Simulation of the Boreal Winter East Asian Cold Surge by IAP AGCM4.1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model, Data, and Methods
3. Results
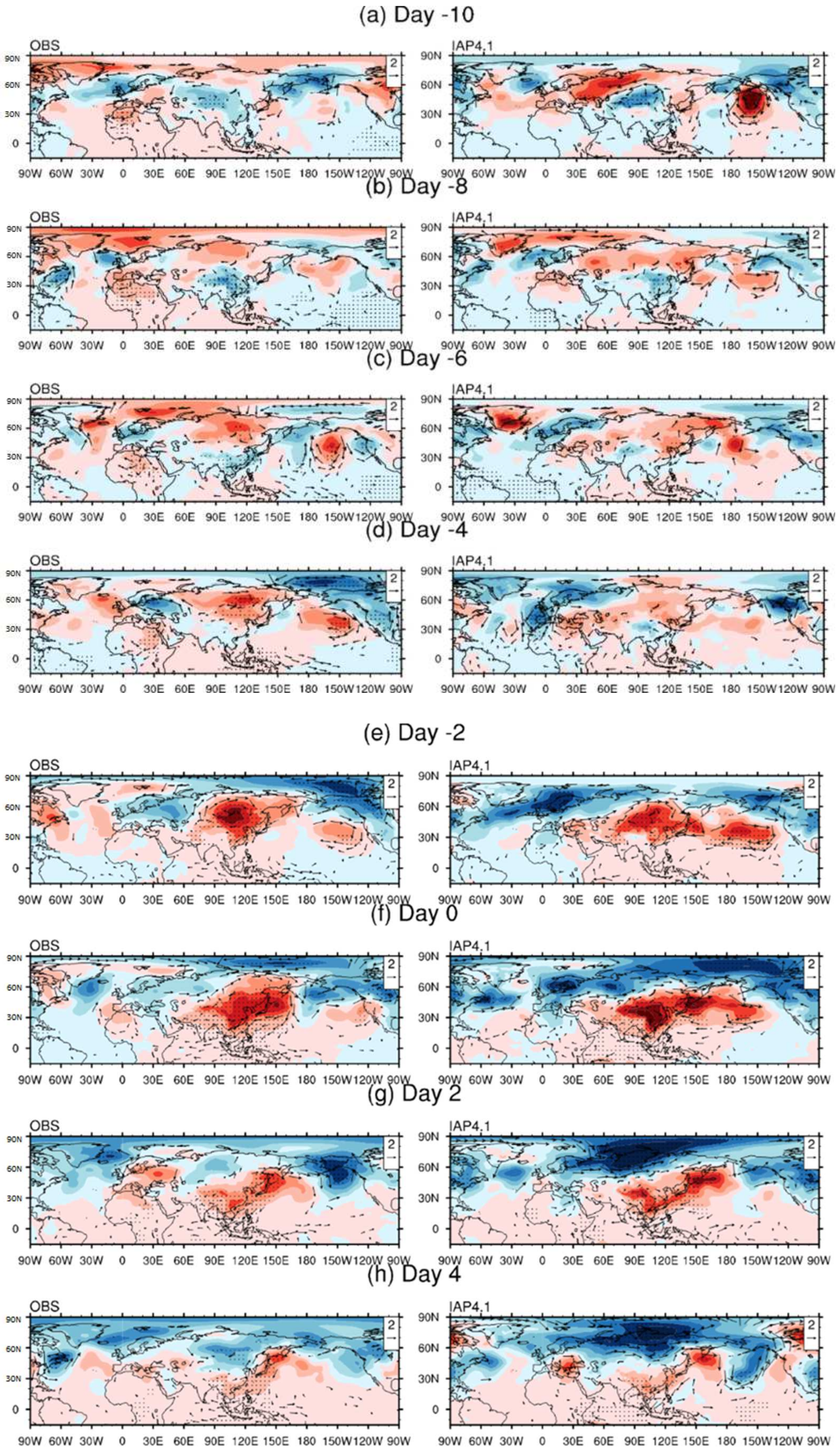
3.1. Mid-to-High Latitude Circulation Associated with CS Events
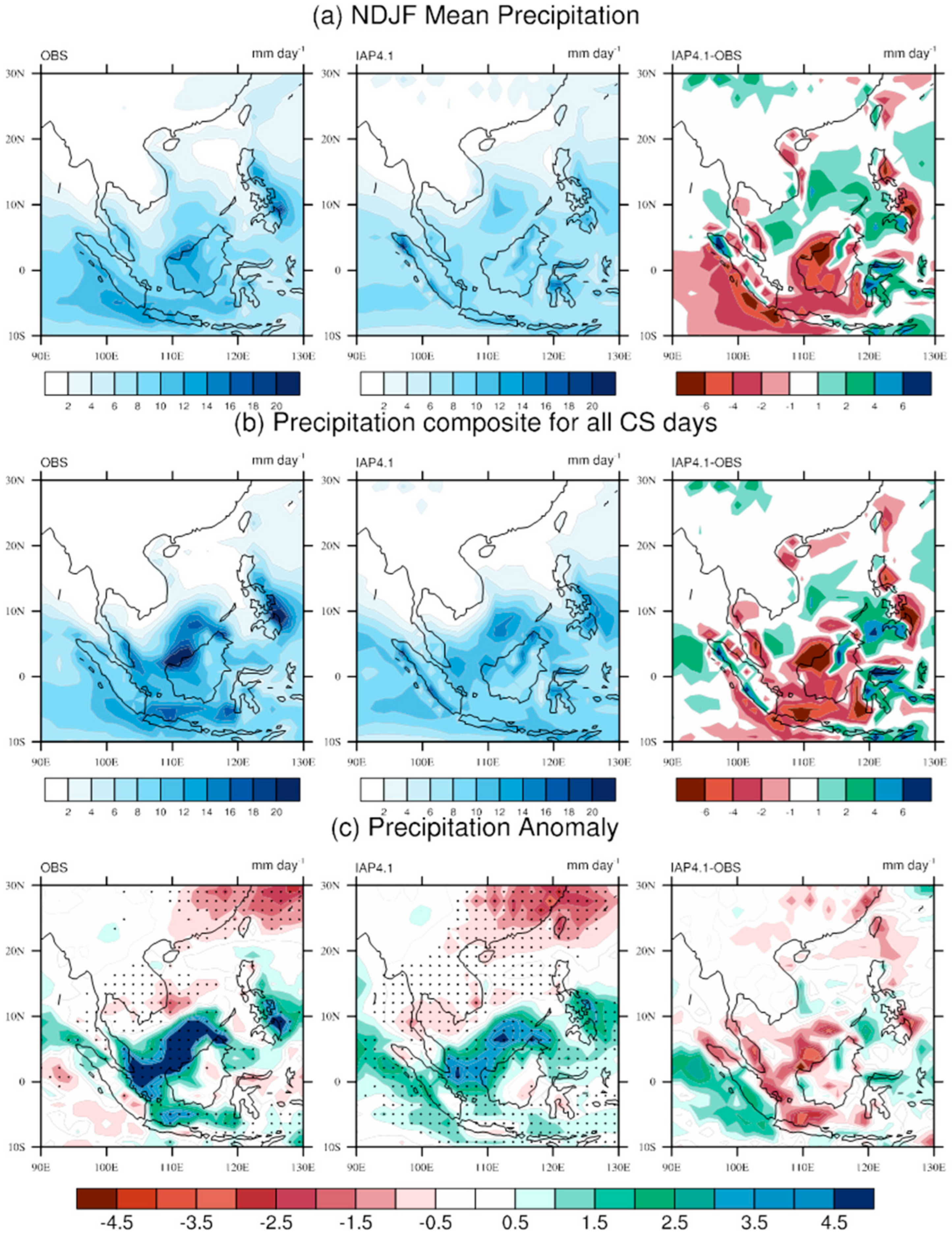
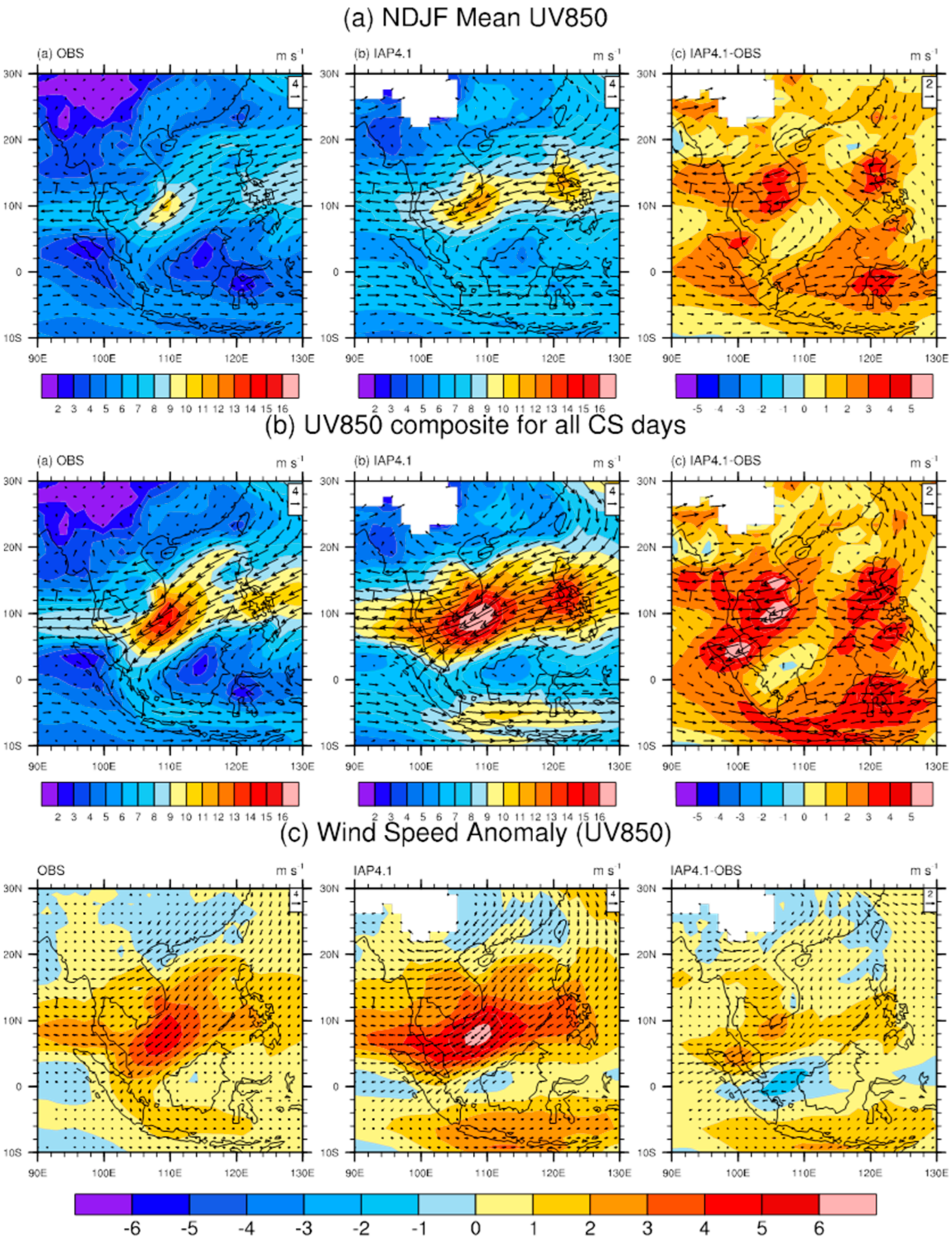
3.2. Rainfall and Circulation Associated with CS Days
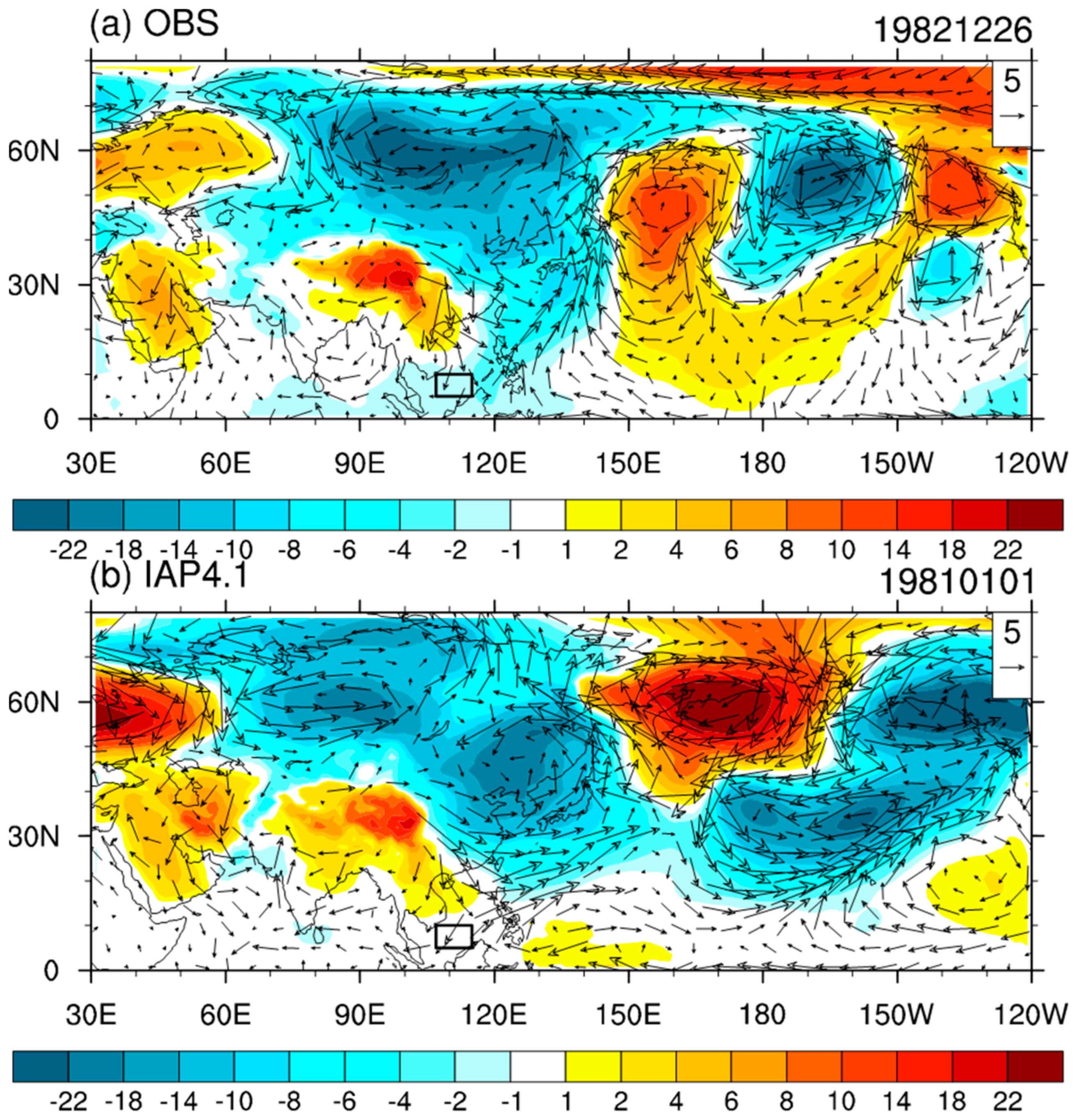
3.3. Negative W-Index Events
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compo, G.P.; Kiladis, G.N.; Webster, P.J. The horizontal and vertical structure of east Asian winter monsoon pressure surges. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-C.; Li, T. The Extreme Cold Anomaly over Southeast Asia in February 2008: Roles of ISO and ENSO*. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3786–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tian, W. Eurasian Cold Air Outbreaks under Different Arctic Stratospheric Polar Vortex Strengths. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 76, 1245–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, S.W.; Huang, C.S.Y.; Nakamura, N.; Omrani, N.-E.; Jucker, M. Role of Finite-Amplitude Rossby Waves and Nonconservative Processes in Downward Migration of Extratropical Flow Anomalies. J. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 75, 1385–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizadeh, E.; Lubis, S.W.; Hassanzadeh, P. The 3D structure of northern hemisphere blocking events: Climatology, role of moisture, and response to climate change. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Zeng, Q.C. A Study of East Asia Strong Cold Wave Surge Crossing Equator and Influencing the Development of Tropical Cyclone and Heavy Rainfall in the Southern Hemisphere. Clim. Environ. Res. 2005, 10, 507–525. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhang, X.; Wan, H.; Stott, P.; Lu, C. Anthropogenic Influence on the Eastern China 2016 Super Cold Surge. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, S123–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Ma, X.K.; Wang, F. Analysis of the January 2016 atmospheric circulation and weather. Meteorol. Mon. 2016, 42, 514–520. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wu, R. Processes for Occurrence of Strong Cold Events over Eastern China. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 9247–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Lu, R. Two Distinct Types of Extratropical Circulation Anomalies Associated with Cold Surges over the South China Sea. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 5069–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.Y.; Marzin, C.; Xavier, P.; Chang, C.-P.; Timbal, B. Impacts of Boreal Winter Monsoon Cold Surges and the Interaction with MJO on Southeast Asia Rainfall. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 4267–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-W.; Heo, J.-W.; Jeong, J.-H.; Ho, C.-H. Characteristics of East Asian Cold Surges in the CMIP5 Climate Models. Atmos. Kerean Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 27, 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Mailler, S.; Lott, F. Dynamical influence of the Tibetan Plateau on the winter monsoon over southeastern Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Q.-C. Sensitivity of Simulated Climate to Two Atmospheric Models: Interpretation of Differences between Dry Models and Moist Models. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 1558–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Jin, J.; Fei, K.; Ji, D.; Wu, C.; Zhu, J.; He, J.; Chai, Z.; Xie, J.; et al. CAS-ESM2: Description and Climate Simulation Performance of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Earth System Model (ESM) Version 2.0. J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2020, 12, e2020MS002210. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, R.B.; Gettelman, A.; Park, S.; Chen, C.-C.; Lauritzen, P.H.; Williamson, D.L.; Conley, A.J.; Garcia, R.; Kinnison, D.; Lamarque, J.F.; et al. Description of the NCAR Community Atmosphere Model (CAM 5.0) (No. NCAR/TN-486+STR); UCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Xue, F.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q. Evaluation of Surface Air Temperature Change over China and the Globe during the Twentieth Century in IAP AGCM4.0. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2012, 5, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, X.; Su, T.; Wang, J.; Lin, R. Decadal variation of the Aleutian Low-Icelandic Low seesaw simulated by a climate system model (CAS-ESM-C). Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2014, 7, 110–114. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Xue, F. Phase transition of the Pacific decadal oscillation and decadal variation of the East Asian summer monsoon in the 20th century. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Xue, F.; Zhang, H. Simulating the Intraseasonal Variation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon by IAPAGCM4.0. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, H. The Relationship between the East Asian Subtropical Westerly Jet and Summer Precipitation over East Asia as Simulated by the IAP AGCM4.0. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2014, 7, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.W. Evaluation of the Simulated Tropical Cyclones over the Western North Pacific with IAP AGCM4.1 Based on K-means Method. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 44, 1141–1154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, W.L. AMIP: The Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 73, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinski, S.; Maher, N.; Olonscheck, D. How large does a large ensemble need to be? Earth Syst. Dyn. 2020, 11, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tam, C.-Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, S.; Lau, N.-C.; Chen, J.; Laohalertchai, C. Roles of land-surface properties and terrains on Maritime Continent rainfall and its seasonal evolution. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 6681–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Chan, A.; Ashfold, M.; Ooi, C.; Azari, M. Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, S.W.; Jacobi, C. The modulating influence of convectively coupled equatorial waves (CCEWs) on the var-iability of tropical precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1465–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaeda, N.; Kiladis, G.; Dias, J. The Diurnal Cycle of Rainfall and the Convectively Coupled Equatorial Waves over the Maritime Continent. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3307–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peatman, S.C.; Schwendike, J.; Birch, C.E.; Marsham, J.H.; Matthews, A.J.; Yang, G. A Local-to-Large scale view of Maritime Continent rainfall: Control by ENSO, MJO, and equatorial waves. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 8933–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubis, S.W.; Respati, M.R. Impacts of convectively coupled equatorial waves on rainfall extremes in Java, Indonesia. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, 2418–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, F.R.; Lubis, S.W.; Setiawan, S. Impacts of the Madden–Julian oscillation on precipitation extremes in Indonesia. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 1970–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, S.V.; Liu, J.; Nguyen, N.S.; Vu, M.T.; Liong, S.-Y. Assessment of CMIP5 historical simulations of rainfall over Southeast Asia. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bioclimatol. Ser. B 2017, 132, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Time Period | Full Definition | CS Definition without SLP Limitation | CS Definition without Meridional Wind Limitation | CS Definition without Zonal Wind Limitation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observation | IAP4.1 | Obs | IAP4.1 | Obs | IAP4.1 | Obs | IAP4.1 | |
| NDJF 1979–2005 | ||||||||
| Vclm (m/s) | 8.07 | 8.65 | 8.07 | 8.65 | 8.07 | 8.65 | 8.07 | 8.65 |
| Vstd (m/s) | 2.95 | 3.58 | 2.95 | 3.58 | 2.95 | 3.58 | 2.95 | 3.58 |
| Vmin (m/s) | 10.28 | 11.34 | 10.28 | 11.34 | 10.28 | 11.34 | 10.28 | 11.34 |
| CS days | 619 | 489 | 701 | 641 | 619 | 508 | 628 | 490 |
| CS events | 120 | 97 | 132 | 108 | 120 | 102 | 120 | 97 |
| AD (days) | 5.18 | 4.93 | 5.52 | 5.97 | 5.18 | 4.90 | 5.28 | 4.93 |
| D10 (days) | 10 | 7 | 13 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 11 | 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, R.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Jin, J. Simulation of the Boreal Winter East Asian Cold Surge by IAP AGCM4.1. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081176
Lin R, Dong X, Zhang H, Wu C, Jin J. Simulation of the Boreal Winter East Asian Cold Surge by IAP AGCM4.1. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081176
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Renping, Xiao Dong, He Zhang, Chenglai Wu, and Jiangbo Jin. 2022. "Simulation of the Boreal Winter East Asian Cold Surge by IAP AGCM4.1" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081176
APA StyleLin, R., Dong, X., Zhang, H., Wu, C., & Jin, J. (2022). Simulation of the Boreal Winter East Asian Cold Surge by IAP AGCM4.1. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081176









