Some Results of Photometric Measurements of Ionospheric Artificial Airglow at 557.7 and 630 nm Lines of Atomic Oxygen Caused by High-Frequency Radio Emission of the SURA Facility during Development of Sporadic E Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Equipment and Methods
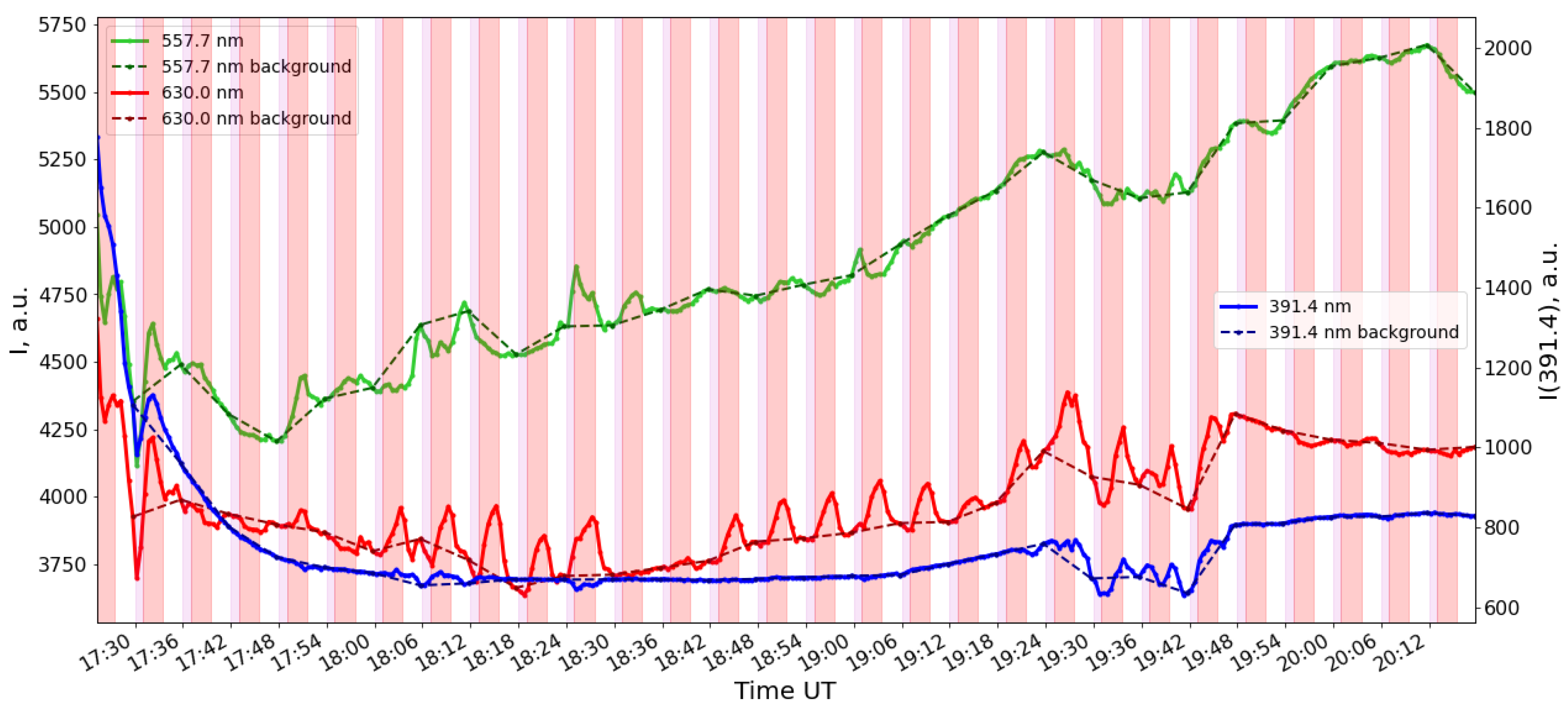
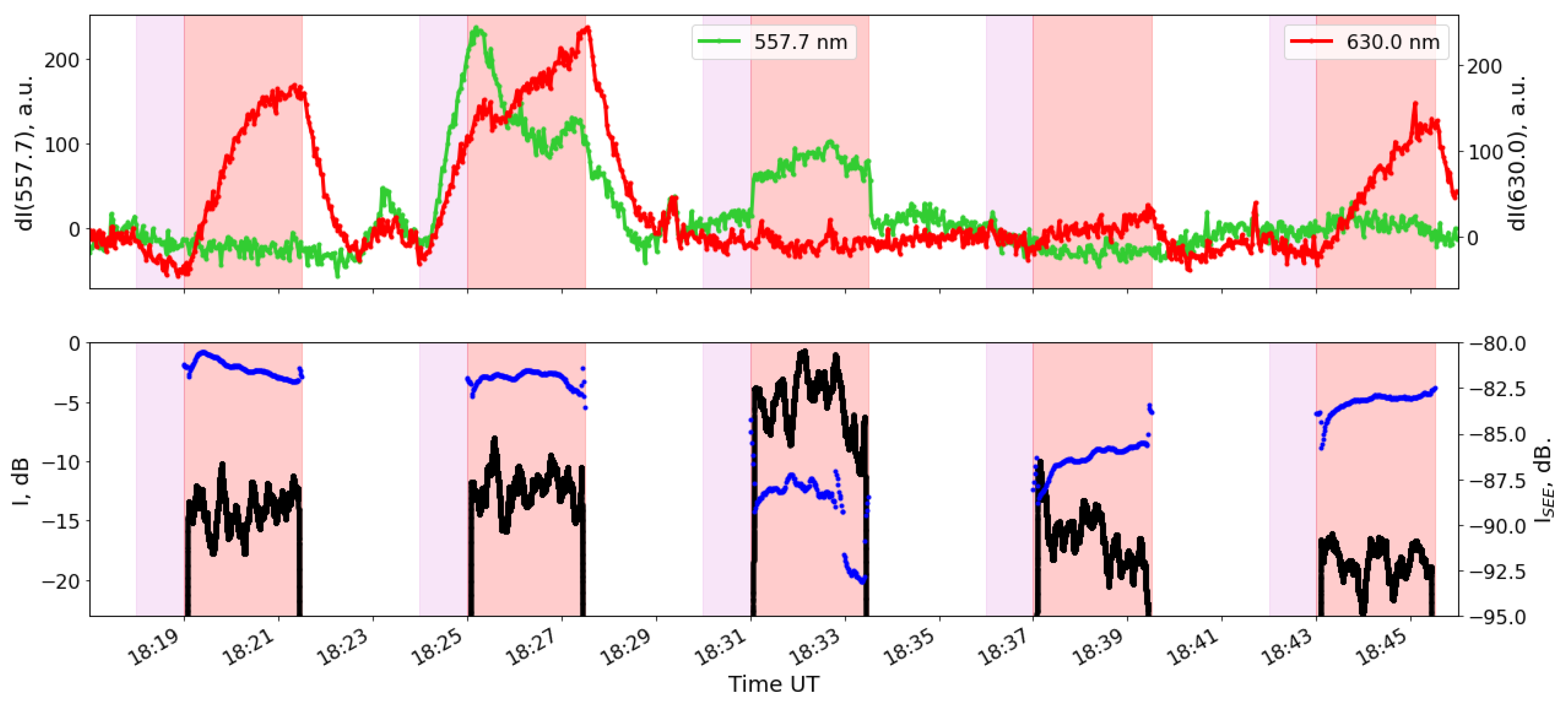
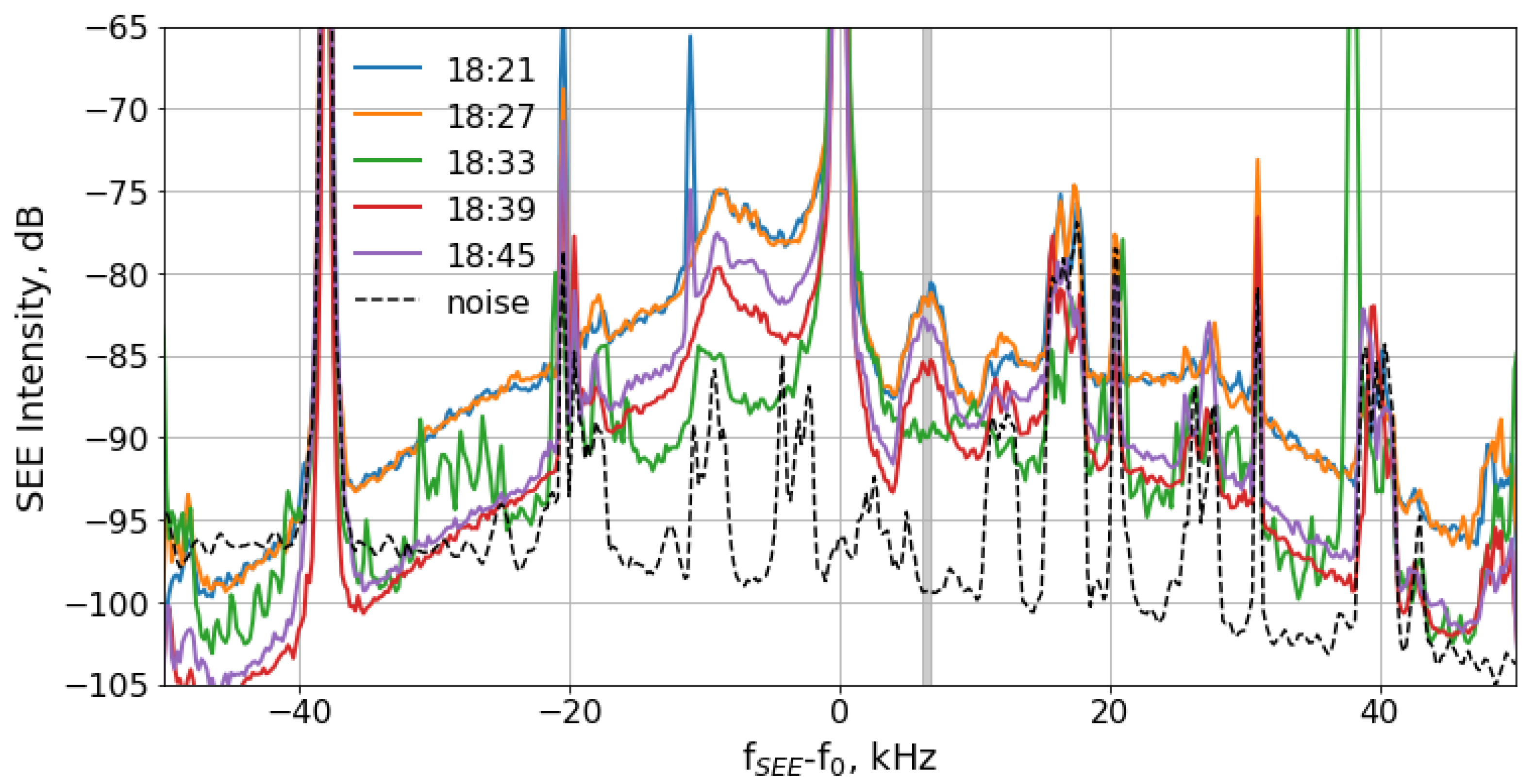
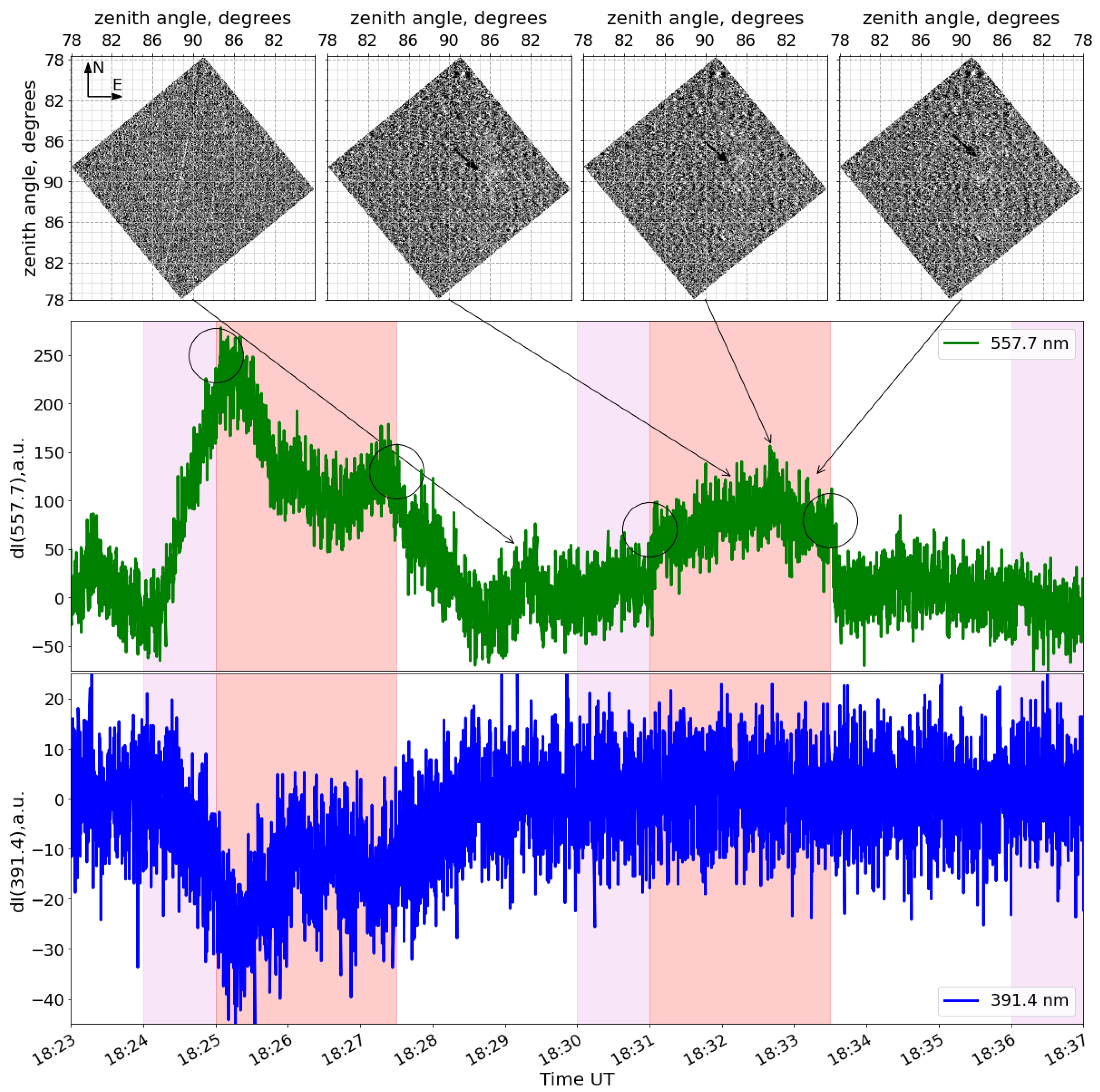
3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biondi, A.A.; Sipler, D.P.; Hake, R.D. Optical (λ6300) detection of radio frequency heating of electrons in theFregion. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 6421–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utlaut, W.F.; Cohen, R. Modifying the ionosphere with intense radio waves. Science 1971, 174, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sipler, D.P.; Biondi, M.A. Equatorial F-region neutral winds from nightglow OI 630.0 nm Doppler shifts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1978, 5, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, H.C.; Wickwar, V.B.; Mantas, G.P. Observations of fluxes of suprathermal electrons accelerated by HF excited instabilities. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1982, 44, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.A.; Duncan, L.M.; Tepley, C.A. Heater-induced cavities as optical tracers of plasma drifts. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1989, 94, 7003–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.A.; Tepley, C.A.; Duncan, L.M. Airglow enhancements associated with plasma cavities formed during ionospheric heating experiments. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1989, 94, 9071–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, M.J.; Rietveld, M.T.; Hagfors, T.; Leyser, T.B. High-latitude HF-induced airglow displaced equatorwards of the pump beam. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 2817–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.R.; Carlson, H.C. First observations of HF heater-produced airglow at the high frequency active auroral research program facility: Thermal excitation and spatial structuring. Radio Sci. 2001, 36, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, B.; Sergienko, T.; Rietveld, M.T.; Honary, F.; Steen, A.; Brändström, B.U.E.; Leyser, T.B.; Aruliah, A.L.; Aso, T.; Ejiri, M.; et al. First Tomographic estimate of volume distribution of HF-pump enhanced airglow emission. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 29105–29123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, M.J.; Rietveld, M.T.; Kavanagh, A.J.; Davis, C.; Yeoman, T.K.; Honary, F.; Hagfors, T. High-latitude pump-induced optical emissions for frequencies close to the third electron gyro-harmonic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, M.T.; Kosch, M.J.; Blagoveshchenskaya, N.F.; Kornienko, V.A.; Leyser, T.B.; Yeoman, T.K. Ionospheric electron heating, optical emissions, and striations induced by powerful HF radio waves at high latitudes: Aspect angle dependence. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, M.J.; Rietveld, M.T.; Senior, A.; McCrea, I.W.; Kavanagh, A.J.; Isham, B.; Honary, F. Novel artificial optical annular structures in the high latitude ionosphere over EISCAT. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuth, F.T.; Pedersen, T.R.; Gerken, E.A.; Bernhardt, P.A.; Selcher, C.A.; Bristow, W.A.; Kosch, M.J. Ionospheric modification at twice the electron cyclotron frequency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, B.; Sergienko, T.; Kosch, M.J.; Rietveld, M.T.; Brändström, B.U.E.; Leyser, T.B.; Isham, B.; Gallop, P.; Aso, T.; Ejiri, M.; et al. The electron energy distribution during HF pumping, a picture painted with all colors. Ann. Geophys. 2005, 23, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, B.; Newsome, R.; Leyser, T.; Kosch, M.; Norin, L.; McCarrick, M.; Pedersen, T.; Watkins, B. First observations of X-mode suppression of O-mode HF enhancements at 6300 Å. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, E.; Marshall, R.; Parris, R.T.; Bhatt, A.; Coster, A.; Pedersen, T.; Bernhardt, P.; Selcher, C. Decameter structure in heater-induced airglow at the High frequency Active Auroral Research Program facility. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.; Gustavsson, B.; Mishin, E.; MacKenzie, E.; Carlson, H.C.; Starks, M.; Mills, T. Optical ring formation and ionization production in high-power HF heating experiments at HAARP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, M.J.; Bryers, C.; Rietveld, M.T.; Yeoman, T.K.; Ogawa, Y. Aspect angle sensitivity of pump-induced optical emissions at EISCAT. Earth Planets Space 2014, 66, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Blagoveshchenskaya, N.; Borisova, T.; Kosch, M.; Sergienko, T.; Brändström, U.; Yeoman, T.K.; Häggström, I. Optical and ionospheric phenomena at EISCAT under continuous X-mode HF pumping. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 10483–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.A.; Scales, W.A.; Grach, S.M.; Keroshtin, A.N.; Kotik, D.S.; Polyakov, S.V. Excitation of artificial airglow by high power radio waves from the “Sura” Ionospheric Heating Facility. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 1477–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, P.A.; Wong, M.; Huba, J.D.; Fejer, B.G.; Wagner, L.S.; Goldstein, J.A.; Selcher, C.A.; Frolov, V.L.; Sergeev, E.N. Optical remote sensing of the thermosphere with HF pumped artificial airglow. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 10657–10671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumerov, R.I.; Kapkov, V.B.; Komrakov, G.P.; Nasyrov, A.M. Artificial ionospheric glow caused by the short-term effect of high-power RF radiation. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 1999, 42, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosch, M.J.; Pedersen, T.; Mishin, E.; Starks, M.; Gerken-Kendall, E.; Sentman, D.; Oyama, S.; Watkins, B. Temporal evolution of pump beam self-focusing at the high-frequency active auroral research program. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.M.; Sergeev, E.N.; Nasyrov, A.M.; Gumerov, R.I.; Shaimukhametov, R.R.; Nasyrov, I.A.; Komrakov, G.P. Simultaneous observations of the 557.7 nm airglow and stimulated electromagnetic emission during HF pumping of the ionosphere with diagnostic schedule: First results. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 2422–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.M.; Sergeev, E.N.; Komrakov, G.P.; Kotov, P.V.; Nasyrov, A.M.; Gumerov, R.I.; Shaimukhametov, R.R.; Nasyrov, I.A. Studies of artificial airglow emission at 557.7 nm (green line) of upper atmosphere caused by “Sura” facility. Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2006, 6522, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.; Kosch, M.; Yashnov, V.; Sergeev, E.; Atroshenko, M.; Kotov, P. On the location and structure of the artificial 630-nm airglow patch over Sura facility. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogerakis, K.S.; Slanger, T.G.; Kendall, E.A.; Pedersen, T.R.; Kosch, M.J.; Gustavsson, B.; Rietveld, M.T. Remote oxygen sensing by Ionospheric excitation (ROSIE). Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grach, S.; Klimenko, V.; Shindin, A.; Nasyrov, I.; Sergeev, E.; Yashnov, V.; Pogorelko, N. Airglow during ionospheric modifications by the sura facility radiation. Experimental results obtained in 2010. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2012, 55, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindin, A.; Grach, S.; Klimenko, V.; Nasyrov, I.; Sergeev, E.; Beletski, A.; Taschilin, M.; I.Gumerov, R. The 630 nm and 557.7 nm Airglow during HF Ionosphere Pumping by the SURA Facility Radiation for Pump Frequencies Near the Fourth Electron Gyroharmonic. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2015, 57, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimenko, V.; Grach, S.; Sergeev, E.; Shindin, A. Features of the Ionospheric Artificial Airglow Caused by Ohmic Heating and Plasma Turbulence-Accelerated Electrons Induced by HF Pumping of the Sura Heating Facility. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2017, 60, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.; Nasyrov, I.; Kogogin, D.; Shindin, A.; Dementiev, V.; Sergeev, E.; Akchurin, A. On the Connection between the Spatial Behavior of the Total Electron Content of the Ionosphere on the GPS Signal Path and the Ionospheric Artificial Airglow in the 630 nm Line. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2018, 61, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.; Nasyrov, I.; Kogogin, D.; Shindin, A.; Sergeev, E.; Razi Mousavi, S. Mutual Allocation of the Artificial Airglow Patches and Large-Scale Irregularities in the HF-Pumped Ionosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 12749–12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindin, A.; Klimenko, V.; Kogogin, D.; Beletsky, A.; Grach, S.; Nasyrov, I.; Sergeev, E. Spatial Characteristics of the 630-nm Artificial Ionospheric Airglow Generation Region During the Sura Facility Pumping. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2018, 60, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogogin, D.; Nasyrov, I.; Shindin, A.; Grach, S.; Maksimov, D.; Zagretdinov, R.; Dementiev, V. Dynamic Changes of the Ionospheric Artificial Airglow Region Caused by High-Power Radio Waves Based on a Joint Analysis of Night-Sky Snapshots in the 630 nm Line and Total Electron Content Variation Maps. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2020, 63, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, M.; Phillips, L. Chemistry of the Atmosphere; Arnold: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Khomich, V.Y.; Semenov, A.I.; Shefov, N.N. Airglow as an Indicator of Upper Atmospheric Structure and Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuth, F.; Bernhardt, P.; Tepley, C.; Gardner, J.; Kelley, M.; Broadfoot, A.; Kagan, L.; Sulzer, M.; Elder, J.; Selcher, C.; et al. Large airglow enhancements produced via wave-plasma interactions in sporadic E. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1557–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagan, L.; Kelley, M.; Garcia, F.; Bernhardt, P.; Djuth, F.; Sulzer, M.; Tepley, C. Structure of electromagnetic wave induced 557.7 nm emission associated with a sporadic E event over Arecibo. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, G.; Ashley, M.C.B.; Cui, X.; Everett, J.R.; Feng, L.L.; Gong, X.; Hengst, S.; Hu, Z.; Lawrence, J.S.; Luong-Van, D.M.; et al. Airglow and Aurorae at Dome A, Antarctica. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2012, 124, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thide, B.; Kopka, H.; Stubbe, P. Observations of stimulated scattering of a strong high–frequency radio wave in the ionosphere. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 1561–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbe, P.; Kopka, H.; Thide, B.; Derblom, H. Simulated electromagnetic emission: A new technique to study the parametric decay instability in the ionosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 7523–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grach, S.; Sergeev, E.; Mishin, E.; Shindin, A. Dynamic properties of ionospheric plasma turbulence driven by high-power high-frequency radiowaves. Physics-Uspekhi 2016, 59, 1091–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A. Nonlinear effects in the ionosphere. Physics-Uspekhi 2007, 50, 1091–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.; Goldman, M.; Djuth, F.; Bernhardt, P. Langmuir turbulence associated with ionospheric modification: Challenge associated with recent observations during a sporadic-E event. Phys. Space Plasmas 1998, 15, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Kagan, L.; Bakhmet’eva, N.; Belikovich, V.; Tolmacheva, A.; Kelley, M. Structure and dynamics of sporadic layers of ionization in the ionospheric E region. Radio Sci. 2002, 37, 18-1–18-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Altitude, km | HWM14 | Light Spots | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zonal Wind, m/s | Meridional Wind, m/s | Zonal Wind, m/s | Meridional Wind, m/s | |
| 100 | −6.7 | −9.3 | −49.5 | 39.6 |
| 105 | −17.8 | −19.6 | −52 | 41.6 |
| 110 | −4.8 | −17 | −54.5 | 43.6 |
| 115 | −27.4 | −17.5 | −57 | 45.6 |
| 120 | −50 | −23.1 | −59.4 | 47.6 |
| 125 | −49.9 | −28 | −61.9 | 49.5 |
| 130 | −43.3 | −26.3 | −64.4 | 51.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beletsky, A.B.; Tkachev, I.D.; Nasyrov, I.A.; Grach, S.M.; Kogogin, D.A.; Shindin, A.V.; Vasilyev, R.V. Some Results of Photometric Measurements of Ionospheric Artificial Airglow at 557.7 and 630 nm Lines of Atomic Oxygen Caused by High-Frequency Radio Emission of the SURA Facility during Development of Sporadic E Layer. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111794
Beletsky AB, Tkachev ID, Nasyrov IA, Grach SM, Kogogin DA, Shindin AV, Vasilyev RV. Some Results of Photometric Measurements of Ionospheric Artificial Airglow at 557.7 and 630 nm Lines of Atomic Oxygen Caused by High-Frequency Radio Emission of the SURA Facility during Development of Sporadic E Layer. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(11):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111794
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeletsky, Alexander B., Ivan D. Tkachev, Igor A. Nasyrov, Savely M. Grach, Denis A. Kogogin, Alexey V. Shindin, and Roman V. Vasilyev. 2022. "Some Results of Photometric Measurements of Ionospheric Artificial Airglow at 557.7 and 630 nm Lines of Atomic Oxygen Caused by High-Frequency Radio Emission of the SURA Facility during Development of Sporadic E Layer" Atmosphere 13, no. 11: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111794
APA StyleBeletsky, A. B., Tkachev, I. D., Nasyrov, I. A., Grach, S. M., Kogogin, D. A., Shindin, A. V., & Vasilyev, R. V. (2022). Some Results of Photometric Measurements of Ionospheric Artificial Airglow at 557.7 and 630 nm Lines of Atomic Oxygen Caused by High-Frequency Radio Emission of the SURA Facility during Development of Sporadic E Layer. Atmosphere, 13(11), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13111794








