Abstract
The differentially weighted operator-splitting Monte Carlo (DWOSMC) method is further developed to describe the droplet aerosol dynamic behaviors, including coagulation, deposition, condensation, and evaporation processes. It is first proposed that the droplet aerosols will experience firstly condensation and then evaporation, and this phenomenon is first implemented into the Monte Carlo method and sectional method with considering coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes in both single-component and two-component aerosol particle systems. It is found that the calculated results of the DWOSMC method agree well with both the analytical solutions and the sectional method. The further developed DWOSMC method can predict the variation of particle number density, total particle volume, mean particle diameter, particle size distributions, and the component-related particle volume densities in both single component and two-component droplet aerosol systems considering coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes.
1. Introduction
Respiratory infections caused by droplet aerosol transmission are major killers of humans. The outbreak of SARS, MERS, and the Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 illustrates that virus transmission and infection are very complex problems. Droplet aerosol is one of the crucial ways for most microorganisms (including viruses, bacteria and fungi) to spread in the air [1,2,3,4]. People usually release droplet aerosols by coughing or breathing, and then the droplet aerosols spread through the air until they are inhaled into the body or deposited on surfaces [5,6]. In the transmission process, droplet aerosols will experience a series of dynamical behaviors, such as coagulation, deposition, condensation, and evaporation processes, which significantly affect the particle size distributions and the transportation mechanism of aerosols [7,8,9,10].
Another characteristic of droplet aerosols is that they cannot be regarded as single-component particles. Wells’ study showed that droplet aerosols evaporate and contract during propagation, and eventually evolve into a condensation core [11]. Besides water, which can evaporate, the droplet aerosols also contain compositions that do not evaporate such as proteins and ions, which could be regarded as a solid condensation nucleus. Therefore, the droplet aerosols can be considered as solid–liquid two-phase multicomponent aerosol particles [12,13]. Furthermore, as the relative humidity of human exhaled gas is close to 100% with relatively high temperature, water is likely to condense on the droplet aerosols when they are just exhaled, and afterward evaporate. The deposition mechanism of droplet aerosols on different surfaces is also different [14]. Thus, the evolutionary process of the droplet aerosols is complicated and the study of the propagation and spread process, deposition behavior, evolution of particle size distributions, and the dynamical evolutions of the droplet aerosols is significant.
Since the toxicity, sedimentation rate, capture strategy, and hazard to human beings of aerosol particles are all related to the size distribution, the aerosol particle size distribution is determined by dynamical events, and it is very difficult to find the analytical solutions of equations for describing particle dynamics considering such complicated behaviors, the establishment of efficient and accurate numerical algorithms to solve aerosol dynamic equations has become the focus of researchers. At present, the most popular numerical methods include the method of moment (MOM) [15,16], sectional method (SM) [7,17], and Monte Carlo (MC) method [18,19]. Compared with the MC method, the MOM method and sectional method both have their own advantages and disadvantages.
The SM tends to be more accurate; however, the sectional representations may lead to complicated algorithms. MOM is relatively computational time-saving and simple. Nevertheless, the initial form of the particle size distribution should be assumed to obtain the closure of the moment equations, and it is difficult to give particle size distributions. Moreover, it becomes complicated and difficult when solving multi-component particle systems using the MOM and SM [20,21,22]. While the MC method is relatively straightforward for solving the complex multidimensional and multicomponent particle systems, it is also easy to find the internal information and the historical trajectory of the aerosols [23,24].
The disadvantage of the MC method is that it is difficult to balance computational accuracy and computational cost. To solve this problem, researchers put forward the concept of “weighted fictitious particles”, meaning that each fictitious particle can represent a certain number of real particles of the same physical properties, which dramatically reduces the computational consumption of the MC methods [25,26]. In order to reduce use of computing memory and simulation time of the MC algorithm, Zhao et al. [27,28,29] put forward a differentially weighted Monte Carlo (DWMC) method to solve the particle balance equation. Based on this DWMC method, Liu et al. further developed a differentially weighted operator-splitting Monte Carlo (DWOSMC) method which tends to be more efficient and precise in predicting the variation of aerosol particles [24,30,31].
Herein, the DWOSMC method is further updated to describe the droplet aerosol dynamical behaviors including coagulation, deposition, condensation, and evaporation processes. It is first proposed that the droplet aerosols will experience condensation first and then evaporation, and this phenomenon is first implemented into the Monte Carlo method and sectional method while considering coagulation and deposition processes in both single-component and two-component aerosol systems. This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 briefly introduces the droplet aerosol dynamics and the DWOSMC method. Section 3 presents the simulation and validation results of the DWOSMC method in predicting the evolution of aerosol particles considering different dynamical processes. Section 4 presents the conclusions of the present study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Droplet Aerosol Dynamics
Respiratory droplet aerosols are the primary carriers of respiratory infectious pathogens and the aerosols will experience coagulation, condensation or evaporation, and deposition behaviors in the process of spreading. Figure 1 shows the mechanism of droplet aerosol diffusion, coagulation condensation/evaporation, and deposition processes. Considering the large difference between the relative humidity of human exhaled gas and the atmosphere, the droplet aerosols will first experience condensation, then evaporation.
Figure 1.
Droplet aerosol diffusion and coagulation–condensation/evaporation–deposition mechanism.
The evolution of the particle number density considering coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes is expressed by the following equation [32],
where n(υ,t) is the particle number density of size υ at time t, is the coagulation rate between particles with size υ and particles with size , R(υ) is the deposition rate of particles with volume υ, and I(υ) is the condensation/evaporation rate of particles with volume υ.
If a two-component aerosol system is considered, Equation (1) becomes the following,
where υX and υY are the size of X-component and Y-component within particle i whose total size is υX + υY, respectively; IX and IY are the condensation/evaporation rate coefficients correspondingly.
2.2. Implementation of the DWOSMC Algorithm
In this study, the DWOSMC method is further developed to describe droplet aerosol dynamics, including coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes in both single-component and two-component systems. In this further developed DWOSMC algorithm, the effect of relative humidity of gas on the phase transformation behavior is considered. Condensation is considered in the first half of the simulation time, and then evaporation is considered in the remaining simulation time.
The implementation of the DWOSMC algorithm is described as follows.
- (1)
- Start with a predetermined total MC loop number, M.
- (2)
- Predetermine the simulation stopping time, Tstop.
- (3)
- Initialize the particle system. The weight, component, and size distribution of the droplet aerosols are initialized first. The weight of numerical particle i, wi is defined aswhere Nr(υX, υY) is the real particle number of particles with volume (υX, υY) and Nn(υX, υY) is the numerical particle number that representing the corresponding real particles.
- (4)
- Determine a time step τ for the simulation.
The timescales for coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes are determined as follows, respectively.
The characteristic time step of the coagulation behavior is described as Equation (4) [29,33],
where Ns and Vs are the numerical particle number and the volume of simulation system, respectively. is the normalized coagulation rate of simulated particles i and j, which is described as Equation (5).
The characteristic time step of the deposition behavior is expressed as Equation (6):
where Ri is the deposition kernel.
For condensation/evaporation processes, the characteristic time step is shown as
The selected time step should ensure both the accuracy and efficiency for simulating all the dynamical processes mentioned above. Thus, the following equation is used to determine the time step.
The empirical parameter, α is usually set as smaller than 0.01 to ensure that the several aerosol dynamical processes are uncoupled within a time step [25,31,34].
- (5)
- Algorithm integration. In this DWOSMC method, the coagulation event is simulated by the stochastic Monte Carlo method; and the deposition and condensation/evaporation events are calculated by the deterministic method. Then, the simulation results are integrated by the operator splitting method expressed by Equation (9) [35], which means that in one time step, the deposition and condensation/evaporation events will be firstly calculated within the first half time step. Then, the coagulation event will be calculated, at last, the deposition and the condensation/evaporation events will be calculated within the second half time step.where ψ represents the total particle dynamical processes, ψd represents the deposition event, ψc represents the condensation/evaporation event, and ψs represents the coagulation event.
Herein, the treatment of coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes in two-component systems is described as follows.
- (a)
- Coagulation
The probability of coagulation process occurring on particle i is the following [25,27]:
where Ci is the coagulation rate of simulated particle i which is written as:
Particle i is selected as the first coagulation partner when Pi meets the following inequality,
The second coagulation partner j is chosen when Equation (13) is satisfied, then the coagulation process is treated between particles i and j; otherwise, the remaining particles will be checked until Equation (13) is satisfied.
where r1 and r2 are both random numbers that satisfy a uniform distribution between 0 and 1.
When the coagulation pair particles i and j are selected, coagulation event would be treated and calculated as Equation (14) [36].
where , , , and represent the weight or volume of newly updated simulation particles i and j after the coagulation process. , , and are the volumes of components X and Y in the updated simulation particles i and j after the coagulation process.
- (b)
- Deposition
The probability of deposition on particle i is calculated by Equation (15) [37].
where τ is the simulation time step, Ri (υX, υY) is the deposition kernel of particles with the volume of (υX, υY).
The following equation will be used to update the weight of the particles after deposition.
- (c)
- Condensation and evaporation
In two-component aerosol systems, the condensation/evaporation kernels for the two components X and Y are different. In the DWOSMC method, the total volume of particle i is summation of the two components after the condensation/evaporation process, which is described as Equation (17).
After the condensation/evaporation event, the total volume of particle i, the volume of component X, and component Y in particle i, the particle weights are calculated as the following equations, respectively.
In the present study, the effect of relative humidity of gas to the phase transformation behavior is considered. Condensation is considered in the first half of the simulation time, Tstop/2, then evaporation is considered in the remaining simulation time, where the particle surface growth rate will be minus Ii(υ).
- (6)
- The properties of the numerical particles (component composition, size distribution, weight, etc.) are updated.
- (7)
- If the present simulation time, T, reaches Tstop, stop the present MC loop. Otherwise, repeat step (4) to step (6).
- (8)
- If the current MC loop number N equals M, the mean value of the particle parameters should be calculated and output. Otherwise, start a new MC loop.
In the present study, the simulation results of the DWOSMC method are compared with the sectional method (SM) [38] in some complicated cases and two-component aerosol systems. Herein, the SM is further developed to describe aerosol coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation behaviors in two-component aerosol systems.
3. Results
The DWOSMC method is validated in both single component and two-component aerosol systems. In single component aerosol systems, the particles can be regarded as water droplets that condense or evaporate; in two-component aerosol systems, besides water, the droplet aerosols also contain compositions that do not evaporate, which could be regarded as a solid condensation nucleus. In the first two cases, the DWOSMC method is verified by analytical solutions [39,40] considering coagulation and condensation/evaporation behaviors for single-component aerosols. Next, the DWOSMC method is verified by the more developed sectional method considering coagulation, condensation/evaporation, and deposition behaviors for both single-component and two-component aerosols.
3.1. Coagulation and Condensation/Evaporation Processes in Single Component Aerosol Systems
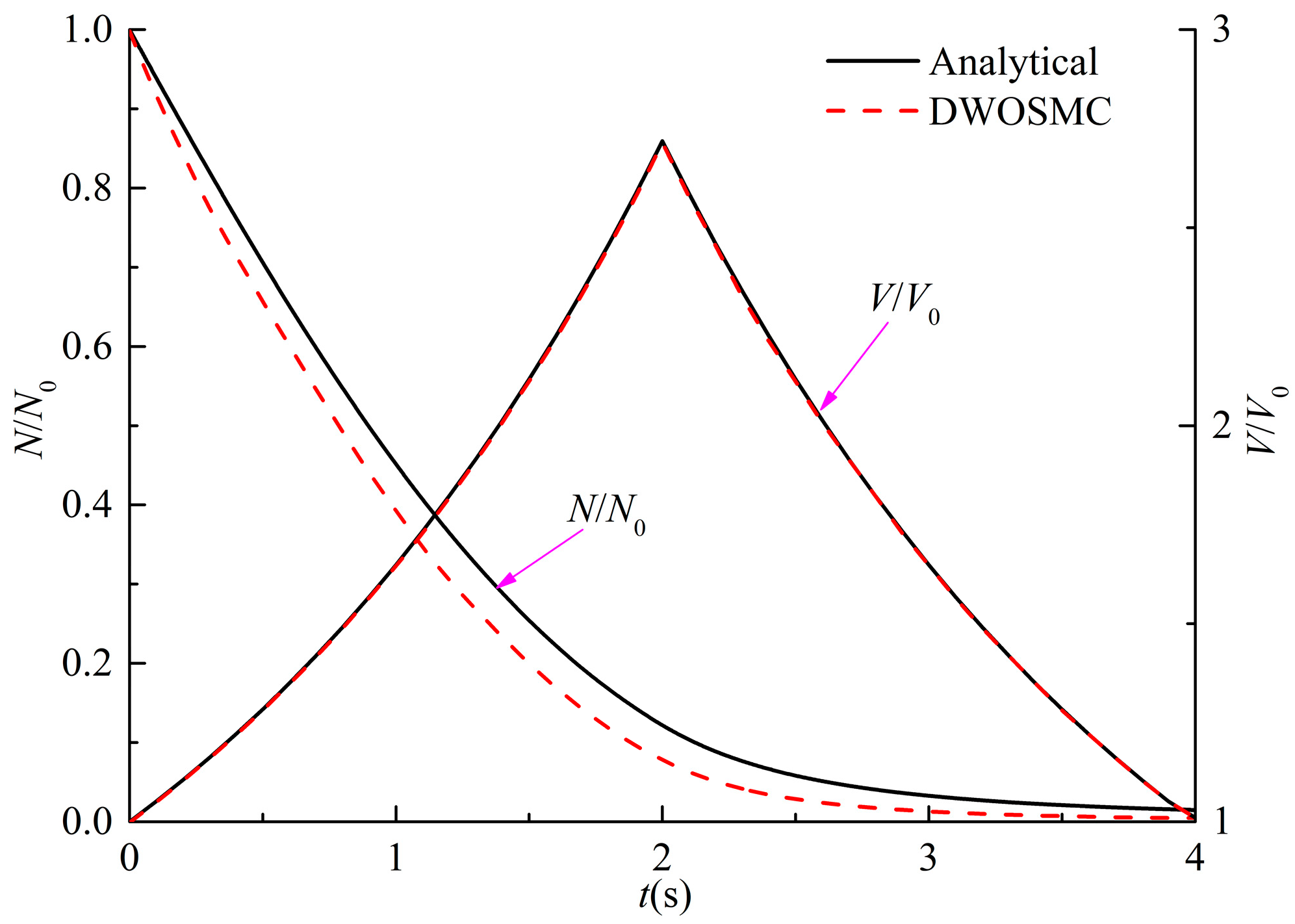
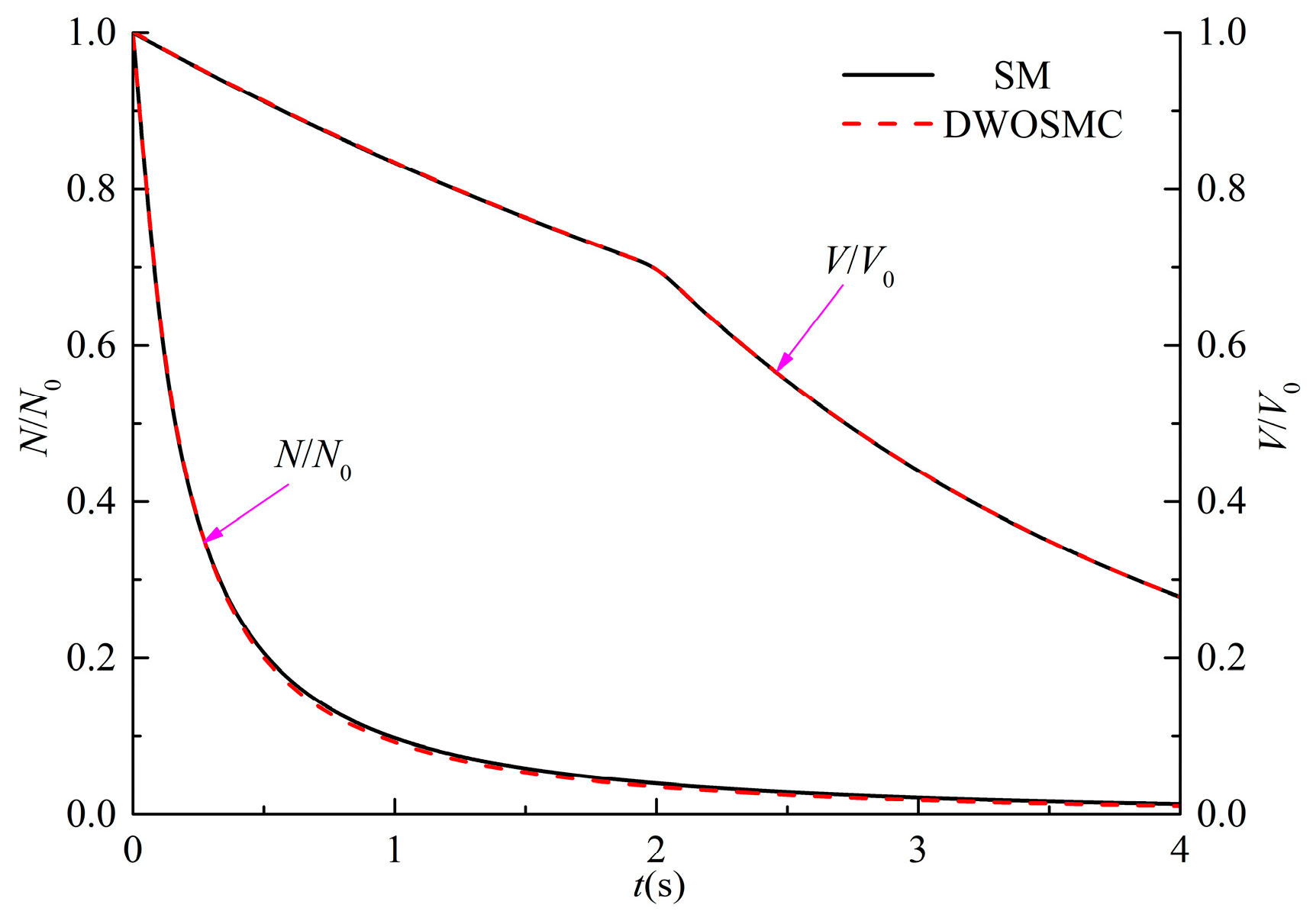
In Cases I and II, the initial particles have a uniform diameter of 1.5μm and the DWOSMC method is validated by analytical solutions [39,40]. In Case I, constant rate coagulation kernel (β = β0) and linear rate condensation/evaporation kernel (I = I1υ) are considered; in Case II, linear rate coagulation kernel (β = β1 (υ1 + υ2)) and linear rate condensation/evaporation kernel (I = I1υ) are considered; and the analytical solutions for Cases I and II are shown as Equations (22,23) and (24,25), respectively. In Cases I and II, the simulation time is 4s. It is assumed that condensation and coagulation occurred in the first half of the simulation, and evaporation and coagulation occurred in the second half of the simulation.
where N and V are the particle number density and total particle volume, respectively; N0 and V0 are the initial particle number density and total particle volume, respectively.
The evolution of the normalized particle number density and total particle volume for Cases I and II are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
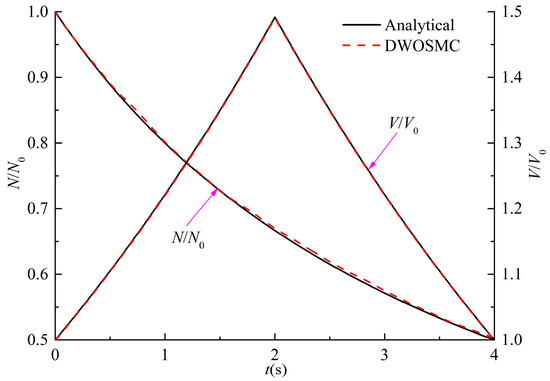
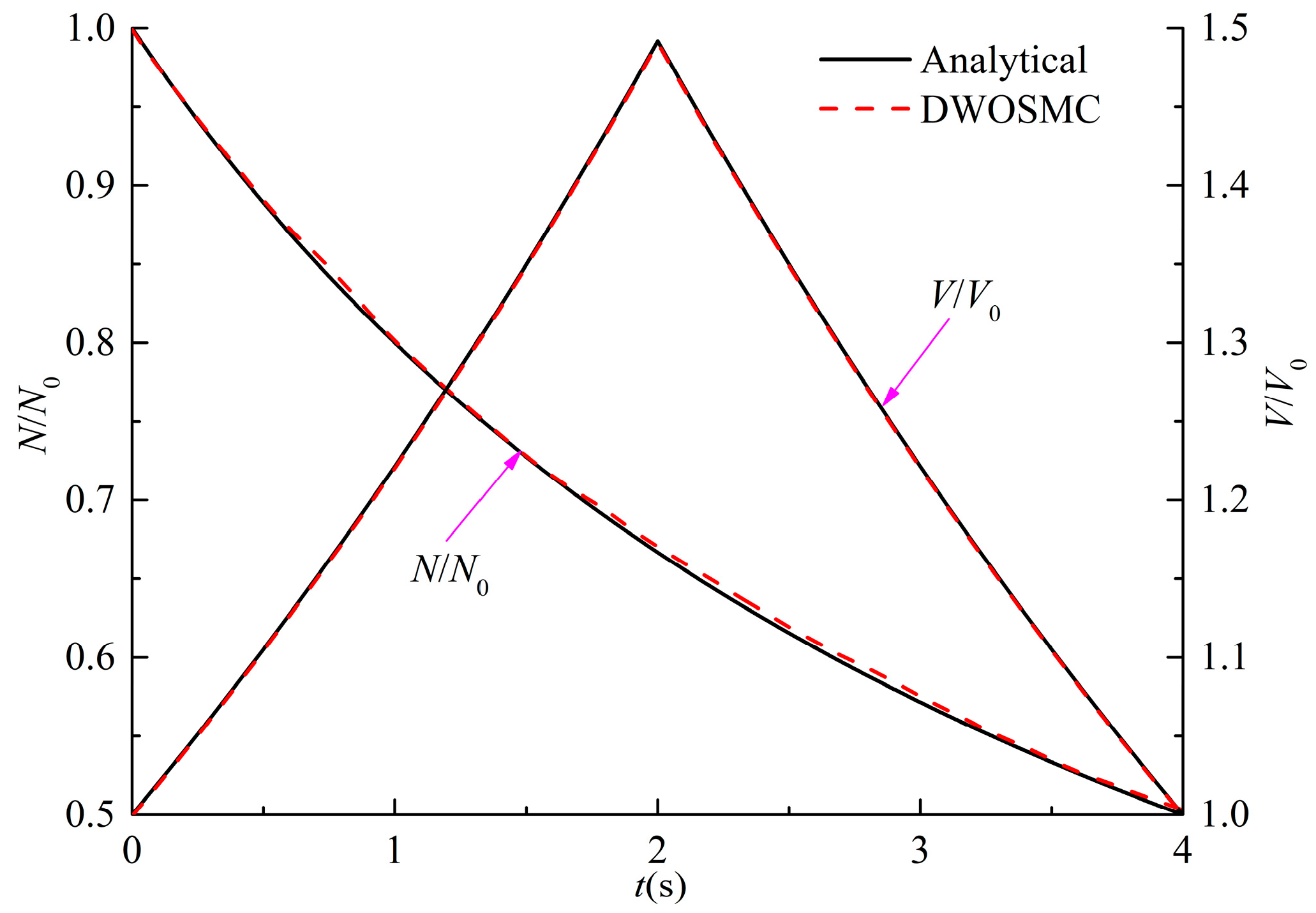
Figure 2.
Evolution of N/N0 and V/V0 for Case I.
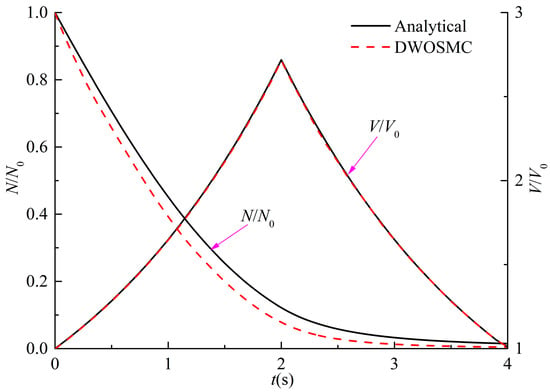
Figure 3.
Evolution of N/N0 and V/V0 for Case II.
It can be seen that in Cases I and II, the particle number density decreases and the total particle volume initially increases, and then decreases over time. This is because condensation occurs in the first half and evaporation occurs in the second half, and the coagulation process does not have influence on the total particle volume. In Case I, the total particle volume varies linearly over time because of the condensation kernel and the constant coagulation kernel. In case II, the total particle volume has the same variation tendency as Case I, but does not show a linear relationship over time. This is because both the coagulation kernel and the condensation/evaporation kernel are related to the particle volume, which will affect the particle size distribution and the condensation/evaporation behaviors. From Figure 2 and Figure 3, the calculated results of the DWOSMC method are consistent with the analytical solutions.
In Case III, the particles initially have an exponential size distribution which satisfies Equation (26). The coagulation kernel in the free molecular regime is used which is expressed as Equation (27). The condensation/evaporation kernel used is I = I1υ. The simulation time is 4 s.
where N0 = 1 × 1014/m3 and υg0 = 2.7 × 10−18 m3 are the initial particle number density and initial geometric mean particle volume, respectively.
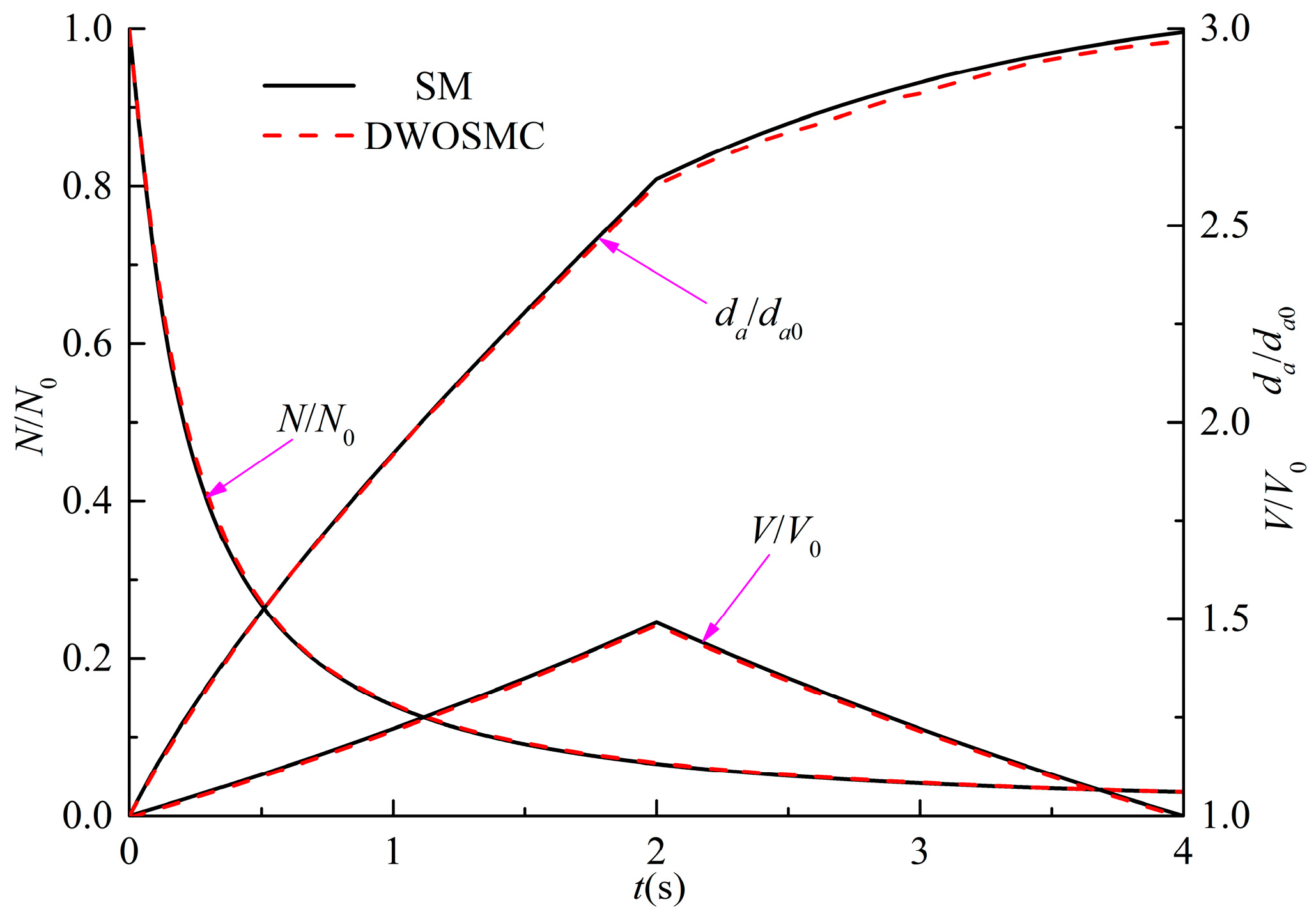
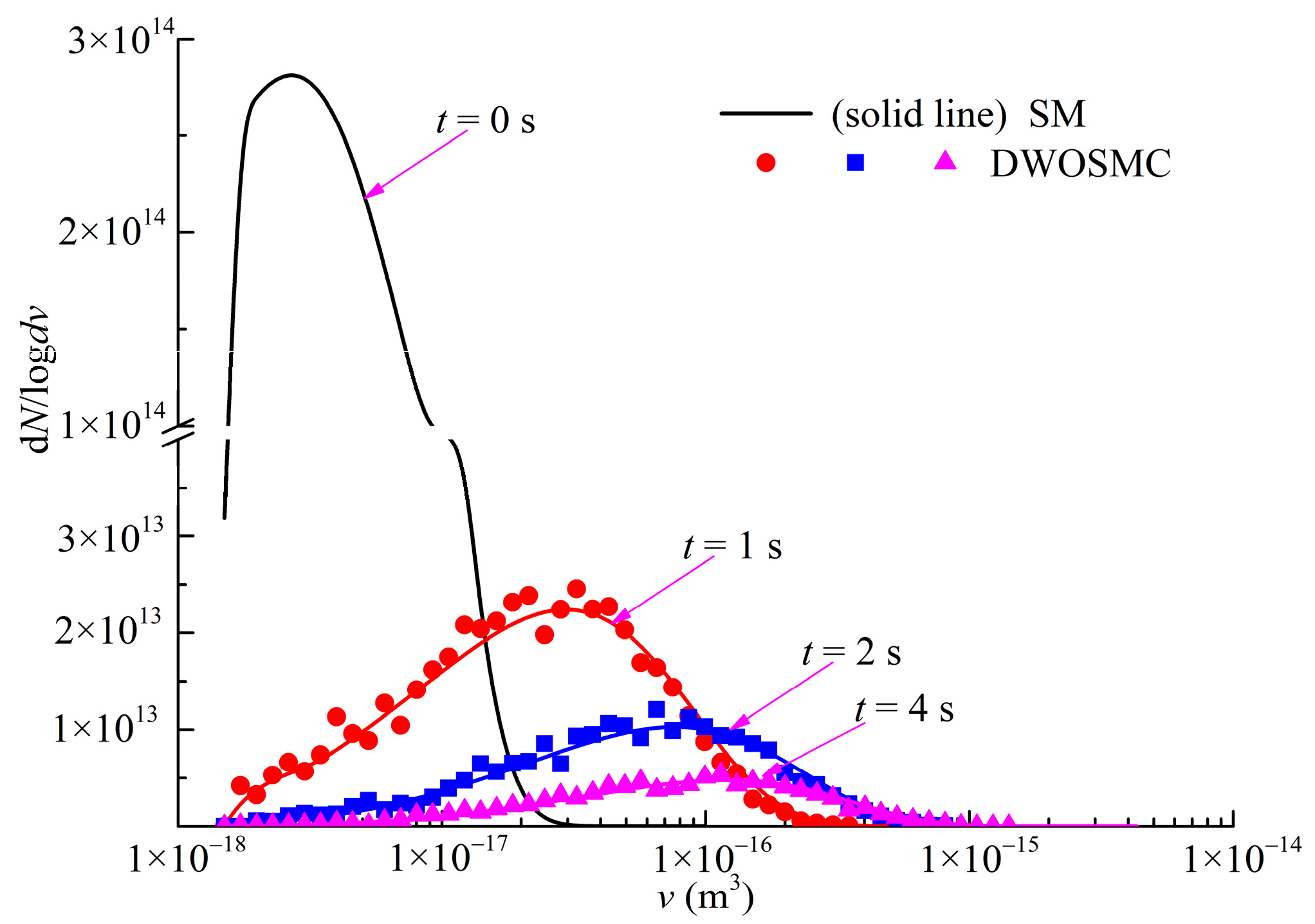
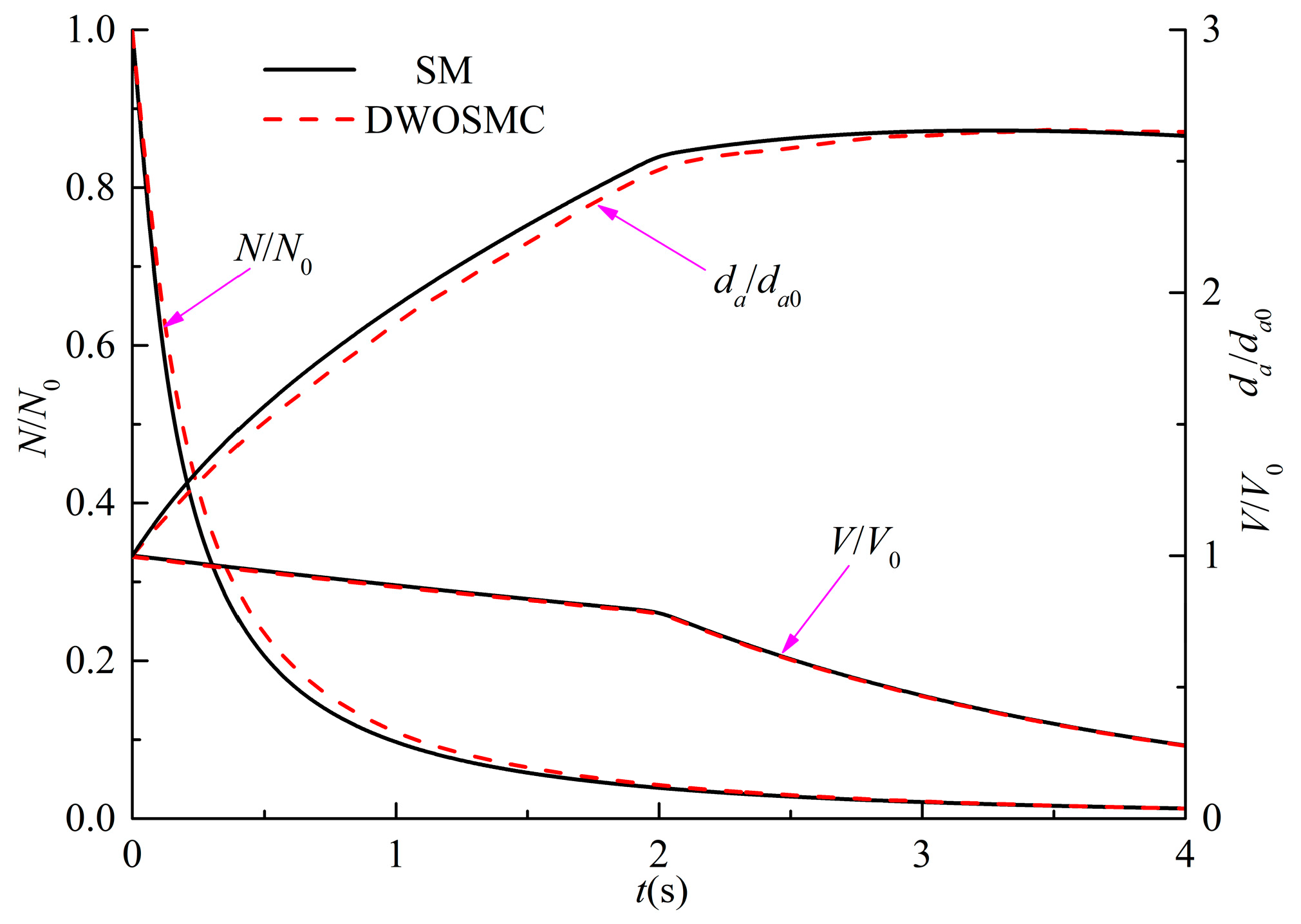
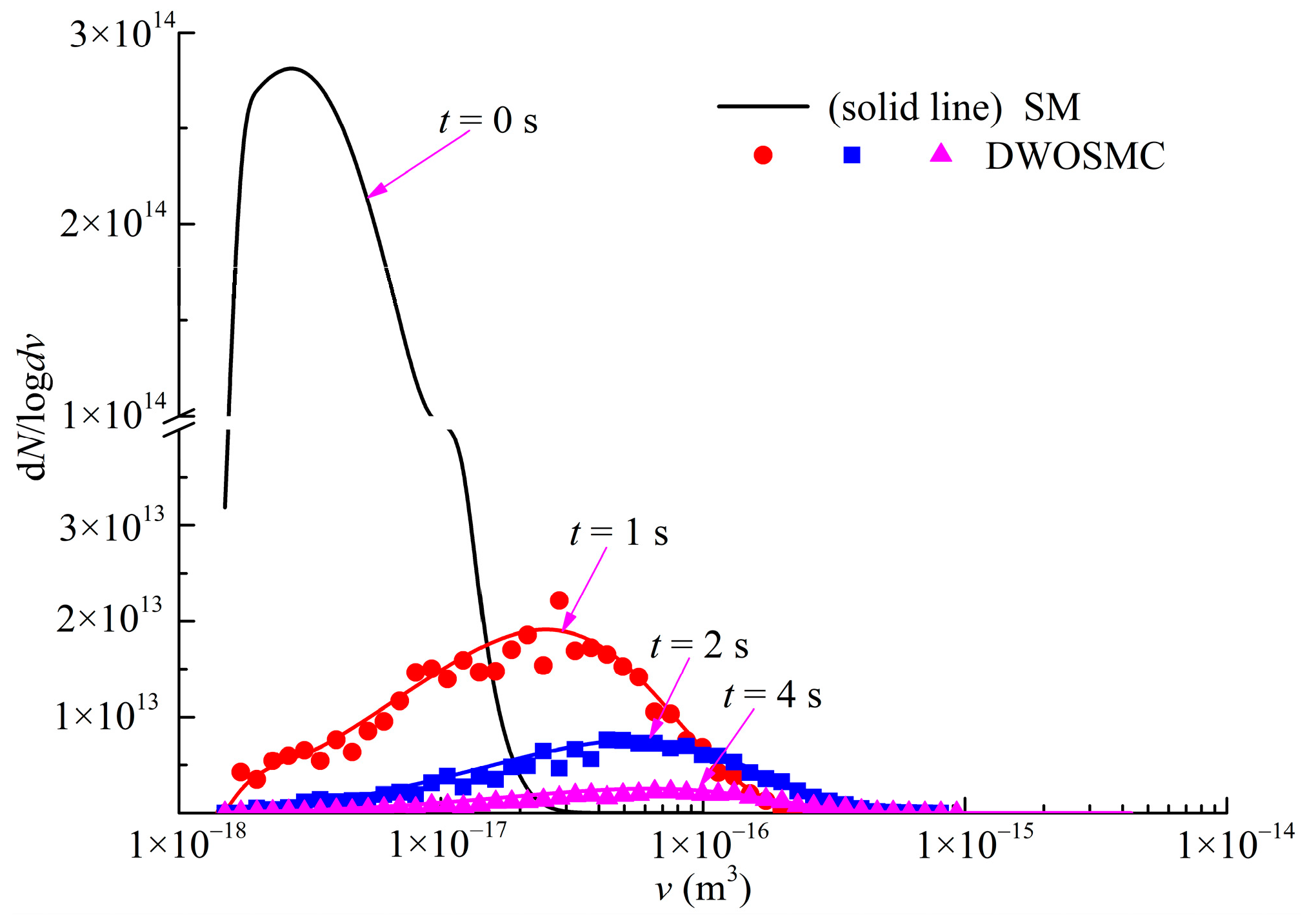
For Case III, the further developed DWOSMC method is validated by the sectional method, and the evolution of the normalized particle number density, total particle volume, and the average particle diameter for Cases III are shown in Figure 4; the evolution of particle size distribution is shown in Figure 5.
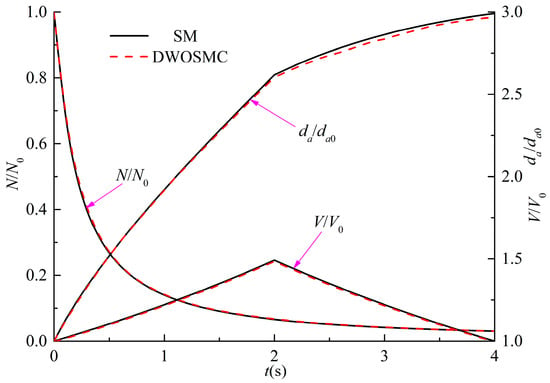
Figure 4.
Variation of N/N0, V/V0 and da/da0 for Case III.
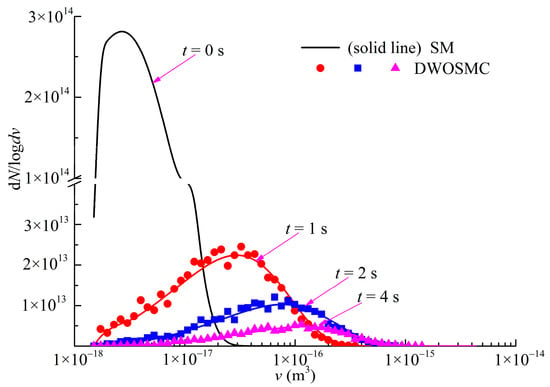
Figure 5.
Evolution of PSDs for Case III.
In Case III, the variations of particle number density and total particle volume are similar with Cases I and II. The particle number density decreases and the total particle volume initially increases, then decreases over time. From Figure 4, it can be seen that the particle average diameter increases over time over the whole simulation. It can be concluded that, in the second half of the simulation time, the coagulation process dominated the entire process because the particle diameter would increase due to the coagulation effect, while the particle diameter would decrease due to the evaporation effect. From Figure 5, it can be seen that the curve of the particle size distribution (PSD) becomes lower and wider over time, and the peak volume of the PSD becomes larger distinctly at the first half simulation time. During the second half of the simulation, the peak volume becomes larger very slightly because the evaporation process makes the particle diameter smaller. From Figure 4 and Figure 5, the simulation results of the DWOSMC method are consistent with the sectional method.
3.2. Coagulation, Deposition, and Condensation/Evaporation Processes in Single Component Aerosol Systems
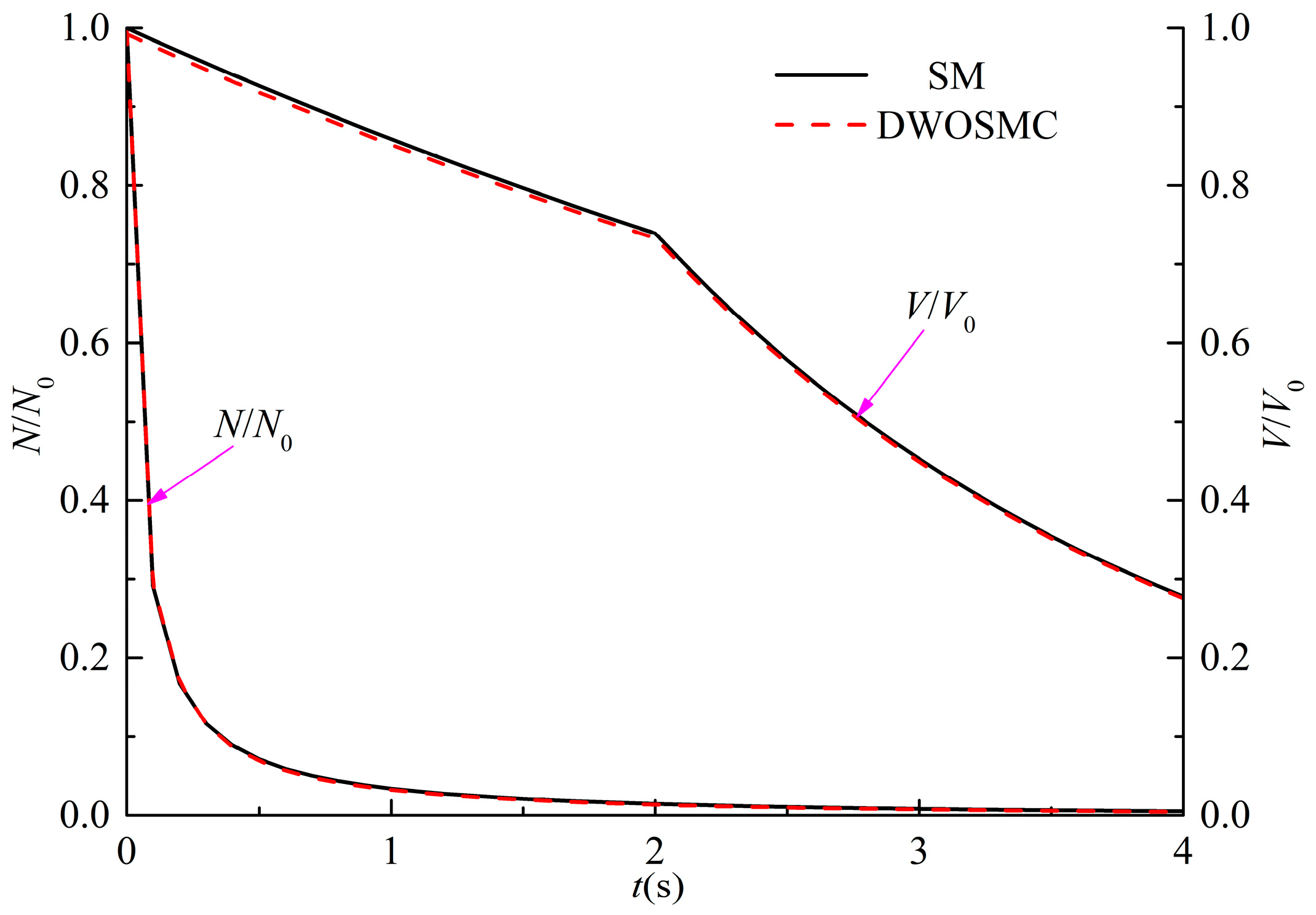
In Case IV, particle dynamical behaviors including coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes are considered. The coagulation kernel in the free molecular regime is used which is expressed as Equation (25). The condensation/evaporation kernel used is I = I1υ. The constant rate deposition kernel is used as R = 0.32/s. The initial particle size distribution is the same with Case III, and the simulation time is also 4 s. The variation of the normalized particle number density, total particle volume, and the mean particle diameter for Cases IV are shown in Figure 6; the evolution of particle size distribution is shown in Figure 7. The simulation results are compared with the sectional method.
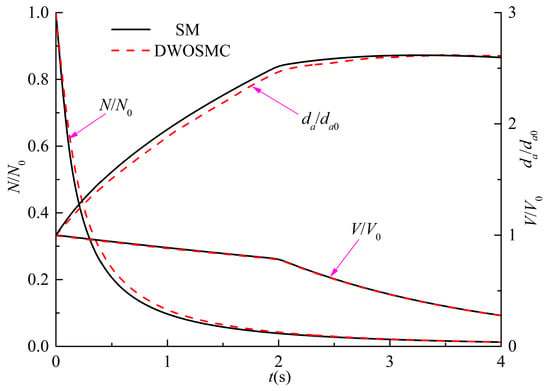
Figure 6.
Variation of N/N0, V/V0 and d/d0 for Case IV.
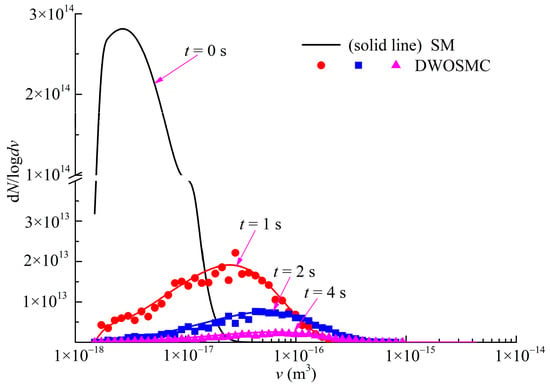
Figure 7.
Evolution of PSDs for Case IV.
Compared with Case III, the particle number density decreases faster, the total particle volume does not increase in the first half simulation time, and the mean particle diameter increases slower in Case IV. Since the deposition process will contribute to the decrease in both the particle number and total particle volume. It demonstrates that in the first half of the simulation time, the deposition effect exceeded the condensation effect because the total particle volume decreases over time. The deposition process also weakened the coagulation process, as the average particle diameter shows a slower growth rate. From Figure 7, the PSD curves are narrower and lower than those in Case III and the peak volume of the PSD curve is smaller, which is consistent with the conclusions from Figure 6. From Figure 6 and Figure 7, the calculated results of the DWOSMC method are consistent with the sectional method.
3.3. Coagulation, Deposition and Condensation/Evaporation Processes in Two-Component Aerosol Systems
Besides water, it is found that the droplet aerosols released by people also contain compositions that do not evaporate, which could be regarded as a solid condensation nucleus [12,13]. Therefore, in Cases V and VI, particle dynamical behaviors including coagulation, deposition, and condensation/evaporation processes in two-component aerosol systems are examined. For a two-component particle system, qm,n is used to express the component-related volume density. The particles are divided into several sections according to their size. The component-related volume density of particles with volume, vl,k < vk < vu,k in the k-th section is
where v = vX + vY. Specifically, and are the particle volume densities, where “0” represents component X and “1” represents component Y in the k-th section.
In Case V, the initial PSD is set as the same with Case IV; the initial particle number density is N0 = 1 × 1015/m3. The initial particles consist of two components X and Y, and the volumes of components X and Y are vX0 = v0/3 and vY0 = 2v0/3, respectively. The constant rate coagulation kernel (β = β0 = 1 × 10−14 m3/s) and linear rate condensation/evaporation kernel (I = I1v) are considered, where IX = 0.1/s and IY = 0.2/s are the condensation/evaporation kernels for component X and component Y, respectively. The constant rate deposition kernel is used as R = 0.32/s. The simulation time is 4s; condensation is considered in the first 2 s, and evaporation is considered in the last 2 s.
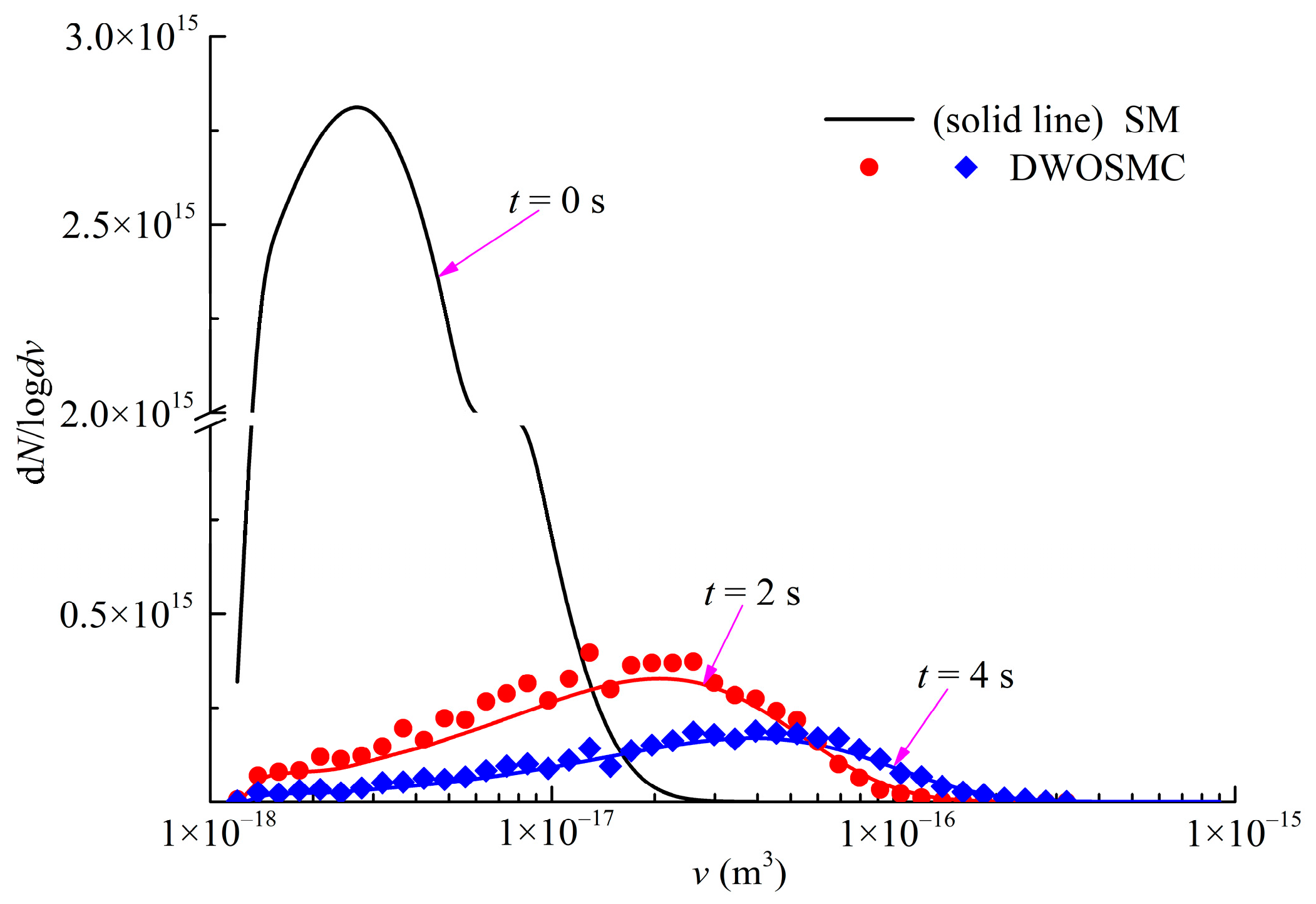
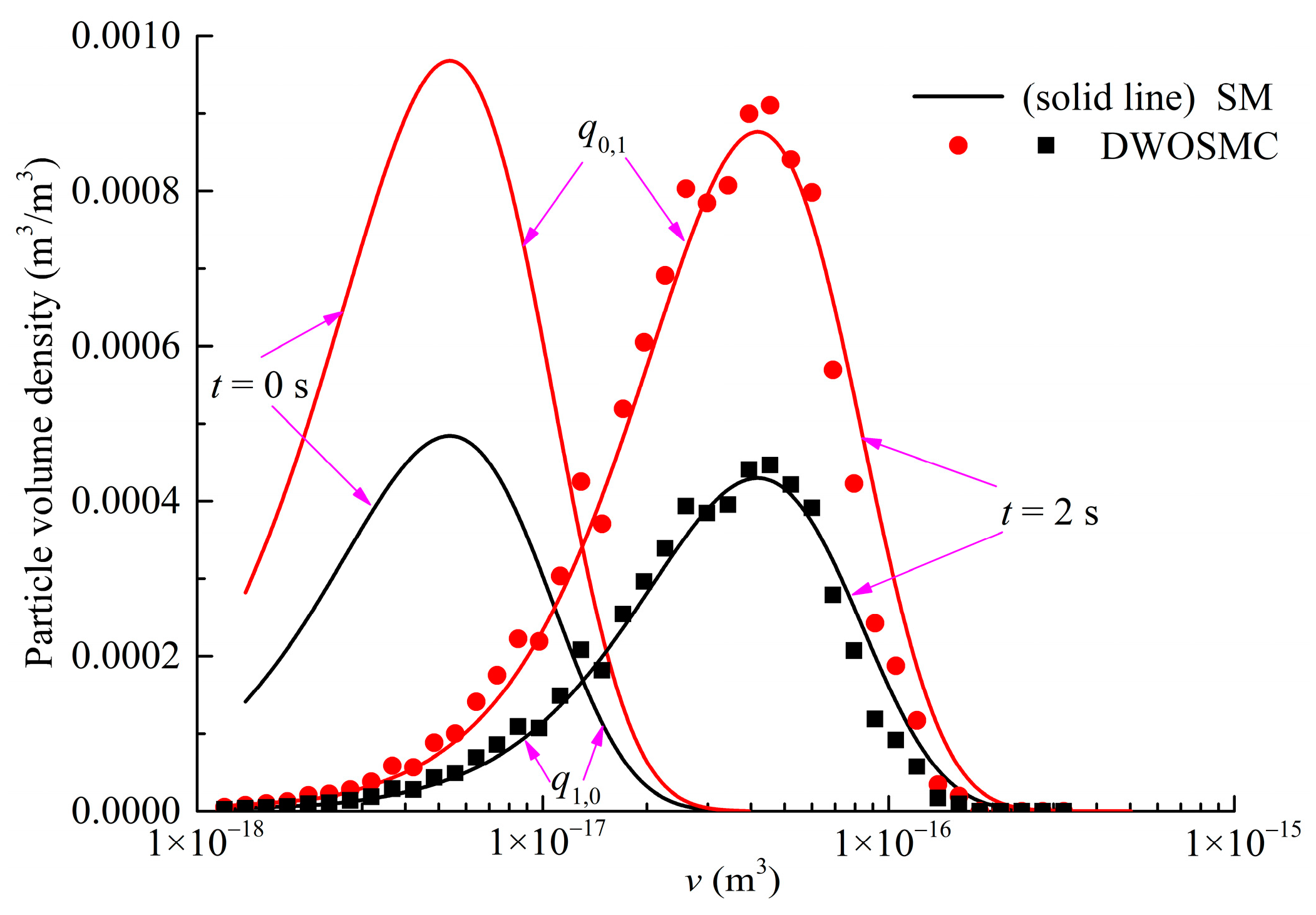
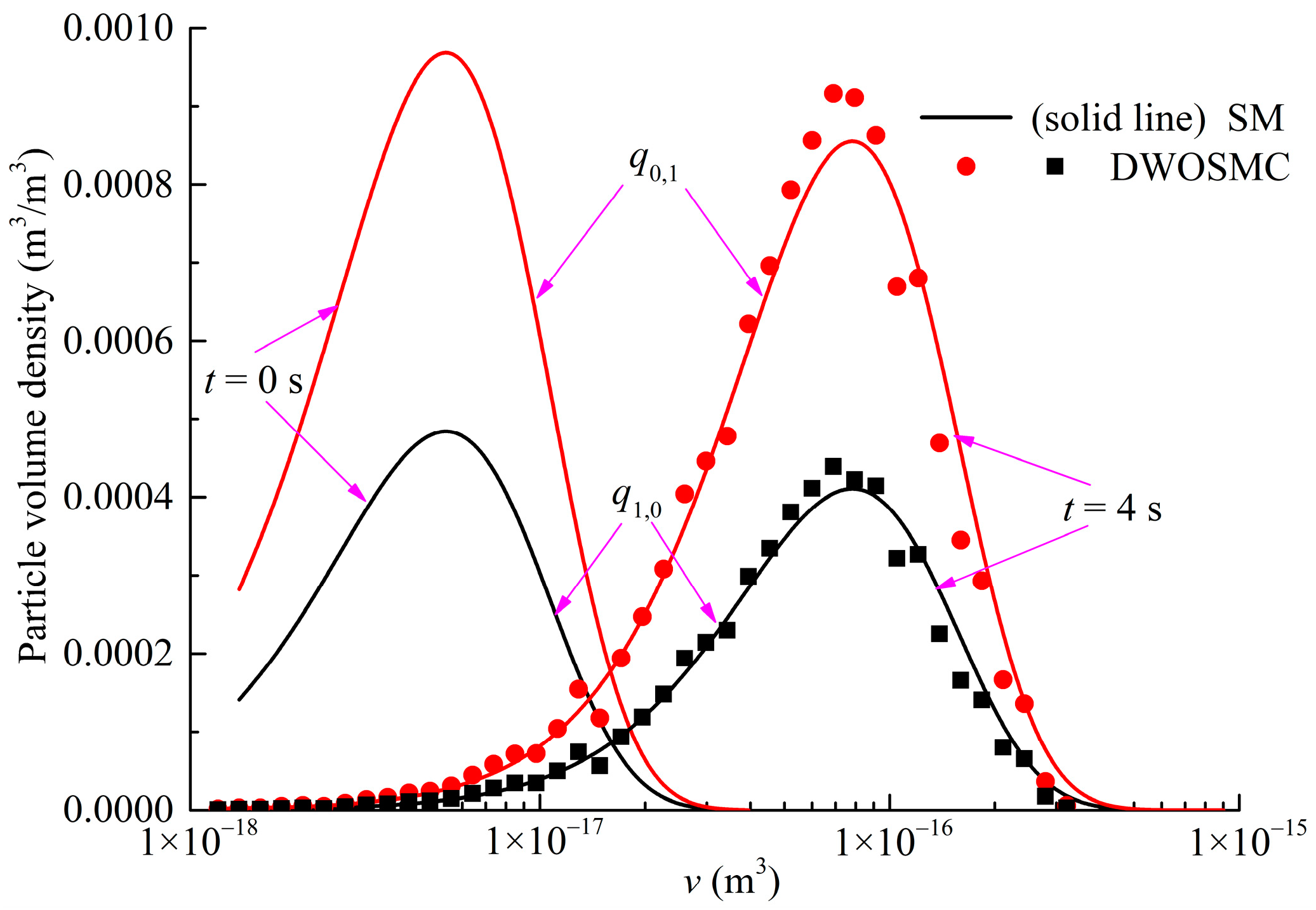
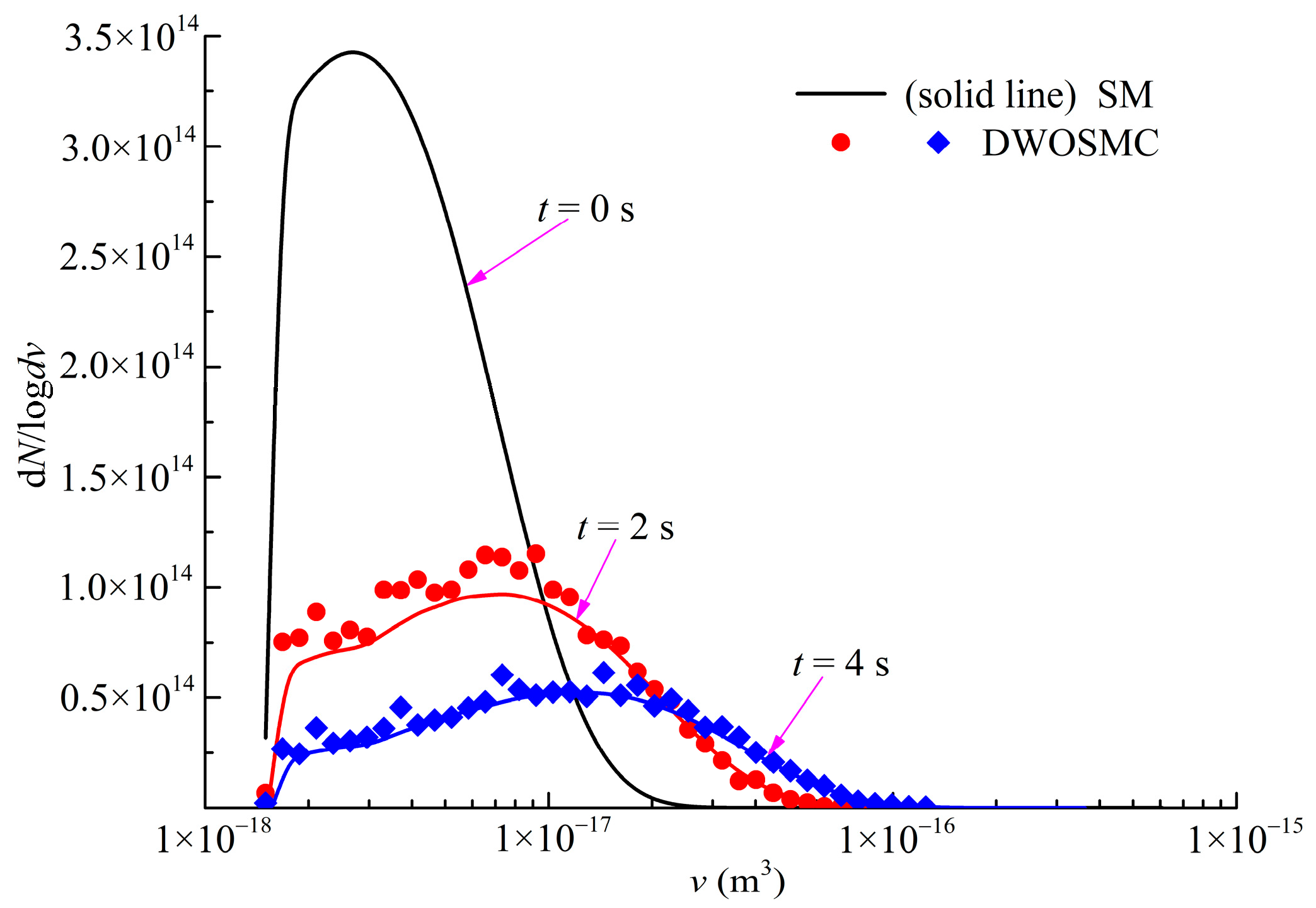
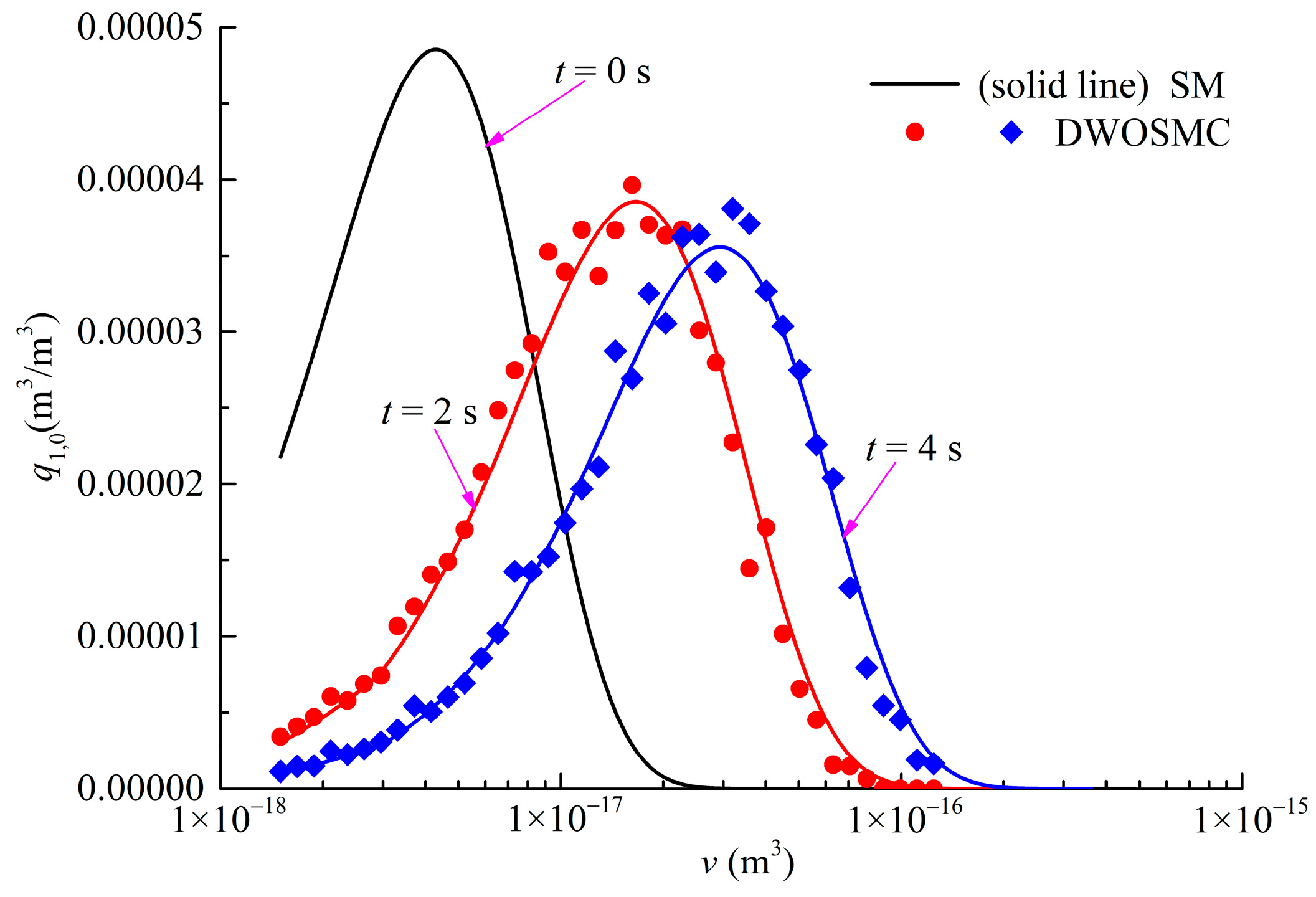
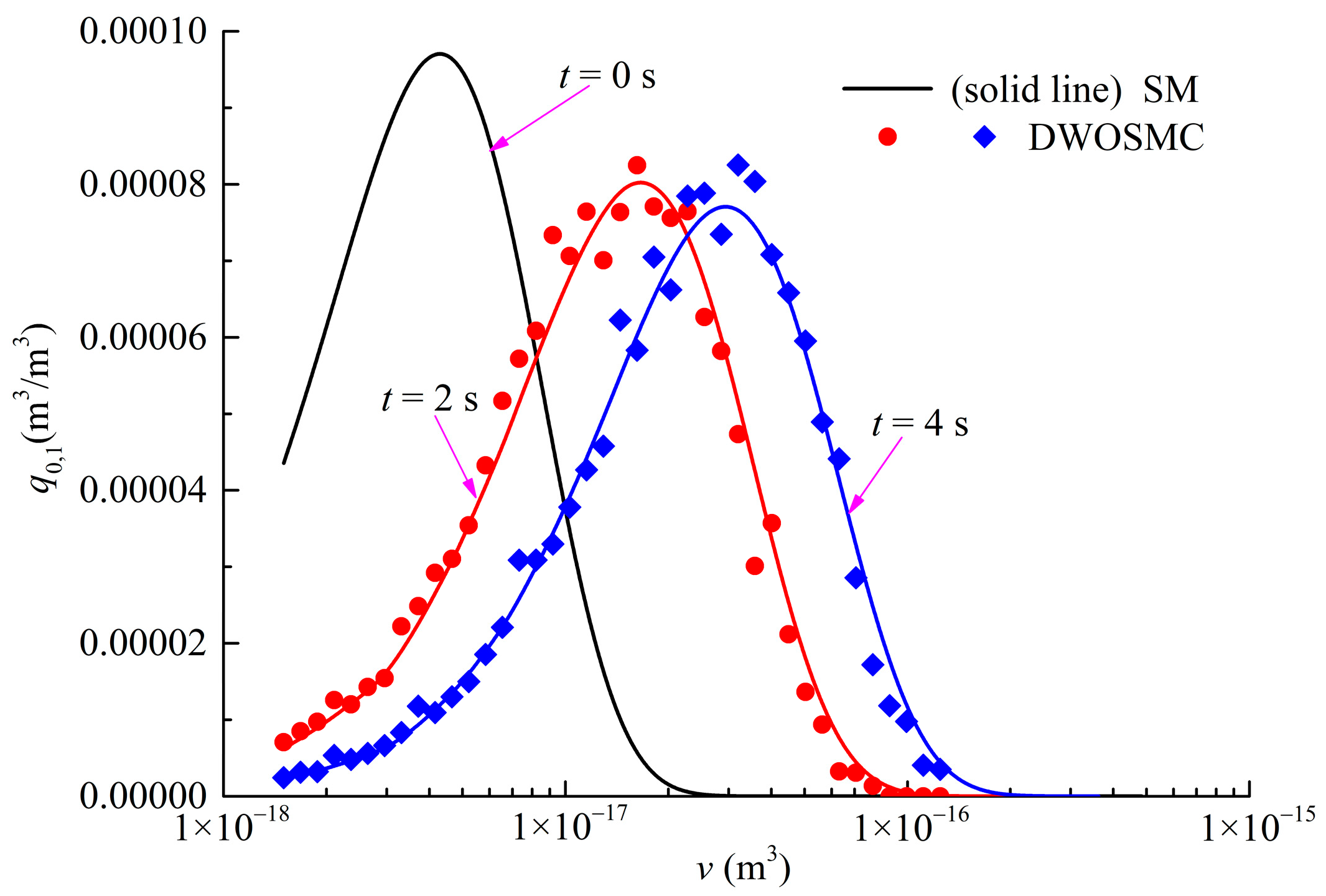
The evolution of the normalized particle number density and total particle volume for Case V is shown in Figure 8, the evolution of PSDs (t = 0 s, 2 s, 4 s) is shown in Figure 9. The component-related particle volume density distributions (PVDD) of q1,0, and q0,1 obtained at t = 2 s and t = 4 s are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively.
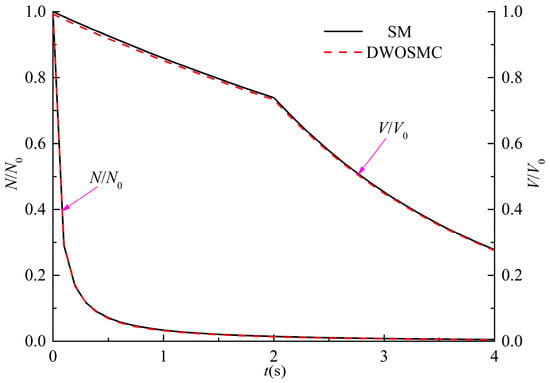
Figure 8.
Evolution of N/N0 and V/V0 for Case V.
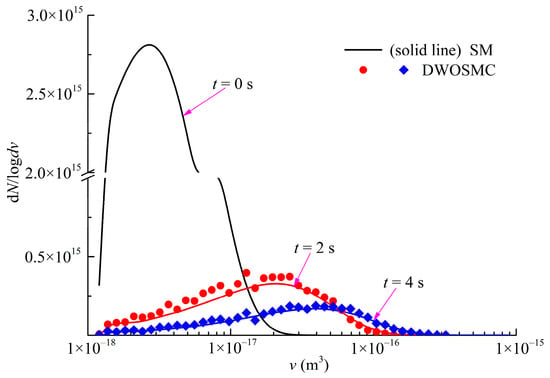
Figure 9.
Evolution of PSDs for Case V.
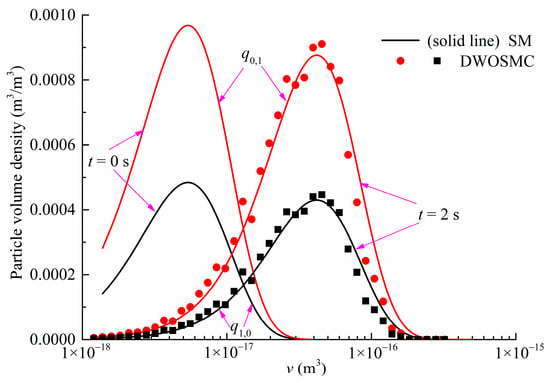
Figure 10.
Evolution of PVDDs at t = 2 s for Case V.
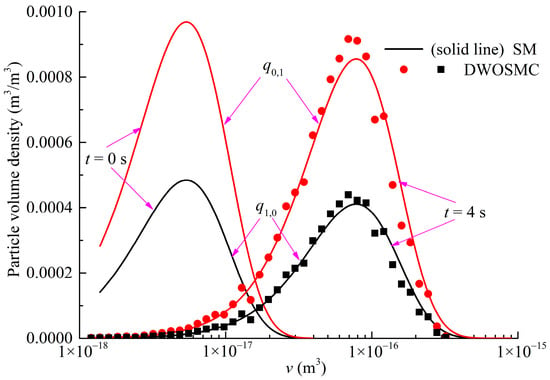
Figure 11.
Evolution of PVDDs at t = 4 s for Case V.
It can be seen that the curves of particle volume density for components X and Y both become wider and lower, and the peak volume becomes larger distinctly in the first 2 s of simulation time. In the second half of the simulation, the curves evolve relatively slowly because the evaporation process makes the particle volume smaller and also weakens the coagulation effects. From Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11, it can be concluded that the calculated results of the DWOSMC method are consistent with the sectional method.
In Case VI, two component droplet aerosols are examined, where component X is considered as a condensation nucleus, which means that no condensation/evaporation would occur, and component Y is considered as water on which condensation/evaporation phenomena usually occur. The initial volumes of components X and Y are vX0 = v0/3 and vY0 = 2v0/3, respectively. The coagulation kernel in the free molecular regime is used, which is expressed as Equation (25). The condensation/evaporation kernel used for component Y is I = I1v. The constant rate deposition kernel is used as R = 0.32/s. The initial particle size distribution is the same with Case IV, and the simulation time is also 4s. The simulation results for Case VI are shown in Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15.
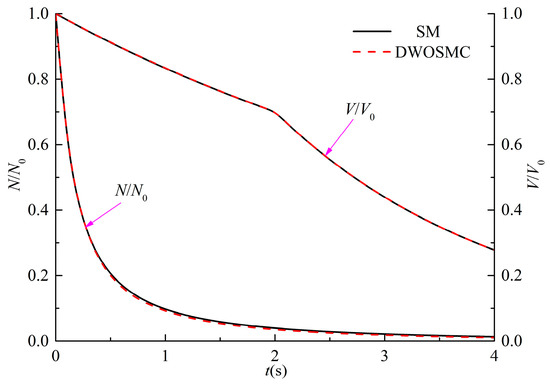
Figure 12.
Evolution of N/N0 and V/V0 for Case VI.
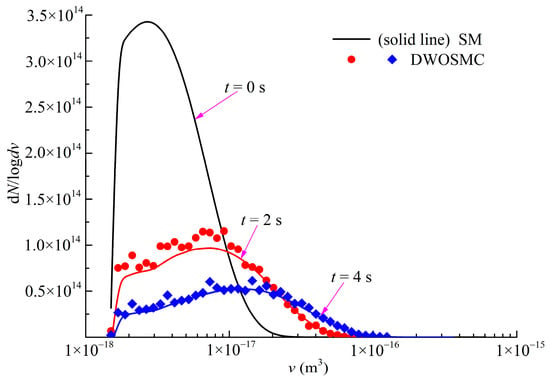
Figure 13.
Evolution of PSDs for Case VI.
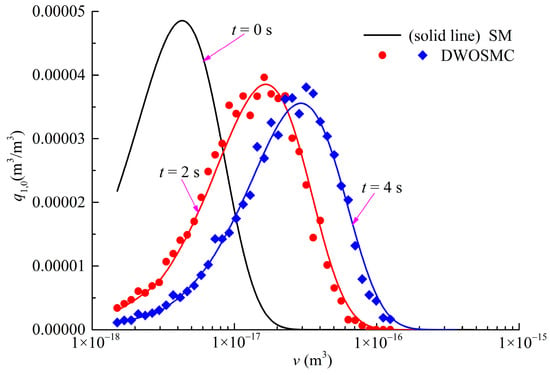
Figure 14.
Evolution of PVDDs of X-component for Case VI.
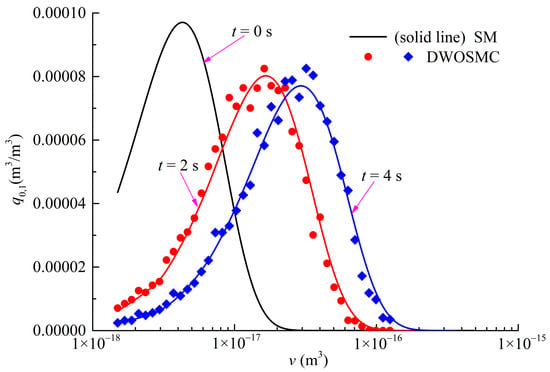
Figure 15.
Evolution of PVDDs of Y-component for Case VI.
From Figure 14 and Figure 15, the evolutions of the PVDD curve of X-component and Y-component share the same variation tendency: the peak volume becomes larger over time, and the shape of the curve do not change much from 2 s to 4 s. From Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15, the Variation of N/N0 and V/V0, PSDs and PVDDs from the DWOSMC method agree well with the sectional method.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the DWOSMC algorithm is further updated to describe the droplet aerosol dynamic behaviors including coagulation, deposition, condensation and evaporation processes in both single component and two component systems. During simulation, the aerosols will firstly experience condensation, and then the evaporation will be considered during the second half of the simulation. The further developed DWOSMC method is firstly validated by the analytical solutions in single component aerosol systems for some relatively simple cases. Then, the calculated results are verified by the sectional method for relatively complicated cases in both single-component and two-component aerosol particle systems. It is concluded that the calculated results of the DWOSMC method show good consistency with both the analytical solutions and the sectional method. The further developed DWOSMC method is found to be able to describe the evolution of particle number density, total particle volume, average particle diameter, particle size distributions, and component-related particle volume densities in both single-component and two-component aerosol systems considering coagulation, deposition and condensation/evaporation processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L.; methodology, H.L.; software, J.S.; validation, H.L., J.S. and W.J.; formal analysis, J.S. and W.J.; investigation, X.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.S. and W.J.; writing—review and editing, H.L.; visualization, X.L.; supervision, X.L.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant number: BK20210854), the Natural Science Fund Project of Colleges in Jiangsu Province (grant number: 20KJB470009) and the Jiangsu Provincial Double-Innovation Doctor Program (grant number: JSSCBS20210883).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and forecasting the potential domestic and international spread of the 2019-nCoV outbreak originating in Wuhan, China: A modelling study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prather, K.A.; Wang, C.C.; Schooley, R.T. Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2: Masks and testing are necessary to combat asymptomatic spread in aerosols and droplets. Science 2020, 368, 1422–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiti, M.; Castanet, G.; Corber, A.; Alden, M.; Berrocal, E. Transition from saliva droplets to solid aerosols in the context of COVID-19 spreading. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Q. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 indoor and outdoor environments. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, H.T.; Kim, K.-S. Behavior of cough droplets emitted from Covid-19 patient in hospital isolation room with different ventilation configurations. Build. Environ. 2022, 209, 108649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.K.H.; Moon, J.Y.; Chae, M.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.C. Prediction of aerosol deposition in the human respiratory tract via computational models: A review with recent updates. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, J.; Peglow, M.; Warnecke, G.; Heinrich, S. An efficient numerical technique for solving population balance equation involving aggregation, breakage, growth and nucleation. Powder Technol. 2008, 182, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yu, M. Thermodynamic analysis of Brownian coagulation based on moment method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 122, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Lucci, F.; Kuczaj, A.K. Multispecies aerosol evolution and deposition in a bent pipe. J. Aerosol Sci. 2019, 129, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadloo-Jahromi, A.; Bavi, O.; Hossein Heydari, M.; Kharati-Koopaee, M.; Avazzadeh, Z. Dynamics of respiratory droplets carrying SARS-CoV-2 virus in closed atmosphere. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, W.F. On air-borne infection: Study II. Droplets and droplet nuclei. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1934, 20, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Interaction between water and acetic acid-sodium halide aerosol: A molecular dynamics study. Powder Technol. 2017, 314, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.; Melekidis, S.; Koch, R.; Bauer, H.J. Insights into the evaporation characteristics of saliva droplets and aerosols: Levitation experiments and numerical modeling. J. Aerosol Sci. 2021, 154, 105760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.T.; Chan, W.Y.; Mui, K.W.; Lai, A.C.K. An experimental and numerical study on deposition of bioaerosols in a scaled chamber. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGraw, R. Description of aerosol dynamics by the quadrature method of moments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1997, 27, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Chan, T.L.; Liu, H.J. Numerical simulation of particle formation and evolution in a vehicle exhaust plume using the bimodal Taylor expansion method of moments. Particuology 2019, 43, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochenburger, T.M.; Fernández, F.J.; Prieto, M.M. Study and modification of a size-discrete semi-implicit simulation model for polydisperse aerosol coagulation. J. Aerosol Sci. 2017, 114, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisels, A.; Kruis, F.E.; Fissan, H. Direct simulation Monte Carlo for simultaneous nucleation, coagulation, and surface growth in dispersed systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotalczyk, G.; Kruis, F.E. A Monte Carlo method for the simulation of coagulation and nucleation based on weighted particles and the concepts of stochastic resolution and merging. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 340, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, J.; Yu, M. Direct expansion method of moments for nanoparticle Brownian coagulation in the entire size regime. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 67, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotalczyk, G.; Kruis, F.E. Fractional Monte Carlo time steps for the simulation of coagulation for parallelized flowsheet simulations. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J. A fast monte carlo method based on an acceptance-rejection scheme for particle coagulation. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.M.; Chan, T.L. Two-component aerosol dynamic simulation using differentially weighted operator splitting Monte Carlo method. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 62, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chan, T.L. A coupled LES-Monte Carlo method for simulating aerosol dynamics in a turbulent planar jet. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2020, 30, 855–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kruis, F.E.; Zheng, C. Reducing statistical noise and extending the size spectrum by applying weighted simulation particles in monte carlo simulation of coagulation. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Jiang, X.; Chan, T.L. Error analysis in stochastic solutions of population balance equations. Appl. Math. Model. 2020, 80, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kruis, F.E.; Zheng, C. A differentially weighted Monte Carlo method for two-component coagulation. J. Comput. Phys. 2010, 229, 6931–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, C. Monte Carlo solution of wet removal of aerosols by precipitation. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1510–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, C. A new event-driven constant-volume method for solution of the time evolution of particle size distribution. J. Comput. Phys. 2009, 228, 1412–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, S. Monte Carlo simulation of polydisperse particle deposition and coagulation dynamics in enclosed chambers. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chan, T.L. Differentially weighted operator splitting Monte Carlo method for simulating complex aerosol dynamic processes. Particuology 2018, 36, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourti, N.; Schatz, A. Solution of the general dynamic equation (GDE) for multicomponent aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Monte Carlo Simulation of Aerosol Dynamics in Turbulent Flows. Ph.D. Thesis, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, C. Fast Monte Carlo simulation for particle coagulation in population balance. J. Aerosol Sci. 2014, 74, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, R.I.; Quispel, G.R.W. Splitting methods. Acta Numer. 2002, 11, 341–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, C. Two-component brownian coagulation: Monte carlo simulation and process characterization. Particuology 2011, 9, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liffman, K. A direct simulation Monte-Carlo method for cluster coagulation. J. Comput. Phys. 1992, 100, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Bapat, A.P.; Zachariah, M.R. A Simple Numerical Algorithm and Software for Solution of Nucleation, Surface Growth, and Coagulation Problems. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabhadran, T.E.; Peterson, T.W.; Seinfeld, J.H. Dynamics of aerosol coagulation and condensation. AIChE J. 1976, 22, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniswaamy, G.; Loyalka, S.K. Direct simulation, Monte Carlo, aerosol dynamics: Coagulation and condensation. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2008, 35, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).