Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TSP Sampling
2.2. WSIIs Analysis
2.3. Backwards Trajectory Analysis
2.4. Non-Sea Salt Analysis
2.5. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3. Results and Discussions
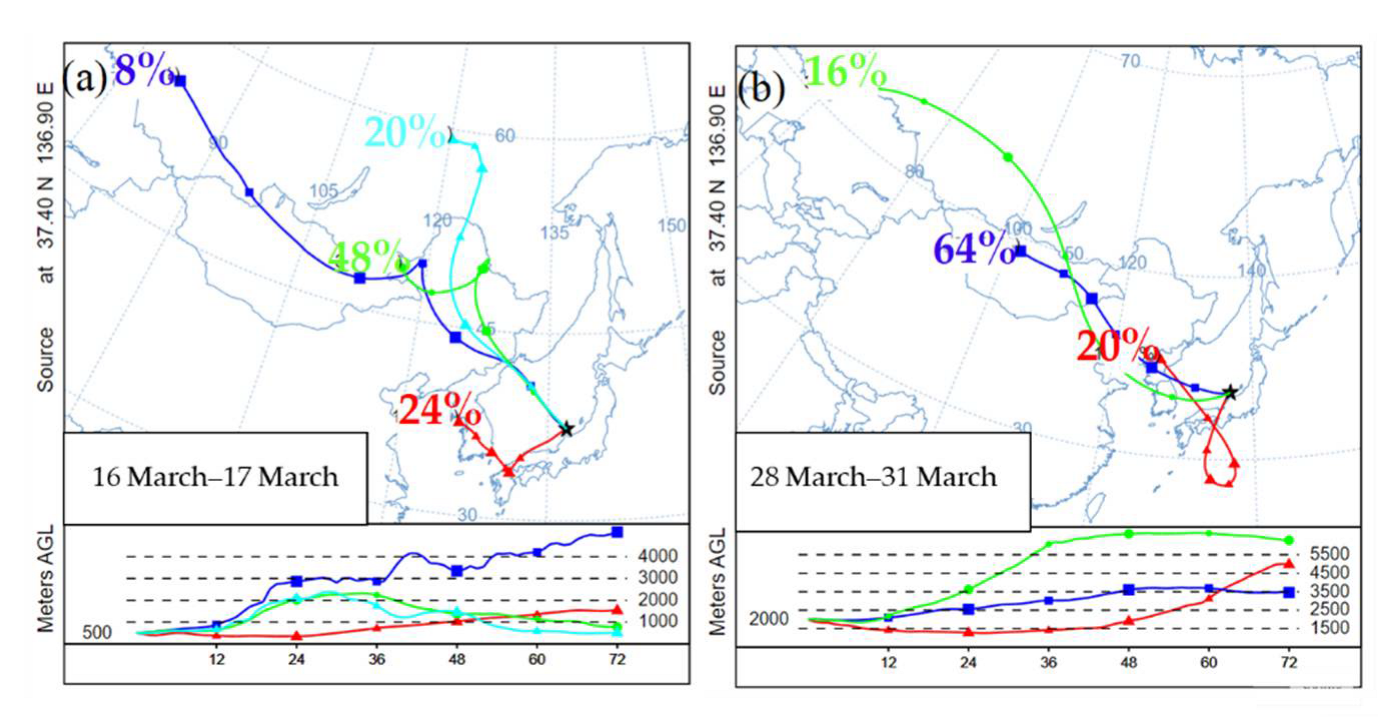
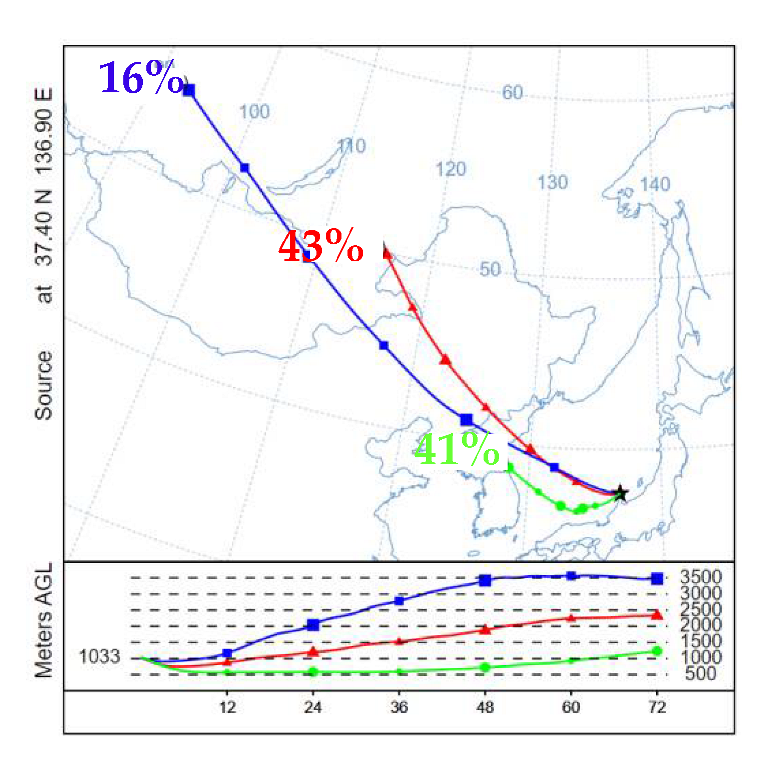
3.1. Optical Properties and Time-Height Evolution of AD
3.2. Characteristics of Aerosols in AD
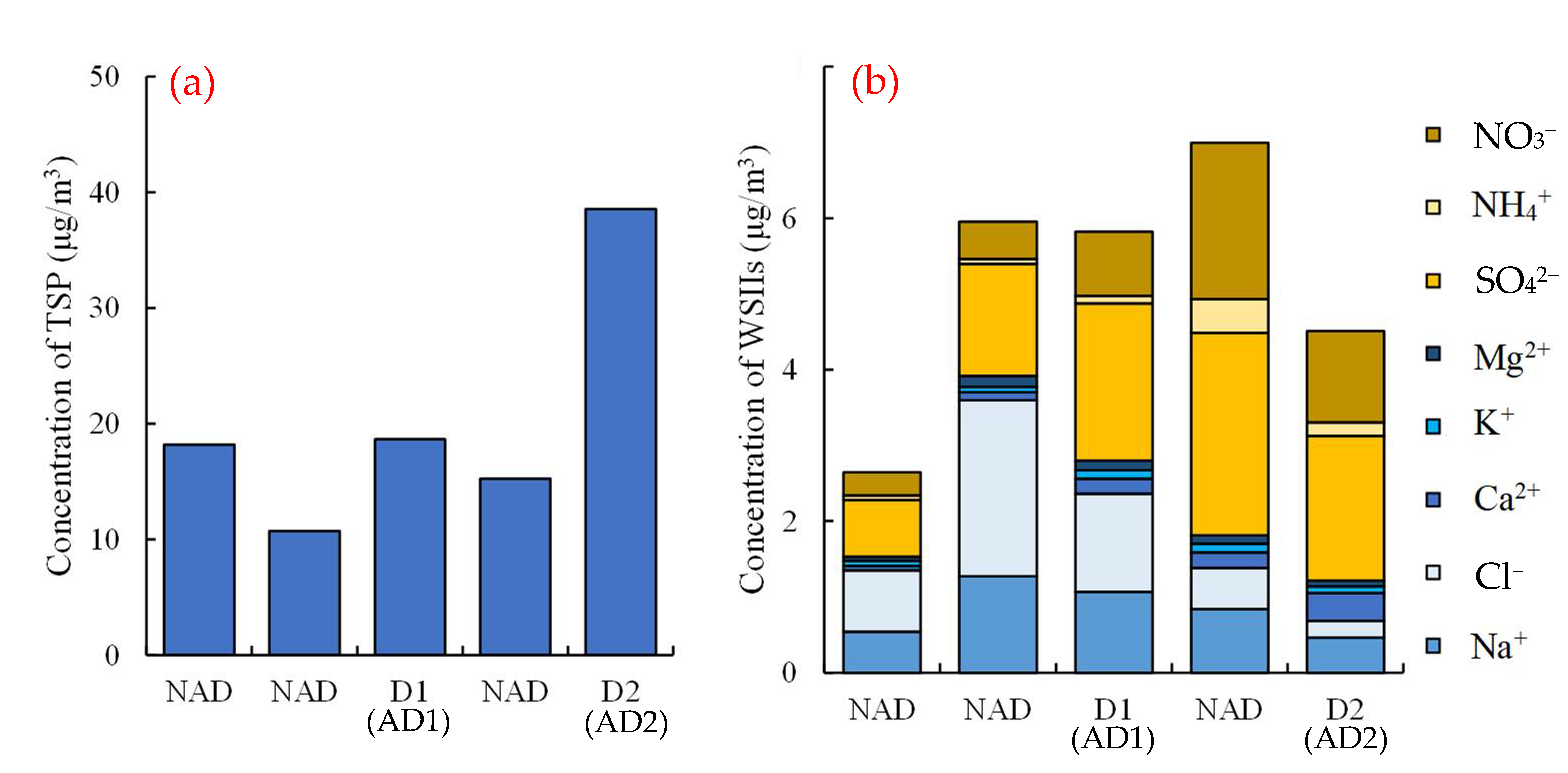
3.2.1. Concentration of TSP
3.2.2. Concentration of WSIIs
3.2.3. Aerosol Acidity and Neutralisation Factor
3.3. Long-Term Observation of AD
3.3.1. General Description of ADs
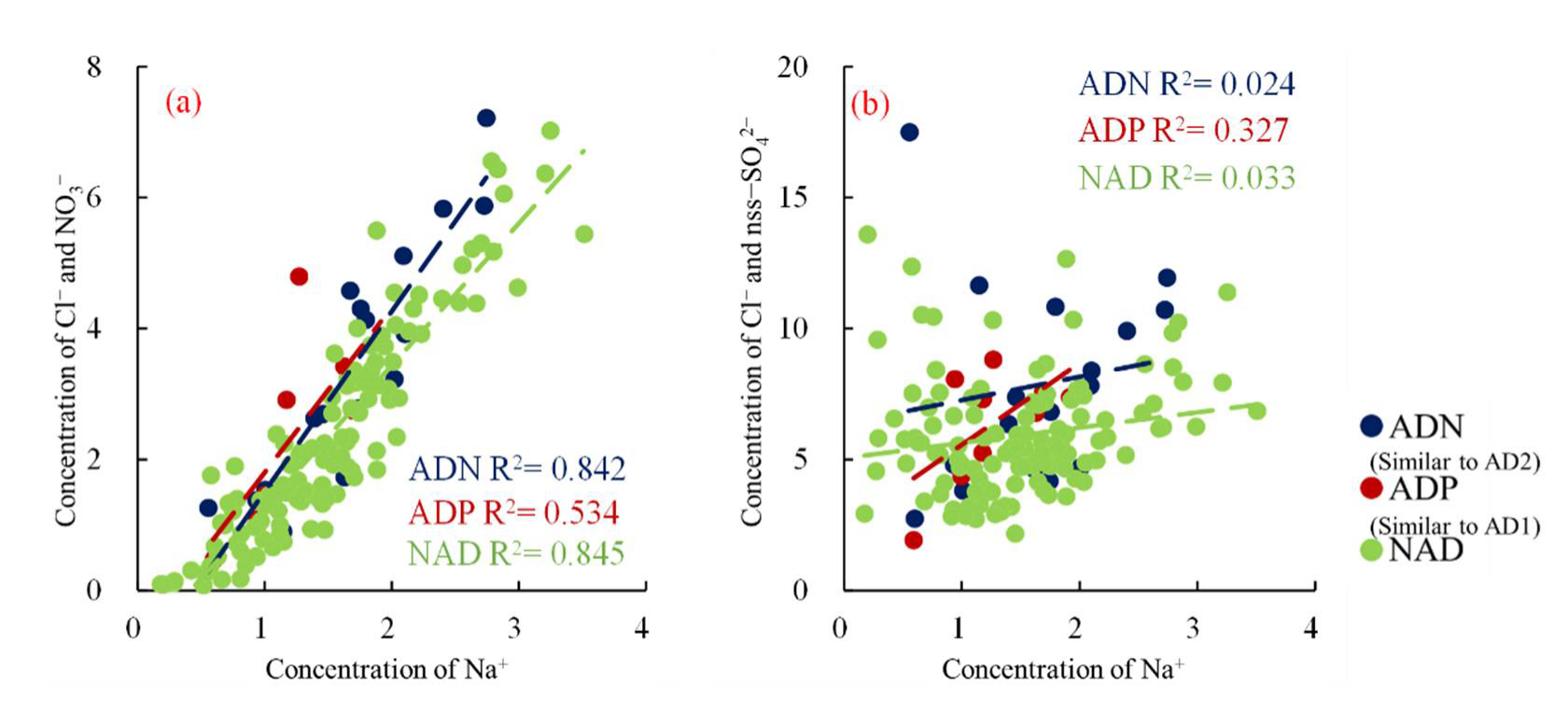
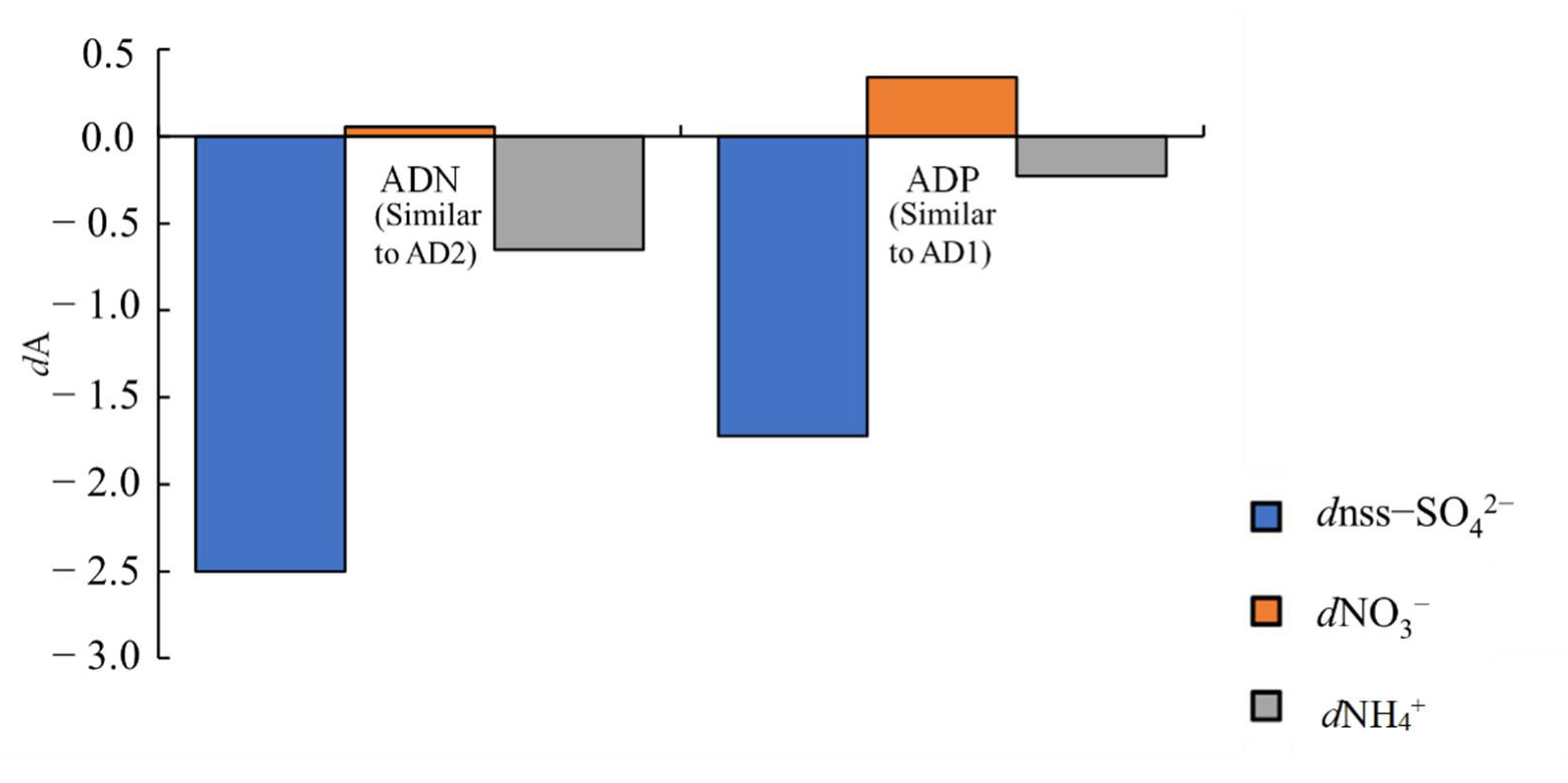
3.3.2. Cl Depletion
3.3.3. Secondary Formation of Sulphate and Nitrate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, T.L.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Blanchet, J.-P.; Mckendry, I.G.; Zhou, Z.J. A Simulated Climatology of Asian Dust Aerosol and Its Trans-Pacific Transport. Part I: Mean Climate and Validation. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Zhuang, G.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J.S. Mixing of Dust with Pollution on the Transport Path of Asian Dust-Revealed from the Aerosol over Yulin, the North Edge of Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prijith, S.S.; Rajeev, K.; Thampi, B.V.; Nair, S.K.; Mohan, M. Multi-Year Observations of the Spatial and Vertical Distribution of Aerosols and the Genesis of Abnormal Variations in Aerosol Loading over the Arabian Sea during Asian Summer Monsoon Season. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2013, 105–106, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Weather 2002, 57, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, B.; Marticorena, B.; Bergametti, G.; Chazette, P.; Maignan, F.; Schmechtig, C. Simulation of the Mineral Dust Emission Frequencies from Desert Areas of China and Mongolia Using an Aerodynamic Roughness Length Map Derived from the POLDER/ADEOS 1 Surface Products. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosaki, Y.; Mikami, M. Recent Frequent Dust Events and Their Relation to Surface Wind in East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, ASC 2-1-2-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, N.; Kinoshita, K.; Iwasaki, R.; Masumizu, T.; Yano, T. NOAA and GMS Observations of Asian Dust Events during 2000–2002. In Proceedings of SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; Volume 4895, pp. 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yu, X.; Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Si, Y. Climatology and Trends of the Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Sandstorms in Inner Mongolia. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2003, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Kim, H.; Ro, C.-U. Single-Particle Characterization of Aerosol Samples Collected before and during an Asian Dust Storm in Chuncheon, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8738–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Dong, J.; Chen, T.; Li, A.; Zou, X.; Shi, X. Long Eccentricity Forcing Asian Dust Input into the Northwestern Pacific during the Early Pleistocene. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2022, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Honda, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Yi, S. Effect of Asian Dust Storms on Daily Mortality in Seven Metropolitan Cities of Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Xie, C.; Zhao, K.; Zhuang, B.; Li, S. Characterizing a Persistent Asian Dust Transport Event: Optical Properties and Impact on Air Quality through the Ground-Based and Satellite Measurements over Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Fu, J.S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, A.; et al. Asian Dust over Northern China and Its Impact on the Downstream Aerosol Chemistry in 2004. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, S.; Yorifuji, T.; Bae, S.; Honda, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Hong, Y.-C. Asian Dust Effect on Cause-Specific Mortality in Five Cities across South Korea and Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansell, R.A.; Tsay, S.-C.; Hsu, N.C.; Ji, Q.; Bell, S.W.; Holben, B.N.; Welton, E.J.; Roush, T.L.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; et al. An Assessment of the Surface Longwave Direct Radiative Effect of Airborne Dust in Zhangye, China, during the Asian Monsoon Years Field Experiment (2008). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D00K39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, H.; Naoe, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Inomata, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Aerosol Concentrations Observed at Mt. Haruna, Japan, in Relation to Long-Range Transport of Asian Mineral Dust Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4638–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebert, B.J.; Bates, T.; Russell, P.B.; Shi, G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kawamura, K.; Carmichael, G.; Nakajima, T. An Overview of ACE-Asia: Strategies for Quantifying the Relationships between Asian Aerosols and Their Climatic Impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, ACE 1-1–ACE 1-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J. Transport Routes and Source Regions of Asian Dust Observed in Korea during the Past 40 Years (1965–2004). Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4778–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Um, J.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, Y.P. Chemical Composition Based Aerosol Optical Properties According to Size Distribution and Mixture Types during Smog and Asian Dust Events in Seoul, Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 54, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, K.; Kurosaki, Y.; Otani, S.; Yoshida, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Kurozawa, Y. Atmospheric Transport Route Determines Components of Asian Dust and Health Effects in Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira-Filho, M.; Pedrotti, J.J.; Fornaro, A. Water-Soluble Ions Species of Size-Resolved Aerosols: Implications for the Atmospheric Acidity in São Paulo Megacity, Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2016, 181, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, K.-L.; Lee, W.-J.; Lin, W.-Y.; Liao, C.-J.; Chaung, H.-C.; Chiu, C.-H. Water-Soluble Ions in Nano/Ultrafine/Fine/Coarse Particles Collected near a Busy Road and at a Rural Site. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.-F.; Cao, J.-J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High Secondary Aerosol Contribution to Particulate Pollution during Haze Events in China. Nature 2015, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Wen, T.-X.; Miao, H.-Y.; Gao, W.-K.; Wang, Y.-S. Concentrations and Size Distributions of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Aerosol Particles in Taiyuan, Shanxi. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3249–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Du, W.; Hong, Z.; Dai, N.; Yuan, C.-S. Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Components and Acidity of PM2.5 in a Coastal City of China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2152–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Kong, S.-F.; Liu, H.-B.; Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zheng, M.-M.; Zheng, S.-R.; Yang, G.-W.; Wu, F.-Q. Emission Inventory of Water Soluble Ions in Fine Particles from Residential Coal Burning in China and Implication for Emission Reduction. Zhongguo Huanjing Kexue/China Environ. Sci. 2017, 37, 3708–3721. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Kong, S.; Yan, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Zheng, H.; Wu, J.; Yao, L.; et al. Emission and Simulation of Primary Fine and Submicron Particles and Water-Soluble Ions from Domestic Coal Combustion in China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Hu, M.; Chen, B.; Han, C.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K.; et al. Long-Term Variability of Inorganic Ions in TSP at a Remote Background Site in Japan (Wajima) from 2005 to 2015. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Takami, A.; Sato, K.; Shimizu, A.; Yoshino, A.; et al. Comparative Analysis of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHS), Nitro-Pahs (NPAHS), and Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions (WSIIS) at Two Background Sites in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Song, C.B.; Kim, M.C.; Kwon, S.B.; Lee, K.W. Study on Size Distribution of Total Aerosol and Water-Soluble Ions during an Asian Dust Storm Event at Jeju Island, Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 93, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, T.; Schauer, J.J. Increases in the Formation of Water Soluble Organic Nitrogen during Asian Dust Storm Episodes. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-J.; Hsieh, L.-T.; Kao, M.-J.; Lin, W.-Y.; Huang, K.-L.; Lin, C.-C. Characteristics of Particles Sampled in Southern Taiwan during the Asian Dust Storm Periods in 2000 and 2001. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5925–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; He, H. Synergistic Reaction between SO2 and NO2 on Mineral Oxides: A Potential Formation Pathway of Sulfate Aerosol. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: https://www.data.jma.go.jp/gmd/env/kosahp/kosa_table_1.html (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Tang, N.; Hattori, T.; Taga, R.; Igarashi, K.; Yang, X.; Tamura, K.; Kakimoto, H.; Mishukov, V.F.; Toriba, A.; Kizu, R.; et al. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Nitropolycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Air Particulates and Their Relationship to Emission Sources in the Pan-Japan Sea Countries. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 5817–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Sato, K.; Tokuda, T.; Tatematsu, M.; Hama, H.; Suematsu, C.; Kameda, T.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Factors Affecting Atmospheric 1-, 2-Nitropyrenes and 2-Nitrofluoranthene in Winter at Noto Peninsula, a Remote Background Site, Japan. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, W.L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Hayakawa, K.; Nagao, S.; Tang, N. Variations in Traffic-Related Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Kanazawa, Japan, after the Implementation of a New Vehicle Emission Regulation. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.L.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Yang, L.; Nakatsubo, R.; Wei, Y.; Bi, J.; Shima, M.; Toriba, A.; et al. Natural Aeolian Dust Particles Have No Substantial Effect on Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A Laboratory Study Based on Naphthalene. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becagli, S.; Proposito, M.; Benassai, S.; Gragnani, R.; Magand, O.; Traversi, R.; Udisti, R. Spatial distribution of biogenic sulphur compounds (MSA, nssSO42–) in the northern Victoria Land–Dome C–Wilkes Land area, East Antarctica. Ann. Glaciol. 2005, 41, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sarin, M.M. Atmospheric Water-Soluble Constituents in Fine and Coarse Mode Aerosols from High-Altitude Site in Western India: Long-Range Transport and Seasonal Variability. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AD-Net/GALION Data Center. Available online: https://www-lidar.nies.go.jp/AD-Net/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Jin, Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.; Batdorj, D.; Sugimoto, N. Evolution of a Lidar Network for Tropospheric Aerosol Detection in East Asia. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 031219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.-C.; Li, J.; Che, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, H. Transport of East Asian Dust Storms to the Marginal Seas of China and the Southern North Pacific in Spring 2010. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasilo, T.; Hutchins, R.; Ruiz-González, C.; Giorgio, P. Transport and Transformation of Soil-Derived CO2, CH4 and DOC Sustain CO2 Supersaturation in Small Boreal Streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment and Tourism of Mongolia. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Air Quality Online Monitoring and Analysis Platform. Available online: https://www.aqistudy.cn/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Natural Earth. Available online: https://earth.nullschool.net/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Hong, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Chang, X. Analysis of Compositional Variation and Source Characteristics of Water-Soluble Ions in PM2.5 during Several Winter-Haze Pollution Episodes in Shenyang, China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Song, W.; Yang, X.; Fan, M.-Y. Specific Sources of Health Risks Caused by Size-Resolved PM-Bound Metals in a Typical Coal-Burning City of Northern China during the Winter Haze Event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, S.-S.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.-H. Pollution Characteristics and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Heating and Non-Heating Periods in Shenyang. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.E.; Chun, Y. The Comparison of Two Severe Hwangsa (Asian Dust) Cases of Spring and Winter in Seoul, Korea. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, T. Summertime PM2.5 Ionic Species in Four Major Cities of China: Nitrate Formation in an Ammonia-Deficient Atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, N.; Hakamata, M.; Sato, K.; Okada, Y.; Yang, X.; Tatematsu, M.; Toriba, A.; Kameda, T.; Hayakawa, K. Atmospheric Behaviors of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons at a Japanese Remote Background Site, Noto Peninsula, from 2004 to 2014. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.-K.; Lee, H.K.; Jun, N.-Y. Analysis of Regional and Temporal Characteristics of PM10 during an Asian Dust Episode in Korea. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yin, L.; Shang, X.; Xu, L. Chemical Characteristics of Particulate Matter during a Heavy Dust Episode in a Coastal City, Xiamen, 2010. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A. Environmental Impact of Residential Wood Combustion Emissions and Its Implications. J. Air Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1980, 30, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Hong, M.-S.; Ueda, H. Seasonal Variation of Aerosol Composition at Cheju Island, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 2407–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udisti, R.; Bazzano, A.; Becagli, S.; Bolzacchini, E.; Caiazzo, L.; Cappelletti, D.; Ferrero, L.; Frosini, D.; Giardi, F.; Grotti, M.; et al. Sulfate source apportionment in the Ny-Ålesund (Svalbard Islands) Arctic aerosol. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2016, 27, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Q. The Influence of Continental Air Masses on the Aerosols and Nutrients Deposition over the Western North Pacific. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 172, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Guazzotti, S.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Prather, K.A. Direct Observations of the Atmospheric Processing of Asian Mineral Dust. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 1213–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, C.C.-K.; Lee, C.T.; Yuan, C.S.; Hsu, W.C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsu, S.-C.; Liu, S.C. Implications of the Chemical Transformation of Asian Outflow Aerosols for the Long-Range Transport of Inorganic Nitrogen Species. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7508–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Cheng, C.L.; Huang, Y.; Tao, J.; Ren, Y.Q.; Wu, F.; Meng, J.J.; Li, J.J.; Cheng, Y.T.; Cao, J.J.; et al. Evolution of Aerosol Chemistry in Xi’an, Inland China, during the Dust Storm Period of 2013 – Part 1: Sources, Chemical Forms and Formation Mechanisms of Nitrate and Sulfate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 11571–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitby, K.T. The Physical Characteristics of Sulfur Aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1978, 12, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Z.; Ren, W.-H.; Yu, X.-N.; Hou, S.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-X. Characteristics and Sources of Water-Soluble Ion Pollution in PM2.5 in Winter in Shenyang. Huanjing Kexue/Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.P.; Shim, S.-G.; Moon, K.C.; Hu, C.-G.; Kang, C.H.; Park, K.Y. Monitoring of Air Pollutants at Kosan, Cheju Island, Korea, during March-April 1994. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1998, 37, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K. Sampling Artifacts of Acidity and Ionic Species in PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Chan, C.K. Inter-Particle and Gas-Particle Interactions in Sampling Artifacts of PM2.5 in Filter-Based Samplers. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Ji, G.; Ying, R.; Shan, Y.; Lin, Y. Seasonal Variations and Source Apportionment of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Nanjing, a Megacity in Southeastern China. J. Atmos. Chem. 2019, 76, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson-Pitts, B.J.; Wingen, L.M.; Sumner, A.L.; Syomin, D.; Ramazan, K.A. The Heterogeneous Hydrolysis of NO2 in Laboratory Systems and in Outdoor and Indoor Atmospheres: An Integrated Mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anttila, T.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; Tillmann, R.; Mentel, T.F. On the Reactive Uptake of Gaseous Compounds by Organic-Coated Aqueous Aerosols: Theoretical Analysis and Application to the Heterogeneous Hydrolysis of N2O5. J. Phys. Chem. A 2006, 110, 10435–10443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez, M.; Perner, D.; Hackenthal, E.-M.; Külzer, S.; Schütz, L. NO3 at Helgoland during the NORDEX Campaign in October 1996. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 22685–22695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallquist, M.; Stewart, D.J.; Stephenson, S.K.; Cox, R.A. Hydrolysis of N2O5 on Sub-Micron Sulfate Aerosols. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.H.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Reaction Probabilities for N2O5 Hydrolysis on Sulfuric Acid and Ammonium Sulfate Aerosols at Room Temperature. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, E.W.; Dibb, J.; Scheuer, E.; Jost, P.C.; Nault, B.A.; Jimenez, J.L.; Peterson, D.; Knote, C.; Fenn, M.; Hair, J.; et al. Asian Dust Observed during KORUS-AQ Facilitates the Uptake and Incorporation of Soluble Pollutants during Transport to South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Nagao, S.; Chen, B.; Tang, N. Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081210
Bai P, Zhang H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Nagao S, Chen B, Tang N. Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081210
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Pengchu, Hao Zhang, Xuan Zhang, Yan Wang, Lulu Zhang, Seiya Nagao, Bin Chen, and Ning Tang. 2022. "Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081210
APA StyleBai, P., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Nagao, S., Chen, B., & Tang, N. (2022). Chemical Characteristics of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in Different Types of Asian Dust in Wajima, a Background Site in Japan. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1210. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081210






