Abstract
Clay minerals composed of Si and Al could help reduce ultrafine particulate matter (PM) formation as an additive during coal combustion while currently unacceptable high adding dosages (normally 3–5 wt.%) are required due to their inadequate capture efficiency. To find additives that could effectively reduce the formation of ultrafine PM, coal combustion with a novel nano SiO2 additive (<100 nm) was performed to evaluate its effects on reducing ultrafine PM. The generated PM10 was sampled to characterize their particle size distribution, mass yield, size-resolved composition and micromorphology. The results showed that adding a small dosage (0.6%) of nano SiO2 reduced the mass yield of ultrafine PM by 30.70%, showing a much higher ultrafine PM capture efficiency than an existing micron-sized natural clay mineral. However, its performance on different coals varied due to disparities in ash content and composition in coal. A composition analysis revealed that the Na content in the ultrafine PM was decreased after adding nano SiO2, indicating that nano SiO2 inhibited the migration of volatile alkali metals such as Na into ultrafine PM because the Na-containing mineral vapor reacted with the nano SiO2 additive particles with a large specific surface area at a high temperature and inhibited their transformation into ultrafine PM via homogenous nucleation. Changes in the element size distributions and micromorphology showed that the majority of the added nano SiO2 particles reacted or coalesced with each other and/or the minerals embedded in coal, finally growing into a larger PM.
1. Introduction
Ultrafine particulate matter (PM) is an important part of the fine particulate matter (PM2.5, PM with an aerodynamic diameter of <2.5 μm) emitted from the combustion process [1,2,3,4]. What is worse, due to its small particle size, ultrafine PM is much more harmful to the health of human beings [5,6,7,8,9,10]. On the one hand, ultrafine PM is apt to be enriched with hazardous substances (e.g., heavy metals [11,12], polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons [13], viruses and germs) due to its high specific area. On the other hand, ultrafine PM could easily penetrate the respiratory system and get deep into our body, bringing damage to the cardiovascular system, brain and so on. Coal combustion in utility boilers is one of the major emission sources of ultrafine PM. Additionally, increasing efforts are being made to control the formation of ultrafine PM during coal combustion processes [3,14,15,16,17,18].
As is well known, ultrafine PM is formed mainly via the vaporization and nucleation of minerals in coal during coal combustion [1,2]. Additionally, volatile mineral matter such as alkali metal elements (e.g., Na, K) and alkali earth metal elements (e.g., Ca, Mg) that easily form mineral vapor at a high combustion temperature are normally major constituents of the combustion-derived ultrafine PM [19,20,21,22]. Therefore, in-furnace additives have been proposed and developed to mitigate the formation of ultrafine PM via capturing mineral vapor (the so-called vapor-capture mechanism) and/or via enhancing the coalescence of generated ultrafine particles with the partially molten surface (the so-called liquid phase) [23,24,25]. Various in-furnace de-PM additives have been studied, including clay minerals (e.g., kaolinite, montmorillonite, consisting of Si and Al as major constituents) [26,27,28,29,30], such as Ca-based additives (e.g., limestone, calcium hydroxide) [28,31], Ti-based additives (e.g., TiO2) [18], P-based additives [32,33] and Fe-based additives [34]. Kaolinite is one of the most widely studied de-PM additives, which is revealed to inhibit the formation of ultrafine PM via capturing Na-contained mineral vapor into aluminosilicates. Currently, it is well recognized that additives composed of Si and Al are more effective for coal with high content of alkali metals.
The performance of additives in reducing the formation is closely related to not only their chemical composition but also their particle size. Usually, additives of a particle size of several microns are used at present. For example, Chen et al. [3] determined the PM reduction performance of a kaolin of a particle size 8.5 μm (D50) in lab-scale experiments on the drop tube furnace and observed an ultrafine PM (PM0.3) reduction efficiency of 33.35% at an adding dosage of 3% (defined as 3 g_kaolin/100 g_coal). Some other studies [18,35] also investigated the performance of kaolin and found an ultrafine PM (PM0.2) reduction efficiency of ~22% (for lignite coal) and ~17% (for anthracite coal) at an adding dosage of 5% for the particle size of kaolin of 1.43 μm (D [3, 2], surface area volume mean diameter) and <200 μm, respectively. Chen et al. [3] further investigated the influence of kaolin particle size and adding dosage on PM reduction efficiency via numerical modeling. Based on simulation results, it was shown that the chemical adsorption of the mineral precursors was the dominant mechanism for PM reduction and they claimed that increasing the kaolin size had a negative impact on PM reduction. Meaningfully, it was pointed out that a larger particle size would result in a smaller specific surface area and a larger diffusion resistance, which would reduce the performance of the alkali mineral vapor capture of the kaolin particles. Accordingly, nano additives have been proposed in our previous studies to reduce fine PM formation [14], and the results showed that adding a small dose (0.6%) of nano Al2O3 and TiO2 particles reduced the mass yield of PM2.5 by 12.85–19.59%, indicating quite different PM reduction characteristics than the conventional micron-sized clay-mineral-derived additives. However, the reduction efficiency of the above additives on the ultrafine PM was still not good enough.
In this study, coal combustion experiments were performed on a lab-scale drop tube furnace system with/without a novel nano SiO2 additive addition. PM with an aerodynamic diameter of <10 μm (i.e., PM10) was collected to evaluate the effects of nano SiO2 on ultrafine PM formation, and a detailed analysis of the particle size distribution, mass yield, element size distribution and micromorphology were conducted to reveal the underlying mechanism.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
Two typical Chinese coals, one bituminous coal and one lignite were used in the experiments. The proximate analysis, ultimate analysis and ash analysis of the tested coals are listed in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. Briefly, coal Shanxi (SX) had a higher ash content (17.92%) than coal Wucaiwan (WCW) (4.57%). Regarding ash composition, coal SX had a much higher content of Si and Al (e.g., a Si content of 49.22% in oxide form) than coal WCW while coal WCW had much higher contents of alkali and alkali earth metals (e.g., a Na content of 4.46% and a Ca content of 44.55% in oxide form) than coal SX. Raw coals were pulverized and samples in the size range of 60–100 μm were screened out for experiments.

Table 1.
Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of coals Shanxi (SX) and Wucaiwan (WCW) (air-dried basis).

Table 2.
Composition of nano SiO2 particles and the low-temperature ash of coals SX and WCW with/without nano SiO2 addition (wt.%).
Nano SiO2 particles were selected as additives. As shown in Table 2, the tested nano SiO2 sample was of a high purity, with a SiO2 content of >96%. Additionally, observations under the scanning electron microscope (SEM) confirmed that the sample had a diameter of <100 nm. Prior to combustion experiments, nano SiO2 particles were dispersed in alcohol and were added into pulverized coal samples via spraying at an adding dosage of 0.6%, namely 0.6 g additive per 100 g coal powder. To ensure the mixing uniformity, the spraying of the additive–alcohol mixture into coal powder was repeated 5 times with sufficient drying and dispersion after each spraying time. Detailed information on the blending procedures and uniformity check can be found in our previous study [14]. Most importantly, the elemental compositions of the low-temperature ash of coals SX and WCW before and after nano SiO2 addition are shown in Table 2. As expected, adding the nano SiO2 additive led to an increase in Si content in the ash and a much higher increase in Si content was observed in coal WCW than that in coal SX due to their disparities in ash content. As can also be seen in Table 2, the Na content in the low-temperature ash increased after nano SiO2 addition as well, indicating enhanced Na fixation and inhibited Na vaporization in coal.
2.2. Coal Combustion and PM Measurement
Combustion of pulverized coal samples with/without nano SiO2 additive addition was performed on a high-temperature drop tube furnace system (shown in Figure 1). Briefly, the furnace consisted of a corundum tube reactor (length: 1440 mm, inner diameter: 56 mm), and more details of the combustion system can be found in our previous studies [14,16,18,19,36]. During the experiments, coal samples were fed into the reactor from the top inlet at a feed rate of 0.3 g/min and they were burned in the reactor at a wall temperature of 1500 °C. The air feed rate was 5 L/min for the high burn-off rate. The combustion-derived ash particles were collected at the bottom outlet of the reactor via a low-pressure impactor (LPI) sampling system (sketched in Figure 1).
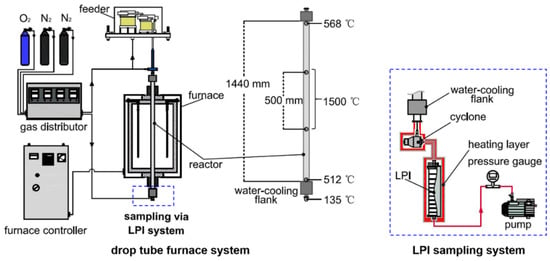
Figure 1.
Sketch of the drop tube furnace system and particulate matter (PM) sampling system.
As can be seen, the LPI sampling system was made up of a cyclone, a Dekati low-pressure impactor, a vacuum pump, a pressure gauge monitoring the pump inlet pressure and a heating jacket covering the LPI, as well as a cyclone and the pipe connecting them [14,19,36,37,38]. During sampling, flue gas loaded with ash particles was firstly introduced into a cyclone and particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of >10 μm (PM>10) was separated and collected. Then, residual ash particles (PM10) were classified into 13 stages and were collected in the LPI according to the particle size. Both the LPI and cyclone were heated to 135 °C via the heating jacket to avoid the condensation of steam and acid gases in the flue gas.
The collected PM10 samples were characterized from three aspects to evaluate the effects of the nano SiO2 additive addition on the formation of ultrafine PM. Firstly, the mass of the size-classified particles was obtained via a microbalance (MSA6.6S-0CE-DM, Sartorius, Gottingen, Germany) to calculate the mass yield and mass size distribution [14,16]. Secondly, the elemental composition of the size-classified PM at each stage was determined via an X-ray fluorescence probe (XRF, EAGLE III, EDAX) to obtain the element size distribution of the PM10 and the effects of the nano SiO2 additive addition on the partitioning behaviors of the mineral matter into ultrafine PM [14,16,18]. Thirdly, the micromorphology of the PM in typical size ranges was characterized via an electro-probe microanalyzer (EPMA, EMPA-8050G, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) to visually show the influence of the nano SiO2 additive addition on the coalescence and coagulation of the ash particles [14,16,18]. Additionally, coal samples with/without the nano SiO2 additive addition were ashed in a plasm asher (PT-5SM, Potentlube, Shenzhen, China) and then the elemental composition and melting behavior of the low-temperature ash were determined via the above-mentioned XRF and a digital imaging coal ash fusibility system (CAF) produced by Carbolite (Sheffield, UK).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size Distributions (PSDs) and Yields of Ultrafine PM Subsection
Mass-based particle size distribution (PSD) curves of the PM10 formed during the combustion of the tested coals SX and WCW before and after nano SiO2 addition are presented in Figure 2. Additionally, based on the PSD curves, mass yields of PM0.1, PM0.1–2.5, PM2.5, PM2.5–10 and PM10 as well as their reduction ratio after adding nano SiO2 into coals SX and WCW were further calculated and are listed in Table 3, straightforwardly showing the effects of the nano SiO2 additive addition on the formation of particulate matter during pulverized coal combustion.
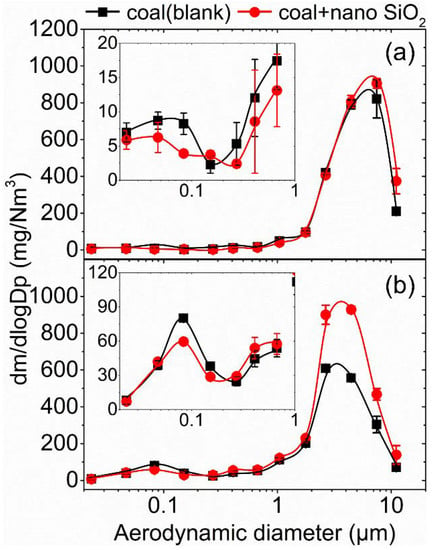
Figure 2.
Particle size distributions of the PM10 formed during the combustion of coals with/without nano SiO2 addition: (a) SX; (b) WCW.

Table 3.
Mass yields of PM0.1, PM0.1–2.5, PM2.5, PM2.5–10 and PM10 and their reduction ratio after adding nano SiO2 into coals SX and WCW.
As shown in Figure 2, PSDs curves of the PM10 derived from the combustion of coals SX and WCW contained two peaks, namely an ultrafine modal with the modal peak at 0.08–0.10 μm and a coarse modal with the modal peak at 4–6 μm. The observed bimodal size distribution of PM10 has been well illustrated in the existing literature [1,2]. Briefly, it was generally concluded that the ultrafine PM was formed via the vaporization and nucleation of the mineral matter embedded in coal while the coarse PM was formed via the fragmentation, melting and coalescence of the mineral particles and PM. Most importantly, adding the nano SiO2 clearly changed the PSD curves of the formed PM10 while its effects on the fine PM were different from that on the course PM. For both coal SX and coal WCW, the results showed that the modal peak in the fine modal was reduced while the peak in the coarse modal after adding nano SiO2 increased, indicating that adding nano SiO2 would help reduce the formation of ultrafine PM and promoted their growth and migration into coarse PM. Based on the PSD curves, the PM with an aerodynamic diameter of <0.1 μm was defined as ultrafine PM (expressed as PM0.1 below) to quantify the mass yields of ultrafine PM and the performance of the nano SiO2 additive.
As can be seen in Table 3, the ash-based mass yields of the PM0.1 of coals SX and WCW were 0.743 and 5.408 mg_PM/g_ash, and the mass yields of the PM2.5 of the above coals were 4.781 and 21.491 mg_PM/g_ash, corresponding to the PM0.1/PM2.5 ratios of 15.54% and 25.16%. Comparatively speaking, coal WCW exhibited a higher ultrafine PM and fine PM (PM2.5) formation tendency, and in the PM2.5 from coal WCW, there was a higher percentage of ultrafine PM, which resulted from the different ash compositions in the coal. As listed in Table 2, there was much more volatile or semi-volatile mineral matter such as Na, S and Ca in coal WCW than in coal SX, which was more easily vaporized at the high combustion temperature and formed ultrafine PM via the above-mentioned vaporization–nucleation mechanism. Most importantly, adding nano SiO2 into coal SX reduced the mass yield of the PM0.1 to 0.515 mg_PM/g_ash, corresponding to an ultrafine PM reduction ratio of 30.70% and finally led to the reduction in PM2.5 by 12.62%. Simultaneously, it was observed that the mass yield of coarse PM in the size range of 2.5–10 μm (PM2.5–10) was increased from 48.176 mg_PM/g_ash to 53.087 mg_PM/g_ash, finally leading to the increase in PM10 (by 8.13%). Similarly, adding nano SiO2 into coal WCW also reduced the mass yield of ultrafine PM (with a reduction ratio of 13.01%); however, the ultrafine PM reduction performance of adding nano SiO2 into coal WCW was relatively lower than that into coal SX. Differently, as can be seen in Table 3, adding nano SiO2 into coal WCW finally brought about an increase in the mass yield of fine PM by 3.56% and a more significant increase in PM2.5–10 and PM10 (by 58.56% and 41.68%, respectively). The above difference was most likely caused by the different ash content and compositions in the coal, which are further discussed with changes in the chemical composition of particulate matter in the different size ranges below.
3.2. Composition of Ultrafine PM before and after Nano SiO2 Addition
To probe into the reduction mechanism of adding nano SiO2 to particulate matter, the size-resolved elemental composition of the PM10 formed during the combustion of coals SX and WCW before and after nano SiO2 addition were determined and are provided in Figure 3 and Figure 4, respectively.
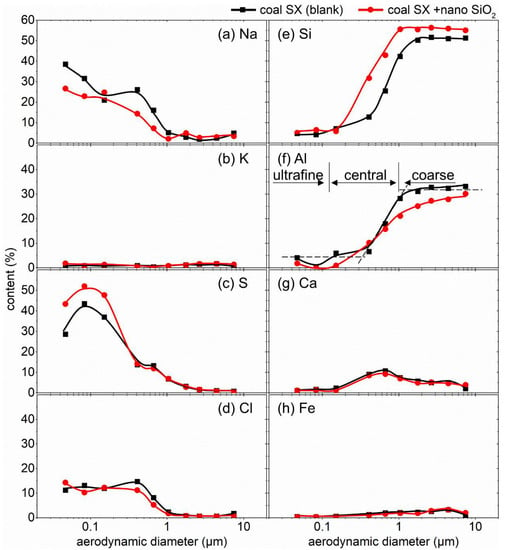
Figure 3.
Size-resolved elemental composition distribution in PM10 generated from coal SX combustion with/without nano SiO2 addition: (a) Na; (b) K; (c) S; (d) Cl; (e) Si; (f) Al; (g) Ca; (h) Fe.
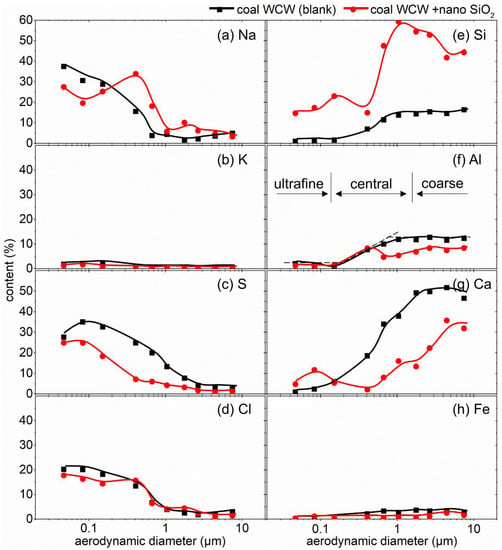
Figure 4.
Size-resolved elemental composition distribution in PM10 generated from coal WCW combustion with/without nano SiO2 addition: (a) Na; (b) K; (c) S; (d) Cl; (e) Si; (f) Al; (g) Ca; (h) Fe.
As expected, the composition-based size distributions of the PM10 from both coal SX and coal WCW were in patterns of tri-model distributions, namely an ultrafine modal with the particle size of <0.1 μm, a central modal with the particle size of 0.1–1 μm (for coal SX)/0.1–2.5 μm (for coal WCW) and a coarse modal with the particle size of >1 μm (for coal SX)/>2.5 μm (for coal WCW). It is worth noting that the identification of the PM modal based on both mass-based and composition-based PSD curves suggested a consistent ultrafine PM (i.e., PM0.1) and further revealed that the PM2.5 was made up of both ultrafine PM and central PM. As pointed out by Yu et al. [39,40,41], the central modal PM was formed via the heterogeneous condensation of the mineral vapor on the fine mineral fragments, which was well consistent with the transition of the content of the volatile mineral matter such as Na and S in the central PM. Compared with the PM2.5 derived from coal SX, there was more Ca in the PM2.5 from coal WCW, which agreed well with the high Ca content in coal WCW (see Table 2) and contributed to the higher PM2.5 yield.
The partitioning of mineral matter from coal to particulate matter changed after nano SiO2 was added, which led to the change in the formation behavior of the PM. Firstly, as shown in Figure 3, the Na content in the ultrafine PM was reduced after adding nano SiO2 in both coals SX and WCW, indicating that the nano SiO2 inhibited the migration of volatile alkali metals such as Na into ultrafine PM. This occurred because the Na-containing mineral vapor reacted with the SiO2 additive particles at a high temperature and inhibited their transformation into ultrafine PM via homogenous nucleation. Interestingly, the high specific surface of the nano SiO2, which resulted from its tiny particles size, significantly facilitated the heterogeneous reactions between the gaseous ultrafine PM precursors and the solid nano SiO2 particles, which made the nano additive have a high ultrafine PM reduction efficiency (30.70%) at quite a low addition dosage (0.6%). In our previous studies, adding micron-sized clay-mineral-based additives (with a particle size of 3.7–10.7 μm) at a dosage as high as 5 g-sorbent/100 g-coal achieved an ultrafine PM reduction ratio of 4.89–26.27%. It should also be noted that the reduced Na content in the ultrafine PM caused the relative increase in the S content, as the sum of all the elements was fixed to be one in the semiquantitative XRF determination.
Secondly, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, adding nano SiO2 additives led to a significant increase in Si content in both the central and coarse PM, revealing that the added nano additives mainly migrated into the central and coarse PM. It was implied that the raw SiO2 additive particles (mainly <100 nm) reacted or coalesced with each other and/or the minerals embedded in the coal at the same time that they scavenged the vaporized the ultrafine PM precursors, finally growing into a larger PM. Particularly, during the coal WCW combustion, some SiO2 additive particles also migrated into the ultrafine PM, resulting in the increase in Si content after nano SiO2 addition. This was because there was less mineral matter (the lower ash content shown in Table 2) in coal WCW compared with coal SX, most possibly due to the insufficient reaction or coalescence with the included minerals in the coal.
The increase in coarse PM was most likely caused by three factors. On the one hand, as indicated in Figure 3 and Figure 4, a large proportion of the added nano SiO2 finally migrated into the coarse PM, bringing in extra mass from the additive. On the other hand, the additive particles scavenged some of the mineral vapors released from coal burnout. Thirdly and also finally, the added nano SiO2 particles acted as binders after melting at the high combustion temperature, which inhibited the fragmentation of the fine included minerals in the coal and enhanced their coagulation into large ash particles during coal burnout. It is worth noting that there was a large number density of the nano additive particles even though the mass-based adding dosage was low, and the large number density as well as the tiny particle size of the nano additives facilitated the melting and coalescence behavior, which played a rather important role and are specially investigated in Section 3.3 below.
3.3. Interactions between the Nano SiO2 and Minerals in Coal
The micromorphology of the PM2.5 in some typical size ranges (e.g., stage 7 PM0.67–1.04, stage 11 PM4.45–7.46) after adding the nano SiO2 additive was depicted in Figure 5 to visually show the melting and coalescence behavior of the ash particles. Furthermore, the melting behavior (i.e., the deformation temperature [DT], softening temperature [ST] and flowing temperature [FT]) of the low-temperature ash of coal WX with different amounts of nano SiO2 additions was determined and is listed in Table 4.
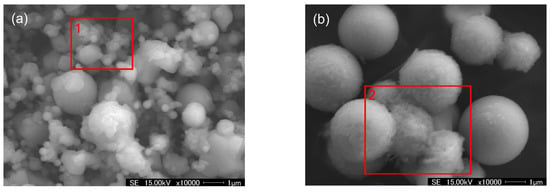
Figure 5.
Micromorphology of the PM (stages 7 (a) and 11 (b)) generated from the combustion of coal WX + 0.6%SiO2.

Table 4.
Melting behavior of the low-temperature ash of coal WX with different amounts of nano SiO2 additions.
As is clearly shown in Figure 5, large quantities of small ash or additive particles adhered to the surface of the relatively larger particles. Additionally, regularly large particles covered with nano additive particles further adhered to each other (see region 2 in Figure 5b) thanks to the molten additive particles acting as the binder. What is more, aggregation and agglomeration also extensively occurred among the nano particles (see region 1 in Figure 5a), which straightforwardly confirmed that some of the raw SiO2 additive particles (mainly <100 nm) reacted or coalesced with each other and grew into central modal PM.
The determination results of the melting behavior of the coal ash listed in Table 4 further confirmed the above observations. As can be seen, adding nano SiO2 generally reduced the deformation temperature, softening temperature and flowing temperature, i.e., by ~50 K at an adding dosage of 0.6%. Moreover, increasing the adding dosage of the nano additive to 3% further reduced the melting temperature of the low-temperature ash by ~100 K. This is thought to have resulted from the formation of alkali metal or alkali earth metal silicates due to the reactions between the added SiO2 particles and alkali metal or alkali earth metals in the coal [35,42,43]. Interestingly, adding nano SiO2 at an adding dosage as low as 0.6% could help reduce the formation of ultrafine PM as the nano additive particles can properly scatter on the surface of the coal particles and react with the minerals easily.
4. Conclusions
Coal combustion experiments with/without novel nano SiO2 additive addition were performed with a lab-scale drop tube furnace system. PM with an aerodynamic diameter of <10 μm (i.e., PM10) was collected to evaluate the effects of nano SiO2 on ultrafine PM formation, and detailed analyses of the particle size distribution, mass yield, element size distribution and micromorphology were conducted to reveal the underlying mechanism. The results showed that adding a small dose (0.6%) of nano SiO2 reduced the mass yield of ultrafine PM by 30.70%, showing a much higher ultrafine PM capture efficiency than an existing micron-sized natural clay mineral. However, its performance on different coals varied due to the disparities in ash content and composition in coal. A composition analysis revealed that the Na content in the ultrafine PM was reduced after adding nano SiO2, indicating that the nano SiO2 inhibited the migration of the volatile alkali metals such as Na into ultrafine PM. This occurred because the Na-containing mineral vapor reacted with the nano SiO2 additive particles with a large specific surface area at a high temperature and inhibited their transformation into ultrafine PM via homogenous nucleation. Changes in the element size distributions and micromorphology showed that the majority of the added nano SiO2 particles reacted or coalesced with each other and/or the minerals embedded in the coal, finally growing into a larger PM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X.; methodology, H.W. and K.Z.; validation, Y.L. and J.Z.; formal analysis, H.W. and K.Z.; investigation, H.W. and K.Z.; resources, Y.X. and B.Z.; data curation, H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W.; writing—review and editing, H.W. and Y.X.; supervision, Y.X., B.Z., S.M. and J.M.; project administration, Y.X.; funding acquisition, Y.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Fund of China (No. 51806075) and the Foundation of the State Key Laboratory of the High-efficiency Utilization of Coal and Green Chemical Engineering (Grant No. 2022-K01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data reported in this study will be available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the help from Huazhong University of Science and Technology Analytical and Testing Center for the sample analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, W.; Pudasainee, D.; Gupta, R.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Sun, L. An overview of inorganic particulate matter emission from coal/biomass/MSW combustion: Sampling and measurement, formation, distribution, inorganic composition and influencing factors. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 213, 106657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yu, D.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y. Coal combustion-generated aerosols: Formation and properties. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 1681–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cheng, M.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Xu, M. Numerical Analysis on Reduction of Ultrafine Particulate Matter by a Kaolin Additive during Pulverized Coal Combustion. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 9538–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, G.; Jiang, H.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Others, Mitigation of ultrafine particulate matter emission from agricultural biomass pellet combustion by the additive of phosphoric acid modified kaolin. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, T.; Ahmed, M.; Shohel, M.; Ferdousi, F.K.; Salam, A. Particulate matters and gaseous pollutants in indoor environment and Association of ultra-fine particulate matters (PM1) with lung function. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5475–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogbe, P.H.; Ayi-Fanou, L.; Autrup, H.; Loft, S.; Fayomi, B.; Sanni, A.; Vinzents, P.; Møller, P. Ultrafine particulate matter and high-level benzene urban air pollution in relation to oxidative DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.L.; Liu, X.; Pelkowski, S.; Palmer, B.; Conrad, K.; Oberdörster, G.; Weston, D.; Mayer-Pröschel, M.; Cory-Slechta, D.A. Early postnatal exposure to ultrafine particulate matter air pollution: Persistent ventriculomegaly, neurochemical disruption, and glial activation preferentially in male mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Deng, F.; Wei, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, C.; Qin, Y.; Lv, H.; Shima, M. Association of cardiopulmonary health effects with source-appointed ambient fine particulate in Beijing, China: A combined analysis from the Healthy Volunteer Natural Relocation (HVNR) study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3438–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Lee, L.J.; Luo, K.; Fang, P.; Yang, C.; Chuang, H. The Association of Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) and Air Pollutants—A Population-Based Study. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S.; Wang, W.; Chowdhury, T.; Enyoh, C.E.; Rabin, M.H. Characteristics and Potential Inhalation Exposure Risks of Environmentally Persistent Free Radicals in Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Solid Fuel Combustion Particles in High Lung Cancer Incidence Area, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, S.; Lu, C.; Luo, G.; Yao, H. Fate of chromium with the presence of HCl and steam during oxy-coal combustion: Quantum chemistry and experimental study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Dong, Y. Mechanism of CaO and Fe2O3 capture gaseous arsenic species in the flue gas: DFT combined thermodynamic study. Fuel 2022, 312, 122838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Qi, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X.; Xu, J. Insight into soot formed in coal combustion flame: Evolution of physiochemical structure, oxidation reactivity. Fuel 2022, 312, 122948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Xu, M. Reducing the central mode particulate matter in coal combustion by additives: Impacts of nano Al2O3 and TiO2 addition. Fuel 2022, 312, 122989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, M. Effects of kaolin-limestone blended additive on the formation and emission of particulate matter: Field study on a 1000 MW coal-firing power station. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, J.; Xu, M. Investigation of Simultaneously Reducing the Emission of Ultrafine Particulate Matter and Heavy Metals by Adding Modified Attapulgite During Coal Combustion. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Xu, M.; Pan, S. Influences of In-Furnace Kaolin Addition on the Formation and Emission Characteristics of PM2.5 in a 1000 MW Coal-Fired Power Station. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8718–8724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M. A novel Ti-based sorbent for reducing ultrafine particulate matter formation during coal combustion. Fuel 2017, 193, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, M. Role of chlorine in ultrafine particulate matter formation during the combustion of a blend of high-Cl coal and low-Cl coal. Fuel 2016, 184, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanc, F.; Levendis, Y.A.; Maffei, T. Chemical Composition of Submicron Particulate Matter (PM1) Emitted from Combustion of Coals of Various Ranks in O2/N2 and O2/CO2 Environments. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 4984–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Huang, Q.; Gao, Q.; Li, S. Effects of Na and Fe on the formation of coal-derived soot in a two-stage flat-flame burner. Fuel 2020, 265, 116914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Yao, Q. Mechanisms on the size partitioning of sodium in particulate matter from pulverized coal combustion. Combust. Flame 2017, 182, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linak, W.P.; Miller, C.A.; Santoianni, D.A.; King, C.J.; Shinagawa, T.; Wendt, J.O.; Yoo, J.; Seo, Y. Formation of fine particles from residual oil combustion: Reducing nuclei through the addition of inorganic sorbent. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2003, 20, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Wu, C.Y. Control of toxic metal emissions from combustors using sorbents: A review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1998, 48, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, T.K.; Wendt, J.O. In-furnace capture of cadmium and other semi-volatile metals by sorbents. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2005, 30, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Sun, W.; Xu, M. Investigation of reducing ultrafine particulate matter formation by adding modified montmorillonite during coal combustion. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 158, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Sun, W.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. Effects of H2O and HCl on Particulate Matter Reduction by Kaolin under Oxy-coal Combustion. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 6455–6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yao, H.; Zhang, P.A.; Xiao, L.; Luo, G.; Xu, M. Control of PM1 by kaolin or limestone during O2/CO2 pulverized coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2011, 33, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Pudasainee, D.; Gupta, R.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, B.; Sun, L. Particulate emission from municipal solid waste combustion: Effect of Si-Al-based additives for its mitigation. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15399–15410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, R.; An, Q.; Tan, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Li, P. Effect of calcined kaolin on PM0. 4 formation from combustion of Zhundong lignite. Fuel 2022, 319, 123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, S.; Mizuno, K.; Awaya, I. Effect of Additives on the Reduction of PM2.5 Emissions during Pulverized Coal Combustion. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 3412–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, J.; Yang, P.; Cheng, W.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.; Shao, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. P-Based Additive for Reducing Fine Particulate Matter Emissions during Agricultural Biomass Combustion. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 11274–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tan, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, Z.; Shao, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, H.; Chen, H. Effects of P-based additives on agricultural biomass torrefaction and particulate matter emissions from fuel combustion. Renew. Energy 2022, 190, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Long, H.; Dai, B.; Gao, X. Investigation of reducing particulate matter (PM) and heavy metals pollutions by adding a novel additive from metallurgical dust (MD) during coal combustion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Xu, M. Effects of the modified kaolin sorbents on the reduction of ultrafine particulate matter (PM0.2) emissions during pulverized coal combustion. Fuel 2018, 215, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Sheng, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, M. The role of steam in silica vaporization and ultrafine particulate matter formation during wet oxy-coal combustion. Appl. Energy 2014, 133, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, M.; Pan, S.; Gao, X. Field Measurements on the Emission and Removal of PM2.5 from Coal-Fired Power Stations: 3. Direct Comparison on the PM Removal Efficiency of Electrostatic Precipitators and Fabric Filters. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5930–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Pan, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, L.; Gao, X. Field measurements on the emission and removal of PM2.5 from coal-fired power stations: 1. a case study for a 1000 MW ultra-supercritical utility boiler. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 6547–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xu, M.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, K.; Li, L.; Wen, C. Mechanisms of the central mode particle formation during pulverized coal combustion. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2075–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.X.; Xu, M.H.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.W.; Zhou, K. A new method for identifying the modes of particulate matter from pulverized coal combustion. Powder Technol. 2008, 183, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.X.; Xu, M.H.; Yao, H.; Liu, X.W.; Zhou, K. Effective identification of the three particle modes generated during pulverized coal combustion. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwabe, P.O.; Wendt, J.O. Mechanisms governing trace sodium capture by kaolinite in a downflow combustor. Symp. Int. Combust. 1996, 26, 2447–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, T.K.; Wendt, J.O. High-temperature interactions between multiple-metals and kaolinite. Combust. Flame 2002, 131, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).