Abstract
Precipitable water vapor (PWV) is a parameter used to estimate water vapor content in the atmosphere. In this study, estimates of PWV from PIMO, PLEG and PPPC global navigation satellite system (GNSS) stations are evaluated regarding the PWV obtained from its collocated radiosonde (RS) stations. GNSS PWV were highly correlated with RS PWV (R ~ 0.97). Mean bias error (MBE) between −0.18 mm and −13.39 mm, and root mean square error (RMSE) between 1.86 mm and 2.29 mm showed a good agreement between GNSS PWV and RS PWV. The variations of PWV are presented. Daily variations of PWV conformed to the daily data of rainfall which agrees to the climate types of Quezon City (Type I), Legaspi (Type II), and Puerto Princesa (Type III) based on the Coronas climate classification. Moreover, PWV monthly variation at all sites is high from May to October (~62 mm) and low from November to April (~57 mm). The relationship between PWV and rainfall at all stations showed positive correlation coefficients between +0.49 to +0.83. Meanwhile, it is observed that when PWV is high (low), its variability is low (high). This study shows the potential of GNSS to study water vapor and its contribution to weather analysis.
1. Introduction
Water vapor is one of the essential components in the atmosphere since it transports moisture and latent heat to influence the weather [1]. Although its impact on weather is significant, the distribution of atmospheric water vapor is highly fluctuating seasonally and diurnally [2]. Because of this, it is difficult to measure. Atmospheric water vapor content is expressed in precipitable water vapor (PWV) and defined as the integrated amount of water vapor condensed in a vertical column from the surface to the top of the atmosphere [3]. Conventional meteorological instruments, such as radiosonde [4,5,6] and GNSS [7,8,9,10] have been widely used to estimate PWV.
The traditional approach in obtaining information from the atmosphere to measure PWV is the atmospheric sounding from radiosonde (RS). RS is a battery-powered telemetry instrument system carried into the atmosphere, typically by a weather balloon. Due to its high cost, RS usually operates twice a day (0000 UTC and 1200 UTC). With this limitation, it results in poor spatial and temporal resolution [11,12,13].
Moreover, global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) have been used to estimate PWV by utilizing the tropospheric signal delays. This technique has been more advantageous due to its 24-h variability, global coverage, high spatial and temporal resolution, low cost, long-term stability, and high accuracy [14,15,16,17]. However, temperature profiles required in calculating the weighted mean temperature are obtained from radiosonde or nearby weather stations [18,19].
As with previous studies’ results, the temporal variations of PWV from RS and GNSS showed a good agreement with each other [15,20,21,22,23]. Li et al. [24] analyzed the PWV derived from RS, GNSS, and moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) from the United Kingdom Met Office and University of Wyoming and concluded that RS PWV and GNSS PWV agreed better with each other than MODIS-PWV. Ohtani and Naito [25] claimed a significant difference when GNSS and RS stations were not collocated, based on the comparison of PWV over Japanese islands. Although PWV from RS and GNSS have a similar trend, Perdiguer-López et al. [26] found that GNSS PWV was overestimated compared with RS PWV in Spain. This result was also demonstrated in Suparta et al. [27,28,29], where PWV was obtained in Australia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, and Singapore. These results imply the reliability of RS and GNSS to remote sense the atmosphere and estimate PWV.
In recent years, the established GNSS receiver stations have been increasing in the Philippines but only a limited number of local studies using the GNSS data are reported [8,9,17]. An improvement in the accuracy of PWV estimation and rainfall forecasting can pave the way for providing more climate models and improved weather analysis.
This work aims to measure and analyze the temporal variation of GNSS PWV during rainy days over the Philippines from 2015 to 2017. The structure of the paper is outlined as follows. Section 2 describes the data and methodologies adopted in this study. GNSS PWV is evaluated concerning RS PWV in the same section. The variations of PWV along with rainfall are presented in Section 3. The conclusion is given in Section 4.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Location
The climate of the Philippines is tropical, generally characterized by the amount of monthly rainfall received in a year [30]. Type I climate has two pronounced seasons—wet from May to October and dry from November to April. Locations with Type II climate have no dry season and with a distinct maximum period from December to February. Type III climate closely resembles Type I but with a shorter dry season. Lastly, Type IV climate has an evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year [31,32]. Thus, this study aims to analyze the temporal variation of precipitable water vapor in the regions of the Philippines based on the climate type (excluding Type IV).
2.2. Selection of Experimental Data
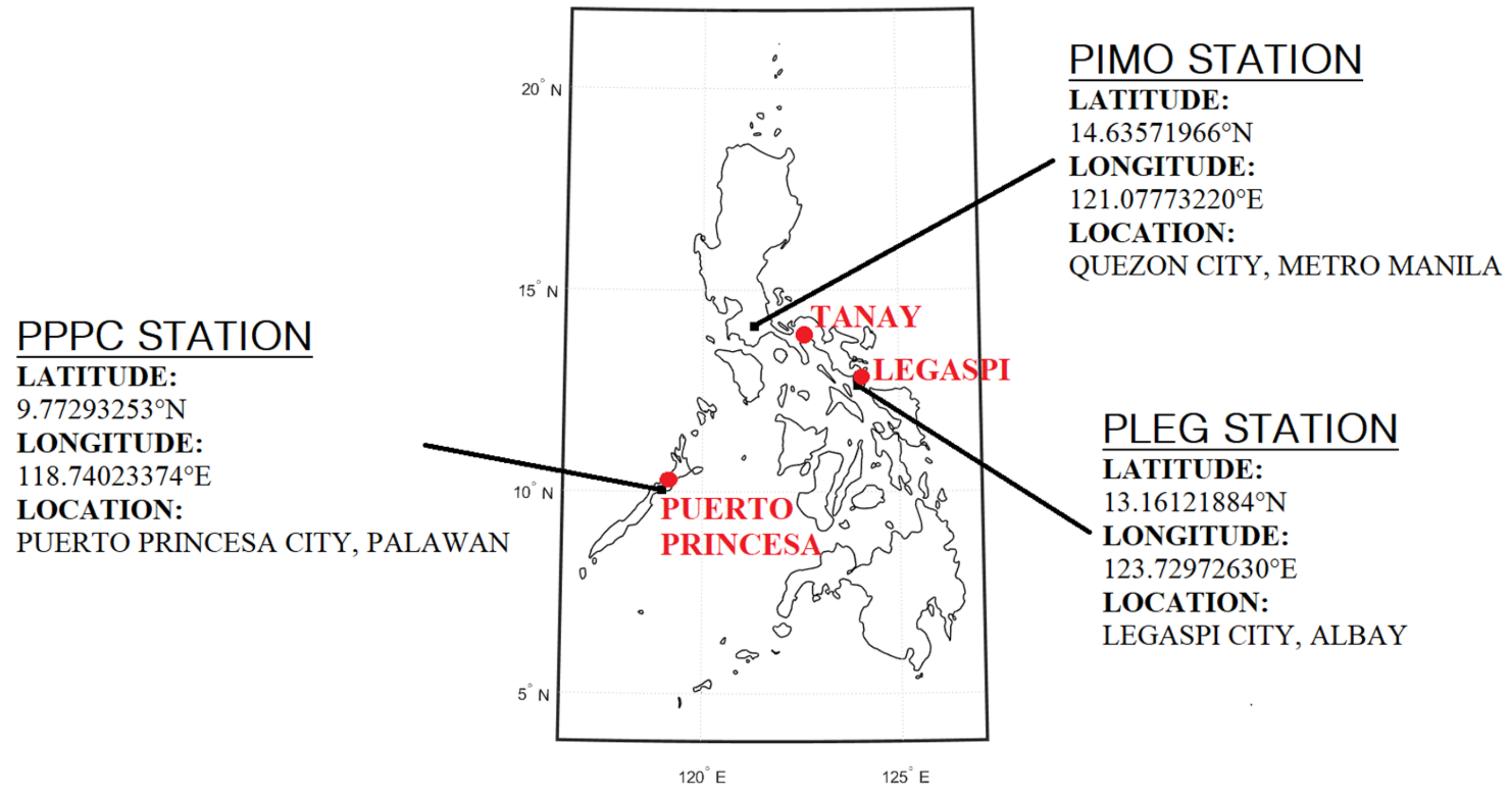
RS PWV profiles are collected from the compiled data of Integrated Global Radiosonde Archive (IGRA) produced by the NOAA’s National Climatic Data Center to evaluate the estimates of PWV from GNSS. The selection of the GNSS stations is based on the availability of both GNSS observations and PWV data at collocated RS stations from 2015 to 2017. This study used three GNSS stations, namely PIMO in Quezon City, Metro Manila (14°38′8.5884″ N, 121°4′39.8352″ E), PLEG in Legaspi City, Albay (13°9′40.3848″ N, 123°43′47.0136″ E) and PPPC in Puerto Princesa City, Palawan (9°46′22.5552″ N, 118°44′24.8424″ E) as presented in Figure 1. These stations are operated by the National Mapping and Resource Information Authority (NAMRIA), an agency under the Department of Environment and Natural Resources. In addition, Figure 1 also shows the collocated RS stations, and Table 1 lists the distances between the GNSS and RS stations and their height differences.
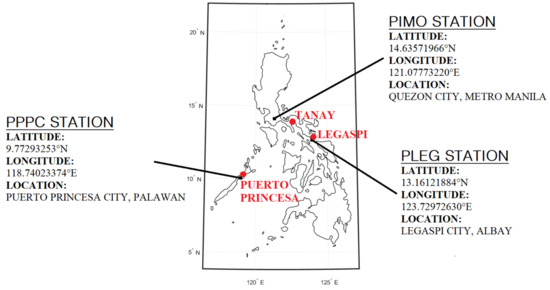
Figure 1.
The locations of the GNSS stations (black dots) and their collocated RS stations (red dots) in the Philippines used in this study.

Table 1.
The distances of the GNSS stations to their collocated RS stations selected in this study. Height differences between the stations are also shown.
Meteorological variables such as temperature, dew point temperature, pressure, and three-hourly rainfall data in the nearby synoptic stations are obtained from Ogimet to analyze the PWV variation. Ogimet is a weather information service that is available for users online at www.ogimet.com (accessed on 6 January 2021). These data are contributed by the Department of Science and Technology—Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical, and Astronomical Services (DOST-PAGASA). It is important to note that synoptic stations might be 100 km distant [18,33]. Table 2 shows the distances between the GNSS and synoptic stations.

Table 2.
The distances of the GNSS stations to their collocated weather stations selected in this study.
2.3. Estimation of GNSS PWV
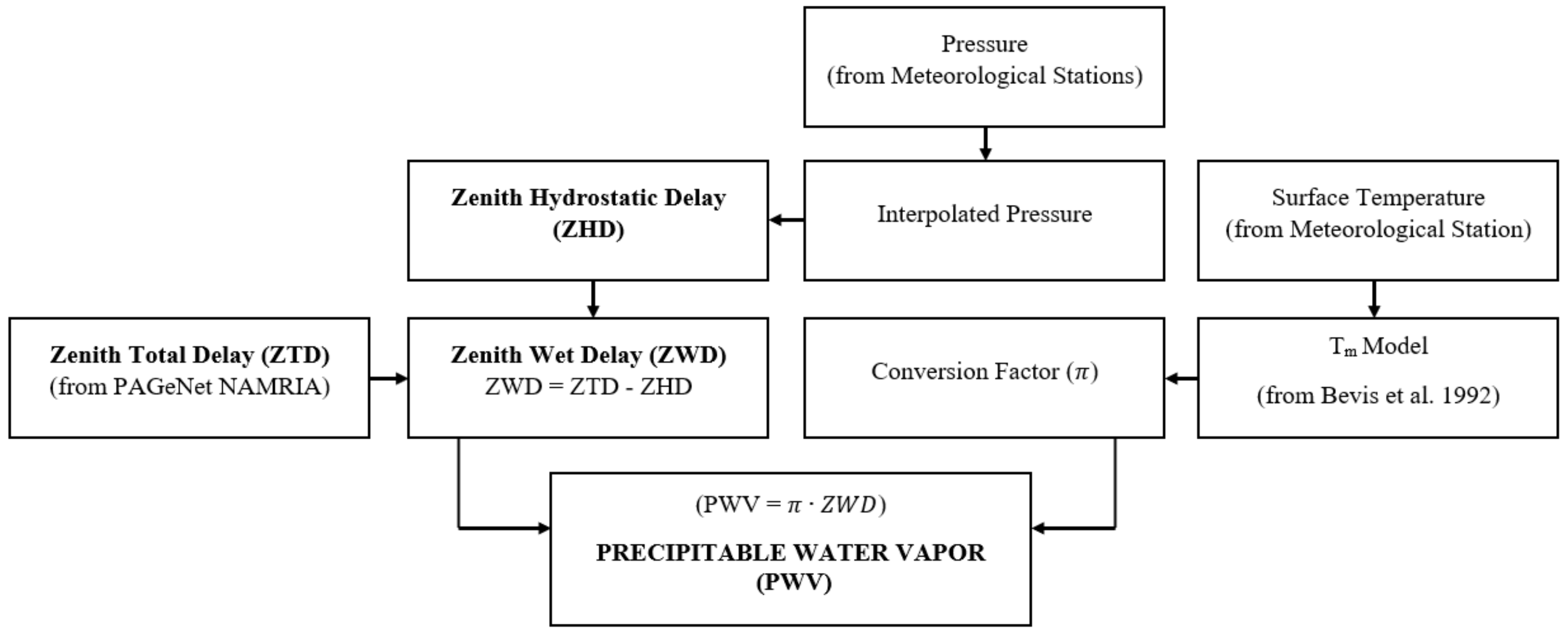
In this study, the total zenith delay (ZTD) data filed from 2015 to 2017 are provided by NAMRIA. ZTD data are used to estimate the tropospheric signal delay in the vertical direction. Figure 2 demonstrates the process flow of calculating PWV utilizing the signal delays between GNSS satellites and receiver stations.
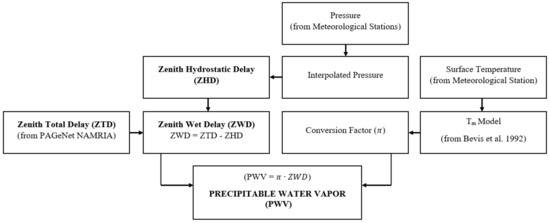
Figure 2.
Flow chart for obtaining GNSS PWV.
Essentially, the Saastamonein model is used for high-precision geodetic application on a global scale because it performs the best for all elevation angles [34]. This model is commonly used to compute for zenith hydrostatic delay (ZHD):
where is surface pressure, is the latitude and and H is the ellipsoidic height in km.
Since the surface pressure and temperature measurements are not always available at GNSS stations, Alshawaf et al. [18] suggests interpolation techniques to provide measurements needed for PWV estimation. The techniques use the pressure and temperature profiles from nearby weather stations.
By subtracting the ZHD from ZTD, zenith wet delay (ZWD) is obtained. Since the wet delay has the information on water vapor, PWV is taken by:
Here, is the conversion factor, and this is expressed as:
where is the density of liquid water in kg/m3, Rv is the specific gas constant for water vapor, Tm is the modeled weighted mean temperature and , where m is the ratio of molar masses of water vapor and dry air [7]. In this study, the globally accepted Tm model by Bevis has been used [7,16,17,22].
2.4. Evaluation of GNSS PWV
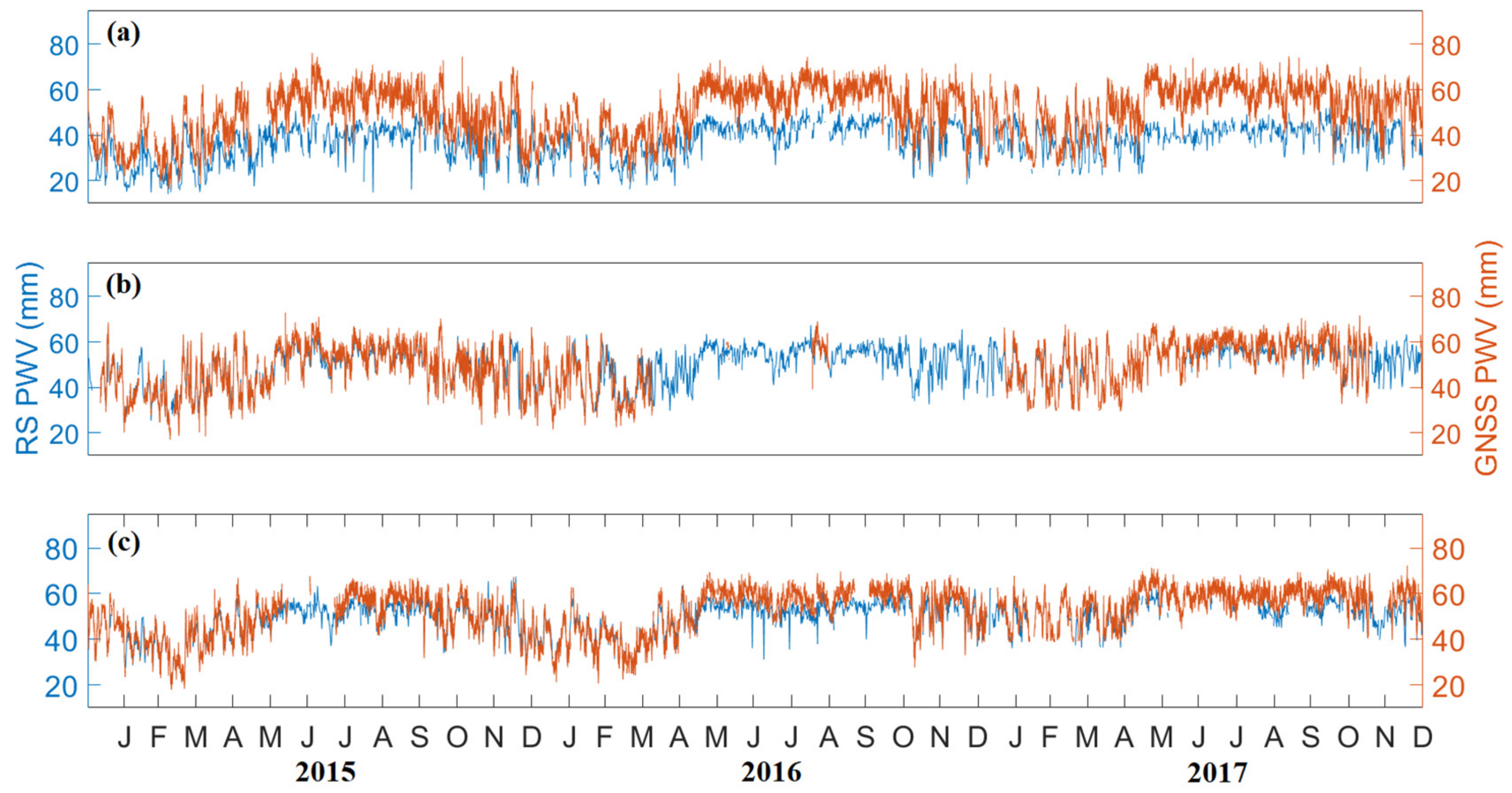
In this study, PWV data from radiosonde are used to evaluate the accuracy of GNSS PWV in the Philippines. The distances between the selected RS and GNSS stations are less than 35 km, as shown in Table 1, to which it is regarded as collocated. Figure 3 shows the time series of RS PWV and GNSS PWV in Tanay and PIMO, Legaspi and PLEG, and Puerto Princesa and PPPC from 2015 to 2017. It shows that GNSS PWV corresponds with RS PWV. It can also be observed that GNSS PWV estimates are generally higher than RS PWV. It has been shown that the accuracy of GNSS PWV is almost equal to RS PWV [14,35,36]. Nevertheless, both PWV from the two instruments follows the same trend.
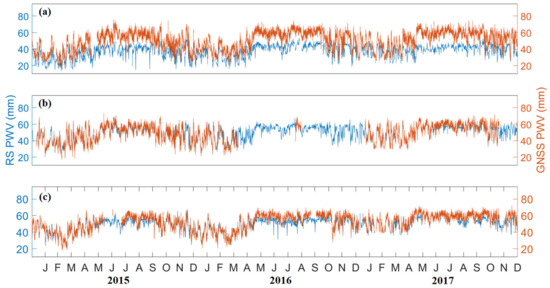
Figure 3.
The time series of RS PWV (blue) and GNSS PWV (orange) in (a) Tanay and PIMO, (b) Legaspi and PLEG, and (c) Puerto Princesa and PPPC from 2015 to 2017.
GNSS PWV in PIMO is significantly higher than RS PWV in Tanay, as shown in Figure 3a. This PWV difference may be due to the differences in their heights (0.545 km) and geographical locations. The RS station is located at the top of the mountain, while the GNSS receiver operates on the ground. Overestimated GNSS PWV compared with RS PWV are also found in the studies of Gui et al. [37], Ohtani and Naito [25], and Perdiguer-Lopez [26]. Uncertainties of the radiosonde and its poor temporal resolution can also be considered as an explanation of the PWV differences.
Furthermore, the differences in PWV may also be caused by typhoons since it generally comes with a strong wind and a large amount of moisture. The most affected meteorological variable by a typhoon is wind speed. Variation patterns of PWV and wind speed were found similar during a typhoon period in the study of He et al. [38]. In addition, abnormal increases in PWV were due to typhoon motion. It is also important to note that high pressure caused by strong wind might cause errors in the atmospheric pressure observation, leading to discrepancies in estimating RS PWV and inaccuracy in ZHD estimation for GNSS PWV [39].
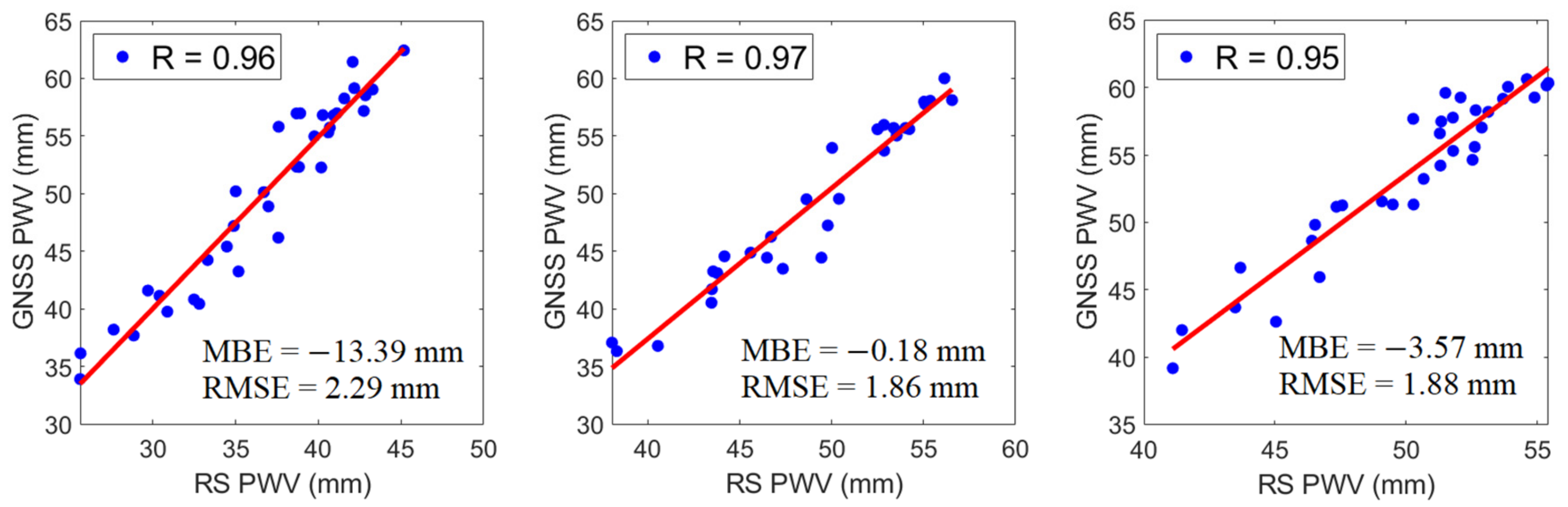
As verified in Figure 4, GNSS PWV were found highly correlated (R ~ +0.97) with RS PWV. The strong positive correlations observed in the stations of Tanay and PIMO; Legaspi and PLEG, and Puerto Princesa and PPPC with correlation coefficients of +0.96, +0.97 and +0.95, respectively, indicate that GNSS can also be used as an instrument to estimate PWV. Moreover, MBE reveals if the model tends to under- or overpredict, with values close to being desirable. Meanwhile, RMSE indicates the level of scattering in a model, comparing the actual deviations between the predicted and observed data. The lower the RMSE, the better the model in terms of absolute deviation [40,41,42].
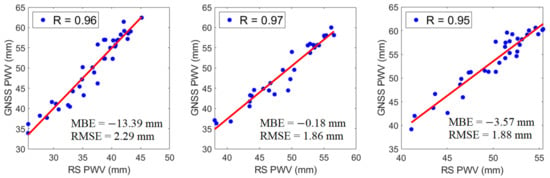
Figure 4.
The correlations of monthly means of RS PWV and GNSS PWV in (a) Tanay and PIMO, (b) Legaspi and PLEG, and (c) Puerto Princesa and PPPC from 2015 to 2017. MBE and RMSE values for each datum are also given.
It can be seen in Figure 4 that the obtained MBE values were less than zero while RMSE values were less than 3 mm. The MBE values were −13.39 mm, −0.18 mm, and −3.57 mm, and the RMSE values were 2.29 mm, 1.86 mm, and 1.88 mm for Tanay and PIMO, Legaspi and PLEG, and Puerto Princesa and PPPC, respectively. Although there are few discrepancies, RS PWV and GNSS PWV manifested a good agreement. Thus, the results of MBE and RMSE implied that GNSS could be used to develop a model for PWV temporal variation.
3. Discussion
3.1. Daily Variation of GNSS PWV and Rainfall
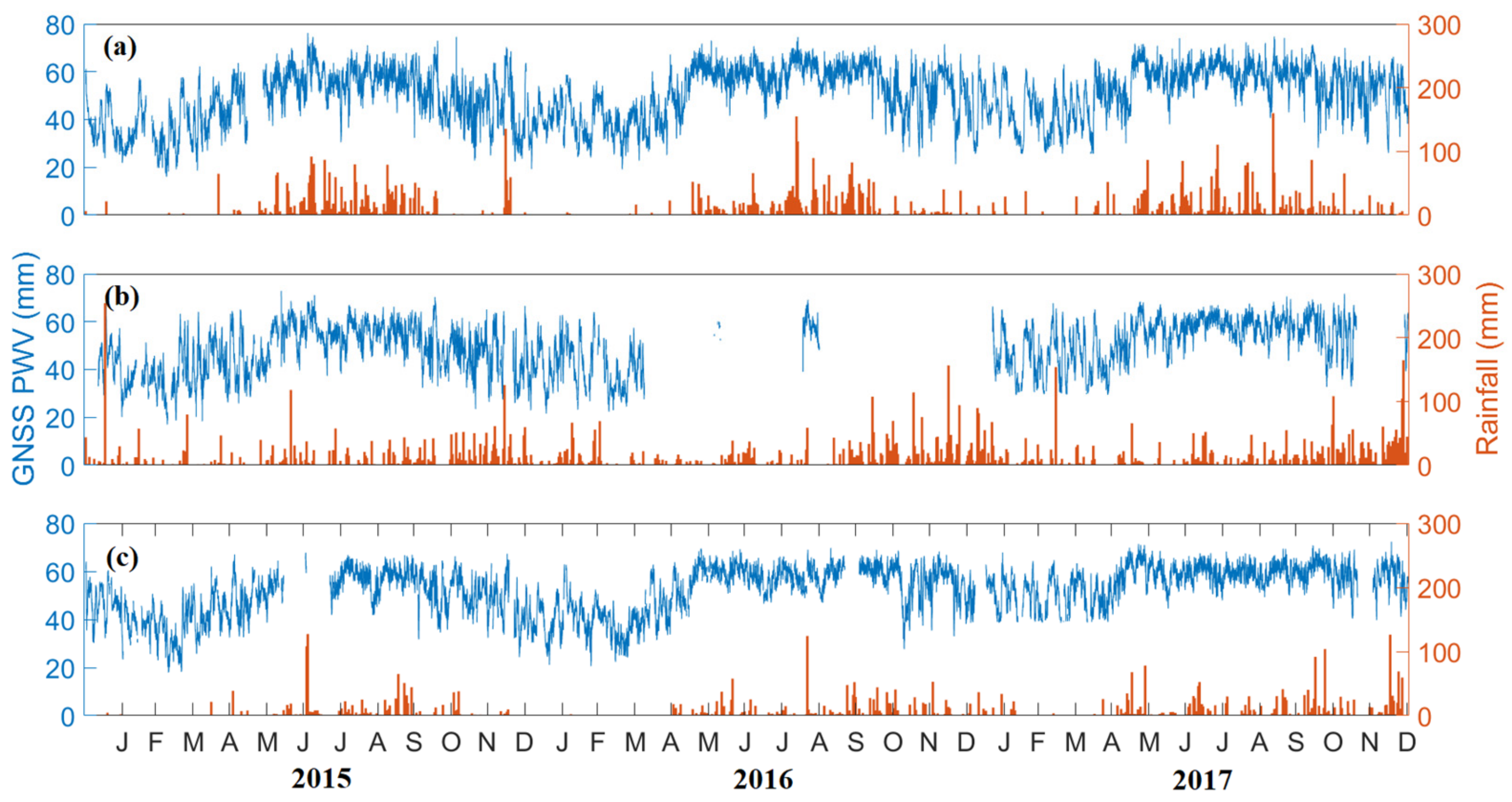
The daily variations of GNSS PWV and the daily data rainfall from 2015 to 2018 in the Philippines are shown in Figure 5. As seen in Figure 5a, PWV in PIMO follows the same trend with the rainfall data obtained from Science Garden, whereas PWV and rainfall are low during the dry season (November to April) and high during the wet season (May to October). It is important to note that Quezon City is categorized as Type I in the climate classification of DOST-PAGASA in terms of precipitation.
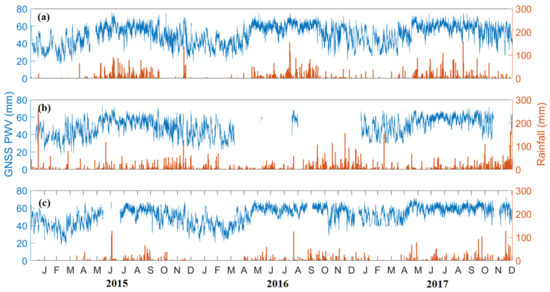
Figure 5.
Daily variation of GNSS PWV (blue) in (a) PIMO, (b) Legaspi, and (c) Puerto Princesa, along with the daily rainfall (orange) from 2015 to 2017.
Moreover, Figure 5b, shows the PWV and rainfall in the Legaspi area. Due to hardware issues, there are no ZTD data available from PLEG for most of 2016. Here, it can be observed that PWV generally follows the rainfall pattern. In contrast to the climate type of Quezon City, Legaspi, which is under Type II, has no real dry season. Notice that PWV values are relative from February to April and high for the rest of the months.
As observed in Figure 5c, PWV and rainfall in Puerto Princesa have similar Type I and Type II features. Under the climate classification of Type III, PWV in Puerto Princesa is relatively high, whereas the maximum peaks during the wet season (May to October) extend from November to January. On the other hand, the minimum is similar to where PWV is low in Legaspi (February to April), which is consistent with the amount of rainfall.
In this study, PWV agrees with rainfall. Most of the significant rainfall prevails when PWV is high; however, high PWV does not indicate the occurrence of rainfall. For instance, there is less rainfall in some high PWV. It has been reported that PWV sharply increases before the rainfall event [16,41,42,43]. There are also reports where PWV has a noticeable decrease in response to heavy rainfall and after its passing [17,44,45,46,47].
3.2. GNSS PWV in Rainy Days
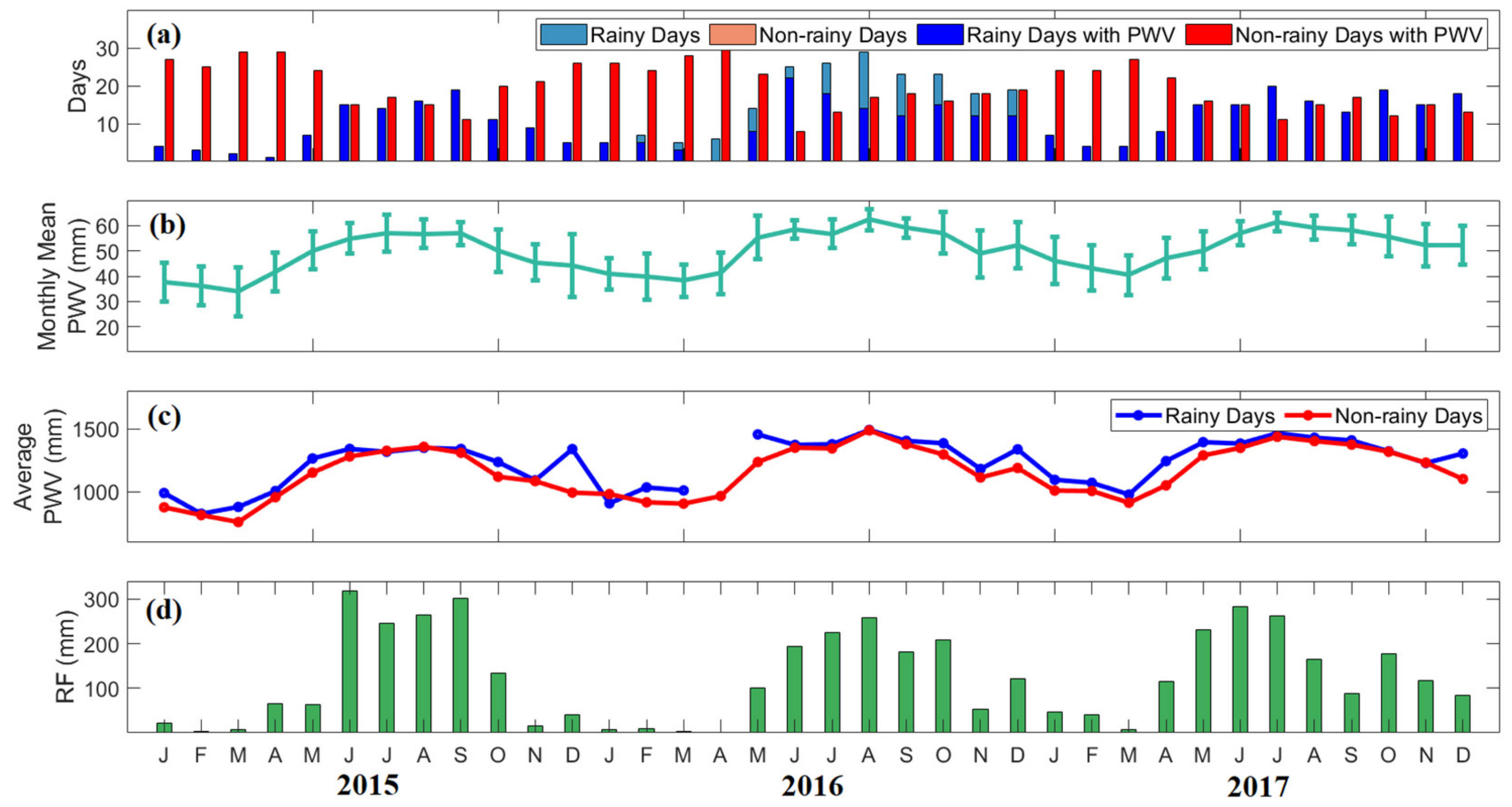
Figure 6 shows the monthly mean values of PWV for all days, the monthly average of daily PWV in rainy and non-rainy days, and the monthly rainfall in Quezon City from 2015 to 2017. As seen in Figure 6b, the monthly mean values of PWV ranged from 33 mm to 59 mm. It is observed that PWV is low from November to April and high from May to October. This result confirms that the PWV has similar variation with rainfall (Figure 6d), whereas the climate type of Quezon City has two seasons: dry from November to April and wet for the rest of the months.
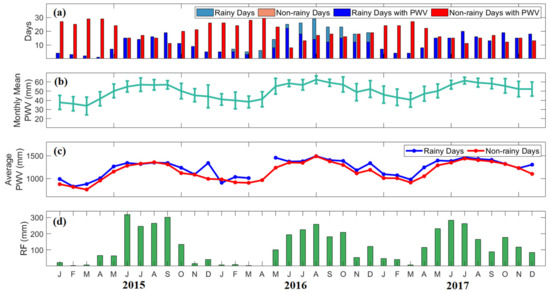
Figure 6.
(a) The number of rainy days (light blue) and non-rainy days (pink) and rainy (blue) and non-rainy days (red) with PWV per month in Quezon City from 2015 to 2017. (b) The monthly mean variations of PWV for all days, (c) monthly average of daily PWV and (d) monthly rainfall are also presented. Blue lines correspond to average PWV on rainy days and red lines are for average PWV in non-rainy days.
Although PWV is low during the dry season, the variability ranged from 6 mm to 12 mm. Low PWV variability varied from 2 mm to 5 mm during the wet season. This result can be possibly explained by two monsoons known as the northeast (NE) monsoon starts from November to March, and the southwest (SW) monsoon starts from mid-May to September. Monsoon winds bring warm moist air from the South China Sea to the western Philippines [48]. It suggests that the air is saturated during the peak of the wet season. Hence, moisture increases due to the tropical cyclones and southwesterly wind in the SW monsoon period, which greatly influenced the high PWV variability during the dry season [8]. Studies in the Philippines, China, and India where high PWV with low standard deviations during the monsoon period and low PWV with high standard deviations were also observed in the papers of Macalalad et al. [8], Jiang et al. [49], and Renju et al. [50]. A dropped in PWV during February to March in the Philippines was found in the paper of Suparta and Iskandar [27]. Then, there was an increase in PWV variation during the first April to May.
The days of a month were separated into rainy and non-rainy days with PWV, as shown in Figure 6a. While the monthly average of daily PWV ranged from 700 mm to 1500 mm, it is seen in Figure 6c that PWV is higher on rainy days than on non-rainy days. In addition, Figure 6d showed the monthly rainfall during the dry season ranged from 2 mm to 150 mm and during the wet season ranged from 100 mm to 300 mm. Notice that the monthly means of PWV for all days and the monthly total PWV on rainy days conform to the monthly rainfall.
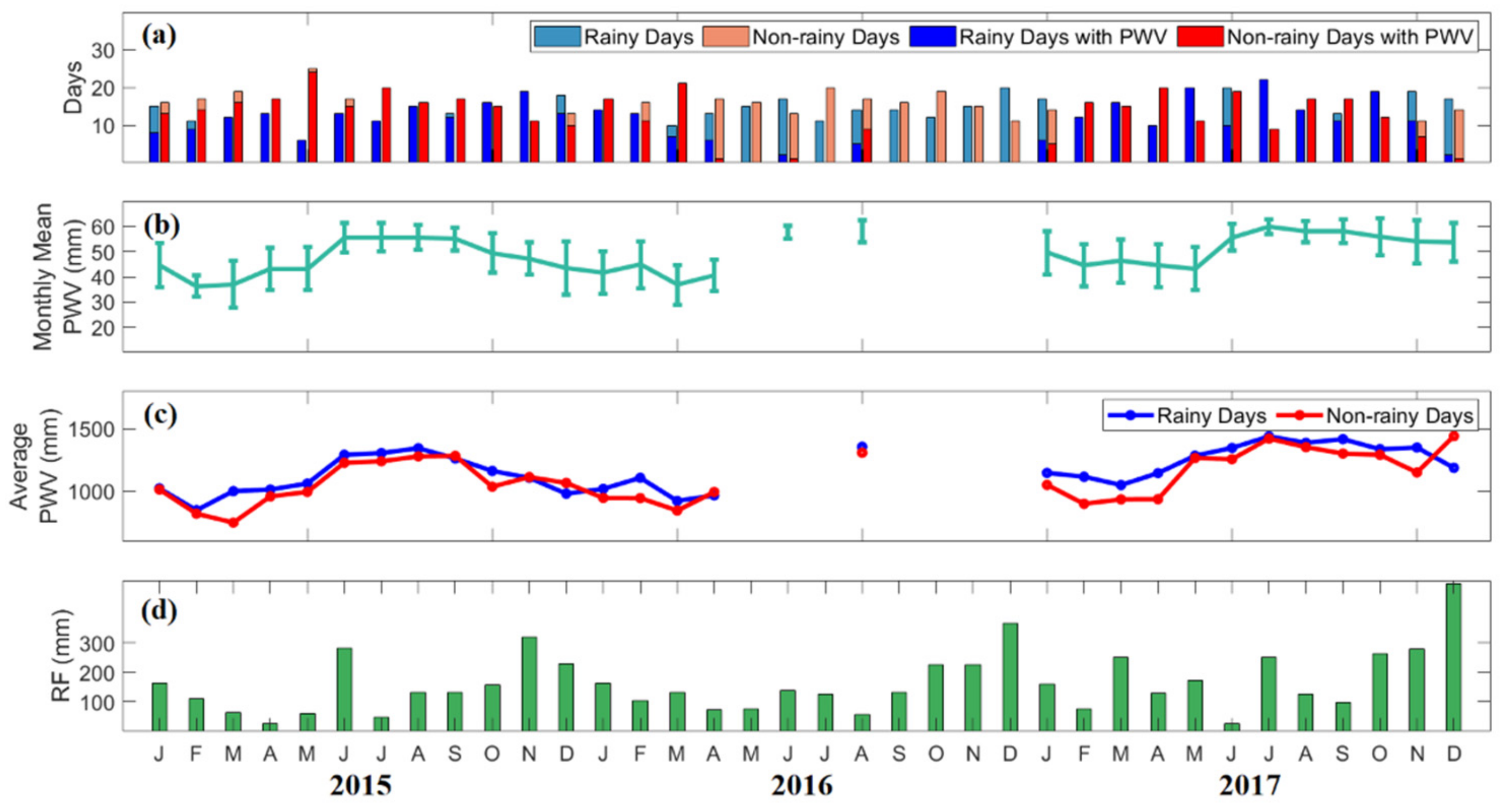
The monthly means of PWV for all days in Legaspi, along with the monthly average of daily PWV in rainy and non-rainy days, and the monthly rainfall from 2015 to 2017, are presented in Figure 7. Like in Quezon City, PWV in Legaspi is high from May to October, ranging from 43 mm to 60 mm. On the contrary, PWV is low from November to April, ranging from 36 mm to 49 mm, as shown in Figure 7b. This result confirms that monsoons highly affect the amount of water vapor. In Figure 7d, monthly rainfall in this area ranged from 12 mm to 500 mm. Heavy rainfall is most likely the effect of orographic land–air interaction and trade winds during the NE monsoon [32,51]. Furthermore, England et al. [52] reported that an increasing trend in the west Pacific winds, causing water temperature, was observed. This finding is conceivable to account for the explanation of the anomalous rainfall in Legaspi.
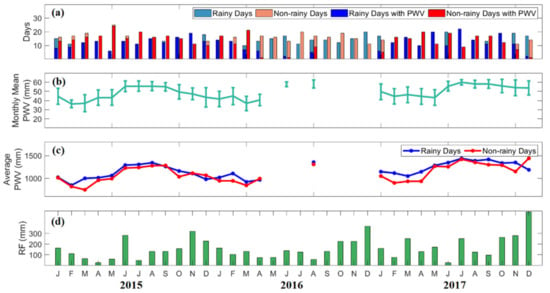
Figure 7.
(a) The number of rainy and non-rainy days, and rainy and non-rainy days with PWV per month in Legaspi from 2015 to 2017. (b) The monthly mean variations of PWV for all days, (c) monthly average of daily PWV, and (d) monthly rainfall are also presented. The color scales are in Figure 6.
While PWV from June to September is high, it has low PWV variability ranging from 2 mm to 5 mm. The moisture in these months is possibly influenced by the wind direction caused by the SW monsoon. The wind direction during the monsoon period is highly variable but weak, occurring from the ocean or the land [50]. Moreover, the variability of PWV for the rest of the months is high, ranging from 6 mm to 10 mm. Enhanced moisture content due to the regional convective systems contributes to the large PWV variability [53].
In general, the number of rainy days is lower than the number of non-rainy days except from October to December. In Figure 7c, a monthly average of daily GNSS PWV during rainy and non-rainy days are somewhat similar, ranging from 700 mm to 1400 mm. It can be noticed that PWV on rainy days is higher compared to PWV on non-rainy days.
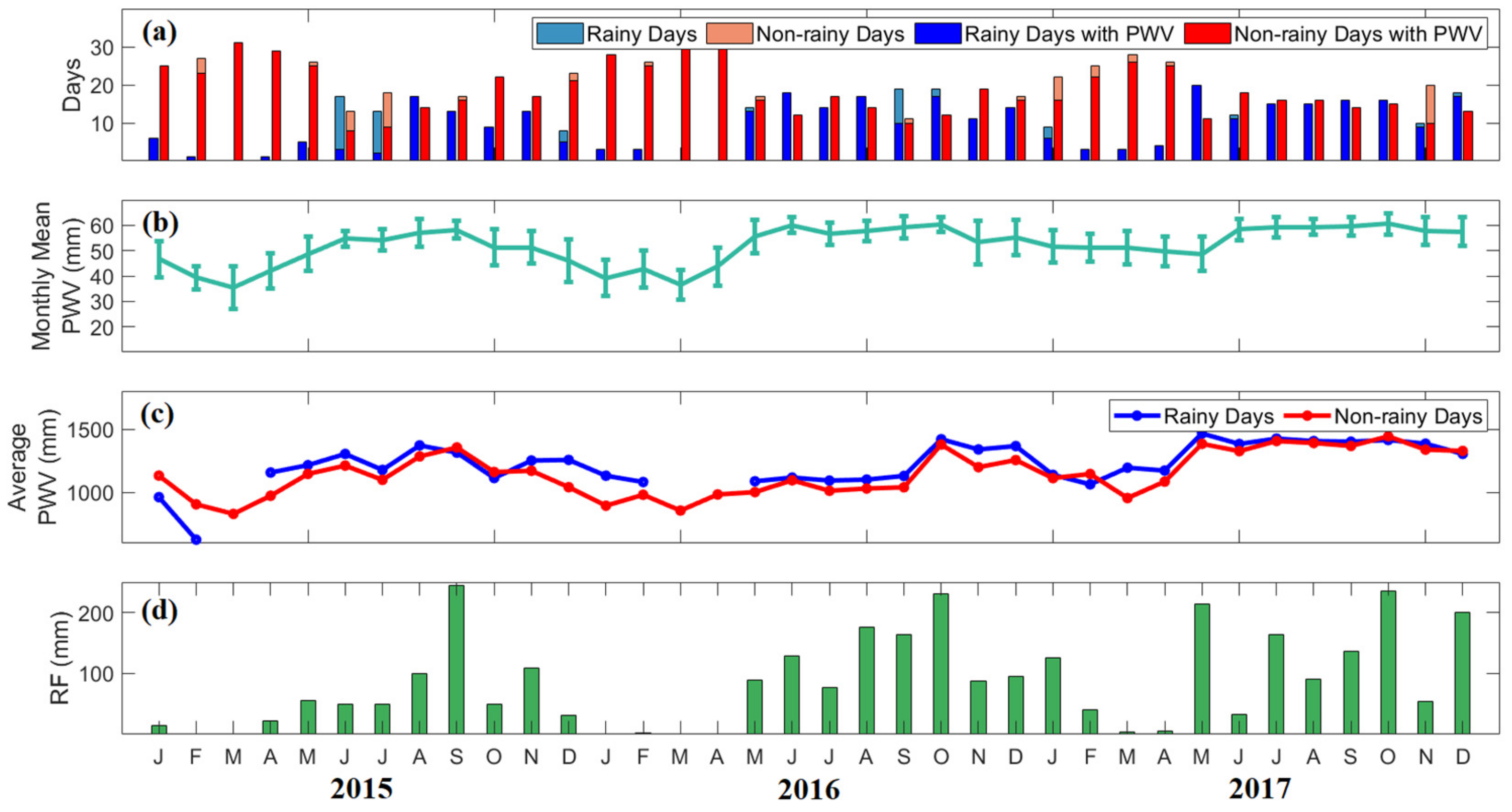
Figure 8 shows the monthly means of PWV for all days, the monthly average of daily PWV in rainy and non-rainy days, and the monthly rainfall in Puerto Princesa from 2015 to 2017. It can be observed in Figure 8b that the monthly means of PWV from May to October are also high, ranging from 39 mm to 60 mm, while PWV from November to April are low, ranging from 35 mm to 57 mm. Correspondingly, as shown in Figure 8d, the monthly rainfall from May to January ranged from 14 mm to 245 mm, and from February to April ranged from 0.4 mm to 40 mm.
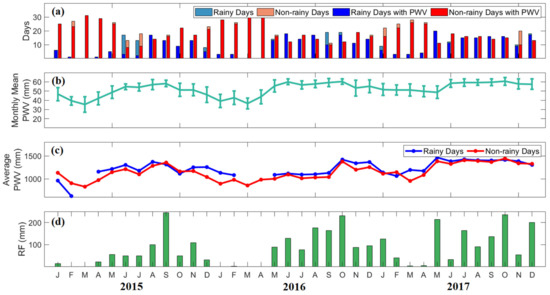
Figure 8.
(a) The number of rainy and non-rainy days, and rainy and non-rainy days with PWV per month in Legaspi from 2015 to 2017. (b) The monthly mean variations of PWV for all days, (c) monthly total PWV, (d) monthly average of daily PWV, and (d) monthly rainfall are also presented. The color scales are in Figure 6.
For the same reason, PWV and rainfall in Puerto Princesa are possibly influenced by the local convection and monsoons. An increase in moisture results in more rainfall [54]. Higher water vapor promotes vertical convection by affecting the static stability of the atmosphere [55,56,57,58,59]. In addition, the anomalous rainfall from December to February in this region is caused by the NE monsoon. It is noted in the study of Bagtasa et al. [32] that NE monsoon prevails in these months and brings rain in the southwestern Luzon.
Similar to the PWV variability in Quezon City and Legaspi, even PWV in Puerto Princesa is high, the variability is low; when PWV is low, the variability is high. From May to January, the PWV variability ranged from 4 mm to 8 mm, while from February to April, it ranged from 2 mm only up to 3 mm. This result confirms that PWV variability is most likely due to the effects of the SW and NE monsoons.
Overall, a finding in PWV variability of Quezon City is consistent with PWV variabilities of Legaspi and Puerto Princesa. In contrast, the variability in May is high then becomes steeply low from June to September. This result is similar to the studies of Macalalad et al. [8] and Renju et al. [50] in the Philippines and India, respectively. Note that the SW monsoon period starts from mid-May to September. This large variability in May is due to the transitions between NE monsoon to SW monsoon [8]. The findings in Renju et al. [50] showed that the low PWV variability from June to September is attributed to the persistent wind from the ocean, which brings moisture to these areas. The sudden increase in PWV variability in October is due to the transition of SW monsoon to NE monsoon.
Additionally, the high PWV variability is explained by the enhanced moisture flow during SW monsoon due to extreme weather events such as typhoons. Although PWV corresponds to rainfall patterns, it does not have the same variation during the monsoon period. Variation in PWV only exists at the onset of monsoons.
In Puerto Princesa, the number of rainy days is mostly lower than the number of non-rainy days. Nevertheless, Figure 8c showed that the monthly average of daily PWV in rainy and non-rainy days is closely comparable with a range from 600 mm to 1500 mm. However, PWV on rainy days is slightly higher than PWV on non-rainy days.
Such variations and conditions in the average daily PWV in Quezon City, Legaspi, and Puerto Princesa show the roles of PWV in the distribution of rainfall. The results confirm that PWV helps describe the moisture content in the air.
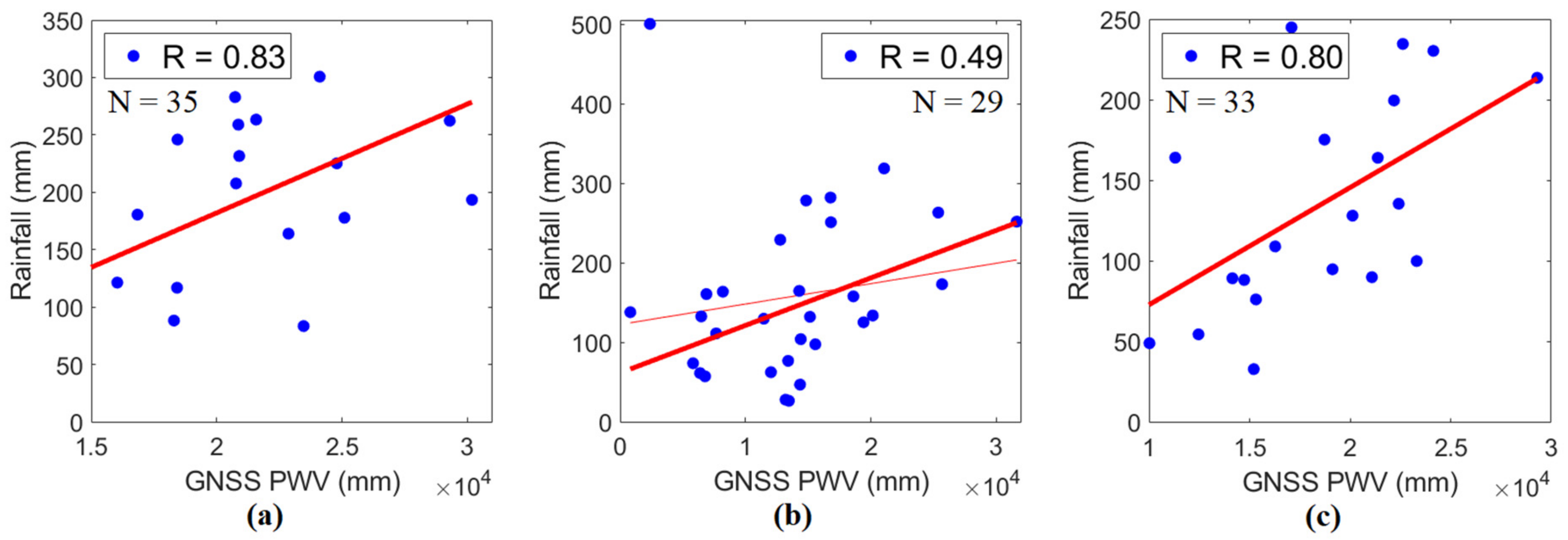
To further analyze the relation between PWV and rainfall, monthly total PWV from PIMO, PLEG, and PPPC in rainy days are correlated with monthly rainfall in Science Garden, Legaspi, and Puerto Princesa from 2015 to 2017, as shown in Figure 9. Strong, positive correlations between PWV and rainfall are shown in Quezon City (R = +0.83) and Puerto Princesa (R = +0.80), while PWV in Legaspi shows a weak, positive correlation (R = +0.49) with rainfall. Considering only the PWV on rainy days, those correlations between PWV and rainfall are more substantial than those of rainfall to PWV, including non-rainy days. These correlations imply that PWV can be used as a parameter to relate to rainfall.
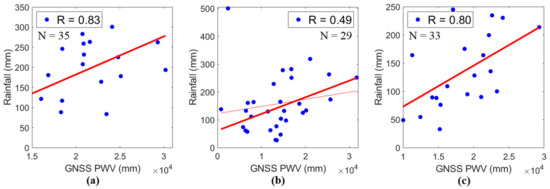
Figure 9.
The correlations of monthly total PWV in rainy days and monthly rainfall in (a) Quezon City, (b) Legaspi, and (c) Puerto Princesa from 2015 to 2017.
It is important to note that atmospheric water vapor is only one of the three main factors affecting the amount of rainfall; the other two factors are the degree of saturation and the presence of dynamic mechanisms such as orographic effects and convection, which provides cooling necessary to produce saturation [60]. In addition, an increase in PWV does not necessarily imply a rainfall event. This possibly explains the poor correlation between PWV and rainfall in Legaspi.
4. Conclusions
Based on the evaluation of GNSS PWV from PIMO, PLEG, and PPPC stations from 2015 to 2017 with RS PWV collected from Tanay, Legaspi, and Puerto Princesa, it clearly showed that both PWV agrees well with each other (R ~ +0.97). Furthermore, it is observed that daily PWV variations followed the climate types of Quezon City (Type I), Legaspi (Type II), and Puerto Princesa (Type III), corresponding with the daily data of rainfall. However, it was observed that PWV in these areas was high from May to October and low from November to April. Moreover, PWV variabilities were found small at their most significant rainfall while large with less rainfall.
Variations in rainfall occur due to SW and NE monsoons. Although PWV conformed with rainfall and have continual patterns, it was noticed that the behavior of PWV does not have the same variation during the monsoons as the rainfall does. However, it was found that there is variation in PWV during the onset of monsoons. Moreover, PWV on rainy days was analyzed to see its contribution to the rainfall. The monthly averages of daily PWV on rainy days were observed higher than PWV on non-rainy days at all sites. The relationship of PWV with rainfall in Quezon City (R = +0.83), Legaspi (R = +0.49), and Puerto Princesa (R = +0.80) were positively strong as the rainfall was correlated only with PWV on rainy days. Thus, PWV influences the rainfall in most instances.
The main objective of this study is to analyze the temporal variations of GNSS-based PWV during rainy days over the the Philippines from 2015 to 2017. The results of this study will serve as underlying data in monitoring the variations of PWV. The next phase of this analysis is to pursue a study of hourly variation of PWV involving cases from light to torrential rain as well as typhoons. Moreover, the effects of monsoons, the presence of dynamic mechanisms, sea and land surface temperature and relative humidity will be considered in a more in-depth study to analyze further the temporal variations of PWV in the country and its relationship with rainfall for forecasting weather.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, A.L.S.D. and E.P.M.; resources and data curation, software and visualization, writing—original draft preparation A.L.S.D.; writing—review and editing, E.P.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the NOAA’s National Climatic Data Center (NCDC), Philippine Active Geodetic Network (PAGeNet) of the National Mapping and Resource Information Authority (NAMRIA) and Department of Science and Technology—Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (DOST-PAGASA) for the data used in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Boutiouta, S.; Lahcene, A. Preliminary study of GNSS meteorology techniques in Algeria. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 5105–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, S.; Wang, C.-S.; Yeh, T.-K.; Dawson, J.; Jia, M.; Kuleshov, Y. Precipitable Water Vapor Estimates in the Australian Region from Ground-Based GPS Observations. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 956481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Realini, E.; Sato, K.; Tsuda, T.; Susilo, N.; Manik, T. An observation campaign of precipitable water vapor with multiple GPS receivers in western Java, Indonesia. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2014, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.J.; Elliott, W.P. Radiosonde-Based Northern Hemisphere Tropospheric Water Vapor Trends. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer, K.M.R.; Vallar, E.A.; Galvez, M.C.D. A Preliminary Study on the Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) from the Davao Radiosonde Station for 2014. In Proceedings of the DLSU Congress, Manila, Philippines, 7–9 March 2016; p. 4. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/305729806_A_Preliminary_Study_on_the_Precipitable_Water_Vapor_PWV_from_the_Davao_Radiosonde_Station_for_2014 (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Carnicer, K.M.R.; Castilla, R.M.; Vallar, E.A.; Galvez, M.C. On the variability of precipitable water vapor and its probabilistic modeling of precipitation occurrence in Davao city. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevis, M.; Businger, S.; Herring, T.A.; Rocken, C.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H. GPS meteorology: Remote sensing of atmospheric water vapor using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 15787–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macalalad, E.P.; Macalalad, R.V. Variation of GNSS-derived Precipitable Water Vapor Over Manila in 2017. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Space Science and Communication (IconSpace), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 28–30 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, F.; Villarin, J. An Analysis of the Precipitable Water Vapor Observed over the PIMO GPS Station. Sci. Diliman 2001, 15, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, A.H.; Chen, W.; Penna, N.T.; Baker, H.C. GPS estimation of atmospheric water vapour from a moving platform. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2001, 63, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, M.; Matsumoto, J.; Ogino, S.-Y.; Enomoto, T.; Miyoshi, T. The Impact of Additional Radiosonde Observations on the Analysis of Disturbances in the South China Sea during VPREX2010. Sci. Online Lett. Atmos. 2016, 12, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Shirooka, R.; Matsumoto, J.; Cayanan, E.O.; Hilario, F.D. Tropical cyclone influence on the long-term variability of Philippine summer monsoon onset. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.L.; Anthes, R.A.; Ware, R.H.; Rocken, C.; Bonner, W.D.; Bevis, M.G.; Businger, S. Sensing climate change using the global positioning system. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 1993, 98, 14925–14937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocken, C.; Van Hove, T.; Ware, R. Near real-time GPS sensing of atmospheric water vapor. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 3221–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Bevis, M.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Chiswell, S.; Businger, S.; Rocken, C.; Solheim, F.; van Hove, T.; Ware, R.; et al. GPS Meteorology: Direct Estimation of the Absolute Value of Precipitable Water. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, K.; Chen, X.; Qiu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, M.; Li, L. Development of an Improved Model for Prediction of Short-Term Heavy Precipitation Based on GNSS-Derived PWV. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer, K.M.R.; Vallar, E.A.; Galvez, M.C.D. On The Assimilation of GNSS PWV Measurements in Heavy to Torrential Rain Events in Davao City, Philippines. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2020, 15, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshawaf, F.; Fuhrmann, T.; Knöpfler, A.; Luo, X.; Mayer, M.; Hinz, S.; Heck, B. Accurate Estimation of Atmospheric Water Vapor Using GNSS Observations and Surface Meteorological Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3764–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isioye, O.A.; Combrinck, L.; Botai, J.O.; Munghemezulu, C. The Potential for Observing African Weather with GNSS Remote Sensing. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 723071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coster, A.J.; Niell, A.E.; Solheim, F.S.; Mendes, V.B.; Toor, P.C.; Buchmann, K.P.; Upham, C.A. Measurements of Precipitable Water Vapor by GPS, Radiosondes, and a Microwave Water Vapor Radiometer. In Proceedings of the ION GPS-96, the 9th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Kansas City, MO, USA, 17–20 September 1996; pp. 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- Gurbuz, G.; Jin, S. Long-time variations of precipitable water vapour estimated from GPS, MODIS and radiosonde observations in Turkey. Int. J. Clim. 2017, 37, 5170–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, N.; Lan, P. Variability and Trends in Global Precipitable Water Vapor Retrieved from COSMIC Radio Occultation and Radiosonde Observations. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregoning, P.; Boers, R.; O’Brien, D.; Hendy, M. Accuracy of absolute precipitable water vapor estimates from GPS observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 28701–28710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Muller, J.-P.; Cross, P. Comparison of precipitable water vapor derived from radiosonde, GPS, and Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtani, R.; Naito, I. Comparisons of GPS-derived precipitable water vapors with radiosonde observations in Japan. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2000, 105, 26917–26929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdiguer-López, R.; Berné-Valero, J.L.; Garrido-Villén, N. Application of GNSS Methodologies to Obtain Precipitable Water Vapor (PWV) and Its Comparison with Radiosonde Data. Proceedings 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suparta, W.; Iskandar, A. Monitoring of GPS Water Vapor Variability During ENSO Events over the Borneo Region. Asian J. Earth Sci. 2012, 5, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suparta, W.; Iskandar, A.; Singh, M.S.J.; Ali, M.A.M.; Yatim, B.; Tangang, F. A study of El Niño-Southern oscillation impacts to the South China Sea region using ground-based GPS receiver. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 423, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suparta, W.; Iskandar, A.; Singh, M.S.J.; Ali, M.A.M.; Yatim, B.; Yatim, A.N.M. Analysis of GPS water vapor variability during the 2011 La Niña event over the western Pacific Ocean. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 56, R0330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, M.Q., II; Juanillo, E.L.; Hilario, F.D. Climatic Insights on Academic Calendar Shift in the Philippines. Philipp. J. Sci. 2017, 146, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, J.; Olaguera, L.M.P.; Nguyen-Le, D.; Kubota, H.; Ii, M.Q.V. Climatological seasonal changes of wind and rainfall in the Philippines. Int. J. Clim. 2020, 40, 4843–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagtasa, G. Contribution of Tropical Cyclones to Rainfall in the Philippines. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3621–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Feng, Y. GPS Water Vapor Estimation Using Interpolated Surface Meteorological Data from Australian Automatic Weather Stations. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2003, 2, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Li, F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, F.; Barriot, J.-P. Assessment of the Accuracy of the Saastamoinen Model and VMF1/VMF3 Mapping Functions with Respect to Ray-Tracing from Radiosonde Data in the Framework of GNSS Meteorology. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Koizumi, K.; Mannoji, N. Data Assimilation of GPS Precipitable Water Vapor into the JMA Mesoscale Numerical Weather Prediction Model and its Impact on Rainfall Forecasts. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2004, 82, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-G.; Baek, J.-H.; Cho, J.-H. Analysis on Characteristics of Radiosonde Bias Using GPS Precipitable Water Vapor. J. Astron. Space Sci. 2010, 27, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Liao, T.; Wang, H.; et al. Evaluation of radiosonde, MODIS-NIR-Clear, and AERONET precipitable water vapor using IGS ground-based GPS measurements over China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 197, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, Z.; Li, L.; Wan, M.; Liu, X. Real-Time GNSS-Derived PWV for Typhoon Characterizations: A Case Study for Super Typhoon Mangkhut in Hong Kong. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, Y.; Sato, K.; Yabuki, M.; Tsuda, T. Comparison of shipborne GNSS-derived precipitable water vapor with radiosonde in the western North Pacific and in the seas adjacent to Japan. Earth Planets Space 2017, 69, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghrabi, A.H.; Alothman, A.O.A.; Fernandes, R.M.S.; Almutairi, M.M.; Aldosari, A.F.; Aldakhil, A.A.; Allehyani, B.I.; Aljabar, G.A.; Altilasi, M.I. Modelling and Validation of the Precipitable Water Vapour from Zenith Wet Delay using Radiosonde and GNSS Data in the Central Arabian Peninsula. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2020, 25, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yao, W. GPS-based PWV for precipitation forecasting and its application to a typhoon event. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2018, 167, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J. A New Method for Refining the GNSS-Derived Precipitable Water Vapor Map. Sensors 2019, 19, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Shan, L.; Zhao, Q. Establishing a method of short-term rainfall forecasting based on GNSS-derived PWV and its application. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barindelli, S.; Realini, E.; Venuti, G.; Fermi, A.; Gatti, A. Detection of water vapor time variations associated with heavy rain in northern Italy by geodetic and low-cost GNSS receivers. Earth Planets Space 2018, 70, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruppacher, H.R.; Klett, J.D. Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Gao, T.; Wang, Q.; Song, Y.; Hua, D. Investigation of Precipitable Water Vapor Obtained by Raman Lidar and Comprehensive Analyses with Meteorological Parameters in Xi’an. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Li, W.; Ou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B. GPS PPP-derived precipitable water vapor retrieval based on T m /P s from multiple sources of meteorological data sets in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4165–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagmay, A.M.F.; Bagtasa, G.; Crisologo, I.A.; Racoma, B.A.B.; David, C.P.C. Volcanoes magnify Metro Manila’s southwest monsoon rains and lethal floods. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yuan, P.; Chen, H.; Cai, J.; Li, Z.; Chao, N.; Sneeuw, N. Annual variations of monsoon and drought detected by GPS: A case study in Yunnan, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renju, R.; Raju, C.S.; Mathew, N.; Antony, T.; Moorthy, K.K. Microwave radiometer observations of interannual water vapor variability and vertical structure over a tropical station. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4585–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaguera, L.M.; Matsumoto, J.; Kubota, H.; Inoue, T.; Cayanan, E.O.; Hilario, F.D. Interdecadal Shifts in the Winter Monsoon Rainfall of the Philippines. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, M.; McGregor, S.; Spence, P.; Meehl, G.A.; Timmermann, A.; Cai, W.; Gupta, A.S.; McPhaden, M.J.; Purich, A.; Santoso, A. Recent intensification of wind-driven circulation in the Pacific and the ongoing warming hiatus. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, M.; Reddy, N.A.; Varma, S. Analytical study of MHD free convective, dissipative boundary layer flow past a porous vertical surface in the presence of thermal radiation, chemical reaction and constant suction. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2014, 5, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalihal, C.; Srinivasan, J.; Chakraborty, A. Modulation of Indian monsoon by water vapor and cloud feedback over the past 22,000 years. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A.J.; Lambert, F.H.; Collins, M.; Miles, G.M. Physical Mechanisms of Tropical Climate Feedbacks Investigated Using Temperature and Moisture Trends. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 8968–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, B.J.; Held, I.M. An Assessment of Climate Feedbacks in Coupled Ocean–Atmosphere Models. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, T.; Webb, M.J. The Dependence of Global Cloud and Lapse Rate Feedbacks on the Spatial Structure of Tropical Pacific Warming. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soden, B.J.; Jackson, D.L.; Ramaswamy, V.; Schwarzkopf, M.D.; Huang, X. The Radiative Signature of Upper Tropospheric Moistening. Science 2005, 310, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, F.H.; Ferraro, A.J.; Chadwick, R. Land–Ocean Shifts in Tropical Precipitation Linked to Surface Temperature and Humidity Change. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 4527–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Fetzer, E.J.; Wong, S.; Behrangi, A.; Olsen, E.T.; Cohen, J.; Lambrigtsen, B.H.; Chen, L. Impact of increased water vapor on precipitation efficiency over northern Eurasia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).