Resource-Based Industries and CO2 Emissions Embedded in Value Chains: A Regional Analysis for Selected Countries in Latin America
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geography of Resource-Based Industries in Selected Latin American Countries
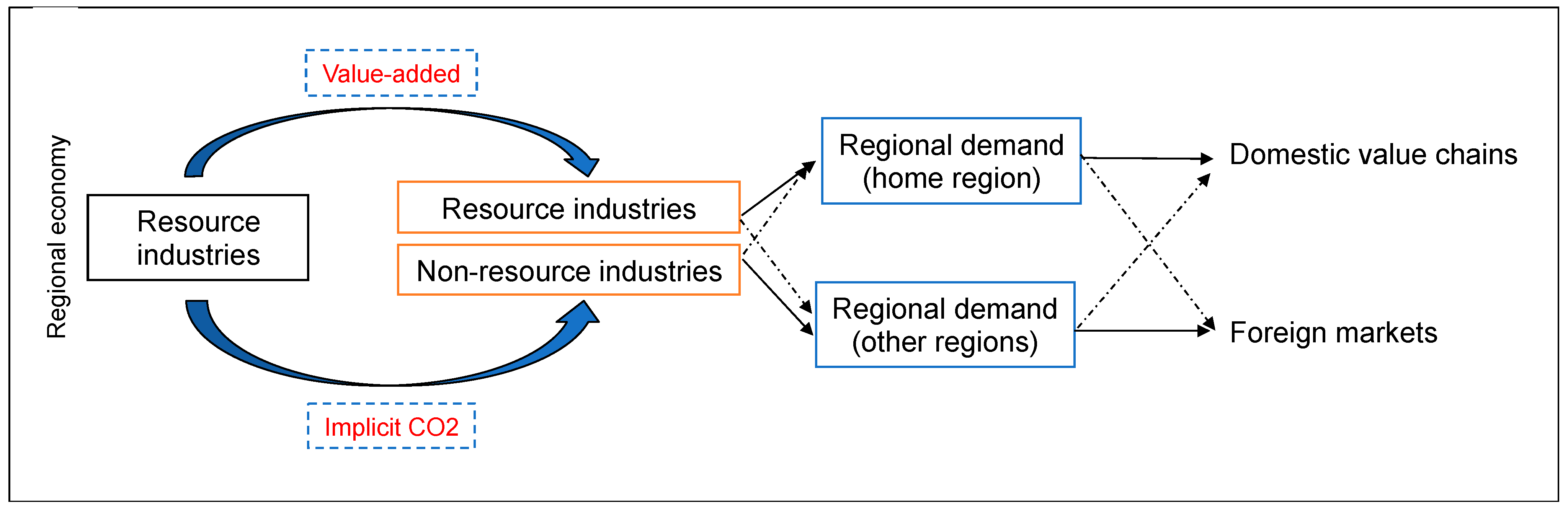
3. Methodology
3.1. Estimation Procedure
3.2. Data
4. Empirical Results
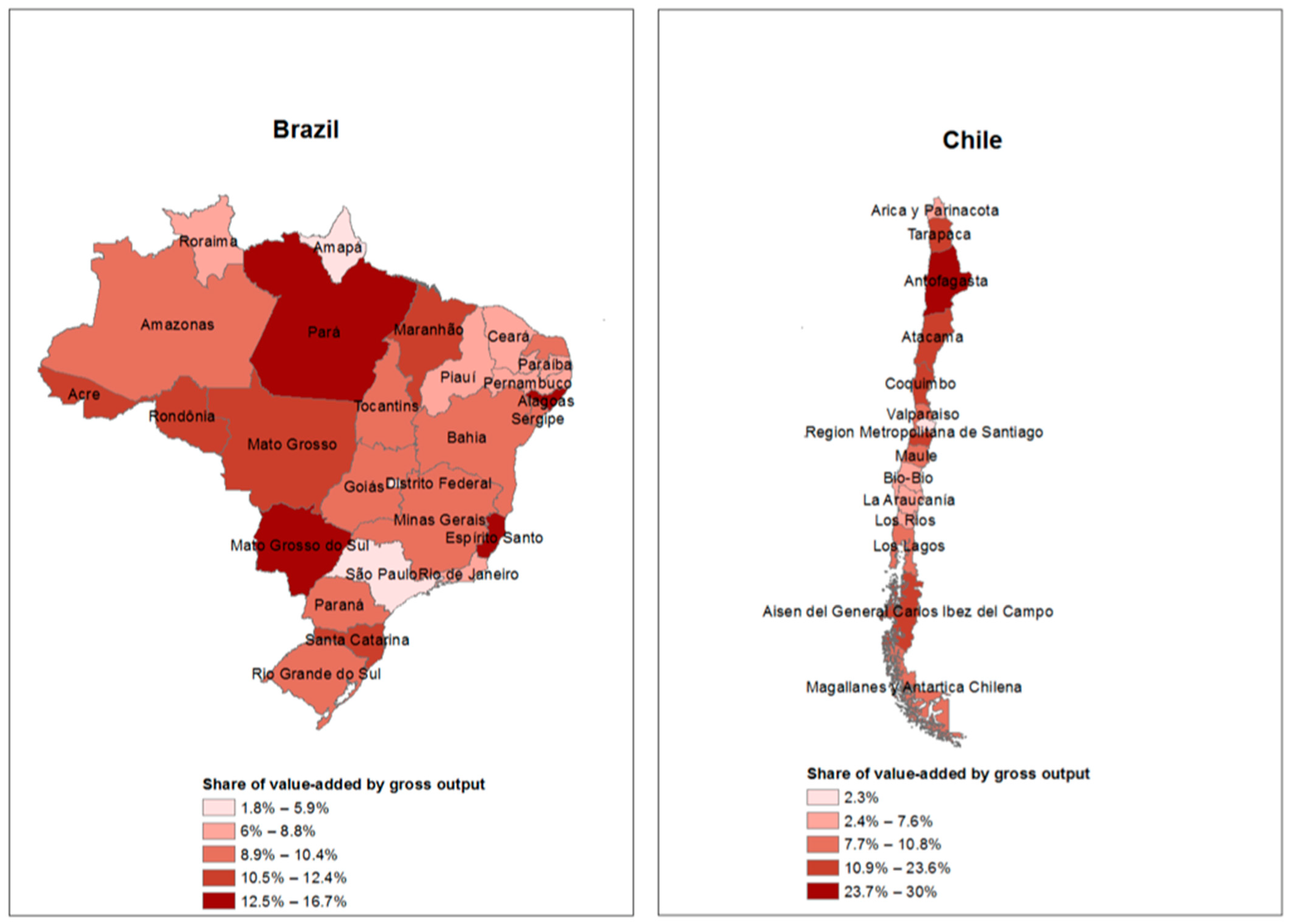
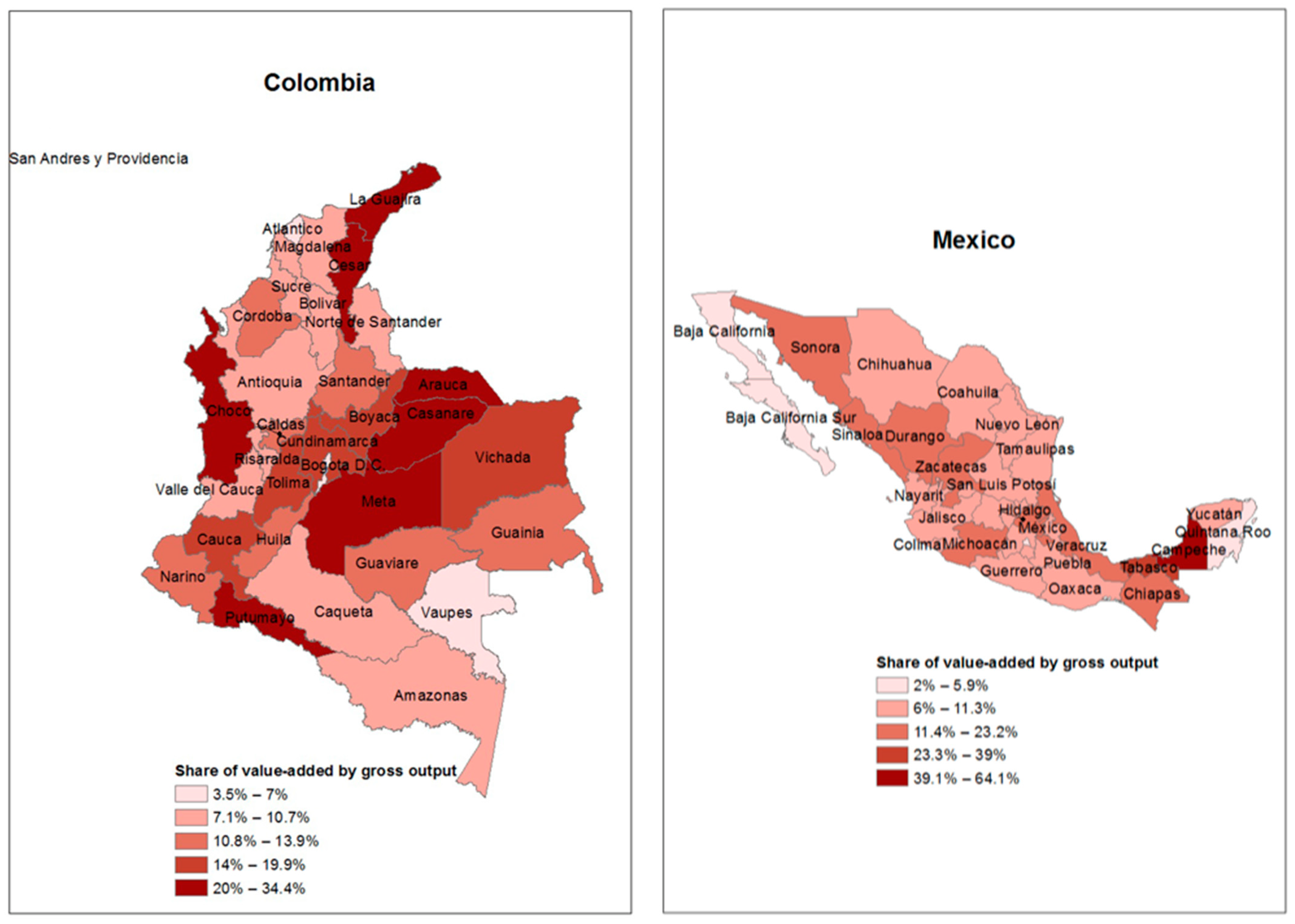
4.1. Interplay between Resource and Non-Resource Industries
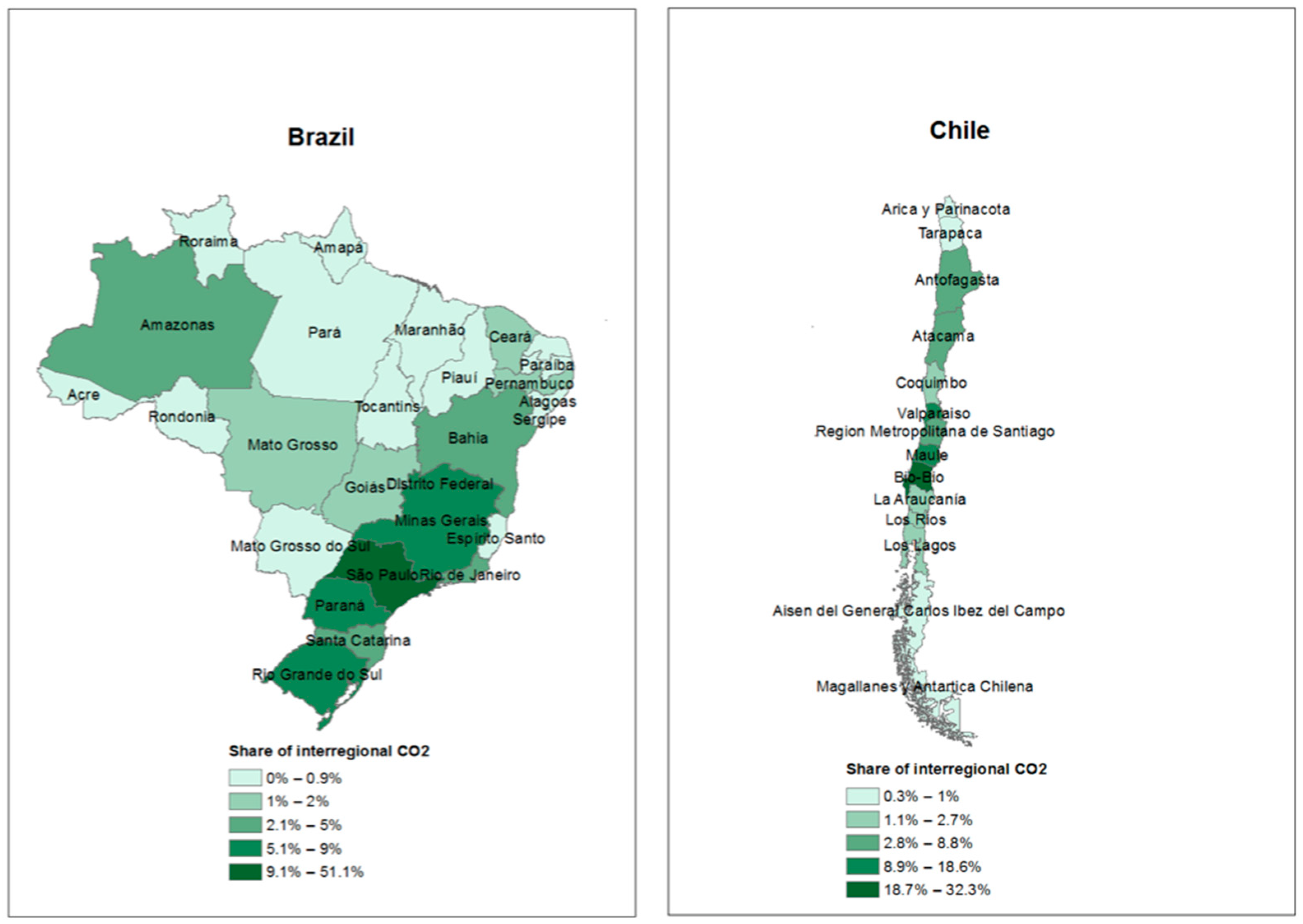
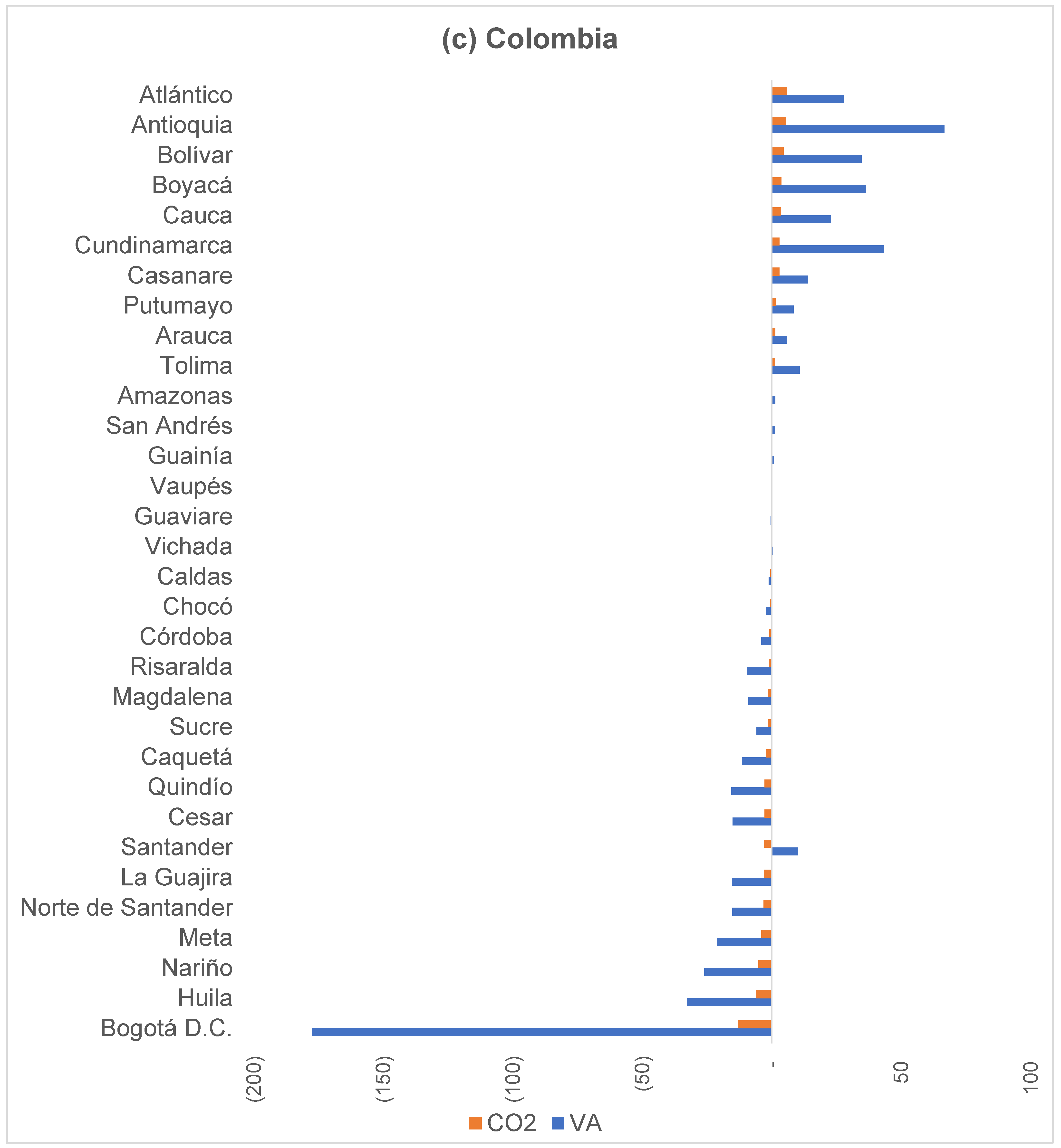
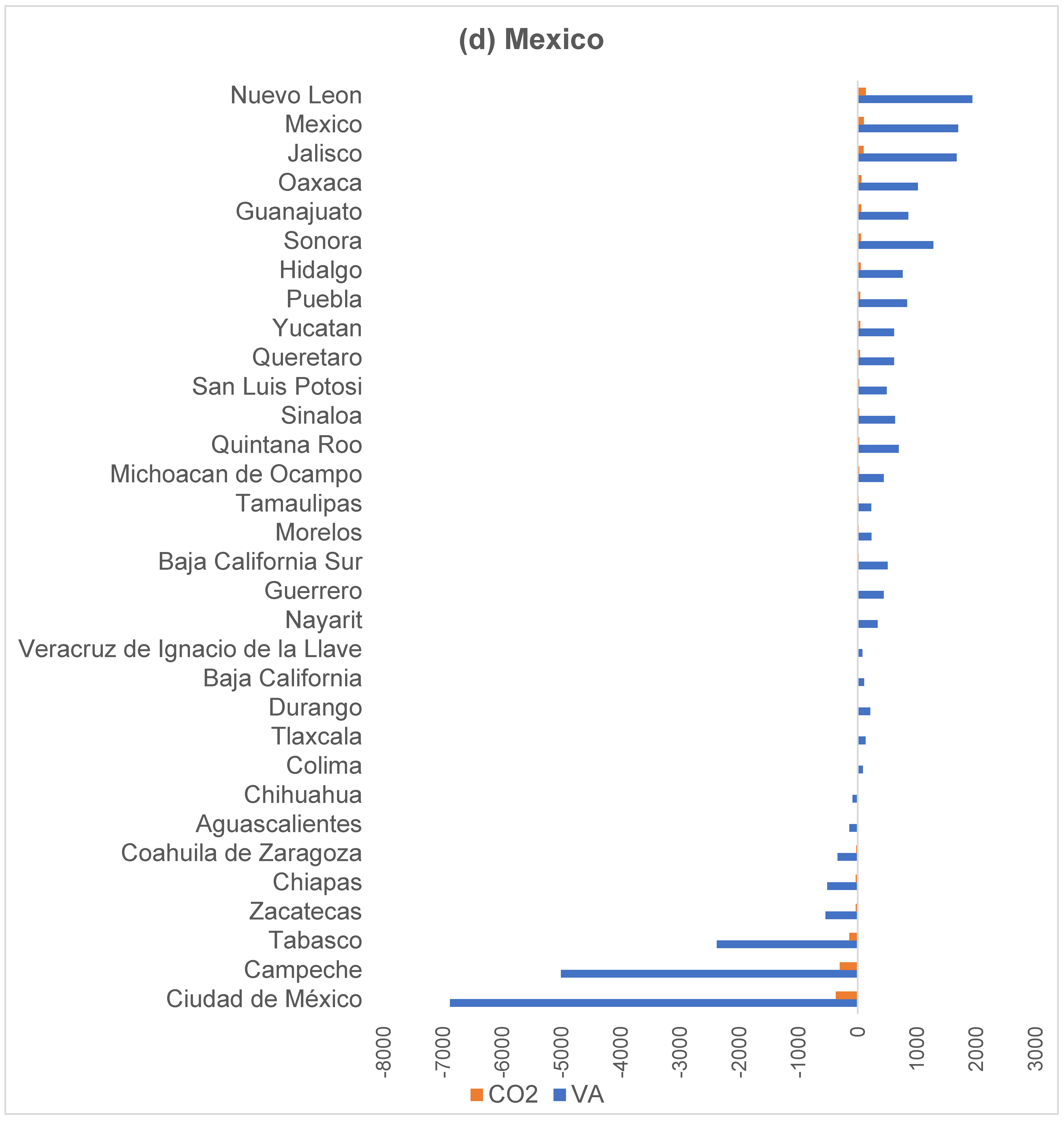
4.2. Spatial Organisation of Interregional VA and CO2 Transfers
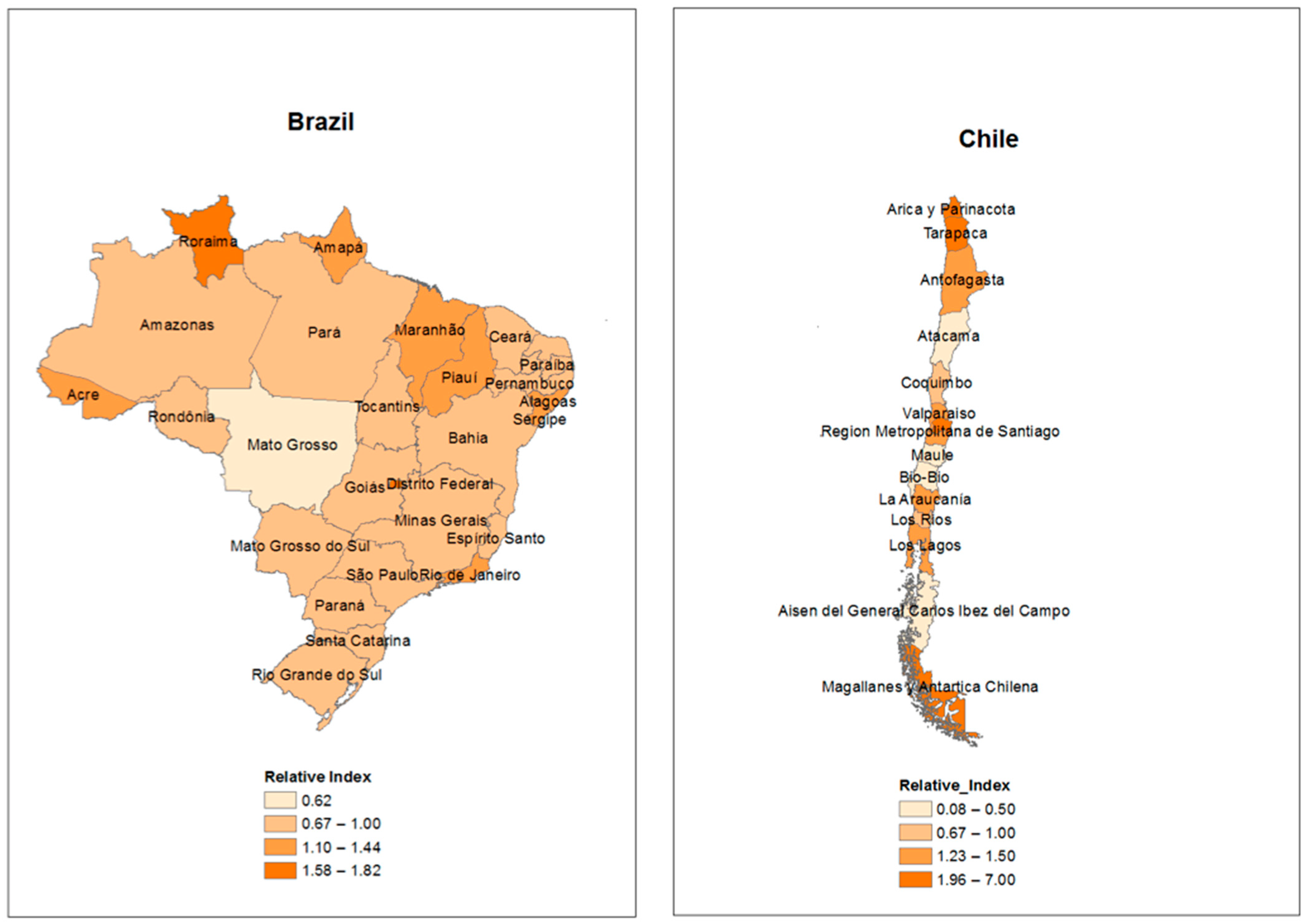
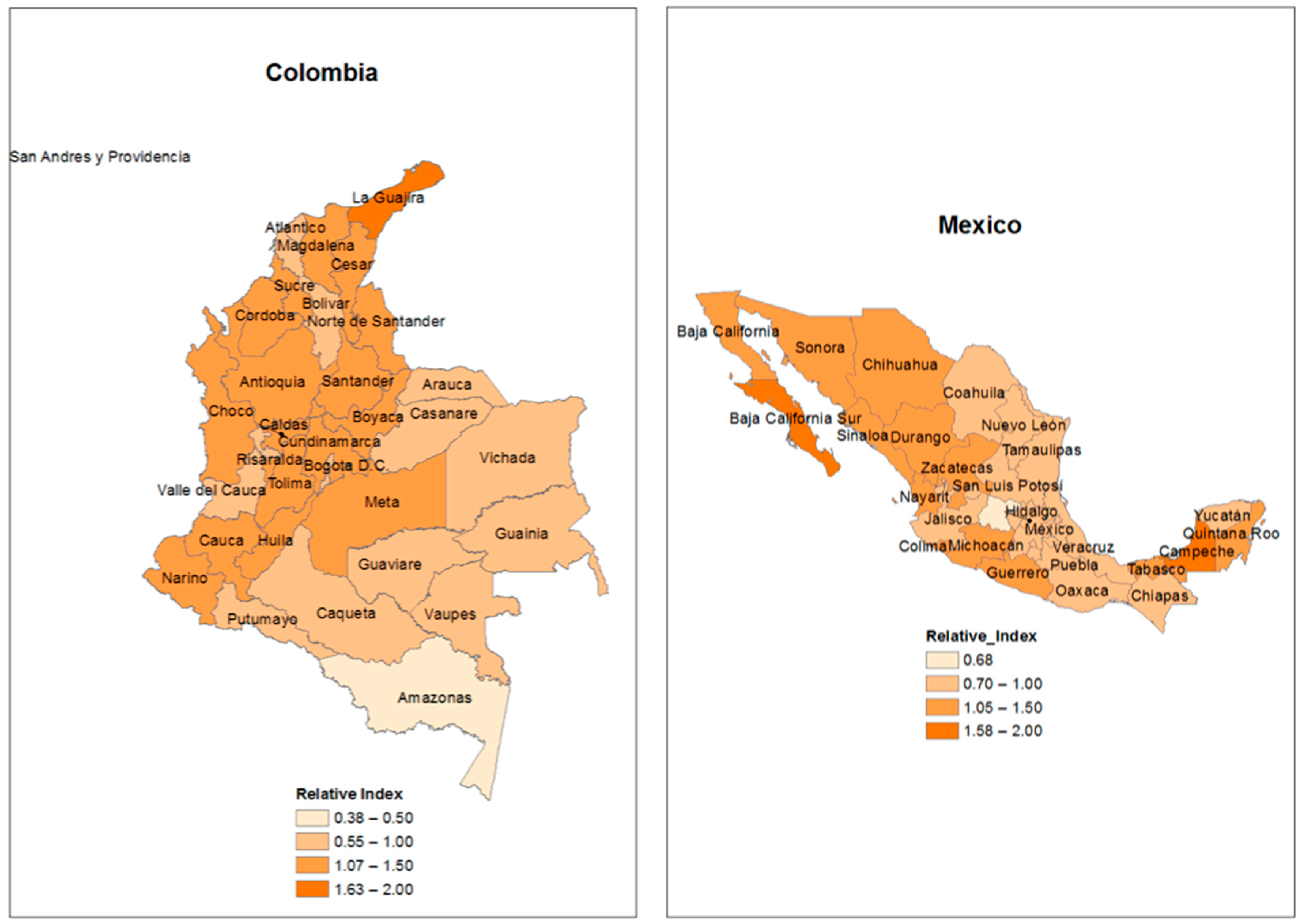
4.3. Relative CO2 Emission Intensity in Value Chains at the Subnational Level
5. Final Remarks and Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, A.; Ma, H.; Ozturk, I.; Murshed, M.; Dagar, V. The dynamic impacts of CO2 emissions from different sources on Pakistan’s economic progress: A roadmap to sustainable development. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 17857–17880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Alvarado, R.; Toledo, E.; Caraguay, L. Greenhouse gas emissions, non-renewable energy consumption, and output in South America: The role of the productive structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14477–14491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillaguango, B.; Alvarado, R.; Dagar, V.; Murshed, M.; Pinzón, Y.; Méndez, P. Convergence of the ecological footprint in Latin America: The role of the productive structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59771–59783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, R.; Tillaguango, B.; Dagar, V.; Ahmad, M.; Işık, C.; Méndez, P.; Toledo, E. Ecological footprint, economic complexity and natural resources rents in Latin America: Empirical evidence using quantile regressions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank Data. Popular Indicators Data, 1 January 2022. 2022. Available online: https://databank.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.CD/1ff4a498/Popular-Indicators (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Jahanger, A.; Usman, M.; Murshed, M.; Mahmood, H.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. The linkages between natural resources, human capital, globalization, economic growth, financial development, and ecological footprint: The moderating role of technological innovations. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, E.A.; Araújo, I.F. The internal geography of services value-added in exports: A Latin American perspective. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2021, 100, 713–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes, E.R.; Camacho, A.R.; Ciravegna, L.; Pichardo, C.A. Strategy and innovation in emerging economies after the end of the commodity boom—Insights from Latin America. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 4363–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, A.C.; Mollick, A.V. Threshold effects of terms of trade on Latin American growth. Econ. Syst. 2021, 45, 100882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzoni, C.R.; Haddad, E.A. Regional disparities. In Oxford Handbook of the Brazilian Economy; Amann, E., Azzoni, C.R., Baer, W., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Aroca, P.; Azzoni, C.; Sarrias, M. Regional concentration and national economic growth in Brazil and Chile. Lett. Spat. Resour. Sci. 2018, 11, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, O.A.; Castañeda, G.; Trujillo, G.; Hackett, L.; Chávez-Juárez, F. Subnational sustainable development: The role of vertical intergovernmental transfers in reaching multidimensional goals. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, B.; Xie, R.; Long, H. China’s aggregate embodied CO2 emission intensity from 2007 to 2012: A multi-region multiplicative structural decomposition analysis. Energy Econ. 2020, 85, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemoto, K.; Moran, D.; Hertwich, E. Mapping the carbon footprint of nations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10512–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguinet, E.R.; Alvim, A.M.; Atienza, M.; Fochezatto, A. The subnational supply chain and the COVID-19 pandemic: Short-term impacts on the Brazilian regional economy. Reg. Sci. Policy Pract. 2021, 13, 158–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhoto, J.M.; Hewings, G.J.D. Revival: Structure and Structural Change in the Brazilian Economy (2001); Taylor and Francis: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 1–390. [Google Scholar]
- Sanguinet, E.R. Regional inequality and CO2 emissions-based trade across value chains networks: A multiscalar analysis from Brazilian states. Reg. Stud. Reg. Sci. 2022, 9, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pan, C.; Zhou, P. Assessing the role of domestic value chains in China’s CO2 emission intensity: A multi-region structural decomposition analysis. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2019, 74, 865–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Reiner, D.M.; Wu, M. Changing trends of the elasticity of China’s carbon emission intensity to industry structure and energy efficiency. Energy Econ. 2020, 86, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Long, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Guan, D. Drivers of provincial SO2 emissions in China—Based on multi-regional input-output analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, W.; Song, M.; Dietzenbacher, E.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Shan, Y.; Ou, J.; Guan, D. Regional determinants of China’s consumption-based emissions in the economic transition. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Mi, Z.; Coffman, D.; Milcheva, S.; Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Wang, S. Regional development and carbon emissions in China. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Wang, J.; Andrew, R.; Xiao, H.; Xue, J.; Peters, G. Spatial spillover effects in determining China’s regional CO2 emissions growth: 2007–2010. Energy Econ. 2017, 63, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piorski, K.A.O.D.S.; Xavier, C. Especialização em recursos naturais e cadeias globais de valor (1995 e 2009). Econ. Soc. 2017, 27, 89–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atienza, M.; Arias-Loyola, M.; Phelps, N. Gateways or backdoors to development? Filtering mechanisms and territorial embeddedness in the Chilean copper GPN’s urban system. Growth Chang. 2021, 52, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaka, T.; Kanemoto, K.; Kagawa, S. Multi-perspective structural analysis of supply chain networks. Econ. Syst. Res. 2021, 1883552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Peters, G.P.; Wang, Z.; Li, M. Tracing CO2 emissions in global value chains. Energy Econ. 2018, 73, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Jiang, X. Visualizing the change of embodied CO2 emissions along global production chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaye, A.; Feng, K.; Oppon, E.; Salhi, S.; Ibn-Mohammed, T.; Genovese, A.; Hubacek, K. Measuring the environmental sustainability performance of global supply chains: A multi-regional input-output analysis for carbon, sulphur oxide and water footprints. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 187, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke-Sather, A.; Qu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y. Carbon inequality at the sub-national scale: A case study of provincial-level inequality in CO2 emissions in China 1997–2007. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shao, S.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X. Structural transformation of manufacturing, natural resource dependence, and carbon emissions reduction: Evidence of a threshold effect from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, F. What determines the diversity of CO2 emission patterns in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China? An analysis focusing on industrial structure change. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudambi, R.; Puck, J. A global value chain analysis of the “regional strategy” perspective. J. Manag. Stud. 2016, 53, 1076–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Hewings, G. A multi-regional input–output analysis of the pollution haven hypothesis from the perspective of global production fragmentation. Energy Econ. 2017, 64, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, G. Can global value chain participation affect embodied carbon emission intensity? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, R.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, Z. Carbon endowment and trade-embodied carbon emissions in global value chains: Evidence from China. Appl. Energy 2020, 277, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Guo, J.; Chai, J.; Zhang, Z. China’s regional CO2 emissions: Characteristics, inter-regional transfer and emission reduction policies. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 6136–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucak, R.; Khan, S.U.-D. Determinants of the ecological footprint: Role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Zafar, M.W.; Ali, S. Danish Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: An empirical analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.A.; Wang, B. Analyzing the role of governance in CO2 emissions mitigation: The BRICS experience. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2019, 51, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Ye, B.; Liu, J. Research on the peak of CO2 emissions in the developing world: Current progress and future prospect. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perobelli, F.S.; Faria, W.R.; Vale, V.D.A. The increase in Brazilian household income and its impact on CO2 emissions: Evidence for 2003 and 2009 from input–output tables. Energy Econ. 2015, 52, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, V.A.; Perobelli, F.S.; Chimeli, A. International trade, pollution, and economic structure: Evidence on CO2 emissions for the North and the South. Econ. Syst. Res. 2017, 30, 1361907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Guan, D.; López, L.A. The global CO2 emission cost of geographic shifts in international sourcing. Energy Econ. 2018, 73, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, E.A.; Porsse, A.A.; Rabahy, W. Domestic tourism and regional inequality in Brazil. Tour. Econ. 2013, 19, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.; Haddad, E.A.; Hewings, G.J. Energy policy and regional inequalities in the Brazilian economy. Energy Econ. 2013, 36, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, C.G.E., Jr.; Nascimento, T. Matriz Interestadual de Insumo-Produto para o Brasil: Uma aplicacao do Método IIOAS. RBERU. 2017. Available online: https://revistaaber.org.br/rberu/article/view/271 (accessed on 25 December 2021).
- Haddad, E.A.; Mengoub, F.E.; Vale, V.A. Water content in trade: A regional analysis for Morocco. Econ. Syst. Res. 2020, 32, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valbuena GJ, P.; Ricciulli, D.; Bonet, J.; Haddad, E.; Araújo, I.; Perobelli, F. Regional differences in the economic impact of lockdown measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19: A case study for Colombia. Cuad. Econ. 2021, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardones, C.; Lipski, M. A carbon tax on agriculture? A CGE analysis for Chile. Econ. Syst. Res. 2019, 32, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, R.; Cansino, J.M.; Rueda-Cantuche, J.M. A multi-regional input-output analysis of ozone precursor emissions embodied in Spanish international trade. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dietzenbacher, E. A structural decomposition analysis of the emissions embodied in trade. Ecol. Econ. 2014, 101, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Wiedenhofer, D.; Virág, D.; Kalt, G.; Plank, B.; Brockway, P.; Fishman, T.; Hausknost, D.; Krausmann, F.; Leon-Gruchalski, B.; et al. A systematic review of the evidence on decoupling of GDP, resource use and GHG emissions, Part II: Synthesizing the insights. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Murshed, M.; Chen, F.; Shahbaz, M.; Kirikkaleli, D.; Khan, Z. An empirical analysis of the household consumption-induced carbon emissions in China. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, C.; Peng, S. How do urbanization and consumption patterns affect carbon emissions in China? A decomposition analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ang, B.W.; Li, Y. Input-output and structural decomposition analysis of Singapore’s carbon emissions. Energy Policy 2017, 105, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, B.; Du, J.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Wang, S. Internationalization trends of carbon emission linkages: A case study on the construction sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z. Reevaluation of the carbon emissions embodied in global value chains based on an inter-country input-output model with multinational enterprises. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Ji, T.; Yu, T. Reassessing pollution haven effect in global value chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Los, B.; McCann, P.; Ortega-Argilés, R.; Thissen, M.; van Oort, F. The continental divide? Economic exposure to Brexit in regions and countries on both sides of the Channel. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2018, 97, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Feng, K.; Hubacek, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, H.; Liu, N.; Zhang, P.; et al. Revealing Environmental Inequality Hidden in China’s Inter-regional Trade. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7171–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, B.; Timmer, M.P.; De Vries, G.J. Tracing value-added and double counting in gross exports: Comment. Am. Econ. Rev. 2016, 106, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, M.; Fan, Z. How important is domestic and foreign demand for China’s income growth by business function? Econ. Syst. Res. 2020, 33, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, B.; Fang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y. Measuring China’s domestic production networks through trade in value—Added perspectives. Econ. Syst. Res. 2017, 29, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmer, M.P.; Miroudot, S.; De Vries, G.J. Functional specialisation in trade. J. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 19, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, C.; Andersson, M.; Norman, T.; Hewings, G.J.D.; Oosterhaven, J. Handbook of Research Methods and Applications in Economic Geography; Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd.: Cheltenham, UK, 2015; pp. 369–390. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzen, M.; Moran, D.; Kanemoto, K.; Geschke, A. Building Eora: A global multi-region input–output database at high country and sector resolution. Econ. Syst. Res. 2013, 25, 20–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gereffi, G. Economic upgrading in global value chains. In Handbook on Global Value Chains; Ponte, S., Gereffi, G., Raj-Reichert, G., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing Ltd.: Cheltenham, UK, 2019; pp. 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variar, A.G.; Ramyashree, M.S.; Ail, V.U.; Sudhakar, K.; Tahir, M. Influence of various operational parameters in enhancing photocatalytic reduction efficiency of carbon dioxide in a photoreactor: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 99, 19–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicator | Country Name | 2000 | (%) | 2005 | (%) | 2010 | (%) | 2015 | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population, total (in thousands) | Brazil | 175 | 3.4% | 186 | 3.3% | 196 | 3.4% | 204 | 3.3% |
| Population, total (in thousands) | Chile | 15 | 0.3% | 16 | 0.3% | 17 | 0.3% | 18 | 0.3% |
| Population, total (in thousands) | Colombia | 40 | 0.8% | 43 | 0.8% | 45 | 0.8% | 48 | 0.8% |
| Population, total (in thousands) | Mexico | 99 | 1.9% | 106 | 1.9% | 114 | 2.0% | 122 | 2.0% |
| Selected Countries in Latin America | 329 | 6.3% | 351 | 6.3% | 372 | 6.4% | 392 | 6.4% | |
| Population in Latin America (in millions) | 5209 | 100.0% | 5565 | 100.0% | 5834 | 100.0% | 6160 | 100.0% | |
| Surface area (thousands sq. km) | Brazil | 8.5 | 41.7% | 8.5 | 41.7% | 8.5 | 41.7% | 9 | 41.7% |
| Surface area (thousands sq. km) | Chile | 0.8 | 3.7% | 0.8 | 3.7% | 0.8 | 3.7% | 1 | 3.7% |
| Surface area (thousands sq. km) | Colombia | 1.1 | 5.6% | 1.1 | 5.6% | 1.1 | 5.6% | 1 | 5.6% |
| Surface area (thousands sq. km) | Mexico | 2.0 | 9.6% | 2.0 | 9.6% | 2.0 | 9.6% | 2 | 9.6% |
| Selected Countries in Latin America | 12.4 | 60.6% | 12.4 | 60.6% | 12.4 | 60.6% | 12.4 | 60.6% | |
| Surface area in Latin America (thousands sq. km) | 20 | 100.0% | 20 | 100.0% | 20 | 100.0% | 20 | 100.0% | |
| Forest area (thousands sq. km) | Brazil | 5.5 | 54.3% | 5.3 | 54% | 5.2 | 53% | 5.0 | 53% |
| Forest area (thousands sq. km) | Chile | 0.2 | 1.6% | 0.2 | 2% | 0.2 | 2% | 0.2 | 2% |
| Forest area (thousands sq. km) | Colombia | 0.6 | 6.2% | 0.6 | 6% | 0.6 | 6% | 0.6 | 6% |
| Forest area (thousands sq. km) | Mexico | 0.7 | 6.7% | 0.7 | 7% | 0.7 | 7% | 0.7 | 7% |
| Selected Countries in Latin America | 7.0 | 68.7% | 6.8 | 69% | 6.6 | 68% | 6.5 | 69% | |
| Forest area in Latin America (thousands sq. km) | 10 | 100.0% | 10 | 100% | 10 | 100% | 9 | 100% | |
| CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita) | Brazil | 1.8 | - | 1.8 | - | 1.8 | - | 2.5 | - |
| CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita) | Chile | 3.2 | - | 3.4 | - | 3.9 | - | 4.3 | - |
| CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita) | Colombia | 1.5 | - | 1.4 | - | 1.4 | - | 1.7 | - |
| CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita) | Mexico | 3.9 | - | 4.1 | - | 4.1 | - | 3.8 | - |
| Selected Countries in Latin America (average) | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 3.1 | |||||
| CO2 emissions in Latin America (metric tons per capita) | 2.4 | - | 2.5 | - | 2.6 | - | 2.9 | - | |
| GDP (current billions US$) | Brazil | 65,545 | 28.6% | 89,163 | 31.1% | 166,700 | 38.6% | 245,604 | 38.2% |
| GDP (current billions US$) | Chile | 7786 | 3.4% | 12,296 | 4.3% | 17,239 | 4.0% | 26,054 | 4.1% |
| GDP (current billions US$) | Colombia | 9989 | 4.4% | 14,562 | 5.1% | 23,240 | 5.4% | 38,111 | 5.9% |
| GDP (current billions US$) | Mexico | 70,791 | 30.9% | 87,748 | 30.6% | 90,005 | 20.8% | 131,535 | 20.5% |
| Selected Countries in Latin America (current billions US$) | 154,110 | 67.2% | 203,769 | 71.2% | 297,183 | 68.8% | 441,305 | 68.7% | |
| GDP in Latin America (current billions of US$) | 229,189 | 100.0% | 286,324 | 100.0% | 431,835 | 100.0% | 642,694 | 100.0% | |
| Selected Value Chains | Natural Resources Industrial Classification | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Agri-food value chains | Resource-based |
| 2 | Mining value chains | Resource-based |
| 3 | Resource-based manufacturing value chains | Resource-based |
| 4 | Non-resource-based manufacturing value chains | Non-resource based |
| 5 | Business services value chains | Non-resource based |
| 6 | Other services value chains | Non-resource based |
| Endogenous | Exogenous | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate Consumption | Final Demand | Total Demand | ||||||||
| Intermediate Demand | Region 1, Sector 1 | Region R, Sector J | Household | Investment | Government | Stock Variation | Exports | |||
| Region 1, Sector 1 | ||||||||||
| Region R, Sector j | ||||||||||
| Imports () | ||||||||||
| Value-added () | ||||||||||
| Output () | ||||||||||
| Selected VC | Brazil | (%) | Chile | (%) | Colombia | (%) | Mexico | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agri-food value chains | 168,104 | 19% | 2807 | 4% | 12,933 | 16% | 33,658 | 7% |
| Mining value chains | 7658 | 1% | 3650 | 5% | 5459 | 7% | 22,980 | 5% |
| Resource-based manufacturing value chains | 67,044 | 8% | 29,637 | 38% | 8116 | 10% | 53,277 | 11% |
| Non-resource-based manufacturing value chains | 69,860 | 8% | 14,569 | 18% | 6639 | 8% | 66,967 | 14% |
| Business services value chains | 239,836 | 28% | 7767 | 10% | 15,746 | 19% | 199,596 | 41% |
| Other services value chains | 318,488 | 37% | 20,385 | 26% | 32,797 | 40% | 115,906 | 24% |
| Total | 870,991 | 100% | 78,815 | 100% | 81,689 | 100% | 492,385 | 100% |
| Value Chains | Brazil | (%) | Chile | (%) | Colombia | (%) | Mexico | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agri-food | 155 | 4.24% | 490 | 11% | 106 | 18% | 9865 | 2% |
| Mining | 21 | 0.56% | 160 | 4% | 20 | 3% | 49,335 | 11% |
| Resource-based manufacturing | 84 | 2.30% | 107 | 2% | 11 | 2% | 16,687 | 4% |
| Non-resource manufacturing | 92 | 2.52% | 1387 | 32% | 4 | 1% | 69,211 | 16% |
| Business Services | 1085 | 29.63% | 1004 | 23% | 252 | 42% | 82,224 | 19% |
| Other value chains | 2224 | 60.76% | 1172 | 27% | 210 | 35% | 205,218 | 47% |
| Total | 3661 | 100.00% | 4319 | 100% | 603 | 100% | 432,540 | 100% |
| Trade-Related Measure | Brazil | (%) | Chile | (%) | Colombia | (%) | México | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource to resource industries | ||||||||
| Domestic TiVA | 168,921 | 48% | 1133 | 7% | 22,371 | 36% | 761,683 | 47% |
| VA exports | 183,288 | 52% | 15,452 | 93% | 39,326 | 64% | 868,041 | 53% |
| Total TiVA | 352,209 | 100% | 16,585 | 100% | 61,697 | 100% | 1,629,724 | 100% |
| Domestic CO2 | 62,781 | 55% | 3236 | 31% | 7047 | 56% | 25,446 | 51% |
| CO2 exports | 51,018 | 45% | 7222 | 69% | 5533 | 44% | 24,245 | 49% |
| Total CO2 | 113,799 | 100% | 10,458 | 100% | 12,580 | 100% | 49,691 | 100% |
| Resource to non-resource industries | ||||||||
| Domestic TiVA | 12,702 | 73% | 515 | 46% | 1885 | 79% | 31,425 | 44% |
| VA exports | 4623 | 27% | 595 | 54% | 503 | 21% | 40,289 | 56% |
| Total TiVA | 17,324 | 100% | 1110 | 100% | 2388 | 100% | 71,714 | 100% |
| Domestic CO2 | 3061 | 72% | 3236 | 31% | 314 | 75% | 1743 | 45% |
| CO2 exports | 1219 | 28% | 7222 | 69% | 105 | 25% | 2128 | 55% |
| Total CO2 | 4280 | 100% | 10,458 | 100% | 419 | 100% | 3871 | 100% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanguinet, E.R.; Azzoni, C.R.; Alvim, A.M. Resource-Based Industries and CO2 Emissions Embedded in Value Chains: A Regional Analysis for Selected Countries in Latin America. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060856
Sanguinet ER, Azzoni CR, Alvim AM. Resource-Based Industries and CO2 Emissions Embedded in Value Chains: A Regional Analysis for Selected Countries in Latin America. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(6):856. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060856
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanguinet, Eduardo Rodrigues, Carlos Roberto Azzoni, and Augusto Mussi Alvim. 2022. "Resource-Based Industries and CO2 Emissions Embedded in Value Chains: A Regional Analysis for Selected Countries in Latin America" Atmosphere 13, no. 6: 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060856
APA StyleSanguinet, E. R., Azzoni, C. R., & Alvim, A. M. (2022). Resource-Based Industries and CO2 Emissions Embedded in Value Chains: A Regional Analysis for Selected Countries in Latin America. Atmosphere, 13(6), 856. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060856






