Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Point Sources with Mobile Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Gaussian Plume Model
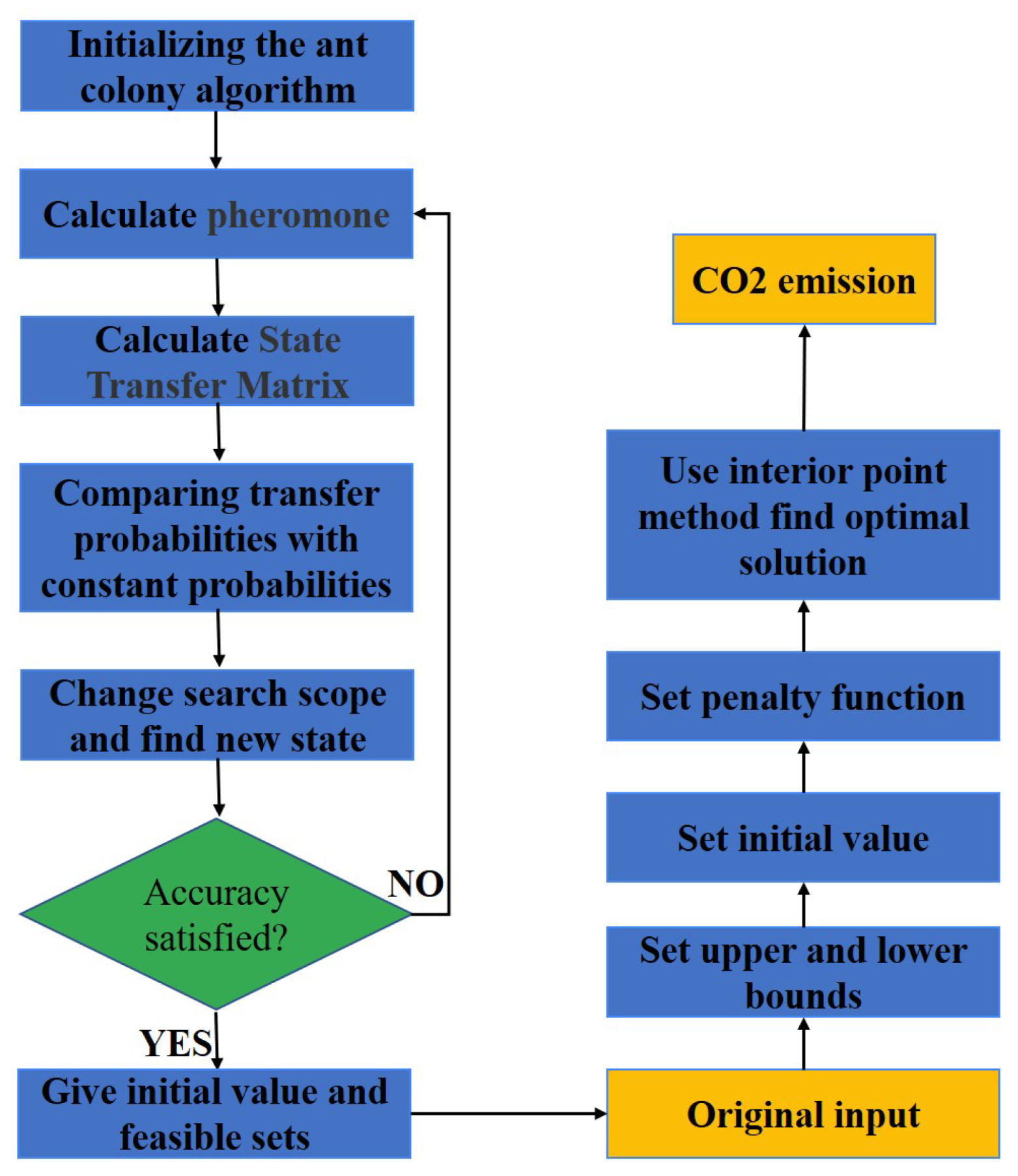
2.2. ACA–IPFM Model
3. Results
3.1. Simulation
3.2. Stability Analysis
3.3. Joint Error Analysis
3.4. Actual Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Jones, M.W.; O’sullivan, M.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; Quéré, C.L.; et al. Global Carbon Budg. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1783–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Jin, S.; Fan, R.; Gong, W. The relationship between atmospheric boundary layer and temperature inversion layer and their aerosol capture capabilities. Atmos. Res. 2022, 271, 106121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, N.; Chen, B. A new algorithm for himawari-8 aerosol optical depth retrieval by integrating regional PM2.5 concentrations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Yang, J.; Song, S.; Shi, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, A.; Du, L. Target classification of similar spatial characteristics in complex urban areas by using multispectral lidar. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, G.; Mao, H.; Pei, Z.; Ma, X.; Jia, W.; Gong, W. The spatial and temporal distribution patterns of xch4 in china: New observations from tropomi. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shi, Y. Estimating CO2 emissions from large scale coal-fired power plants using OCO-2 observations and emission inventories. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovensmann, H.; Buchwitz, M.; Burrows, J.; Reuter, M.; Krings, T.; Gerilowski, K.; Schneising, O.; Heymann, J.; Tretner, A.; Erzinger, J. A remote sensing technique for global monitoring of power plant CO2 emissions from space and related applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 781–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G. The net climate impact of coal-fired power plant emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3247–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delre, A.; Mønster, J.; Scheutz, C. Greenhouse gas emission quantification from wastewater treatment plants, using a tracer gas dispersion method. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Z.; Gou, H.; Bu, L. Quantifying CO2 uptakes over oceans using lidar: A tentative experiment in bohai bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Chevallier, F.; Ciais, P.; Broquet, G.; Wang, Y.; Lian, J.; Zhao, Y. Observing carbon dioxide emissions over china’s cities and industrial areas with the orbiting carbon observatory-2. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8501–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaaßen, L.; Stoll, C. Harmonizing corporate carbon footprints. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Duncan, B.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Beirle, S.; Griffin, D.; McLinden, C.A.; Goldberg, D.L.; Lu, Z. A methodology to constrain carbon dioxide emissions from coal-fired power plants using satellite observations of co-emitted nitrogen dioxide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.S.; Andres, R.J.; Marland, G. China: Emissions pattern of the world leader in CO2 emissions from fossil fuel consumption and cement production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Shao, S.; Wang, P.; Guan, D. New provincial CO2 emission inventories in china based on apparent energy consumption data and updated emission factors. Appl. Energy 2016, 184, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Ehret, G.; Kiemle, C.; Amediek, A.; Quatrevalet, M.; Wirth, M.; Fix, A. Determination of the emission rates of CO2 point sources with airborne lidar. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2021, 14, 2717–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.; Hill, T.G.; McLinden, C.A.; Wunch, D.; Jones, D.B.; Crisp, D. Quantifying CO2 emissions from individual power plants from space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, J.; Hölzle, E.; Goede, A.; Visser, H.; Fricke, W. Sciamachy—Scanning imaging absorption spectrometer for atmospheric chartography. Acta Astronaut. 1995, 35, 45–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuze, A.; Suto, H.; Nakajima, M.; Hamazaki, T. Thermal and near infrared sensor for carbon observation fourier-transform spectrometer on the greenhouse gases observing satellite for greenhouse gases monitoring. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 6716–6733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, C.; Connor, B.; Bösch, H.; O’Brien, D.; Frankenberg, C.; Castano, R.; Christi, M.; Eldering, D.; Fisher, B.; Gunson, M.; et al. The Acos CO2 retrieval Algorithm-1: Description and validation against synthetic observations. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2012, 5, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Shi, T.; Gong, W. A method for estimating the background column concentration of CO2 using the lagrangian approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 4108112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Maksyutov, S.; Bousquet, P.; Bréon, F.-M.; Saito, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Yokota, T. On the accuracy of the CO2 surface fluxes to be estimated from the gosat observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Cui, X.; Liang, A.; Ma, X.; Zhang, T.; Gong, W. A co 2 profile retrieving method based on chebyshev fitting for ground-based dial. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6099–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, R.; Mastrogiacomo, J.-P.; Bateman-Hemphill, W.; McCracken, C.; MacDonald, C.G.; Hill, T.; O’Dell, C.W.; Kiel, M.; Crisp, D. Advances in quantifying power plant CO2 emissions with OCO-2. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Martin, R.V.; Philip, S.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Jiang, X.; He, K. Satellite measurements oversee china’s sulfur dioxide emission reductions from coal-fired power plants. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhang, Z. Contaminant dispersion prediction and source estimation with integrated gaussian-machine learning network model for point source emission in atmosphere. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 311, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Zhang, M.; Pei, Z.; Xu, H.; Qiu, R.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W. An inversion method for estimating strong point carbon dioxide emissions using a differential absorption lidar. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.; Vinkovic, K.; de Vries, M.; Kers, B.; Necki, J.; Swolkien, J.; Roiger, A.; Peters, W.; Chen, H. Quantifying methane emissions from coal mining ventilation shafts using an unmanned aerial vehicle (uav)-based active aircore system. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 12, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Gong, W.; Lin, H.; Ma, X.; Xiang, Z. Study on influences of atmospheric factors on vertical profile retrieving from ground-based dial at 1.6 μm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 3221–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Ma, X.; Liang, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gong, W. Performance evaluation for china’s planned CO2-ipda. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, G.; Kiemle, C.; Wirth, M.; Amediek, A.; Fix, A.; Houweling, S. Space-borne remote sensing of CO2, CH4, and N2O by integrated path differential absorption lidar: A sensitivity analysis. Appl. Phys. B 2008, 90, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, G.; Bousquet, P.; Pierangelo, C.; Alpers, M.; Millet, B.; Abshire, J.B.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Chevallier, F.; Ciais, P.; et al. Ger. Space Lidar Mission Dedic. Atmos. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, W.; Pei, Z.; Xu, H.; Qiu, R.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Potential of ground-based multiwavelength differential absorption lidar to measure δ13c in open detected path. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, G.; Zhang, W.; Chen, B.; Liang, A.; Gong, W. Design of inversion procedure for the airborne co 2-ipda lidar: A preliminary study. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11840–11852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, T.; Gerilowski, K.; Buchwitz, M.; Reuter, M.; Tretner, A.; Erzinger, J.; Heinze, D.; Pflüger, U.; Burrows, J.; Bovensmann, H. Mamap–a new spectrometer system for column-averaged methane and carbon dioxide observations from aircraft: Retrieval algorithm and first inversions for point source emission rates. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2011, 4, 1735–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, Z.; Gong, W.; Ma, X.; Han, G. High-precision methodology for quantifying gas point source emission. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Su, H.; Gong, W. Response of major air pollutants to covid-19 lockdowns in china. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arystanbekova, N.K. Application of gaussian plume models for air pollution simulation at instantaneous emissions. Math. Comput. Simul. 2004, 67, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Hively, L. A review of validation studies for the gaussian plume atmospheric dispersion model. Nucl. Saf. 1987, 28, 5588029. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Birattari, M.; Stutzle, T. Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2006, 1, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Ant colony optimization: Overview and recent advances. In Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 311–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeniay, Ö. Penalty function methods for constrained optimization with genetic algorithms. Math. Comput. Appl. 2005, 10, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | Actual Sets | Retrieval Results |
|---|---|---|
| CO Emission q (g/s) | 300 | 298.29 ± 3.01 |
| Wind speed u (m/s) | 3 | 3 ± 0.02 |
| a | 0.11 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
| b | 0.92 | 0.90 ± 0.05 |
| c | 0.11 | 0.12 ± 0.04 |
| d | 0.83 | 0.80 ± 0.02 |
| H | 10 | 10.2 ± 0.02 |
| 0.95 | 0.93 ± 0.05 | |
| B | 1500 | 1503 ± 2.5 |
| Wind direction | 90 | 90.2 ± 0.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, M.; Mao, H.; Chen, C.; Wei, X.; Shi, T. Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Point Sources with Mobile Systems. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081249
Cai M, Mao H, Chen C, Wei X, Shi T. Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Point Sources with Mobile Systems. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081249
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Mengyang, Huiqin Mao, Cuihong Chen, Xvpeng Wei, and Tianqi Shi. 2022. "Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Point Sources with Mobile Systems" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081249
APA StyleCai, M., Mao, H., Chen, C., Wei, X., & Shi, T. (2022). Measuring Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Point Sources with Mobile Systems. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081249





