Multiparametric Sensor Node for Environmental Monitoring Based on Energy Harvesting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System Configuration
2.1. Air Quality Sensors
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- Infrared gas sensor [36];
- -
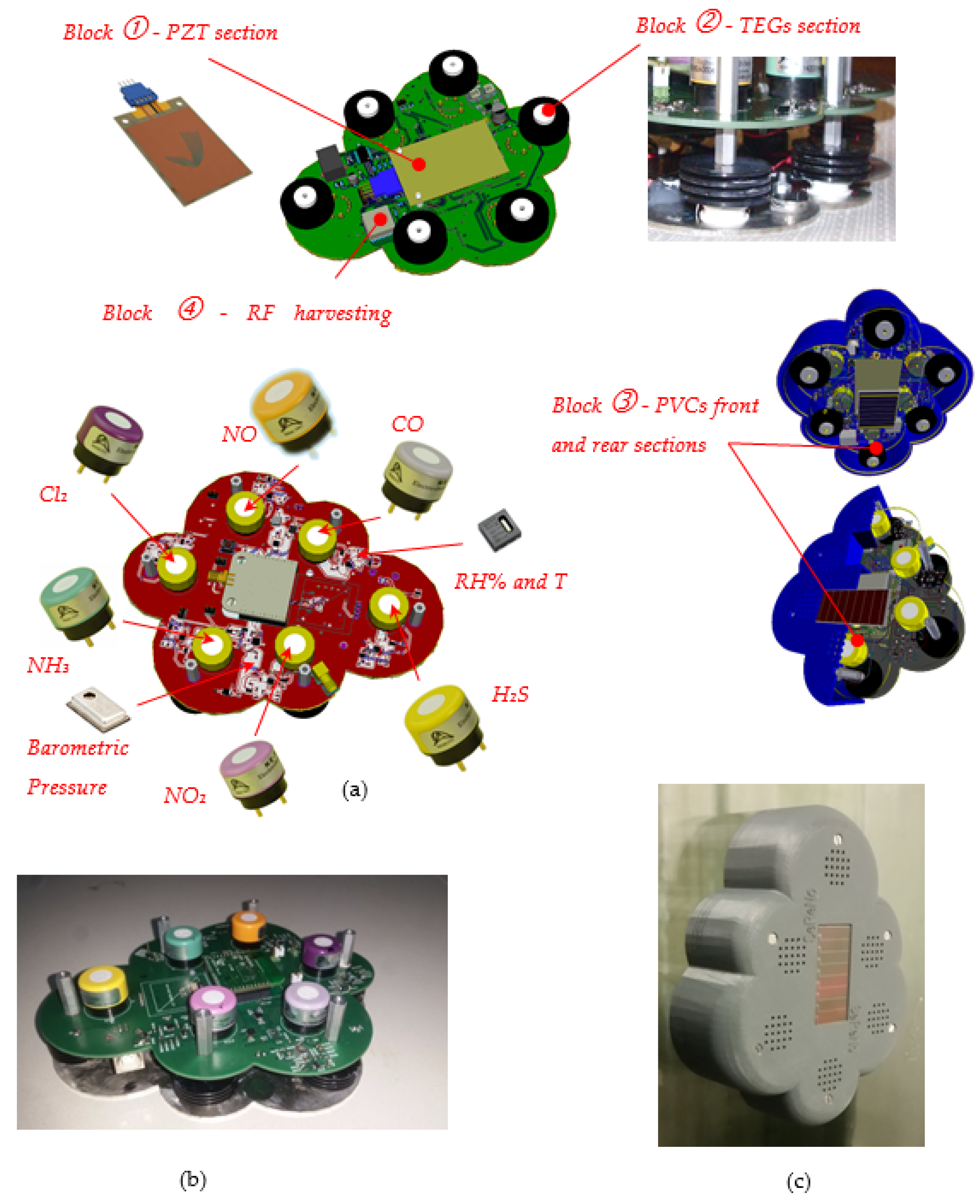
2.2. Power Harvesting Section
- A vibration energy harvester (Block ①) devoted to the transformation of otherwise wasted energy from oscillations into usable electric energy. The PZT-based electromechanical resonator was installed in a custom-fit configuration. The goal of this configuration was matching the natural frequency of the harvester with the vibration sources.
- Six TEGs generators (Block ②) with highly efficient thermoelectric effect and 17 N&P stacks for each one. An example of peak power generated with a temperature gradient of 15 °C is ≅0.5 mW.
- One thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell (Block ③ front section) as an energy source for indoor artificial light energy harvesting with power density of 0.042 μW/mm2 @ 200 Lux (reference number AM-1801 from Sanyo semiconductor). The current/voltage ratio under this illumination level was 18.5 μA @ 3.0 Vdc.
- One (through window) thin-film amorphous silicon solar cell (Block ③ rear section) as an energy source for OUTDOOR solar harvesting with power density of 1 μW/mm2 @ 50 kLux (reference number AM-5904 from SANYO semiconductor). The current/voltage ratio under this illumination level was 4.5 mA @ 5.0 Vdc.
- One RF power source at 915 MHz (Block ④) based on the Powercast P2110 harvester receiver and RF to DC converter. This module features high efficiency and ultralow power consumption.
2.3. The Sensor Board
2.4. Data Transmission Protocol
3. Methods and Results
- Nemoto NE4–CO electrochemical sensor with a sensitivity of 82 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 28 s (average of six samples);
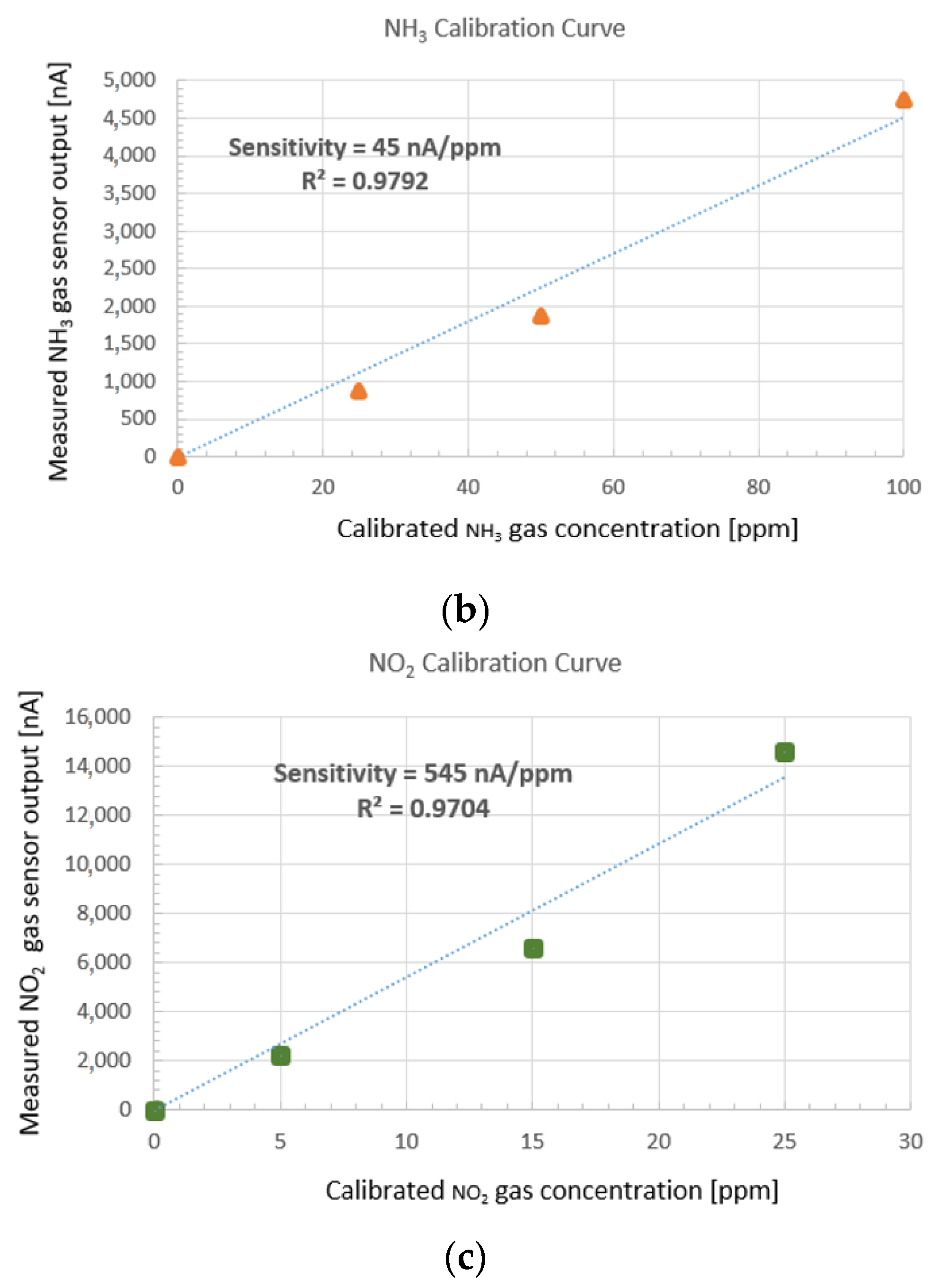
- Nemoto NE4–NO2 electrochemical sensor with a sensitivity of 545 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 41 s (average of six samples);
- Nemoto NE4–H2S–100 electrochemical sensor with a sensitivity of 705 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 37 s (average of three samples);
- Nemoto NE4–NH3 electrochemical sensor with a sensitivity of 45 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 105 s (average of four samples);
- Nemoto NE4–NO electrochemical sensor with sensitivity of 403 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 54 s (average of seven samples);
- Nemoto NE4–Cl2 electrochemical sensor with a sensitivity of 586 nA/ppm with response time T90% = 43 s (average of seven samples);
- cross-sensitivity of H2S sensor to CO was less than 2.4%;
- cross-sensitivity of NH3 sensor to H2S was around 164%;
- cross-sensitivity of NH3 sensor to NO2 was less than 6%;
- cross-sensitivity of NO sensor to NO2 was around 3%;
- cross-sensitivity of Cl2 sensor to NO2 was around 93%.
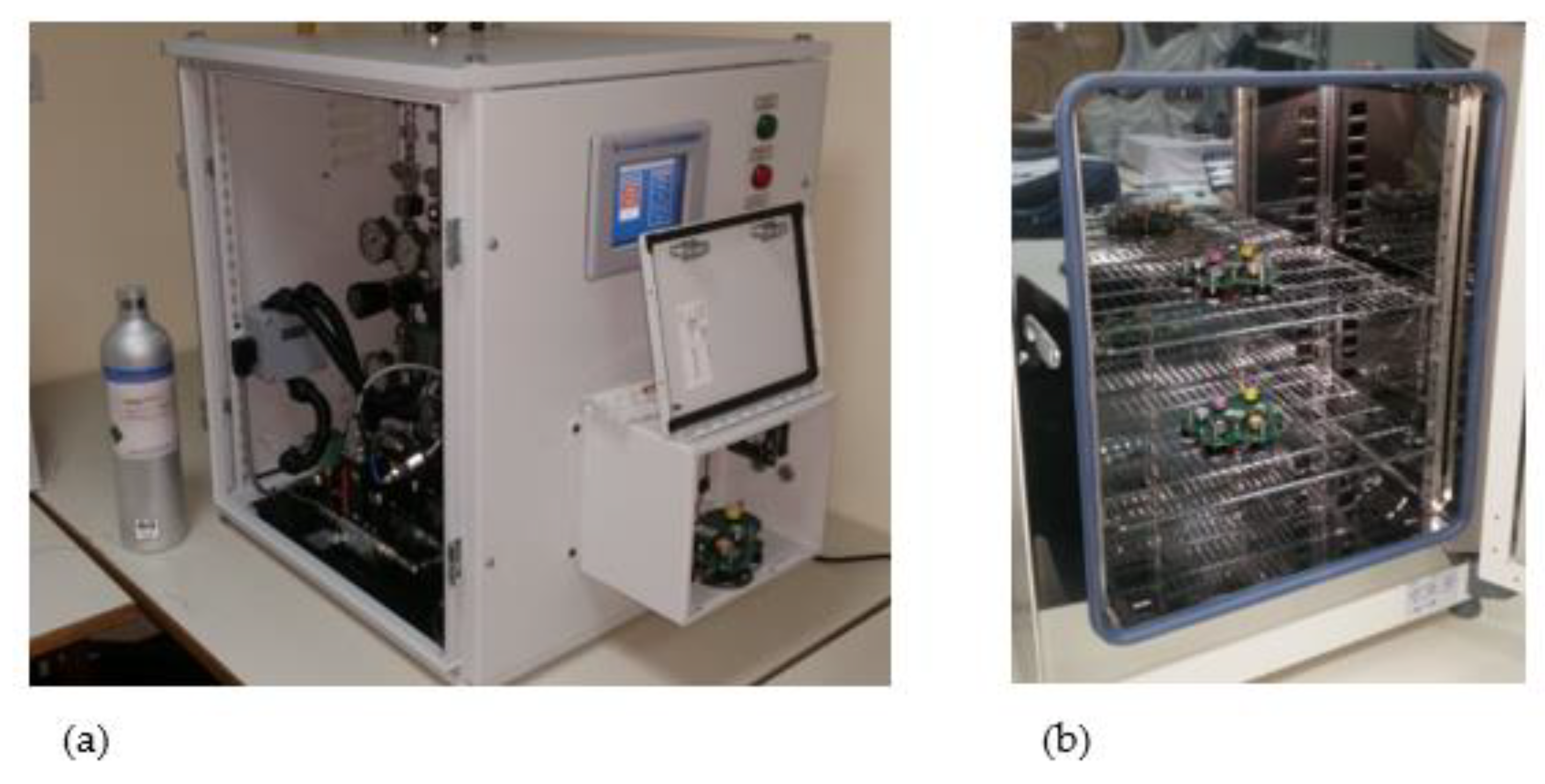
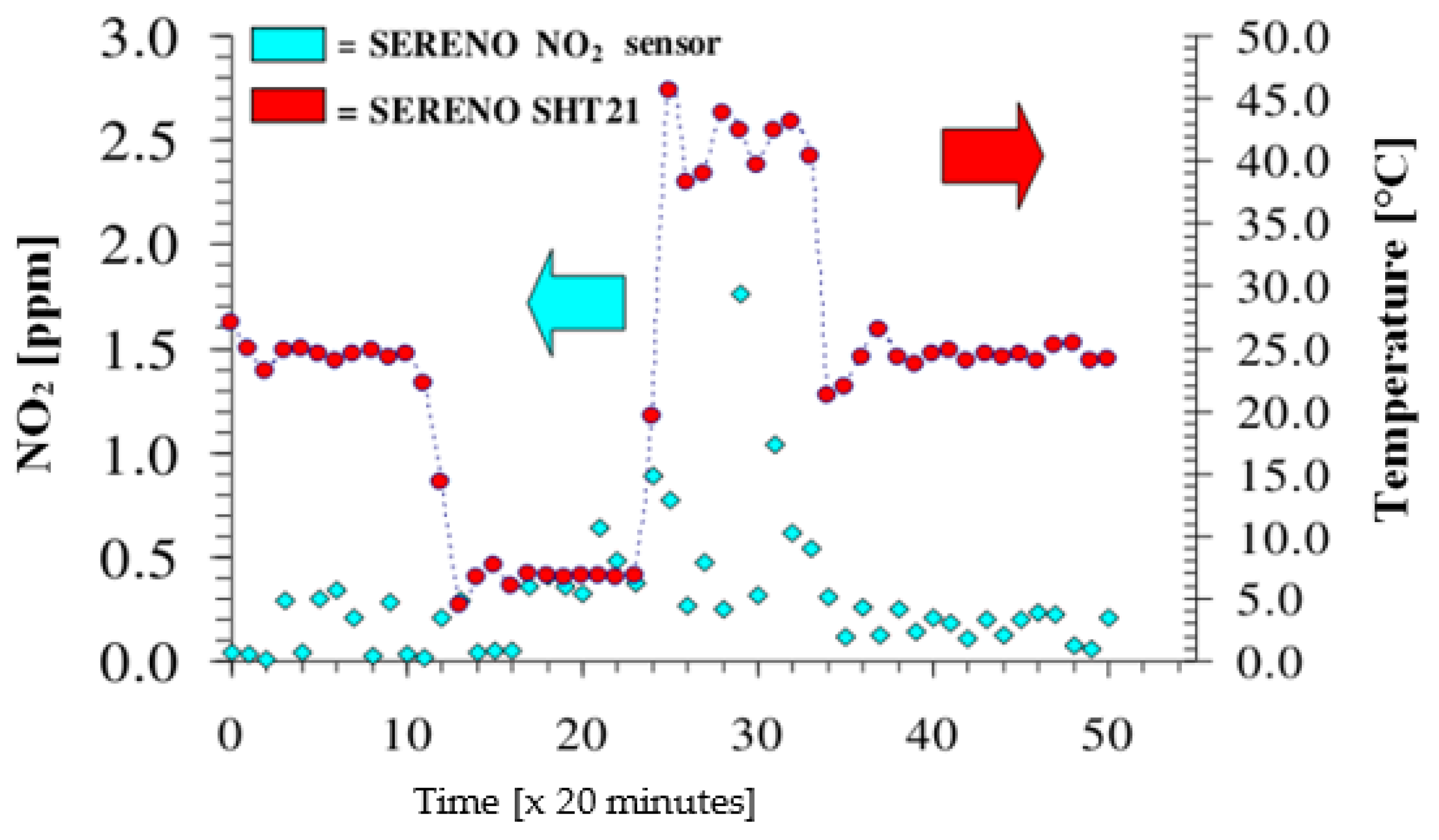
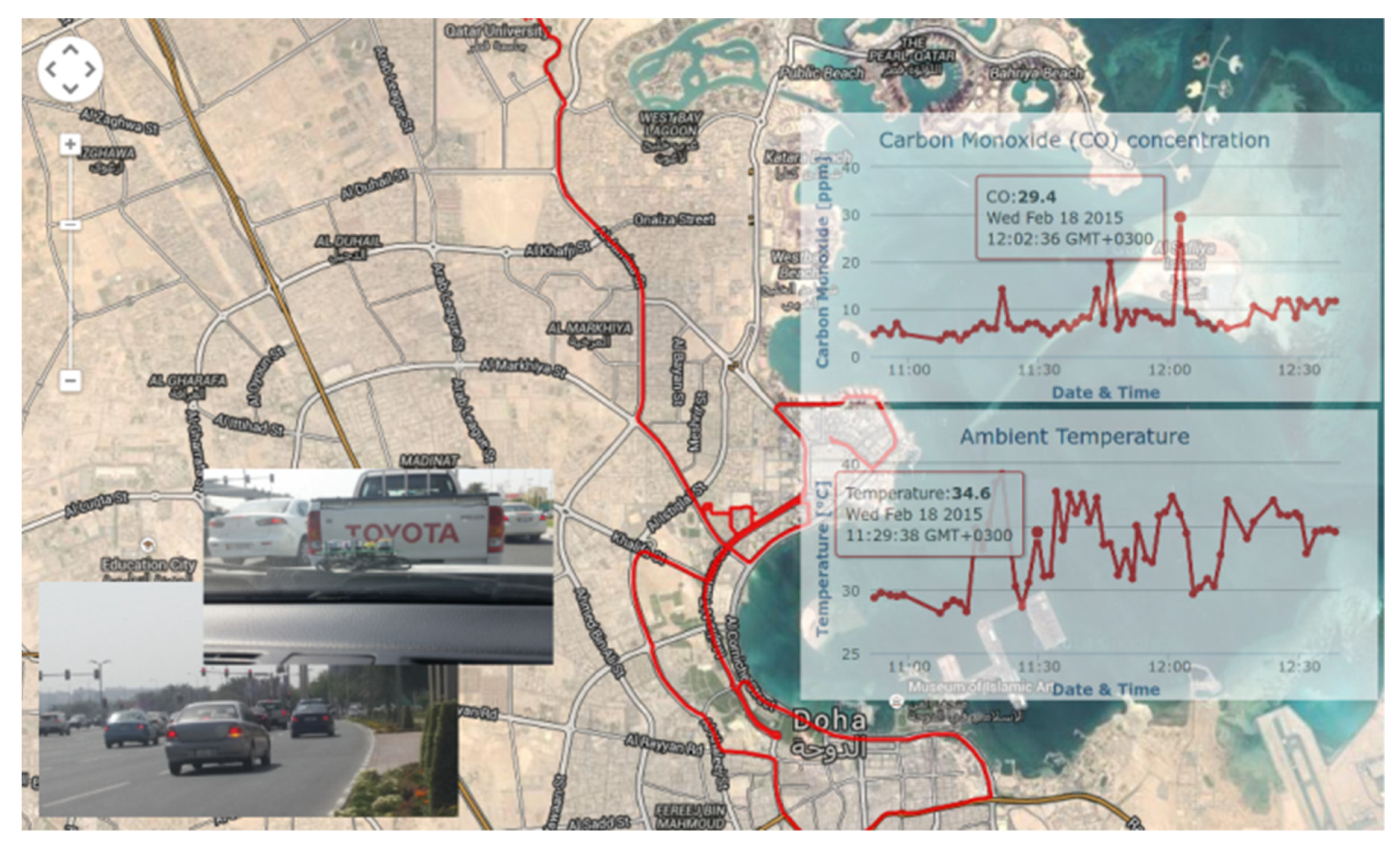
3.1. Measurement Results
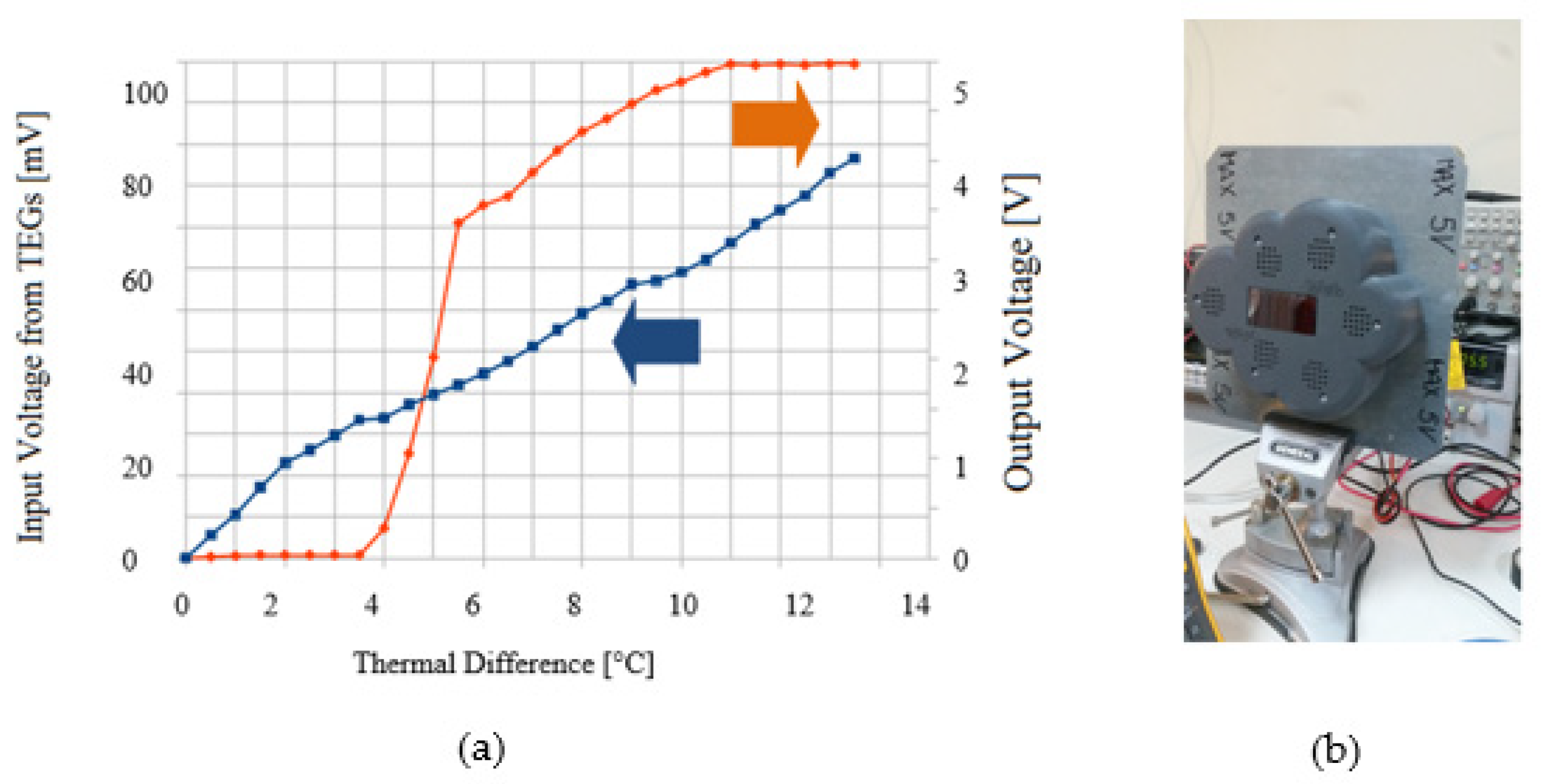
3.2. Energy Harvesting Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chau, C.K.; Hui, W.K.; Tse, M.S. Evaluation of health benefits for improving indoor air quality in workplace. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, W.S.; Samet, J.M.; Hodgson, M.J. The quest for negligible health risks from indoor air. ASHRAE J. 1995, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B.; Goldbohm, S.; Fischer, P.; Van den Brandt, A. Association between mortality and indicators of traffic-related air pollution in the Netherlands: A cohort study. Lancet 2002, 360, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kjellstrom, T.E.; Neller, A.; Simpson, R.W. Air Pollution and Its Health Impacts: The Changing Panorama. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, M.; Ghanem, M.; Osmond, M.; Guo, Y.; Hassard, J. Grid-based Analysis of Air Pollution Data. Ecol. Model. 2006, 194, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarakonda, S.; Sevusu, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Iftode, L.; Nath, B. Real-time air quality monitoring through mobile sensing in metropolitan areas. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGKDD International Workshop on Urban Computing, Chicago, IL, USA, 11–14 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chaiwatpongsakorn, C.; Lu, M.; Keener, T.C.; Soon-Jai, K. The Deployment of Carbon Monoxide Wireless Sensor Network (CO-WSN) for Ambient Air Monitoring. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 6246–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- North, R.J.; Cohen, J.; Wilkins, S.; Richards, M.; Hoose, N.; Polak, J.W.; Bell, M.C.; Blythe, P.; Sharif, B.; Neasham, J.; et al. Field deployment of the MESSAGE System for environmental monitoring. Traffic Eng. Control 2009, 50, 484–488. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, K.; Tian, L.; Piedrahita, R.; Yun, X.; Mansata, O.; Liv, O.; Dick, R.P.; Hannigan, M.; Shang, L. MAQS: A person-alized mobile sensing system for indoor air quality monitoring. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Beijing, China, 17–21 September 2011; pp. 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Jiang, X. AirCloud: A Cloud-based Air-Quality Monitoring System for Every-one. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM Conference of Embedded Network Sensor Systems, SenSys’ 14, Memphis, TN, USA, 3–6 November 2014; pp. 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Ling, Z. The Research and Implement of Air Quality Monitoring System Based on ZigBee. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Istanbul, Turkey, 4–8 July 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, J.; Suárez, J.I.; Arroyo, P.; Ordiales, J.M.; Álvarez, F. Wireless sensor networks for indoor air quality monitoring. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2012, 30, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Yajie, M.; Richards, M.; Ghanem, M.; Guo, Y.; Hassard, J. Air Pollution Monitoring and Mining Based on Sensor Grid in London. Sensors 2008, 8, 3601–3623. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Mishra, B.; Sutaria, R.; Zele, R. Design and Development of Low-cost Wireless Sensor Device for Air Quality Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Annual International Conference, Proceedings/TENCON, Osaka, Japan, 17–20 October 2019; pp. 2345–2350. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzelman, W.B.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Balakrishnan, H. An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2002, 1, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jelicic, V.; Magno, M.; Paci, G.; Brunelli, D.; Benini, L. Design, characterization and management of a wireless sensor network for smart gas monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th IEEE International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), Savelletri di Fasano, Italy, 28–29 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, L.; Salti, T.E.; Nasser, N.; Mahmoud, Q.H. The Significant Impact of a Set of Topologies on Wireless Sensor Net-works. J. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2012, 2012, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavi, K.K.; Rajeev, P.; Avinash, M. A Wireless Sensor Network Air Pollution Monitoring. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. (IJWMN) 2010, 2, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Lin, T.-S.; Lai, D.-W.; Wen, T.-H.; Sun, C.-H.; Juang, J.-Y.; Jiang, J.-A. Developed urban air quality monitoring system based on wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 Fifth International Conference on Sensing Technology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 28 November–1 December 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Alhmiedat, T.; Samara, G. A low cost ZigBee sensor network architecture for indoor air quality monitoring. Int. J. Comp. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2017, 15, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.C.; Shiledar, A.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Jin, K.; Janamian, S.; Yang, Z.; et al. Air quality monitoring using mobile microscopy and machine learning. Light Sci. Appl. 2017, 6, e17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampolli, S.; Elmi, I.; Ahmed, F.; Passini, M.; Cardinali, G.C.; Nicoletti, S.; Dori, L. An electronic nose based on solid state sensor arrays for low-cost indoor air quality monitoring applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 101, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Chu, C.H.; Shin, S.M. ISSAQ: An integrated sensing systems for real-time indoor air quality monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 4230–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benammar, M.; Abdaoui, A.; Ahmad, S.H.M.; Touati, F.; Kadri, A. A modular IoT platform for real-time indoor air quality monitoring. Sensors 2018, 18, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiele, A.; Esfahani, S.; Covington, J. Design and development of a low-cost, portable monitoring device for indoor environment quality. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 5353816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yin, H.; Lin, L.; Zeng, X.; Mason, A.J. Miniaturized Planar Room Temperature Ionic Liquid Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Rapid Multiple Gas Pollutants Monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255 Pt 1, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.H.; Rao, M.V.; Li, Q. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors for Detecting Toxic Gases: NO2, SO2 and H2S. Sensors 2019, 19, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhall, S.; Mehta, B.R.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sood, K. A review on environmental gas sensors: Materials and technologies. Sens. Int. 2021, 2, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brauns, E.; Morsbach, E.; Kunz, S.; Bäumer, M.; Lang, W. A fast and sensitive catalytic gas sensors for hydrogen detection based on stabilized nanoparticles as catalytic layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, H.; Chiu, Y. Performance Improvement of Nitrogen Oxide Gas Sensors Using Au Catalytic Metal on SnO2/WO3 Complex Nanoparticle Sensing Layer. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7581–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Xibo, D.; Yuechao, C.; Gen, H.; Long, B. Temperature drift and compensation techniques for the thermal conductivity Gas sensor. In Ifost; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tardy, P.; Coulon, J.-R.; Lucat, C.; Menil, F. Dynamic thermal conductivity sensor for gas detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 98, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. Detecting gases with light: A review of optical gas sensor technologies. Sens. Rev. 2015, 35, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson, J.; Tatam, R.P. Optical gas sensing: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, T.-V.; Choi, I.-Y.; Son, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-C. A review on non-dispersive infrared gas sensors: Improvement of sensor detection limit and interference correction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A. Semiconductor metal oxide gas sensors: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2018, 229, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, H.; Joseph, A.; Park, J.; Emadi, A. Advanced Micro-and Nano-Gas Sensor Technology: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crescini, D.; Touati, F.; Galli, A. Multiparametric Sensor Node for Environmental Monitoring Based on Energy Harvesting. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020321
Crescini D, Touati F, Galli A. Multiparametric Sensor Node for Environmental Monitoring Based on Energy Harvesting. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(2):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020321
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrescini, Damiano, Farid Touati, and Alessio Galli. 2022. "Multiparametric Sensor Node for Environmental Monitoring Based on Energy Harvesting" Atmosphere 13, no. 2: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020321
APA StyleCrescini, D., Touati, F., & Galli, A. (2022). Multiparametric Sensor Node for Environmental Monitoring Based on Energy Harvesting. Atmosphere, 13(2), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020321





