Abstract
Although combustion is considered a common source of ammonia (NH3) in the atmosphere, field measurements quantifying such emissions of NH3 are still lacking. In this study, online measurements of NH3 were performed by a cavity ring-down spectrometer, in the cold season at a rural site in Xianghe on the North China Plain. We found that the NH3 concentrations were mostly below 65 ppb during the study period. However, from 18 to 21 November 2017, a close burn event (~100 m) increased the NH3 concentrations to 145.6 ± 139.9 ppb. Using a machine-learning technique, we quantified that this burn event caused a significant increase in NH3 concentrations by 411%, compared with the scenario without the burn event. In addition, the ratio of ∆NH3/∆CO during the burn period was 0.016, which fell in the range of biomass burning. Future investigations are needed to evaluate the impacts of the NH3 combustion sources on air quality, ecosystems, and climate in the context of increasing burn events worldwide.
1. Introduction
As an important alkaline gas in the atmosphere, atmospheric ammonia (NH3) has a crucial influence on atmospheric chemistry and the nitrogen cycle [1,2]. It can react with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), and enhance the formation of secondary inorganic aerosols (SIAs) [3]. Additionally, NH3 can enhance the yield of secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) through aqueous chemistry [4]. These particulate SIAs and SOAs in the air decrease visibility, damage human health, and affect the climate [5,6,7,8,9]. After deposition, NH3 can directly or indirectly affect terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, such as soil acidification, water eutrophication, and reduction in biodiversity [10,11,12]. Thus, identifying and quantifying the sources of NH3 is essential to understanding its vital role in atmospheric chemistry and reducing its negative impacts on the ecosystem and climate.
Although livestock waste and nitrogen fertilization are considered the most important sources of NH3 emissions on a global or regional scale [13,14], NH3 is also emitted into the atmosphere during the fuel combustion process through pyrolysis [15]. Biomass burning, such as forest fires, plays a critical role in NH3 emissions in rural areas. For example, 1.4–8.2 and 0.7–2.6 Tg of NH3 were emitted from forest fires in Indonesia in autumn in 2015, and Russia in July–August 2010, respectively [16,17], and 0.12 Mt of NH3 was emitted from agricultural crop residue burning in India from 2008 to 2009 [18]. In urban areas, the nitrogen isotopic approach indicates that NH3 originated primarily from combustion sources, including coal combustion, NH3 slip from power plants, and vehicle exhausts [19,20,21]. A high-resolution global inventory revealed that NH3 emissions from combustion sources continued to increase from 1960 to 2013 [22]. In China, an average of 8182 forest fires occurred from 1987 to 2007 [23]. The elevated fire frequencies were partially due to climate change [24]. Thus, the impact of combustion sources on NH3 concentrations and related consequences needs further attention.
China is a global hotspot of atmospheric NH3 emissions, with an annual increasing rate of 1.9% [25]. Notably, the North China Plain (NCP) is confirmed to be the largest region with high surface concentrations, and the highest emissions in China [26]. Despite the pollution reduction actions implemented since 2013, severe haze pollution events still occur in the cold season in this region. For example, the highest PM2.5 concentration reached approximately 250 μg/m3 in winter in 2020 [27], and it was dominated by sulfate–nitrate–ammonium (SNA), especially nitrate aerosols [28]. Recent studies have suggested that NH3 plays an important role in determining nitrate concentrations [29,30]. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the concentrations of NH3 and investigate its emission sources in this region.
In this study, we performed online measurements of NH3 in the cold season in Xianghe, a rural site in NCP. During the observation campaign, we detected an unexpected burn event that had a significant influence on the NH3 concentrations. Finally, we attempted to combine a novel machine-learning technique based on the random forest (RF) algorithm, to quantify the impact of burn events. Such an understanding could be beneficial for controlling NH3 emissions and further improving air quality in the future.
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Site Description
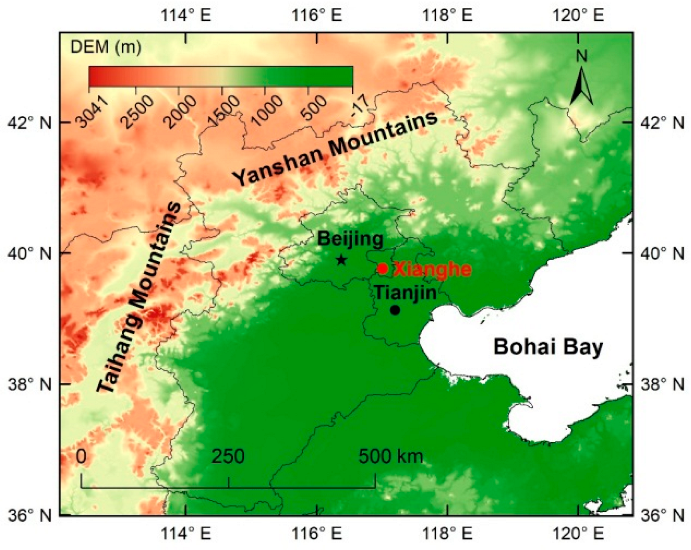
Since 2017, online measurements of NH3 concentrations have been performed in Xianghe, NCP (39.75° N, 116.96° E) (Figure 1). The site is surrounded by residential areas that lack tall buildings and obvious industrial emission sources. Based on its location in the northern part of the NCP between Beijing (~45 km) and Tianjin (~70 km), the instruments at the site can detect pollutants of urban, rural, background or mixed origins, reflecting the complex changes in NH3 in the NCP.
Figure 1.
Location of the NH3 observation site in Xianghe.
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Measurements of NH3
Hourly concentrations of NH3 were measured at a high temporal resolution of 1 Hz, online, using a standard cavity ring-down spectrometer (CRDS) (G2103, Picarro Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA). CRDS is a direct absorption technique that uses pulsed or continuous light sources and has a significantly higher sensitivity than conventional spectrometers [31]. In CRDS, two high reflectivity mirrors are used in the optical cavity to increase the absorption optical path length, thereby enhancing the contrast of the absorption signal of NH3. The CRDS setting measures how long it takes for the light to drop to a certain percentage of its original intensity, and the “ring-down time” is used to calculate the concentration of NH3 in the cavity [32].
To prevent water vapor from affecting the NH3 spectrum, the manufacturer has incorporated a correction procedure for the reported NH3 values [33]. In addition, to reduce the adsorption of NH3, the Teflon tubing was insulated and warmed with heating tape (~45.7 °C). Meanwhile, a filter was installed at the front of the inlet to induce ambient air flow. According to the air conditions, the filter was replaced every 2 weeks to 1 month. The instrument was placed in an air-conditioned cabin laboratory; more detailed descriptions are documented elsewhere [34].
2.2.2. Other Supporting Data
Air pollutants and meteorological data are also used in this study. The hourly concentrations of SO2, NOx, CO, and PM2.5 were measured at the same height as NH3. Meteorological parameters, including temperature (T), relative humidity (RH), wind speed (WS), and wind direction (WD), were obtained from the China Meteorological Administration (http://data.cma.cn (accessed on 14 October 2021)).
2.2.3. Burn Event
During the observation campaign, a burn event occurred from 18 to 21 November, 2017. This burn event was caused by the combustion of garbage in the nearby residential area, which was approximately 100 m away from the observation site. The burned material was complex and included discarded paper, kitchen waste, crop residues, weeds, branches, and leaves.
2.3. RF Models
The temporal variations in NH3 in this study demonstrated a cycle ranging from 4 to 7 days. These strong cycles are regional in nature and controlled by the passage of cold fronts [35]. This unique temporal feature indicated that the results presented are reproducible on a regular basis, and applicable for the RF model in predicting NH3 dynamics with meteorological conditions.
In this study, we used a machine-learning technique to quantify the influence of burn events on NH3 concentrations. First, we established a model (RF1) with observed NH3 concentrations as the dependent variable, and predictors (meteorological parameters, time predictors, and regional transport parameters) as the independent variables (Table 1). RF1 was trained on datasets during the nonburning period (8–17 and 22–30 November 2017). The training set accounted for 80% of data, and the testing set included the remaining 20%. On the basis of RF1, a series of models (RF2–RF11) were established, according to the relative importance of the predictor variables for eliminating or adding some predictors (Table S1). A detailed evaluation of all the established models is provided in Table S2, including the coefficients of determination (R2), the fraction of predictions within a factor of 2 (FAC2), mean bias, normalized mean bias, root-mean-square error (RMSE), and Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC). The performance of RF5 was considered the best due to its higher R2 and lower RMSE.

Table 1.
All possible predictors for the RF models in this study.
The RF models were developed using the rmweather R package. However, unlike previous studies, we further adjusted two important parameters of RF5, namely, the number of trees (ntree) and the number of variables split in each node (mtry). Mtry values from 1 to 8 with an interval of 1, and ntree values from 50 to 500 with an interval of 50, were selected. As shown in Figure S1, when ntree was 300 and mtry was 5, the simulation effect of the model was best, as indicated by the higher R2 value and lower prediction error (MSE).
After the RF model was adjusted and optimized, the testing datasets were randomly selected to assess the correlation between the observed and predicted concentrations (Figure S2), to ensure that this model could make better predictions. Finally, we used this model to predict NH3 concentrations under the assumption of no burn events. To evaluate the impact of the burn events (18–21 November 2017) on NH3 concentrations, relative changes (R) between the observed concentrations (Cobserved) and predicted concentrations (Cpredicted) for NH3 were defined using the following equation:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Observed Concentrations of NH3
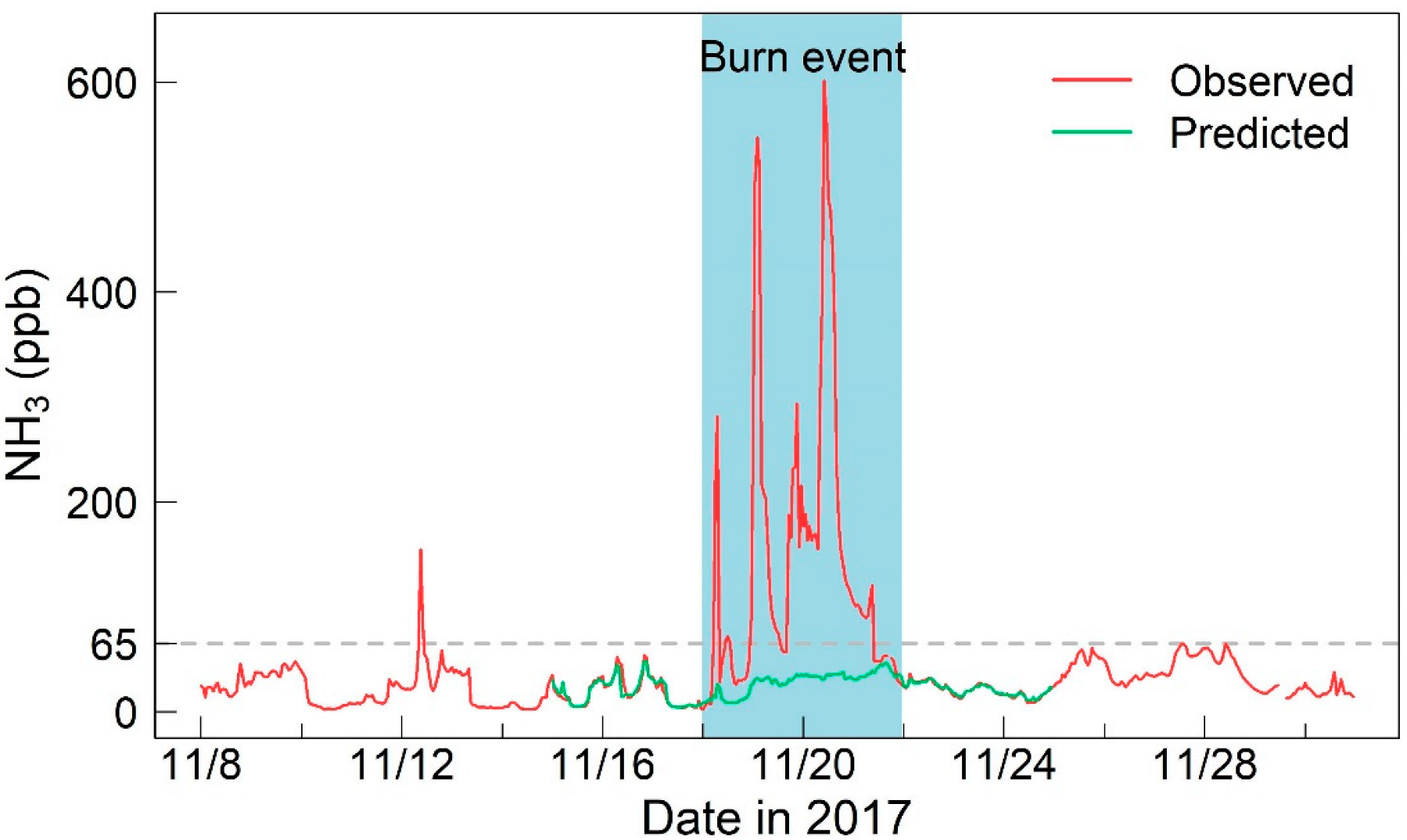
Hourly concentrations of NH3 were selected from 8 to 30 November 2017 in this study, and their temporal variations are shown in Figure 2. We found that the NH3 concentrations were mostly below 65 ppb during the study period, with the exception of 18–21 November, when a burn event occurred. Therefore, in the following sections, we have separated the dataset into two periods, i.e., the burning period (18–21 November 2017) and the nonburning period (8–17 and 22–30 November 2017).
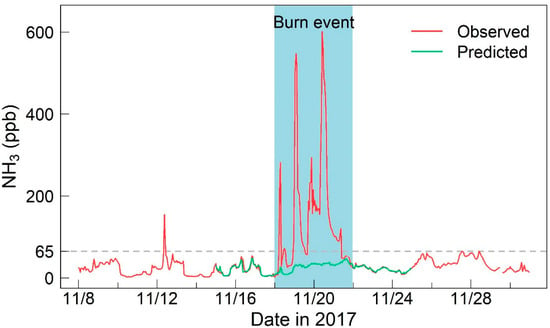
Figure 2.
Temporal variation in hourly concentrations of NH3. The gray line indicates an NH3 concentration of 65 ppb. The blue shaded area represents the burning period, and the non-shaded area represents the nonburning period.
During the nonburning period, the NH3 concentrations in Xianghe ranged from 1.9 to 154.3 ppb, with a mean value of 25.4 ± 16.9 ppb. The NH3 concentrations in this study were comparable to the urban observations (28.5 ± 11.6 ppb) in autumn in Beijing [36]. Moreover, the average NH3 level measured in Xianghe was generally similar to observations in India (24.6 ± 5.0 ppb) [37], but much higher than those in Europe (1.2 ppb) and the United States (2.4 ppb) in autumn [10,38].
After the start of the burn event, the observed concentrations of NH3 significantly increased, with the highest value exceeding 600 ppb. In addition, three concentration spikes occurred: at 7:00, 18 November (281.6 ppb); 2:00, 19 November (547.1 ppb); and 10:00, 20 November (601.4 ppb). During the burning period, the average NH3 concentration was 145.6 ± 139.9 ppb, which is five times that in a previous report (26.6 ± 13.9 ppb) at the Xianghe site in the cold season [39].
In addition to NH3, the concentrations of other air pollutants also significantly increased during the burning period, e.g., by 209.7%, 84.3%, 69.1%, and 79.8% for PM2.5, SO2, NOx, and CO, respectively (Figure S3). These air pollutants had a positive correlation with NH3 during the burning period, especially CO (R2 = 0.74, p < 0.01) and NOx (R2 = 0.72, p < 0.01). However, their positive correlation was not significant in the nonburning period (Table S3). These results all indicated the potential influence of combustion sources on air quality. In addition, the intensity of combustion was closely related to weather conditions [40]. In our study, the NH3 concentrations were higher during the burning period when the air mass originated from the northwest, and had a higher RH (56.2 ± 26.3%) and lower T (−1.1 ± 5 °C) and WS (1.6 ± 1.5 m s−1) (Figure S4). To quantify the impact of the burn events on NH3, we predicted NH3 concentrations without burn events using a machine-learning technique in the next section.
3.2. Changes in Predicted Concentrations of NH3
We first established a model (RF5) to predict the NH3 concentrations assuming that no burn event occurred from 18 to 21 November 2017. The predicted results are shown in Figure 2, with all predicted concentrations lower than 65 ppb. In addition, the temporal variation in predicted NH3 concentrations was basically similar to its observed value in the nonburning period. This finding indicates that the concentrations and temporal pattern of NH3 will not change significantly if there is no burn event.
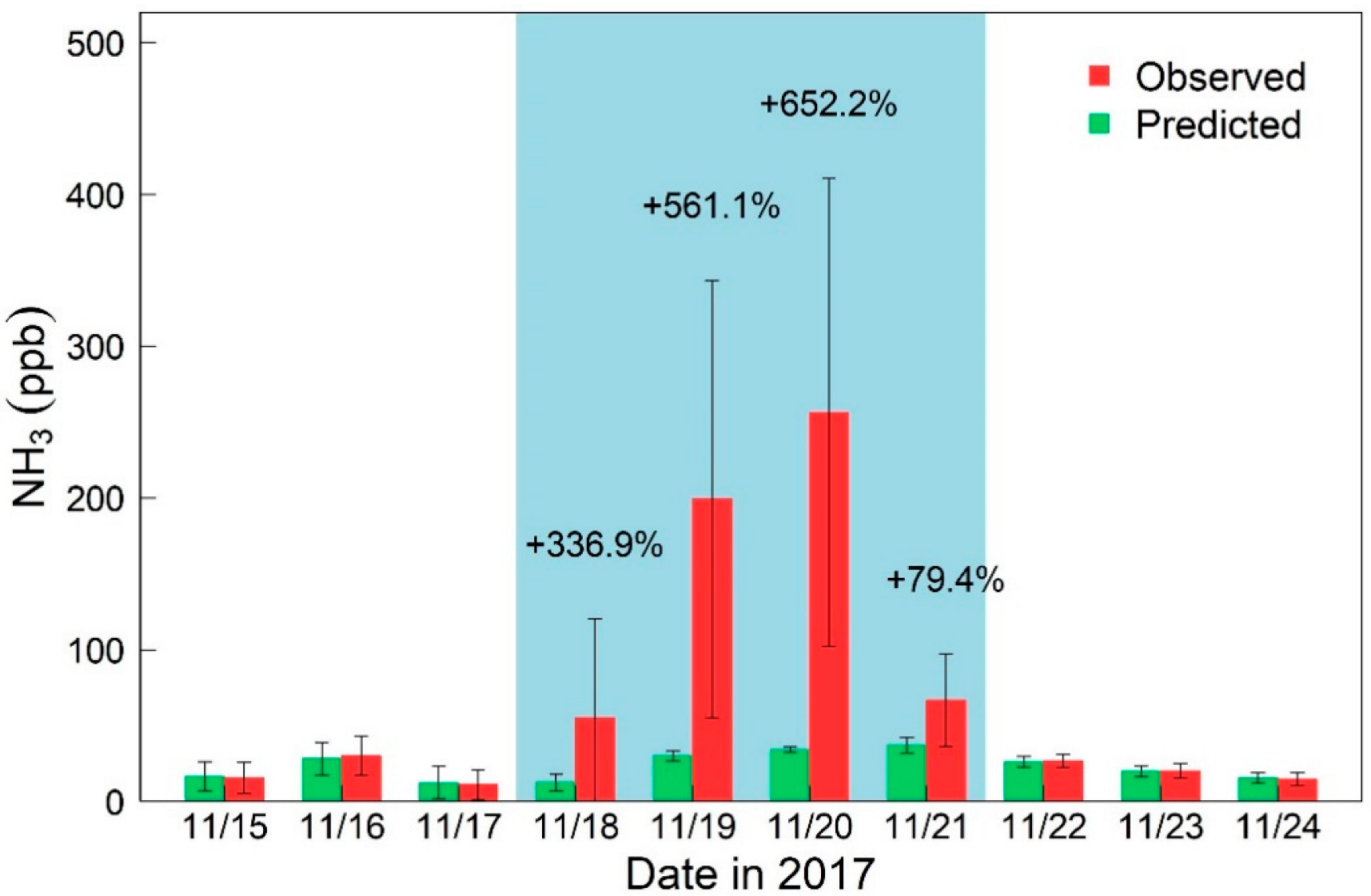
The difference between the predicted and observed concentrations of NH3 allows us to quantify the impacts of burn events on NH3 emissions. As shown in Figure 3 and Table S4, remarkable differences were not found between the observed and predicted concentrations of NH3 before the burn event, indicating that our model captured the variations in NH3 concentrations well. However, the observed concentration of NH3 increased drastically compared with the predicted value during the burning period, with increased ratios of 336.9%, 561.1%, and 652.2% in the first three days of the burn event. At the end of the burning period and with the resumption of “normal emissions”, the predicted values were consistent with the observations after 22 November. Overall, the observed and predicted concentrations of NH3 during the burning period were 145.6 ± 139.9 and 28.5 ± 10.4 ppb, respectively, resulting in an increase of 411%. These results indicated that the combustion source is an important factor of NH3 emissions.
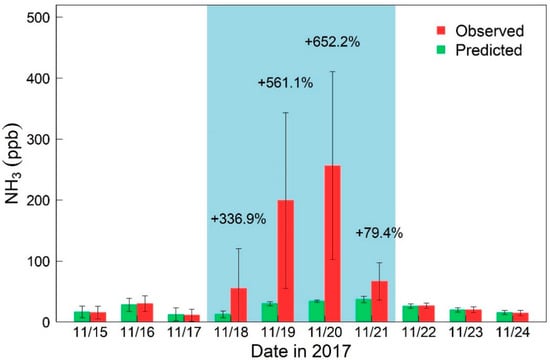
Figure 3.
Observed and predicted concentrations of NH3 before, during and after the burning period at the Xianghe site. Percentages on bars indicate relative changes (R) between the observed and predicted concentrations.
3.3. Dominant Source of NH3 during the Burn Event
Although the overall impacts of the burn event on NH3 concentrations were identified in the above sections, the potential dominant source contributing to the substantial increase in NH3 was still unclear. To address this concern, we further investigated the relationship between NH3 and other air pollutants.
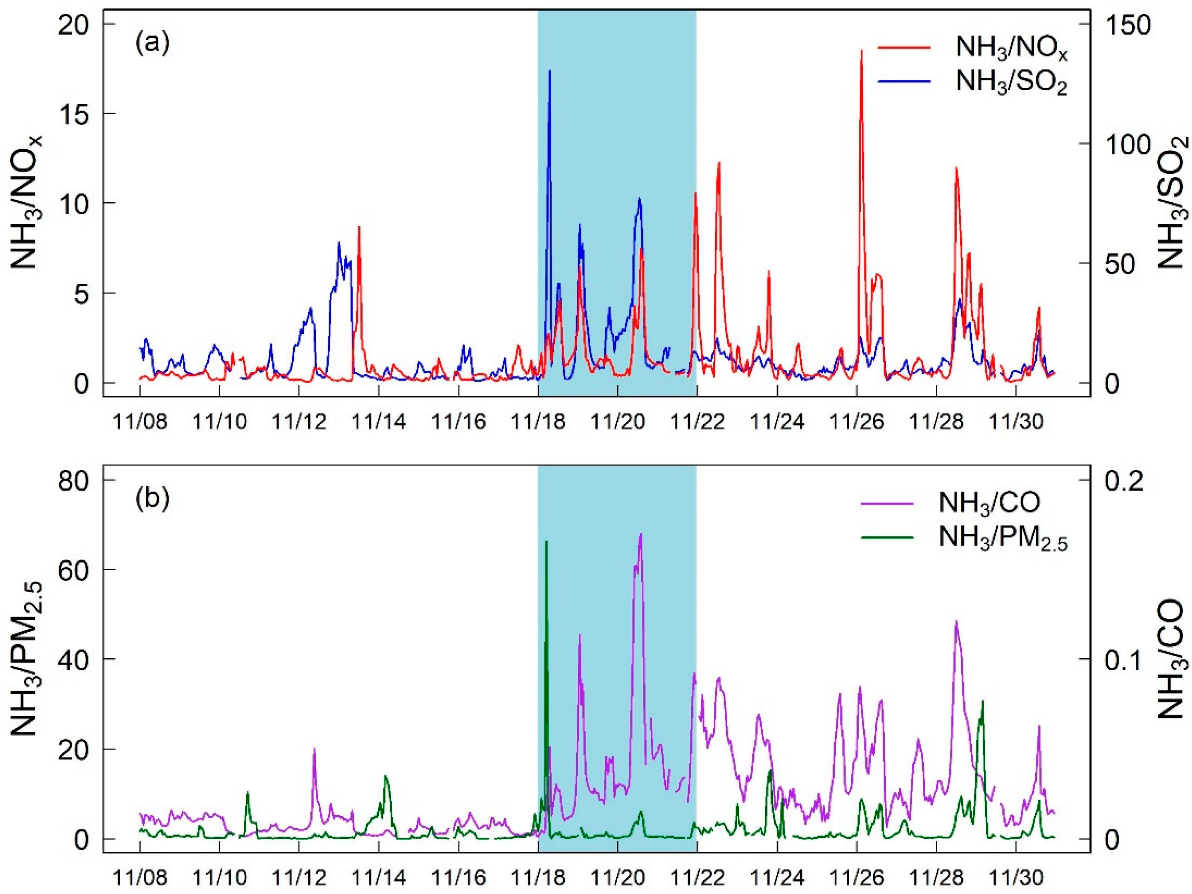
As shown in Figure 4, we found that the ratio of NH3 to other air pollutants significantly increased after the burn event occurred. Compared with those before burn events, the ratio of NH3/PM2.5, NH3/SO2, NH3/NOx, and NH3/CO increased by a factor of 1.6, 2.5, 3.0, and 5.4 during the burning period, respectively (Table S5). This finding indicated a dramatic change of CO during the burn event. Thus, CO was selected as a tracer of fire [41]. Then, the emission ratio (ER) was defined as ∆NH3/∆CO in our study [17,42], where ∆NH3 and ∆CO represented the difference in the corresponding concentrations of NH3 and CO before and during the burn event. In this study, the calculated ∆NH3/∆CO value was 0.016, which was consistent with the characteristics of biomass burning (Table 2). Therefore, the dominant source emitting substantial NH3 might be biomass burning in this burn event. Future control measures on NH3 emissions should pay more attention to potential contributions from biomass burning.
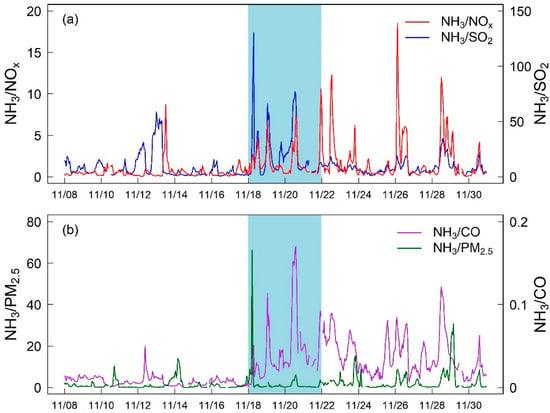
Figure 4.
Temporal variation in the ratio of NH3 relative to NOX, SO2 (a), CO and PM2.5 (b).

Table 2.
Summary of the NH3 concentration and its emission ratio (ER = ∆NH3/∆CO) in different burn events.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the NH3 concentrations were measured by the CRDS technique in the cold season at a rural site in the NCP. The hourly NH3 concentrations were mostly below 65 ppb during the study period. However, an unexpected burn event caused a significant increase in NH3 concentration from 18 to 21 November 2017, with peak values exceeding 600 ppb. With the aid of a machine-learning technique, we found that the burn event could cause a 411% increase in the NH3 concentration. Notably, the ∆NH3/∆CO ratio was 0.016 during the burning period, indicating that biomass burning might be the dominant emission source. Due to the increasing occurrence of burn events worldwide, the impacts of the combustion sources of NH3 on air quality, ecosystems, and climate need to be further explored.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos13020170/s1: Figure S1: Influence of different ntree and mtry values on RF model; Figure S2: Performance of the RF model in predicting the NH3 concentrations; Figure S3: Temporal variation of hourly concentrations of PM2.5, SO2, NOx, and CO; Figure S4: Hourly variation of meteorological parameters; Table S1: Summary of 11 RF models and their predictors in this study; Table S2: Model validation in 11 RF models in this study; Table S3: Correlation matrix of NH3, other air pollutants and meteorological parameters during the burning period; Table S4: Observed and predicted concentrations of NH3 at the Xianghe site during the burning period; Table S5: Range and average of the ratio between NH3 and other air pollutants before and during the burn event.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.P.; methodology, J.H.; software, J.H., Y.W. and Y.H.; validation, J.H.; formal analysis, J.H.; investigation, J.H. and Y.L.; resources, Y.P., D.J. and T.L.; data curation, J.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, Y.P. and W.S.; visualization, J.H.; supervision, Y.P. and W.S.; project administration, Y.P. and X.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.P., T.L. and X.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant number 42077204] and the Open Research Fund Program of Plateau Atmosphere and Environment Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Project PAEKL-2020-C3).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Paulot, F.; Henze, D.K. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition to the northwestern Pacific: Seasonal variation and source attribution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10905–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Q.; Han, M.; Tang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Li, K.; et al. Changes of nitrogen deposition in China from 1980 to 2018. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, S.; Liu, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Michalski, G.; Wang, Y. Fossil fuel combustion-related emissions dominate atmospheric ammonia sources during severe haze episodes: Evidence from 15N-stable isotope in size-resolved aerosol ammonium. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8049–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Hao, J. Increasing ammonia concentrations reduce the effectiveness of particle pollution control achieved via SO2 and NOx emissions reduction in east China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tong, D.Q.; Dan, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y. Typical atmospheric haze during crop harvest season in northeastern China: A case in the Changchun region. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ji, D. Reductions of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomerations during the 2008 Olympic Games. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Wu, Y.; Xue, R.; Zeng, L.; Qu, Y.; An, J. Characteristics and formation mechanism of regional haze episodes in the Pearl River Delta of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 63, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Y. Association between ambient fine particulate matter and adult hospital admissions for pneumonia in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 231, 117497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Henze, D.K.; Bash, J.O.; Cady-Pereira, K.E.; Shephard, M.W.; Luo, M.; Capps, S.L. Sources and impacts of atmospheric NH3: Current understanding and frontiers for modeling, measurements, and remote sensing in North America. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felix, J.D.; Elliott, E.M.; Gay, D.A. Spatial and temporal patterns of nitrogen isotopic composition of ammonia at U.S. ammonia monitoring network sites. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Huang, X.; Song, Y.; Tang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, T.; Kang, L.; et al. Ammonia emission control in China would mitigate haze pollution and nitrogen deposition, but worsen acid rain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Gu, M.; He, Y.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.; Song, L.; Tian, S.; Lü, X.; Sun, Y.; Song, T.; et al. Revisiting the concentration observations and source apportionment of atmospheric ammonia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, L.; Wu, Q.; He, Y.; Tian, S.; et al. Improved inversion of monthly ammonia emissions in China based on the Chinese ammonia monitoring network and ensemble kalman filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12529–12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Huang, X.; Yao, H.; Cai, X.; Zhang, H.; Kang, L.; Liu, X.; Yan, X.; et al. High-resolution ammonia emissions inventories in China from 1980 to 2012. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2043–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgen, S.; Cernuschi, S.; Caserini, S. An overview of nitrogen oxides emissions from biomass combustion for domestic heat production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitburn, S.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Turquety, S.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F. Doubling of annual ammonia emissions from the peat fires in Indonesia during the 2015 El Niño. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11007–11014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R’Honi, Y.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Hurtmans, D.; Duflot, V.; Turquety, S.; Ngadi, Y.; Coheur, P.F. Exceptional emissions of NH3 and HCOOH in the 2010 Russian wildfires. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, N.; Bhatia, A.; Pathak, H. Emission of air pollutants from crop residue burning in India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, S.; Liu, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, M.; Gao, J.; Michalski, G.; Wang, Y. Isotopic evidence for enhanced fossil fuel sources of aerosol ammonium in the urban atmosphere. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, S.; Liu, D.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, M.; Wentworth, G.R.; Michalski, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. Source apportionment of aerosol ammonium in an ammonia-rich atmosphere: An isotopic study of summer clean and hazy days in urban Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Pan, Y.; Walters, W.W.; Sun, Q.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Fang, Y. Vehicular emissions enhanced ammonia concentrations in winter mornings: Insights from diurnal nitrogen isotopic signatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Zhong, Q.; Yun, X.; Zhu, X.; Huang, T.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; et al. Improvement of a global high-resolution ammonia emission inventory for combustion and industrial sources with mew data from the residential and transportation sectors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2821–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Bu, R.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y. Environmental controls on the characteristics of mean number of forest fires and mean forest area burned (1987–2007) in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 356, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Luo, X.; Liang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, H.; Pan, K.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Pang, X. Fire from policy, human interventions, or biophysical factors? Temporal–spatial patterns of forest fire in southwestern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 474, 118381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Reis, S.; Jin, J.; Dragosits, U.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Whitburn, S.; Coheur, P.-F.; et al. Ammonia emissions may be substantially underestimated in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12089–12096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Gao, J.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Identifying ammonia hotspots in China using a national observation network. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhou, W.; Chen, C.; He, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Ji, D.; et al. A chemical cocktail during the COVID-19 outbreak in Beijing, China: Insights from six-year aerosol particle composition measurements during the Chinese New Year holiday. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Ren, L.; Wang, W.; Tao, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, X.; Han, Z.; Zhang, R. Variation in PM2.5 sources in central North China Plain during 2017–2019: Response to mitigation strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; He, K.; Zhang, Q.; Chai, L. Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols over China: Response to 2000–2015 emission changes of sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2635–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.; Zhou, T.; et al. High efficiency of livestock ammonia emission controls in alleviating particulate nitrate during a severe winter haze episode in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5605–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berden, G.; Peeters, R.; Meijer, G. Cavity ring-down spectroscopy: Experimental schemes and applications. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2000, 19, 565–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bobrutzki, K.; Braban, C.F.; Famulari, D.; Jones, S.K.; Blackall, T.; Smith, T.E.L.; Blom, M.; Coe, H.; Gallagher, M.; Ghalaieny, M.; et al. Field inter-comparison of eleven atmospheric ammonia measurement techniques. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, N.A.; Ferracci, V.; Cassidy, N.; Hoffnagle, J.A. The application of a cavity ring-down spectrometer to measurements of ambient ammonia using traceable primary standard gas mixtures. Appl. Phys. B 2016, 122, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ji, D.; Tian, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Tracking ammonia morning peak, sources and transport with 1 Hz measurements at a rural site in North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 235, 117630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Rahn, K.A.; He, K.; Wen, T.; Wang, Y. A novel technique for quantifying the regional component of urban aerosol solely from its sawtooth cycles. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D21309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, W.; Ma, Z.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Guo, H.; Lin, W.; Cheng, Y.; Quan, W.; Li, Y.; Dong, F.; He, D. Regional transport and urban emissions are important ammonia contributors in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswati; Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. Five-year measurements of ambient ammonia and its relationships with other trace gases at an urban site of Delhi, India. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, A.; Aulinger, A.; Bieser, J.; Matthias, V.; Quante, M. Ammonia emissions in Europe, part I: Development of a dynamical ammonia emission inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Pan, Y.; Gu, M.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Changes of ammonia concentrations in wintertime on the North China Plain from 2018 to 2020. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Han, H.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, M. Collective impacts of biomass burning and synoptic weather on surface PM2.5 and CO in Northeast China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitburn, S.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F. IASI-derived NH3 enhancement ratios relative to CO for the tropical biomass burning regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12239–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, L.; Walters, W.W.; Pan, Y.; Li, Z.; Gu, M.; Duan, Y.; Lü, X.; Fang, Y. 15N natural abundance of vehicular exhaust ammonia, quantified by active sampling techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 255, 118430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegg, D.A.; Radke, L.F.; Hobbs, P.V.; Riggan, P.J. Ammonia emissions from biomass burning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1988, 15, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yokelson, R.J.; Crounse, J.D.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Karl, T.; Urbanski, S.; Atlas, E.; Campos, T.; Shinozuka, Y.; Kapustin, V.; Clarke, A.D.; et al. Emissions from biomass burning in the Yucatan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5785–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akagi, S.K.; Craven, J.S.; Taylor, J.W.; McMeeking, G.R.; Yokelson, R.J.; Burling, I.R.; Urbanski, S.P.; Wold, C.E.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Coe, H.; et al. Evolution of trace gases and particles emitted by a chaparral fire in California. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1397–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedict, K.B.; Prenni, A.J.; Carrico, C.M.; Sullivan, A.P.; Schichtel, B.A.; Collett, J.L. Enhanced concentrations of reactive nitrogen species in wildfire smoke. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.; Koplitz, S.; Foley, K.; Avey, L.; Hawkins, A. Characterizing grassland fire activity in the Flint Hills region and air quality using satellite and routine surface monitor data. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindaas, J.; Pollack, I.B.; Calahorrano, J.J.; O’Dell, K.; Garofalo, L.A.; Pothier, M.A.; Farmer, D.K.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Campos, T.; Flocke, F.; et al. Empirical insights into the fate of ammonia in western U.S. Wildfire smoke plumes. J. Geophys. Res. 2021, 126, e2020JD033730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).