Abstract
Ground-level ozone (O3) is a significant source of air pollution, mainly in most urban areas across the globe. Ground-level O3 is not emitted directly into the atmosphere. It results from photo-chemical reactions between precursors and is influenced by weather factors such as temperature. This study investigated the spatial and temporal analysis of ground-level ozone and analyzed the significant anthropogenic precursors and the weather parameters associated with ground-level ozone during daytime and nighttime at three cities in peninsular Malaysia, namely, Kuala Terengganu, Perai, and Seremban from 2016 to 2020. Secondary data were acquired from the Department of Environment (DOE), Malaysia, including hourly data of O3 with trace gases and weather parameters. The secondary data were analyzed using temporal analysis such as descriptive statistics, box plot, and diurnal plot as well as spatial analysis such as contour plot and wind rose diagram. Spearman correlation was used to identify the association of O3 with its precursors and weather parameters. The results show that a higher concentration of O3 during the weekend due to “ozone weekend effects” was pronounced, however, a slightly significant effect was observed in Perai. The two monsoonal seasons in Malaysia had a minimal effect on the study areas except for Kuala Terengganu due to the geographical location. The diurnal pattern of O3 concentration indicates bimodal peaks of O3 precursors during the peak traffic hours in the morning and evening with the highest intensity of O3 precursors detected in Perai. Spearman correlation analysis determined that the variations in O3 concentrations during day and nighttime generally coincide with the influence of nitrogen oxides (NO) and temperature. Lower NO concentration will increase the amount of O3 concentration and an increasing amount of O3 concentration is influenced by the higher temperature of its surroundings. Two predictive models, i.e., linear (multiple linear regression) and nonlinear models (artificial neural network) were developed and evaluated to predict the next day and nighttime O3 levels. ANN resulted in better prediction for all areas with better prediction identified for daytime O3 levels.
1. Introduction
Ground-level ozone (O3) is one of the most common pollutants found in the Earth’s troposphere layers. It is therefore commonly referred to as a ‘bad’ ozone. The increased O3 content in the Earth’s surface has consequences for human health, natural ecosystems, and vegetation development [1]. O3 is primarily created by complex photochemical processes caused by anthropogenic precursors. A large percentage of ground-level ozone formation occurs in the presence of sunlight, typically the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum, when nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), non-methane hydrocarbons (NmHCs), methane (CH4), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the atmosphere. These are referred to as ozone precursors [2]. Ozone absorbs radiation and thus works as a powerful greenhouse gas. Despite rising temperatures, O3 affects evaporation rates, cloud formation, precipitation amounts, and atmospheric circulation. These effects are most noticeable in areas where ozone precursors are emitted [3].
Ozone is an uncommon pollutant since it is not emitted directly into the environment. The transformation of land use from forest to agronomic, residential, and town creates a change, causing the O3 precursor to rise, which can be seen clearly between urban and rural areas [4]. This process usually results in the development of large concentrations of O3 downwind and in suburban regions resulting in higher anthropogenic precursors causing a high concentration of O3 [5]. A greater source of ground-level ozone can be found in urban areas due to greater emissions from vehicles, power stations, industrial boilers, refineries, and chemical factories. The increasing population, industrial activities, and automobiles are the concrete reason for significantly increased emissions of VOCs and NOx and, consequently, higher O3 production can be expected in more populous areas.
In urban areas in particular, the concentration of NO released from traffic affects the formation of NO2. During the day, sunlight plays an important role in starting reactions among O3 precursors [4,6]. A high concentration of NO produced by motor vehicles may result in reduced O3 concentration in busy areas, but it will increase the concentration of NO2. High NO concentration will effective the titrate of atom (O) in urban areas due to emissions from the large amount of transportation activity. Through titration reactions with NO, O3 is depleted, resulting in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and oxygen (O2). The NO2 produced can react along with O3 to produce nitrate (NO3) and O2 [7]. On the contrary, at night there is no sunlight to react with precursors forming ozone. Thus, the presence of NOx at night should have a significant decreasing impact on the concentrations of O3 in an area. Many studies focus on the effect of ground-level ozone in the daytime rather than nighttime due to the significant relationship between O3 with UVB. However, nighttime ozone is related to daytime ozone as the high preference may be carried over to the daytime. Likewise, the nighttime dispersion or accumulation of the precursors has a large impact on the ozone growth after sunrise. In addition, the overnight aloft ozone residual layer can play a role in morning time ozone rise [8].
In addition to O3 precursors, meteorology plays a vigorous part in the atmospheric fate of ground-level O3 in the lower boundary layer, including accumulation, dilution, and transport. Therefore, changes in meteorological conditions such as wind speed/direction, temperature, and relative humidity, can impact temporal variations of O3 and anthropogenic precursors [9]. Correlation analysis is usually used to measure the relationship between the meteorological influences and parameters on tropospheric ozone [10,11]. Its positive or negative orientation provides a reliable reference for determining how specific climatic factors affect ozone concentrations. Temperature directly influences O3 formation pathways by enhancing reaction rates of ozone precursors, ozone formation rates, and mechanism pathways [12]. On the one hand, high temperature is usually associated with sunshine duration, high solar irradiation, and low relative humidity that enhances ground-level ozone formation [13]. On the other hand, wind can significantly influence ground-level O3 through dispersion and transportation [14]. The upwind and downwind geographical features affect O3 levels at a site, hence, favorable wind conditions will help transport O3 and its precursors downwind [10]. In general, wind speed negatively correlates with O3 levels. Tong et al. [11] revealed that low wind speed (<4 ms−1) enhanced O3 accumulation. The boundary layer is stable at low wind, thus stabilizing O3 levels. As for Malaysia, which has tropical weather with two distinct monsoonal seasons—the wet monsoon, i.e., northeast monsoon (NEM) from November to March and the dry monsoon, i.e., southwest monsoon (SWM) from June to September, with inter-monsoon seasons in between—the influence of O3 levels on the seasonal monsoon are yet to be discovered [15].
The prediction of ozone levels using mathematical tools is very useful in providing early warnings to the population. Thus, statistical approaches have been widely used by researchers to study variations in O3 concentrations with its precursors and weather parameters. Multiple linear regression (MLR) is one of the most common techniques used in the prediction of ground-level O3 levels. MLR models a linear relationship between the independent and the dependent variables, thus the relationship of the O3 level and other variables (including other air pollutants, its precursors, and meteorology parameters) can be determined [16]. Therefore, due to its simplicity and reliability, MLR has been successfully used as a predictive tool worldwide [17,18,19,20]. Besides providing a simple linear relationship of ozone concentration with its precursors and weather parameters, MLR may not deliver accurate forecasts in some complex situations such as non-linear data and extreme values data. Artificial neural networks (ANN), one of the most common machine learning techniques, can be a useful tool to extract information from non-linear data such as air quality and meteorology. Currently, the application of neural networks has become more popular for predicting ground-level O3 concentrations. A lot of researchers have effectively adopted ANN as a predictive tool to model O3 concentration [21,22,23,24,25] and its precursor, NO2 [26]. Even though many studies have been carried out in the world investigating the association between the weather and ozone concentration using MLR and ANN, there is still a shortage of work, especially in Malaysia.
In this research, the main aim was to analyze the spatial and temporal variability of O3 concentrations with its precursors and weather parameters during daytime and nighttime in selected urban areas in peninsular Malaysia. Studying the characteristics of O3 concentrations especially in the rarely pronounced urban areas in peninsular Malaysia are helpful toward a better understanding of the variation in O3. At the local level, the photochemical characteristics of O3 vary with geographical location because the generation of O3 is significantly affected by local environmental conditions, especially temperature, solar radiation, and atmospheric stagnation. In addition, two predictive models (i.e., linear and nonlinear models) were developed and attempted to forecast daytime and nighttime O3 levels. Most of the O3 level predictive models focused on daytime prediction, however, it is important to model the accumulation of O3 at nighttime as some of the places are showing an increasing trend of O3 during nighttime.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Air Pollutant Dataset
Continuous hourly air quality data from 2016 to 2020 were obtained from the Air Quality Division of the Department of Environment (DOE) Malaysia. This study used 12 variables that were divided into two groups. One group comprised seven air pollutants, such as O3 (ppm), NOx (ppm), NO (ppm), SO2 (ppm), NO2 (ppm), CO (ppm), and PM10 (µg/m3). While weather parameters are wind speed (km/h), temperature (°C), humidity (%), UVB (W/m2), and wind direction (o). These data were sorted in Microsoft Excel according to the diurnal cycle since the O3 level significantly varies during daytime and nighttime. The diurnal cycle of daytime O3 was from 7:00 am to 7:00 pm and the nighttime cycle was from 8:00 pm to 6:00 am. Malaysia experiences a slightly longer daytime period due to its location near the equator.
In this study, urban areas located in peninsular Malaysia, namely, Kuala Terengganu, Perai, and Seremban were chosen. According to Wan Mahiyuddin et al. [27], ground-level ozone exposure has reached levels that pose severe health hazards inside the larger Klang Valley sprawling city, which is Malaysia’s most densely populated area. However, there are very limited studies of O3 variation reported in Kuala Terengganu, Seremban, and Perai. The details of the study areas are tabulated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Details of Study Areas.
2.2. Spatial Analysis
In this study, two spatial analyses were conducted: contour plot and wind rose diagram. Contour plot was used to examine the monthly distribution of O3 levels at a regional spatial scale. The spatial interpolation method can effectively estimate the pollutant concentration at any point within the regional ambient air range. Applying the first law of geography, the ordinary kriging method (OKM) was used to analyze the continuous distribution of the concentration of O3 among the stations. A monthly wind rose diagram was generated using Microsoft Excel.
2.3. Measure of Association Using Spearman Correlation
In this research, Spearman Correlation was used to analyze the significant precursors and weather parameters toward O3 concentration and the results are presented in the form of a heat matrix. A nonparametric measure of the relationship between the two sets of ordinal-ranked values is Spearman rank correlation (ρ) [29]. A Spearman coefficient is essentially a Pearson correlation coefficient calculated using the ranks of the values of the two variables rather than their actual values. The formula is shown below [30]:
where ρ = Spearman’s Correlation coefficient; di = difference between two ranks of each observation; and n = number of observations.
The analysis was divided into two different time cycles: daytime and nighttime. Table 2 shows the description of the correlation using the following guide for the absolute value of “ρ”:

Table 2.
Description of the correlation related to the value of ρ [31].
2.4. Prediction Model
In this study, the daytime and nighttime O3 levels for the next day (the next 24 h) are predicted. As shown in Figure 1, data acquisition, exploration, cleaning, and partitioning are part of the data preparation. The data acquisition describes the information of data and parameters included in this study (as presented in Section 2.1). Secondly, a descriptive analysis including central tendency (mean and median) and dispersion (standard deviation) analyses were measured in data exploration. Next, data cleaning explained the technique involved in imputing the missing observation. In this study, expectation maximization (EM) was used to fill in the missing data as this method was reported as the most reliable method in estimating missing air pollutant observation data [32]. Before developing the model, the original dataset was partitioned into two datasets for training and validation. Out of the total data, 80% were used to develop the model, whereas the rest of the data were used to validate the model. Parameters that had moderate to strong correlation (ρ ≥ 0.4) with the O3 level from Spearman correlation analysis were used as the inputs for the prediction models. The details of predictive models are discussed in Section 2.4.1 and Section 2.4.2 and the performance evaluation for comparing the performances of the model is explained in Section 2.4.3.
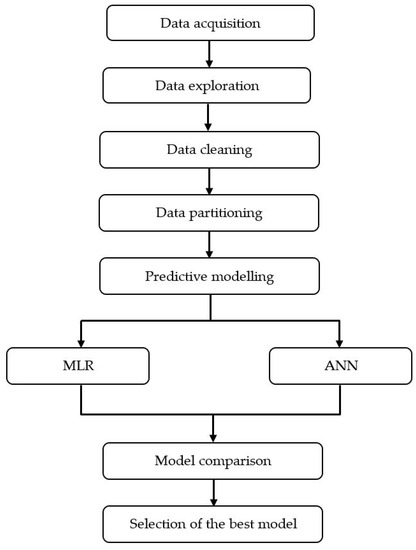
Figure 1.
Modeling framework.
2.4.1. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR)
MLR is a conventional method used to model air pollutants. MLR models the connection between two or more independent variables and a dependent variable by fitting a linear equation to the observed data. Multiple linear regression analysis is a statistical technique that can be used to examine the relationship between a single dependent (criterion) variable, Y, and several independent (predictor) variables, Xs. A random response Y relates to a set of independent variables X1, X2, …, Xi based on the multiple regression model. The equation can be read as [33]:
where, i is equal to n observations; Yi = dependent variable (daytime and nighttime O3 levels); Xi is the explanatory variables (ozone precursors and weather parameters); Β0 is the y-intercept (constant term); Βk is the slope coefficients for each explanatory variable; and ϵ = the model’s error term (also known as the residuals).
Yi = β0 + β1·X1 + … + βk·Xi + ϵi
2.4.2. Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
A feed-forward backpropagation neural network (FFBP) was used in this study. The structure of FFBP was composed of three layers of neurons called the input, hidden, and output layers. The first layer of neurons consisted of an input layer, representing independent variables. The second layer was the hidden layer, which is responsible for processing the input weight from the input layer and transferring it to the output layer. The third layer was the output layer, which represents the next-day prediction of daytime and nighttime O3 levels. The operation was conducted using the usual sigmoid function as the activation function.
2.4.3. Performance Indicators
Performance indicators are used to evaluate the predictive model by MLR and ANN. It was used to assess the model’s applicability in predicting daytime and nighttime O3 concentrations. The performance measures applied in this study are mean absolute error (MAE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and correlation (r) Table 3 [34].

Table 3.
Performance indicators.
Table 3.
Performance indicators.
| Performance Indicators | Equation | Better Predictability if |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Absolute Error | Closer to 0 | |
| Root Mean Squared Error | ||
| Correlation | Closer to −1 or +1 |
where;
| n | = | total number of hourly measurements at a particular site; |
| = | predicted values of a single set of hourly monitoring data; | |
| = | the observed values from a single set of hourly monitoring records; | |
| = | the mean of the predicted values from a single set of hourly monitoring data; | |
| = | the mean of the observed values from a single set of hourly monitoring data; | |
| = | the standard deviation of the predicted values from a single set of hourly monitoring data; | |
| = | the standard deviation of the observed values from a single set of hourly monitoring data. |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation of Ground-Level Ozone
Table 4 represents a data summary for ground-level ozone measurement in the three study areas for the period of 5 years. Overall, the mean concentration of ozone levels for Perai, Kuala Terengganu, and Seremban is below the limit (0.1 ppm) as postulated in the Malaysia Ambient Air Quality Standard (MAAQS). The maximum O3 level in 2018 was recorded as the highest value compared with all study areas during the five year period. The highest ozone concentration reading in Perai was 0.095 ppm in 2018 with a mean of 0.0175 ppm while the lowest maximum value was 0.080 ppm in 2020 with a mean value of 0.01718 ppm. From the mean concentration, Perai and Seremban showed an incremental trend from 2015 to 2019 whereas Kuala Terengganu showed a decremental trend of O3 levels. As a result, the smallest range of data was observed, i.e., 0 ppm to 0.009 ppm. Seremban recorded the highest concentration of O3 starting from 2018 with a mean value of 0.022 ppm. Lower concentrations were recorded in Kuala Terengganu and the lowest was in Perai. The standard deviation indicates that the O3 measurement records showed less variables and a smaller range of O3 levels was observed in Kuala Terengganu.

Table 4.
Descriptive statistic of ground-level ozone concentration in Perai, Seremban, and Kuala Terengganu from 2016 to 2020.
Figure 2 represents the box plot of hourly O3 concentrations in Seremban, Perai, and Terengganu from 2016 to 2020. The O3 levels in Seremban and Perai were observed to have higher variability in 2018 and 2019. Seremban had the maximum O3 level of 0.103 ppm in 2019 and recorded the lowest maximum concentration in 2020 with the value of 0.094 ppm. The highest concentration in Perai was 0.095 ppm in 2018 while the concentration decreased in 2019 and 2020 with maximum values of 0.093 ppm and 0.80 ppm, respectively. The data distribution for all years at Perai were skewed to the right which indicates a positive skew. Conversely, the concentration of O3 at Kuala Terengganu was the lowest compared with Perai and Seremban. The maximum O3 concentration was 0.082 ppm in 2017 while the lowest was 0.057 ppm in 2020 as illustrated in Figure 2. Kuala Terengganu experienced a decrease in O3 concentration values by year starting from 2016 to 2020. It was observed that O3 levels in Kuala Terengganu were less variable compared with Seremban and Perai.
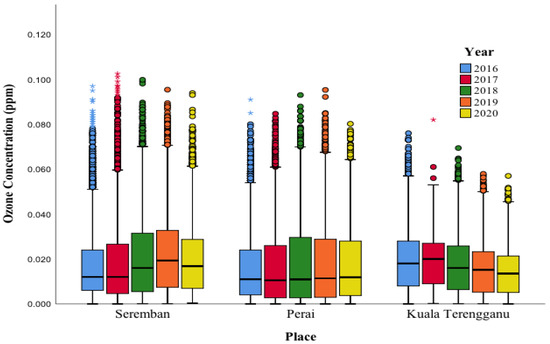
Figure 2.
Hourly box plot of O3 levels in Seremban, Perai, and Kuala Terengganu. The asterisk (*) on the boxplot indicate the extreme outlier that lie >1.5 times the size of the box.
Overall, the distribution of O3 levels in all study areas were skewed to the right which indicates that extreme concentration occurred. Seremban was observed to have a high exceedance of O3 levels especially in 2017. The monitoring station observed a decrease in 2020 due to less transportation use and factory shutdowns because of epidemic transmission of COVID-19. Malaysia’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in unprecedented reductions in economic activity in 2019 to 2021. After accounting for weather changes, lockdown events lowered population-weighted concentrations of NO2 and particulate matter by around 60% and 31%, respectively, as well as O3 concentrations [32]. Reductions in transportation sector emissions are largely responsible for the NO2 variances. The different results in three monitoring stations are believed to be influenced by variations in temperature, humidity, and wind speed.
Monthly variations of tO3 levels for the three study areas can be analyzed using contour plots and a wind rose diagram as depicted in Figure 3. During the early months of the year, Perai recorded the highest concentrations compared with Seremban and Kuala Terengganu with mean O3 concentrations of 0.0168 ppm in January, 0.0213 ppm in February, and 0.0219 ppm in March. Perai experienced very light wind (1 km/h to 3 km/h) in January and February that came from the southeast and light wind (3 km/h to 5 km/h) in March from the southeast and south. Latif et al. [6] reported that the northern area of Peninsular Malaysia experienced a hot and dry wind from the northeast, especially from Indochina and the South China Sea to the north of peninsular Malaysia. Nonetheless, the wind rose diagram indicates that Perai did not receive any wind from the northeast direction; hence, the high O3 levels during this month were most probably due to the low speed of wind. On the other hand, Seremban was observed to experience the highest concentrations of O3 levels during the inter-monsoon (April) with the value of 0.0224 ppm. During this month, Seremban mostly received light wind (3 km/h to 5 km/h).
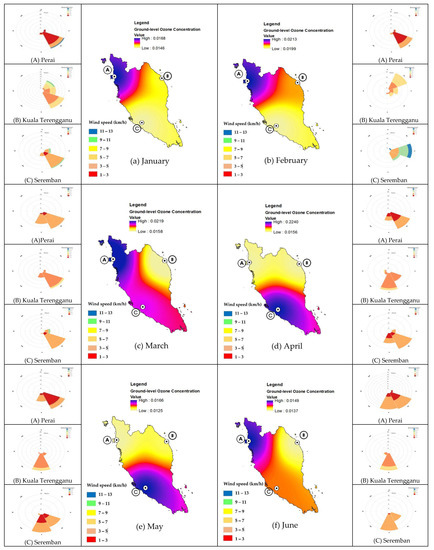
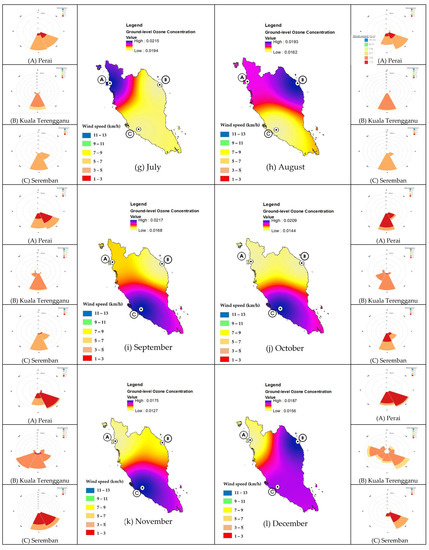
Figure 3.
Monthly contour plot and wind rose diagram of ground-level O3 in Seremban, Kuala Terengganu and Perai.
Perai once again recorded the highest levels of O3 compared with other areas during the early dry monsoon (June and July), which is the southwest monsoon, while Seremban recorded high O3 levels at the end of the summer monsoon (September) and during inter-monsoon (October and November). Weak wind (1 km/h to 5 km/h) was detected during the early season of the dry monsoon in Perai which might have influenced the dispersion of pollutants [10]. A gentle breeze (12 km/h to 19 km/h) is at least required to impact the greater dispersion of air pollutants, resulting in lower air pollution concentrations in areas with stronger winds. A similar situation can be observed in Seremban where very light wind (1 km/h to 3 km/h) was detected especially from October to December resulting in almost stagnant air in the inland areas.
In the other hand, O3 levels in Kuala Terengganu were detected to be higher at the end of the dry monsoon, i.e., in September and October. Light air (3 km/h to 5 km/h) from the south and southwest was detected in Kuala Terengganu during this time, hence confirming the influence of the southwest monsoon on O3 levels at this area.
Overall, higher O3 levels at all areas can be observed from June to October, i.e., during the southwest monsoon (dry monsoon). However, only Kuala Terengganu shows the influence of the monsoon in contributing to higher O3 levels in that area. Other areas, i.e., Perai and Seremban received light wind (1 km/h to 5 km/h) from the south and southeast. However, during this hot and dry climate, a low amount of precipitation and lower wind speed can be expected, hence it might influence the formation of ozone via complex photochemical reactions with other pollutants in the atmosphere that remain longer in the atmosphere due to poor dispersion [35].
Figure 4 shows weekly variations of O3 levels in Seremban, Kuala Terengganu, and Perai. Generally, the same diurnal trend of O3 variations were observed for the three monitored areas. On a weekly basis, the weekend and weekdays exhibited higher O3 levels starting from 10:00 am until 5:00 pm, whereas the O3 levels started to decrease starting at 6:00 pm until the next-day morning at around 9:00 am. The lowest O3 level was detected in Perai at 8:00 am during the weekday compared with other places, while the highest O3 concentration was found in Seremban at 5:00 pm during the weekdays.
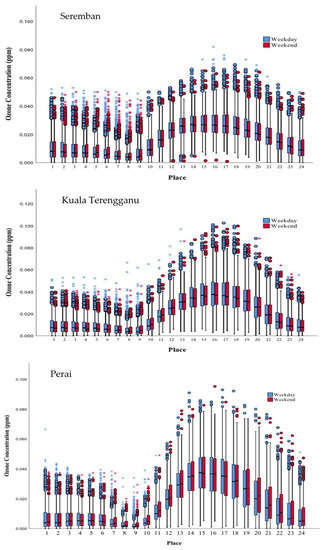
Figure 4.
Diurnal plot of O3 level during weekdays and weekends. The asterisk (*) on the boxplot indicate the extreme outlier that lie >1.5 times the size of the box.
Seremban showed a higher distribution of O3 levels during weekdays compared with the weekend. Extreme concentrations of O3 levels were observed early in the morning (from 1:00 am to 9:00 am) and in the evening (3:00 pm to 6:00 pm). During nighttime, the absence of UV light reduced the O3 photochemical reaction rate and the O3 concentrations because of continuous chemical degradation by NO and titration [36].
In Kuala Terengganu, a higher variability of O3 concentration was monitored during weekdays compared with the weekend. However, during the weekend, a higher concentration of O3 was detected in the morning (from 8:00 am to 12:00 pm) and the concentration was slightly low during the peak wavelength of solar radiation (from 2:00 pm to 4:00 pm) if compared with the variation during weekdays. However, the O3 level increased again from 5:00 pm onwards compared with the weekday variations. Similar O3 variations can be found in Perai with a higher degree of difference in O3 between the weekend and weekdays, especially in Perai because the monitoring areas are located next to the main highway of the South–North and Butterworth–Kulim Express Highway, which results in higher concentrations of O3 during the weekend because many people use the highway to travel to their hometowns on weekends.
Higher O3 levels during the weekend compared with weekdays may be caused by the differences in the number of vehicles. A high level of ozone on the weekend is a well-known phenomenon known as the “ozone weekend effect” (OWE) [37]. The OWE is not pronounced in all areas except for Perai. Low levels of traffic on weekends are thought to be the primary source of OWE, as low levels of NO emission reduce local ozone elimination. The greater amount of ozone compared with other weekdays is most likely due to the residual effect of ozone from the weekend. Ozone concentrations in all cities follow a similar twenty-four-hour cycle, with lower levels during the night and early morning hours and higher levels during the day. The largest concentrations are obtained in the afternoon from 12:00 am to 5:00 pm due to photochemical ozone generation as a result of high UV radiation intensity during these hours. During this time, the high release of vehicle emissions contributes to the high amount of NO that will react with more O3 to produce NO2. Hence, lower O3 concentrations during this period can be expected during weekdays compared with weekends due to traffic emissions. Conversely, the concentration of ozone decreases after 5:00 pm until the next morning due to less intense or no UV radiation [38]. In addition, the population and the background of the area play a major role in influencing the OWE and the amount of O3 produced daily.
3.2. Association of O3 Level with Its Precursors
Figure 5 shows the diurnal pattern of ground-level O3 and its precursors, namely, NO, NOx, NO2, and CO, at all monitoring stations. Generally, a similar pattern of variation of O3 levels with its precursors can be observed for all places except different intensities of pollutants. Higher concentrations of O3 precursors, i.e., CO, NO, NOx, and NO2 were monitored in the morning (7:00 am to 9:00 am) and evening (6:00 pm to 10:00 pm) to coincide with people travelling to perform their daily routines. Photochemical reactions of O3 precursors to form O3 took place more significantly when greater solar radiation was detected during the day starting from 9:00 am. The highest O3 formation was observed in Seremban and Seberang Perai during the maximum intensity solar radiation period (2:00 pm to 4:00 pm). O3 concentration started to drop significantly at the night when no UVB radiation was available.
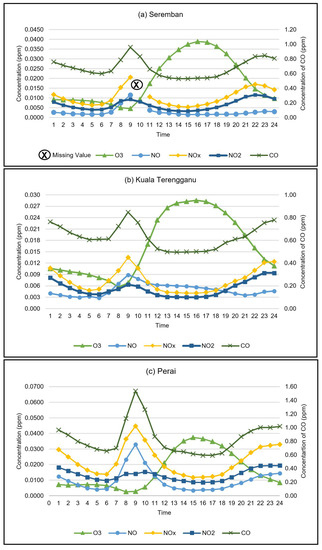
Figure 5.
Diurnal plot of O3 precursors in (a) Seremban, (b) Kuala Terengganu, and (c) Perai.
A noticeable higher concentration of NO, NOx, and CO were observed in Perai compared with other areas. There is a lot of housing near the monitoring station and the whole Seberang Perai population was about 428,500 in 2020 [28]. The Butterworth–Kulim Express highway and North–South highway are close to the monitoring area. Furthermore, an industrial area in the Free Industrial Zone (FIZ) is also located within 5 km of the monitoring area. Hence, high air pollutant emissions from vehicles can be expected. High NO concentrations will effective atom titration of (O) in urban areas due to emissions from the large amount of transportation. The negative relationship between O3 and NO2 is expected as NO2 is a precursor of O3 [39]. This phenomenon is shown in (Equation (3)):
NO + O3 → NO2 + O2
Hence, it can be seen that the O3 levels in Perai were significantly less if compared with its precursors, i.e., NO and NO2. If compared with Seremban and Kuala Terengganu, the least amount of NO and NO2 were released and the amount of O3 formation was greater compared with its precursors. The NO formed inside vehicle engines reacts with O2 in the air to form NO2. Ozone is formed when a combination of nitrogen (N) and O2 is exposed to UVB by the photolysis of NO2. ‘M’ represents an unstable molecule such as nitrogen (N2) or O2, and O (3P) represents an equilibrium state or low-energy oxygen atom that interacts with molecular O2 to produce O3 [40]:
NO2 + hν → NO + O (3P)
O + O2 + M → O3 + M
Since in Seremban and Kuala Terengganu there is less NO compared with Perai, less O3 was converted to NO2 and O2 as in Reaction (3). In addition, Perai has the largest value of CO due to the monitoring station being located at a main highway, and slow traffic during peak hours influenced CO concentrations. The location located near the FIZ also contributed many pollutions to that area. While during midday, the photochemical O3 formation consumes CO which causes O3 concentrations to increase and CO concentrations to decrease, which explains the negative association [41].
The oxidation of trace gases in the atmosphere, such as VOCs, probably contributed to O3 formation in this location, which was largely initiated by the reaction with OH whose concentration is controlled by the concentrations of local VOCs and NOx [42]. The phenomenon is shown below [41]:
CO + OH → H + CO2
H + O2 + M → HO2 + M
HO2 + NO → NO2 + OH
Then, NO2 undergoes photolysis and O3 is formed according to Reactions (4) and (5).
3.3. Association of O3 Level with Other Trace Gases and Weather Parameters
Figure 6 illustrates the Spearman Correlation heat matrix for daytime and nighttime in Perai, Kuala Terengganu, and Seremban. Overall, O3 concentration was negatively correlated with its precursors, i.e., NO2, NOx, NO, and CO for all places during day and nighttime. While for weather parameters, the most correlated parameter was temperature followed by wind speed, UVB, and humidity. All weather parameters were positively correlated with O3 except for humidity, which was negatively correlated. Remarkably, a moderate to strong correlation of CO with NO2, NOx, and NO were observed in the study areas with a higher correlation value during nighttime.
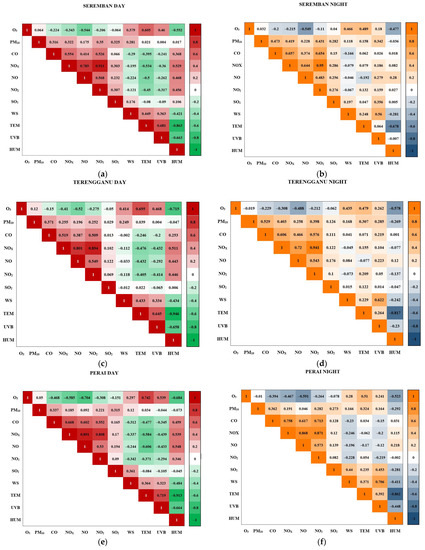
Figure 6.
Spearman correlation matrix of O3 with trace gases and weather parameters: (a) Seremban daytime, (b) Seremban nighttime, (c) Kuala Terengganu daytime, (d) Kuala Terengganu nighttime, (e) Perai daytime, and (f) Perai nighttime.
Figure 6a shows the association of daytime and nighttime O3 levels with its precursors and weather parameters at Seremban. A moderate to strong correlation of O3 with weather parameters during daytime was observed with the strongest positive correlation in the temperature (ρ = 0.605). A moderate negative correlation was detected with NO and a weak negative correlation of O3 with other precursors (NOx and CO) were calculated. A similar trend of association of O3 levels with its precursors and weather parameters were observed during nighttime except with lower calculated ρ values. A very strong to strong correlation of NOx with NO2 and NO was observed during daytime and nighttime in Seremban due to its inter-convertible reaction from NO to NO2 and reactions of NOx with VOCs.
In Kuala Terengganu, a similar association between O3 levels with the gases and weather parameters during daytime and nighttime was observed if compared with Seremban (Figure 6c,d). Temperature was positively correlated while humidity was negatively correlated with O3 while its precursors also showed a negative correlation with ozone during daytime and nighttime. However, a higher calculated ρ-value between O3 level and wind speed was calculated in Kuala Terengganu compared with other places as it is situated near the coastal area, hence land and sea breeze might have influences on air pollutant dispersion.
In Perai, the highest correlation value of CO with O3 concentration was calculated compared with other areas with the value of −0.468. In addition, during the daytime, a strong negative correlation was observed with NO (ρ = −0.704), temperature, and humidity with ρ-values of −0.742 and −0.684, respectively, while during the nighttime, a strong negative correlation was detected with NO (ρ = −0.591). NOx recorded a moderate correlation with O3 that was (ρ = −0.467). CO not only had a high correlation with O3, it also had a significant positive correlation with NOx, NO2, and NO compared with other areas of study with higher values observed during nighttime.
Overall, high temperature contributes to photochemical ozone chemistry which is significant in the generation of secondary aerosols such as sulfate (SO4−2) and nitrate (NO3−) that are generated from SO2 and NOx [43]. This mechanism most likely reduces the negative link between the two species over time. NO is significantly associated with O3 concentration, as increases in its concentration are usually influenced by the complex reaction between NOx and VOCs in the atmosphere produced by motor vehicles and industrial combustion processes [44]. Humidity is negatively correlated with O3 due to humid days with enhanced cloud cover and thus results in a reduced photochemistry reaction in O3 formation [42]. O3 level has a positive association with temperature due to its formation requiring high UV radiation. Conversely, temperature is negatively correlated with humidity resulting in less humidity in the ambient air with the increase in temperature [43]. Obviously in Perai, SO2 concentration is among the highest associated with O3 compared with other places due to industrial areas being located near the monitoring station. According to Latif et al. [45], the fluctuations of SO2 in the study area may be due to the contributions of SO2 from local and regional sources of biomass burning. As Penang Port is near the monitoring areas, it might be the cause of the high concentrations of SO2 in that area. The distribution of SO2 is influenced by the shipping port because it transfers SO2 to the surrounding areas [46].
In conclusion, parameters that had moderate to strong correlation (ρ ≥ 0.4) with O3 level were used as input for daytime and nighttime prediction of O3 levels. In the next section, the performances of the linear and nonlinear models were compared and evaluated using several performance measures.
3.4. Prediction of Daytime and Nighttime O3 Levels
The linear relationship of O3 levels in daytime and nighttime at all study areas are tabulated in Table 5. The independent parameters for the linear model were the parameters that were strong and moderately correlated (ρ > 0.4) with O3 level. From the table, it can be seen that O3 level was correlated with previous O3 concentrations, NOx and NO. However, no relation was detected with weather parameters indicating that very minimal to no correlation between weather parameters and O3 levels was identified using MLR. NO is a significant predictor of variables during the daytime at Seremban. However, NO and temperature are significant during the nighttime. The O3 concentration decreased 0.027 units when the one unit of NO decreased during the daytime and 0.042 and 0.001 units of NO and temperature during nighttime. In addition, Kuala Terengganu indicated an increase of one unit of NOx will result in an increase of 0.331 units of O3 during the daytime and a decrease of 0.024 of NO during the nighttime. Perai showed that the increase of one unit of NOx will result in an increase of 0.197 units of O3. The O3 concentration decreased about 0.002 and 0.325 when the one unit of CO and NO decreased.

Table 5.
Model summary for O3 level predictions.
Validation of MLR and ANN predictive models were performed using performance indicators. Table 6 shows the results of the predictive model evaluation of O3 levels using mean absolute error (MAE), root mean squared error (RMSE), and correlation (r). Generally, ANN outperformed MLR in predicting the daytime and nighttime O3 levels in the study areas as a lower error measurement and higher correlation value were calculated. Both of the models estimated better daytime O3 levels compared with nighttime O3 in Kuala Terengganu and Perai with average r differences between daytime and nighttime of 6.66% and 6.97% using MLR and ANN, respectively. Meanwhile, in Seremban, ANN predicted better nighttime O3 levels compared with daytime and the performances of ANN was observed to be the worst in Seremban (r = 0.699) compared with other areas (r value ranging from 0.765 to 0.862). Similarly, MLR predicted better nighttime O3 concentration (r = 0.615) and MLR prediction in Seremban was observed to be the worst compared with other places with r values ranging from 0.683 to 0.747.

Table 6.
Predictive Model Performance.
Ground-level ozone is produced by nonlinear photochemical reactions involving its precursors and is affected by many factors including precursor concentrations, local meteorological conditions, air transportation, deposition, etc. These factors control the production, loss, and transformation of O3, and thus its concentrations and spatial distribution. Hence, ANN that is a nonlinear model can better represent the complex relationship of O3 with its precursors and weather parameters. Feed forward backpropagation neural network (FFBP) is one of the most known ANNs. In several applications, including regression problems, classification problems, or time series predictions, FFBP has been successfully implemented using single autoregressive models [47]. Each input neuron represents one of the input variables (precursors or weather parameters), which are weighted before entering the hidden layer. The output of the hidden layer is based on the output of nonlinear transfer function (sigmoid function), which is applied to modify the sum of the entering weighted values. Thus, multi-variable problems can be managed by ANN as they may describe highly nonlinear connections, such as ozone production, that were overlooked by a conventional statistical technique (e.g., regression model [21]).
4. Conclusions
In this study, three urban areas located in peninsular Malaysia were selected. Hourly air pollutants and a weather parameters dataset from 2016 to 2020 were used to analyze the spatiotemporal variation of O3 levels and its relation to the weather parameters. Seremban recorded the highest annual concentration of O3 levels in 2017, whereas Kuala Terengganu experienced a decrement in annual O3 levels starting from 2016. Slightly lower concentrations were observed in 2020 due to less emission of VOCs and NOx as a result of the total lockdown in Malaysia caused by COVID-19. The diurnal plot O3 concentration with its precursors (NOx, NO, NO2, and CO) showed similar trends at the three study areas. The peak of O3 precursors was observed during rush traffic hours in the morning and evening and O3 formation was observed to reach its peak hour during the maximum solar intensity of the day (2:00 pm to 5:00 pm) and started to decrease steeply after 6:00 pm. The concentration of ground-level ozone varies according to the population and the location of the monitoring station. VOCs react with ozone precursors during photochemical reaction and increase concentrations of ozone while decreasing concentrations of precursors. The association of ozone and its precursors including weather parameters were tested using non-parametric correlation. Spearmen correlation was used to analyze the relation of ozone with one independent variable. The result indicates that there was a strong correlation between ozone with temperature and NO, whereas a moderate correlation between NOx and CO was observed. A similar trend of association of O3 levels with its precursors and weather parameters was observed during nighttime except with a lower calculated ρ value. A very strong to strong correlation of NOx with NO2 and NO during daytime and night-time was observed in Seremban due to its inter-convertible reaction from NO to NO2 and reactions of NOx with VOCs. Two predictive models, i.e., a linear model (multiple linear regression) and a nonlinear model (ANN, feed forward back propagation) were attempted to model the daytime and nighttime O3 levels at all study areas. FFBP outperformed the prediction of O3 levels during daytime and nighttime compared with MLR due to a better agreement between the predicted and observed measurement.
In this study, an association between daytime and nighttime O3 levels can only be made with NOx concentration due to the missing measurement of non-methane hydrocarbon (NmHC) that represents VOC. Excluding VOC as one of the important O3 precursors might cause the loss of important information/findings related to a place. However, this research successfully analyzed daytime and nighttime O3 levels with its precursors at the selected areas. Variation of nighttime O3 levels is usually neglected because O3 cannot be formed photochemically due to the lack of sunlight at night, and NOx will continuously react with O3, which is hypothetically the main period of O3 depletion. Reduced O3 depletion because of the decline in NOx emission would lead to the accumulation of O3 at night, which would provide higher initial concentrations for photochemical reactions during the daytime, further leading to higher O3 concentrations and exposure hazards at daytime. Therefore, the possible long-term effects on ecosystems caused by nighttime O3 concentrations has important research implications. Prior to this, a long-term study of nighttime O3 variation together with its precursors is required to determine the increment/decrement trend of this pollutant. Local authorities can strategize mitigation plans accordingly, especially by controlling anthropogenic precursors such as NOx and VOC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.E.B. and N.M.N.; methodology, N.M.N.; software, Z.H.; validation and visualization, N.M.N., A.Z.U.-S., A.V.S., and P.V.; formal analysis, N.M.N.; investigation, G.D.; resources, M.R.R.M.A.Z.; data curation, A.A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, S.E.B.; writing—review and editing, N.M.N.; visualization, Z.H.; supervision, N.M.N.; project administration, M.R.R.M.A.Z.; funding acquisition, A.V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research publication was supported by TUIASI from the University Scientific Research Fund (FCSU).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thank to Department of Environment Malaysia for the air pollutant dataset.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tang, H.; Takigawa, M.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Kobayashi, K. A projection of ozone-induced wheat production loss in China and India for the years 2000 and 2020 with exposure-based and flux-based approaches. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Mandal, T.K. Ozone sensitivity factor NOX or NMHCs. A case study over an urban site in Delhi, India. Urban Clim. 2021, 39, 100980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.; Makar, P.A.; Plummer, D.A. Projections of mid-century summer air-quality for North America: Effects of changes in climate and precursor emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5367–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Bortoli, D.; Domingues, A.; Silva, A.M. Surface ozone variability and trend over urban and suburban sites in Portugal. Aerosol Air Qual. 2016, 16, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Zou, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Zhu, B. Differences in ozone photochemical characteristics between the megacity Nanjing and its suburban surroundings, Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Resour. 2015, 22, 19607–19617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Huey, L.S.; Juneng, L. Variations of surface ozone concentration across the Klang Valley, Malaysia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, N.R.; Ramli, N.A.; Yahaya, A.S.; Elbayoumi, M. High night time ground level ozone concentrations in Kemaman: NO and NO2 concentrations attributions. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Rappenglueck, B. A study of model nighttime ozone bias in air quality modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, Z.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Lee, S.Y. Spatiotemporal variations of air pollutants in western China and their relationship to meteorological factors and emission sources. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, L.; Ying, F.; White, S.J.; Jang, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Hong, S.; Shen, J.; Azzi, M.; et al. Meteorological and chemical impacts on ozone formation: A case study in Hangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; He, M.; Xu, N.; Zhang, J.; Qian, F.; Feng, J.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides at urban, suburban and rural sites in Ningbo, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, P.S.; Duffey, K.C.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Edgerton, E.; Baumann, K.; Feiner, P.A.; Miller, D.O.; Brune, W.H.; Koss, A.R.; de Gouw, J.A.; et al. Effects of temperature-dependent NO x emissions on continental ozone production. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 2601–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujabar, S.; Chintaginjala Venkateswara, R. Empirical models for estimating the global solar radiation of Jubail Industrial City, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, A.K.; Tuluri, F.; Tchounwou, P.B.; Ambinakudige, S. Influence of local meteorology and NO2 conditions on ground-level ozone concentrations in the eastern part of Texas, USA. Air Quality. Atmos. Health 2015, 8, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaluddin, A.F.; Tangang, F.; Chung, J.X.; Juneng, L.; Sasaki, H.; Takayabu, I. Investigating the mechanisms of diurnal rainfall variability over Peninsular Malaysia using the non-hydrostatic regional climate model. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 130, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Satsangi, A.; Lakhani, A.; Kumari, K.M. Prediction of Ground level Ozone concentration in Ambient Air using Multiple Regression Analysis. J. Chemstry Biol. Phys. Sci. 2015, 5, 3685–3696. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Hosseinibalam, F.; Omidvari, M. Statistical methods and regression analysis of stratospheric ozone and meteorological variables in Isfahan. Phys. A Stat. Mechacnic Appl. 2008, 387, 2317–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrero, M.A.; Grimalt, J.O.; Canto’n, L.M. Prediction of daily ozone concentration maxima in the urban atmosphere. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2006, 80, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banja, M.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. Atmospheric Pollution Research Development of a short–term ozone prediction tool in Tirana area based on meteorological variables. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allu, S.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Maddala, R.K.; Reddy, A.; Anupoju, G.R. Seasonal ground level ozone prediction using multiple linear regression (MLR) model. Modeling Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alawi, S.M.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Bakheit, C.S. Combining principal component regression and artificial neural networks for more accurate predictions of ground-level ozone. Environ. Modeling Softw. 2008, 23, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma, K.; Samuel Selvaraj, R.; Arputharaj, S.; Milton Boaz, B. Improved Artificial Neural Network Performance on Surface Ozone Prediction Using Principal Component Analysis. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2014, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, I.; Jarosławski, J. Forecasting of surface ozone concentration by using artificial neural networks in rural and urban areas in central Poland. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, M.; Shkoukani, M.; Hijjawi, M. Ground-level Ozone Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Case Ground-level Ozone Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Case Study in Amman, Jordan. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2020, 17, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Hernández, B.A.; Tello-Leal, E.; Ramirez-Alcocer, U.M.; Hernandez-Resendiz, J.D. Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Concentration Forecasting through an Artificial Neural Network in Port City Environment. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 19, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahremanloo, M.; Lops, Y.; Choi, Y.; Yeganeh, B. Deep Learning Estimation of Daily Ground-Level NO2 Concentrations from Remote Sensing Data. JGR Atmos. 2021, 126, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wan Mahiyuddin, W.R.; Sahani, M.; Aripin, R.; Latif, M.T.; Thach, T.Q.; Wong, C.M. Short-term effects of daily air pollution on mortality. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 65, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Statistic 2020. Available online: https://www.dosm.gov.my/v1 (accessed on 12 May 2022).
- Astivia, O.L.O.; Zumbo, B.D. Population models and simulation methods: The case of the Spearman rank correlation. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2017, 70, 347–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Lan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chan, P.; Fan, S.; Feng, Y. Diagnostic analysis of the sulfate aerosol pollution in spring over Pearl River Delta, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sukatis, F.F.; Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Noor, N.M.; Zakaria, N.A.; Suwardi, A. Estimation of Missing Values in Air Pollution Dataset by Using Various Imputation Methods. Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2019, 10, 791–804. [Google Scholar]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Springer Texts in Statistics and Introduction to Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Saufie, A.Z.; Yahaya, A.S.; Ramli, N.A.; Hamid, H.A. Performance of multiple linear regression model for longterm PM10 concentration prediction based on gaseous and meteorological parameters. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavassalis, S.C.; Murphy, J.G. Understanding ozone-meteorology correlations: A role for dry deposition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Lal, S.; Sarkar, U. High nocturnal ozone levels at a surface site in Kolkata, India: Trade-off between meteorology and specific nocturnal chemistry. Urban Clim. 2013, 5, 82–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkin, M.E. Trends in ozone concentration distributions in the UK since 1990: Local, regional and global influences. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5434–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, M.; Fowler, D.; Smith, R.I.; Weston, K.; Stedman, J.R. Quantifying the spatial distribution of surface ozone concentration in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Ahamad, F.; Shuhada, N.; Khan, M.F.; Juneng, L.; Xiang, C.J.; Nadzir, M.S.M.; Robinson, A.D.; Ismail, M.; et al. Seasonal and long-term variations of surface ozone concentrations in Malaysian Borneo. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnung, S.E.; Johnson, M.S. Chemistry and the Environment; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, S.; Chen, H.; Ropkins, K. Characterising the temporal variations of ground level ozone and its relationship with traffic-related air pollutants in the UK: A quantile regression approach. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2012, 9, 29–41. [Google Scholar]
- Heard, D.E.; Pilling, M.J. Measurement of OH and HO2 in the troposphere. Chem. Revolut. 2003, 103, 5163–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Kulmala, M. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1-year data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, F.; Latif, M.T.; Tang, R.; Juneng, L.; Diminick, D.; Juahir, H. Variation of surface ozone exceedance around Klang Valley, Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2014, 139, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Dominick, D.; Ahamad, F.; Khan, M.F.; Juneng, L.; Hamzah, F.M.; Nadzir, M.S.M. Long term assessment of air quality from a background station on the Malaysian Peninsular. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, A.A.A.; Latif, M.T.; Baharudin, N.H.; Ahamad, F.; Chung, J.X.; Othman, M.; Juneng, L. Variation of major air pollutants in different seasonal conditions in an urban environment in Malaysia. Geosci. Lett. 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Ran, L.; Deng, Z.Z.; Liu, P.F.; Ma, N.; Chen, L.L. Characteristics of pollutants and their correlation to meteorological conditions at a suburban site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4353–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).