Source Apportionment of Ambient Aerosols during a Winter Pollution Episode in Yinchuan by Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
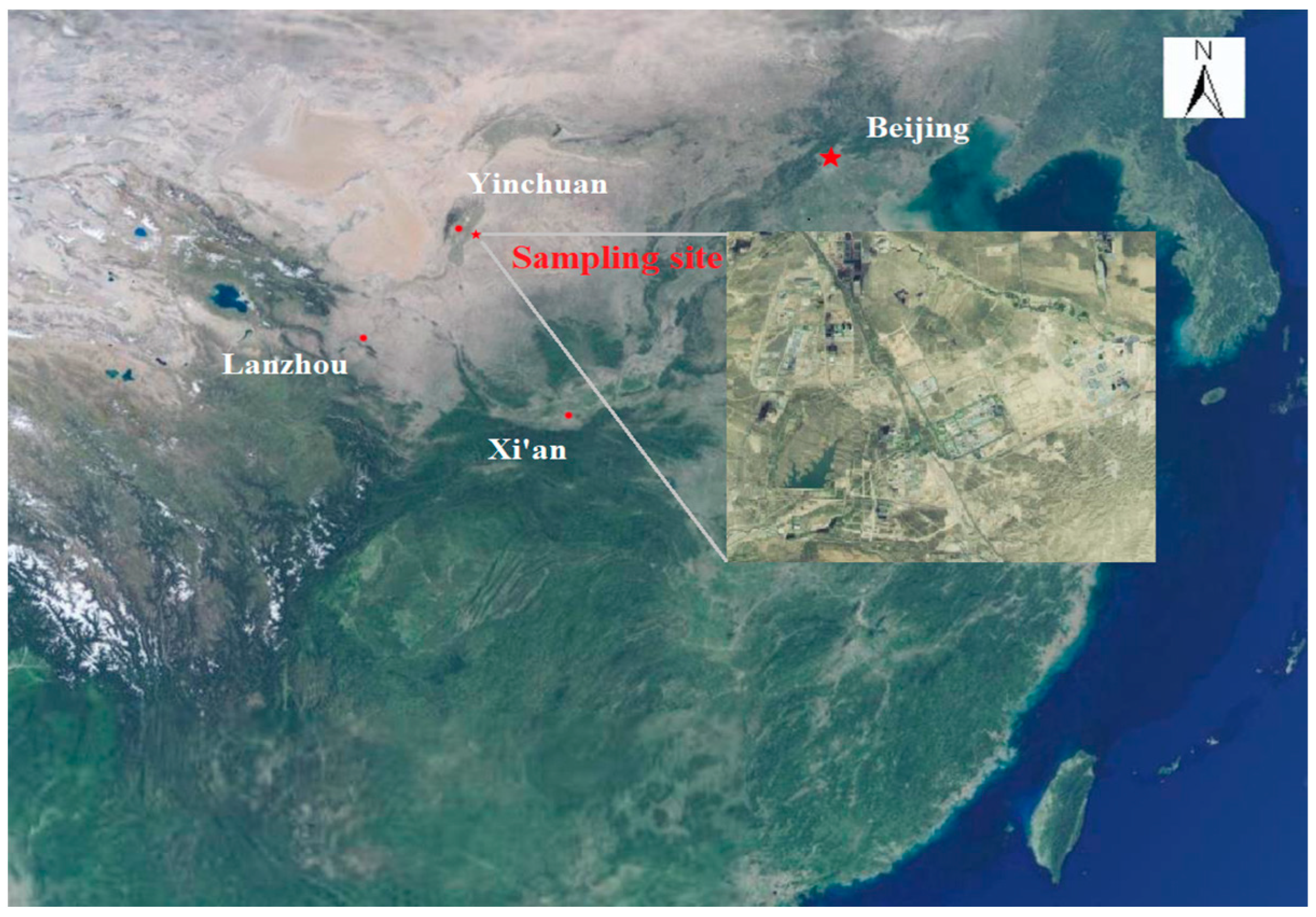
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
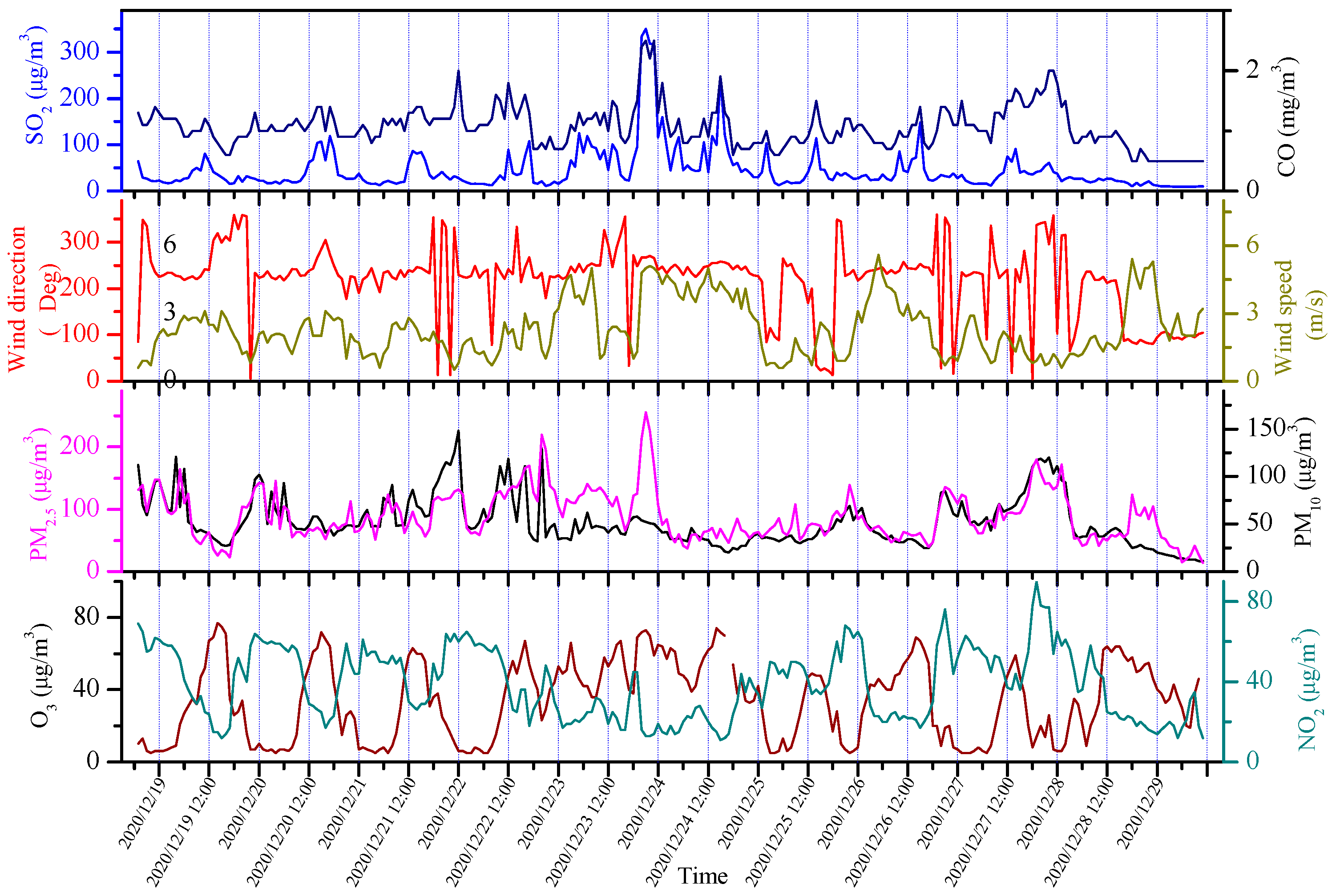
3.1. Air Quality and Meteorological Conditions
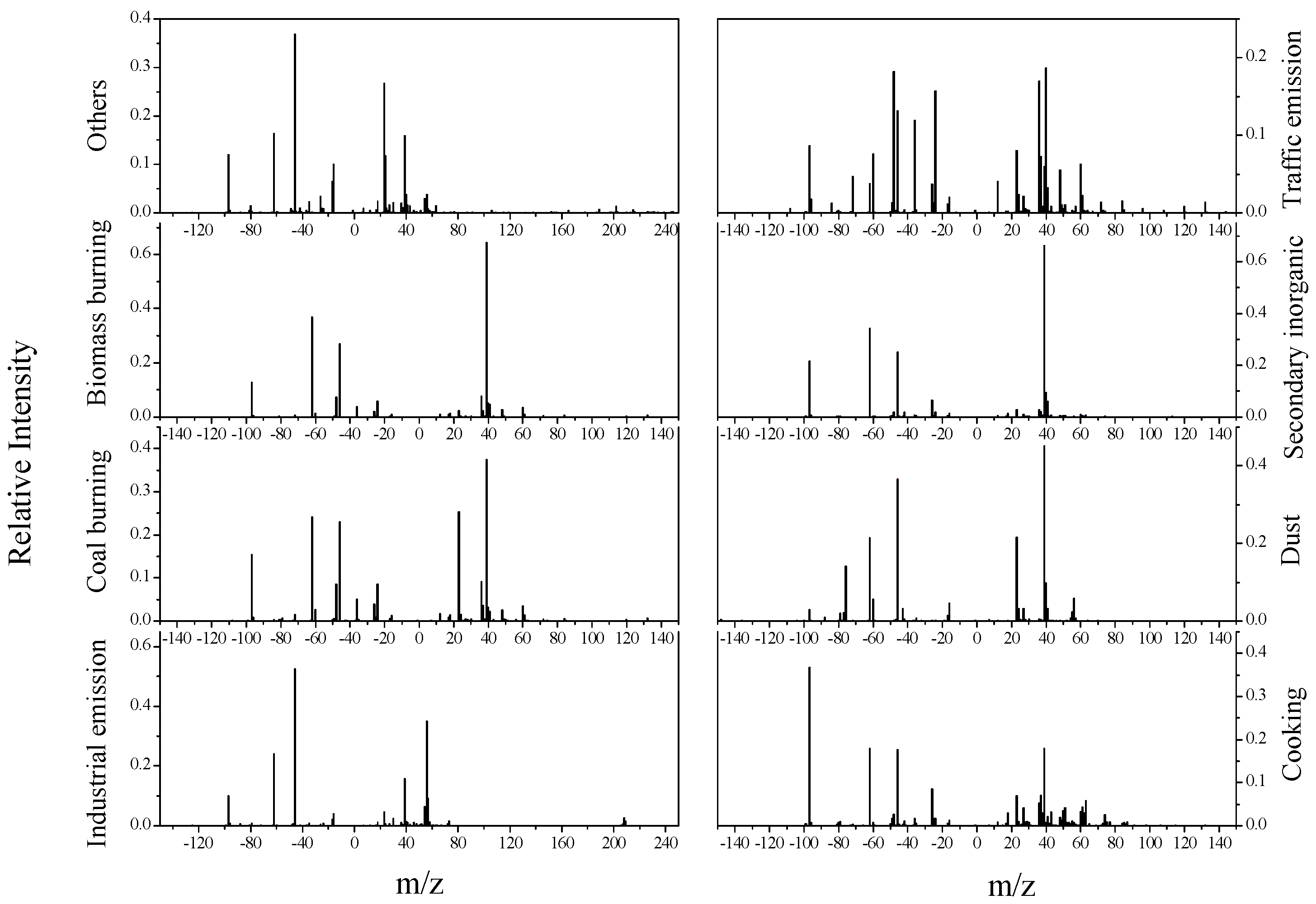
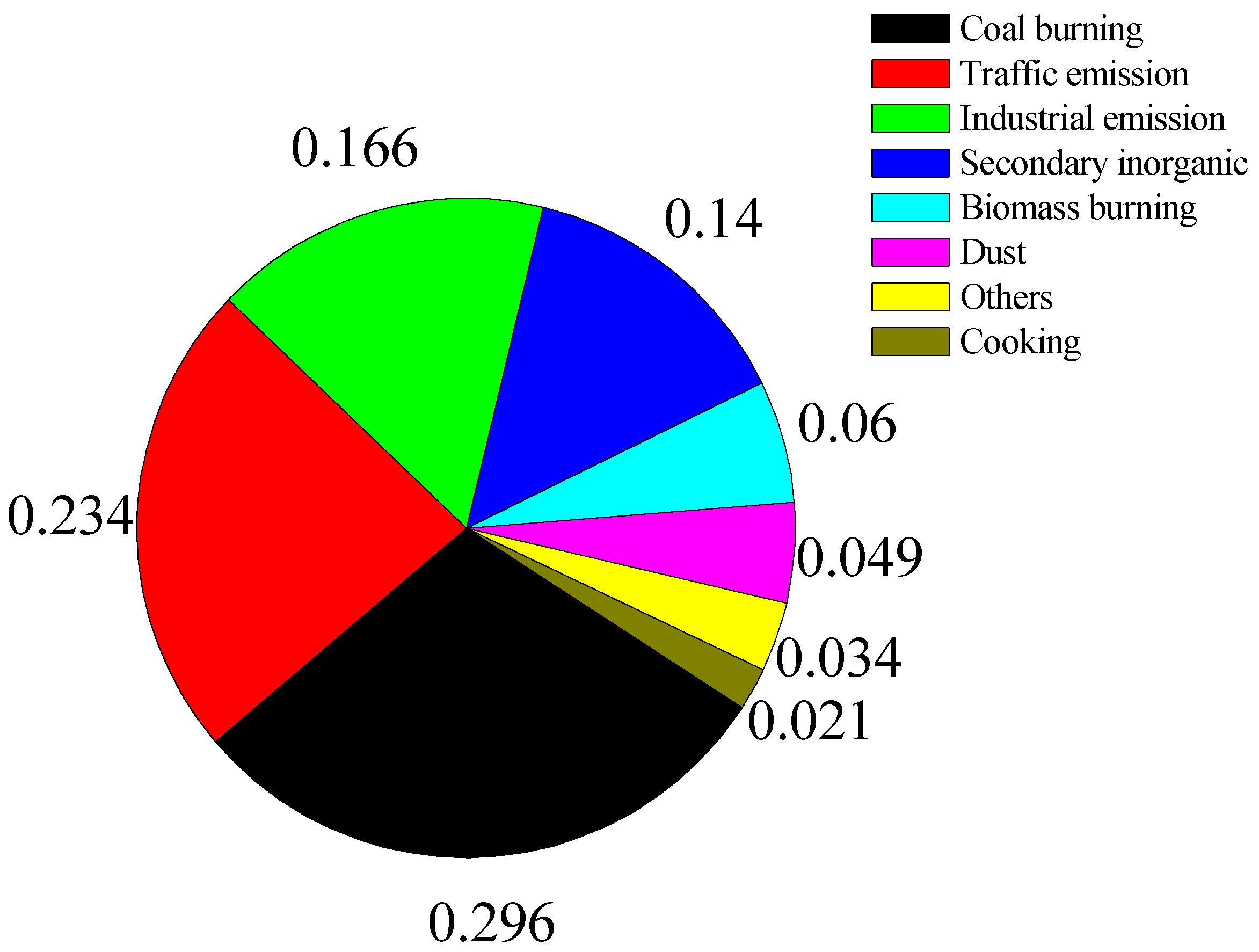
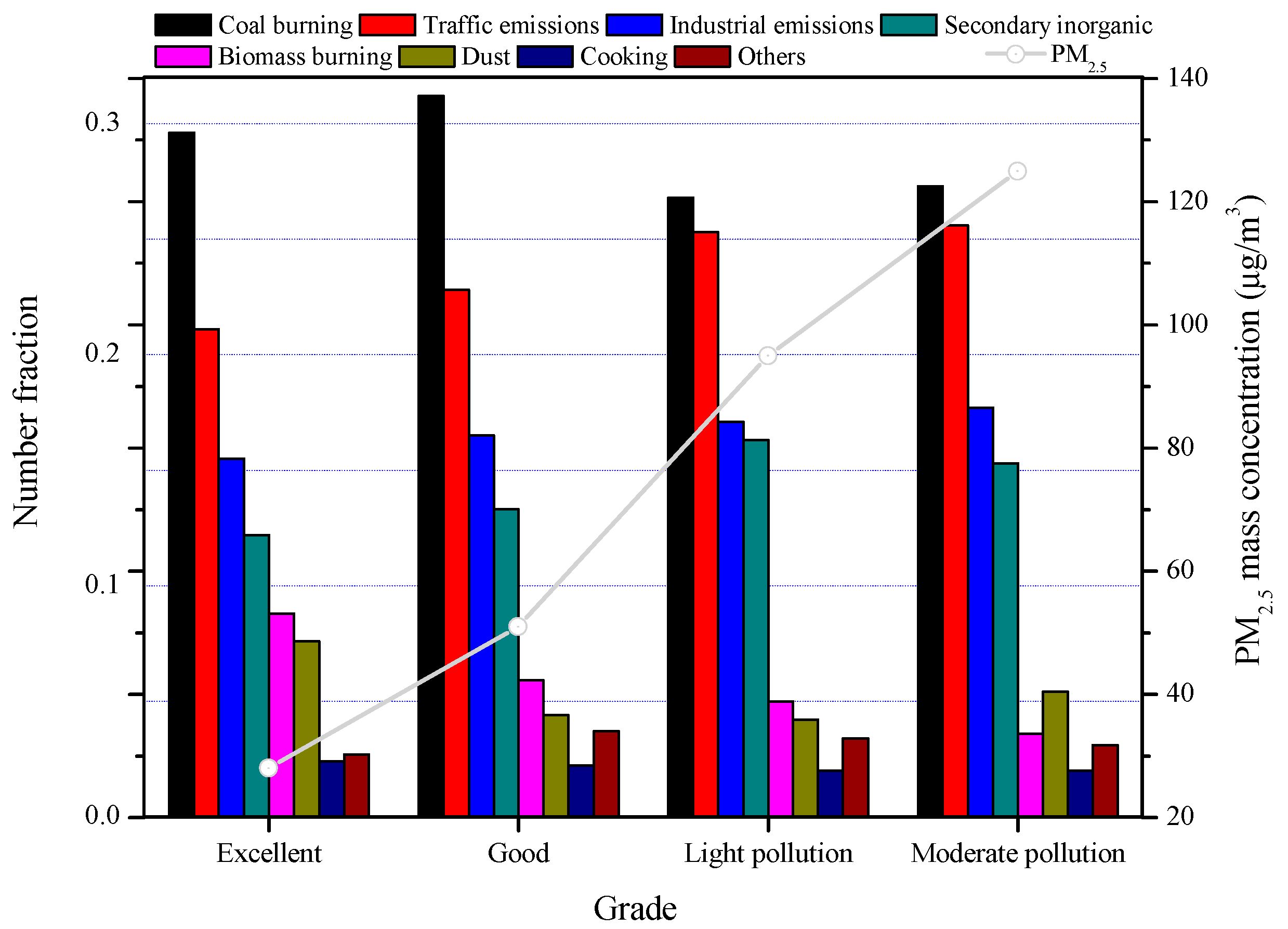
3.2. Overall Source Apportionment
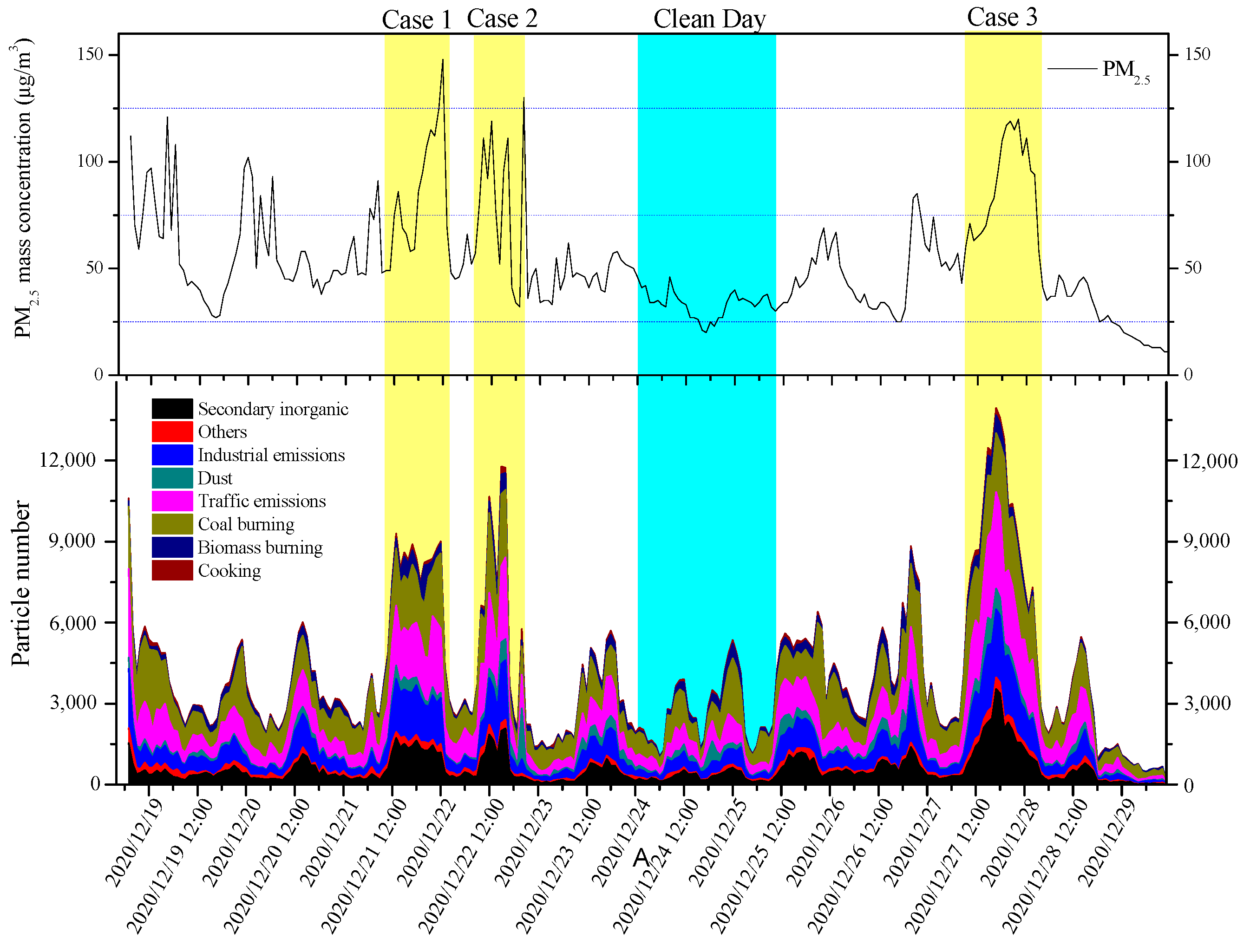
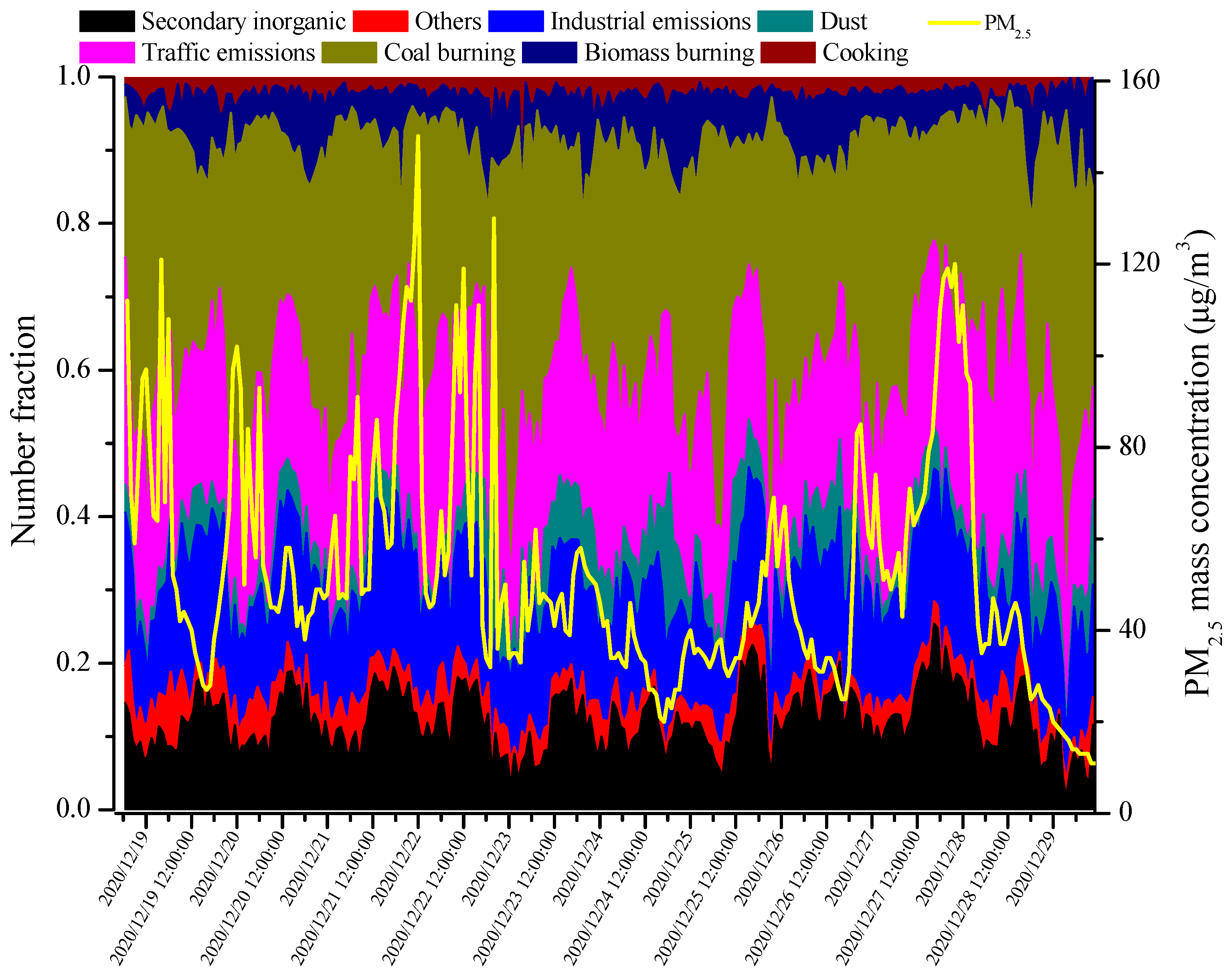
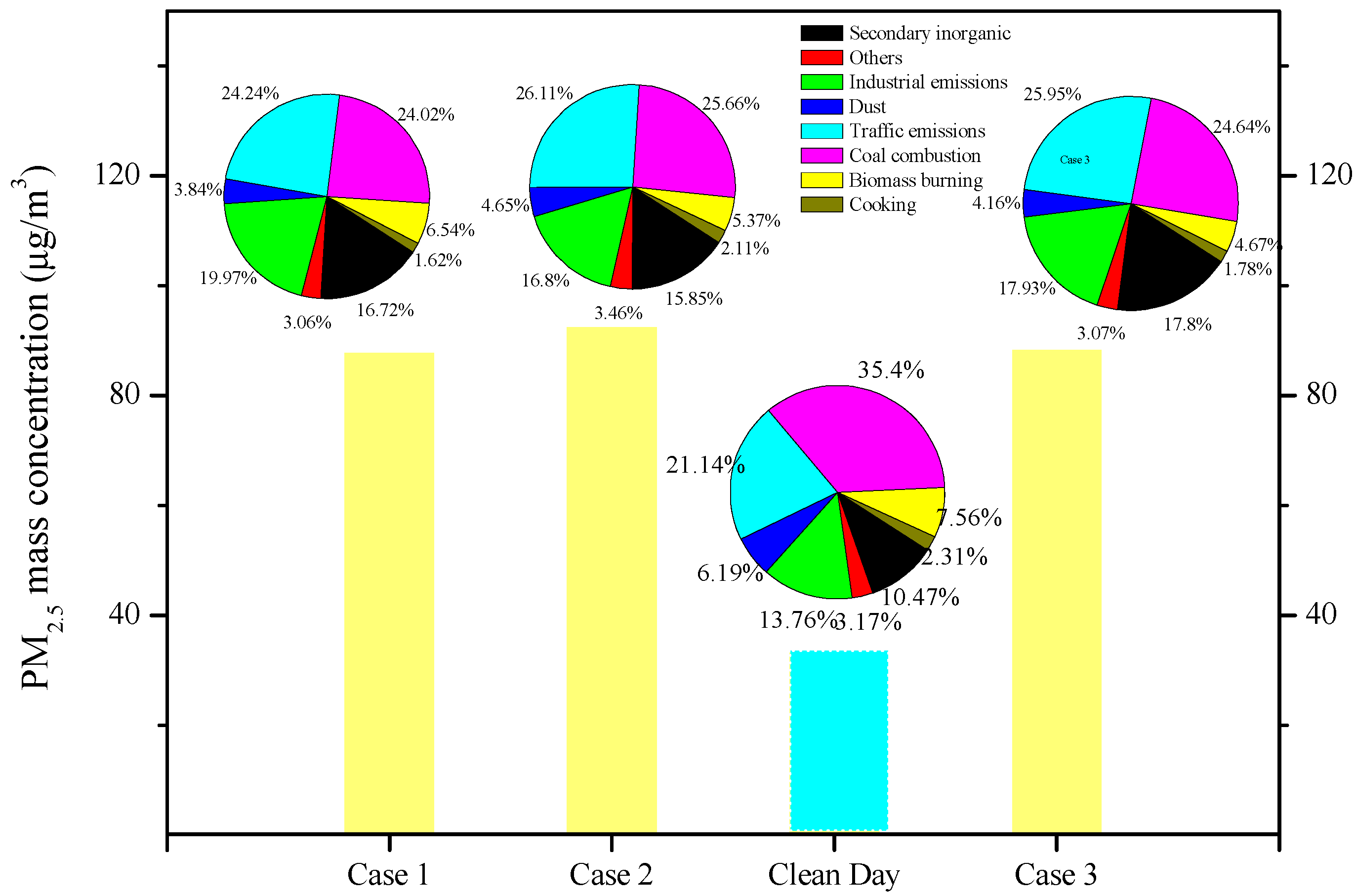
3.3. Temporal Variation in Ambient Aerosols
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gard, E.E.; Kleeman, M.J.; Gross, D.S.; Hughes, L.S.; Allen, J.O.; Morrical, B.D.; Fergenson, D.P.; Dienes, T.; Gälli, M.E.; Johnson, R.J.; et al. Direct observation of heterogeneous chemistry in the atmosphere. Science 1998, 279, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Change, I.C. The Scientific Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Du, Z.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Duan, F.; Chen, G. Characteristics of PM 2.5 speciation in representative megacities and across China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5207–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Qu, J.J.; Hao, X. Haze trends over the capital cities of 31 provinces in China, 1981–2005. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 97, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, B.; Tang, G.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D. Researching significance, status and expectation of haze in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Adv. Earth Sci. 2014, 29, 388–396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, M.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Bi, X.; Cheng, P. Real time bipolar time-of-flight mass spectrometer for analyzing single aerosol particles. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 303, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Yan, C.; Zheng, M.; Cai, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Fu, Z.; Li, M.; Li, L. Application of on-line single particle aerosol mass spectrometry (SPAMS) for studying major components in fine particulate matter. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2014, 35, 4070–4077. [Google Scholar]
- Bhave, P.V.; Allen, J.O.; Morrical, B.D.; Fergenson, D.P.; Cass, G.R.; Prather, K.A. A field-based approach for determining ATOFMS instrument sensitivities to ammonium and nitrate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4868–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Song, X.-H.; Hopke, P.K.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Classification of single particles analyzed by ATOFMS using an artificial neural network, ART-2A. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Harrison, R.M. Chemical characterisation of single airborne particles in Athens (Greece) by ATOFMS. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7614–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.C.; Gietl, J.K.; Olatunbosun, O.A.; Yang, X.; Harrison, R.M. Characteristics of tyre dust in polluted air: Studies by single particle mass spectrometry (ATOFMS). Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Gross, D.; Wang, H.; Qiao, L. A case study of the highly time-resolved evolution of aerosol chemical and optical properties in urban Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3931–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ren, Y.; Hong, G.; Lu, N.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Jin, W. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a multi-day haze in the winter of Shijiazhuang using a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer (SPAMS). Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 3972–3980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Ma, L.; Cheng, C.; Pei, C.; Chan, C.K.; Bi, X.; Qin, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M. Real time analysis of lead-containing atmospheric particles in Guangzhou during wintertime using single particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 168, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Huang, Z.; Gao, W.; Chen, D.; Fu, Z.; Nian, H.; Zou, L. Comparative analysis of chemical composition and sources of aerosol particles in urban Beijing during clear, hazy, and dusty days using single particle aerosol mass spectrometry. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.; De Foy, B.; Molina, L.A.; Molina, M.; Prather, K. Measurement of ambient aerosols in northern Mexico City by single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4499–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Shi, X.-R.; Tian, Y.-Z.; Xu, J.; Shi, G.-L.; Feng, Y.-C. Analysis of chemical composition of the fine particulate matter in summer in Tianjin city via a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer (SPAMS). Huan Jing Ke Xue 2018, 39, 3492–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Shi, G.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Huangfu, Y.; Xu, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, W. Source apportionment using receptor model based on aerosol mass spectra and 1 h resolution chemical dataset in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wen, J.; Xu, J.; Tian, Y.; Shi, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, M. Characteristics of single urban raised dust and soil dust in Tianjin city. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 844–852. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Chen, H.; Du, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Geng, F. Evolution of the mixing state of fine aerosols during haze events in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.-Y.; Lou, S.-R.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhou, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Zhou, Z.; Qiao, L.-P.; Huang, C.; Li, M.; Li, L. Aging and mixing state of particulate matter during aerosol pollution episode in autumn Shanghai using a single particle aerosol mass spectrometer (SPAMS). Huan Jing Ke Xue 2013, 34, 2071–2080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Han, B.; Bi, X.; Dai, S.; Huang, W.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Z. Characteristics of individual particles in the atmosphere of Guangzhou by single particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, X.; Lin, Q.; Peng, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Brechtel, F.J.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Peng, P.A.; Sheng, G. In situ detection of the chemistry of individual fog droplet residues in the Pearl River Delta region, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 9105–9116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wenger, J.C.; Yang, F.; Cao, J.; Huang, R.; Shi, G.; Zhang, S.; Tian, M.; Wang, H. Source characterization of urban particles from meat smoking activities in Chongqing, China using single particle aerosol mass spectrometry. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M. The design of single particle laser mass spectrometers. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.H.; Xu, F.X.; Zou, B.; Li, S.X.; Yang, Z.L. Spatial-temporal characteristics of haze in the key tourism cities of China. Trop. Geogr. 2018, 38, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Xu, T.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J. Thermal desorption single particle mass spectrometry of ambient aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ye, X.; Pang, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Temporal variations in the hygroscopicity and mixing state of black carbon aerosols in a polluted megacity area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15201–15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, X. Effect of Pollution Level on Size Distributions and Mixing State of Ambient Black Carbon Particles in an Urban Area during Wintertime. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Huang, Z.; Gao, W.; Nian, H.; Fu, Z.; Gao, J.; Chai, F.; Zhou, Z. Ambient particle characterization by single particle aerosol mass spectrometry in an urban area of Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, X. Effects of Volatile Components on Mixing State and Size Distribution of Individual Black Carbon Aerosols. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.T.; Shields, L.G.; Prather, K.A. Simultaneous measurement of the effective density and chemical composition of ambient aerosol particles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, K.; Li, L.; Huang, B.; Han, Z. Source Apportionment of Ambient Aerosols during a Winter Pollution Episode in Yinchuan by Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081174
Li K, Li L, Huang B, Han Z. Source Apportionment of Ambient Aerosols during a Winter Pollution Episode in Yinchuan by Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(8):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081174
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Kangning, Liukun Li, Bin Huang, and Zengyu Han. 2022. "Source Apportionment of Ambient Aerosols during a Winter Pollution Episode in Yinchuan by Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry" Atmosphere 13, no. 8: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081174
APA StyleLi, K., Li, L., Huang, B., & Han, Z. (2022). Source Apportionment of Ambient Aerosols during a Winter Pollution Episode in Yinchuan by Using Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry. Atmosphere, 13(8), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13081174




