The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resources and Methods
3. Results
3.1. The Temperature
3.1.1. Diurnal, Monthly and Seasonal Variations of Air Temperature
3.1.2. Surface Temperature
3.2. Albedo
3.3. Soil Moisture Content
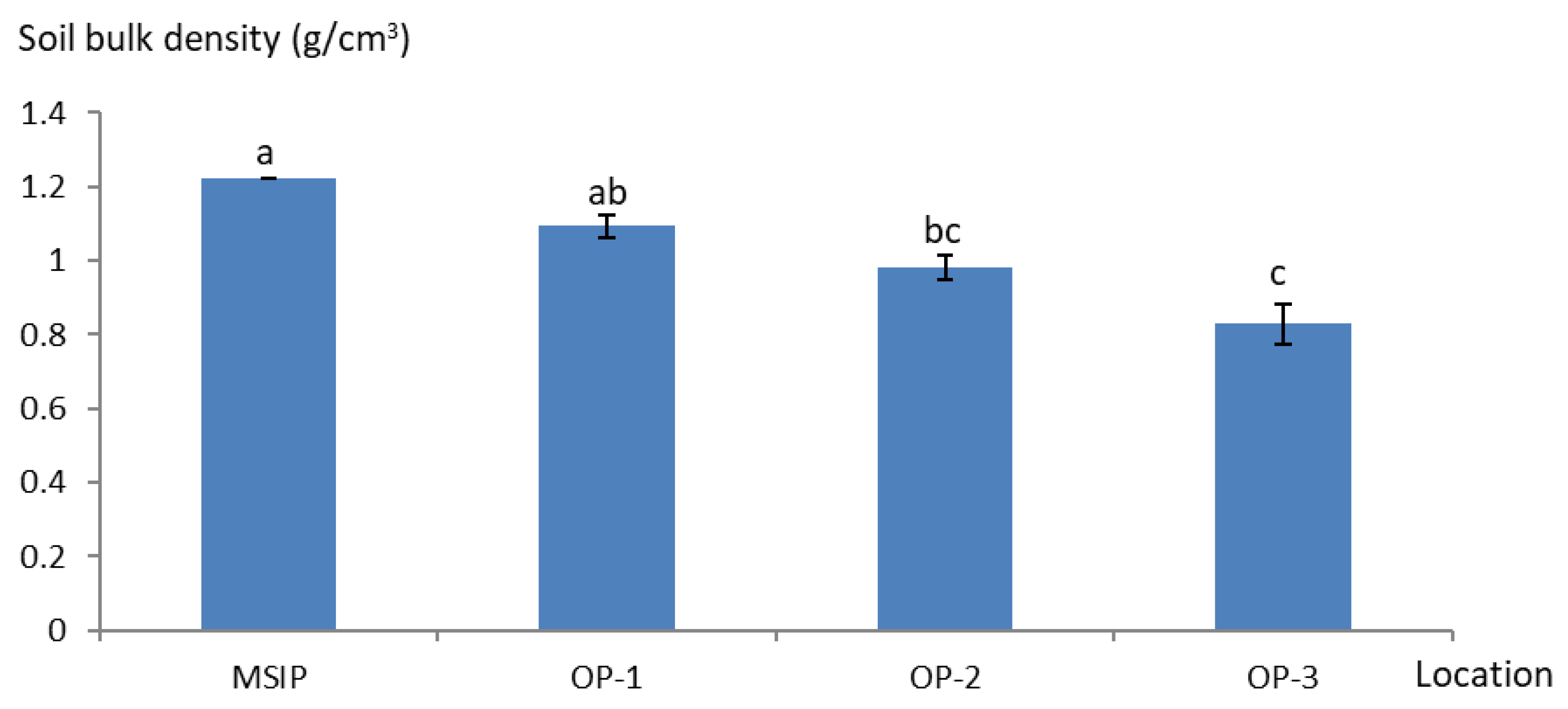
3.4. Soil Bulk Density
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, Y.P.; Oliphant, M.; Hu, E.J. Development of renewable energy in Australia and China: A comparison of policies and status. J. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century (REN21). Renewables 2021 Global Status Report. Available online: https://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/GSR2021_Full_Report.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Li, P.D.; Gao, X.Q. The impact of photovoltaic power plants on ecological environment and climate: A literature review. J. Plateau Meteorol. 2021, 40, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron-Gafford, G.; Minor, R.; Allen, N.; Cronin, A.; Brooks, A.; Pavao-Zuckerman, M. The Photovoltaic Heat Island Effect: Larger solar power plants increase local temperatures. J. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millstein, D.; Menon, S. Regional climate consequences of large-scale cool roof and photovoltaic array deployment. J. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.; Yu, Y. Analysis of the potential for a heat island effect in large solar farms. In Proceedings of the IEEE 40th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 8 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, A.M.; Krayenhoff, E.S.; Georgescu, M.; Sailor, D.J. The observed effects of utility-scale photovoltaics on near-surface air temperature and energy balance. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2019, 58, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X. Research on Influence of Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Air Temperature and Humidity. J. West. Resour. 2016, 3, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R.; Shen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Guo, P. Observed surface radiation and temperature impacts from the large-scale deployment of photovoltaics in the barren area of Gonghe, China. J. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H. The potential for air-temperature impact from large-scale deployment of solar photovoltaic arrays in urban areas. J. Sol. Energy 2013, 91, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamanca, F.; Georgescu, M.; Mahalov, A.; Moustaoui, M.; Martilli, A. Citywide impacts of cool roof and rooftop solar photovoltaic deployment on near-surface air temperature and cooling energy demand. J. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2016, 161, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson, V.; Bonhomme, M.; Salagnac, J.; Briottet, X.; Lemonsu, A. Solar panels reduce both global warming and urban heat island. J. Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, M.Q.; Qiao, S. Analysis of Environmental Effects of Photovoltaic Power Station Construction in Gobi Area. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2013. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201302&filename=1013237744.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=8Av73w4juY05EqYB6-H3BUls-Yok-DmzyTrpYB_ygQyittsNOEKzoZyxyjMIro4- (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Gao, X.Q.; Yang, L.W.; Lv, F.; Ma, L.Y.; Li, H.L.; Hui, X.Y.; Hou, X.H. Observational study on the impact of the large solar farm on air temperature and humidity in desert area of Golmud. J. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2016, 37, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.W.; Gao, X.Q.; Lv, F.; Hui, X.Y.; Ma, L.Y.; Hou, X.H.; Li, H.L. Influence of photovoltaic power station on solar radiation field in desert area of Golmud. J. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2015, 36, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Weigand, J.; Ganguly, S. The potential for climate impact from widespread deployment of utility-scale solar energy installations: An environmental remote sensing perspective. J. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2017, 6, 1000190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kalnay, E.; Motesharrei, S.; Rivas, J.; Kucharski, F.; Kirk-Davidoff, D.; Bach, E.; Zeng, N. Climate model shows large-scale wind and solar farms in the Sahara increase rain and vegetation. J. Sci. 2018, 361, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.Q.; Yang, L.W.; Lv, F.; Ma, L.Y.; Hui, X.Y.; Hou, X.H.; Li, H.L. Observational research on the effect of photovoltaic power station on air temperature and humidity in desert area of Golmud. J. Acta Energ. Sol. Sin. 2016, 37, 1339–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. Research on the Influence of Photovoltaic Power Station Construction on Soil and Vegetation in Jingbian County. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2015. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CMFD&dbname=CMFD201601&filename=1015329905.nh&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=y8MkYTPmQca8ymU07QVGAu2IeHxUK3TjL-VQA_DU4R19mQYORQGZUiKyZLAj8FlU (accessed on 7 May 2022).
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Dang, X.H.; Meng, Z.J. Impacts of photovoltaic power station construction on ecology environment in sandy area. J. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 39, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, S.X. Study on the characteristics of climate change in Dunhuang oasis in recent 54 years. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2010, 24, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H. Analysis on the characteristics of arid climate in Dunhuang City, Gansu Province. J. Beijing Agric. 2015, 29, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunhuang Municipal People’s Government. Overview of Dunhuang. Available online: http://www.dunhuang.gov.cn/dunhuang/dh10/common_index_list.shtml (accessed on 22 February 2022).
- Huang, C.Y.; Xu, J.M. Soil Science, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 25. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Ma, S.Y.; Shang, L.P.; Ding, A.J.; Teng, Z.Y. Effects of wind farm on surface soil in desert steppe, China. J. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 131, 01030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemet, G.F. Net radiative forcing from widespread deployment of photovoltaics. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, R. Simulated local climatic impacts of large-scale photovoltaics over the barren area of Qinghai, China. J. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

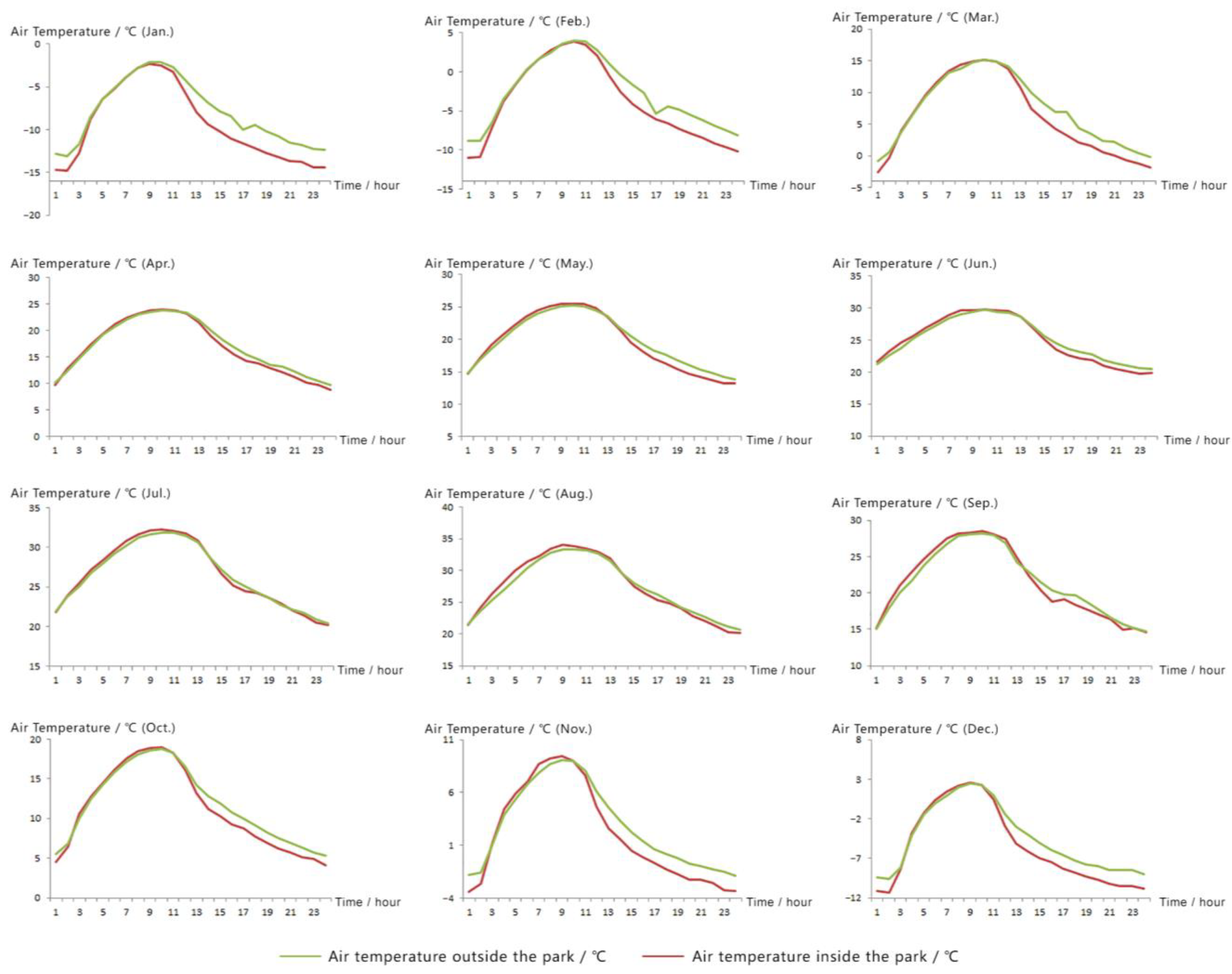
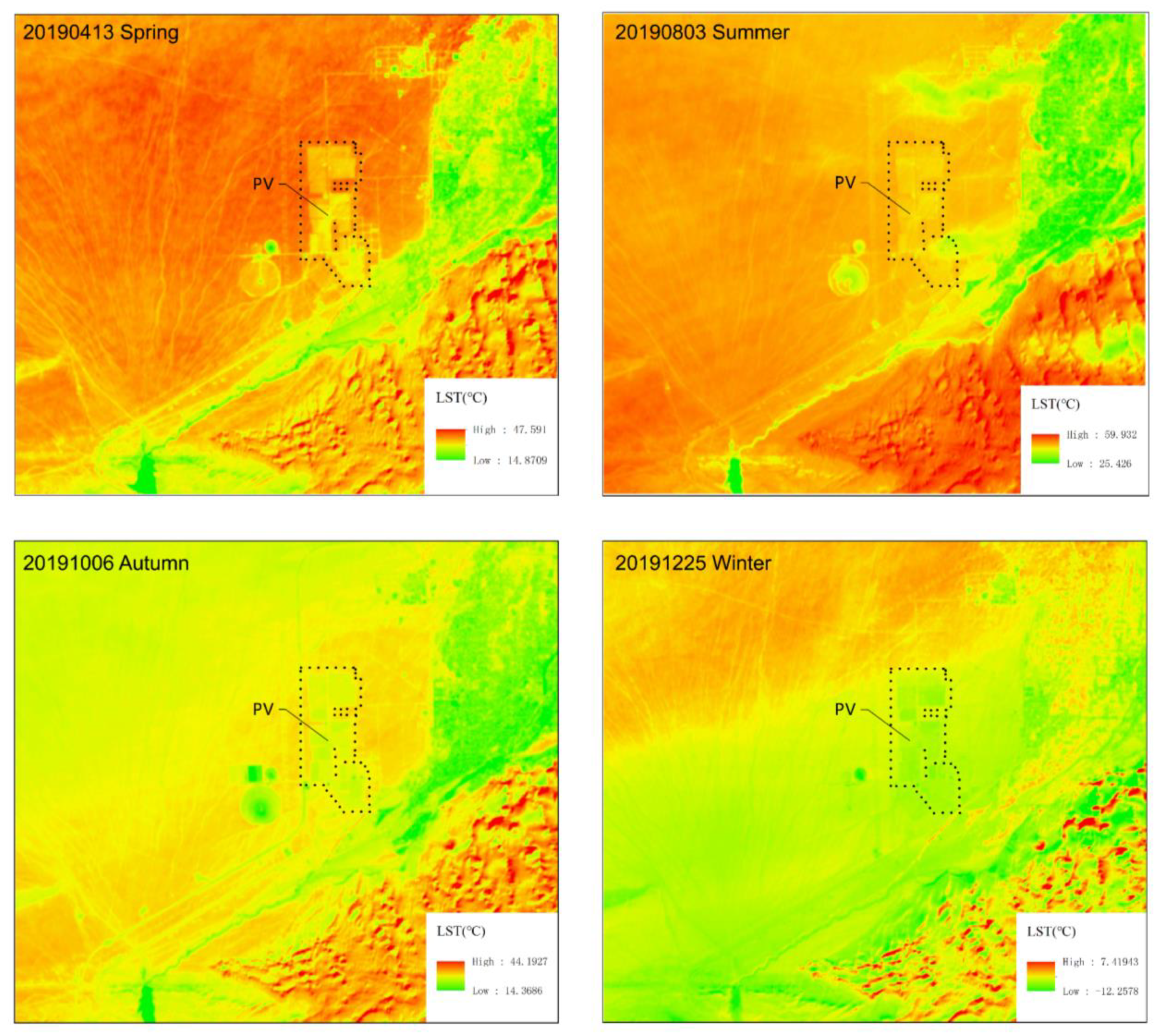
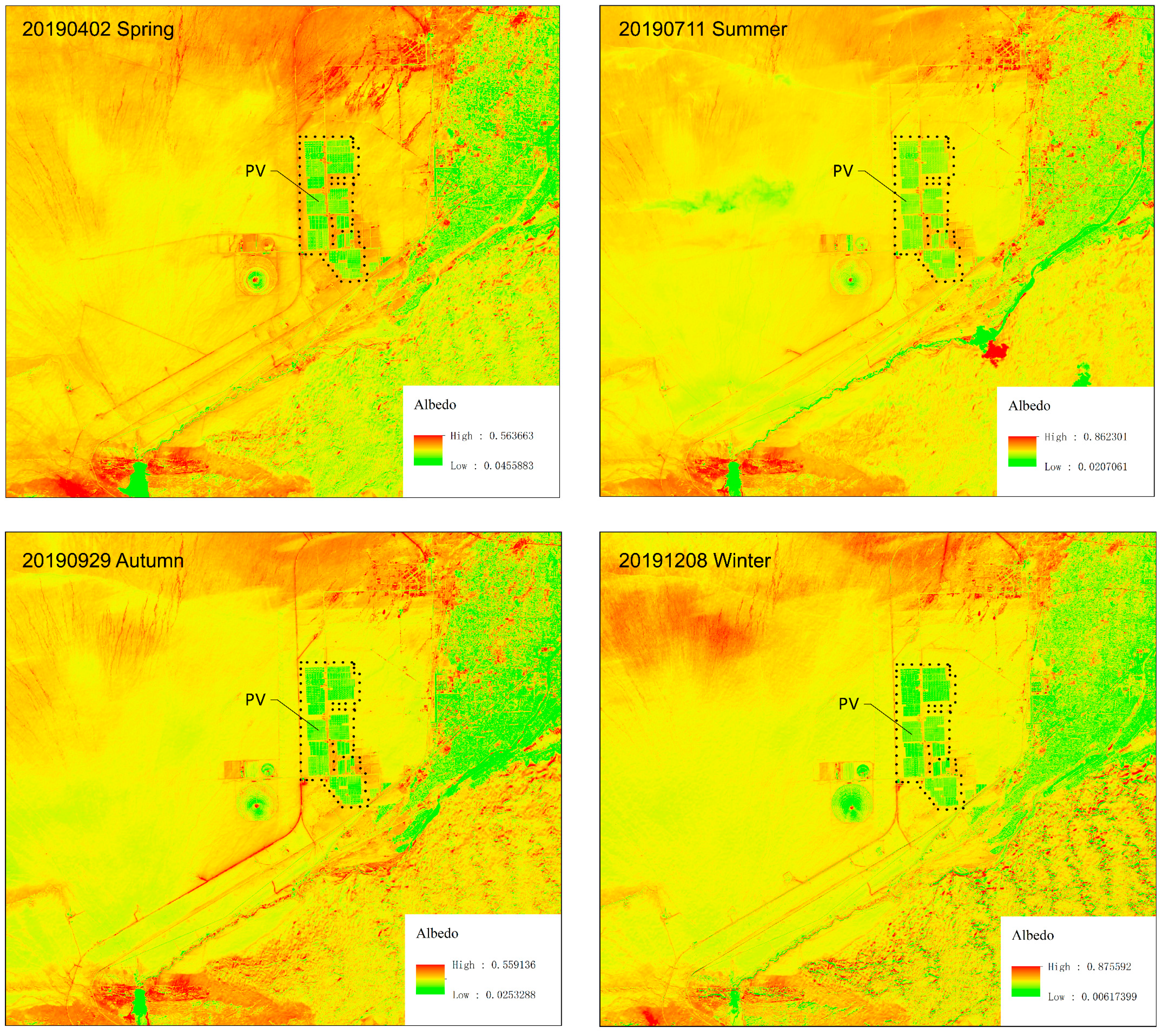
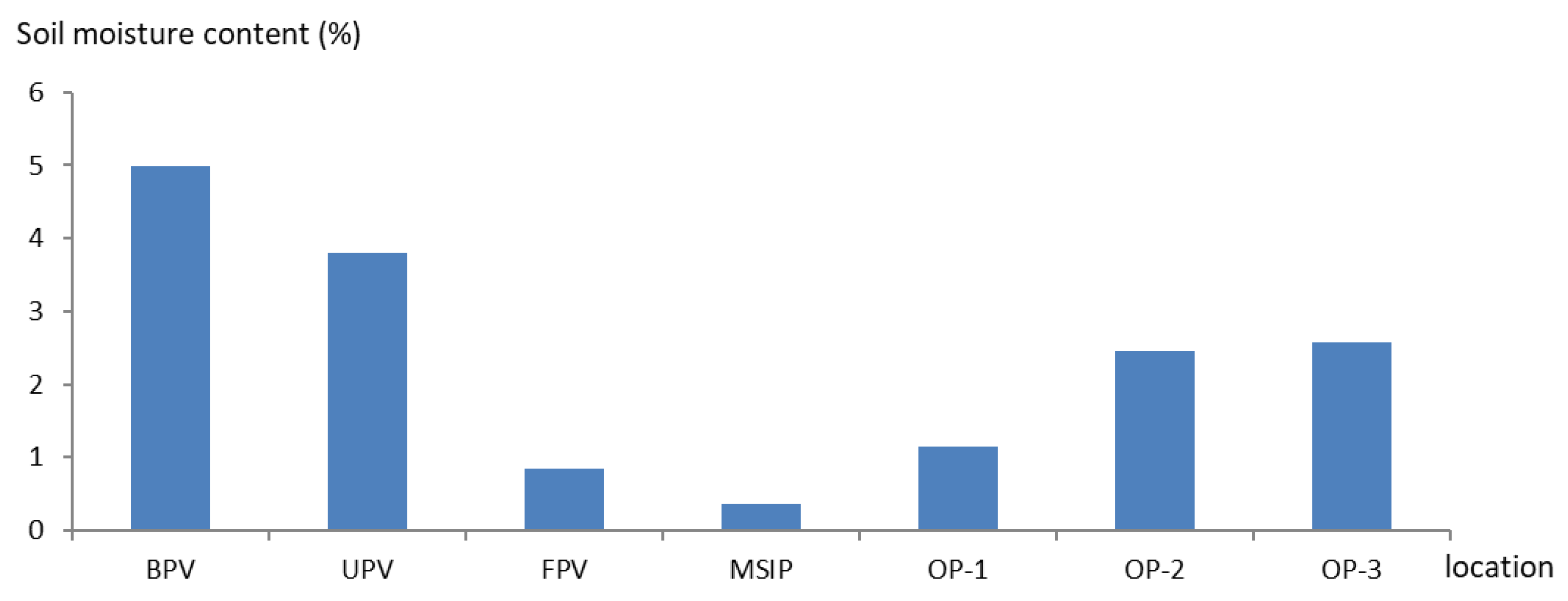
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinside | −9.48 | −3.94 | 6.15 | 16.77 | 19.53 | 24.95 | 26.58 | 27.38 | 21.47 | 11.15 | 2.01 | −5.55 |
| Toutside | −8.03 | −2.62 | 7.28 | 17.17 | 19.82 | 25.12 | 26.52 | 27.27 | 21.48 | 11.75 | 2.85 | −4.48 |
| ΔT | −1.45 | −1.32 | −1.14 | −0.41 | −0.30 | −0.16 | 0.06 | 0.11 | −0.01 | −0.60 | −0.83 | −1.07 |
| RE | 18.10 | 50.2 | 15.61 | 2.36 | 1.50 | 0.65 | 0.23 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 5.08 | 29.25 | 23.97 |
| Season | Spring | Summer | Fall | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinside | 14.14 | 26.30 | 11.55 | −6.32 |
| Toutside | 14.75 | 26.30 | 12.03 | −5.04 |
| ΔT | −0.61 | 0.00 | −0.48 | −1.28 |
| RE | −4.15 | 0.00 | −3.99 | 25.39 |
| Season | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinside | 35.35 | 45.55 | 27.64 | −5.66 |
| Toutside | 36.38 | 45.89 | 28.34 | −5.027 |
| ΔT | −1.03 | −0.34 | −0.7 | −0.633 |
| RE | 2.8 | 0.74 | 2.4 | 12.6 |
| Season | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albedoinside | 0.2471 | 0.228 | 0.2105 | 0.2007 |
| Albedooutside | 0.2738 | 0.2489 | 0.2366 | 0.2418 |
| ΔAlbedo | −0.0267 | −0.0209 | −0.0261 | −0.0411 |
| RE | 9.75 | 8.4 | 11.03 | 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, Y.; Chai, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, P. The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081235
Hua Y, Chai J, Chen L, Liu P. The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081235
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Yaping, Juan Chai, Long Chen, and Puxing Liu. 2022. "The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081235
APA StyleHua, Y., Chai, J., Chen, L., & Liu, P. (2022). The Influences of the Desert Photovoltaic Power Station on Local Climate and Environment: A Case Study in Dunhuang Photovoltaic Industrial Park, Dunhuang City, China in 2019. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081235






