Abstract
In recent years, air pollution has become a serious threat, causing adverse health effects and millions of premature deaths in China. This study examines the spatial-temporal characteristics of ambient air quality in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) from January 2015 to December 2018. For this purpose, surface-level aerosol pollutants, including particulate matter (PMx, x = 2.5 and 10) and gaseous pollutants (sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and ozone (O3)) were obtained from China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). The results showed that fine particulate matter (PM2.5), coarse particulate matter (PM10), SO2, NO2, and CO decreased by 28.2%, 32.7%, 41.9%, 6.2%, and 27.3%, respectively, while O3 increased by 3.96% in NWC during 2018 as compared with 2015. The particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) levels exceeded the Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) Grade II standards as well as the WHO recommended Air Quality Guidelines, while SO2 and NO2 complied with the CAAQS Grade II standards in NWC. In addition, the average air quality index (AQI), calculated from ground-based data, improved by 21.3%, the proportion of air quality Class I (0–50) improved by 114.1%, and the number of pollution days decreased by 61.8% in NWC. All the pollutants’ (except ozone) AQI and PM2.5/PM10 ratios showed the highest pollution levels in winter and lowest in summer. AQI was strongly positively correlated with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO, while negatively correlated with O3. PM10 was the primary pollutant, followed by O3, PM2.5, NO2, CO, and SO2, with different spatial and temporal variations. The proportion of days with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, and CO as the primary pollutants decreased but increased for NO2 and O3. This study provides useful information and a valuable reference for future research on air quality in northwest China.
1. Introduction
Unprecedented economic activity, urbanization, industrialization, and motorization have deteriorated the ambient air quality in China [1,2,3,4,5,6]. China is the manufacturing hub of the world, with the majority of the industries in northwest China (NWC). Several studies have reported higher pollution levels in NWC due to increased industry, coal consumption, distinct topography, and adverse meteorology [2,5,7,8,9,10,11]. Increased pollution levels have attracted the attention of the general public, the scientific community, and relevant authorities because of their detrimental health effects [4,12,13,14,15,16]. To combat increasing pollution levels, China has made significant efforts, e.g., establishing Chinese ambient air quality standards (CAAQS) for six criteria pollutants [17], implementing the Atmospheric Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan 2013 (APPCAP) [18], technical regulation on ambient air quality index (HJ 633–2012) [19], nationwide air quality monitoring, online data-sharing networks, etc. [20,21]. These measures have helped to reduce pollution to some extent; e.g., from Ref. [22], a 12.3% reduction in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) was observed in China between 2013 and 2015, while other authors [23] observed a one-third reduction in PM2.5 from 2013 to 2017 due to APPCAP in China. In Ref. [24], it was observed that the annual average concentration (PM2.5), coarse particulate matter (PM10), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and carbon monoxide (CO) decreased by 27.9%, 23.8%, 51.2%, 10.6%, and 25.3%, respectively, in China from 2015 to 2019. Even after strict environmental regulations, the air pollution in some areas of NWC is beyond certain limits and causes serious health effects [25,26,27,28].
Most of the spatio-temporal studies in China focused on central China, north China, considered few parameters, fewer cities, mostly provincial capitals, and lacked detailed assessment, with few exceptions. Multiple studies, e.g., [3,29], observed higher PM2.5 pollution in northern China, western China, northwestern China, etc. due to increased industrial emissions, coal combustion, stagnant meteorology, etc. Similarly, other researchers [30,31] carried out a more detailed assessment, covered six criteria pollutants in provincial capitals, and observed higher pollution levels in the north and northwestern region. In Ref. [1], they analyzed the criteria pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3) in 336 cities of China, while other researchers [31] analyzed the criteria pollutants in 367 cities of China and observed higher pollution in industrialized areas of north China. Further, Ref. [2] thoroughly assessed the air pollution in NWC by analyzing the criteria pollutants in six cities of Gansu province in NWC and observed higher pollution in Lanzhou, the provincial capital, with increased energy consumption and industrial activity and facing serious health concerns [25].
PM2.5 is more dangerous than PM10 and is ranked as the first leading risk factor for disease in China, causing more than 1.1 million premature deaths, with the highest share being stroke, ischemic heart disease (IHD), lung cancer, lower respiratory infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), etc. [32,33,34]. Other criteria pollutants, e.g., PM10, CO, O3, SO2, and NO2, cause multiple health disorders, e.g., headaches, dizziness, nausea, respiratory disorders, inflammatory reactions, reduced lung function, hampered neurological function, etc. [35,36,37]. Apart from jeopardizing human health, air pollution is also responsible for visibility reduction, economic losses, and climate change [13]. PM2.5 and O3 can cause gross domestic production (GDP) losses of 2.09% in health expenditure [38].
In view of such circumstances, we examined the spatial and temporal distribution of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 in 53 cities located in five provinces of NWC for a period of four years (2015 to 2018). Besides the criteria pollutants, we also examined the PM2.5/PM10 ratio, Air Quality Index (AQI), AQI class distributions, major pollutant on a representative day, number of pollution days, and correlations among different pollutants to explicate the pollution status, spatial, and temporal distribution of air quality in NWC over time. This study provides useful information and a valuable reference for future research on air quality in NWC and is of considerable significance to environmental protection and human health.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Selection
In this study, we examined the ambient air quality in the northern and western parts of China, known as northwest China (NWC), from January 2015 to December 2018 to understand the spatio-temporal variation across NWC better. NWC is a mixture of agricultural areas, deserts, mountains, etc. with significant coal reserves, industrial activity, covering an area of 3.1 million sq. km area (32.4% of China), having a population of more than 96.65 million, and experiencing degraded air quality. NWC consists of five provinces, namely Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH) (Supplementary Material Figure S1). Table 1 gives detailed information about 5 provinces and 53 cities.

Table 1.
Description of cities under observation in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC).
2.2. Data Collection
To meet the objectives of the study, we analyzed the ambient air quality in 53 cities located in five provinces (SN, XJ, GS, NX, and QH) of NWC (Table 1) for a period of four years (2015–2018). The hourly concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 was collected from China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). The online data-sharing platform covers 367 cities of China, and dispatch/publish information according to the Technical Guideline on Environmental Monitoring Quality Management (HJ 630-2011) [39].
2.3. Air Quality Index (AQI)
The air quality index (AQI) includes 24-h average measurement of PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, CO, and 8-h average concertation of O3 and reflects the overall air quality [8,28,40]. Individual air quality index (IAQI) for six criteria pollutants is determined by using Equation (1), and the overall AQI is calculated based on the highest IAQI by using Equation (2) according to the instruction given in technical regulation on ambient air quality index (on trial) (HJ-633-2012) [19].
IAQIp = individual sub air quality index of the pollutant p
Cp = concentration of the pollutant p
Chigh = concentration breakpoint that is ≥ Cp
Clow = concentration breakpoint that is ≤ Cp
Ihigh = index breakpoint corresponding to Chigh
Ilow = index breakpoint corresponding to Clow
In Equation (2), “n” indicates the number of criteria pollutants. When AQI is higher than 50, the highest IAQI is considered as a major pollutant for that given day [23,28,41,42,43,44]. Air Quality Index (AQI) has the following six categories:
- Class I: 0–50 (Green), Good
- Class II: 51–100 (Yellow), Moderate
- Class III: 101–150 (Orange), Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups
- Class IV: 151–200 (Red), Unhealthy
- Class V: 201–300 (Purple), Very unhealthy
- Class VI: 300–500 (Maroon), Hazardous
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA&AR)
Quality assurance and control procedures for ambient air quality data were strictly in accordance with Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) (GB-3095-2012) [17]. The daily average value was calculated when we have valid data for more than 16 h of that day (except for ozone, minimum 6-h value for 8-h ozone value); the monthly average was calculated only when we have 27 daily mean values; an annual value was calculated only when we have 324 daily mean values. Besides this, manual inspection was carried out to remove abnormal values, e.g., PM2.5 values higher than PM10 values.
2.5. Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) Spatial Interpolation
Many spatial interpolation methods, such as kriging (universal or ordinary) and inverse distance weighted (IDW) spatial interpolation, have been used in different studies [45,46]. IDW geospatial interpolation is a type of deterministic method for multivariate interpolation with a known scattered set of points. IDW assigns values to unknown points according to the weighted average of the values of the known points and is more suitable for regional interpolation [47]. In this study, we used IDW spatial interpolation technique to interpolate spatial distribution of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, O3, AQI, and PM2.5/PM10 ratio in NWC. Equation (3) describes the interpolation analysis.
where Zp refers to the value of unknown point, Zi is the value observed at the point of I; I represents the nearest neighborhood of interpolated point produced; p is the weighting absolute value, and p is equal to inverse distance weight, respectively.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
In this study, we used Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) for Windows (IBM SPSS Statistics, Version 25) to find the Pearson’s correlation coefficient for criteria pollutants on an annual and seasonal basis [48], and used RStudio for graphical representation [49]. The high (low) value of the Pearson’s correlation represents the same (different) variations in one criteria pollutant with respect to another pollutant. The effect of a certain variable was considered statistically significant for P (0.01, and 0.05) (two-tailed). Annual mean values, mean absolute deviation (MAD), mean square error (MSE), root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), and mean percentage error (MPE) of six criteria pollutants between 2015 and 2018 were calculated by Microsoft Excel 2016.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Six Criteria Pollutants
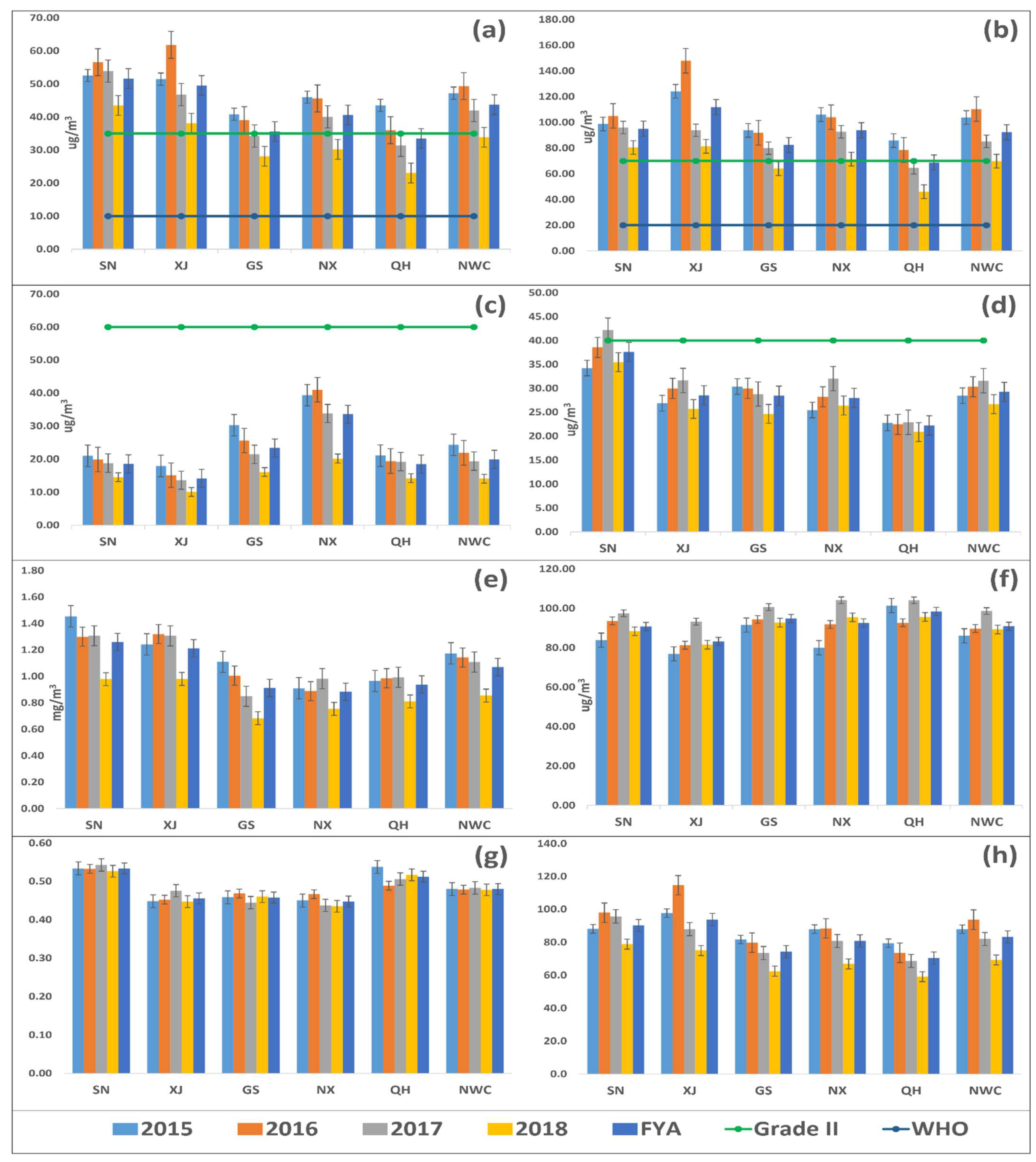
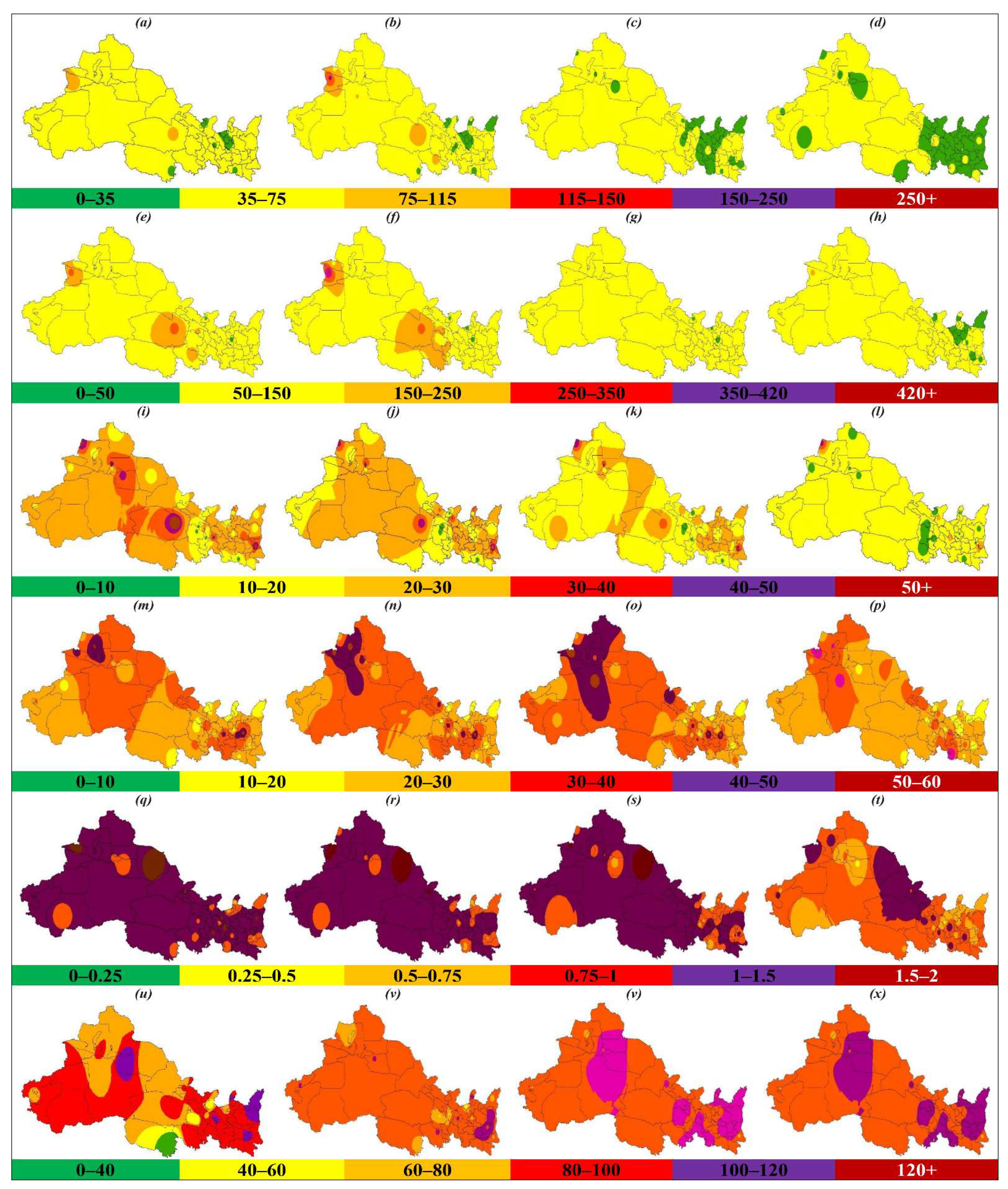
During the study period (2015–2018), the average concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO decreased by 28.2% (14.2%, 25.8%, 31.1%, 34.4%, 47.1%) (Figure 1a), 32.7% (18.5%, 32.5%, 31.8%, 32.7%, 46.3%) (Figure 1b), 41.9% (30.6%, 43.8%, 46.8%, 48.7%, 32.3%) (Figure 1c), 6.2% (+3.59%, 4.44%, 18.8%, +3.72%, 8.45%) (Figure 1d), and 27.3% (32.7%, 21%, 38.4%, 17.2%, 16%) (Figure 1e), respectively, in NWC (SN, XJ, GS, NX, QH). In contrast to the other pollutants, the ozone levels increased by 3.69% (5.4%, 6.04%, 1.32%, 19.3%, 5.66%) in NWC (SN, XJ, GS, NX, QH) between 2015 and 2018 (Figure 1f). The annual average concentration of PM2.5 and PM10 failed to comply with CAAQS Grade II standards (35 µg/m3 and 70 µg/m3, annual mean) and exceeded them by 25% and 31.9%, respectively, and exceeded them by 3.37 and 3.61 times, respectively, for the WHO air quality guidelines (10 µg/m3 and 20 µg/m3, annual mean) in NWC. PM2.5 and PM10 failed to comply with CAAQS Grade II standards in SN, XJ, GS, NX, and NWC (Figure 1a,b), while SO2 and NO2 complied with CAAQS Grade II standards (60 µg/m3 and 40 µg/m3, annual mean) in SN, XJ, GS, NX, QH, and NWC (Figure 1c,d). CO and O3 do not have annual standards under CAAQS; CO decreased in SN, XJ, GS, NX, QH, and NWC, while O3 decreased in GS and QH during 2018 as compared with 2015 (Figure 1e,f). During the study period, the highest concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 occurred in SN, XJ, NX, SN, SN, and QH, respectively. Figure 2 explains the spatial distribution of the criteria pollutants in 53 cities of NWC during 2015 to 2018, obtained by the inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation technique. The obtained results from spatial interpolation were quite similar to the actual values. In the case of spatial distribution, 92.5%, 96.2%, 92.5%, 64.5%, 88.7%, and 11.3% of the cities of NWC experienced a reduction in PM2.5 (Figure 2a–d), PM10 (Figure 2e–h), SO2 (Figure 2i–l), NO2 (Figure 2m–p), CO (Figure 2q–t), and O3 (Figure 2u–x), respectively, during 2018 as compared 2015. Similarly, 66%, 72.5%, and 13.2% of the cities failed to meet the CAAQS Grade II for PM2.5, PM10, and NO2 (35 µg/m3, 70 µg/m3, 40 µg/m3, annual mean), respectively (Table S1). Most of the cities that were not complying with the CAAQS are cities with a larger population and increased industrial activities.
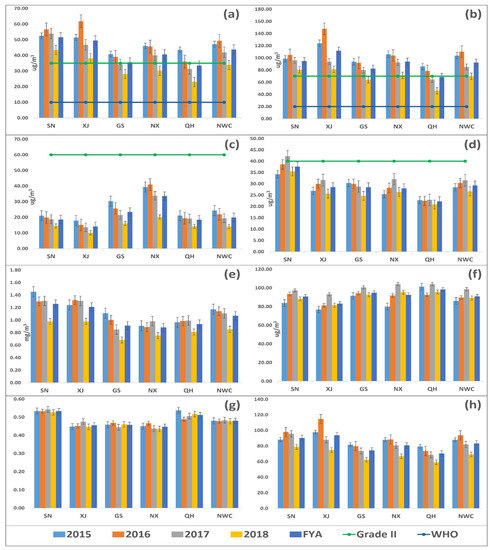
Figure 1.
Annual variation of PM2.5 (a), PM10 (b), SO2 (c), NO2 (d), CO (e), O3 (f), PM2.5/PM10 (g), and AQI (h) in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) and NWC as a whole between 2015 and 2018. Descriptions are as follows: light blue bar (2015), orange bar (2016), grey bar (2017), yellow bar (2018), blue bar (four-year average (FYA)), parrot line with dots (CAAQS Grade II standards, annual mean), and dark blue with dots (WHO standards). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), O3 (ozone), PM2.5/PM10 (ratio of PM2.5 with PM10), and AQI (air quality index).
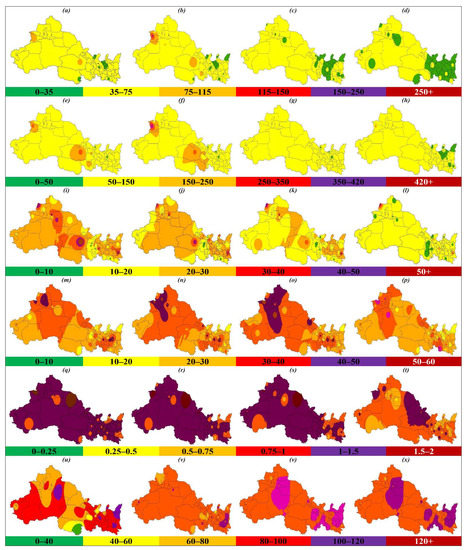
Figure 2.
The spatial distribution of PM2.5 (a–d), PM10 (e–h), SO2 (i–l), NO2 (m–p), CO (q–t), and O3 (u–x) between 2015 and 2018 in northwest China (NWC). Color represents the different pollution levels, e.g., green (good), yellow (moderate), orange (unhealthy for the sensitive group), red (unhealthy for all), purple (very unhealthy), and maroon (hazardous). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone).
3.2. Seasonal Variation of Six Criteria Pollutants
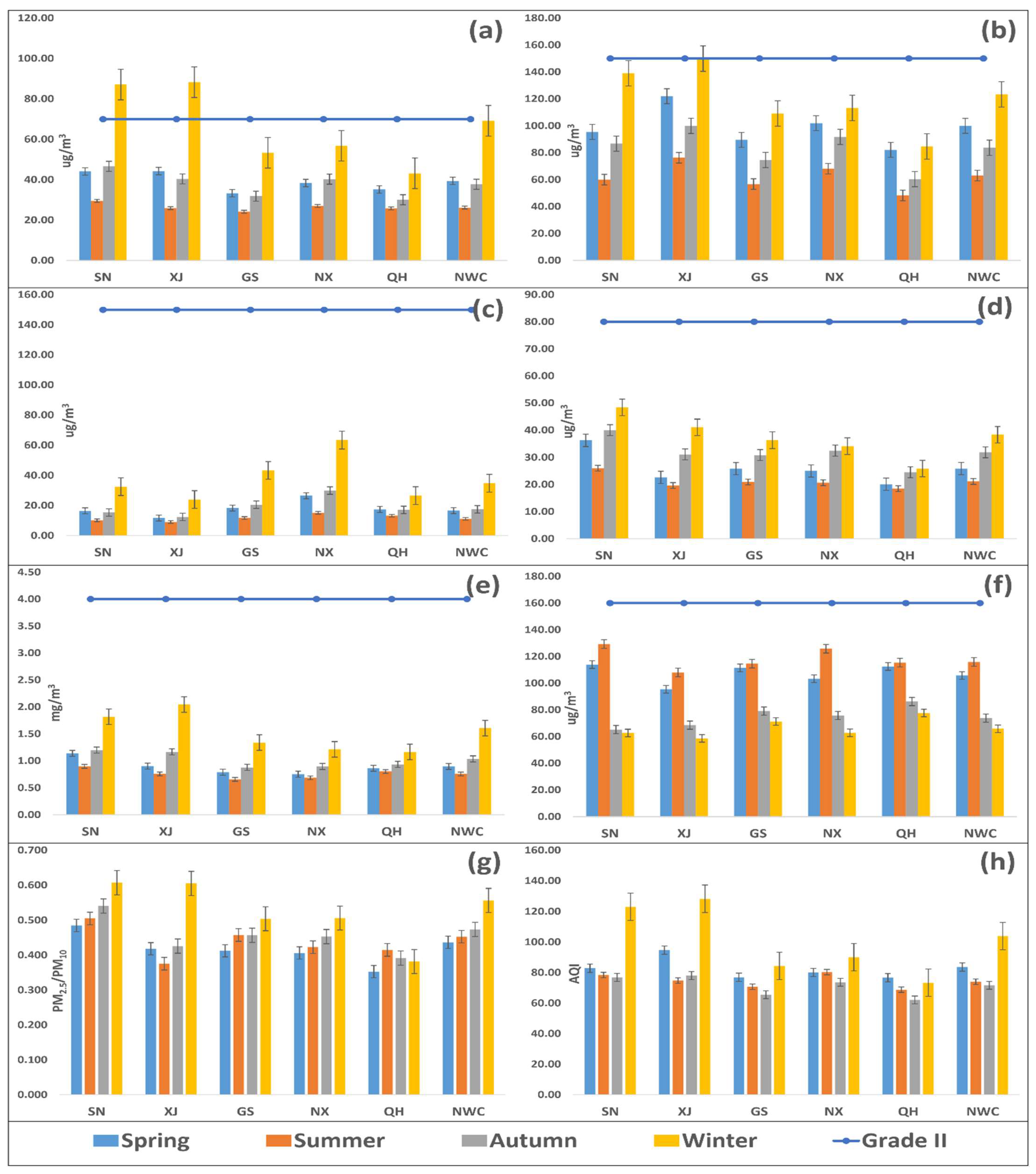
In terms of seasonality, all the pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO) observed the highest concentration in winter and the lowest occurred in summer except O3 (vice versa) between 2015 and 2018 (Figure 3). PM2.5 exceeded CAAQS Grade II (75 µg/m3, daily mean) in SN, and XJ during winter (Figure 3a), while PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 complied with CAAQS Grade II (150 µg/m3, 150 µg/m3, 80 µg/m3, 4 mg/m3, and 160 µg/m3, daily mean) in SN, XJ, GS, NX, QH, and NWC during spring, summer, autumn, and winter (Figure 3b–f). The average concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO decreased in all seasons, e.g., spring, summer, autumn, and winter, while the average concentration of O3 increased in all seasons between 2015 and 2018. Figure S2 explains the spatial distribution of the criteria pollutants in 53 cities of NWC during different seasons. PM2.5 exceeded CAAQS Grade II standards (daily mean) in 1.89%, 5.56%, and 32.1% of the cities during spring, summer, and winter, respectively (Figure S2a). Similarly, PM10 exceeded the daily standard in 5.66%, 7.55%, 1.89%, and 26.4% of the cities in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively (Figure S2b), while, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 complied with CAAQS Grade II standards (daily mean) in all the cities of NWC during all seasons (Figure S2c–f).
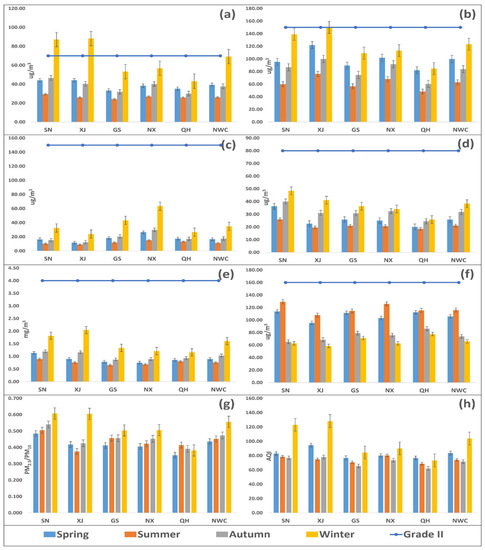
Figure 3.
Seasonal variation of PM2.5 (a), PM10 (b), SO2 (c), NO2 (d), CO (e), O3 (f), PM2.5/PM10 ratio (g), and AQI (h) in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) and NWC as a whole between 2015 and 2018. Descriptions are as follows: light blue bar (spring), orange bar (summer), grey bar (autumn), yellow bar (winter), and blue line with dots (CAAQS Grade II standards, daily mean). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), O3 (ozone), PM2.5/PM10 (ratio of PM2.5 with PM10), and AQI (air quality index).
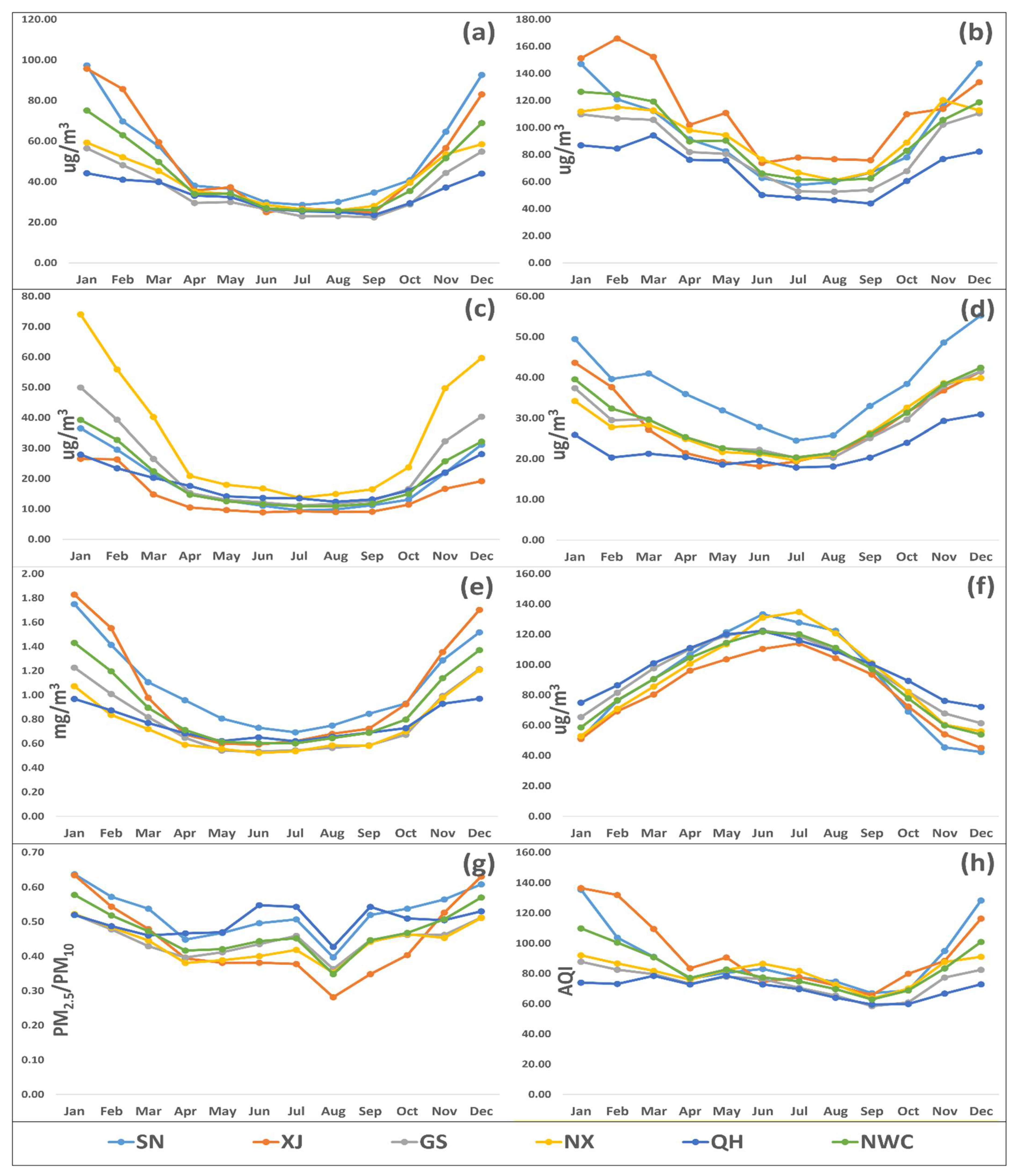
Figure 4 illustrates the monthly variation in the criteria pollutants, PM2.5/PM10 ratio, and AQI in NWC between 2015 and 2018. PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, and CO explicated “U” shaped curves, with the highest concentration in winter (October to January) due to increased coal combustion for civil heating and stagnant meteorological conditions, e.g., lower wind speed, low temperature, etc., while the lowest concentration occurred in summer (June to August) due to seasonal rains and favorable atmospheric conditions that help in pollution dispersion. In the case of PM10, higher pollution levels also occurred in spring (March to May) due to haze events. In contrast to other pollutants, the O3 levels were higher in June to August (summer) and lower in winter.
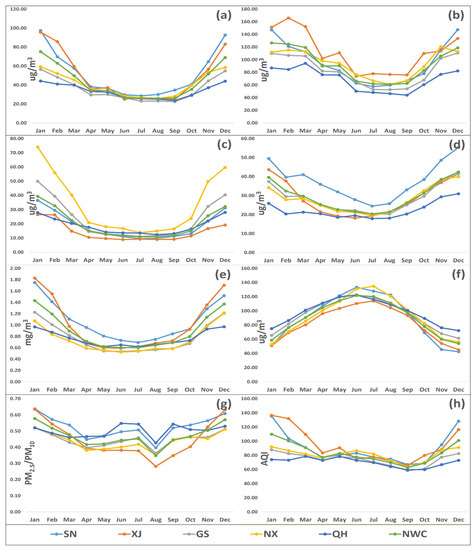
Figure 4.
The monthly average concentration of PM2.5 (a), PM10 (b), SO2 (c), NO2 (d), CO (e), O3 (f), PM2.5/PM10 (g), and AQI (h) in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018. Descriptions are as follows: light blue line with dots (SN), orange line with dots (XJ), grey line with dots (GS), yellow line with dots (NX), blue line with dots (QH), and parrot line with dots (NWC). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone).
3.3. PM2.5/PM10 Ratio
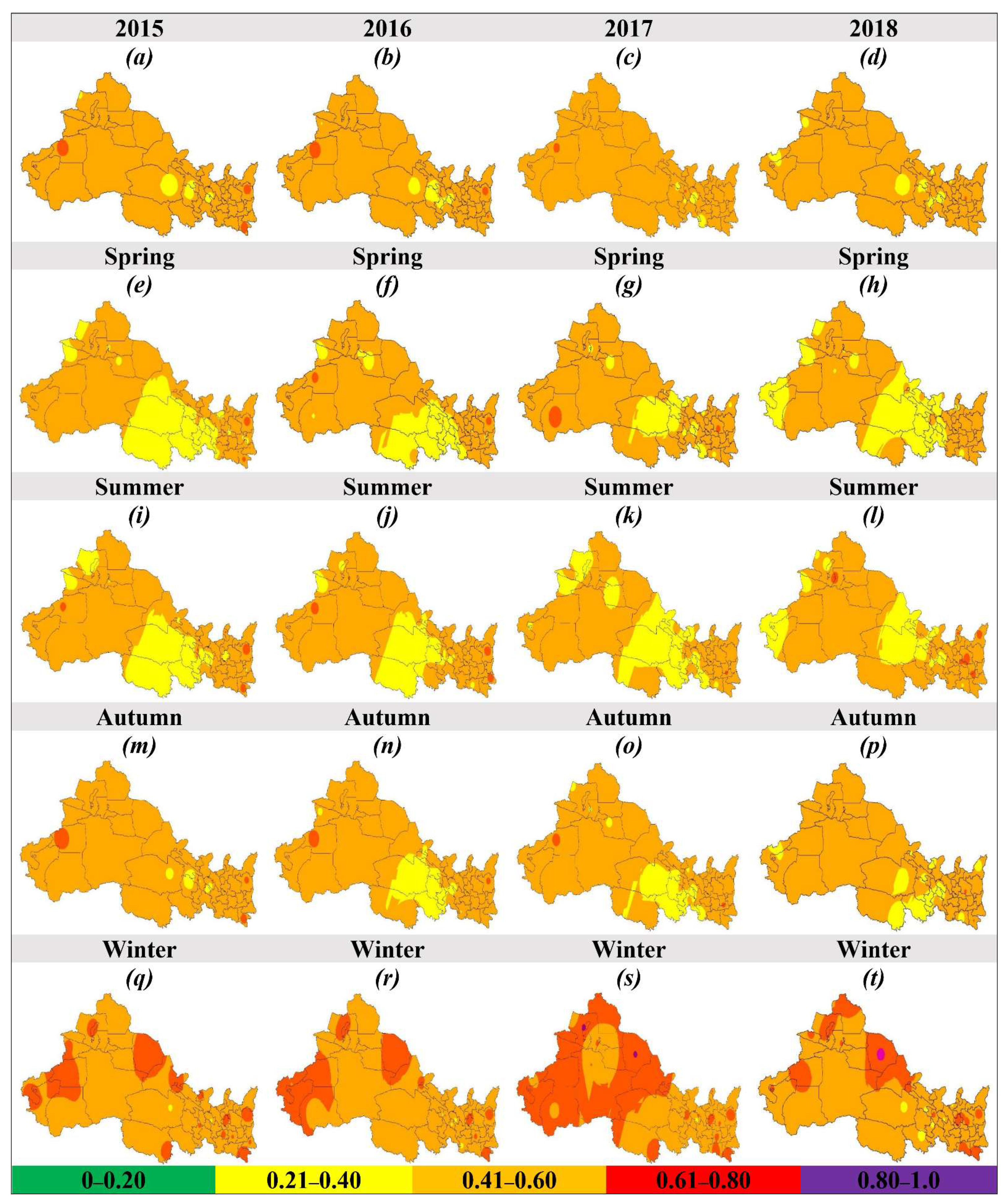
The PM2.5/PM10 ratio normally reflects the composition and quality of air, e.g., a higher PM2.5/PM10 ratio indicates the increased proportion of PM2.5 and a lower PM2.5/PM10 ratio indicates a higher concentration of PM10 in the atmosphere. The annual average PM2.5/PM10 ratio in NWC during 2015 to 2018 was 0.480 ± 0.08, 0.478 ± 0.07, 0.483 ± 0.08, and 0.478 ± 0.07, respectively, and experienced a reduction of 0.43% over time (Figure 1g). The highest PM2.5/PM10 ratio occurred in SN followed by QH, GS, XJ, and NX. In terms of seasonality, the highest PM2.5/PM10 ratio occurred in winter, followed by autumn, spring, and summer, and experienced an average change of −2.77%, −4.98%, 1.82%, and 5.31%, respectively (Figure 3g). In the case of monthly variation, a “U” shaped curve was observed with the highest value in winter and the lowest value in the summer Figure 4g. Figure 5 illustrates the annual (a–d) and seasonal (spring (e–h), summer (i–l), autumn (m–p), and winter (q–t)) spatial distribution of PM2.5/PM10 ratio in NWC during 2015 to 2018. In 2018, 49.1% of the cities of NWC experienced an increase in the PM2.5/PM10 ratio as compared with 2015. Similarly, 49.1%, 62.3%, 35.9%, and 39.6% of the cities of NWC experienced increased PM2.5/PM10 ratio in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively, in 2018 against 2015. From 2015 to 2018, approximately 1.89%, 1.89%, 3.74%, and 26.4% of the cities experienced PM2.5/PM10 ratio higher than 0.60 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively, in NWC.
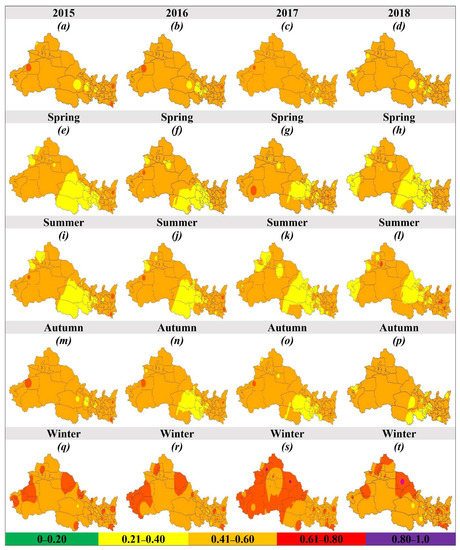
Figure 5.
Annual (a–d) and seasonal (spring (e–h), summer (i–l), autumn (m–p), and winter (q–t)) spatial distribution of PM2.5/PM10 in 53 cities of northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018. Color represents the different pollution levels, e.g., green (good), yellow (moderate), orange (unhealthy for a sensitive group), red (unhealthy for all), purple (very unhealthy), and maroon (hazardous).
3.4. Air Quality Index (AQI)
Air quality index (AQI) is a color-coded scale that simplifies different pollutants concentrations into a single numerical value that reflects overall air quality, health effects, sensitive groups, and required precautionary measures. During the study period (2015–2018), the annual average AQI in NWC was 88.1 ± 24.1, 93.5 ± 36.3, and 82 ± 18.7, 69.2 ± 14.8, respectively, and improved by 21.3% (Figure 1h). The highest AQI occurred in XJ, followed by SN, NX, GS, and QH. The AQI improved in all the cities except a few cities in SN (Weinan, Xian), and XJ (Changji, Ili, Shihezi, Tacheng, Wujiaqu). In 2018, the average AQI was under the threshold value of 100 in all the cities except Shihezi and Wujiaqu in Xinjiang (Figure 6d).
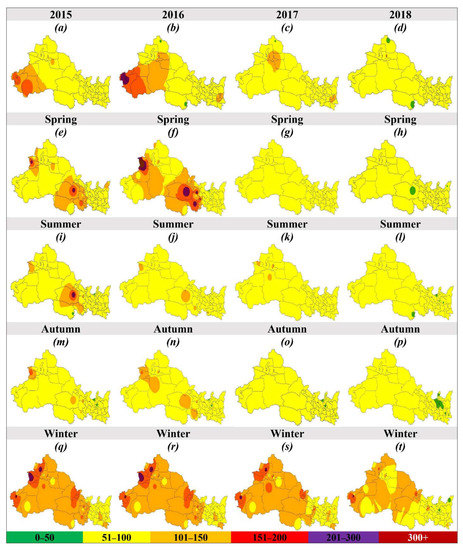
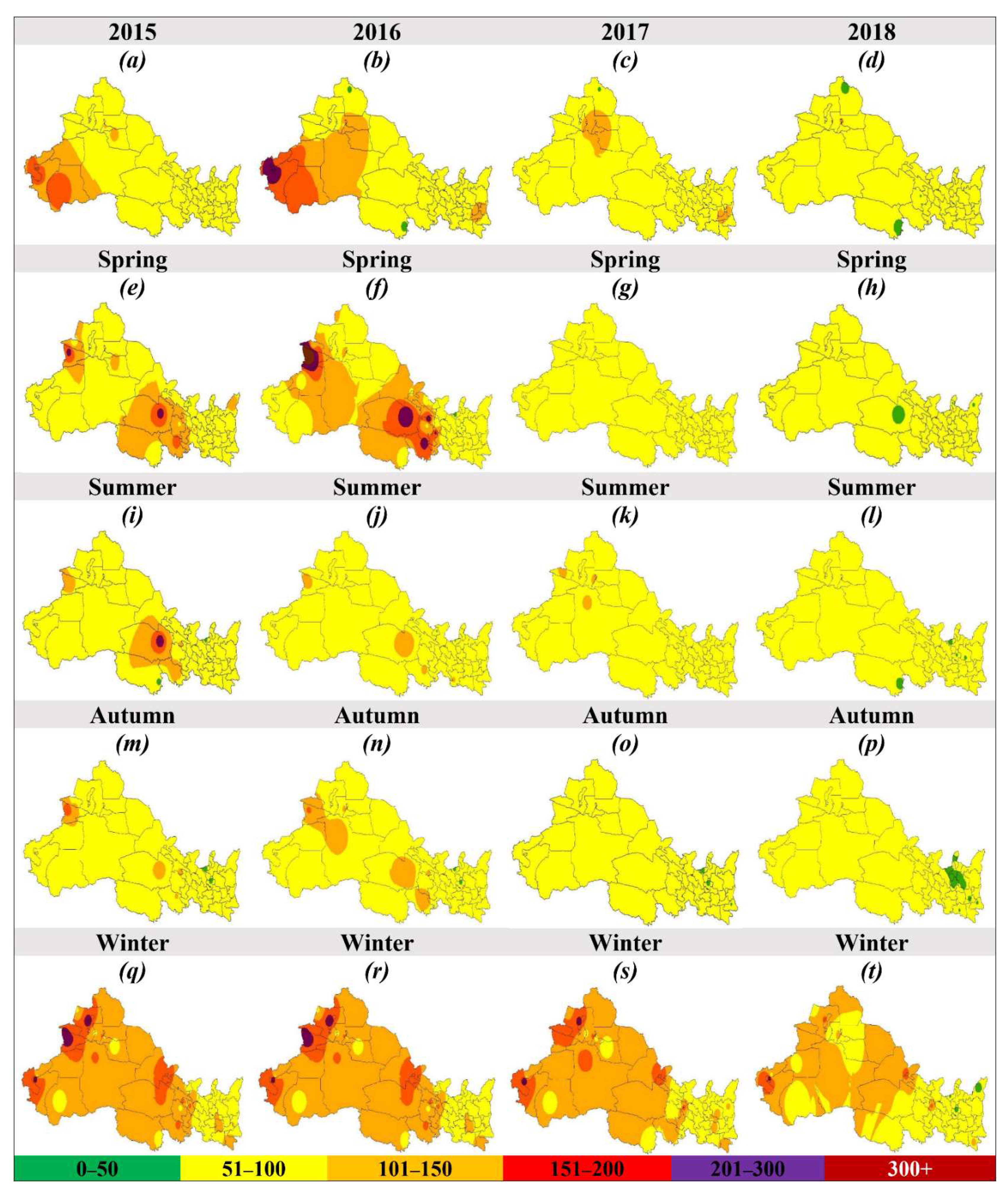
Figure 6.
Annual (a–d) and seasonal (spring (e–h), summer (i–l), autumn (m–p), and winter (q–t)) spatial distribution of AQI between 2015 and 2018 in 53 cities of northwest China (NWC). Color represents the different classes of air quality index, e.g., green (0–50, good), yellow (51–100, moderate), orange (101–150, unhealthy for the sensitive group), red (151–200, unhealthy for all), purple (201–300, very unhealthy), and maroon (300+, hazardous).
In the case of seasonal variation, the highest AQI occurred in winter, followed by spring, summer, and autumn, respectively, and improved by 17.5%, 30.8%, 18.7%, 17.4%, respectively, in NWC during 2018 as compared with 2015. The seasonal variation was consistent throughout NWC, e.g., highest AQI in winter and lowest in autumn, except XJ (Figure 3h). Figure 6 illustrates the seasonal (spring (e–h), summer (i–l), autumn (m–p), and winter (q–t)) spatial distribution of AQI in NWC between 2015 and 2018. In different seasons, e.g., spring, summer, autumn, and winter, the number of cities exceeding the AQI threshold value of 100 decreased from 24.5% to 0% (Figure 6e–h), 7.55% to 0% (Figure 6i–l), 7.55% to 0% (Figure 6m–p), and 50.9% to 22.6% (Figure 6q–t), respectively, in NWC. In the case of the monthly variation, a “U” shaped curve was observed with the highest value in winter and the lowest value in summer Figure 4h.
3.5. Proportion of Six Air Quality Index (AQI) Classes
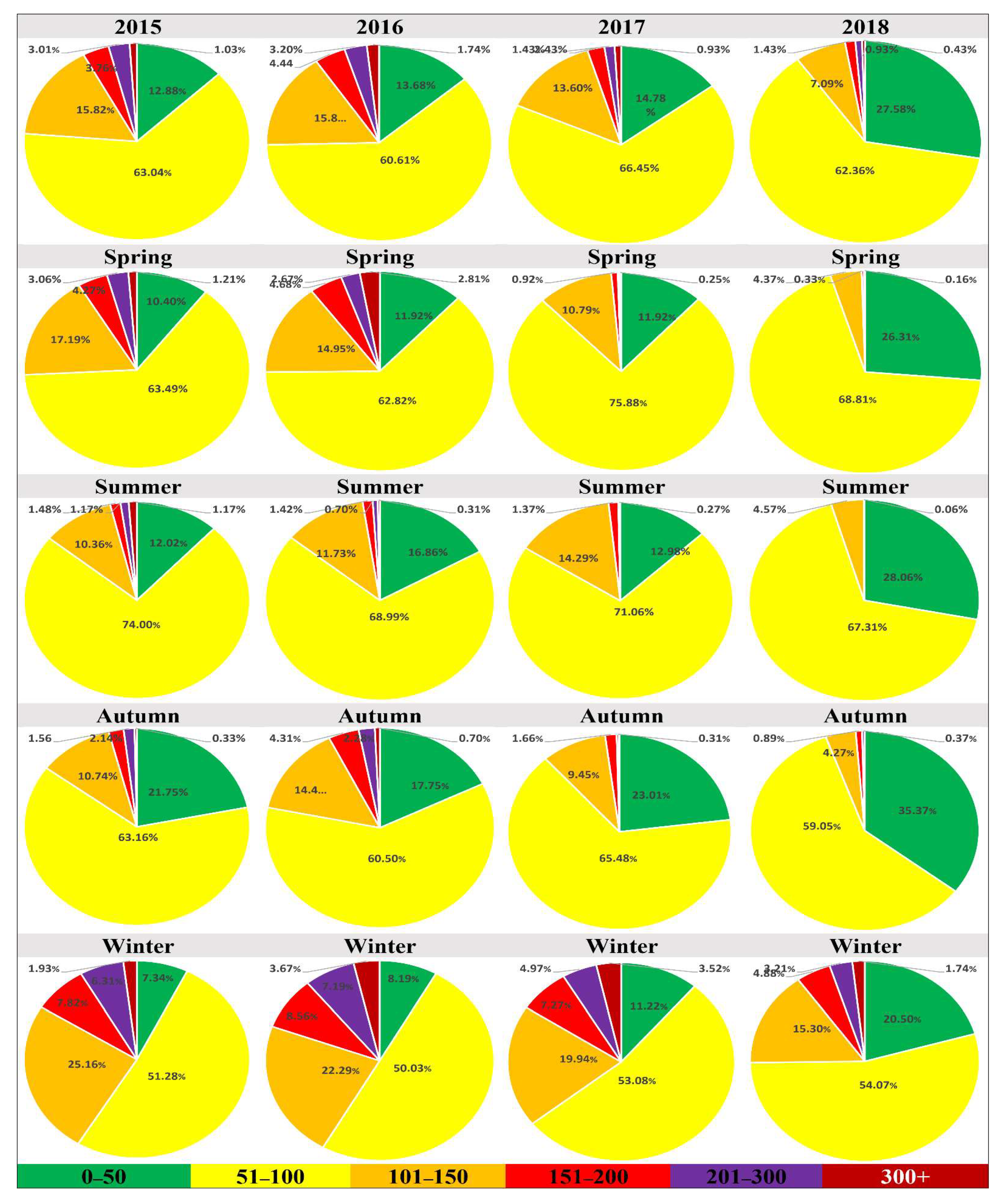
Figure 7 explains the annual (a–d) and seasonal (spring (e–h), summer (i–l), autumn (m–p), and winter (q–t)) proportion of AQI classes in NWC during 2015 to 2018. During the study period, the average proportion of Class I, Class II, Class III, Class IV, Class V, and Class VI accounted for 17.2%, 63.1%, 13.1%, 3.01%, 2.14%, and 1.03% of the days, respectively. In NWC, the proportion of Class I, Class II, Class III, Class IV, Class V, and Class VI experienced an average change of 114.1%, −1.08%, −55.2%, −29.5%, −69.2%, and −58.3%, respectively, in 2018, with respect to 2015. The combined proportion of Class I and II increased by 18.5%, with the highest increase in spring (28.73%), followed by winter (27.2%), autumn (11.2%), and summer (10.9%), indicating significant improvement in air quality over the time span.
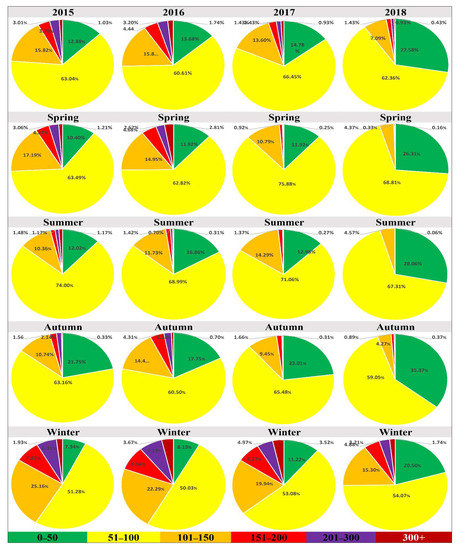
Figure 7.
The annual (1st row) and seasonal (spring (2nd row), summer (3rd row), autumn (4th row), and winter (5th row)) distribution of AQ class, e.g., Class I (0–50, good, green), Class II (51–100, moderate, yellow), Class III (101–150, unhealthy for a sensitive group, orange), Class IV (151–200, unhealthy for all, red), Class V (001-300, very unhealthy, purple), and Class VI (300+, hazardous, maroon) in northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018.
3.6. The Major Pollutants/Primary Pollutants
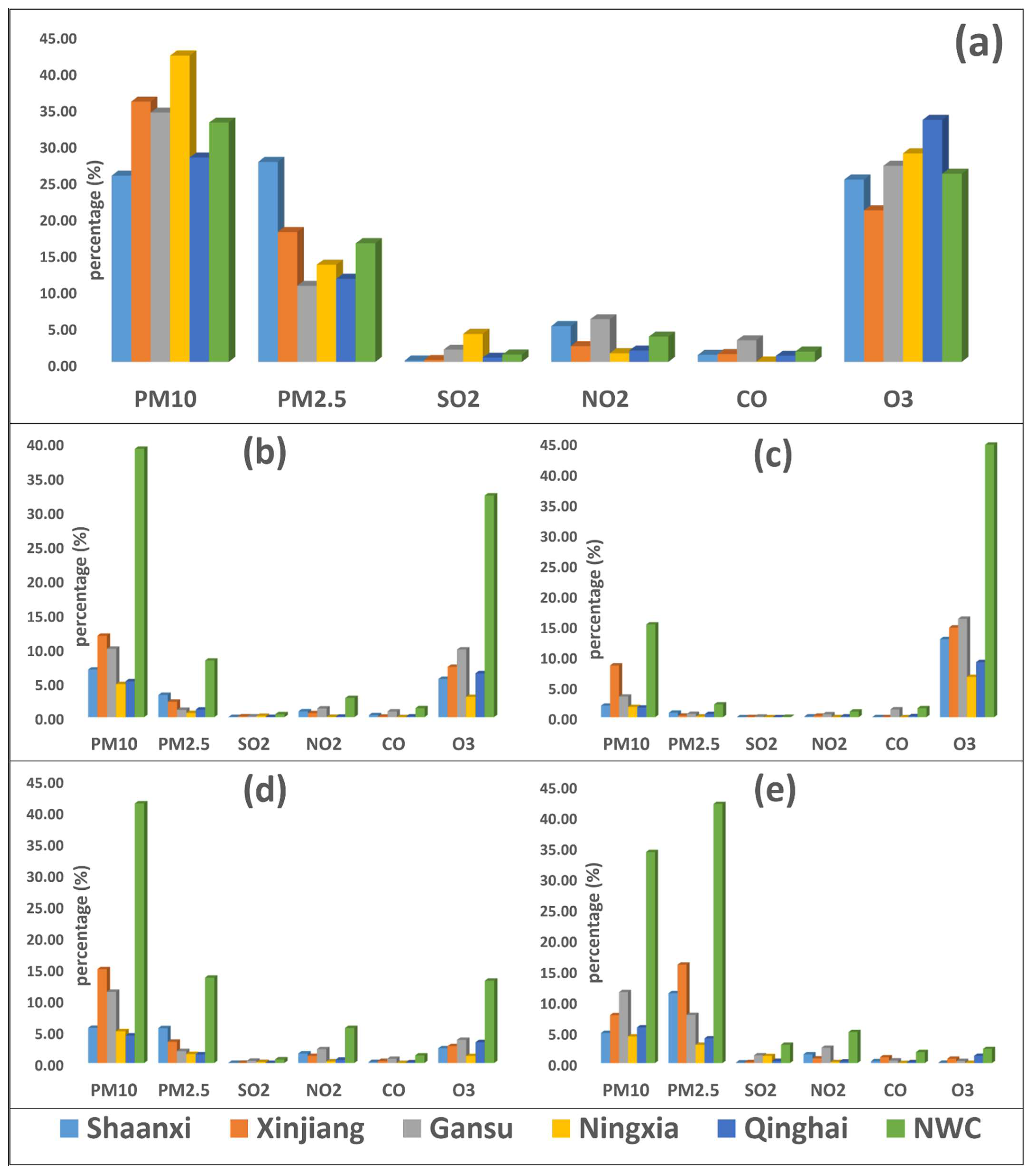
During the study period, PM10 was a major pollutant, accounting for more than 32.9% of the days, followed by O3 (25.9%), PM2.5 (16.4%), NO2 (3.52%), CO (1.43%), and SO2 (1.01%) in NWC (Figure 8). In 2018, the number of days with PM10, PM2.5, SO2, and CO as major pollutants decreased by 35%, 38%, 52%, and 90%, respectively, and increased by 46% and 11% for O3 and NO2, respectively. PM10 was a major pollutant in autumn (41.3%), spring (39.1%), and a second major pollutant in winter (34.3%), while PM2.5 was a major pollutant in winter (42.1%), and O3 was a major pollutant (59.7%) in summer. The number of days with O3 as a major pollutant was higher in the hotter months March–September), and, for PM2.5, it was higher in the colder months (November–February). During the study period, the number of days with PM10 as a major pollutant decreased by 47.2%, 76.3%, and 19.7% in spring, summer, and autumn, respectively, and increased by 4.58% in winter 2018 as compared with 2015. Similarly, the number of days with PM2.5 as a major pollutant decreased by 62.3%, 90.8%, 42.9%, and 24.6% in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively. The number of days with SO2 as a major pollutant decreased in all the seasons except summer, NO2 decreased in summer and winter, CO decreased in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, while O3 increased in all the seasons, e.g., in spring, summer, autumn, and winter 2018 as compared with 2015.
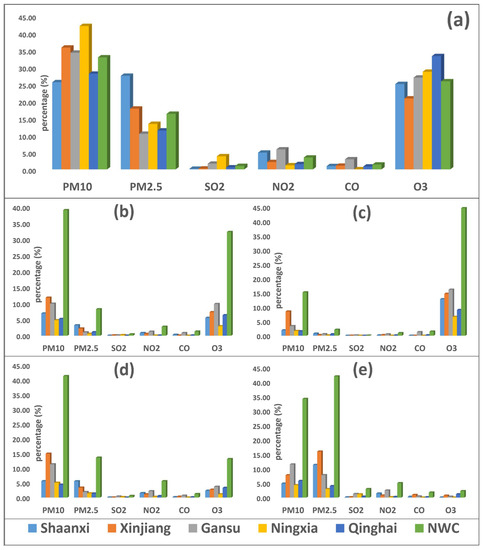
Figure 8.
The annual (a) and seasonal (spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d), winter (e)) percentage of days with different primary pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3) in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018. Descriptions are as follows: light blue bar (Shaanxi), orange bar (Xinjiang), grey bar (Gansu), yellow bar (Ningxia), blue bar (Qinghai), and parrot bar (NWC). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone).
3.7. Pollution Days/Non-Attainment Days
Any day with one or more pollutants exceeding CAAQS (Grade II) standards is considered as a non-attainment/pollution day. In NWC, the proportion of non-attainment days were 23.3%, 23.9%, 16.2%, and 8.9% during 2015 to 2018, respectively. The proportion of non-attainment days decreased by 61.77% (24%, 47.1%, 79.1%, 77.9%, and 73.9%) in NWC (SN, XJ, GS, NX, and QH) during 2015 to 2018 (Table 1). The highest reduction in the proportion of non-attainment days occurred in spring (79.6%), summer (63.1%), autumn (60.4%), and winter (37.6%), respectively.
3.8. Statistical Analysis
The result of Pearson’s correlation (Table S2) indicated that AQI was strongly positively correlated (R > 0.5) with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO on an annual basis and strongly anti-correlated (R > −0.5) with O3 in the NWC (Figure S3a). The seasonal variation in the correlation between AQI and different pollutants was evident (Figure S3b–e). In spring, AQI was strongly correlated (R > −0.5) with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, and CO, moderately correlated (R > −0.3) with NO2, while strongly anti-correlated (R > −0.5) with O3 (Figure S3b). In summer, AQI was strongly correlated (R > 0.5) with PM2.5 PM10, and O3, weakly correlated (R > 0.2) with SO2, weakly anti-correlated (R > −0.1) with CO, and strongly anti-correlated (R > −0.5) with NO2 (Figure S3c). In autumn, AQI was strongly correlated (R > 0.5) with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO), while strongly anti-correlated (R > −0.5) with O3 (Figure S3d). In winter, AQI was strongly correlated (R > 0.5) with PM2.5, PM10, SO2, and CO, moderately correlated (R > 0.3) with NO2, and moderately anti-correlated (R > −0.3) with O3 (Figure S3e). Throughout the study period, all the pollutants were positively correlated with each other except O3 (Table S2).
4. Discussion
During the study period, the average concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3, decreased in 92.5%, 96.2%, 92.5%, 64.5%, 88.7%, and 11.3% of the 53 cities in NWC. Based on the results above, we concluded that strict environmental regulations have significantly improved the air quality in NWC between 2015 and 2018 [3,20,21,22,23]. PM2.5 mainly originates from industrial activities, coal consumption, power generation, biomass burning, automobile exhausts, construction activities, road dust, etc. [28,29,30,50,51,52]. From 2015 to 2018, the average concentration of PM2.5 decreased in all the cities except a few cities (Changji, Ili, Shihezi, Wujiaqu) in the northern part of XJ. Higher pollution in XJ, SN, and GS, PM2.5 hotspots [53,54], is because of increased coal-based industry, vehicular emission, civil heating, construction activities, natural sources (dust storms), and adverse meteorology [55,56,57,58,59,60]. PM10 mainly originates from natural sources, e.g., sand storms, haze events, etc., as well as from anthropogenic sources, e.g., developmental activities, industrial emissions, traffic emissions, road dust, etc. [15,26,27,28]. The highest pollution levels occurred in XJ, followed by SN, NX, GS, and QH. Elevated pollution levels in southern Xinjiang (Kashgar) indicate the influences of emissions from natural sources, e.g., Taklimakan deserts, dust storms, haze events, etc. [61,62,63,64]. Similarly, higher particulate pollution in Shaanxi (FWP region) is associated with increased anthropogenic emissions, e.g., industrial activities, construction activities, etc. [55]. All the cities of NWC experienced a reduction in PM10 except Shihezi and Wujiaqu in northern XJ, indicating the influence of both manmade and natural emission sources. This decrease is associated with strict environmental regulations, e.g., Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS) (GB 3095–2012) [17], Atmospheric Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan (APPCAP, 2013) [18], technical regulation on ambient air quality index (HJ 633–2012) [19], the establishment of nationwide air quality monitoring stations, etc. [3,20,21,22,23].
In the case of gaseous pollutants, the average concentration of SO2, NO2, and CO decreased by 41.9%, 6.19%, and 27.3%, respectively, in NWC. Industrial emissions, coal burning, fossil fuel burning, power generation, traffic exhausts, etc. are major sources of SO2, NO2, and CO [65,66,67,68,69]. The concentration of SO2 decreased in all the cities except Ili, Hami (XJ), Jiuquan (GS), and Yushu (QH), indicating the influence of increased coal combustion, vehicular exhaust, and industrial emission [27,28,57,70]. In the case of NO2, the average concentration decreased in 71.7% of the cities of NWC between 2015 and 2018. The highest pollution level occurred in the provincial capitals, e.g., Xi’an (SN), Urumqi (XJ), Lanzhou (GS), etc., and major cities (Ili, Hami, Jiuquan, Yushu, etc.), indicating increased fossil fuel combustion, e.g., automobile exhaust, industrial emission, etc. [34,63,65,66,67,68,69]. Similarly, the highest concentration of CO occurred in SN, followed by XJ, QH, GS, and NX. Higher CO indicates incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biomass burning, industrial emission, and causes multiple health disorders, e.g., hypoxia, major heart and neural disorders [28,67,68]. In contrast to other pollutants, O3 increased by 3.69% in NWC during the study period. All the cities experienced an increase in O3 concentration except Ankang, Shanglou, Longnan, Haibei, Hainan, and Haixi. This increase in O3 is associated with a decrease in PM2.5 and other pollutants, which slows down the sink of hydroperoxy radicals and helps in the accumulation of ozone [55].
In terms of seasonality, PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO experienced the same seasonal variation, e.g., highest in winter and lowest in summer. Higher pollution in winter is associated with increased coal combustion, civil heating, power generation, fossil fuel burning, industrial activity, vehicular exhausts, and adverse/stagnant meteorology [13,14,15,26,27,28,29,30,50,51,52,71,72,73,74,75]. In the case of PM10, higher pollution levels also occurred from March to May (spring) due to haze events [76,77]. In contrast to other pollutants, the concentration of O3 was highest in summer and lowest in winter [14,28,30,78]. Ozone is a secondary pollutant, formed due to a photochemical reaction between VOCs and NOx [43,44,79]. The concentration of ozone in the summer was approximately twice that in winter due to lower NOx levels in winter as NOx levels decrease the O3 depletion and enhance the accumulation of O3 [80]. Similarly, higher temperatures, e.g., in summer, favor the accumulation of ozone [81,82,83].
The PM2.5/PM10 ratio reflects air quality, pollution sources, and origin, e.g., a higher PM2.5/PM10 ratio indicates the increased proportion of PM2.5, mainly emitted from anthropogenic activities, and a lower ratio indicates an increased proportion of PM10, mainly from natural activities [28,61,62,63,64]. During the study period (2015–2018), the PM2.5/PM10 ratio slightly decreased by 0.43% and in 50.9% of the cities of NWC. This decrease is associated with a reduction in PM2.5 over time. In general, the PM2.5/PM10 ratio was higher in winter (low temperature) as compared with summer (high temperature) due to increased anthropogenic activities that release a significant amount of PM2.5 and stable atmospheric conditions that help the accumulation of pollution [26,27,28,29,53,54,84].
During the study period (2015–2018), the AQI improved by 21.3%, and 86.8% of the cities of NWC experienced AQI improvement. This improvement is associated with a reduction in the criteria pollutants over time. AQI crossed the threshold value of 100 in 10 cities, out of which seven cities are in Xinjiang (Kashgar, Hotan, Aksu, Wujiaqu, Crete, Urumqi, Turpan) and three cities are in Shaanxi (Xiangyang, Xi’an, Weinan) (Table S1). The higher AQI values in Xinjiang and Shaanxi are associated with the increased coal-based industry, civil heating, and vehicular exhaust [3,14,30,51,52,56,69,85]. In the case of seasonal variations, the highest AQI occurred in winter due to increased anthropogenic emissions and stable atmospheric conditions [15,58,84]. In NWC, the proportion of AQI “Class I” improved by 114.1%, while the proportion of Class II, Class III, Class IV, Class V, and Class VI decreased by 1.08%, 55.2%, 29.5%, 69.2%, and 58.3%, respectively, during 2015 to 2018. The proportion of AQI “Class I” improved from 12.9% in 2015 to 27.6% in 2018. Similarly, the proportion of AQI “Class I” improved in all the provinces, e.g., SN, XJ, GS, NX, and QH, in all the seasons, and improved by 2.53 times, 2.33 times, 1.63 times, and 2.79 times in spring, summer, autumn, and winter in 2018 as compared with 2015, which indicates improvement in air quality [28,57].
During the study period (2015–2018), the proportion of days with PM10, PM2.5, SO2, and CO as a major pollutant decreased by 35%, 38%, 52%, and 90%, respectively, due to strict environmental legislation [20,21,22,23]. PM2.5 was a major pollutant in winter (42%), indicating anthropogenic emissions, e.g., coal burning, civil heat, industrial emissions, and vehicular emissions [28,56,57,58]. Similarly, O3 was a major pollutant (44.7%) in summer due to lower NOx levels as lower NOx levels prevent ozone depletion and the higher temperature in summer favors ozone generation and accumulation [78,80,82,83,86,87,88], while PM10 was a major pollutant in autumn (41.3%), spring (39.1%), and the second major pollutant in winter (34.3%). The number of days with PM10 as a major pollutant was higher in southern Xinjiang due to emissions from natural sources, e.g., the Taklimakan desert, sand storms [61,62,63,64,89]. Any day with one or more pollutants exceeding CAAQS (Grade II) is considered as a non-attainment/pollution day [2,30]. During the study period, the proportion of non-attainment days decreased by 61.8% in NWC. Similarly, the proportion of non-attainment days decreased in all the provinces, e.g., SN, XJ, GS, NX, and QH, and experienced a reduction of 79.6%, 63.1%, 60.4%, and 37.6% in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively, which clearly indicates that the ambient air quality improved significantly.
Rapid economic development, industrialization, haze events, dust storms, and adverse meteorological conditions play a crucial role in air quality deterioration [2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The Chinese government is working proactively to combat the pollution levels by revising and implementing strict environmental regulations [3,20,21]. According to this study, the concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, and CO, AQI, the proportion of AQI “Class I”, and pollution days decreased significantly in NWC between 2015 and 2018.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we examined the spatial and temporal variation of ambient air quality in northwest China (NWC) for a period of four years (2015–2018). During the study period, the average concentration of PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3 decreased in 92.5%, 96.2%, 92.5%, 64.5%, 88.7%, and 11.3% of the cities in NWC. The annual average concentration of particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) exceeded the CAAQS Grade II standards and WHO recommended air quality guidelines in NWC, while the annual average concentration of SO2 and NO2 complied with the CAAQS Grade II standards in NWC. In the case of seasonality, the highest pollution level occurred in winter except for ozone, with varying degrees of spatial distribution. The AQI, the proportion of AQI Class I, and the number of pollution days improved by 21.3%, 114.1%, and 61.8%, respectively, in NWC. The AQI improved in all the seasons, with the maximum improvement in spring followed by summer, winter, and autumn. In NWC, PM10 was a major pollutant for most of the days, followed by O3, PM2.5, NO2, CO, and SO2 with different spatial and temporal variations. A strong correlation occurred between AQI and all the pollutants except O3. Stricter regulations, e.g., a three-year action plan to win the blue sky defense war, sector-specific guidelines, and strict enforcement of environmental legislation, are the keys to pollution-free and breathable air. This paper comprehensively discussed the spatio-temporal characteristics of the ambient air quality in NWC and calls for future detailed assessment focusing on source apportionment, health risk assessment, the impact of meteorology, dispersion modeling, and impact of the chemical processes that influence the air quality.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13030375/s1, Figure S1: The locations of 53 cities in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) northwest China (NWC). Color represents the different classes of air quality index, e.g., green (0–50, good), yellow (51–100, moderate), orange (101–150, unhealthy for a sensitive group), red (151–200, unhealthy for all), purple (201–300, very unhealthy), and maroon (300+, hazardous); Figure S2: The seasonal (spring (light blue line), summer (orange line), autumn (grey line), and winter (yellow line)) spatial distribution of PM2.5 (a), PM10 (b), SO2 (c), NO2 (d), CO (e), and O3 (f) in 53 cities of northwest China between 2015 and 2018. Descriptions are as follows: light blue line with dots (spring), orange line with dots (summer), grey line with dots (autumn), yellow line with dots (winter), and the blue line (CAAQS, daily mean). The abbreviations are as follows: PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2. (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone); Figure S3: Annual (a) and seasonal (spring (b), summer (c), autumn (d), winter (e)) relationship between air quality index (AQI) and criteria pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3). The abbreviations are as follows: AQI (air quality index), PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone); Table S1: Lists of cities, their rankings in five provinces (Shaanxi (SN), Xinjiang (XJ), Gansu (GS), Ningxia (NX), and Qinghai (QH)) of northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018; Table S2: Pearson correlation between AQI and six criteria pollutants (PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2, CO, and O3) in northwest China (NWC) between 2015 and 2018. The abbreviations are as follows: AQI (air quality index), PM2.5 (fine particulate matter), PM10 (coarse particulate matter), SO2 (sulfur dioxide), NO2 (nitrogen dioxide), CO (carbon monoxide), and O3 (ozone).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z.; data curation/accumulation, S.Z.; investigation and data validation, J.L. and M.B.; methodology, S.Z.; data modelling, S.Z.; GIS mapping, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z.; review and editing, J.L. and M.B.; supervision, J.L.; funding acquisition, J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21667026), the Social Science Foundation of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps (No. 18YB13), and the Startup Foundation for Introduction Talent of NUIST (2017r107).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge the China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC) for the provision of air quality data. I am also very thankful to Jianjiang Lu and research scholar Anam Arshad from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shihezi University for helping and guiding me throughout the preparation of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Guan, Q.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Tan, Z.; Wang, N. Air pollution characteristics and human health risks in key cities of northwest China. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 269, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, K.J. Substantial changes in PM2.5 pollution and corresponding premature deaths across China during 2015–2019: A model prospective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, T.; Seyler, B.C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, F. Ambient air pollution and male fecundity: A retrospective analysis of longitudinal data from a Chinese human sperm bank (2013–2018). Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ji, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.Y. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants in western China and their relationship to meteorological factors and emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, D.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, D.; Dong, L. PM2.5 and O3 pollution during 2015–2019 over 367 Chinese cities: Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Luo, K.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Kang, S. Spatial variation of air quality index and urban driving factors linkages: Evidence from Chinese cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 4457–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cui, K.; Zhao, R.; Hsieh, L.T.; Lee, W.J. Characterization of the air quality index for Wuhu and Bengbu cities, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1198–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Jia, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, D.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Detection, extinguishing, and monitoring of a coal fire in Xinjiang, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26603–26616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Amini, N.; Sadeghian, B.; Wang, D.; Fang, L. Heavy metals and their source identification in particulate matter (PM2. 5) in Isfahan City, Iran. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 72, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.; Xiao, J. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y. A comprehensive analysis of the spatio-temporal variation of urban air pollution in China during 2014–2018. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Mi, K.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, J. One-year study of PM2.5 in Xinxiang city, North China: Seasonal characteristics, climate impact and source. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, Q. Characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 based on error estimation from EPA PMF 5.0 model at a medium city in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turap, Y.; Rekefu, S.; Wang, G.; Talifu, D.; Gao, B.; Aierken, T.; Nuerla, A. Chemical Characteristics and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 during winter in the Southern Part of Urumqi, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H. Understanding the recent trend of haze pollution in eastern China: Roles of climate change. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 4205–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GB 3095-2012. Chinese Ambient Air Quality Standards (CAAQS); Ministry of Environmental Protection of the Peoples Republic of China (MEP): Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Liao, H. Multi-pollutant air pollution and associated health risks in China from 2014 to 2020. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 268, 118829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 633-2012. Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (on Trial); Ministry of Environmental Protetction of the Peoples Republic of China (MEP): Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.F.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ha, X.Z. Spatial-temporal patterns of PM2.5 concentrations for 338 Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Dai, Q. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Bao, F.; Meng, C. Assessment of PM2.5 concentrations and exposure throughout China using ground observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Ji, H.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z. Spatiotemporal patterns of recent PM2.5 concentrations over typical urban agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Umarova, A.B.; Luan, Y. The spatiotemporal characteristics of the air pollutants in China from 2015 to 2019. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Z.; He, M.Z.; Shi, X. Estimating mortality burden attributable to short-term PM2.5 exposure: A national observational study in China. Environ. Intl. 2019, 125, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turap, Y.; Talifu, D.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A.; Maihemuti, M.; Tursun, Y.; Rekefu, S. Temporal distribution and source apportionment of PM2.5 chemical composition in Xinjiang, NW-China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Ning, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, L. Characteristics and sources analysis of PM2.5 in a major industrial city of northern Xinjiang, China. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Z.; Cui, K.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chao, H.R.; Chang-Chien, G.P. Characterization of the air quality index for Urumqi and Turfan cities, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 282–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, W.; Han, L.; Locke, D. Spatiotemporal variation in PM2.5 concentrations and their relationship with socioeconomic factors in China’s major cities. Environ. Intl. 2019, 133, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013–2014. Environ. Intl. 2014, 73, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerban, M.; Waili, Y.; Fan, F.; Liu, Y.; Qin, W.; Dore, A.J.; Zhang, F. Spatio-temporal patterns of air pollution in China from 2015 to 2018 and implications for health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Feigin, V. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet. 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Ma, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H. Health burdens of ambient PM2.5 pollution across Chinese cities during 2006–2015. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 24, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Ban, J.; Li, T. Estimation of PM2.5 associated disease burden in China in 2020 and 2030 using population and air quality scenarios: A modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health. 2019, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Kou, X.; Geng, H.; Xie, J.; Tian, J.; Cai, Z.; Dong, C. Mitochondrial damage: An important mechanism of ambient PM2.5 exposure-induced acute heart injury in rats. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, P.M.; Franchini, M. Health effects of ambient air pollution in developing countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.L.; Liu, S.Q.; Yin, X.X.; Li, H.C. Ambient air pollution, smog episodes and mortality in Jinan, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hanaoka, T.; Masui, T. Comparison of health and economic impacts of PM2.5 and ozone pollution in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 630-2011. Technical Guideline on Environmental Monitoring Quality Management; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People Republic of China (MEP): Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thach, T.Q.; Tsang, H.; Cao, P.; Ho, L.M. A novel method to construct an air quality index based on air pollution profiles. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health. 2018, 221, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhang, J.; Lyons, T.J.; Pai, J.L.; Chang, S.H. Comparison of the revised air quality index with the PSI and AQI indices. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Q.N.; Peng, X.; Xu, Q.; Long, L.B.; Wei, N.; Liu, M.; Jia, W.X. Air quality and its response to satellite-derived urban form in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Intl. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017, 75, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.H.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, S. Impact of the COVID-19 Event on Air Quality in Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Hsieh, Y.K.; Wan, S.; Zhang, J. Air Quality Index, Indicatory Air Pollutants and Impact of COVID-19 Event on the Air Quality near Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1204–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apak, S.; Atay, E. Industrial Policy and Climate Change Management of Turkey as an EU candidate country. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 75, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, M.; Das, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, R.; Saha, S. Spatio-temporal concentration of atmospheric particulate matter (PM2. 5) during pandemic: A study on most polluted cities of indo-gangetic plain. Urban. Climate 2021, 35, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tripathi, N.K. Geospatial hot spot analysis of lung cancer patients correlated to fine particulate matter (PM2. 5) and industrial wind in Eastern Thailand. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaib, S.; Lu, J.; Shahid, M.Z.; Ahmar, S.; Shahid, I. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 on Ambient Air Quality in Northwest China (NWC). Atmosphere 2021, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. R Studio, PBC, Boston, MA 2020. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Chen, J.; Lu, J.; Ning, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, L. Pollution characteristics, sources, and risk assessment of heavy metals and per fluorinated compounds in PM2.5 in the major industrial city of northern Xinjiang, China. Air Qual. Atmos. Health. 2019, 12, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Lin, J.; Wang, Q.; Deng, C.; Fu, J.S. A Typical Formation Mechanism of Heavy Haze-Fog Induced by Coal Combustion in an Inland City in North-Western China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, J.; Deng, J.; Xiao, H. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 during spring and winter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2165–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lv, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, L.; Xu, S.; Jin, C. Characteristics and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Jiaxing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7497–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, H.; Yu, E.; Luo, T. PM2.5/PM10 Ratios in Eight Economic Regions and Their Relationship with Meteorology in China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da, Y.L.M.A.B.; Limu, D.L.N.T.L.; Miti, A.B.L.Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, X. Autumn and wintertime polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 from Urumqi, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Volatile organic compounds in Shihezi, China, during the heating season: Pollution characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16439–16450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, M.; Gu, Y.; Tang, X. Spatial and temporal variability of the PM2. 5/PM10 ratio in Wuhan, Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 17, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Chen, D. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Lei, Y.; McElroy, M.B.; Hao, J. Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 10, 29075–29111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pey, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Forastiere, F.; Stafoggia, M. African dust outbreaks over the Mediterranean Basin during 2001–2011: PM10 concentrations, phenomenology and trends, and its relation with synoptic and mesoscale meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1395–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, F.; Qiu, X. PM10 concentration in urban atmosphere around the eastern Tien Shan, Central Asia during 2007–2013. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 6864–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Mao, J.; Chen, L. Background concentrations of PMs in Xinjiang, West China: An estimation based on meteorological filter method and Eckhardt algorithm. Atmos. Res. 2019, 215, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Samat, A.; Abuduwaili, J.; Ge, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Satellite-Based PM2.5 Concentrations and Its Determinants in Xinjiang, Northwest of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashraf, A.; Butt, A.; Khalid, I.; Alam, R.U.; Ahmad, S.R. Smog analysis and its effect on reported ocular surface diseases: A case study of 2016 smog event of Lahore. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdrel, T.; Bind, M.A.; Béjot, Y.; Morel, O.; Argacha, J.F. Cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 110, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Simpson, I.J.; Blake, D.R.; Yu, X.M.; Kwok, Y.H.; Li, Y.S. Source contributions to ambient VOCs and CO at a rural site in eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4551–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Shiobara, Y.; Uchiyama, K.; Miura, K.; Okochi, H.; Kobayashi, H.; Hatakeyama, S. Atmospheric CO, O3, and SO2 measurements at the summit of Mt. Fuji during the summer of 2013. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2368–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, C.; Tao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, K. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in a semi-arid and petrochemical-industrialized city, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zheng, S.; Nie, Y.; Weng, J.; Cheng, N.; Hu, X.; Bai, Y. Association between short-term exposure to air pollution and dyslipidemias among type 2 diabetic patients in northwest China: A population-based study. Intl. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018, 15, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Xiao, Z.; He, L.; Shi, Z.; Cao, Y.; Tian, Z.; Liu, J. Chemical Composition and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Urban Areas of Xiangtan, Central South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Che, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hsu, S.C. PM2.5 pollution in a megacity of southwest China: Source apportionment and implication. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 8679–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, K.; Mukhtar, A.; Shahid, I.; Blaschke, T.; Majid, H.; Rahman, S.; Rahman, N. Source Apportionment and Characterization of Particulate Matter (PM10) in Urban Environment of Lahore. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Sarkar, C.; Adak, A.; Mukherjee, U.; Ghosh, S.K.; Raha, S. Ambient air quality during Diwali festival over Kolkata–a mega-city in India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mhawish, A.; Nichol, J.E.; Qiu, Z.; Nazeer, M.; Ali, M.A.; Ke, S. Air pollution scenario over Pakistan: Characterization and ranking of extremely polluted cities using long-term concentrations of aerosols and trace gases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, B.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Water-soluble ions in PM2.5 during spring haze and dust periods in Chengdu, China: Variations, nitrate formation and potential source areas. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1740–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Duan, F.; Ma, Y.; He, K.; Zhu, L.; Ma, T.; Kimoto, T. Case study of spring haze in Beijing: Characteristics, formation processes, secondary transition, and regional transportation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, F.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, C. Spatial and temporal variation of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants in 26 cities in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Contributions of local and regional sources of NOx to ozone concentrations in Southeast Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2877–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chameides, W.L.; Fehsenfeld, F.; Rodgers, M.O.; Cardelino, C.; Martinez, J.; Parrish, D.; Wang, T. Ozone precursor relationships in the ambient atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1992, 97, 6037–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cui, K.P.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, L.C.; Yan, P. Atmospheric PM2.5 and total PCDD/FsWHO2005-TEQ level: A case of Handan and Kaifeng cities, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, M.S.; Ghude, S.D.; Gurnale, D.; Prabhakaran, T.; Mahajan, A.S. Simultaneous Observations of Nitrogen Dioxide, Formaldehyde and Ozone in the Indo- Gangetic Plain. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, A.; Aneja, V.P.; Aiyyer, A.; Rafique, U. Measurements and analysis of air quality in Islamabad, Pakistan. Earth’s Future 2014, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Long, E.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Ma, L. Characterizing spatial distribution and temporal variation of PM10 and PM2.5 mass concentrations in an urban area of southwest China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.Z.; Ge, X.L.; Hu, J.L.; Nie, D.Y.; Tian, L.; Chen, M.D. Air pollution characteristics and health risks in Henan Province, China. Environ. Res. 2017, 156, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M. Air quality changes in Shanghai, China, and the surrounding urban agglomeration during the COVID-19 lockdown. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2020, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauri, B.; Lodhi, A.; Mansha, M. Development of baseline (air quality) data in Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. Influence of ozone precursors and particulate matter on the variation of surface ozone at an urban site of Delhi, India. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; Matsui, I.; Nishikawa, M. A method for estimating the fraction of mineral dust in particulate matter using PM2.5-to- PM10 ratios. Particuology 2016, 28, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).