Abstract
Ground-level ozone (O3) pollution has become a serious environmental issue in major urban agglomerations in China. To investigate the spatiotemporal patterns and regional transports of O3 in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH-UA), the Yangtze River Delta (YRD-UA), the Triangle of Central China (TC-UA), Chengdu–Chongqing (CY-UA), and the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration (PRD-UA), multiple transdisciplinary methods were employed to analyze the O3-concentration data that were collected from national air quality monitoring networks operated by the China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). It was found that although ozone concentrations have decreased in recent years, ozone pollution is still a serious issue in China. O3 exhibited different spatiotemporal patterns in the five urban agglomerations. In terms of monthly variations, O3 had a unimodal structure in BTH-UA but a bimodal structure in the other urban agglomerations. The maximum O3 concentration was in autumn in PRD-UA, but in summer in the other urban agglomerations. In spatial distribution, the main distribution of O3 concentration was aligned in northeast–southwest direction for BTH-UA and CY-UA, but in northwest–southeast direction for YRD-UA, TC-UA, and PRD-UA. O3 concentrations exhibited positive spatial autocorrelations in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, and TC-UA, but negative spatial autocorrelations in CY-UA and PRD-UA. Variations in O3 concentration were more affected by weather fluctuations in coastal cities while the variations were more affected by seasonal changes in inland cities. O3 transport in the center cities of the five urban agglomerations was examined by backward trajectory and potential source analyses. Local areas mainly contributed to the O3 concentrations in the five cities, but regional transport also played a significant role. Our findings suggest joint efforts across cities and regions will be necessary to reduce O3 pollution in major urban agglomerations in China.
1. Introduction
With its rapid industrialization and urbanization, China has experienced increased air pollution caused by fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and/or ozone (O3), which has drawn significant attention [1,2,3]. O3 is an important atmospheric constituent and influences regional air quality with its strong oxidative capacity. High concentrations of ground-level ozone exert significant effects on human health and ecosystems [4,5]. PM2.5 concentrations decreased by 30–50% across China during 2013–2017 due to strict pollution-control policies [2]. Nationwide PM2.5 concentrations have decreased by 4.08 μg/m3/year during 2013–2018 [6]. However, O3 concentrations have increased by 10.8% in China during 2013–2016 [7] and showed an average growth rate of 2.49 μg/m3/year from 2013 to 2020 [8]. O3 has become the secondary pollutant after PM2.5 in most cities of China, which threatens human health and damages further economic development. It has been reported that O3-related premature mortality increased from 67,000 (with a 95% confidence interval (CI95)/26–104) to 103,000 (CI95/40–163) from 2014 to 2018 in China [9], and the long-term O3-associated health costs in 2018 doubled those reported in 2013 [10]. Moreover, high O3 concentrations harm winter wheat biomass and rice yields in China [11,12].
Ozone concentrations in several megacities of China such as Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen are much higher than the World Health Organization (WHO) standard (maximum daily 8 h average (MDA8) O3 > 50 ppbv) [13,14,15]. From the perspective of urban agglomeration, MDA8 O3 had a higher increase in Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH), central China, the Yangtze River Delta (YRD), and the Pearl River Delta (PRD) from 2013 to 2021 [13]. Increased concentrations of O3 were also found in Western China regions such as Chengdu [16]. In addition to spatial patterns, O3 also has significant temporal variations in China. Previous studies found that the O3 concentration was related to the active photochemical reactions with generally low concentrations in winter but relatively high concentrations in spring and summer for almost all regions in China [17]. In the North China Plain (NCP) and the YRD, higher O3 levels were observed in summer, and in PRD the maximum concentration of O3 was in autumn [4]. O3 also exhibited diurnal variations in China, rising in the morning, peaking in the afternoon, and declining at night [18]. The decrease in O3 concentration at night was related to the process of NOx titration [4]. The regional transport of O3 in China has also been a critical issue that has drawn attention. Surface O3 has been identified in both local and regional contributions when measured at any given location [19]. Many studies have studied the impact of regional background contributions to O3 concentration and identified the potential geographical source regions of O3 [20,21,22]. These studies have suggested that the regional transport of ozone is significant to the overall issue.
Previous studies on spatiotemporal variations and regional transport of O3 have focused on a specific city or a limited spatial region (e.g., the NCP, the YRD, or the PRD) with shorter observation times. There is a paucity of comprehensive research on ground-level O3 from the perspective of major urban agglomerations in China.
Based on the hourly O3 data observed from the ground real-time air quality monitoring network in China from 2017 to 2020, spatiotemporal patterns and regional transport of O3 in five major urban agglomerations in China were researched in this study. More specifically, we (1) systematically demonstrated the annual, seasonal, monthly, and diurnal variations in O3 concentrations, (2) analyzed the spatial patterns and variations in five urban agglomerations based on geographical analysis and spatial statistics, and (3) estimated the background contributions of O3 concentration and investigated the regional transport in different regions. The conclusions are conducive to determining the most efficient approach for O3 reduction in each urban agglomeration.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
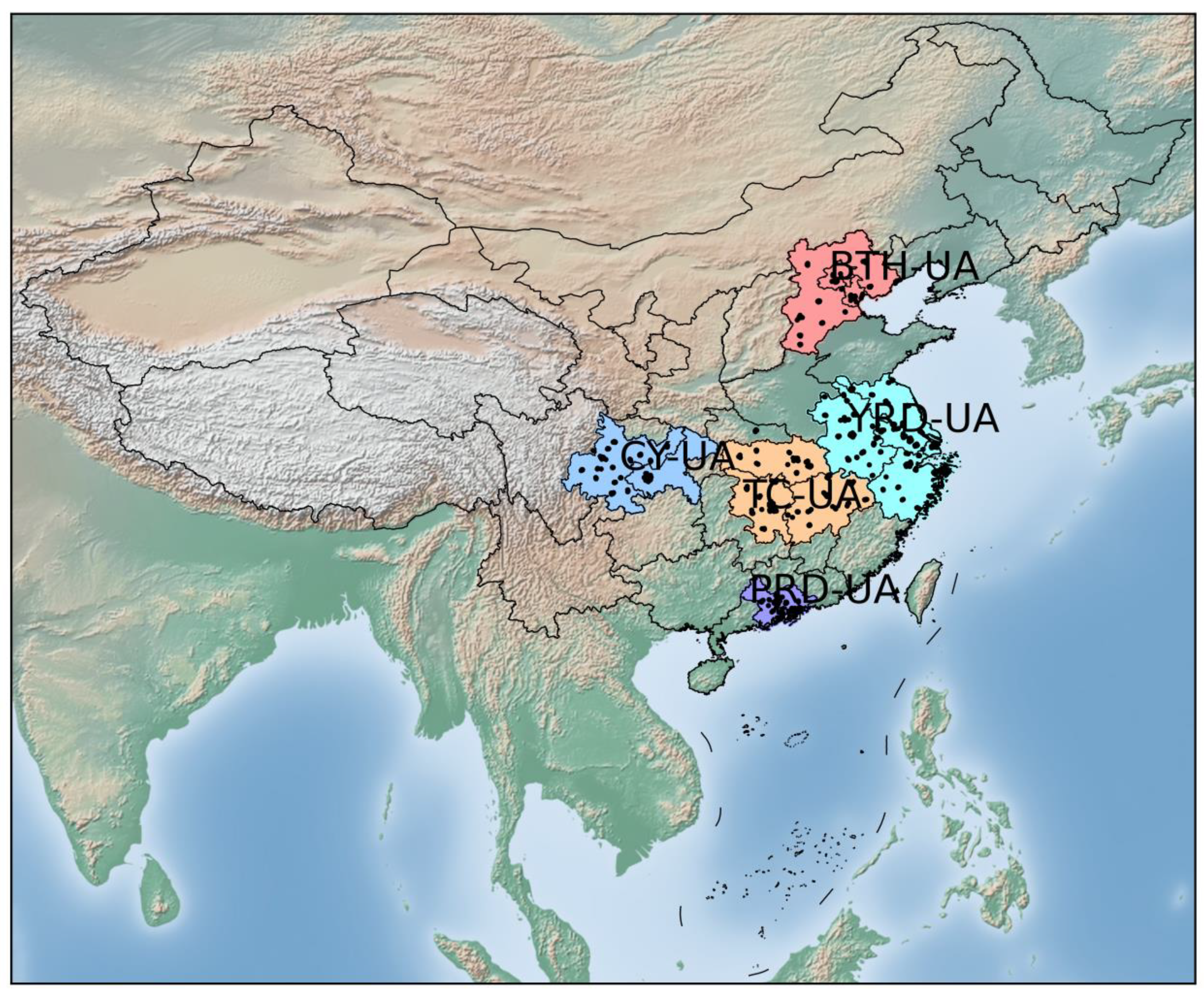
The Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration (BTH-UA), the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration (YRD-UA), the Triangle of Central China urban agglomeration (TC-UA), the Chengdu–Chongqing urban agglomeration (CY-UA), and the Pearl River Delta urban agglomeration (PRD-UA) are five major regions in China (Figure 1) and include the megacities of China such as Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. The BTH-UA is the political and cultural center of China and a core area of the North China economy, with the most severe air pollution in China [23]. The YRD-UA is one of the most economically developed zones between the “Belt and Road” and the “Yangtze River Economic Belt” and has suffered severe air pollution problems in recent years due to increasing energy consumption and air pollutant emissions [24,25]. The TC-UA, a new pillar of China’s economic development with a unique ecosystem, suffers from severe air pollution due to rapid economic growth and a dramatic increase in energy consumption [24,26]. The CY-UA, located in western China, has frequently endured episodes of heavy pollution due to intense resource usage and population agglomeration along with low atmospheric environmental capacity [24,27].
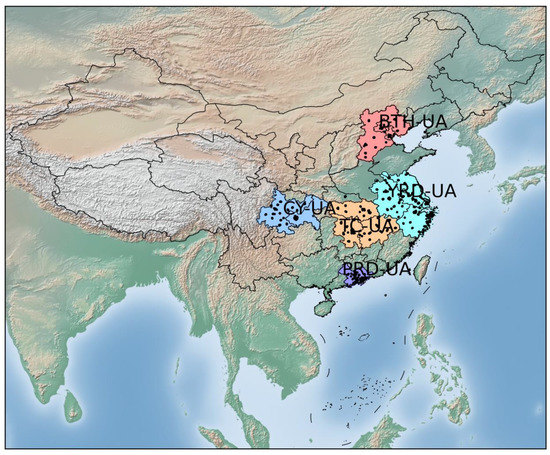
Figure 1.
The five major urban agglomerations in China: Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei (BTH-UA), Yangtze River Delta (YRD-UA), Triangle of Central China (TC-UA), Chengdu–Chongqing (CY-UA), and Pearl River Delta (PRD-UA). The black dots represent air-quality monitoring stations.
2.2. Data Source and Description
The hourly ground-level concentrations of O3 from January 2017 to December 2020 were collected from the national air quality monitoring network operated by the China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). O3 was determined by ultraviolet photometer or differential optical absorption spectroscopy. The instrumental operation, maintenance, quality assurance, and quality control were conducted according to the China Environmental Protection Standards “HJ 818-2018” (https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201808/W020180815358674459089.pdf (accessed on 23 December 2021)). Based on the “Technical Regulation for Ambient Air Quality Assessment of China” (on trial) (HJ 633-2013), we used the O3 daily maximum 8 h sliding average (MDA8) concentration as the O3 level of each day and used the 90th percentile of the MDA8 as the annual assessment standard [28,29]. Beginning 31 August 2018, the reference state of gas observations was changed from the standard condition (i.e., 273 K and 1013 hPa) to room temperature and pressure (i.e., 298 K and 1013 hPa) [8]. Similar to previous studies, we did not consider this effect. The seasonal, monthly, and daily variations of O3 were calculated using the mean of the MDA8 in each city to provide more comprehensive details. The diurnal variations of O3 were calculated using the hourly O3 concentrations of each city.
2.3. Spatiotemporal Variation Analysis Methods
2.3.1. Kernel-Density Estimation
To determine the O3 density function, kernel-density estimation was employed. The kernel-density estimator follows:
where n represents the number of samples, h is the bandwidth, and K is the kernel-weighting function. As in previous studies [30], the Epanechnikov kernel and Silverman’s bandwidth were used in the present study.
2.3.2. Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis
The empirical orthogonal function analysis (EOF) has been widely used to determine the variability of scalar fields, especially in meteorological parameters analysis [31]. The space–time data can be decomposed into spatial vectors and temporal coefficients [32]. A matrix Xmn (where m is the number of sites and n denotes sampling time) can be decomposed into the sum of the product of the orthogonal space matrix V and the orthogonal time matrix T:
where the superscript T denotes the transpose of the matrix, Λ is a diagonal matrix composed of the eigenvalues of the matrix, and V represents a matrix composed of the matrix eigenvectors.
Therefore, the time coefficient can be defined as:
We used the EOF analysis to decompose the monthly O3 concentrations for each region.
2.3.3. Standard Deviational Ellipse
Standard deviation ellipse (SDE) is a spatial statistical method that can reveal variation characteristics of data. The SDE method describes the spatial distribution of elements through four basic parameters including the center point, the major axis, the minor axis, and the azimuth. The mean center identifies the center location for the entire dataset. The major and minor axes of the ellipse indicate the direction and range of the data distribution [33,34]. Azimuth reflects the main trend direction. In this study, the spatial characteristics of O3 concentrations from 2017 to 2020 in each region were quantified to trace their changes. The main parameters of SDE are calculated as follows:
Mean center:
where xi and yi are the coordinates for i (i.e., the observation site of O3 in this study), wi represents the weight value (i.e., annual mean concentration of O3 in each site), and n is equal to the total number of sites.
The angle of rotation is calculated as:
where and indicate the deviation of the xy-coordinates from the mean center.
The standard deviations for the x-axis and y-axis are:
2.3.4. Global and Local Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
The spatial distribution of air pollution is related to complex spatiotemporal and geospatial processes. Previous studies have shown that O3 pollution displays some spatial autocorrelation in geographical space. In this paper, the global Moran’s I was employed to quantitatively measure the global autocorrelation of O3 in each urban agglomeration. The scope of global Moran’s I is (−1, 1), where a negative (positive) value indicates a negative (positive) correlation and the smaller (greater) the value, the stronger the spatial dispersion (agglomeration) of the observed values, while zero indicates no spatial autocorrelation [24,35]. The local Moran’s I can demonstrate the characteristics of an urban spatial agglomeration within a region. The spatial association modes have been classified into four classes [36]: high–high clustering type (hereinafter HH), low–low clustering type (LL), low–high clustering type (LH), and high–low clustering type (HL). In this paper, the HH (LL) type indicates that cities with high (low) O3 concentrations were surrounded by others with high (low) O3 concentrations. The LH (HL) type suggests that cities with low (high) O3 concentrations were surrounded by others with high (low) O3 concentrations. A local Moran’s I that failed the significance test was classified as not significant.
2.4. Regional Background Estimated and Pollution Source Analysis
2.4.1. Texas Commission on Environmental Quality Method
Surface O3 in a certain location was divided into two contribution categories, local and regional. The regional contributions were often defined as “regional background” [37]. The Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) method has been widely used [19], which was based on a well-developed air quality monitoring network. The mature air quality monitoring network covered all directions of the region, so regardless of the wind direction, there was always a station upwind that could capture the regional air masses [38]. Therefore, the minimum MDA8 O3 of all monitoring sites was used as the regional background ozone. The daily local contributions can be calculated by the following formula:
where ρL(O3) denotes O3 concentration from local contribution, ρR(O3) is O3 concentration from regional contribution, ρmax(MDA8 O3) represents maximum MDA8 O3 of all monitoring sites, ρmin(MDA8 O3) represents minimum MDA8 O3 of all monitoring sites, and wTCEQ denotes the regional background contribution estimated by TCEQ method.
2.4.2. Kolmogorov–Zurbenko Filter
Kolmogorov–Zurbenko (KZ) filter is a low-pass filter [39]. The KZ(m, p) filter was defined as p applications of a moving average of m points [40]. The moving average Y of X is expressed as follows:
where denotes the window length and p is the number of iterations. The calculated Yi becomes the input for the second pass, and so on. The variables m and p can be adjusted to control the filtering of different scales of motion. The effective filter width N satisfies the following formula:
According to Rao and Zurbenko [41], a time series of atmospheric pollutants can be partitioned as:
where O(t) denotes the original time series, W(t) represents the short-term component, S(t) is the seasonal component, and e(t) is the long-term (trend) component.
The W(t) variation reflects the weather and short-term fluctuations in precursor emissions, the S(t) variation is attributed to changes in the solar angle, and e(t) variation is a result of changes in overall emissions, pollutant transport, climate, policy, and/or economics [42]. The variables W(t), S(t), and e(t) can be calculated from the following formulae:
More detailed descriptions of the KZ filter have been provided in previous studies [43,44]. Ideally, the three decomposed components are independent of each other, and the covariance should be zero; that is, the following equation should be satisfied.
where D(O), D(W), D(S), and D(e) denote the variance of O(t), W(t), S(t), and e(t), respectively.
The K value is used to reflect the decomposition result, which is calculated as:
The smaller the K value, the better the decomposition result.
2.4.3. Backward Trajectory
Backward trajectory has been widely used to identify the potential transport pathways of air masses [45,46]. The hybrid single-particle Lagrangian integrated trajectory (HYSPLIT) model [47] was run to simulate the air-mass moving path. FNL global analysis data obtained from the National Center for Environmental Prediction’s Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) wind-field reanalysis (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ (accessed on 23 December 2021)) was used to drive the HYSPLIT model. Subsequently, the simulated backward trajectories having similar geographic origins and histories were classified by k-means clustering.
2.4.4. Potential Source Analysis
The potential source contribution function (PSCF), a widely used method to identify the probable locations of emission sources, is a conditional probability describing trajectories with pollutant concentrations larger than a given threshold passing through the receptor site [48]. When the number of endpoints is too small, the uncertainty of PSCF increases significantly [49]. To reduce uncertainty [50], a weighting function is integrated into the PSCF value.
3. Temporal Variations of O3 in Five Urban Agglomerations
3.1. Annual Variation
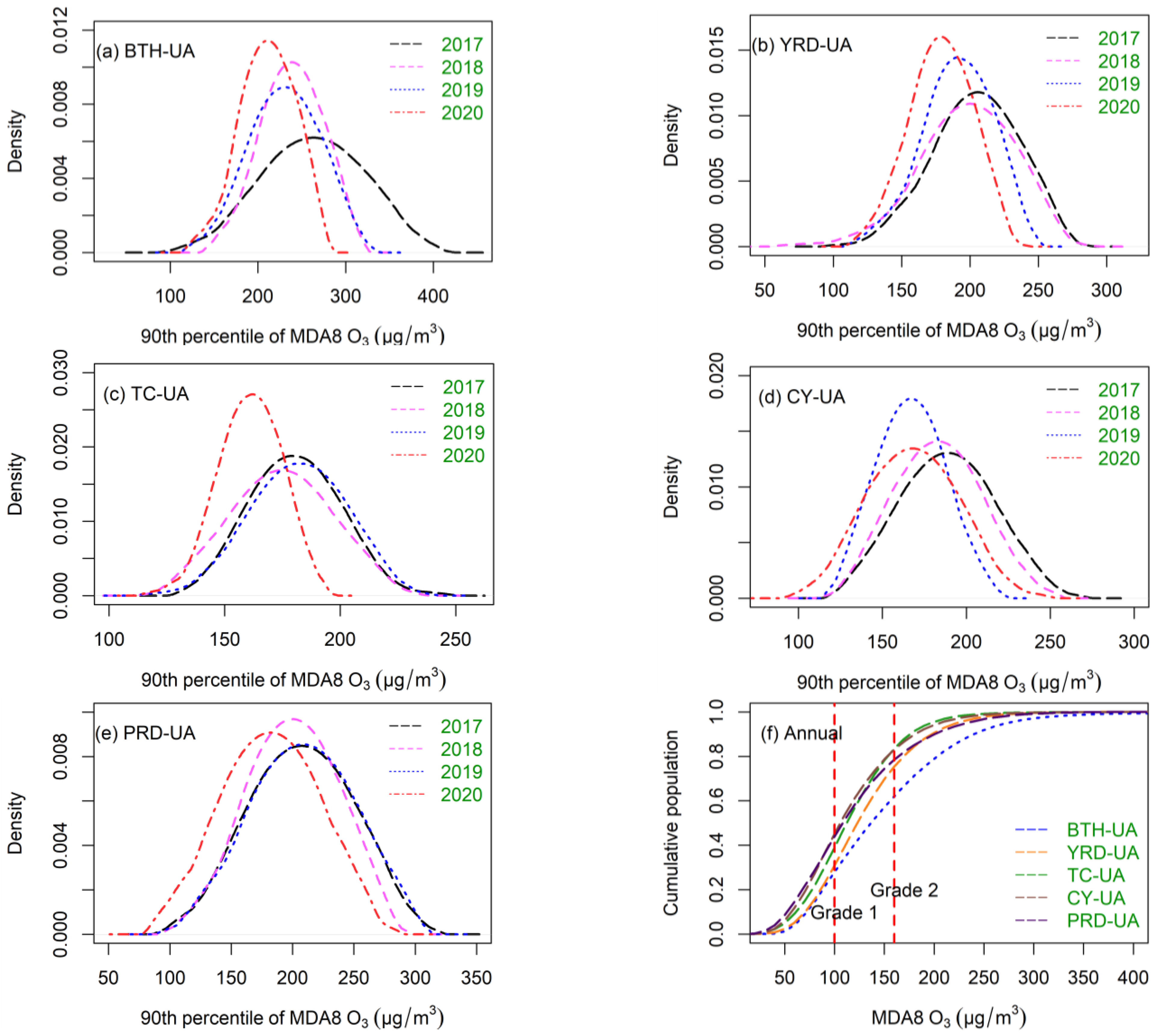
Figure 2 displays the estimated kernel density and over-standard rates of the O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations from 2017 to 2020. The annual average concentration of O3 (90th percentile of MDA8 O3) during 2017–2020 in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, TC-UA, CY-UA, and PRD-UA was 227.9, 180.4, 173.8, 180.2, and 196.4 μg/m3, respectively. In BTH-UA, YRD-UA, and TC-UA (Figure 2a–c), the peak of the kernel-density curves became steeper and moved to the left from 2017 to 2020, in general, indicating that O3 concentrations in most of the cities were continuously reduced. To improve air quality, China formulated the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan in 2013. The decreased O3 concentrations in the five urban agglomerations indicated that the plan worked as intended. The areas covered by density curves decreased over time with O3 concentrations ranging from 250 to 300 μg/m3 in BTH-UA, from 200 to 250 μg/m3 in YRD-UA, and from 180 to 220 μg/m3 in TC-UA, which indicated that reductions in cities with high O3 concentrations benefitted regional O3 pollution alleviation. In CY-UA (Figure 2d), the annual mean concentration of O3 in 2020 (171.5 μg/m3) increased by 1.5 μg/m3 over 2019 (170.0 μg/m3). In PRD-UA (Figure 2e), the kernel-density curves varied slightly. As compared to 2017, O3 concentrations in 2020 decreased by 10.4% in PRD-UA, 21.6% in BTH-UA, 8.4% in YRD-UA, 17.3% in TC-UA, and 11.8% in CY-UA. As shown in Figure 2f, the proportion of MAD8 O3 met the China National Ambient Air Quality Standards I (CAAQS grade I; 100 μg/m3) in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, TC-UA, CY-UA, and PRD-UA, at 27.8%, 30.9%, 40.0%, 45.2%, and 44.0%, respectively. The proportions of MAD8 O3 that exceeded the Grade 2 limit (CAAQS grade II; 160 μg/m3) in the five aforementioned urban agglomerations were 38.0%, 24.6%, 16.4%, 16.9%, and 21.5%, respectively, indicating severe O3 pollution in China.
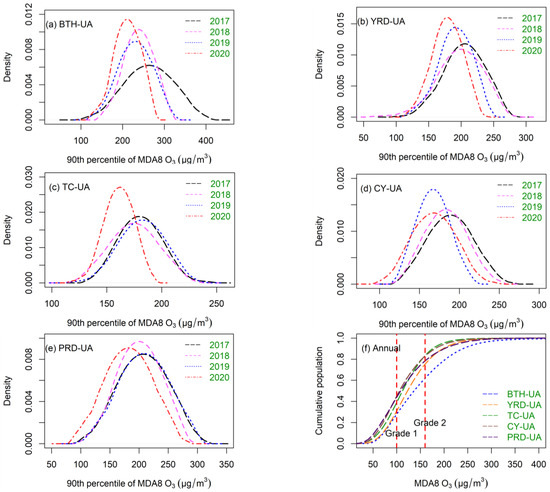
Figure 2.
Kernel-density estimates of annual mean O3 concentrations in (a) BTH-UA, (b) YRD-UA, (c) TC-UA, (d) CY-UA, and (e) PRD-UA. (f) The annual over-standard rate of the O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations in 2017–2020.
3.2. Monthly Variation
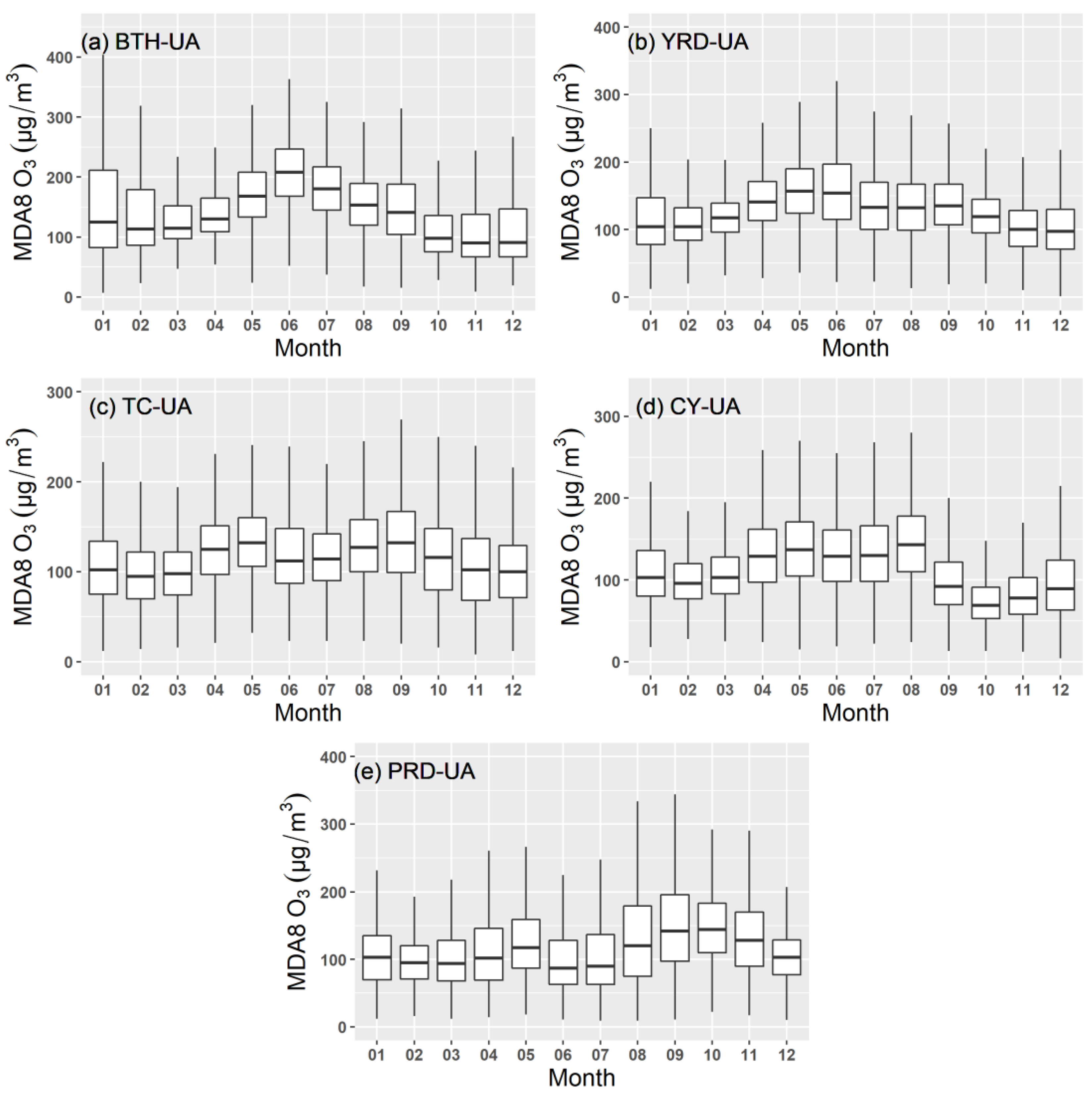
The monthly variations in O3 concentrations in the five urban agglomerations from 2017 to 2020 are illustrated in Figure 3. Monthly changes in O3 in North China are represented by the inverted-V shape curves and by the M-shape curves in South China [7]. The monthly average O3 concentrations in BTH-UA (Figure 3a) exhibit an inverted-V shape (i.e., a unimodal structure) with the highest concentration in summer (Figure S1). The MDA8 O3 gradually increased from February to June, having the highest concentration in June, and then gradually decreased. O3 concentrations in other urban agglomerations are M-shaped (i.e., a bimodal structure). In YRD-UA, TC-UA, and PRD-UA, the O3 variation had two peaks, in May and September. In CY-UA, the two peaks occurred, one in May and one in August. In PRD-UA, MDA8 O3 was high in the summer and the autumn but reached a maximum value in autumn (Figure S1). In the other four urban agglomerations, the maximum values occurred in summer. The formation mechanism of O3 was complicated related to the overall NOx and VOC emissions, topography, and atmospheric circulation in the region [29]. In BTH-UA, the maximum concentration was related to anthropogenic emissions [51]. In PRD-UA, the low value in summer was linked to the onset and retreat of warm, wet air [52]. Based on the conclusion from a previous study [52], we suggest that the distinct seasonal variations of O3 across the five regions could be attributed to the suppression of photochemical production by the monsoonal warm, moist air.
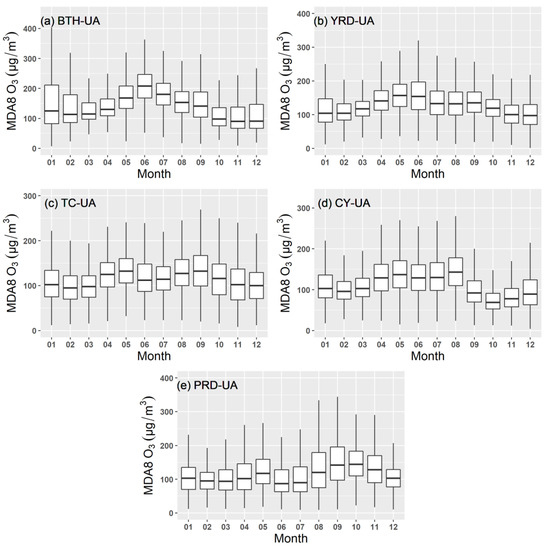
Figure 3.
Monthly variation of MDA8 O3 in (a) BTH-UA, (b) YRD-UA, (c) TC-UA, (d) CY-UA, and (e) PRD-UA during 2017–2020. Shown are the median (central horizontal bar within the boxes), 25th and 75th percentiles (lower and upper bars of the boxes, respectively), and minimum and maximum (lower and upper whiskers, respectively).
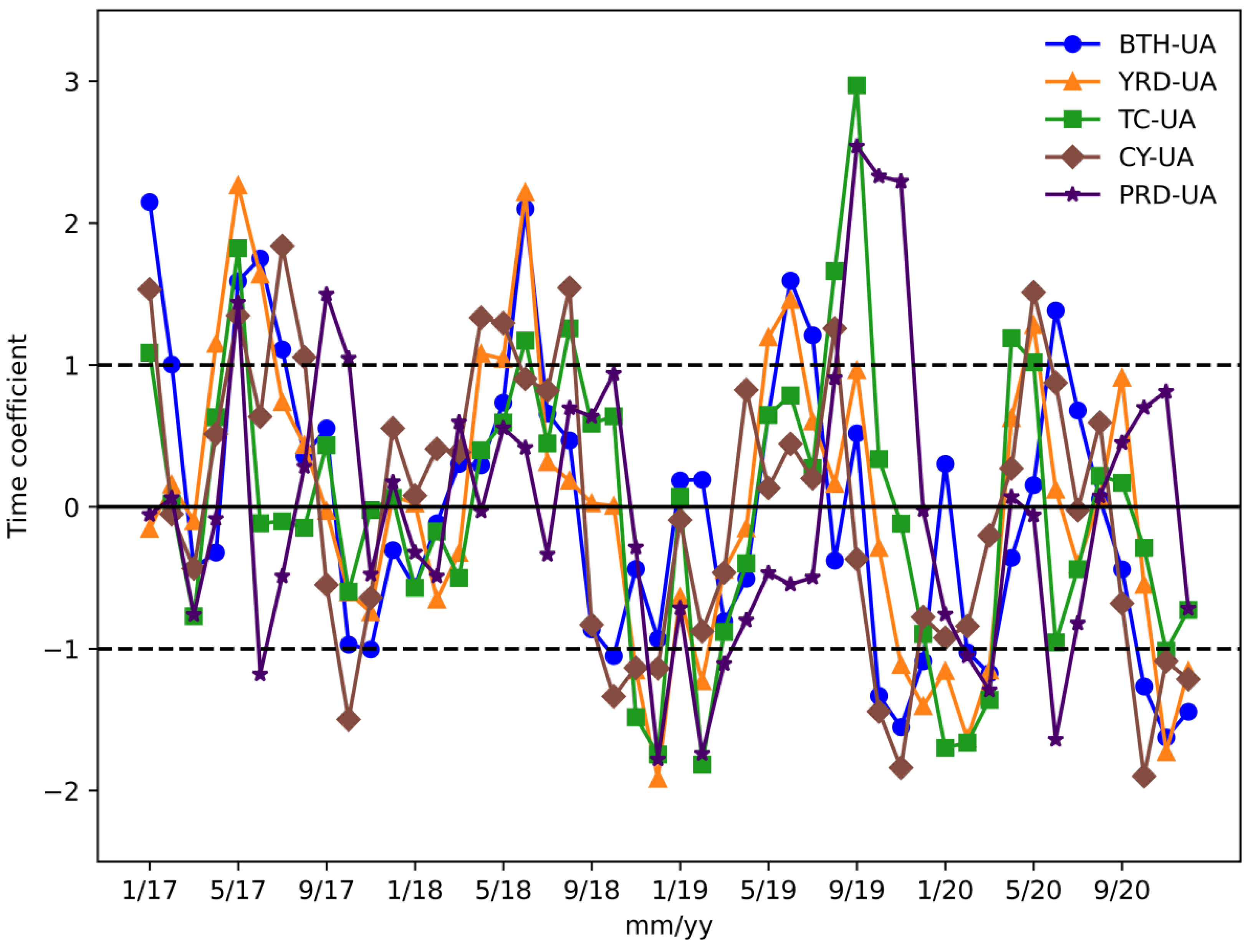
The EOF method was used to decompose the monthly mean MDA8 O3 concentrations of the cities in the five regions. The first EOF model accounted for 82.6%, 68.5%, 69.2%, 86.2%, and 81.5% of the total variance in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, TC-UA, CY-UA, and PRD-UA, respectively, indicating that the decompositions were successful. We specifically examined the time coefficients decomposed by EOF, which reflected the variation trends in the monthly O3 concentrations of the five urban agglomerations. The decomposed time coefficients were standardized to have zero mean and unit variances. Specifically, values that crossed the dash lines at ±1 were regarded as extreme events [30]. As represented in Figure 4, the time coefficients of the five regions changed with the annual cycle, similar to the variation trends of the O3 mass concentrations. Every May, most of the time coefficients fell outside the scope of (−1, 1), indicating extreme events, namely high O3 pollution. In September 2019, intensive extreme O3 pollution events were detected in TC-UA and PRD-UA. In 2020, the cases of time coefficients greater than 1 decreased, and less than −1 increased, which suggest high O3 pollution events alleviating and low O3 cases improving.
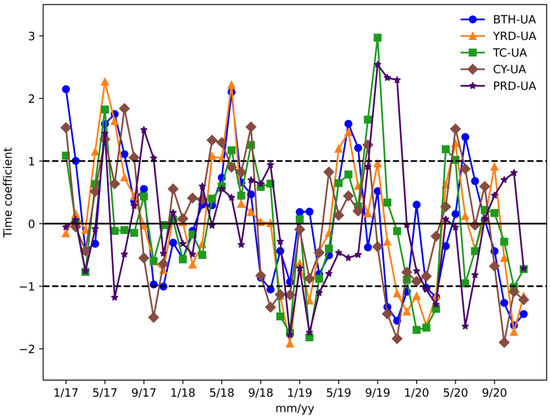
Figure 4.
Time coefficients of the monthly average of MDA8 O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations during 2017–2020.
3.3. Diurnal Variation
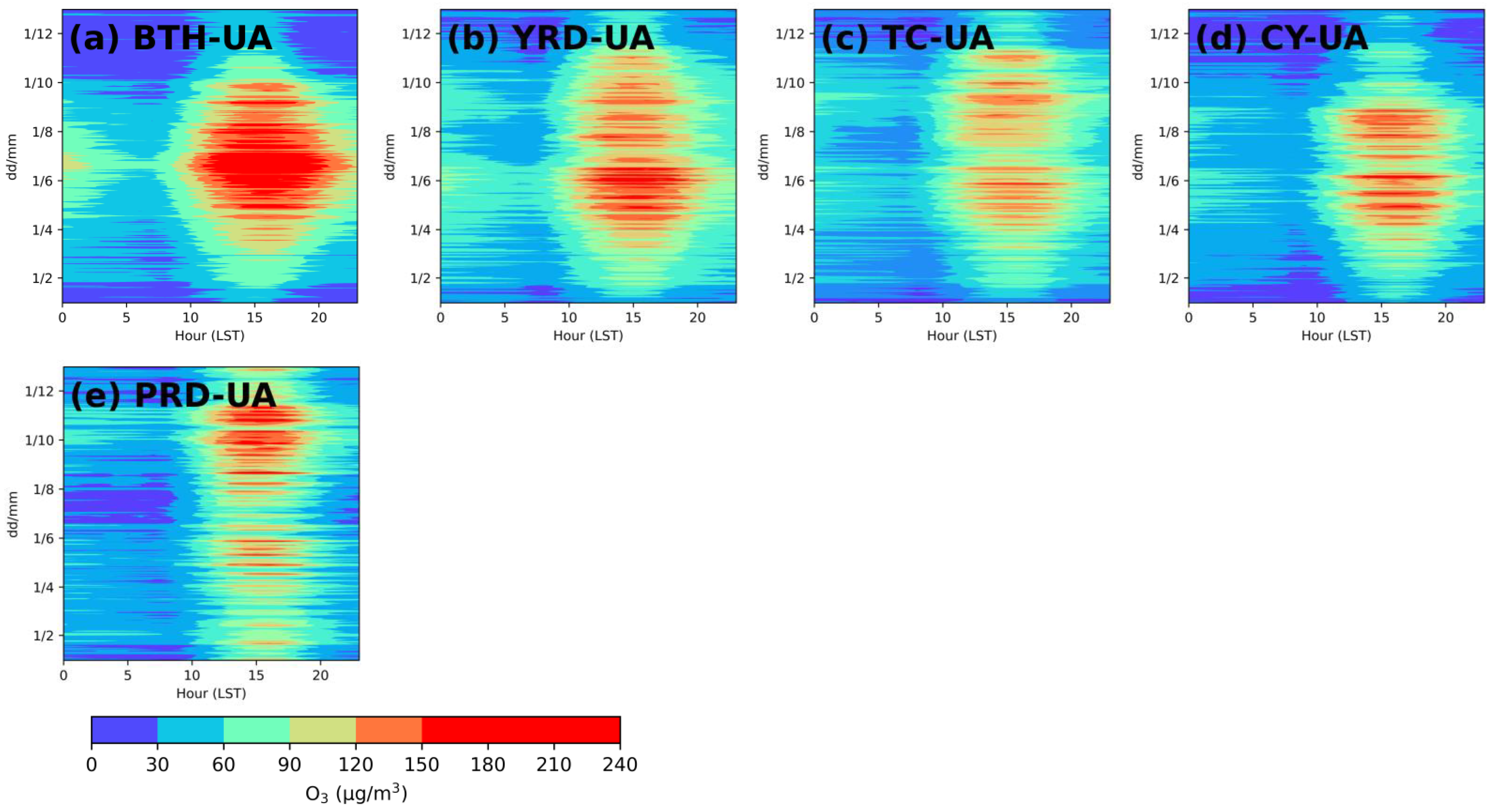
As a typical product of photochemical reactions, O3 diurnal variations were closely related to solar radiation. As displayed in Figure 5, O3 concentrations were much higher in the daytime than in the nighttime in all months in all five regions. At night, due to the absence of solar radiation, the photochemical reactions were weakened, leading to low O3 production. Moreover, the O3 concentration decreased rapidly due to the strong effect of the NO titration. In the daytime, with the sun rising, the O3 concentration increased at 7:00–8:00 (military time) with a peak appearing between 15:00 and 16:00 (Figure S2). All of China uses a single time zone (i.e., Beijing time); however, the five urban agglomerations were located across China, which was why the peak times varied. BTH-UA had the longest hourly O3 concentration of more than 150 μg/m3 (Figure 5a). In October and November, from 11:00 to 18:00, high concentrations of O3 were observed in PRD-UA (Figure 5e).
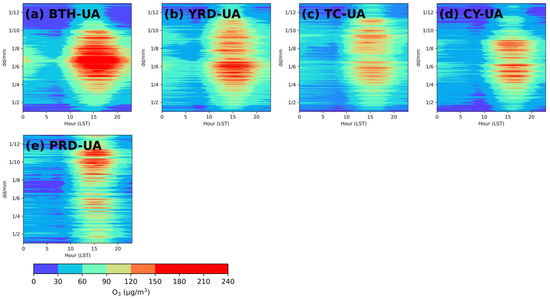
Figure 5.
Diurnal variations of O3 concentrations in (a) BTH-UA, (b) YRD-UA, (c) TC-UA, (d) CY-UA, and (e) PRD-UA during 2017–2020.
4. Spatial Variations of O3 in Five Urban Agglomerations
4.1. Standard Deviational Ellipse Analysis
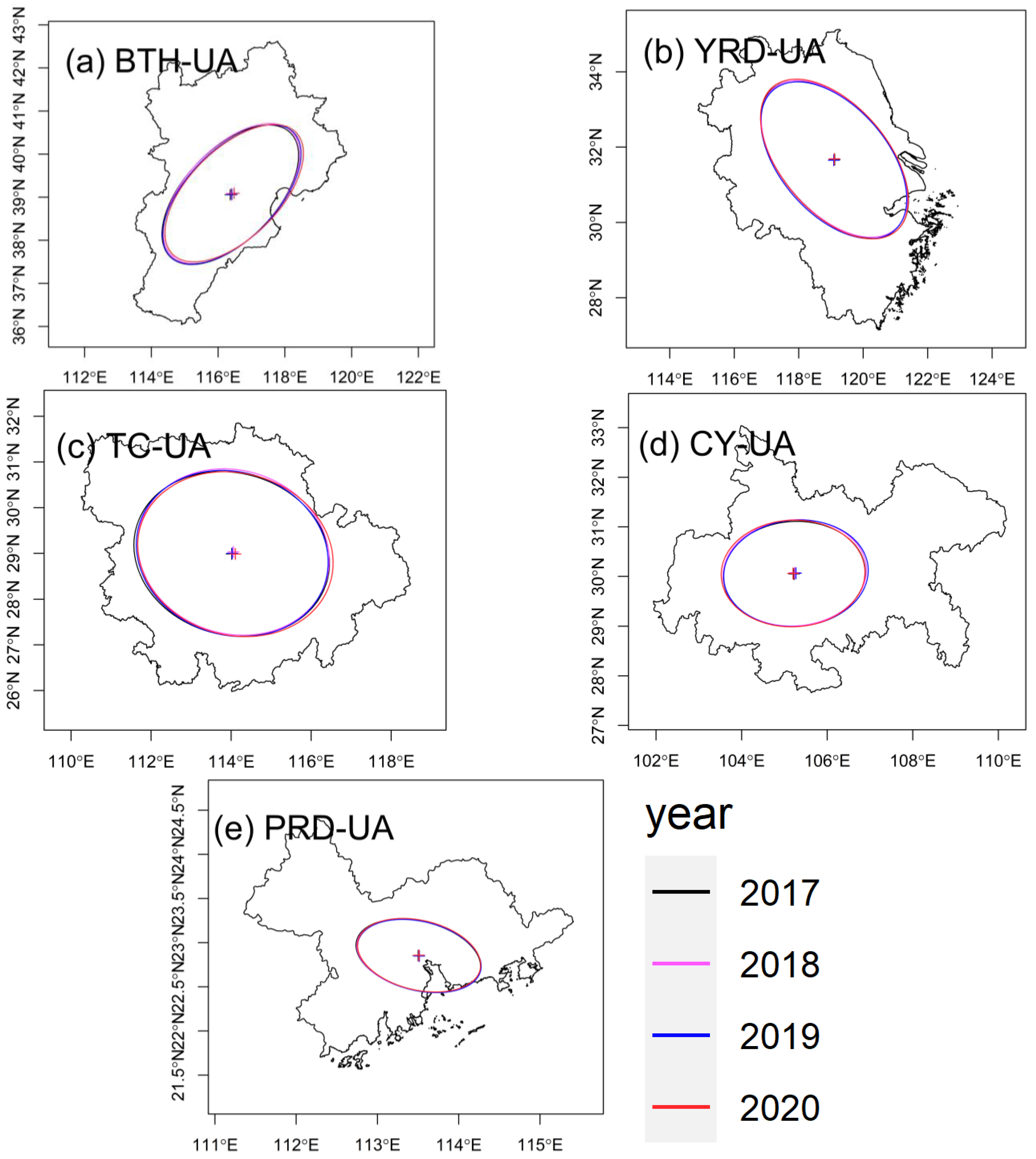
The overall variations in the spatial patterns of O3 across the five urban agglomerations between 2017 and 2020 were evaluated by SDE analysis, which displayed elements distributed within the main region (Figure 6, Table S1). In BTH-UA (Figure 6a), the main distribution of O3 concentration was aligned in northeast–southwest direction. The azimuth of the ellipse in BTH-UA (Table S1) increased from 56.37° in 2017 to 57.32° in 2020, indicating that the spatial pattern was moving eastward. The mean centers detected by SDE were located in southern BTH-UA, which suggest that O3 concentrations in southern BTH-UA were relatively high. The mean centers moved eastward with time, which could be attributed to the improvement of air quality in Xingtai and Handan, cities in southern Hebei Province. The ellipse area in 2020 was 1.4% lower than it had been in 2017, indicating a slight alleviation of regional O3 pollution. In YRD-UA (Figure 6b, Table S1), the main distribution was aligned in northwest–southeast direction and moved westward. The mean centers were located in northern YRD-UA, suggesting higher O3 concentrations in northern YRD-UA. The area covered by the ellipse increased from 2018 to 2020, which indicated O3 pollution expanded in YRD-UA. In TC-UA (Figure 6c, Table S1), the mean centers coincided with the geographical center (114.05° N, 28.95° E), which suggest that the spatial variation of O3 concentrations in TC-UA were slight. The mean centers moved eastward, which indicated a reduction in O3 pollution in the eastern region. Between 2018 and 2020, the ratio between the major and minor axes of the ellipses displayed an increasing tendency, suggesting that the directional trend became increasingly evident. In CY-UA (Figure 6d, Table S1), the main distribution was aligned in northeast–southwest direction. The mean centers were located in western CY-UA and moved westward. The minor axes of the ellipses increased from 236.9 km in 2017 to 240.4 km in 2020, which suggest that the O3 concentrations had spatially diffused. In PRD-UA (Figure 6e), the main distribution was aligned in northwest–southeast direction. The ellipse mainly covered the central PRD-UA, including Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Dongguan, Zhongshan, and Foshan, which indicated O3 concentrations in these cities were relatively high.
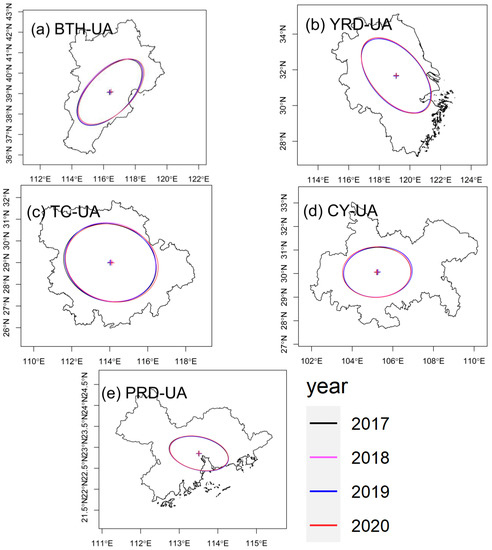
Figure 6.
Standard ellipse deviation in (a) BTH-UA, (b) YRD-UA, (c) TC-UA, (d) CY-UA, and (e) PRD-UA during 2017–2020.
4.2. Spatial Autocorrelation of O3 Concentrations
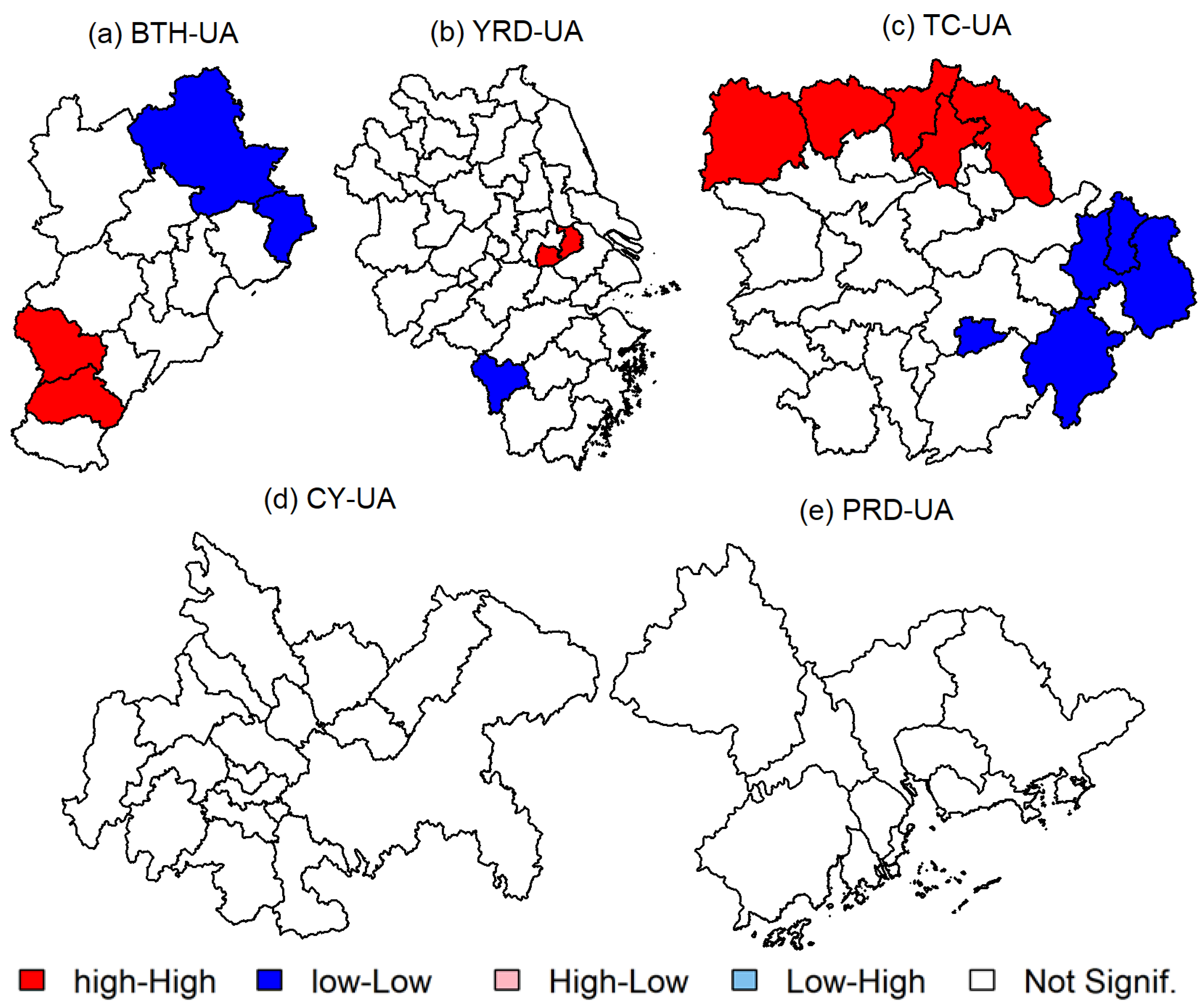
To further discuss the characteristics of O3 spatial correlation, the global Moran’s I was calculated in five regions. As listed in Table 1, all the values passed the significance test. In BTH-UA, the annual Moran’s I was 1.74, 1.94, 2.04, and 2.15 from 2017 to 2020, respectively, which indicated that the O3 concentrations had a positive spatial autocorrelation and the spatial agglomeration was strengthened each year. This also indicated that synergetic control of ozone pollution would be required for the cities in BTH-UA. The highest global Moran’s I in BTH-UA was found in winter (2.41) and the lowest in summer (0.89). We deduced that the strong atmospheric activity in summer contributed to the diffusion and mixing of O3, which made it difficult for O3 to accumulate in that region. In winter, the stable atmosphere led to the spatial agglomeration of O3. The most polluted cities were distributed in southern BTH-UA (Figure 7a), forming a high–high (HH) agglomeration of O3 concentration. Cities in northern BTH-UA had low O3 concentrations, forming a low–low (LL) agglomeration (Figure 7a). In YRD-UA, a positive spatial autocorrelation was also observed, which was consistent with previous research [53]. This indicated that the activities of several cities may have exerted a significant impact on the whole region and the regional transport of O3 may be crucial [53]. Meanwhile, a stronger spatial autocorrelation was found in spring than in autumn. In TC-UA, the global Moran’s I decreased between 2018 and 2020, indicating a weakening spatial autocorrelation of O3. As compared to BTH-UA and YRD-UA, O3 had the strongest spatial autocorrelation in summer in TC-UA. The cities in northern TC-UA, including Wuhan, Yichang, Jingmen, Xiaogan, and Huanggang, formed an HH agglomeration of O3 (Figure 7c). In CY-UA, the global Moran’s I were all less than 0 from 2017 to 2020, which indicated that O3 concentrations were spatially dispersed. The order of spatial dispersion by seasons was spring > autumn > summer > winter. In PRD-UA, O3 concentrations displayed positive spatial autocorrelation in 2017 and negative spatial autocorrelation during 2018–2020. Previous studies had found that O3 concentrations were spatially agglomerated in PRD-UA during 2007–2017 [54,55]. This indicated that the O3 spatial pattern in PRD-UA had changed in recent years. Regarding season variability, O3 concentrations were spatially agglomerated in summer and autumn and were spatially dispersed in spring and winter (Table 1). In summary, O3 mitigation measures by any individual city were insufficient on their own, and joint efforts among these cities would be necessary to reduce regional O3 pollution events.

Table 1.
Annual and seasonal variations of global Moran’s I index of O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations.
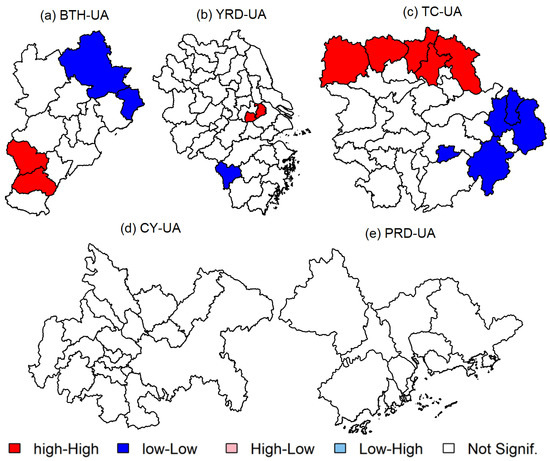
Figure 7.
Spatial agglomeration of MDA8 O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations in 2017–2020.
5. Regional Transport of O3 in Five Typical Cities
5.1. O3 Time Series Separated by KZ Filter
To discuss the regional transport of O3 in five urban agglomerations, five regional center cities were selected for further study: Beijing in BTH-UA, Shanghai in YRD-UA, Wuhan in TC-UA, Chengdu in CY-UA, and Shenzhen in PRD-UA. The KZ filter was employed to separate the original MDA8 O3 into short-term, seasonal, and long-term variations. The decomposition results are listed in Table 2 and Table S2. The time series of different components in five cities are displayed in Figures S3–S6. The covariance terms (K values in Table 2) were 4.4–9.0% for the total variances in the five cities, indicating an effective separation of different components. The seasonal components were 30.9–63.1% for the total variances in the five cities, suggesting O3 concentration was greatly influenced by seasonal change. The long-term components only accounted for 0.2–1.9% of the total variances in the five cities. The long-term components reflected the O3 fluctuations with a period greater than 632 days, which could be attributed to pollution emissions and climate change. The changing trend of long-term components varied in the five cities (Figure S6), with Beijing, Shanghai, and Chengdu initially showing a reduction before increasing, Wuhan consistently increasing, and Shenzhen fluctuating. The short-term components fluctuated between −2.2 and 1.3 (Figure S4). Considering that precursor emissions change slightly in the short term, the fluctuations in the short-term components were mainly caused by weather changes. In Shanghai and Shenzhen, the two coastal cities, the short-term components were 59.6% and 68.8% of the total variances (Table 2), respectively, which indicated O3 concentrations were more closely related to the weather and short-term fluctuations in precursor emissions. In Beijing, Wuhan, and Chengdu, the three inland cities, the season components were 53.3–63.1% of the total variances, which suggest O3 concentrations were more sensitive to seasonal variation.

Table 2.
Contributions of different components to the total variances of MDA8 O3 in five cities.
5.2. Backward Trajectory Analysis
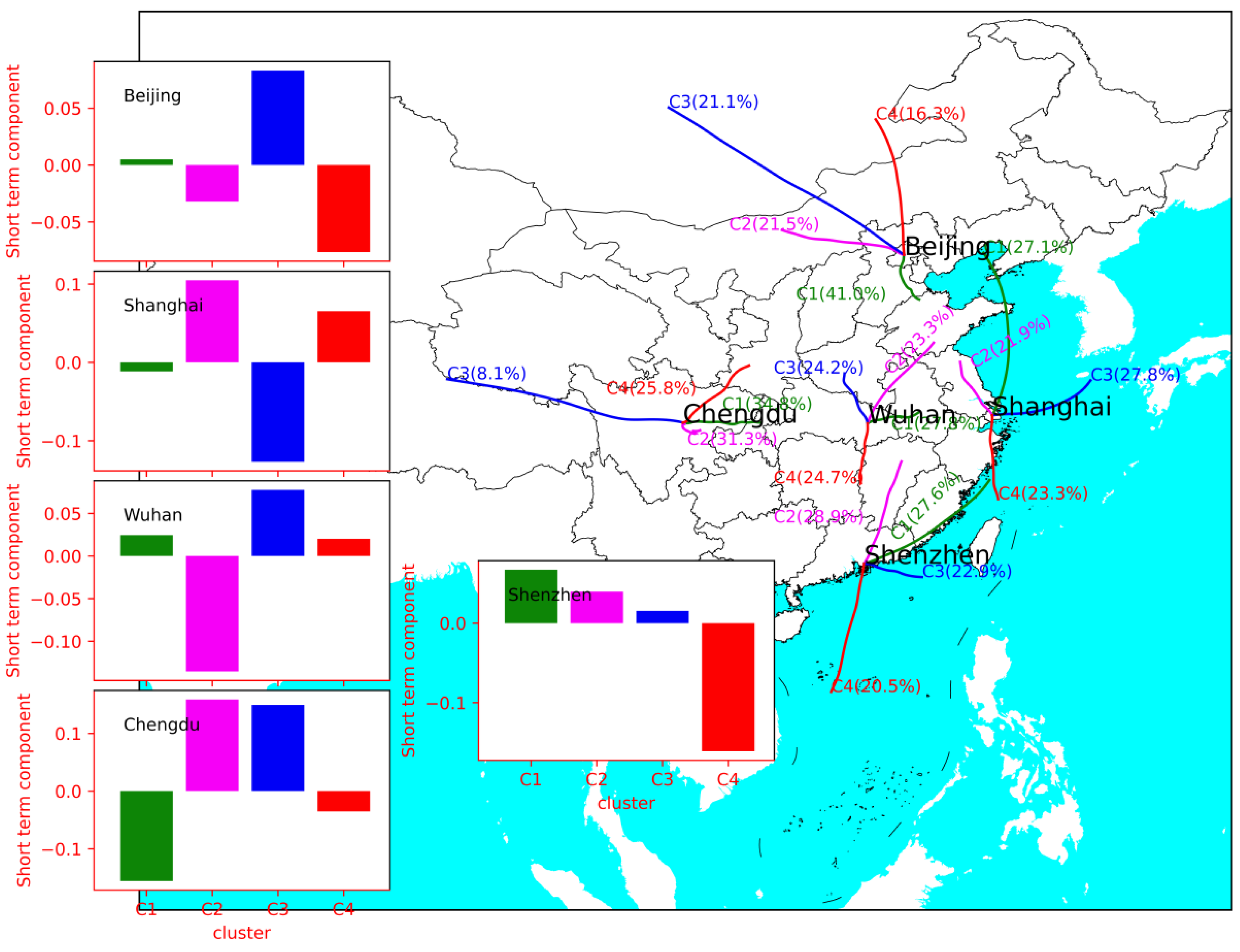
By using the HYSPLIT model, 48 h back trajectories starting at an arrival height of 10 m from Beijing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Chengdu, and Shenzhen were calculated at the hour of MDA8 O3 occurring during 2017–2020. Furthermore, 1461 trajectories in each city were used for cluster analysis. O3 concentration is greatly influenced by solar irradiation and seasonal variations. To further study the contribution of airflow transport in O3 concentrations, the KZ method was used to filter out the seasonal components related to solar radiation. The backward trajectory clustering and the short-term components of MDA8 O3 under the corresponding clusters are displayed in Figure 8.
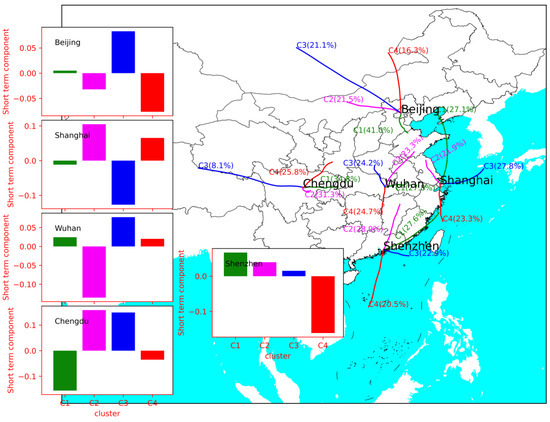
Figure 8.
Back trajectory clusters and the mean short-term components of MDA8 O3 under corresponding clusters in Beijing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Chengdu, and Shenzhen.
All trajectories in Beijing were classified into four categories, C1 (40.0%), C2 (21.5%), C3 (21.1%), and C4 (16.3%), corresponding to the short-term components of 0.005, −0.032, 0.083, and −0.076, respectively. C3, a long-distance transport, crossed Inner Mongolia and northwestern Hebei Province. C4 started in Outer Mongolia and passed through northern Hebei Province. This suggests that Beijing could be influenced by O3 transport from Inner Mongolia and northwestern Hebei Province. The airflow from northwest Shanghai (C2: 21.9%) and southern Shanghai (C4: 23.3%) increased the O3 concentration in Shanghai. Airflow from the sea (C3: 27.8%) reduced the O3 concentration in Shanghai; in Wuhan, C2 (23.3%) starting from Shandong Province and passing through northern Anhui Province corresponded to the short component of −0.135, indicating the scavenging effect on O3. C3 (24.2%), originating from Henan Province, increased O3 concentration in Wuhan. The trajectories of Chengdu were also classified into four categories, among which C1 (34.8%), C2 (31.3%), C3 (8.1%), and C4 (25.8%) corresponded to the short components of −0.156, 0.159, 0.149, and −0.035. This indicated the O3 concentration in Chengdu was influenced by regional transport. In Shenzhen, C1 (27.6%), C2 (28.9%), and C3(22.9%) increased the O3 concentration. C4 (20.5%), a long-distance trajectory from the sea, decreased O3 concentration in Shenzhen.
5.3. Potential Sources
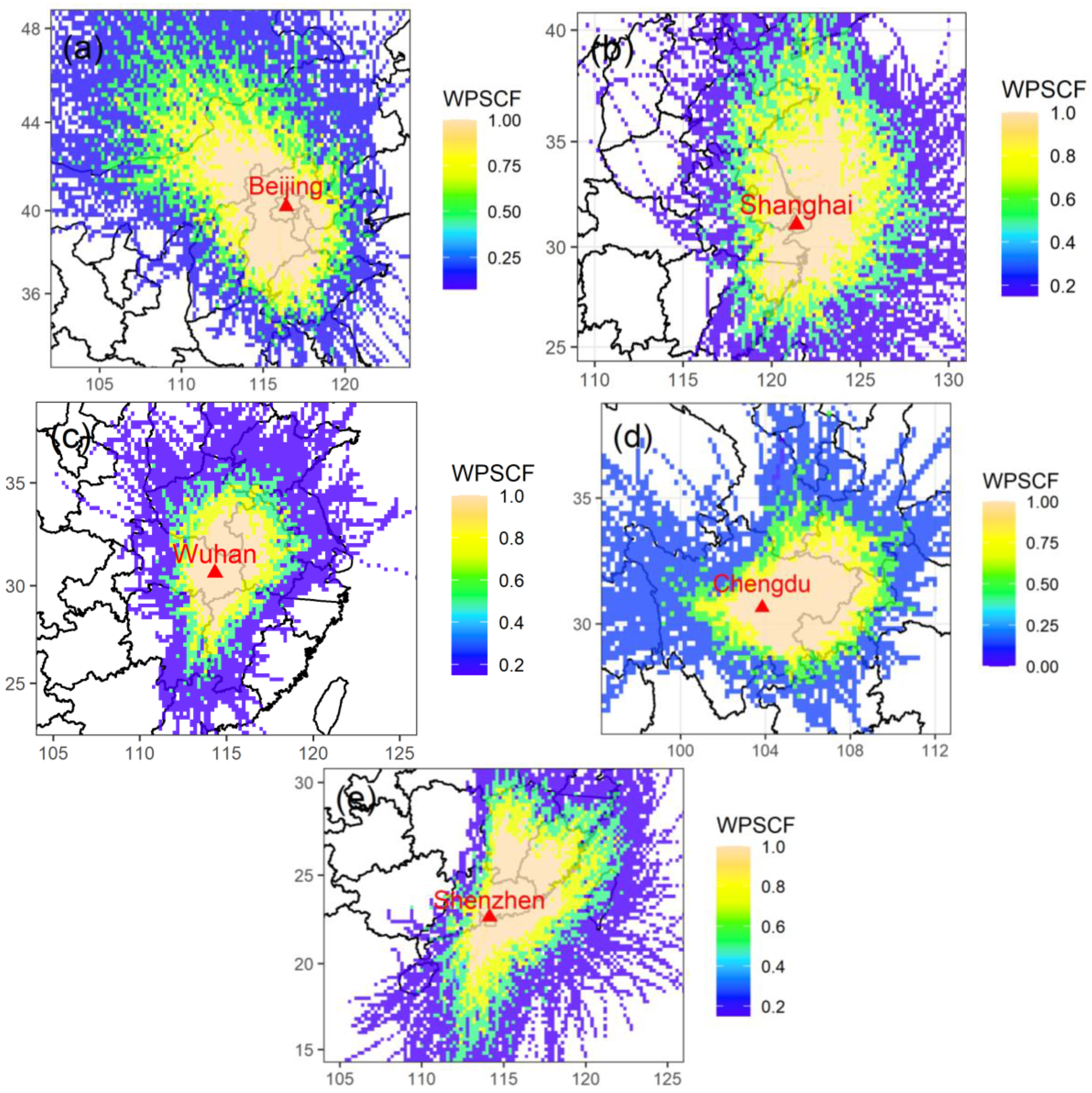
The PSCF model was used to identify the potential source areas for MDA8 O3 in Beijing, Shanghai, Wuhan, Chengdu, and Shenzhen. The spatial resolution of the study domain was 0.2° × 0.2°. As displayed in Figure 9a, cells with high WPSCF values were mainly located in northwestern and southern Beijing, including central Inner Mongolia, Hebei Province, and northwestern Anhui Province, which indicated that those regions were strong potential source areas influencing the O3 concentration of Beijing. In Shanghai, the strong potential source areas of O3 were mainly southern Jiangsu Province and northern Zhejiang Province, including Suzhou, Wuxi, Changzhou, Nantong, Jiaxing, Huzhou, Ningbo, and other cities (Figure 9b). In Wuhan, grids of WPSCF greater than 0.8 covered an area of about 180,000 km2 and fell mainly in eastern Hubei Province, southern Henan Province, and western Anhui Province (Figure 9c). In Chengdu, grids of WPSCF greater than 0.8 covered an area of about 201,000 km2 and fell mainly in eastern Sichuan Province and western Chongqing (Figure 9d). Eastern Guangdong Province, southern Jiangxi Province, and southern Fujian Province were the strongest potential source areas of O3 in Shenzhen (Figure 9e). Moreover, regional contributions of O3 in the five urban agglomerations were estimated by the TCEQ method. The regional contributions of O3 in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, TC-UA, CY-UA, and PRD-UA were 32.3%, 25.4%, 24.9%, 24.2%, and 30.1%, respectively (Figure S7). The photochemical reactions relating to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) were the main source of ground-level O3 [56]. In general, O3 formation regimes have been classified into three categories: VOC-limited, NOx-limited, and a transition regime [4]. In the five urban agglomerations, large O3 precursors were emitted due to intense human activities, such as vehicle emissions, industrial painting, printing production, among others, which caused local O3 pollution. Previous studies have shown that VOC-limited regimes dominated in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, and PRD-UA. The regional contribution in winter was smaller than that reported in other seasons. In summary, the potential source analysis for the five cities and the TCEQ analysis for the five urban agglomerations indicated that the local areas contributed primarily to O3 concentration and regional transport had an impact as well. As a secondary pollutant, O3 cannot be directly mitigated. A useful way to control O3 concentration is to reduce its precursors (e.g., NOx and VOCs). In general, reducing vehicles and industrial emissions is a typical approach. We found that the precise control of O3 precursors is needed. The methods of mitigation should be varied in different urban agglomerations according to each area’s predominant mechanism of O3 formation. To manage regional transport, joint efforts among cities and regions to reduce O3 concentrations would be necessary. In addition, more research is needed to better understand the O3 concentration distribution and sources.
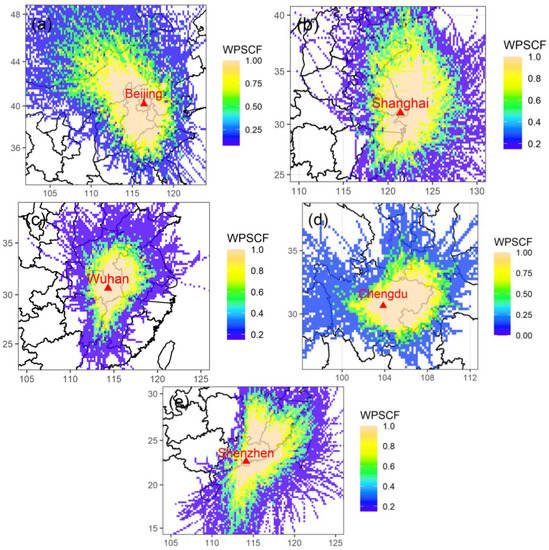
Figure 9.
Results of PSCF analysis for MDA8 O3 in (a) Beijing, (b) Shanghai, (c) Wuhan, (d) Chengdu, and (e) Shenzhen.
6. Conclusions
In this study, multiple transdisciplinary methods, such as statistical analysis, geographical analysis, spatial statistics, filter analysis, and potential source analysis, were employed to investigate the spatiotemporal patterns and regional transport of O3 in China’s five urban agglomerations.
We found that the proportion of MAD8 O3 that exceeded the Grade 2 limit in the five urban agglomerations ranged from 16.4% to 38.0% during 2017–2020, and O3 concentrations decreased 8.4–21.6% in 2020, as compared to 2017. Monthly changes of O3 exhibited a unimodal structure in BTH-UA and a bimodal structure in the other four urban agglomerations. MDA8 O3 had maximum values in autumn in PRD-UA and in summer in the other urban agglomerations. O3 pollution events frequently occurred in May. O3 diurnal variations were closely related to solar radiation in the five regions, with higher values in daytime and lower values at night. Concerning spatial distribution, the main distribution of O3 concentration was aligned in northeast–southwest direction for BTH-UA and CY-UA and was aligned in northwest–southeast direction for YRD-UA, TC-UA, and PRD-UA. The mean pollution centers in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, TC-UA, CY-UA, and PRD-UA were located in the south, north, center, west, and south of the region, respectively. O3 concentrations exhibited positive spatial autocorrelations in BTH-UA, YRD-UA, and TC-UA and negative spatial autocorrelations in CY-UA and PRD-UA. We also found that the O3 spatial correlation in the five urban agglomerations varied by season.
To discuss the regional transport of O3, the five regional center cities were selected for further study. The KZ filter was employed to decompose the original O3 time series. The decomposition results suggest O3 concentrations were influenced mainly by the short-term and seasonal components. The combined analysis of the HYSPLIT model and the KZ filter demonstrate that airflows from different directions have different short-term components. The airflows from the northwest increased O3 concentrations in Beijing and Wuhan. The southeastern airflows increased O3 concentrations in Chengdu. Long-distance airflows from the sea decreased O3 concentration in Shanghai and Shenzhen. PSCF and TCEQ analyses indicate that local areas were the main contributors to O3 concentrations, and regional transports played a significant role, as well. Our findings suggest that joint efforts across cities and regions will be needed to decrease the O3 concentrations in the major urban agglomerations in China.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13020301/s1, Figure S1: Seasonal average values of MDA8 O3 concentrations in five urban agglomerations in 2017–2020, Figure S2: Diurnal variations of O3 in five regions during 2017~2020, Figure S3: The original time series of MDA8 O3 in five cities, Figure S4: The short-term components of MDA8 O3 decomposed by KZ filter in five cities, Figure S5: The seasonal components of MDA8 O3 decomposed by KZ filter in five cities, Figure S6: The long-term components of MDA8 O3 decomposed by KZ filter in five cities, Figure S7: The estimated regional contributions of O3 in different seasons in five urban agglomerations during 2017–2020 by the TCEQ method, Table S1: Parameters of standard deviation ellipse in five urban agglomerations during 2017–2020, Table S2: Variances of different MDA8 O3 components decomposed by KZ filter in five cities.
Author Contributions
X.L., data curation, investigation, methodology, software, supervision, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing; C.Z., methodology; J.N., methodology, software, supervision; D.Y., writing—review and editing; F.X., software; F.S., J.Y., X.S. and T.J., data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41771438), the Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (Grant No. 22IRTSTHN010), and the Key Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province of China (Grant No. 18A170013).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, D.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, D.; Dong, L. PM2.5 and O3 pollution during 2015–2019 over 367 Chinese cities: Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Pan, X.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yue, X.L.; Zhang, D.H.; Ma, Z.G.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Lei, S.D.; et al. Chemical formation and source apportionment of PM2.5 at an urban site at the southern foot of the Taihang mountains. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Lyu, X.; Cheng, H.; Ling, Z.; Guo, H. Overview on the spatial-temporal characteristics of the ozone formation regime in China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 916–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Zhao, B.; Fan, S.; Li, M.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Huang, R. Source impact and contribution analysis of ambient ozone using multi-modeling approaches over the Pearl River Delta region, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 289, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Lyapustin, A.; Sun, L.; Peng, Y.; Xue, W.; Su, T.; Cribb, M. Reconstructing 1-km-resolution high-quality PM2.5 data records from 2000 to 2018 in China: Spatiotemporal variations and policy implications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Lv, J.G.; Tan, Y.F.; Guo, M.; Gu, Y.Y.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.H. Temporospatial variations and Spearman correlation analysis of ozone concentrations to nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matters and carbon monoxide in ambient air, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Dickerson, R.R.; Pinker, R.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, L.; Xue, W.; Cribb, M. Full-coverage mapping and spatiotemporal variations of ground-level ozone (O3) pollution from 2013 to 2020 across China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 270, 112775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shi, Z.H.; Sun, J.J.; Gong, K.J.; Li, J.Y.; Qin, M.M.; Wei, J.; Li, T.T.; Kan, H.D.; et al. Effects of using different exposure data to estimate changes in premature mortality attributable to PM2.5 and O3 in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yin, H.; Tang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.L.; Yi, H.H. Transition in air pollution, disease burden and health cost in China: A comparative study of long-term and short-term exposure. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.Z. Effects of O3 pollution near formation on crop yield and economic loss. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.C.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, H.; Ma, M.R.; Chang, M. Evaluating the effects of ground-level O3 on rice yield and economic losses in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, K.Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Shao, T.; Zhang, H.L. Coordinated control of PM2.5 and O3 is urgently needed in China after implementation of the “air pollution prevention and control action plan”. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 129441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.T.; Alatalo, J.M.; Jiang, B. Temporal variations in ambient air quality indicators in Shanghai municipality, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.W.; Deng, T.; Wu, D.; Wu, C.; Huang, X.F.; Li, Z.N.; Yin, C.Q.; Zou, Y.; Song, L.; Ouyang, S.S.; et al. Characteristics of boundary layer ozone and its effect on surface ozone concentration in Shenzhen, China: A case study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Wu, K.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, Y.M.; Gu, S.; Lu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Hu, Y.S.; Ou, Y.H.; Wang, S.G.; et al. Summertime ozone pollution in Sichuan basin, China: Meteorological conditions, sources and process analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 226, 117392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jia, H.; Sha, T.; An, J.; Tian, R. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of particulate matter and gaseous pollution in China: Implications for control policy. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.Z.; Cui, L.L.; Fu, H.B.; Zhang, L.W.; Kong, L.D.; Chen, W.D.; Chen, J.M. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015-2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, L.G.; Griffin, R.J.; Masiello, C.A. Regional background O3 and NOx in the Houston-Galveston-Brazoria (TX) region: A decadal-scale perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6565–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, K.J.; Li, L.; Li, J.Y.; Qin, M.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Ying, Q.; Liao, H.; Guo, S.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.H.; et al. Quantifying the impacts of inter-city transport on air quality in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China: Implications for regional cooperative controls of PM2.5 and O3. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Yim, S.H.L.; Dong, G.H.; Ho, K.F.; Wong, D.C. Mapping ozone source-receptor relationship and apportioning the health impact in the Pearl River Delta region using adjoint sensitivity analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; An, J.Y.; Huang, L.; Yan, R.S.; Huang, C.; Yarwood, R. Ozone source apportionment over the Yangtze River Delta region, China: Investigation of regional transport, sectoral contributions and seasonal differences. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.N.; Dai, H.C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.Q. Health and economic benefits of cleaner residential heating in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. Energy Policy 2019, 127, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Fang, X.; Ji, H.Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.W. Spatiotemporal patterns of recent PM2.5 concentrations over typical urban agglomerations in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Duan, F.K.; He, K.B.; Qin, Y.; Tong, D.; Geng, G.N.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Ye, S.Q.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relationship with emissions and meteorology in the Yangtze River Delta region during 2014-2016. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 83, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lang, J.L.; Ren, Z.H.; Sun, C. Development of emissions inventory and identification of sources for priority control in the middle reaches of Yangtze River urban agglomerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.T.; Wang, S.; Ai, J.; Gui, K.; Duan, B.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.T.; Sun, Y. Heavy pollution episodes, transport pathways and potential sources of PM2.5 during the winter of 2013 in Chengdu (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.J.; Wang, S.; Gong, Z.Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.Y. Regionalization based on spatial and seasonal variation in ground-level ozone concentrations across China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.F.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, X.N. Spatiotemporal distribution of ground-level ozone in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; He, S.X.; Zhou, H.F. Spatio-temporal characteristics and convergence trends of PM2.5 pollution: A case study of cities of air pollution transmission channel in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, G.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, F. Characteristics of PM2.5 spatial distribution and influencing meteorological conditions in Sichuan basin, southwestern China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 253, 118364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, Z.M.; Chen, K.; Tang, M.; Zheng, N.Y.; Li, P.; Yang, N.; Yang, W.; Deng, X.W. Spatial and temporal distribution, chemical characteristics, and sources of ambient particulate matter in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhao, A.; Li, Z.; Gu, X. Long-term trends and spatial patterns of PM2.5-induced premature mortality in south and southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachowicz, M.; Liu, T.Y. Finding spatial outliers in collective mobility patterns coupled with social ties. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1806–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.F.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ha, X.Z. Spatial-temporal patterns of PM2.5 concentrations for 338 Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, S.; Tan, Y. Temporal characteristic and source analysis of PM2.5 in the most polluted city agglomeration of China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, S.R.; Langford, A.O.; Estes, M.; Dong, M.; Parrish, D.D. Magnitude, decadal changes, and impact of regional background ozone transported into the greater Houston, Texas, area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13985–13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielson-Gammon, J.; Tobin, J.; Mcneel, A.; Li, G. A Conceptual Model. for Eight-Hour Ozone Exceedances in Houston, Texas Part. I: Background Ozone Levels in Eastern Texas; Texas A&M University: College Station, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.T.; Zalewsky, E.; Zurbenko, I.G. Determining temporal and spatial variations in ozone air quality. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1995, 45, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; Quan, W.J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, W.L.; Xu, X.B. Significant increase of surface ozone at a rural site, north of eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3969–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, S.T.; Zurbenko, I.G. Detecting and tracking changes in ozone air quality. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1994, 44, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo-Castaneda, D.M.; Teixeira, E.C.; Pereira, F.N. Time-series analysis of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides concentrations in an urban area at Brazil. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q. The analysis and application of a new hybrid pollutants forecasting model using modified Kolmogorov-Zurbenko filter. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, E.K.; Comrie, A.C. Extending the Kolmogorov-Zurbenko filter: Application to ozone, particulate matter, and meteorological trends. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Lee, K.H. Estimation of potential source regions of PM2.5 in Beijing using backward trajectories. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.P.; Yin, D.Y.; Qu, J.J. Identifying sources of dust based on Calipso, Modis satellite data and backward trajectory model. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. Noaa’s Hysplit atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Wang, Z.F.; He, H.; Wang, D.W.; Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, W.L.; Li, J. Chemical characteristics and potential sources of PM2.5 in Shahe city during severe haze pollution episodes in the winter. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2741–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.R.; Yuan, W.P.; Lv, J.L. Regional sources and the economic cost assessment of PM2.5 in Ji’nan, eastern China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tan, Q.W.; Feng, M.; Qu, Y.; An, J.L.; Deng, Y.J.; Zhai, R.X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Characteristics, source apportionment and chemical conversions of VOCs based on a comprehensive summer observation experiment in Beijing. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, B.; Shao, M.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Lu, K.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Chang, C.C.; Liu, S.C. Variations of ground-level O3 and its precursors in Beijing in summertime between 2005 and 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, C.Q.; Solmon, F.; Deng, X.J.; Zou, Y.; Deng, T.; Wang, N.; Li, F.; Mai, B.R.; Liu, L. Geographical distribution of ozone seasonality over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.P.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.Y.; He, J.J.; Liu, N.; Qu, J.J.; Xiao, J.H. Annual and diurnal variations of gaseous and particulate pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities based on in situ air quality monitoring data from China national environmental monitoring center. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xie, D.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Wu, H.; Han, J.; Liu, L.; Jia, W. Quantification of regional ozone pollution characteristics and its temporal evolution: Insights from identification of the impacts of meteorological conditions and emissions. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Lin, J.; Chen, W.; Lin, M.; Lei, C. Spatial-temporal distribution variation of ground-level ozone in China’s Pearl River Delta metropolitan region. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).