Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
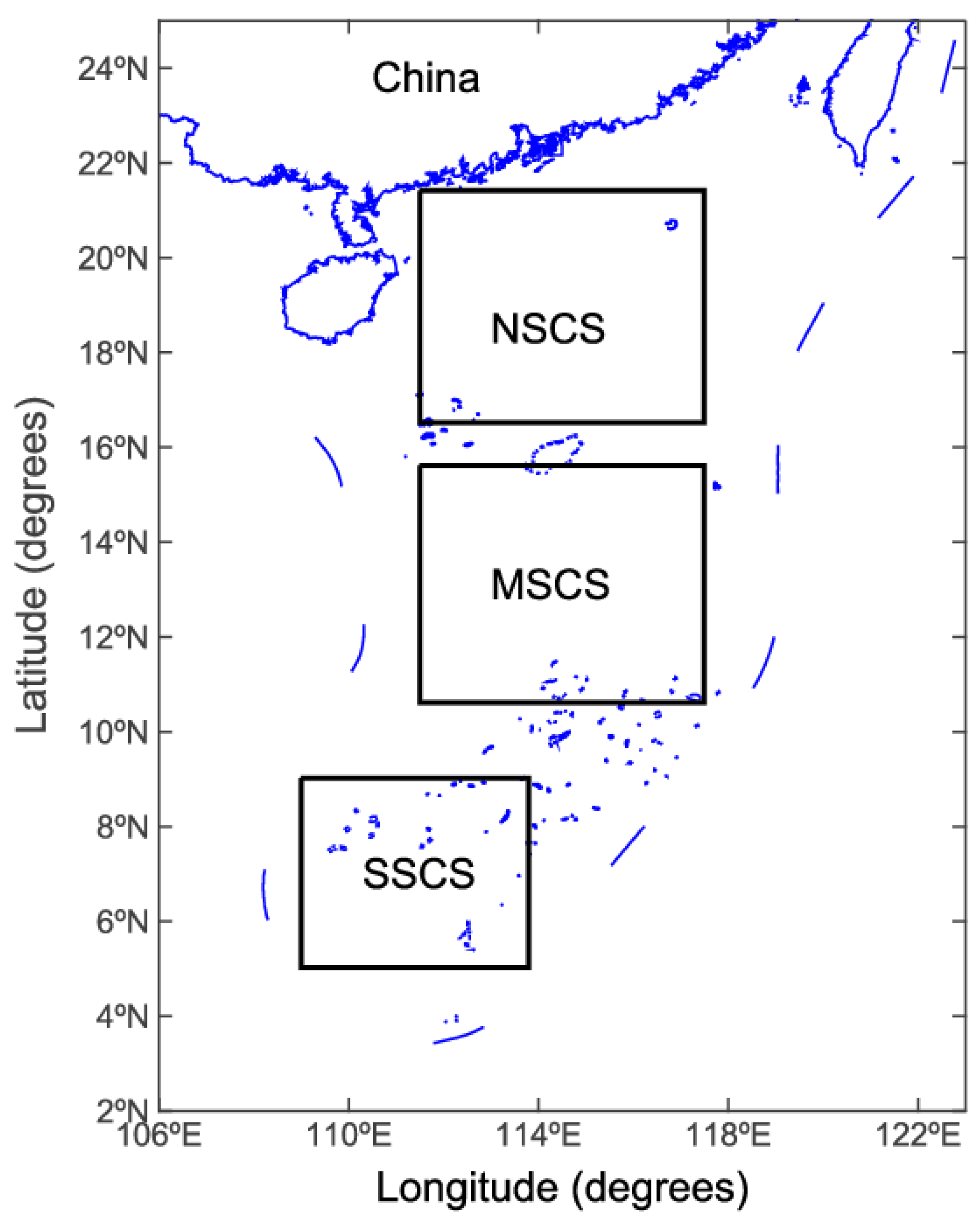
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Accuracy of MERRA-2 AOD
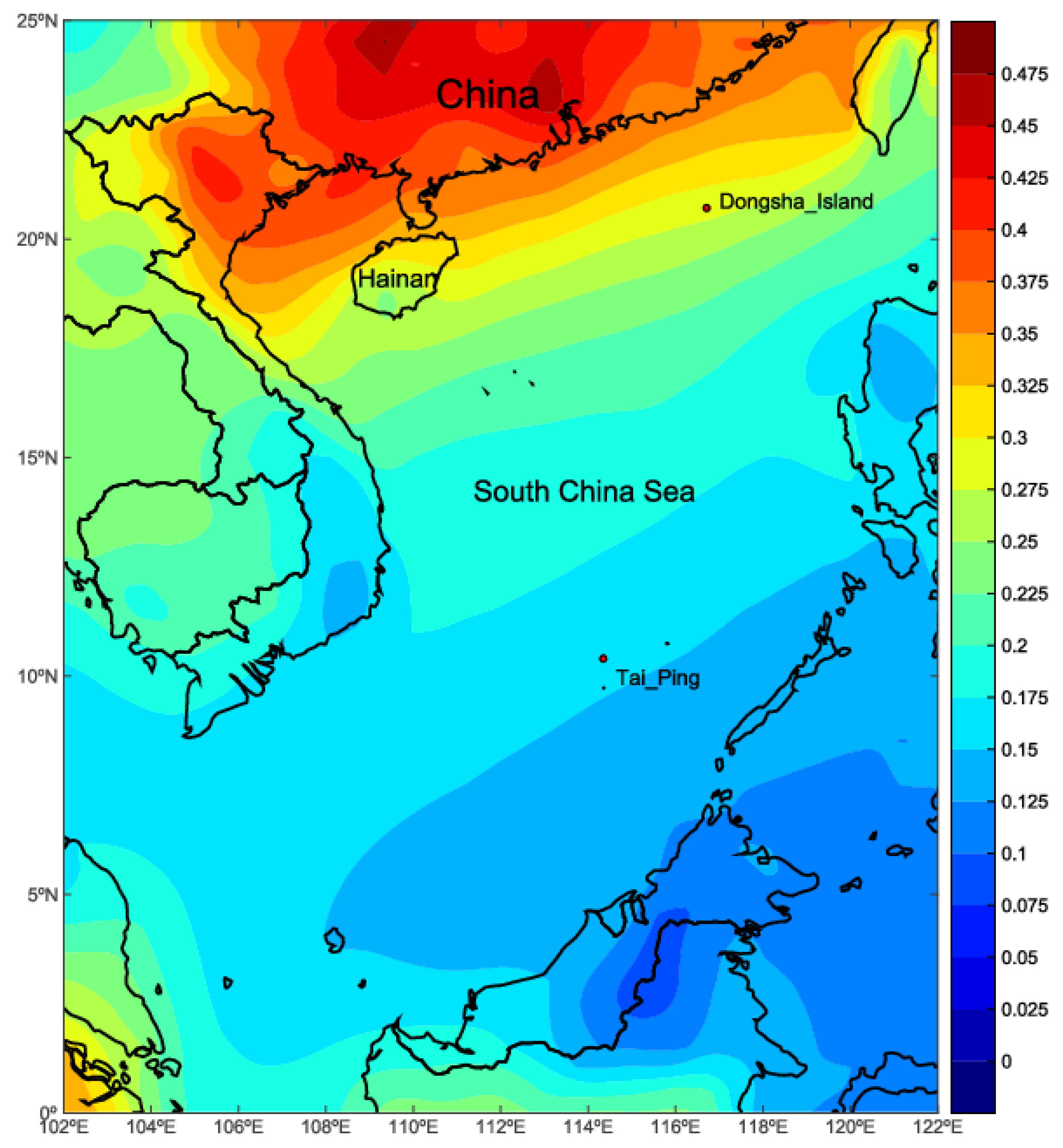
3.2. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variation of MERRA-2 AOD
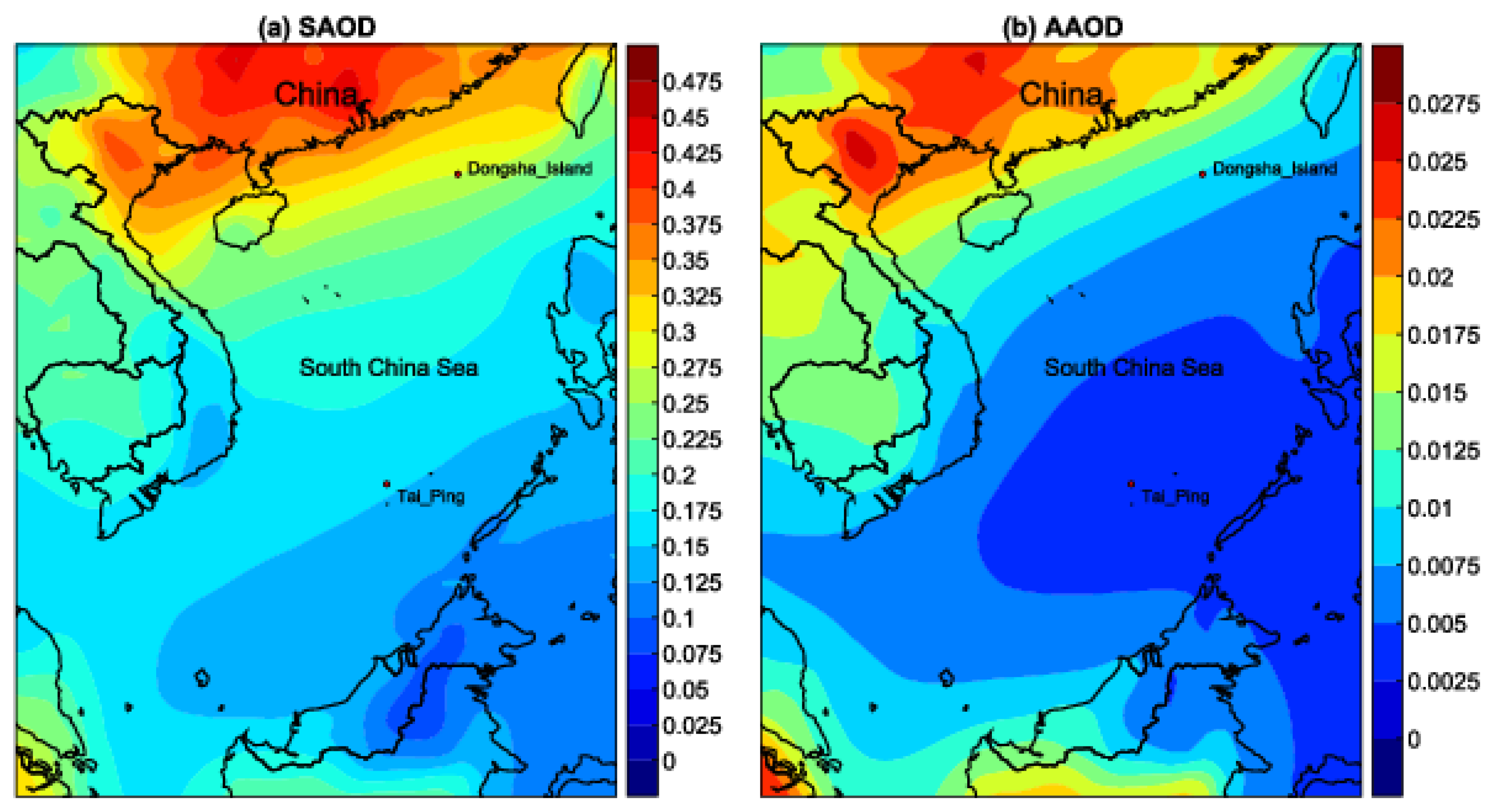
3.3. Spatial Distribution of MERRA-2 SAOD and AAOD
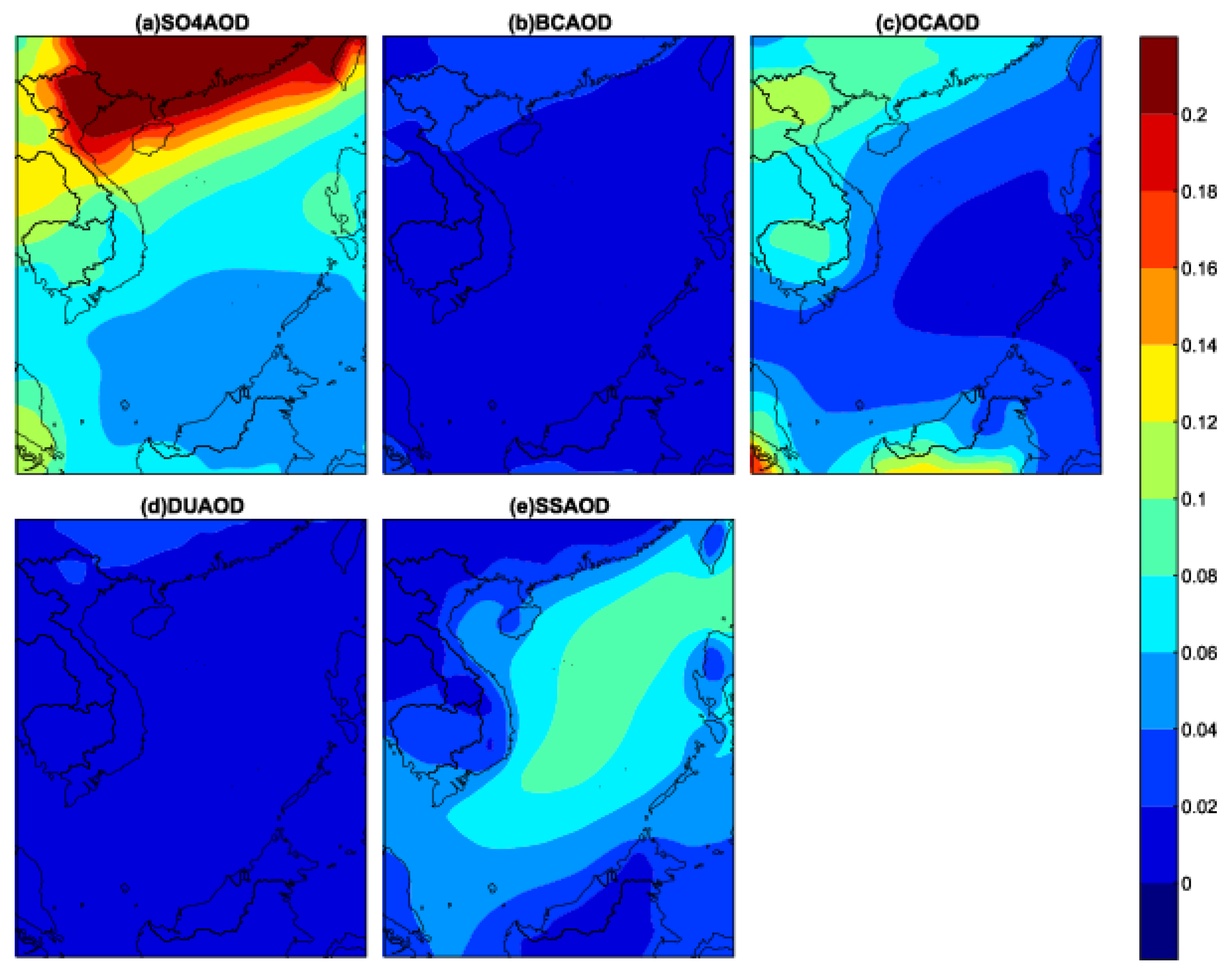
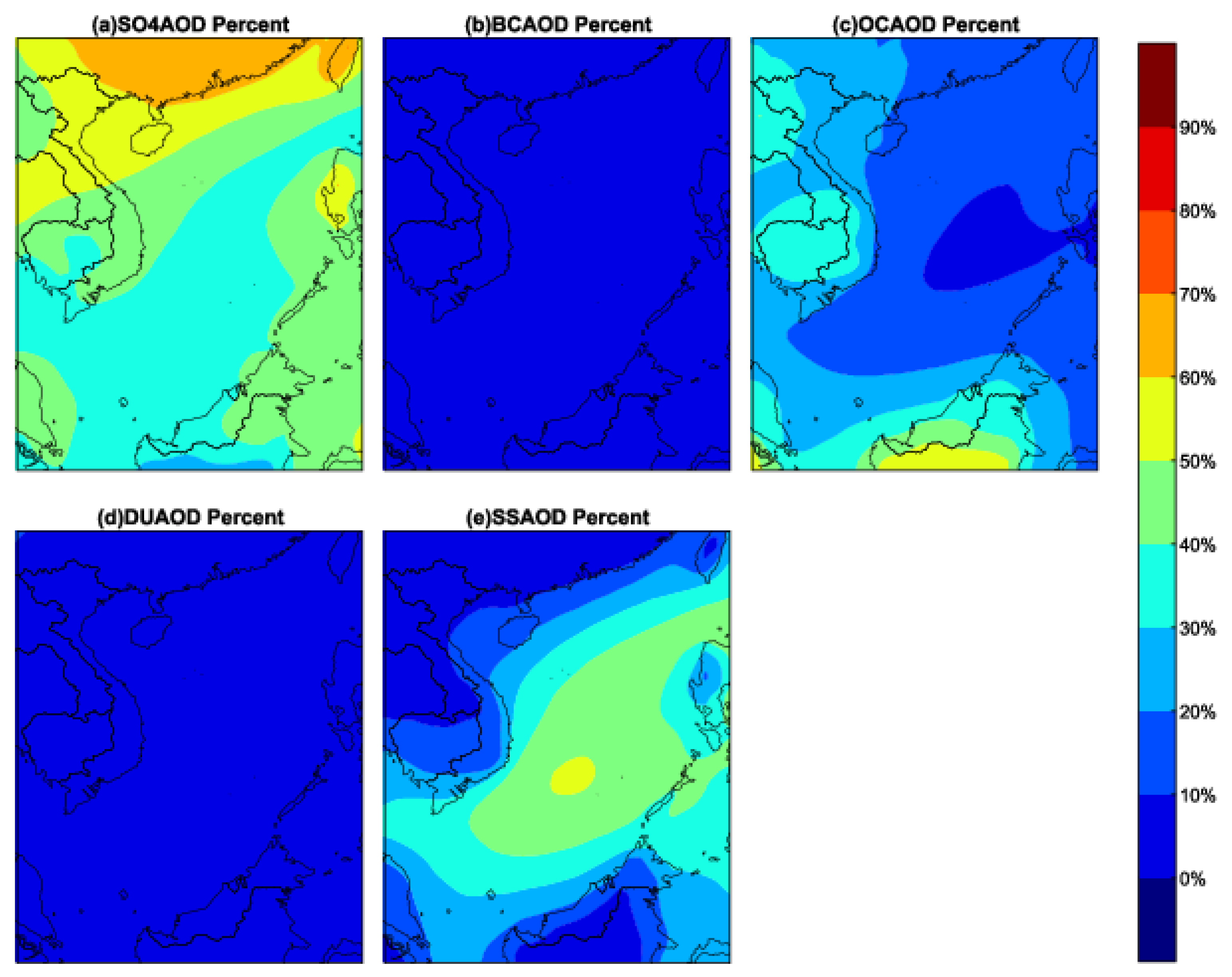
3.4. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variation of MERRA-2 AOD of Different Aerosol Compositions
3.5. Variation Trend of MERRA-2 AOD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filip, L.; Stefan, S. Study of the correlation between the near-ground PM10 mass concentration and the aerosol optical depth. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2011, 73, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Shi, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Z.; Nie, S.; He, D.; Zhang, H. Analysis of aerosol characteristics and their relationships with meteorological parameters over Anhui province in China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109–110, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Hou, B.; Che, H. Aerosol optical properties over urban and industrial region of Northeast China by using ground-based sun-photometer measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Che, H.; Zhang, R.; Gui, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, T. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of aerosol optical depth in the Sichuan basin, China, the recent ten years. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, K.; Reddy, K.; Balakrishnaiah, G.; Arafath, S.; Reddy, N.; Rao, T.; Reddy, T.; Reddy, R. Regional trends of aerosol optical depth and their impact on cloud properties over southern India using MODIS data. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2016, 146, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X. Satellite-derived PM2.5 concentration trends over Eastern China from 1998 to 2016: Relationships to emissions and meteorological parameters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Crippa, P.; Pryor, S. Spatial characteristics and temporal evolution of the relationship between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth over the eastern USA during 2003–2017. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 239, 117718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Che, H.; Gui, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Can MERRA-2 Reanalysis Data Reproduce the Three-Dimensional Evolution Characteristics of a Typical Dust Process in East Asia? A Case Study of the Dust Event in May 2017. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yousefi, R.; Wang, F.; Ge, Q.; Lelieveld, J.; Shaheen, A. Aerosol Trends during the Dusty Season over Iran. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, J.; He, D.; Tian, Q.; Mao, Z.; Pan, D. Retrieval of Urban Aerosol Optical Depth from Landsat 8 OLI in Nanjing, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, J.; Moorthy, K.; Babu, S.; Gogoi, M. Spatio-temporal variations in aerosol properties over the oceanic regions between coastal India and Antarctica. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 104, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandey, B.; Stier, P.; Wagner, T. Investigating relationships between aerosol optical depth and cloud fraction using satellite, aerosol reanalysis and general circulation model data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B.; Tong, X. MODIS 3 km and 10 km aerosol optical depth for China: Evaluation and comparison. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 153, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, B. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of aerosol optical depth and radiative effect in South China and its adjacent area. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Bao, Y.; Boiyo, R.; Tang, W.; Lu, Q.; Min, J. Evaluating MODIS and MISR Aerosol Optical Depth Retrievals over Environmentally Distinct Sites in Pakistan. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2019, 183, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, T.; Boiyo, R.; Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y. Vertical Structures of Dust Aerosols over East Asia Based on CALIPSO Retrievals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Yue, L.; Li, T.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. The relationships between PM2.5 and aerosol optical depth (AOD) in mainland China: About and behind the spatio-temporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Han, Y.; Lu, C.; Yang, J.; Wu, Y. Characteristics of Surface Solar Radiation under Different Air Pollution Conditions over Nanjing, China: Observation and Simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 36, 1047–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Remer, L.; Patadia, F.; Levy, R.; Christopher, S. High-Resolution Gridded Level 3 Aerosol Optical Depth Data from MODIS. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, N.; He, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Zhan, Q. Meteorological conditions and their effects on the relationship between aerosol optical depth and macro-physical properties of warm clouds over Shanghai based on MODIS. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, K.; Dey, S.; Ganguly, D. Diurnal patterns in ambient PM2.5 exposure over India using MERRA-2 reanalysis data. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 248, 118180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Han, Y.; Cheng, X.; Lu, C.; Wu, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations in Particulate Matter and Air Quality over China: National, Regional and Urban Scales. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Arnott, W.; Barnard, J.; Holmes, H. Theoretical Uncertainty Analysis of Satellite Retrieved Aerosol Optical Depth Associated with Surface Albedo and Aerosol Optical Properties. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, J.; Diner, D.; Su, H.; Gu, Y.; Liou, K.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, L.; Takano, Y.; Fan, X.; et al. Intra-annual variations of regional aerosol optical depth, vertical distribution, and particle types from multiple satellite and ground-based observational datasets. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11247–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.; Dubovik, O.; Lacis, A. Recent trends in aerosol optical properties derived from AERONET measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 12271–12289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almazroui, M. A comparison study between AOD data from MODIS deep blue collections 51 and 06 and from AERONET over Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 225, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhetres, A.; Aggarwal, S. An Evaluation of MODIS-Retrieved Aerosol Optical Depth over AERONET Sites in Alaska. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, A.; Chen, W.; Liang, L.; Sun, W.; Lin, Y.; Che, H.; Zhao, X. Evaluation and Comparison of Long-Term MODISC5.1 and C6 Products against AERONET Observations over China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merino, C.; Mateos, D.; Toledano, C.; Prospero, J.; Molinie, J.; Clotilde, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Cachorro, V.E.; Calle, A.; de Frutos, A.M. Impact of long-range transport over the Atlantic Ocean on Saharan dust optical and microphysical properties based on AERONET data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9411–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Qu, J.J.; Che, H. Validation of MODIS aerosol optical depth product over China using CARSNET measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5970–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, G. Analysis of the Error in Retrievals of Aerosol Optical Properties from Sun photometer Measurements of CARSNET Due to a Variety of Objective Factors. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Application of aerosol optical properties to estimate aerosol type from ground-based remote sensing observation at urban area of northeastern China. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2015, 132, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X. Long-term validation of MODIS C6 and C6.1 Dark Target aerosol products over China using CARSNET and AERONET. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Uno, I.; Higurashi, A.; Sohn, B.J.; Oh, S.; Ohta, S.; Takamura, T.; Sekiguchi, M.; Takemura, T.; Kim, H.; et al. Significance of direct and indirect radiative forcings of aerosols in the East China Sea region. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M. Seasonal variability of aerosol optical properties over Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4095–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kumar, K.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over the urban-industrial megacity Nanjing in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17532–17552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.; Xia, X.; Eck, T.F.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Blarel, L.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pani, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, N.; Tsay, S.; Lolli, S.; Chuang, M.; Lee, C.; Chantara, S.; Yu, J. Assessment of aerosol optical property and radiative effect for the layer decoupling cases over the northern South China Sea during the7-SEAS/Dongsha Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4894–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.; Luo, L.; Shen, C.; Long, A.; Chen, L.; Long, Z.; Li, D. Atmospheric aerosol compositions over the South China Sea: Temporal variability and source apportionment. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Q.; Tang, D.; Levy, G.; Shi, P. Variability of aerosol optical thickness in the tropical Indian Ocean and South China Sea during spring inter monsoon season. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4531–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, D. Maritime Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties in the South China Sea Under Multi-source Infuence. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, W. Micro-Pulse Lidar Cruising Measurements in Northern South China Sea. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, C.; Silva, A.; Buchard, V.; Colarco, P.; Darmenov, A.; Govindaraju, R.; Smirnov, A.; Ferrare, R.; Hair, J.; Shinozuka, Y.; et al. The MERRA-2 Aerosol Reanalysis, 1980-onward, Part I: System Description and Data Assimilation Evaluation. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 6823–6850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, B.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, Y. Anthropogenic and meteorological drivers of 1980–2016 trend in aerosol optical and radiative properties over the Yangtze River Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lin, A.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Bilal, M.; Zhang, M. Characteristic and Driving Factors of Aerosol Optical Depth over Mainland China during 1980–2017. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirono, M.; Shibata, T. Enormous increase of stratospheric aerosols over Fukuoka due to volcanic eruption of El Chichon in 1982. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1983, 10, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupper, A.; Oswalt, J.S.; Rosenfeld, D. Satellite and radar analysis of the volcanic-cumulonimbi at Mount Pinatubo, Philippines, 1991. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D09204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prijith, S.; Rao, P.; Mohan, M.; Sai, M.; Ramana, M. Trends of absorption, scattering and total aerosol optical depths over India and surrounding oceanic regions from satellite observations: Role of local production, transport and atmospheric dynamics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 18147–18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. Spatio-temporal variation and impact factors analysis of satellite-based aerosol optical depth over China from 2002 to 2015. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.; Gautam, R.; Sayer, A.; Bettenhausen, C.; Li, C.; Jeong, M.; Tsay, S.; Holben, B. Global and regional trends of aerosol optical depth over land and ocean using SeaWiFS measurements from 1997 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8037–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, E.; Fu, C.; Yu, W.; Xie, Y.; Lu, Y.; Lu, C. Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030372
Sun E, Fu C, Yu W, Xie Y, Lu Y, Lu C. Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(3):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030372
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Enwei, Chuanbo Fu, Wei Yu, Ying Xie, Yiwen Lu, and Chunsong Lu. 2022. "Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020" Atmosphere 13, no. 3: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030372
APA StyleSun, E., Fu, C., Yu, W., Xie, Y., Lu, Y., & Lu, C. (2022). Variation and Driving Factor of Aerosol Optical Depth over the South China Sea from 1980 to 2020. Atmosphere, 13(3), 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13030372




