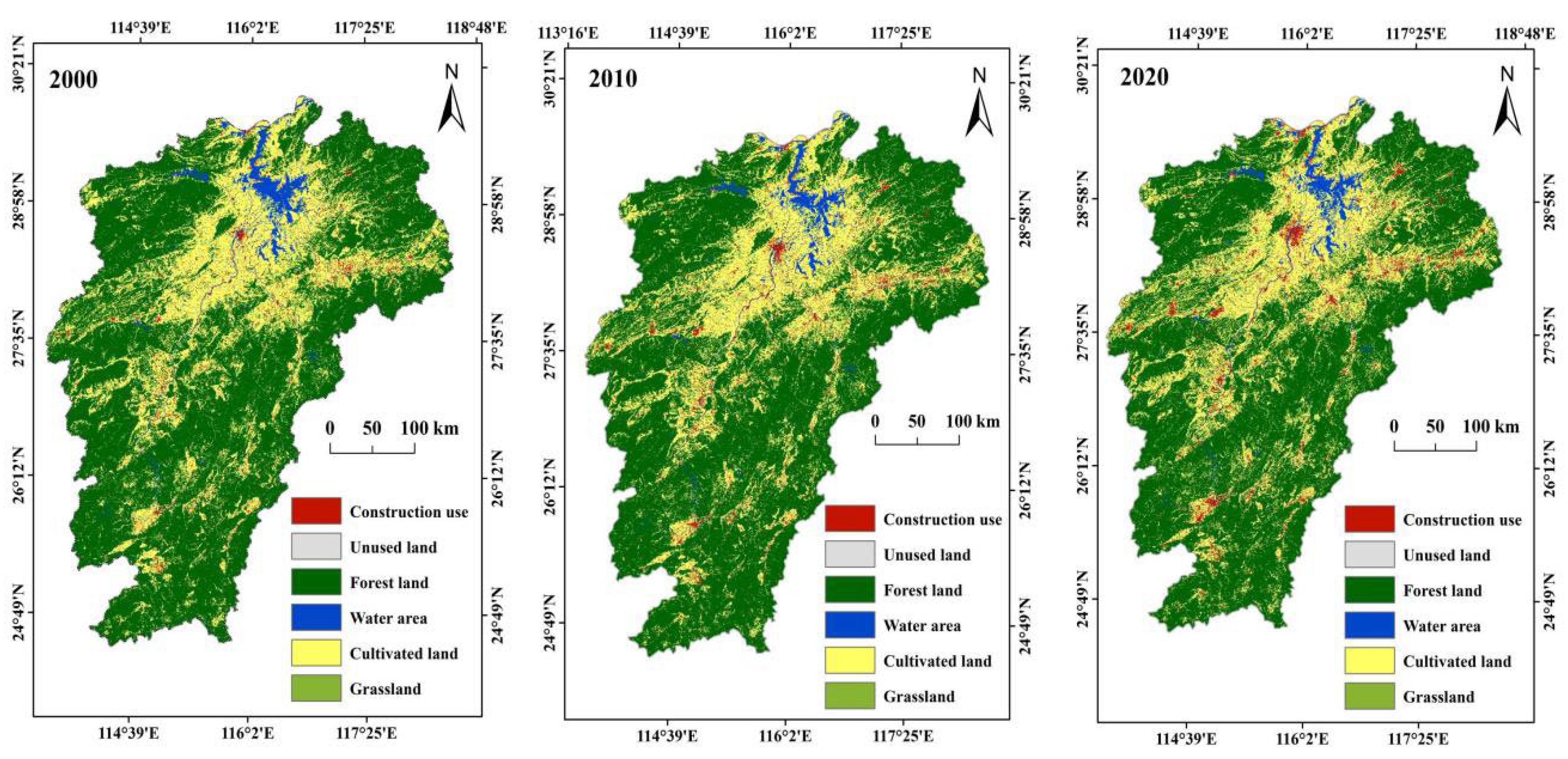
3.2.1. Impact of Land Use Type
3.2.2. Impact of Land Use Structure
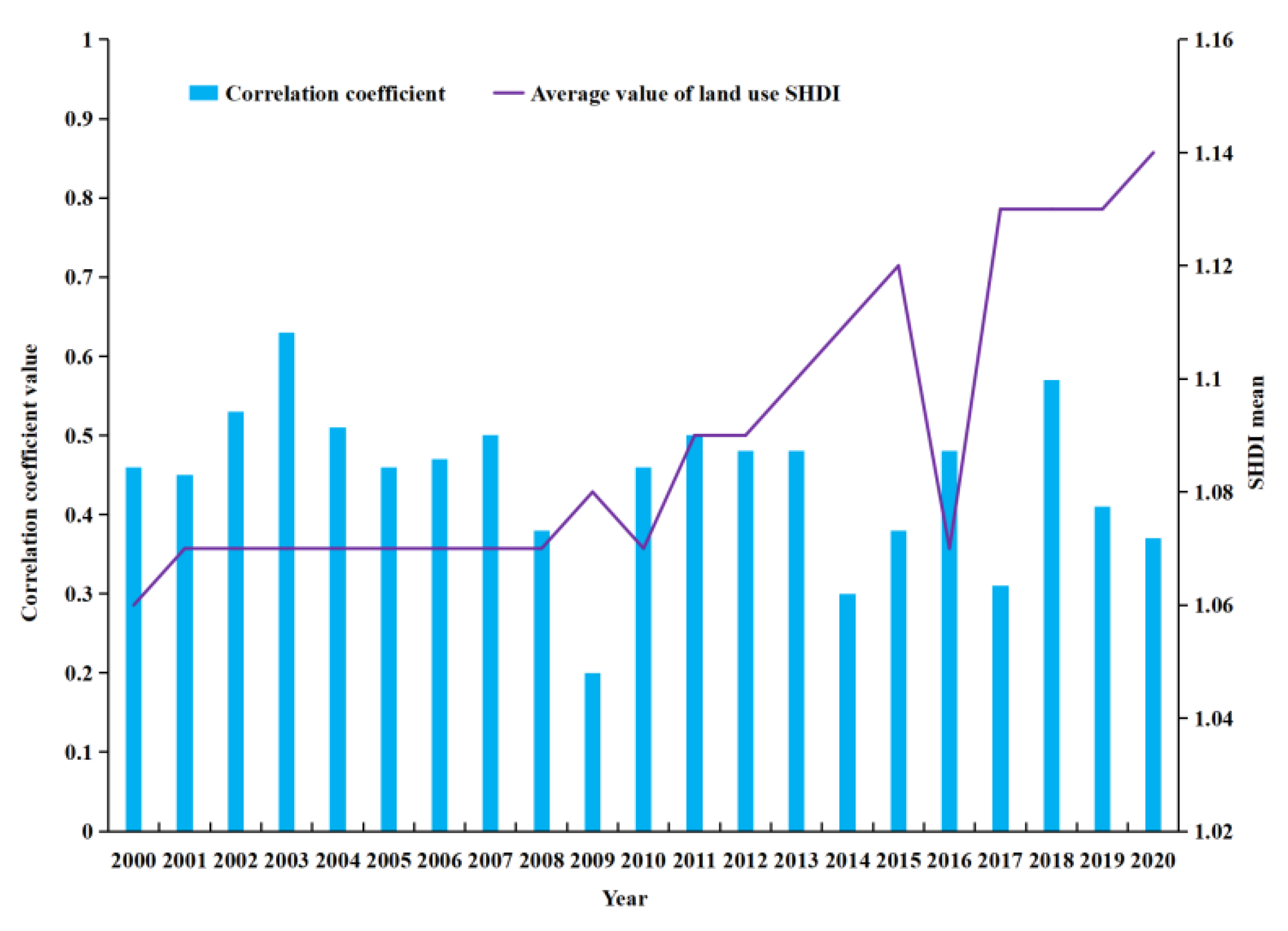
3.2.3. Impact of Land Use Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.D.; Ye, X. Urbanization, urban land expansion and environmental change in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadrevu, K.P.; Ohara, T. Focus on land use cover changes and environmental impacts in South/Southeast Asia. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 100201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Vose, J.M. Urbanization and climate change jointly shift land surface phenology in the northern mid-latitude large cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236, 111477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neog, R. Evaluation of temporal dynamics of land use and land surface temperature (LST) in Agartala city of India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, F.O.; Ikanyeng, M.; Muro, J. Land cover change effects on land surface temperature trends in an African urbanizing dryland region. City Environ. Interact. 2019, 4, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Ma, R. Examining urban thermal environment dynamics and relations to biophysical composition and configuration and socio-economic factors: A case study of the Shanghai metropolitan region. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Maina, M.S.; Dzwairo, R.; Lal, D. Impact of urbanization and land cover change on urban climate: Case study of Nigeria. Urban Clim. 2020, 32, 100600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, B.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Thermal infrared remote sensing for urban climate and environmental studies: Methods, applications, and trends. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Riaz, I.; Ahmad, Z.; Yang, B.; Amin, M.; Kausar, R.; Andleeb, S.; Farooqi, M.A.; Rafiq, M. Land surface temperature relation with normalized satellite indices for the estimation of spatio-temporal trends in temperature among various land use land cover classes of an arid Potohar region using Landsat data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 79, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Rong, Y. Spatio-temporal evolution of surface urban heat islands in the Chang-Zhu-Tan urban agglomeration. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 117, 102865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; He, J.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wen, F.; Li, A. An Analysis of Land Surface Temperature Trends in the Central Himalayan Region Based on MODIS Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lome, J.; Espinoza-Villar, R.; Espinoza, J.; Rojas-Acuña, J.; Willems, B.L.; Leyva-Molina, W. Elevation-dependent warming of land surface temperatures in the Andes assessed using MODIS LST time series (2000–2017). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 77, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J. The GLASS Land Surface Temperature Product. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Huang, X.; Tang, Q. The footprint of urban heat island effect in 302 Chinese cities: Temporal trends and associated factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, J.; Strauch, A.; Heinemann, S.; Steinbach, S.; Thonfeld, F.; Waske, B.; Diekkrüger, B. Land surface temperature trends as indicator of land use changes in wetlands. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 2018, 70, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.B.; Ma, Y.; Tan, X.L.; Shen, X.Y.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, J.M.; Xia, L. Global surface temperature change analysis based on MODIS data in recent twelve years. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Javed, T.; Khan, A.; Lei, H.; Muhammad, I.; Ali, I.; Huo, X. Impact assessment of land use change on surface temperature and agricultural productivity in Peshawar-Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 33076–33085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deilami, K.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Liu, Y. Urban heat island effect: A systematic review of spatio-temporal factors, data, methods, and mitigation measures. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hagan, D.F.T.; Liu, Y. Global Land Surface Temperature Change (2003–2017) and Its Relationship with Climate Drivers: AIRS, MODIS, and ERA5-Land Based Analysis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimoloye, I.R.; Mazinyo, S.P.; Nel, W.; Kalumba, A.M. Spatiotemporal monitoring of land surface temperature and estimated radiation using remote sensing: Human health implications for East London, South Africa. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shan, Y.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, S. Method of calculating land surface temperatures based on the low-altitude UAV thermal infrared remote sensing data and the near-ground meteorological data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Niu, Z.; Zhan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal changes of urban impervious surface area and land surface temperature in Beijing from 1990 to 2014. GI Sci. Remote Sens. 2016, 53, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafanov, M.; Kazakov, E.; Nikitin, N.O.; Kalyuzhnaya, A.V. A Machine Learning Approach for Remote Sensing Data Gap-Filling with Open-Source Implementation: An Example Regarding Land Surface Temperature, Surface Albedo and NDVI. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, G.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Bie, X.; Li, J.; Ji, B. Spatial distribution and influencing factors on urban land surface temperature of twelve megacities in China from 2000 to 2017. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareie, S.; Rangzan, K.; Khosravi, H.; Sherbakov, V.M. Comparison of split window algorithms to derive land surface temperature from satellite TIRS data. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Murayama, Y.; Morimoto, T. Impacts of Land Cover/Use on the Urban Thermal Environment: A Comparative Study of 10 Megacities in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Yin, R.; Cui, S.; Wu, Z.; Cao, X. A radiance-based split-window algorithm for land surface temperature retrieval: Theory and application to MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 76, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiff, S.; Helman, D.; Lensky, I.M. Worldwide continuous gap-filled MODIS land surface temperature dataset. Sci. Data. 2021, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Gao, C.; Tong, X.; Chen, S.; Lei, Z.; Wang, J. Spatial Patterns of Land Surface Temperature and Their Influencing Factors: A Case Study in Suzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hou, H.; Murayama, Y. Spatial Interconnections of Land Surface Temperatures with Land Cover/Use: A Case Study of Tokyo. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, M.; Agarwal, A.; Devadas, V. Analyzing land surface temperature trends using non-parametric approach: A case of Delhi, India. Urban Clim. 2018, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Duan, S.; Li, Z.; Chang, S.; Xing, Z.; Leng, P.; Gao, M. Interannual Spatiotemporal Variations of Land Surface Temperature in China From 2003 to 2018. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 14, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayable, G.; Alemu, G. Spatiotemporal variability of land surface temperature in north-western Ethiopia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Darand, M. Trend analysis of land surface temperature over Iran based on land cover and topography. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 7229–7242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.C.; Maeda, E.E.; Williams, R. Use of remotely sensed land surface temperature as a proxy for air temperatures at high elevations: Findings from a 5000 m elevational transect across Kilimanjaro. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, A.; Ningthoujam, R. Snow cover and vegetation greenness with leaf water content control the global land surface temperature. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; He, B.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Darko, A. Profile and concentric zonal analysis of relationships between land use/land cover and land surface temperature: Case study of Shenyang, China. Energ. Build. 2017, 155, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, R.C.; Murayama, Y.; Myint, S.W. Effects of landscape composition and pattern on land surface temperature: An urban heat island study in the megacities of Southeast Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, V.A.; Gouveia, C.M.; DaCamara, C.C.; Libonati, R.; Trigo, I.F. The roles of NDVI and Land Surface Temperature when using the Vegetation Health Index over dry regions. Glob. Planet Change 2020, 190, 103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Tian, Y.; Wu, L.; Xiao, J.; Chen, F.; Qian, Q. Relationship among land surface temperature and LUCC, NDVI in typical karst area. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekertekin, A.; Zadbagher, E. Simulation of future land surface temperature distribution and evaluating surface urban heat island based on impervious surface area. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Martinez, F.; de Beurs, K.M.; Koch, J.; Widener, J. Multi-Temporal Land Surface Temperature and Vegetation Greenness in Urban Green Spaces of Puebla, Mexico. Land 2021, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, B.; Huang, G. Surface temperature variations and their relationships with land cover in the Pearl River Delta. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 37614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Liu, R.; Men, C.; Wang, Q.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Quantifying and simulating landscape composition and pattern impacts on land surface temperature: A decadal study of the rapidly urbanizing city of Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Jain, K. Analyzing the impact of changing landscape pattern and dynamics on land surface temperature in Lucknow city, India. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yue, W.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y. Investigating the spatiotemporal non-stationary relationships between urban spatial form and land surface temperature: A case study of Wuhan, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Wu, F.; Zhan, J. Impacts of Vegetation Change on the Regional Surface Climate: A Scenario-Based Analysis of Afforestation in Jiangxi Province, China. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Riemann, D.; Vogt, S.; Glaser, R. Impacts of land cover changes on climate trends in Jiangxi province China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, H.; Shi, J.; Lv, T.; Zhou, C.; Liu, W. Assessing Changes in Ecosystem Service Values in Response to Land Cover Dynamics in Jiangxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huo, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, P.; Wu, D. Hot weather event-based characteristics of double-early rice heat risk: A study of Jiangxi province, South China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z. New refinements and validation of the collection-6 MODIS land-surface temperature/emissivity product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Ab Ghani, A.; Fei, S.Y. ANFIS-based approach for predicting sediment transport in clean sewer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2012, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azamathulla, H.M.; Guven, A.; Demir, Y.K. Linear genetic programming to scour below submerged pipeline. Ocean Eng. 2011, 38, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z.L. A physics-based algorithm for retrieving land-surface emissivity and temperature from EOS/MODIS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.L. Quality assessment and validation of the MODIS global land surface temperature. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, T.; Rihan, W.; Deng, G. The Effect of Snow Depth on Spring Wildfires on the Hulunbuir from 2001–2018 Based on MODIS. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30 m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Yadav, S.M. An analysis of rainfall variability and drought over Barmer District of Rajasthan, Northwest India. Water Supply 2021, 21, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingale, S.M.; Khare, D.; Jat, M.K.; Adamowski, J. Spatial and temporal trends of mean and extreme rainfall and temperature for the 33 urban centers of the arid and semi-arid state of Rajasthan, India. Atmos. Res. 2014, 138, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Yadav, S.M. Temporal analysis of rainfall and drought characteristics over Jalore District of S-W Rajasthan. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 17, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.; Mudannyaka, S.; Azamathulla, H.; Rathnayake, U. Recent Climatic Trends in Trinidad and Tobago, West Indies. Asia-Pacific J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Yadav, S. Long-term trend analysis of climate variables for arid and semi-arid regions of an Indian State Rajasthan. Int. J. Hydrol. Sci. Technol. 2020, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriou, M. A change-point model for monitoring the coefficient of variation based on squared ranks test. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Granero, M.A.; Trinidad Segovia, J.E.; García Pérez, J. Some comments on Hurst exponent and the long memory processes on capital markets. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Applications 2008, 387, 5543–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Lusi, A.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Spatiotemporal drought variability on the Mongolian Plateau from 1980–2014 based on the SPEI-PM, intensity analysis and Hurst exponent. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Goswami, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Exploring the pre- and summer-monsoon surface air temperature over eastern India using Shannon entropy and temporal Hurst exponents through rescaled range analysis. Atmos. Res. 2019, 217, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Vejre, H. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of remotely sensed region heat islands during the rapid urbanization (1995–2015) of Southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 674, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Jia, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, J. Seasonal contrast of the dominant factors for spatial distribution of land surface temperature in urban areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.X.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Myint, S.W.; Caetano, M.; Kieu, H.V. Characterizing the relationship between land use land cover change and land surface temperature. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 124, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wu, J. Effects of urban growth on the land surface temperature: A case study in Taiyuan, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 10787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, G.; Luo, Q.; Jia, B. Impacts of Urban land surface temperature on tract landscape pattern, physical and social variables. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


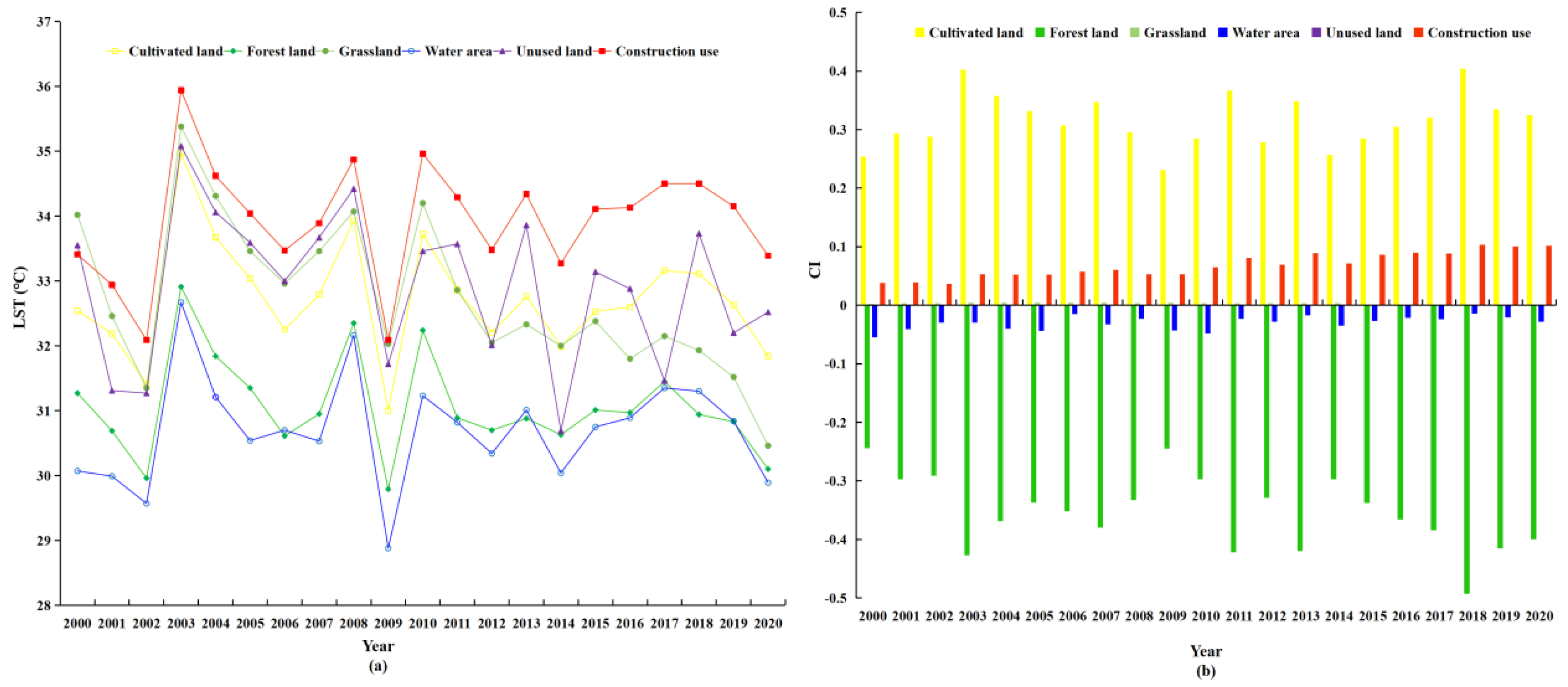
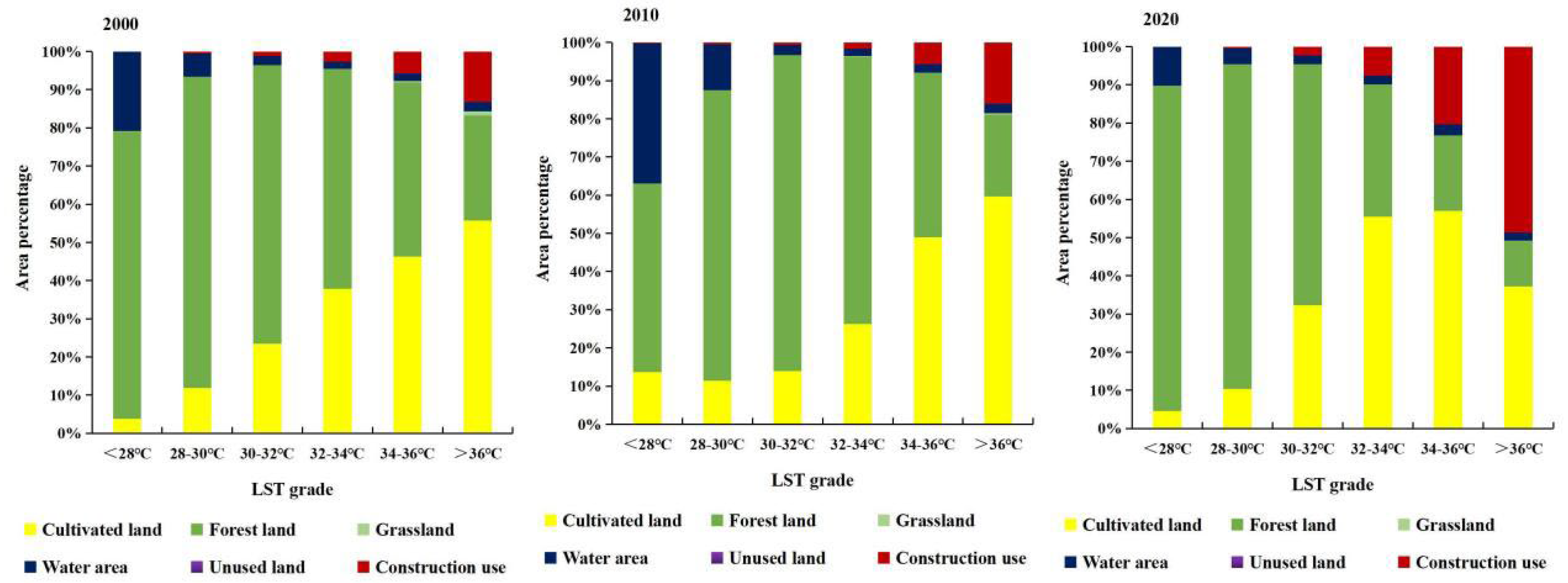
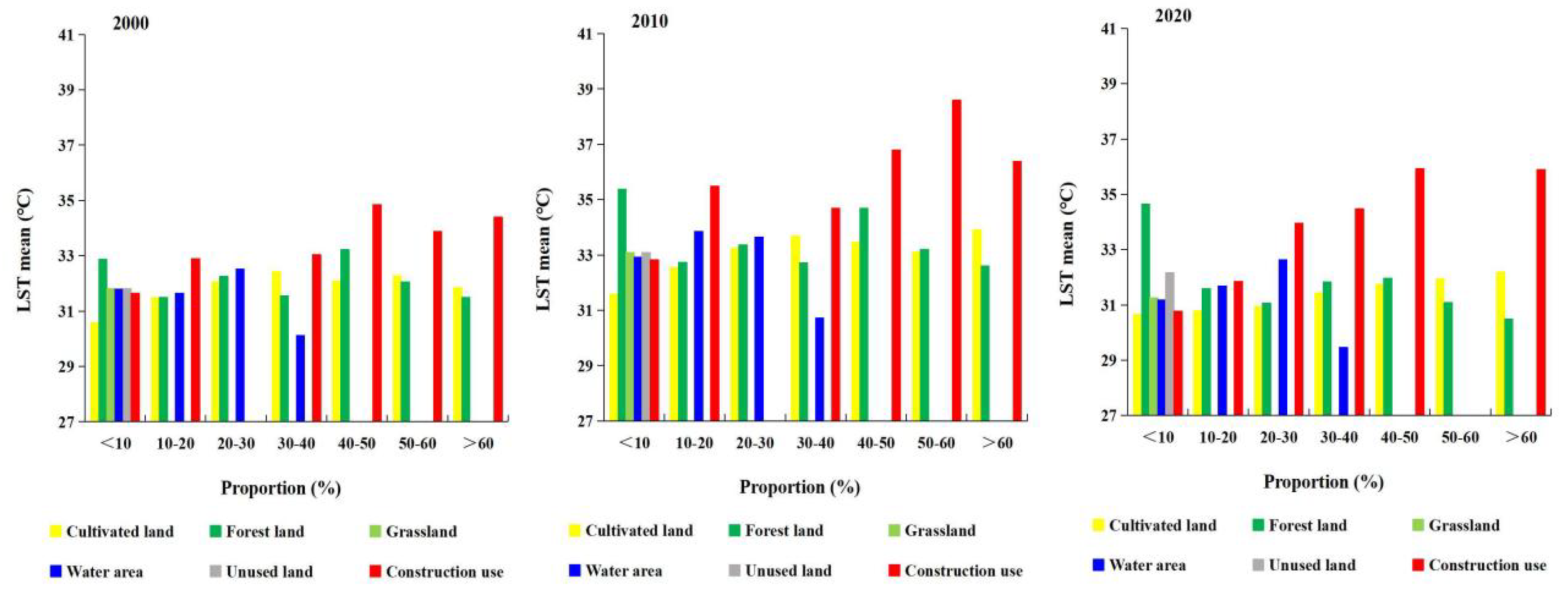
| Sample Number | Nugget | Major Range | Partial Still | Lag Size | R | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 1.5 | 17,728 | 0.9657 | 0.0166 |
| 2 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 1.8 | 17,728 | 0.9684 | 0.0161 |
| 3 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 2.1 | 17,728 | 0.9659 | 0.0166 |
| 4 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 2.5 | 17,728 | 0.9611 | 0.0176 |
| 5 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 2.7 | 17,728 | 0.9591 | 0.0181 |
| 6 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 3 | 17,728 | 0.9566 | 0.0186 |
| 7 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 3.3 | 17,728 | 0.9635 | 0.0171 |
| 8 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 3.6 | 17,728 | 0.9540 | 0.0191 |
| 9 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 3.9 | 17,728 | 0.9534 | 0.0192 |
| 10 | 2.185 | 129,421 | 4.5 | 17,728 | 0.9528 | 0.0193 |
| β Value | Z Value | LST Trend Grade | Percentage of Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| >0.0005 | >1.96 | Significant increase | 2.14% |
| >0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Mild increase | 28.80% |
| −0.0005–0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Stability | 0.77% |
| <−0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | Mild decline | 62.97% |
| <−0.0005 | <−1.96 | Significant decline | 5.32% |
| CV Value | LST Fluctuation Grade | Percentage of Area (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01–0.03 | Minimum fluctuation | 4.98% |
| 0.03–0.04 | Lower fluctuation | 45.39% |
| 0.04–0.05 | Moderate fluctuation | 41.58% |
| 0.05–0.06 | Higher fluctuation | 6.84% |
| >0.06 | Maximum fluctuation | 1.21% |
| LST Persistence Grade | β Value | Z Value | H Value | Percentage of Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Persistent significant increase | >0.0005 | >1.96 | >0.5 | 1.83% |
| Persistent mild increase | >0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | >0.5 | 9.06% |
| Persistent stability | −0.0005–0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | >0.5 | 0.23% |
| Persistent mild decline | >−0.0005 | −1.96–1.96 | >0.5 | 30.35% |
| Persistent significant decline | <−0.0005 | <−1.96 | >0.5 | 4.70% |
| Uncertain future trends | — | — | <0.5 | 53.83% |
| Year | Regression Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | LST = 1.5892SHDI + 30.12 | 0.2126 |
| 2001 | LST = 1.6545SHDI + 29.621 | 0.2059 |
| 2002 | LST = 1.7064SHDI + 28.835 | 0.2833 |
| 2003 | LST = 2.8025SHDI + 30.892 | 0.3985 |
| 2004 | LST = 2.335SHDI + 30.218 | 0.2618 |
| 2005 | LST = 1.9304SHDI + 30.113 | 0.2112 |
| 2006 | LST = 2.1322SHDI + 29.242 | 0.223 |
| 2007 | LST = 2.0615SHDI + 29.627 | 0.2487 |
| 2008 | LST = 1.5567SHDI + 31.406 | 0.1447 |
| 2009 | LST = 0.7713SHDI + 29.529 | 0.0395 |
| 2010 | LST = 1.9095SHDI + 31.052 | 0.2112 |
| 2011 | LST = 2.6835SHDI + 29.18 | 0.2546 |
| 2012 | LST = 1.986SHDI + 29.456 | 0.2348 |
| 2013 | LST = 2.5836SHDI + 29.273 | 0.2296 |
| 2014 | LST = 1.3187SHDI + 29.969 | 0.0918 |
| 2015 | LST = 1.6609SHDI + 30.085 | 0.1456 |
| 2016 | LST = 2.0931SHDI + 29.774 | 0.235 |
| 2017 | LST = 1.579SHDI + 30.564 | 0.0949 |
| 2018 | LST = 2.6474SHDI + 29.203 | 0.3239 |
| 2019 | LST = 1.9633SHDI + 29.758 | 0.1687 |
| 2020 | LST = 1.7568SHDI + 29.252 | 0.1352 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, Q.; Chen, W.; Luo, S.; He, L.; Li, H. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Surface Temperature in Recent 20 Years and Analysis of the Effect of Land Use in Jiangxi Province, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081278
Xiong Q, Chen W, Luo S, He L, Li H. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Surface Temperature in Recent 20 Years and Analysis of the Effect of Land Use in Jiangxi Province, China. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081278
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Qiongbing, Wenbo Chen, Shiqi Luo, Lei He, and Haifeng Li. 2022. "Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Surface Temperature in Recent 20 Years and Analysis of the Effect of Land Use in Jiangxi Province, China" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081278
APA StyleXiong, Q., Chen, W., Luo, S., He, L., & Li, H. (2022). Temporal and Spatial Variation of Land Surface Temperature in Recent 20 Years and Analysis of the Effect of Land Use in Jiangxi Province, China. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081278







