Aerosol Distributions and Transport over Southern Morocco from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations (2004–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
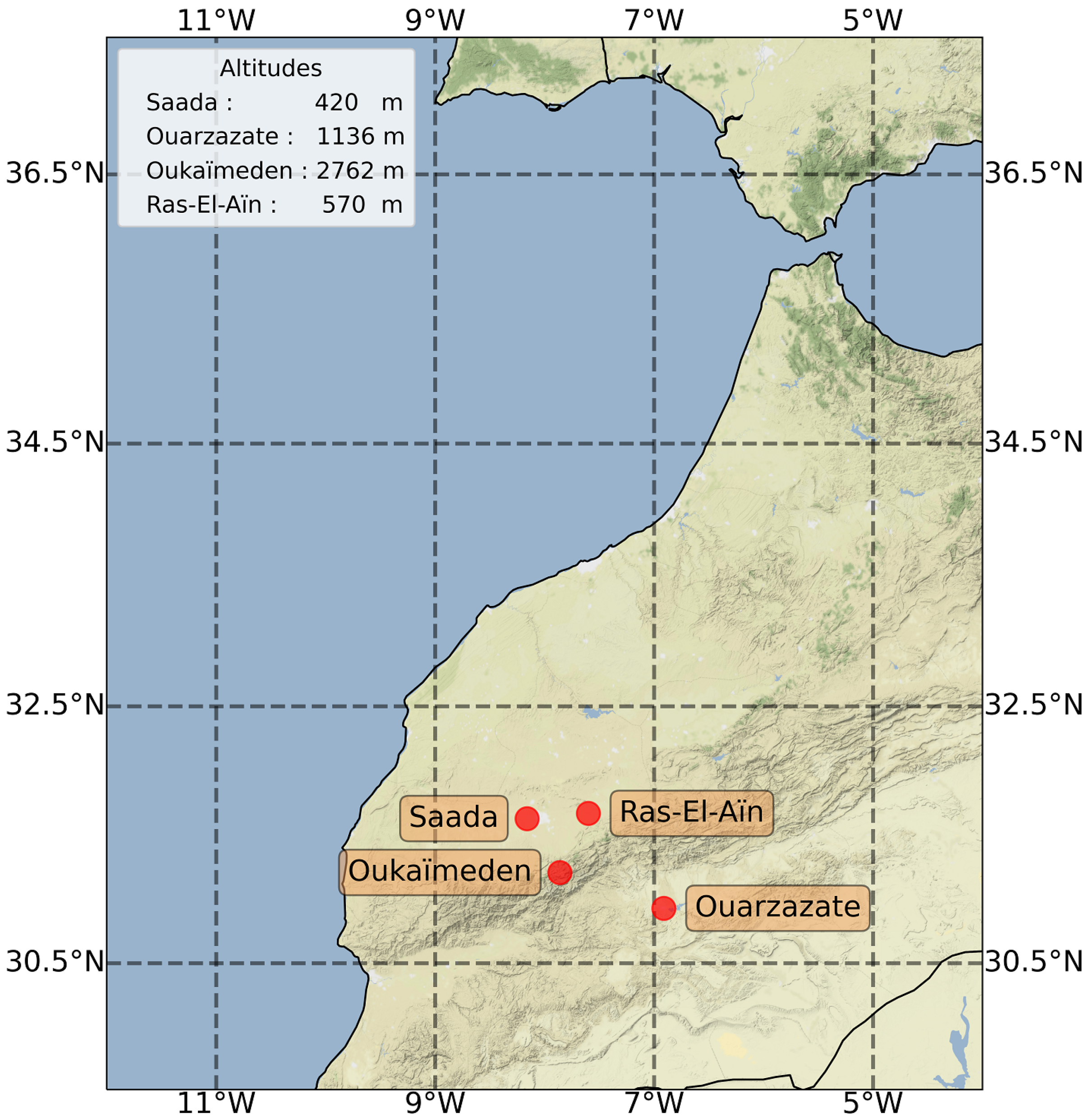
2. Study Area, Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Instruments and Back-Trajectory Model
2.2.1. AERONET Photometers
2.2.2. Aerosol Observations by MODIS
2.2.3. MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis
2.2.4. CAMS Reanalysis
2.3. Methodology
2.4. The HYSPLIT Trajectories
3. Results
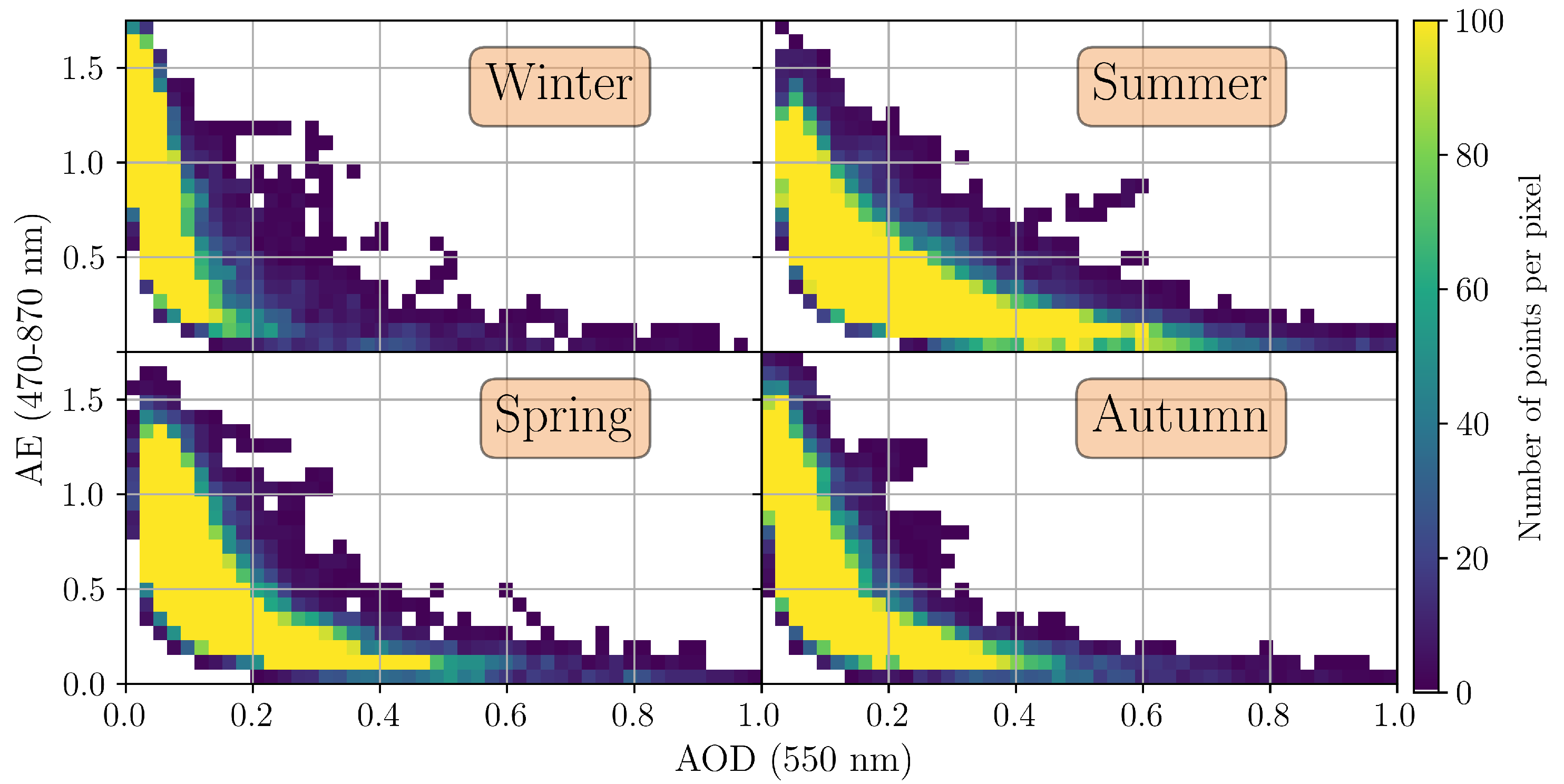
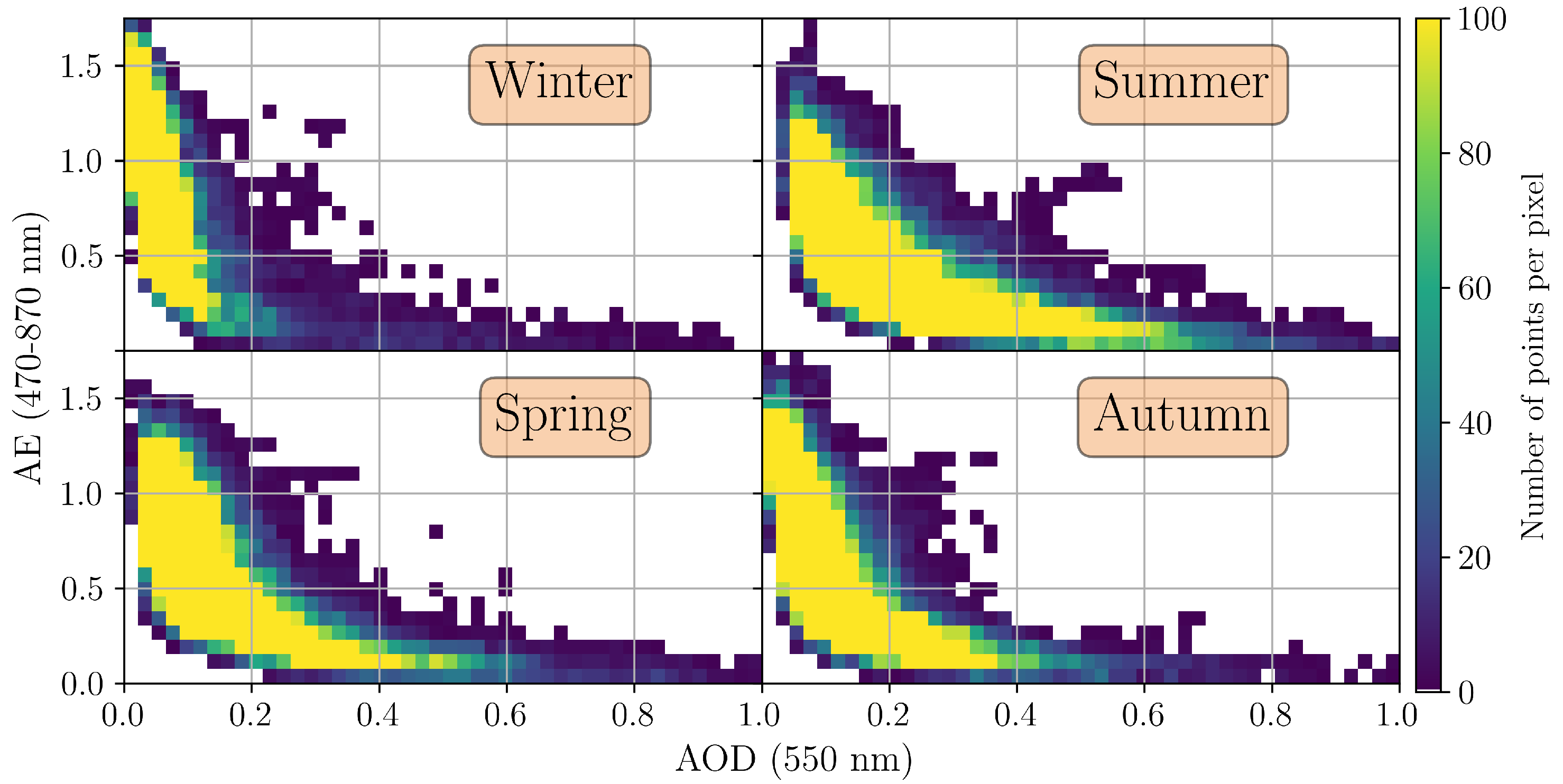
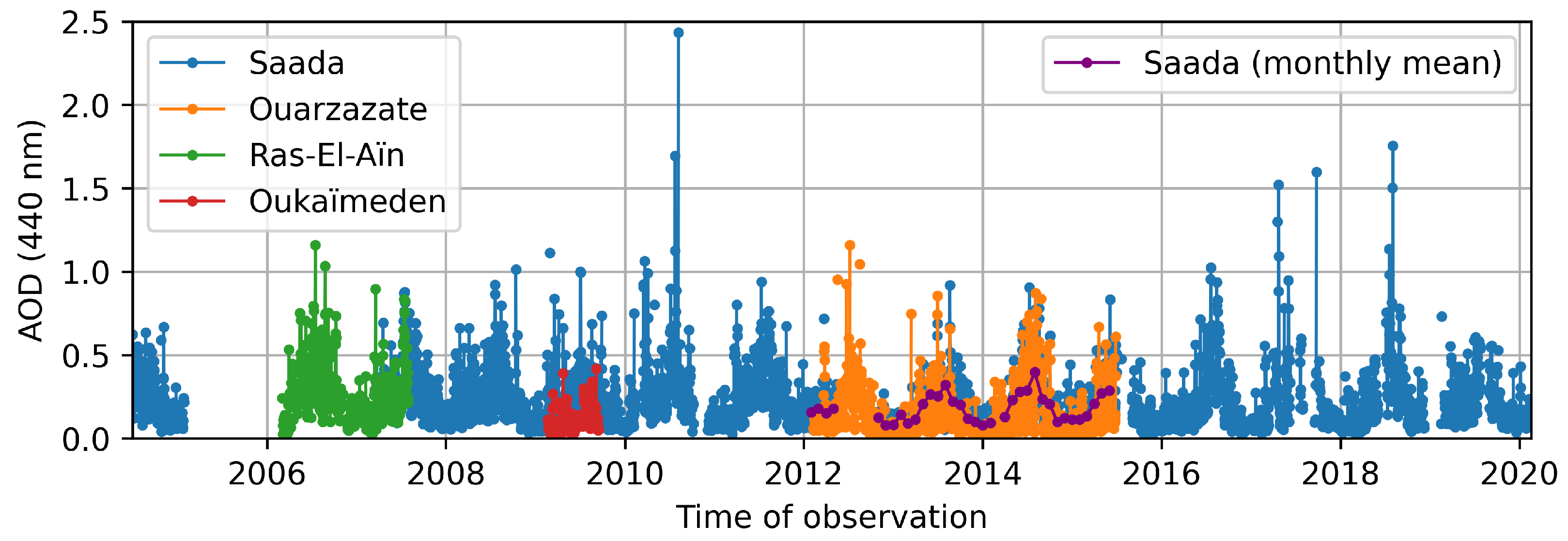
3.1. AERONET Observations
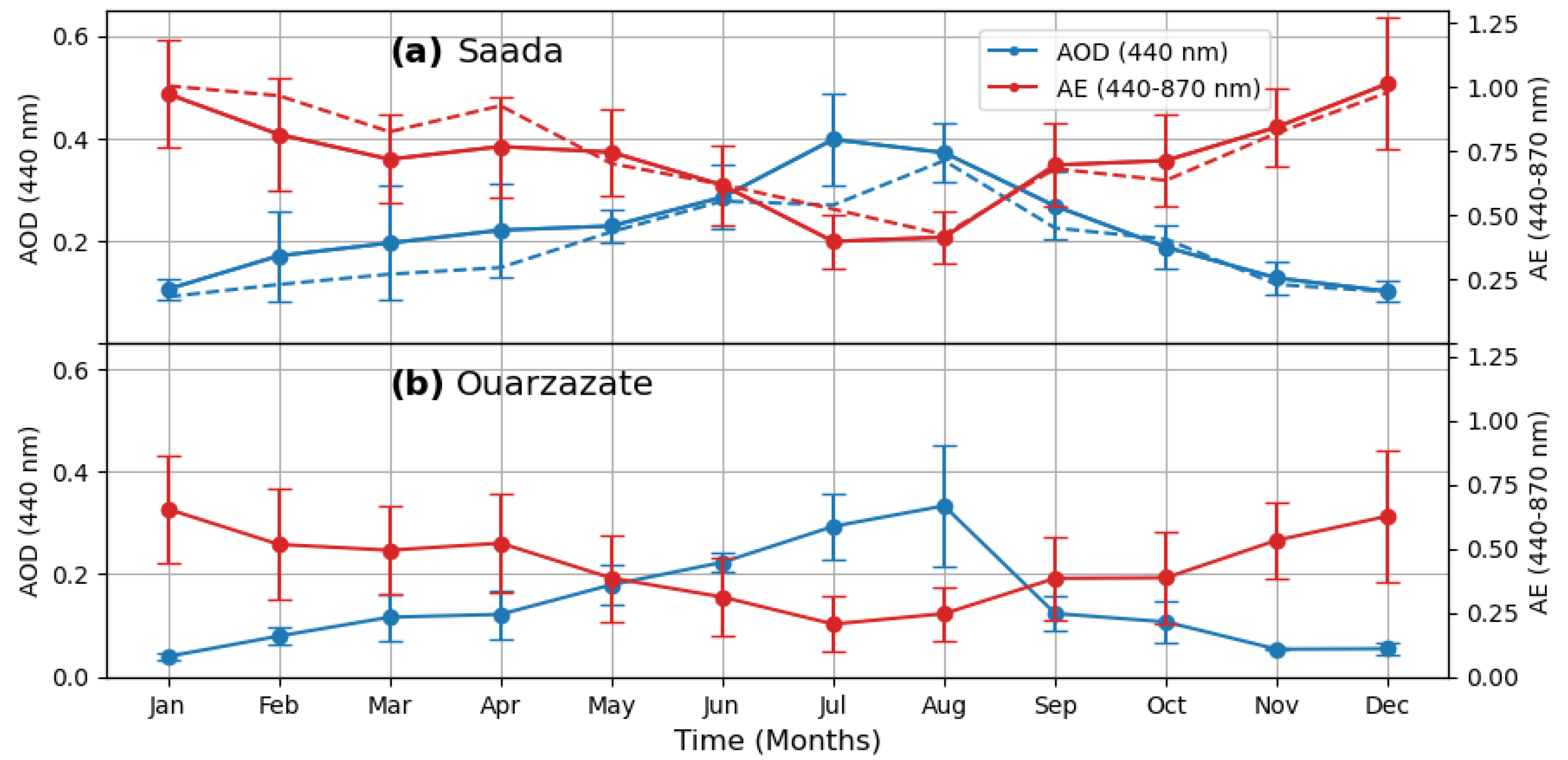
3.1.1. Daily Measurements
3.1.2. Multi-Year Variations
3.2. Inter-Comparison
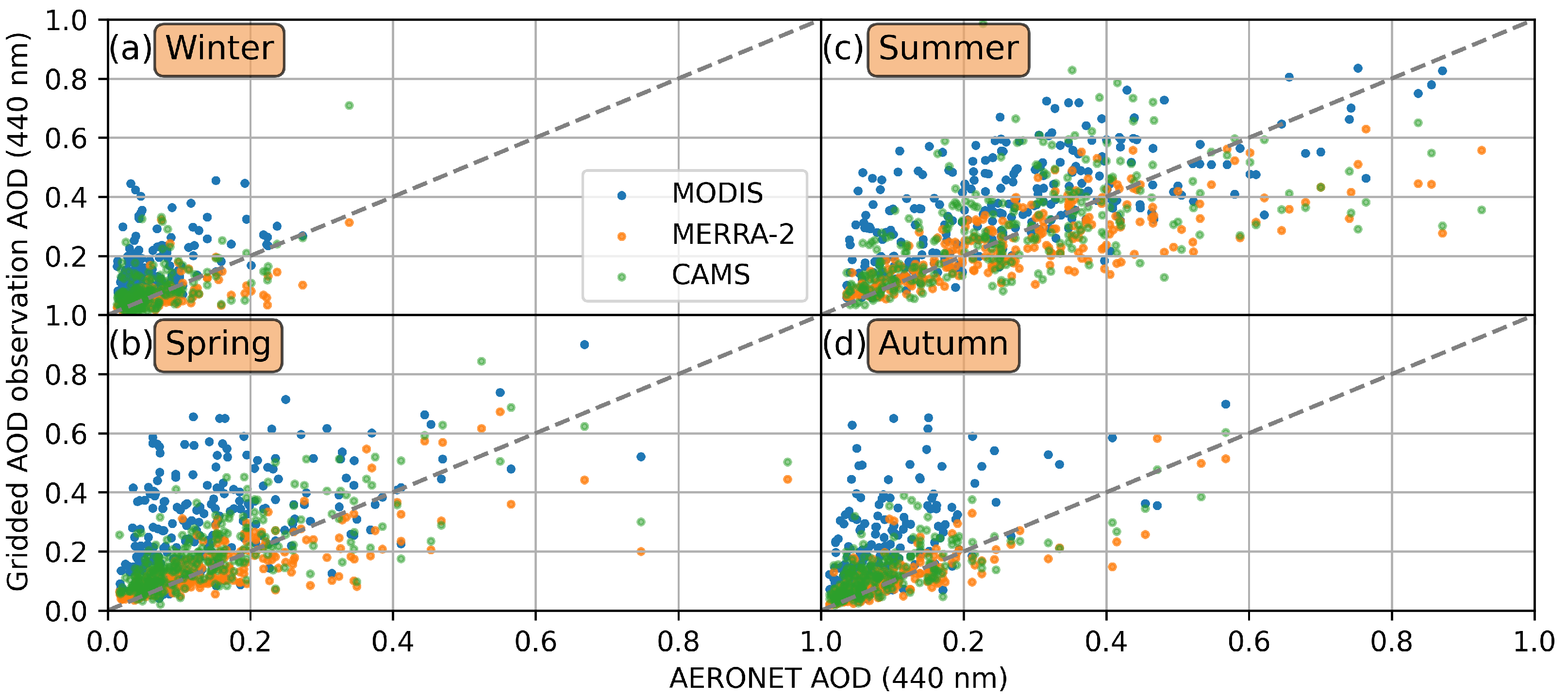
3.2.1. Temporal Comparison
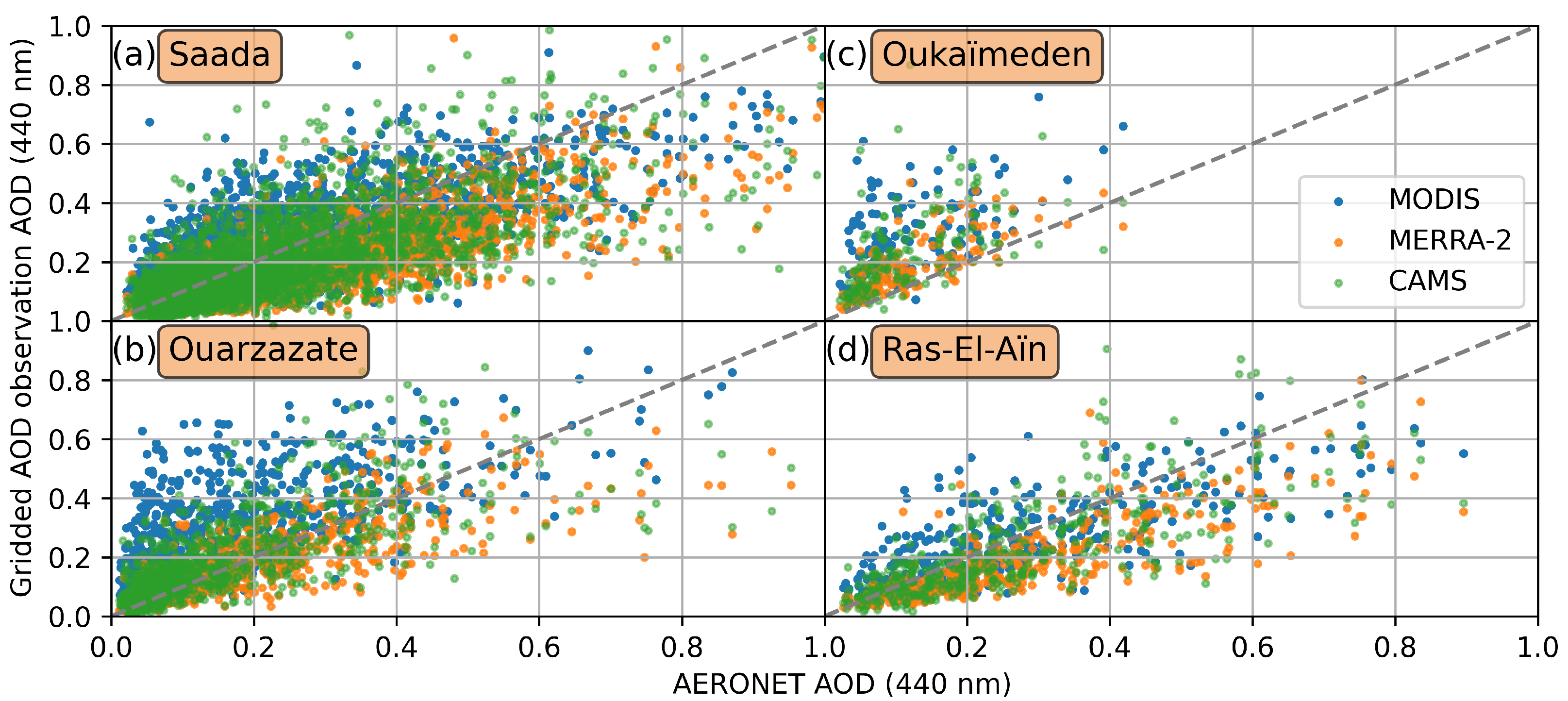
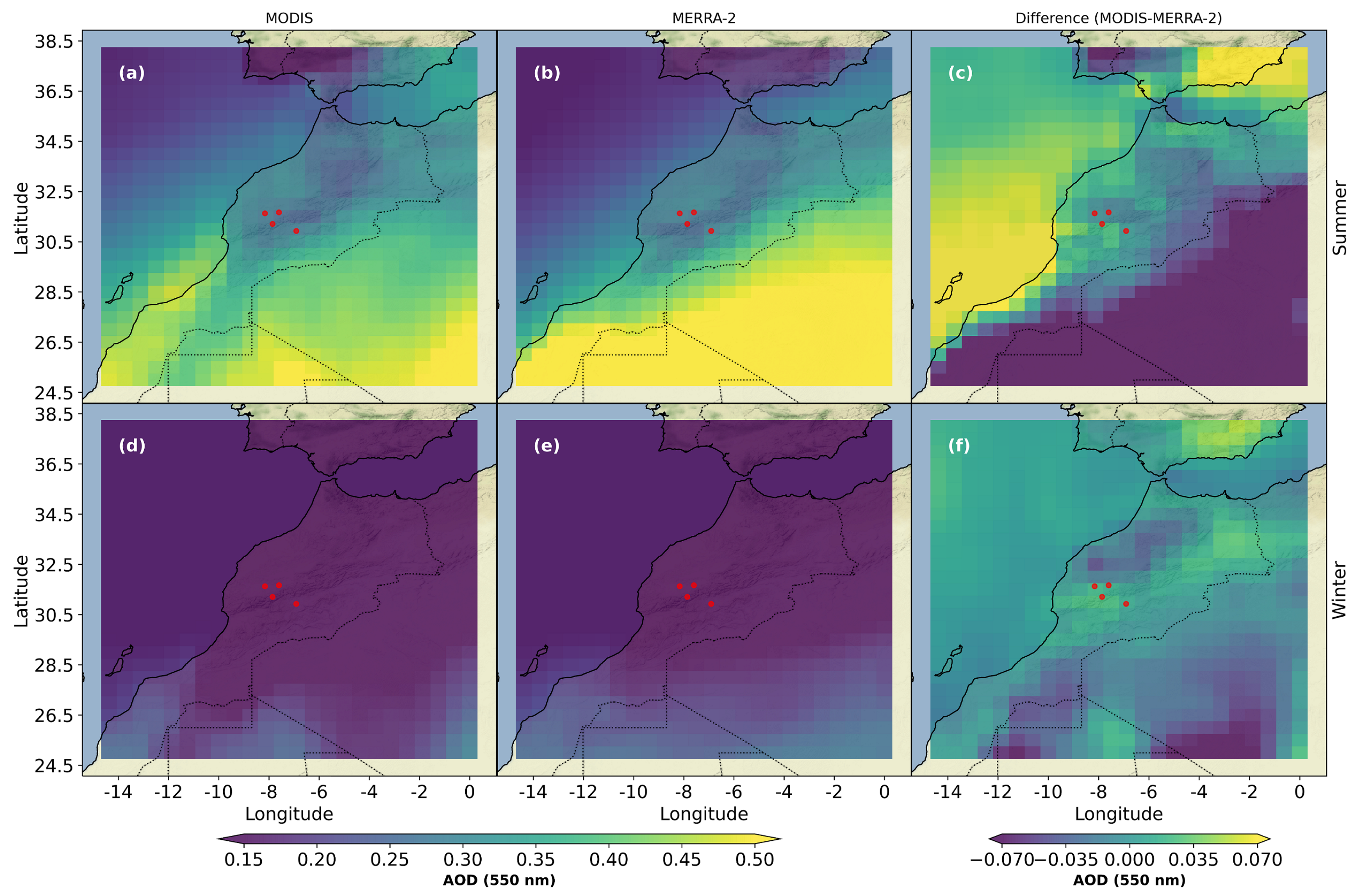
3.2.2. Spatial Comparison
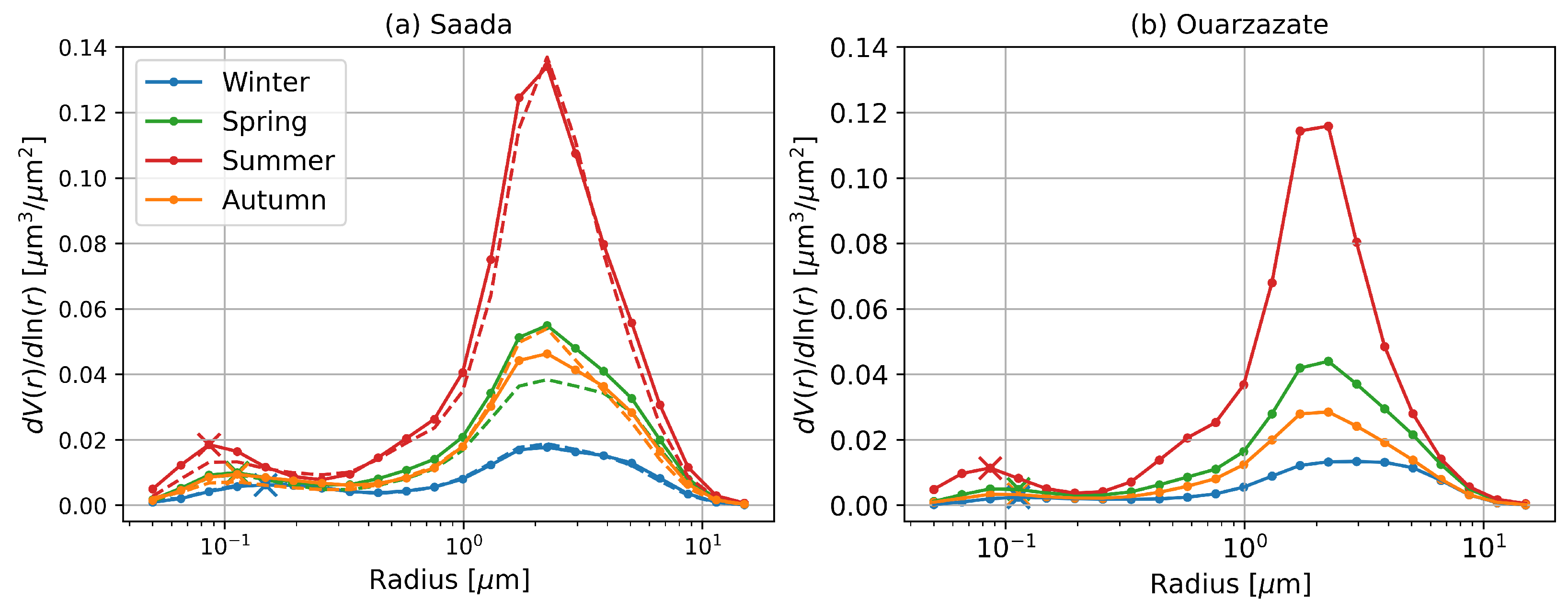
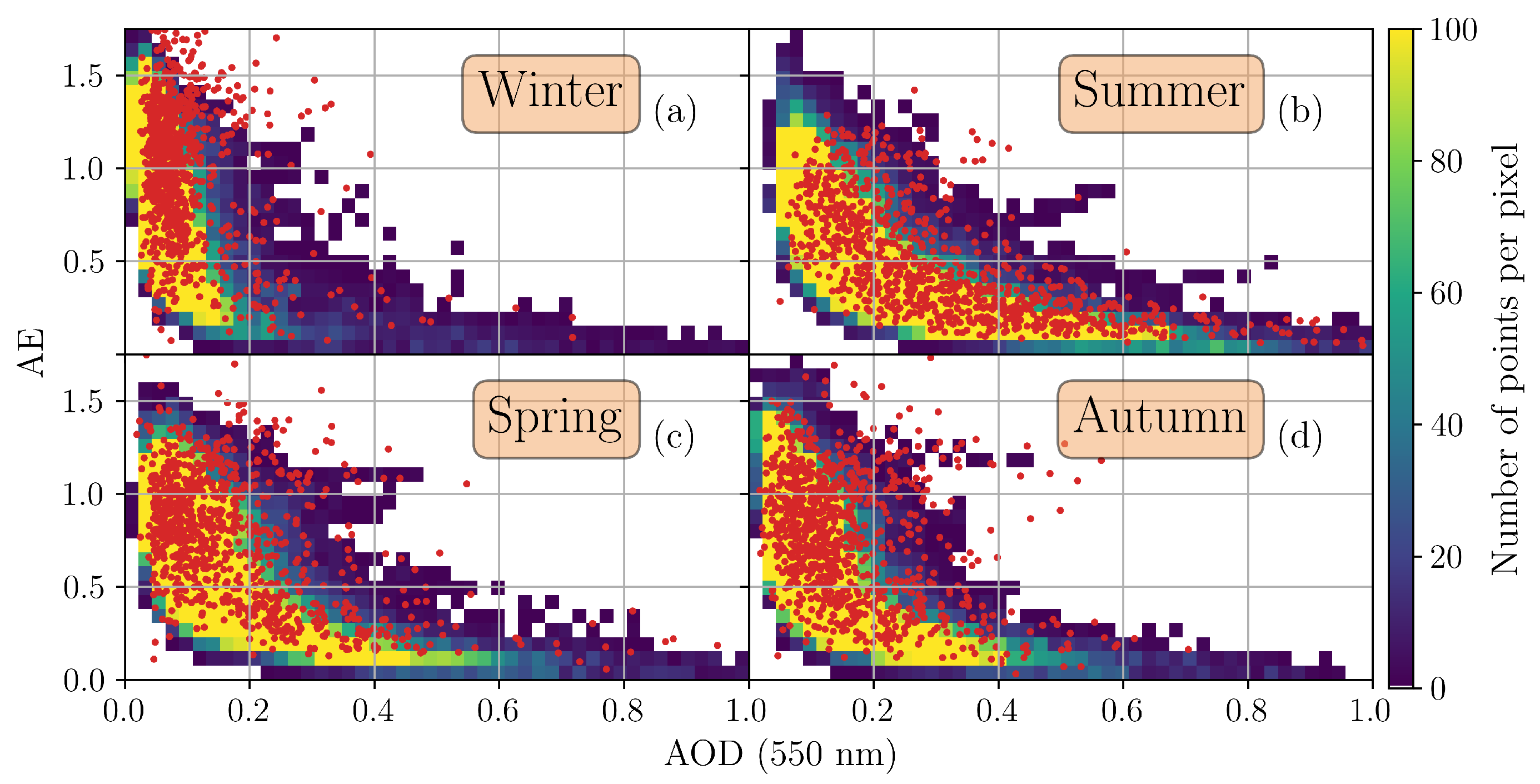
3.3. Classification of Aerosol Types
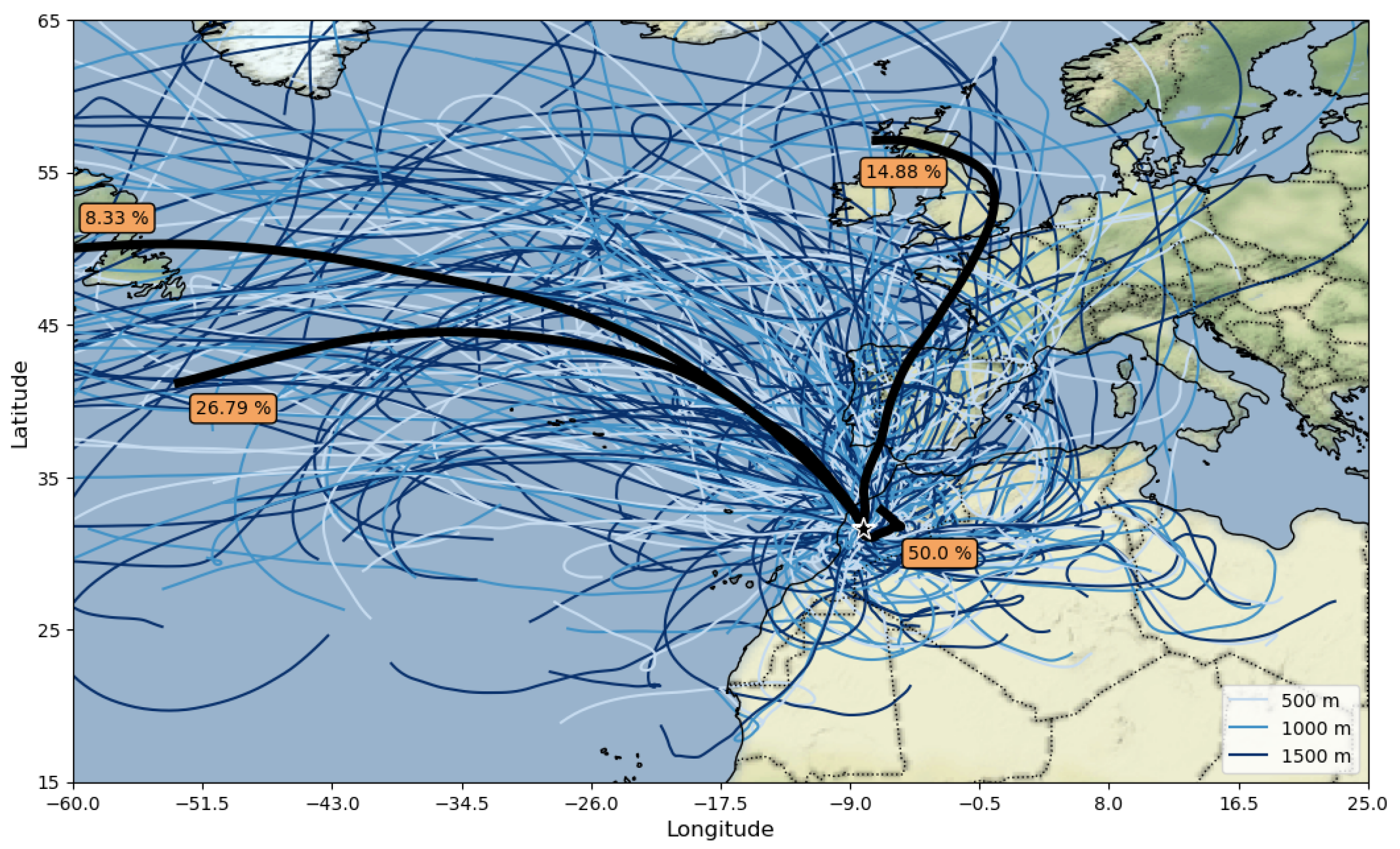
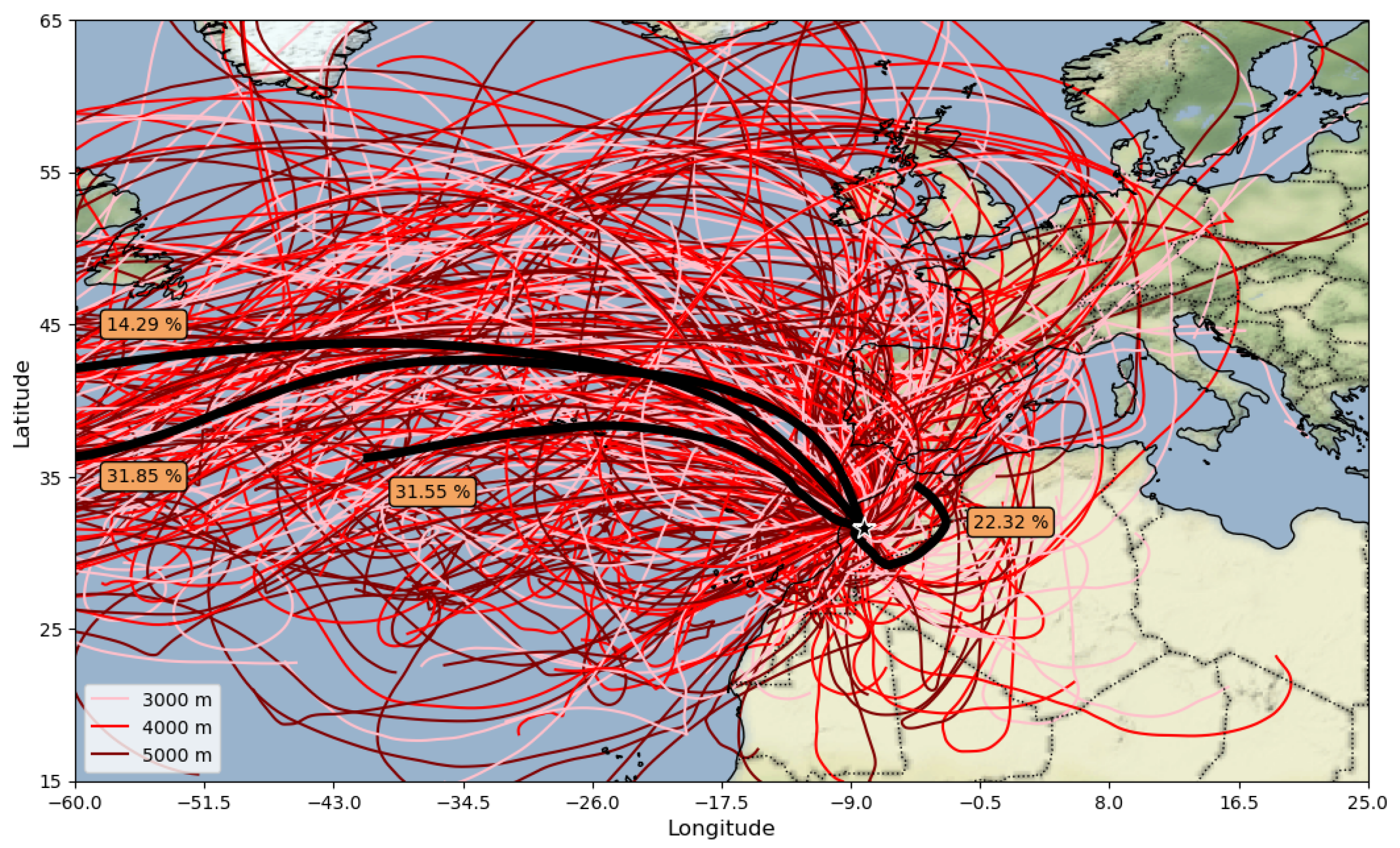
3.4. HYSPLIT Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOD | Aerosol Optical Depth |
| AE | Angström Exponent |
| AVSD | Aerosol Volumetric Size Distribution |
| Relative Root-Mean Squared Error | |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| RMB | Relative Mean Bias |
| AERONET | AErosol RObotic NETwork |
| MODIS | MODerate resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| MERRA-2 | Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications |
| CAMS | Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service |
| HYSPLIT | HYbrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory |
| SAMUM | Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment |
| EUCAARI | European Integrated Project on Aerosol–Cloud–Climate and Air Quality Interactions |
Appendix A
| Dataset | MODIS | MERRA-2 | CAMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Station (I) | Saada | ||
| N | 3087 | 3495 | 3495 |
| Slope | 0.652 | 0.602 | 0.607 |
| Intercept | 0.081 | 0.021 | 0.057 |
| r | 0.778 | 0.844 | 0.718 |
| (%) | 50.055 | 52.890 | 57.280 |
| MAE | 0.079 | 0.078 | 0.084 |
| RMB | 1.056 | 0.737 | 0.906 |
| Station (II) | Ouarzazate | ||
| N | 998 | 1061 | 1061 |
| Slope | 0.862 | 0.651 | 0.729 |
| Intercept | 0.129 | 0.040 | 0.070 |
| r | 0.711 | 0.843 | 0.746 |
| (%) | 113.692 | 55.421 | 74.248 |
| MAE | 0.123 | 0.048 | 0.072 |
| RMB | 1.750 | 0.967 | 1.236 |
| Station (III) | Oukaïmeden | ||
| N | 141 | 154 | 154 |
| Slope | 1.016 | 0.950 | 0.958 |
| Intercept | 0.163 | 0.070 | 0.120 |
| r | 0.568 | 0.758 | 0.530 |
| (%) | 170.515 | 76.188 | 139.868 |
| MAE | 0.166 | 0.069 | 0.121 |
| RMB | 2.472 | 1.656 | 2.088 |
| Station (IV) | Ras-El-Aïn | ||
| N | 385 | 414 | 414 |
| Slope | 0.631 | 0.577 | 0.750 |
| Intercept | 0.085 | 0.024 | 0.031 |
| r | 0.789 | 0.815 | 0.765 |
| (%) | 43.459 | 52.564 | 48.726 |
| MAE | 0.087 | 0.101 | 0.094 |
| RMB | 0.914 | 0.641 | 0.822 |
| Dataset | MODIS | MERRA-2 | CAMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Season (I) | Winter | ||
| N | 735 | 837 | 837 |
| Slope | 0.574 | 0.460 | 0.647 |
| Intercept | 0.060 | 0.015 | 0.024 |
| r | 0.684 | 0.693 | 0.615 |
| (%) | 55.985 | 68.066 | 68.986 |
| MAE | 0.047 | 0.056 | 0.058 |
| RMB | 1.082 | 0.585 | 0.850 |
| Season (II) | Spring | ||
| N | 714 | 881 | 881 |
| Slope | 0.644 | 0.577 | 0.600 |
| Intercept | 0.111 | 0.035 | 0.076 |
| r | 0.683 | 0.813 | 0.673 |
| (%) | 57.680 | 49.994 | 55.916 |
| MAE | 0.092 | 0.072 | 0.083 |
| RMB | 1.161 | 0.739 | 0.950 |
| Season (III) | Summer | ||
| N | 866 | 899 | 899 |
| Slope | 0.618 | 0.561 | 0.561 |
| Intercept | 0.087 | 0.055 | 0.082 |
| r | 0.794 | 0.815 | 0.659 |
| (%) | 38.587 | 45.004 | 50.295 |
| MAE | 0.100 | 0.110 | 0.120 |
| RMB | 0.865 | 0.718 | 0.794 |
| Season (IV) | Autumn | ||
| N | 772 | 878 | 878 |
| Slope | 0.685 | 0.512 | 0.498 |
| Intercept | 0.082 | 0.033 | 0.079 |
| r | 0.690 | 0.752 | 0.623 |
| (%) | 53.956 | 54.889 | 54.894 |
| MAE | 0.076 | 0.073 | 0.072 |
| RMB | 1.110 | 0.681 | 0.904 |
| Dataset | MODIS | MERRA-2 | CAMS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Season (I) | Winter | ||
| N | 234 | 244 | 244 |
| Slope | 1.290 | 0.525 | 0.875 |
| Intercept | 0.064 | 0.021 | 0.026 |
| r | 0.580 | 0.623 | 0.590 |
| (%) | 207.028 | 67.991 | 104.099 |
| MAE | 0.083 | 0.021 | 0.037 |
| RMB | 2.391 | 0.881 | 1.320 |
| Season (II) | Spring | ||
| N | 283 | 303 | 303 |
| Slope | 0.854 | 0.611 | 0.746 |
| Intercept | 0.149 | 0.051 | 0.079 |
| r | 0.574 | 0.766 | 0.734 |
| (%) | 137.357 | 55.716 | 70.456 |
| MAE | 0.141 | 0.048 | 0.073 |
| RMB | 1.935 | 0.972 | 1.304 |
| Season (III) | Summer | ||
| N | 273 | 282 | 282 |
| Slope | 0.703 | 0.548 | 0.540 |
| Intercept | 0.183 | 0.085 | 0.146 |
| r | 0.711 | 0.788 | 0.588 |
| (%) | 64.550 | 44.515 | 59.588 |
| MAE | 0.136 | 0.081 | 0.115 |
| RMB | 1.377 | 0.857 | 1.071 |
| Season (IV) | Autumn | ||
| N | 208 | 232 | 232 |
| Slope | 1.050 | 0.724 | 0.712 |
| Intercept | 0.117 | 0.034 | 0.064 |
| r | 0.563 | 0.812 | 0.718 |
| (%) | 191.513 | 54.366 | 78.222 |
| MAE | 0.127 | 0.034 | 0.055 |
| RMB | 2.348 | 1.085 | 1.384 |
Appendix B

References
- de Oliveira Alves, N.; Vessoni, A.T.; Quinet, A.; Fortunato, R.S.; Kajitani, G.S.; Peixoto, M.S.; de Souza Hacon, S.; Artaxo, P.; Saldiva, P.; Menck, C.F.M.; et al. Biomass burning in the Amazon region causes DNA damage and cell death in human lung cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, K.; Otani, S.; Yoshida, A.; Mu, H.; Kurozawa, Y. Adverse Health Effects of Asian Dust Particles and Heavy Metals in Japan. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2015, 27, NP1719–NP1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.N.; Dey, S.; Chandel, A.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, R.P.; Holben, B.N. Comparison of MODIS and AERONET derived aerosol optical depth over the Ganga Basin, India. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y. Comparison of AOD from CALIPSO, MODIS, and Sun Photometer under Different Conditions over Central China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bègue, N.; Shikwambana, L.; Bencherif, H.; Pallotta, J.; Sivakumar, V.; Wolfram, E.; Mbatha, N.; Orte, F.; Preez, D.J.D.; Ranaivombola, M.; et al. Statistical analysis of the long-range transport of the 2015 Calbuco volcanic plume from ground-based and space-borne observations. Ann. Geophys. 2020, 38, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldabash, M.; Balcik, F.B.; Glantz, P. Validation of MODIS C6.1 and MERRA-2 AOD using AERONET observations: A comparative study over Turkey. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunjobi, K.O.; Awoleye, P.O. Intercomparison and Validation of Satellite and Ground-Based Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) Retrievals over Six AERONET Sites in West Africa. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2019, 3, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Yin, Y.; Sivakumar, V.; Kang, N.; Yu, X.; Diao, Y.; Adesina, A.J.; Reddy, R.R. Aerosol climatology and discrimination of aerosol types retrieved from MODIS, MISR and OMI over Durban (29.88° S, 31.02° E), South Africa. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, J.R.; Brindley, H.E.; Flamant, C.; Garay, M.J.; Hsu, N.C.; Kalashnikova, O.V.; Klüser, L.; Sayer, A.M. Intercomparison of satellite dust retrieval products over the west African Sahara during the Fennec campaign in June 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 136, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaboureau, J.P.; Flamant, C.; Dauhut, T.; Kocha, C.; Lafore, J.P.; Lavaysse, C.; Marnas, F.; Mokhtari, M.; Pelon, J.; Martínez, I.R.; et al. Fennec dust forecast intercomparison over the Sahara in June 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6977–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintzenberg, J. The SAMUM-1 experiment over Southern Morocco: Overview and introduction. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinter, T.; Hoyningen-Huene, W.V.; Burrows, J.P.; Kokhanovsky, A.; Bierwirth, E.; Wendisch, M.; MüLLER, D.; Kahn, R.; Diouri, M. Retrieval of aerosol optical thickness for desert conditions using MERIS observations during the SAMUM campaign. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kandler, K.; SchüTZ, L.; Deutscher, C.; Ebert, M.; Hofmann, H.; JäCKEL, S.; Jaenicke, R.; Knippertz, P.; Lieke, K.; Massling, A.; et al. Size distribution, mass concentration, chemical and mineralogical composition and derived optical parameters of the boundary layer aerosol at Tinfou, Morocco, during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 32–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Garhammer, M.; Seefeldner, M.; Gasteiger, J.; MüLLER, D.; Koepke, P. Spectral aerosol optical depth characterization of desert dust during SAMUM 2006. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2009, 61, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bounhir, A.; Benkhaldoun, Z.; Mougenot, B.; Sarazin, M.; Siher, E.; Masmoudi, L. Aerosol columnar characterization in Morocco: ELT prospect. New Astron. 2008, 13, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bègue, N.; Tulet, P.; Chaboureau, J.P.; Roberts, G.; Gomes, L.; Mallet, M. Long-range transport of Saharan dust over northwestern Europe during EUCAARI 2008 campaign: Evolution of dust optical properties by scavenging. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchrif, A.; Guinot, B.; Bounakhla, M.; Cachier, H.; Damnati, B.; Baghdad, B. Aerosols in Northern Morocco: Input pathways and their chemical fingerprint. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 174, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiri, A.; Diouri, M. Radiative forcing of the desert aerosol at Ouarzazate (Morocco). E3S Web Conf. 2018, 37, 03004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiri, A.; Diouri, M.; Steli, H.; Marsli, I.; Meziane, R.; Ben-tayeb, A. Desert aerosol optical properties in Morocco. Environ. Sci. 2016, 4, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Benkhaldoun, Z.; Abahamid, A.; Azhari, Y.E.; Lazrek, M. Optical seeing monitoring at the Oukaïmeden in the Moroccan high atlas mountains: First statistics. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 441, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the Atmospheric Transmission of Sun Radiation and on Dust in the Air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D07207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, E.; Romero-Campos, P.M.; Kouremeti, N.; Kazadzis, S.; Räisänen, P.; García, R.D.; Barreto, A.; Guirado-Fuentes, C.; Ramos, R.; Toledano, C.; et al. Aerosol optical depth comparison between GAW-PFR and AERONET-Cimel radiometers from long-term (2005–2015) 1 min synchronous measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4309–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raptis, I.P.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Gkikas, A.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. A Decade of Aerosol Optical Properties Measurements over Athens, Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Sinyuk, A.; Sorokin, M.G.; Schafer, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Lewis, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. Advancements in the Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Version 3 database—Automated near-real-time quality control algorithm with improved cloud screening for Sun photometer aerosol optical depth (AOD) measurements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M.; Lanconelli, C.; Lupi, A.; Busetto, M.; Vitale, V.; Tomasi, C. Columnar aerosol optical properties in the Po Valley, Italy, from MFRSR data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D17206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, J.M.; Gueymard, C.A. Climate-specific and global validation of MODIS Aqua and Terra aerosol optical depth at 452 AERONET stations. Sol. Energy 2019, 183, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.O.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Vermote, E.F.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.E.; Saleous, N.; Roy, D.P.; Morisette, J.T. An overview of MODIS Land data processing and product status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.A.; da Silva, A.M.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.R.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; et al. The MERRA-2 aerosol reanalysis, 1980 onward. Part I: System description and data assimilation evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaro, R.; McCarty, W.; Suárez, M.J.; Todling, R.; Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Randles, C.A.; Darmenov, A.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Reichle, R.; et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, version 2 (MERRA-2). J. Clim. 2017, 30, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.M.; Dominguez, J.J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS reanalysis of atmospheric composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.; Hess, G. Description of the HYSPLIT4 Modelling System. NOAA Tech. Mem. ERL ARL-224 1997. Available online: https://www.arl.noaa.gov/documents/reports/arl-224.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Draxler, R.; Hess, G. An overview of the HYSPLIT4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Taubman, B.F.; Hains, J.C.; Thompson, A.M.; Marufu, L.T.; Doddridge, B.G.; Stehr, J.W.; Piety, C.A.; Dickerson, R.R. Aircraft vertical profiles of trace gas and aerosol pollution over the mid-Atlantic United States: Statistics and meteorological cluster analysis. J. Geophys. Res. (Atmos.) 2006, 111, D10S07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, D.; Fonseca, R.; Nelli, N.; Cuesta, J.; Weston, M.; Evan, A.; Temimi, M. The Atmospheric Drivers of the Major Saharan Dust Storm in June 2020. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e90102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencherif, H.; Bounhir, A.; Bègue, N.; Millet, T.; Benkhaldoun, Z.; Lamy, K.; Portafaix, T.; Gadouali, F. Aerosol Distributions and Sahara Dust Transport in Southern Morocco, from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.X.P.; Stowe, L.L.; Smirnov, A.; Crosby, D.; Sapper, J.; McClain, C.R. Development of a Global Validation Package for Satellite Oceanic Aerosol Optical Thickness Retrieval Based on AERONET Observations and Its Application to NOAA/NESDIS Operational Aerosol Retrievals. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A.A. Assessing MODIS Aerosol Products Using AERONET Ground Measurements. 2010. Available online: https://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/sci_team/meetings/201001/presentations/posters/atmos/li.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2021).
- Mokhtari, M.; Tulet, P.; Fischer, C.; Bouteloup, Y.; Bouyssel, F.; Brachemi, O. Three-dimensional dust aerosol distribution and extinction climatology over northern Africa simulated with the ALADIN numerical prediction model from 2006 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 9063–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajhar, L.; Khachine, D.; Bakouri, A.; Kharrim, K.; Belghyti, D. Evolution de la pluviométrie de 1960 à 2015 au Maroc. Int. J. Res. Sci. Manag. 2018, 5, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbar, A.; Wadi, B.; Fougrach, H.; Hsaine, M. Etude de la variabilité du régime pluviométrique au Maroc septentrional (1935–2004). Sécheresse 2011, 22, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, G.; di Sarra, A.; Meloni, D.; Piacentino, S.; Chamard, P. Aerosol optical properties at Lampedusa (Central Mediterranean). 1. Influence of transport and identification of different aerosol types. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouhi, A.; Zamzoum, O.; Islam, M.R.; Saidur, R.; Kousksou, T.; Jamil, A.; Derouich, A. Evaluation of wind energy potential in Morocco’s coastal regions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Millet, T.; Bencherif, H.; Bounhir, A.; Bègue, N.; Lamy, K.; Ranaivombola, M.; Benkhaldoun, Z.; Portafaix, T.; Duflot, V. Aerosol Distributions and Transport over Southern Morocco from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations (2004–2020). Atmosphere 2022, 13, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060923
Millet T, Bencherif H, Bounhir A, Bègue N, Lamy K, Ranaivombola M, Benkhaldoun Z, Portafaix T, Duflot V. Aerosol Distributions and Transport over Southern Morocco from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations (2004–2020). Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060923
Chicago/Turabian StyleMillet, Tristan, Hassan Bencherif, Aziza Bounhir, Nelson Bègue, Kévin Lamy, Marion Ranaivombola, Zouhair Benkhaldoun, Thierry Portafaix, and Valentin Duflot. 2022. "Aerosol Distributions and Transport over Southern Morocco from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations (2004–2020)" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060923
APA StyleMillet, T., Bencherif, H., Bounhir, A., Bègue, N., Lamy, K., Ranaivombola, M., Benkhaldoun, Z., Portafaix, T., & Duflot, V. (2022). Aerosol Distributions and Transport over Southern Morocco from Ground-Based and Satellite Observations (2004–2020). Atmosphere, 13(6), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060923







