Influence of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on Super Cyclone Activities over the Bay of Bengal during the Primary Cyclone Season
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
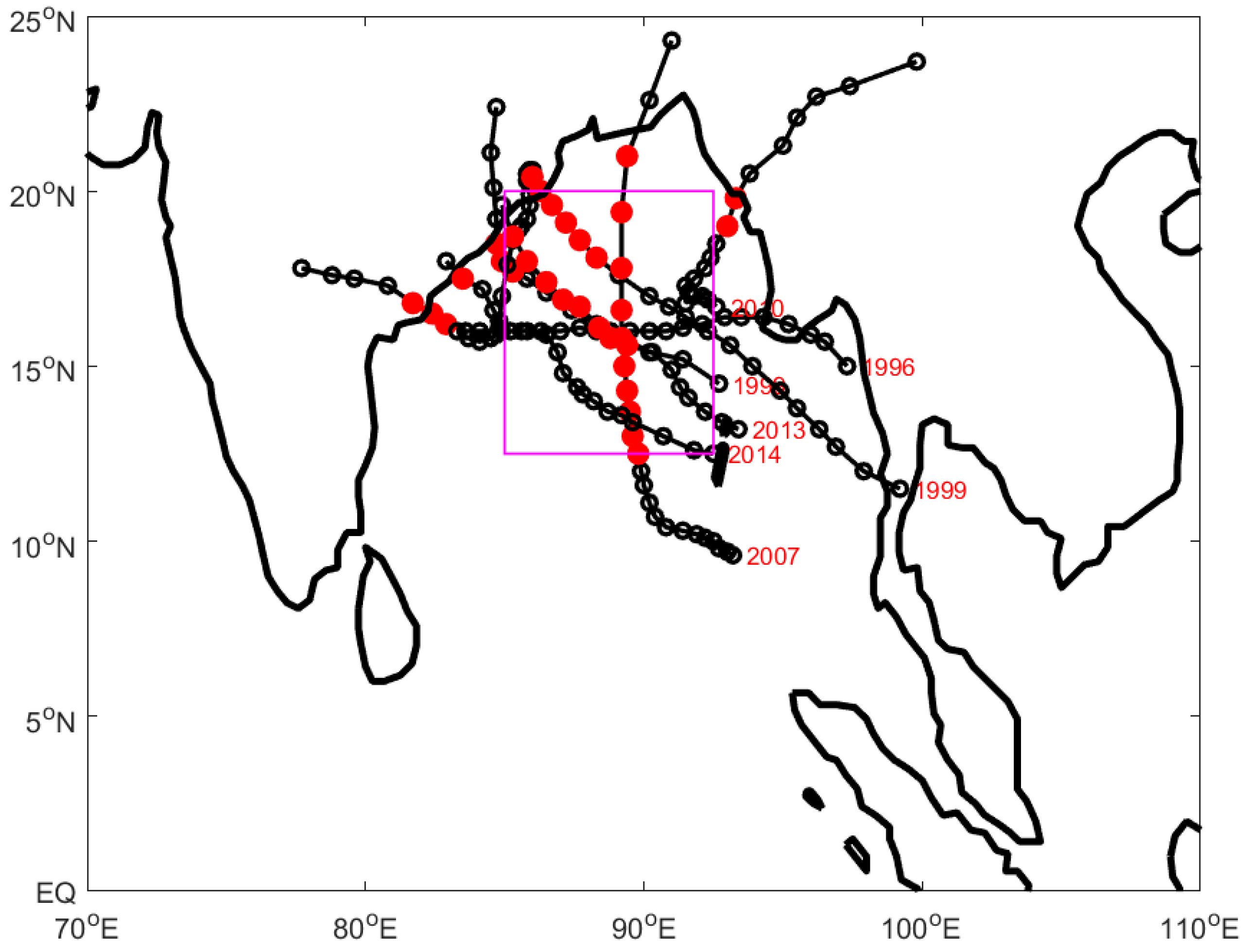
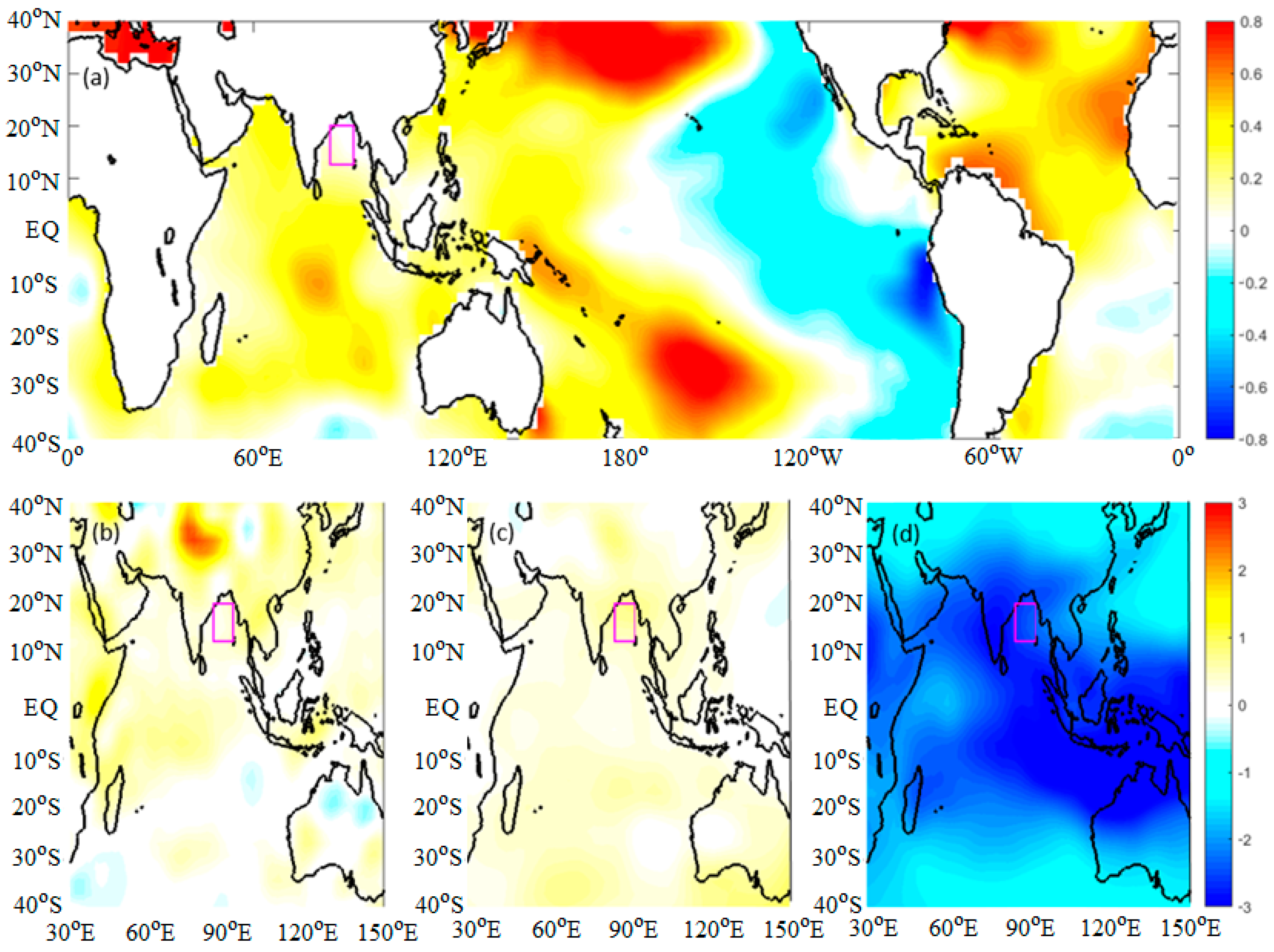
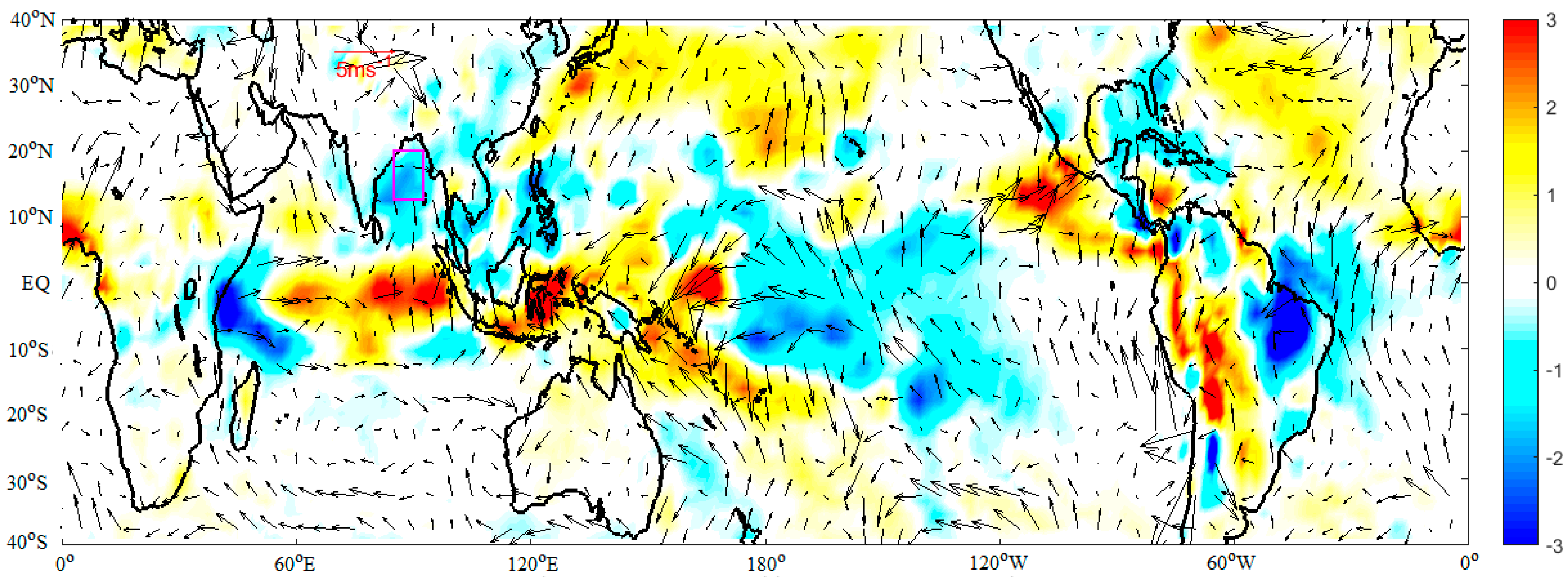
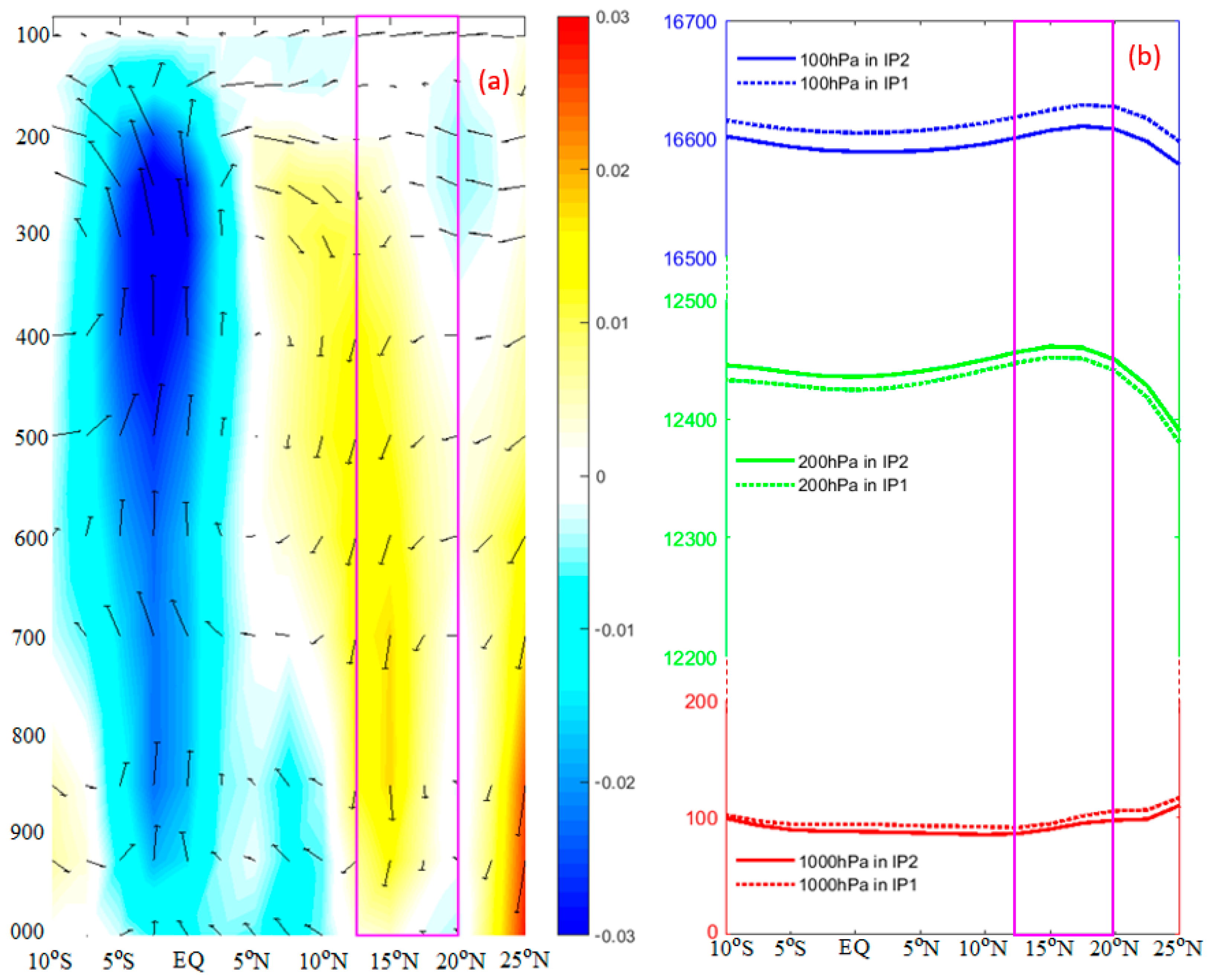
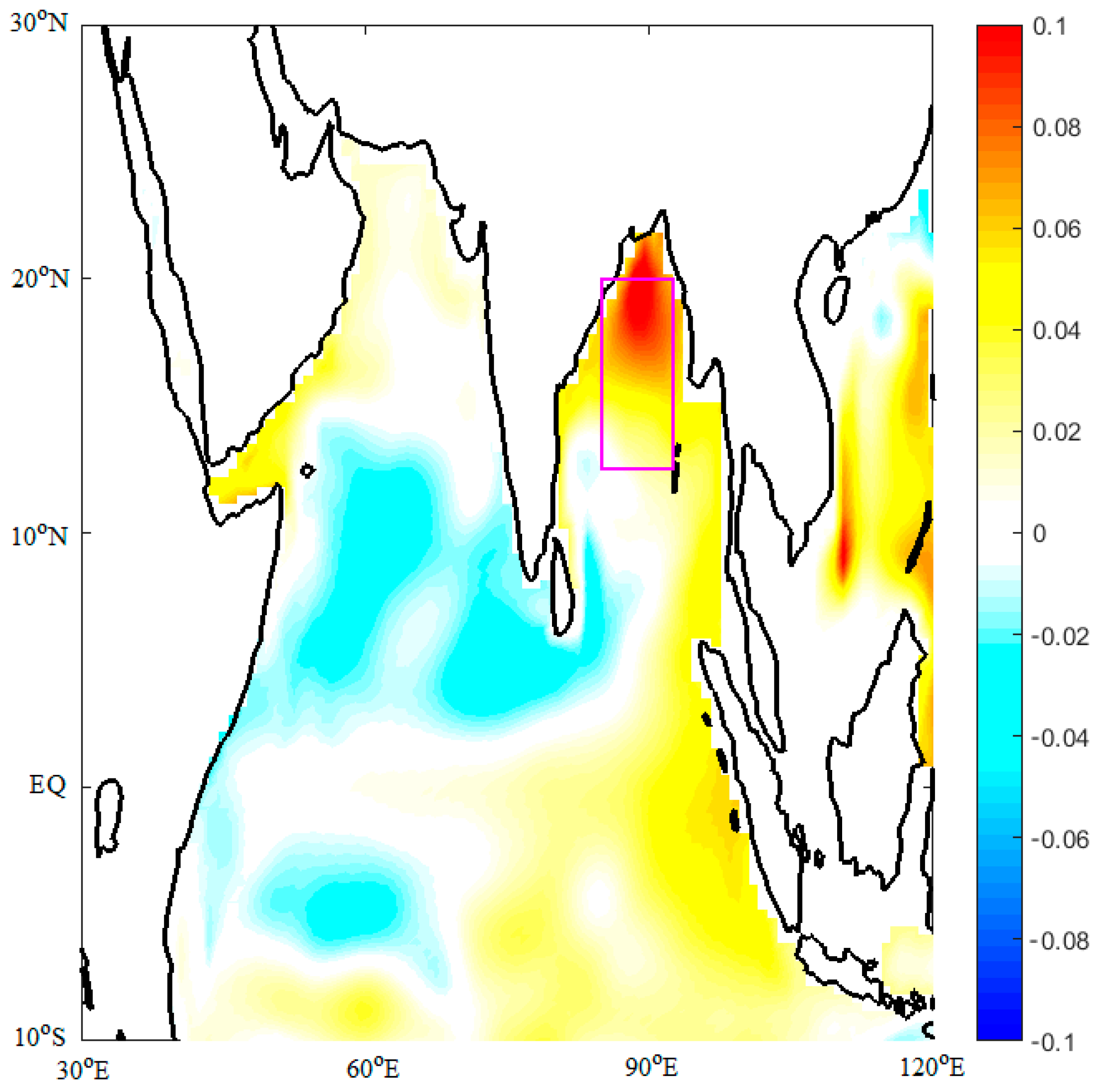
3. Analysis and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emanuel, K.A. Tropical cyclones. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003, 31, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielke, R.A., Jr.; Gratz, J.; Landsea, C.W.; Collins, D.; Saunders, M.A.; Musulin, R. Normalized hurricane damage in the United States: 1900–2005. Nat. Hazards Rev. 2008, 9, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, E.S.; Landsea, C.W.; Gibney, E.J. The Deadliest, Costliest, and Most Intense United States Tropical Cyclones from 1851 to 2010 (and Other Frequently Requested Hurricane Facts); NOAA Technical Memorandum NWS NHC-6; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Weather Service, National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wahiduzzaman, M.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Wotherspoon, J.S.; Holbrook, N.J. A climatological model of North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone genesis, tracks and landfall. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 2585–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahiduzzaman, M.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Klotzbach, P.J.P.; Wotherspoon, J.S.; Holbrook, N.J. A statistical seasonal forecast model of North Indian Ocean tropical cyclones using the quasi-biennial oscillation. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 934–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahiduzzaman, M.; Oliver, E.C.; Wotherspoon, S.; Luo, J.J. Statistical forecasting of tropical cyclones over the North Indian Ocean and the role of El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 1571–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahiduzzaman, M.; Yeasmin, A.; Luo, J.J.; Quadir, D.A.; Amstel, A.V.; Cheung, K. Markov Chain Monte Carlo simulation and regression approach guided by El Niño–Southern Oscillation to model the tropical cyclone occurrence over the Bay of Bengal. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 2693–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahiduzzaman, M.; Cheung, K.; Luo, J.-J.; Bhaskaran, P.K.; Tang, S.; Yuan, C. Impact assessment of Indian Ocean Dipole on the North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone prediction using a Statistical model. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 1275–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, H.; Keim, B.; Sathiaraj, D. A Review of Tropical Cyclone-Generated Storm Surges: Global Data Sources, Observations and Impacts: A Review of Tropical Storm Surges. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 545–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J. Myanmar’s deadly daffodil. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Fudeyasu, H. Genesis of tropical cyclone Nargis revealed by multiple satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Chen, C.H.; Pun, I.F.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.C. Warm ocean anomaly, air sea fluxes, and the rapid intensification of Tropical Cyclone Nargis (2008). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L03817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhaden, M.J.; Foltz, G.R.; Lee, T.; Murty, V.S.N.; Ravichandran, M.; Vecchi, G.A.; Vialard, J.; Wiggert, J.D.; Yu, L. Ocean–atmosphere interactions during Cyclone Nargis. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, W.; Taniguchi, H.; Satoh, M. The genesis of tropical cyclone Nargis (2008): Environmental modulation and numerical predictability. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 88, 497–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yanase, W.; Satoh, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Fujinami, H. Seasonal and intraseasonal modulation of tropical cyclogenesis environment over the Bay of Bengal during the extended summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2914–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yu, W.; Li, T.; Murty, V.S.N.; Tangang, F. Bimodal character of cyclone climatology in Bay of Bengal modulated by monsoon seasonal cycle. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Tsuboki, K. Role of synoptic scale forcing in cyclogenesis over the Bay of Bengal. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 2651–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcphaden, M.J.; Lee, T.; Mcclurg, D. El Nino and its relationship to changing background conditions in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saji, N.H.; Goswami, B.N.; Vinayachandran, P.N.; Yamagata, T. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature 1999, 401, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Moore, A.M.; Loschnigg, J.P.; Leben, R.R. Coupled ocean–atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature 1999, 401, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chan, J.C.L. How strong ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Chen, D. Variation of tropical cyclone activity in the South Indian Ocean: El Nino-South Oscillation and Madden-Julian Oscillation effects. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, S.J.; Emanuel, K.A.; Sobel, A.H. Use of a genesis potential index to diagnose ENSO effects on tropical cyclone genesis. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4819–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, M.F.; Young, S.G. The interannual variability of tropical cyclones. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 3587–3598. [Google Scholar]
- Eric, K.W.; Chan, J.C.L. Interannual variations of tropical cyclone activity over north Indian Ocean. Int. J. Climatol. 2012, 32, 819–830. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yu, W. Modulation of Interannual Variability of TC activity over Southeast Indian Ocean by Negative IOD Phase. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2015, 72, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girishkumar, M.S.; Ravichandran, M. The influences of ENSO on tropical cyclone activity in the Bay of Bengal during October-December. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C02033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.P.; Gupta, M.; Santha, K.; Saikia, D.; Khanuja, S. Indian Ocean dipole mode and tropical cyclone frequency. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.P.; Cao, J. North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone activities influenced by the Indian Ocean Dipole mode. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, W.; Li, K.; Liu, Y. What Controls the Interannual Variation of Tropical Cyclone Genesis Frequency over Bay of Bengal in the Post-Monsoon Peak Season? J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 17, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Interdecadal changes in El Niño onset in the last four decades. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantua, N.J.; Hare, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wallace, M.J.; Francis, C.R. A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Li, T.; Liu, J. Cause of interdecadal change of tropical cyclone controlling parameter in the western North Pacific. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Luo, J.; Huang, G.; Wang, P. Distinct global warming rates tied to multiple ocean surface temperature changes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, J.H.; Neumann, J.C. The international best track archive for climate stewardship (IBTrACS) unifying tropical cyclone data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bister, M.; Emanuel, K.A. Low frequency variability of tropical cyclone potential intensity 1. Interannual to interdecadel variability. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.A.; Nolan, D.S. Tropical cyclone activity and the global climate system. In Proceedings of the 26th Conference on hurricanes and tropical meteorology, Miami, FL, USA, 3–7 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Peng, S.M.; Li, T.; Stevens, D. Developing versus nondeveloping disturbances for tropical cyclone formation, Part II: Western North Pacific. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.M.; Fu, B.; Li, T.; Stevens, D.E. Developing versus nondeveloping disturbances for tropical cyclone formation. Part I: North Atlantic. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1047–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, T.; Yu, W. Environmental conditions regulating the formation of super tropical cyclone during pre-monsoon transition period over Bay of Bengal. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 3857–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. Global view of the origin of tropical disturbances and storms. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 669–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Wang, B. Future change of North Atlantic tropical cyclone tracks: Projection by a 20-km-mesh global atmospheric model. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2699–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.; An, S.; Cai, W.; Ganachaud, A.; Guilyardi, E.; Jin, F.F.; Jochum, M.; Lengaigne, M.; Power, S.; Timmermann, A.; et al. The impact of global warming on the tropical Pacific Ocean and El Niño. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNezio, P.N.; Clement, A.C.; Vecchi, G.A. Reconciling differing views of tropical Pacific climate change. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2010, 91, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. Variability of the depth the 20 °C isotherm along 6°N in the Bay of Bengal: Its response to remote and local forcing and its relation to satellite SSH variability. Deep Sea Res. Part II 2003, 50, 2285–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girishkumar, M.S.; Prakash, V.; Ravichandran, M. Influence of Pacific Decadal Oscillation on the relationship between ENSO and tropical cyclone activity in the Bay of Bengal during October–December. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tvd | Tvr | Ted | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IP2-IP1 | >0 | >0 | >0 | >0 |
| Significance of difference | >95% | >99% | >99% | <90% |
| Tvd and Tvr | Ted | |||
| 89% | 11% | |||
| BDI (IP2-IP1) | 1000 | 925 | 850 | 700 | 600 | 500 | 400 | 300 | 200 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vor | −0.17 | −0.11 | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.30 | −0.01 |
| ω | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.34 * | 0.39 * | 0.39 * | 0.32 | 0.25 | 0.13 | −0.04 | −0.58 * |
| T | 0.50 * | 0.43 * | 0.47 * | 0.59 * | 0.80 * | 0.73 * | 0.24 | 0.44 * | −0.48 * | −1.28 * |
| RH | −0.35 | −0.14 | −0.11 | −0.33 | −0.37 * | −0.62 * | −0.62 * | −0.89 * | ||
| SH | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.08 | −0.20 | −0.23 | −0.47 * | −0.51 * | −0.66 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Li, K. Influence of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on Super Cyclone Activities over the Bay of Bengal during the Primary Cyclone Season. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050685
Li Z, Xu Z, Fang Y, Li K. Influence of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on Super Cyclone Activities over the Bay of Bengal during the Primary Cyclone Season. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(5):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050685
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhi, Zecheng Xu, Yue Fang, and Kuiping Li. 2022. "Influence of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on Super Cyclone Activities over the Bay of Bengal during the Primary Cyclone Season" Atmosphere 13, no. 5: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050685
APA StyleLi, Z., Xu, Z., Fang, Y., & Li, K. (2022). Influence of the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation on Super Cyclone Activities over the Bay of Bengal during the Primary Cyclone Season. Atmosphere, 13(5), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13050685






