Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Method
3. Overview of the Super Typhoon Rammasun
4. Possible Reasons for the Heavy Rainfall
4.1. The 500 hPa Geopotential Height Field
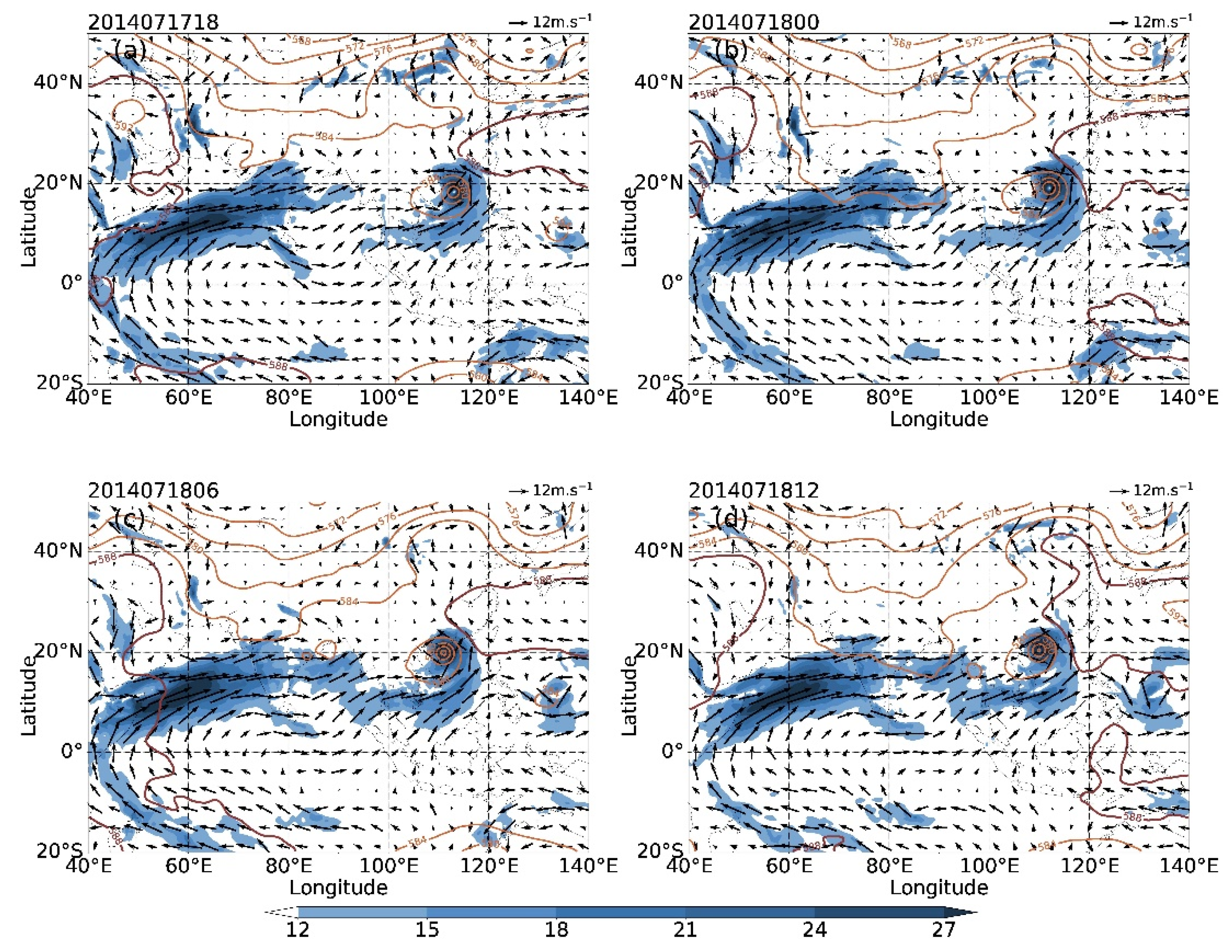
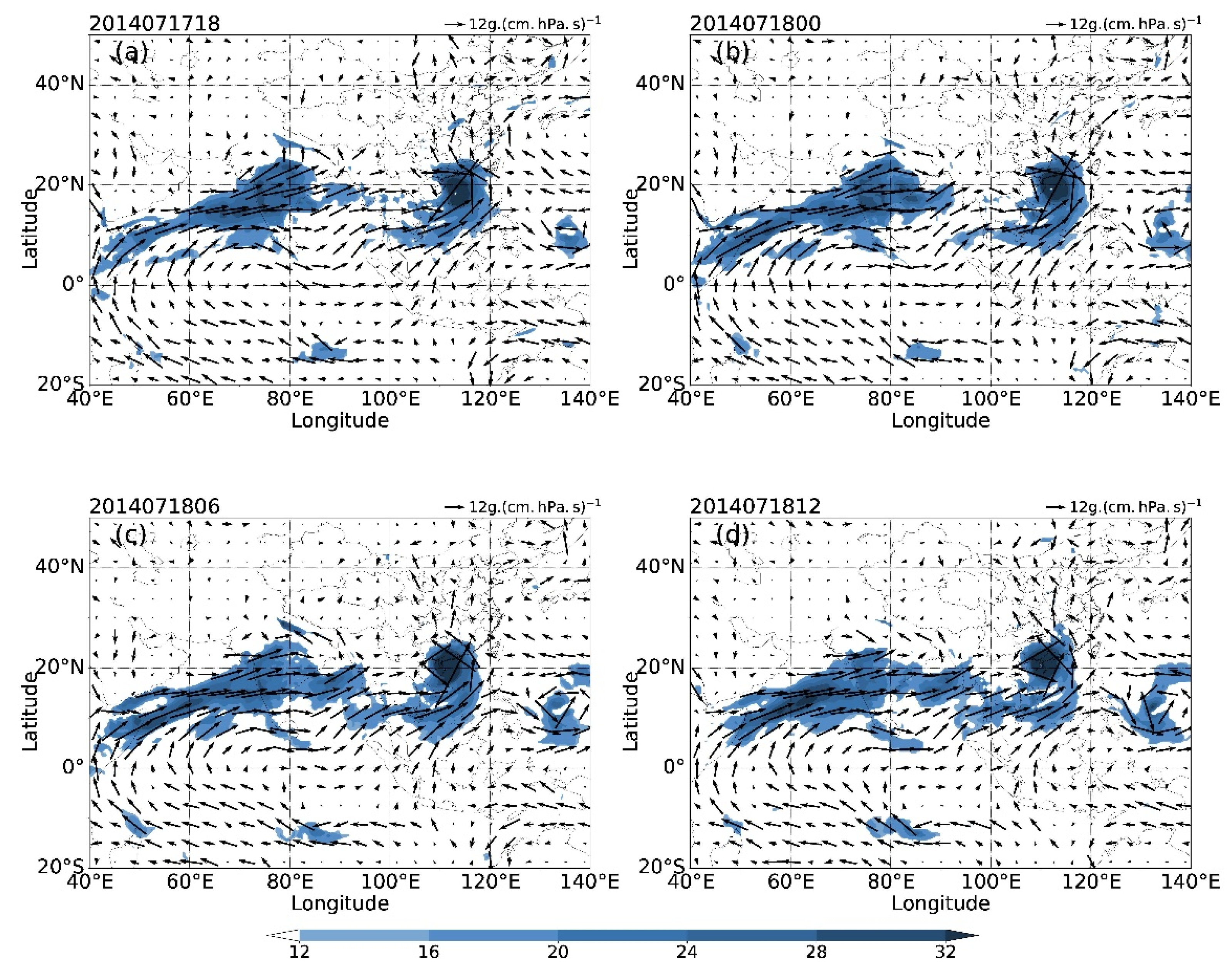
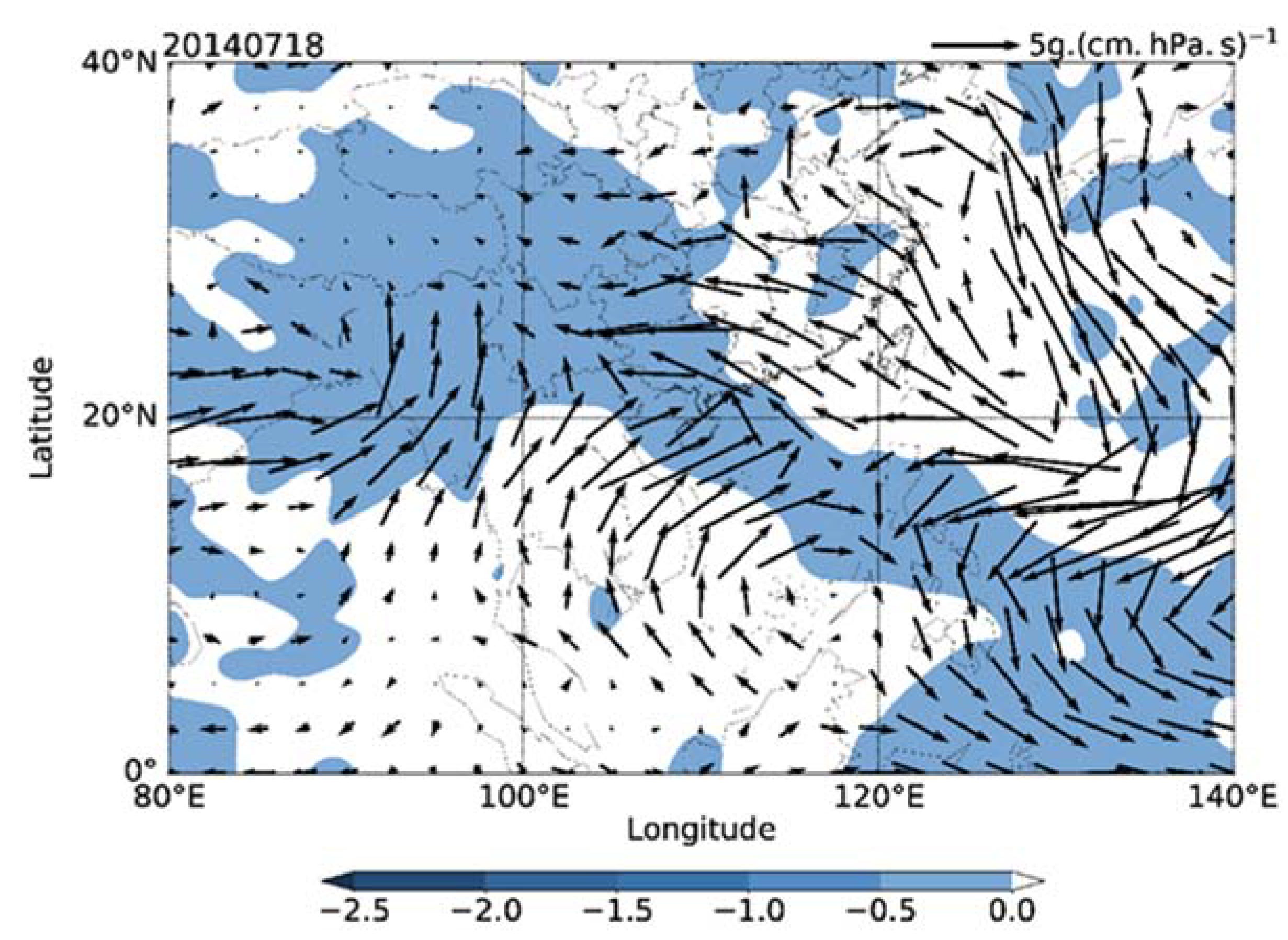
4.2. Characteristics of Wind Field and Water Vapor Flux
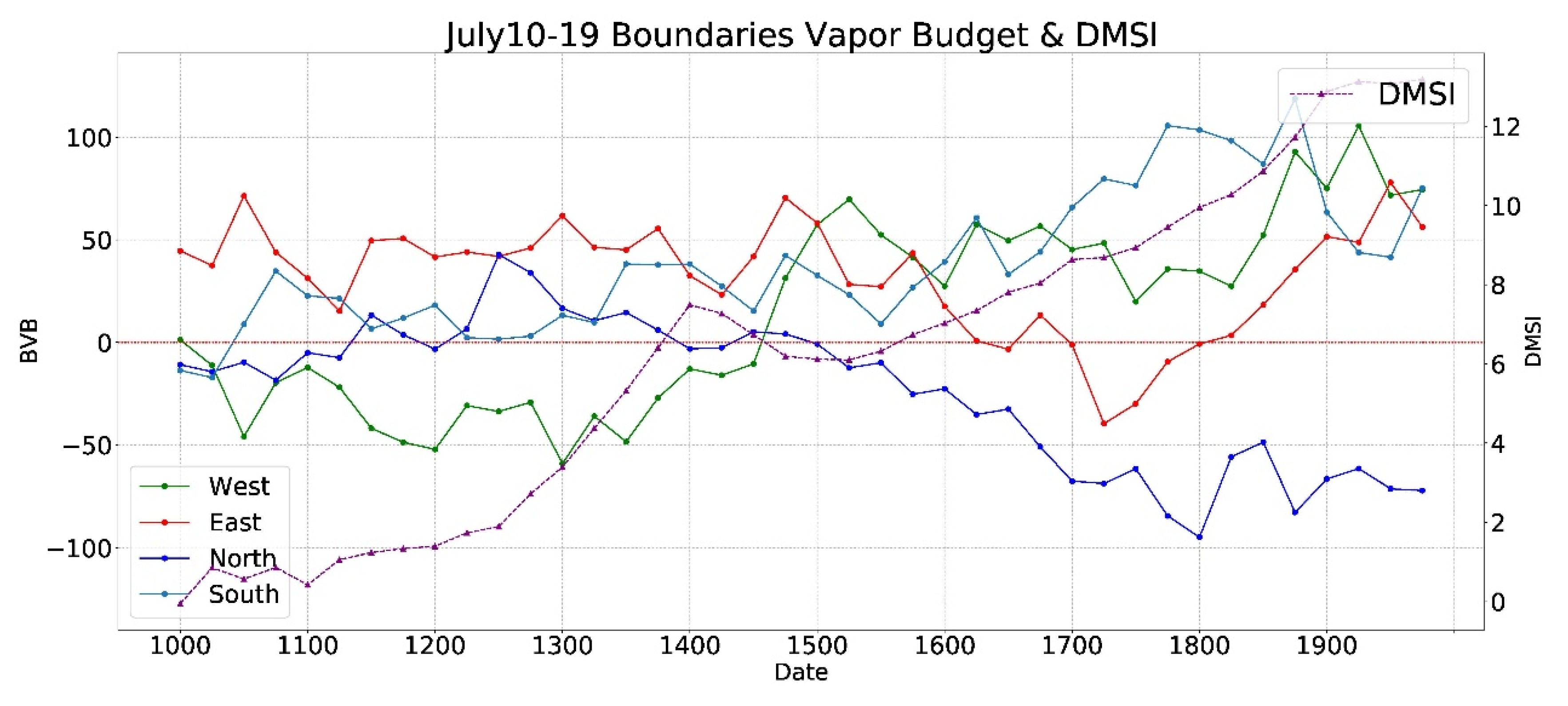
4.3. Dynamic Monsoon Surge Index and Boundary Water Vapor Budget
5. Impact of the Southwest Monsoon Surge on the Heavy Rainfall of Landfalling Rammasun at Hainan
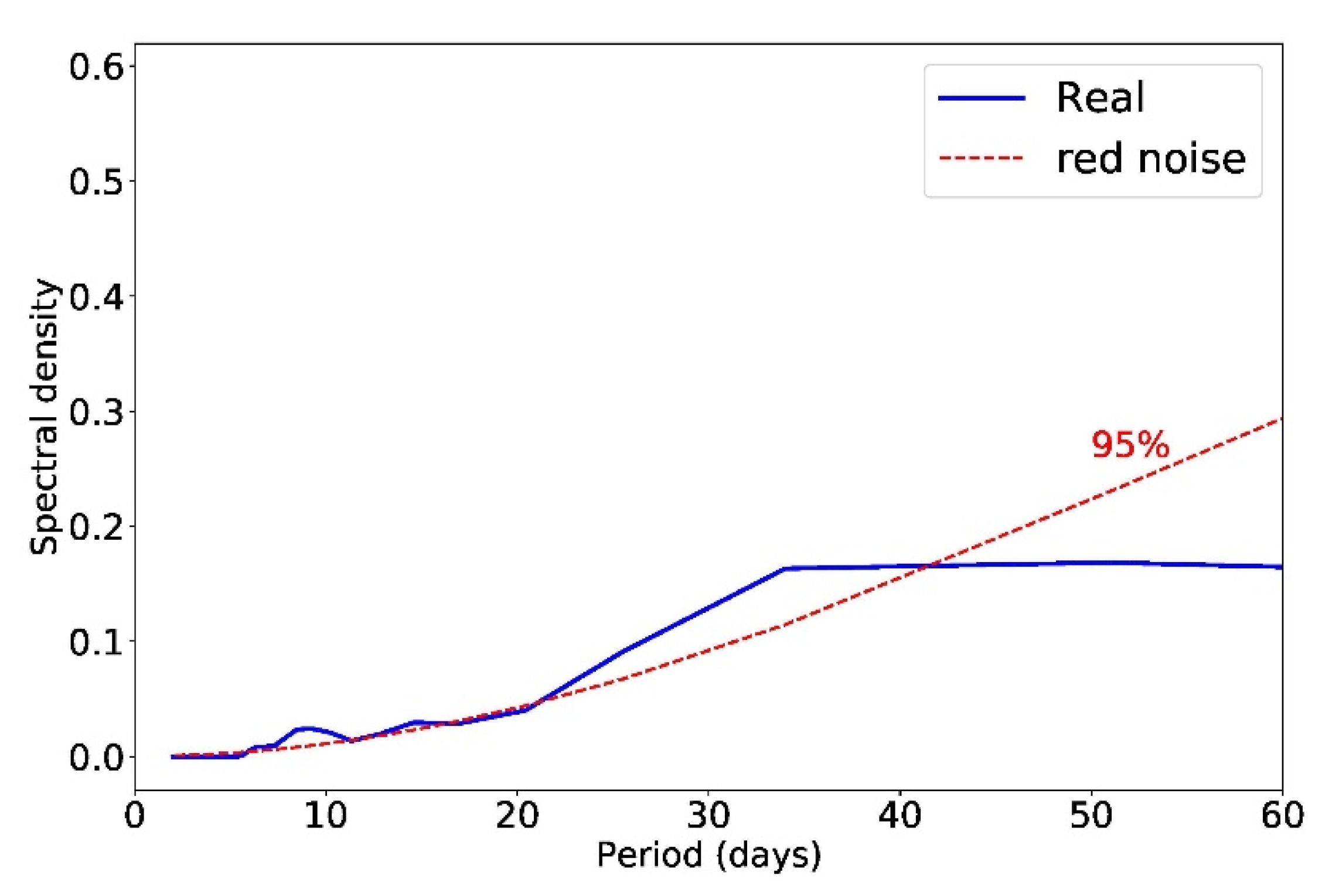
5.1. Characteristics of the Low-Frequency Oscillation of the East Asian Summer Monsoon Surge
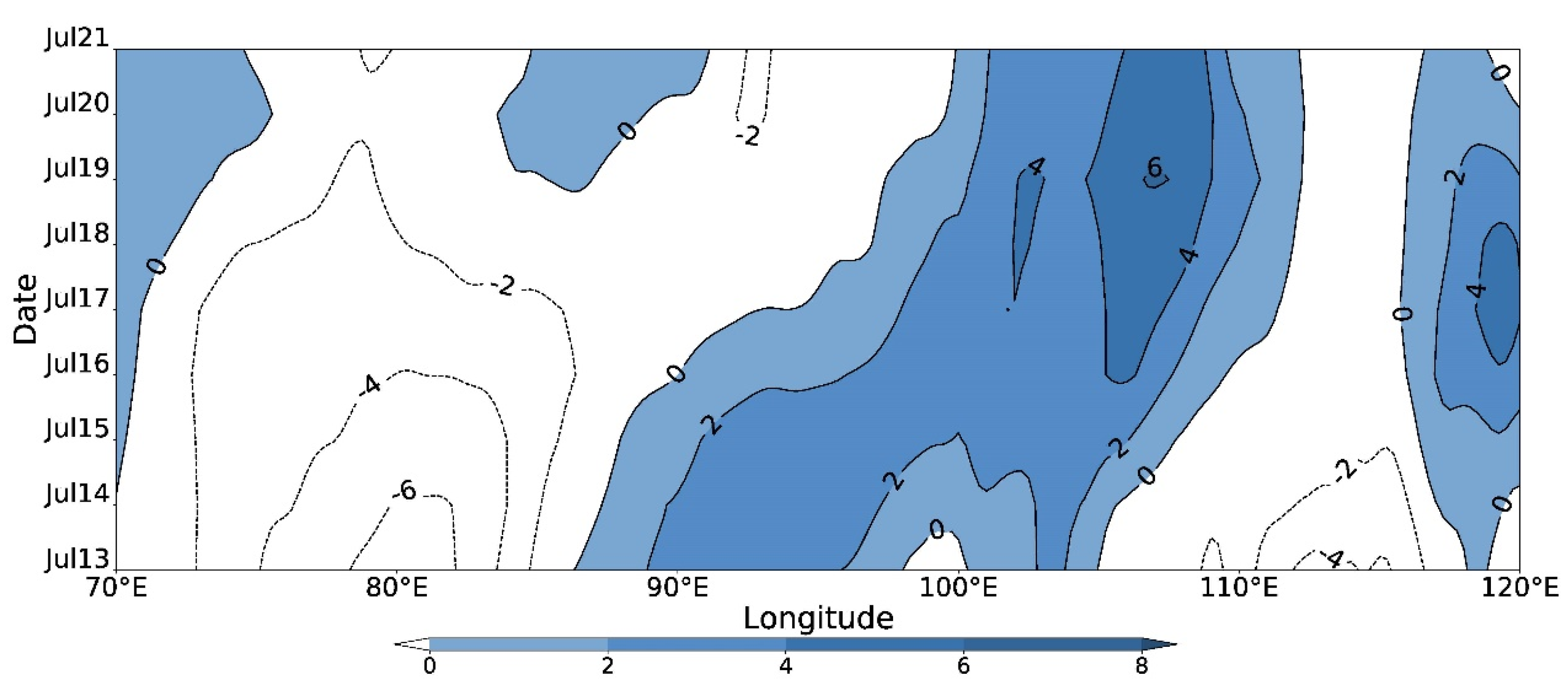
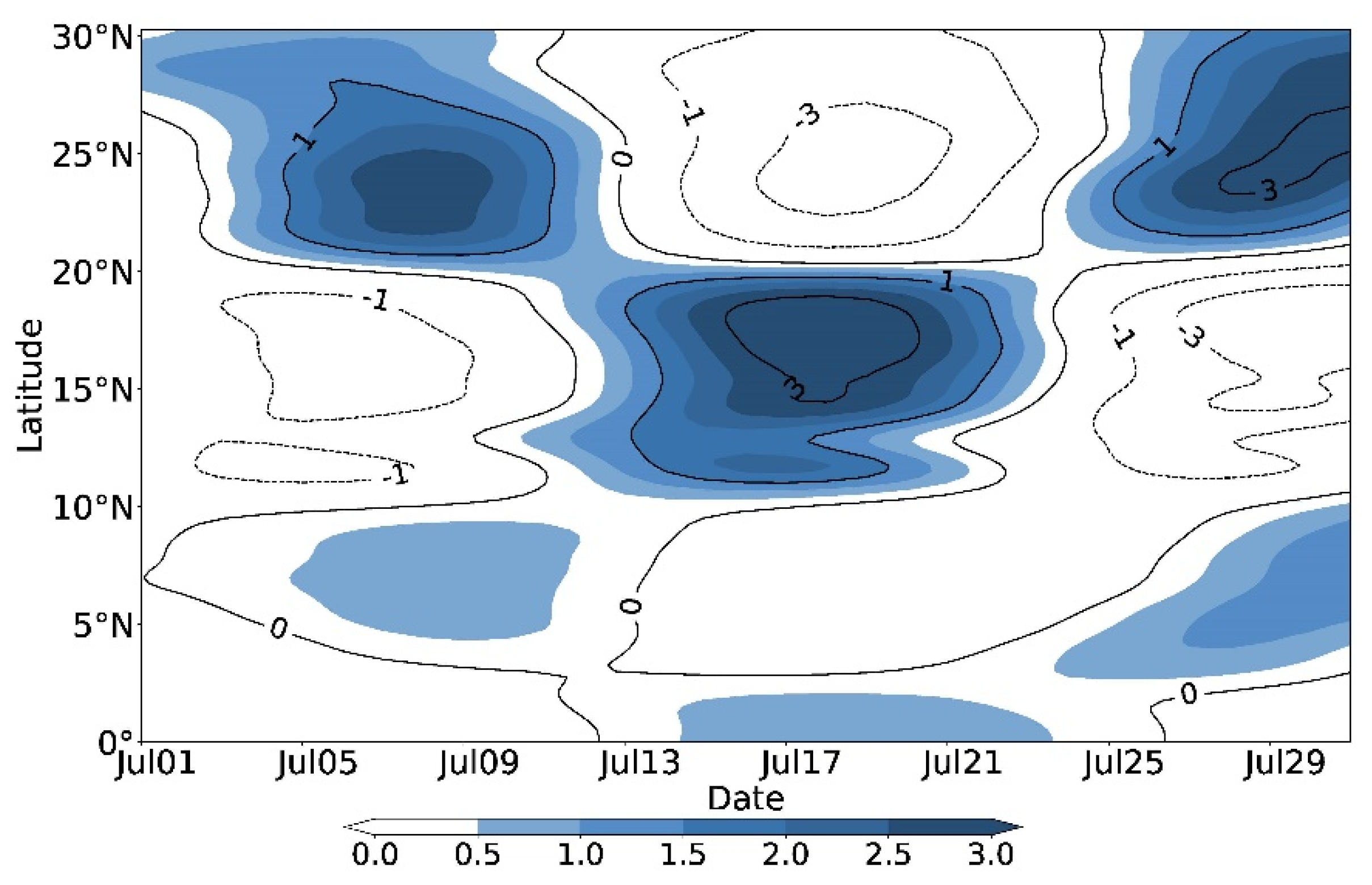
5.2. Characteristics of Low-Frequency Water Vapor Flux
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, S.Y. Rainstorms in China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; p. 225. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.S.; Duan, Y.H.; Song, L.L.; Xu, Y.L. Typhoon Forecast and Disaster; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 370. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, T.C.C.; Elsberry, R.L. Advances in understanding the ‘‘perfect monsoon-influenced typhoon’’: Summary from International Conference on Typhoon Morakot (2009). Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 47, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, F.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, C.-S. Heavy Rainfall and Southwesterly Flow after the Leaving of Typhoon Mindulle (2004) from Taiwan. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 86, 17–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, X. Climate variation and prediction of rapid intensification in tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2007, 99, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-S.; Chen, B.-F.; Elsberry, R.L. Long-lasting convective systems in the outer region of tropical cyclones in the western North Pacific. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 21812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Lu, S.; Guan, Z.Y.; He, J.L. Effects of Low-Latitude Monsoon Surge on the Increase in Downpour from Tropical Storm Bilis. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2010, 16, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.F.; Elsberry, R.L.; Lee, C.S. Origin and maintenance of the long-lasting, outer mesoscale convective system in Typhoon Fengshen (2008). Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 2838–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.F.; Elsberry, R.L.; Lee, C.S. Synoptic controls of outer mesoscale convective systems in western North Pacific tropical cyclones. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 52, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Wu, L.; Ren, F. Monsoonal Influences on Offshore Rapid Intensification of Landfalling Typhoons in a Sheared Environment over the South China Sea. Weather Forecast. 2020, 35, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L. Impact of the Monsoonal Surge on Extreme Rainfall of Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, E.B.; Adler, R.F.; Pierce, H.F. Contribution of Tropical Cyclones to the North Atlantic Climatological Rainfall as Observed from Satellites. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2001, 40, 1785–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. The Relationship between Tropical Cyclone Intensity Change and the Strength of Inner-Core Convection. Mon. Weather Rev. 2012, 140, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Vecchi, G.A.; Smith, J.A.; Knutson, T.R. Causes of large projected increases in hurricane precipitation rates with global warming. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.Q.; Chen, L.S.; Li, Y. Interaction between landfalling tropical cyclone and summer monsoon with influences on torrential rain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2012, 23, 660–671, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Chen, L. An Overview on The Interaction Between Tropical Cyclone and Mid-Latitude Weather Systems. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2001, 17, 452–461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Trends in Landfalling Tropical Cyclone–Induced Precipitation over China. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Kuang, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Xie, M. Geospatial modeling of the tropical cyclone risk in the Guangdong Province, China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2021, 12, 2931–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zuo, J.; Ling, Z.; Yan, Y. Role of ocean upper layer warm water in the rapid intensification of tropical cyclones: A case study of typhoon Rammasun (1409). Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Davidson, N.E.; Duan, Y.; Tory, K.; Sun, Z.; Cai, Q. Analysis of an Ensemble of High-Resolution WRF Simulations for the Rapid Intensification of Super Typhoon Rammasun (2014). Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T. Intra-seasonal variations of OLR in the tropics during the FGGE year. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 64, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T. Mean features of 30–60-day variations as inferred from 8-year OLR data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 64, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- He, J.H.; Murakami, T.; Nakazawa, T. The changes of the 40–50 days periodic oscillation of circulation and the water vapor transportation in the summer of 1979 the Asian monsoon region. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteor. 1984, 2, 163–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, D.L.; Michelsen, M.L.; Klein, S.A. Seasonal Variations of Tropical Intraseasonal Oscillations: A 20–25-Day Oscillation in the Western Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.H.; Qian, C.; Cao, J. The intraseasonal oscillation of East Asian summer monsoon. J. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 29, 187–194. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.A.Y. Relationship between OLR low-frequency oscillation and the formation of typhoon over the western Pacific. J. Meteorol. Mon. 1987, 10, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bister, M.; Emanuel, K.A. Low frequency variability of tropical cyclone potential intensity 1. Interannual to interdecadal variability. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2002, 107, ACL-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, M.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lu, X.; Feng, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D. An Overview of the China Meteorological Administration Tropical Cyclone Database. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2014, 31, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yu, H.; Ying, M.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Lin, L.; Bai, L.; Wan, R. Western North Pacific Tropical Cyclone Database Created by the China Meteorological Administration. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.L.; Joyce, R.J.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J.; et al. Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission (IMERG). In Satellite Precipitation Measurement; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C.D., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Xie, P. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). In Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (ATBD) Version 4.5; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-SatellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Technical Documentation; NASA/GSFC Code: Washington, MD, USA, 2019; p. 47.
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Day 1 IMERG Final Run Release Notes; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015; p. 9.
- Liu, Z. Comparison of Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) and TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Monthly Precipitation Products: Initial Results. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Comparison of IMERG Level-3 and TMPA 3B42V7 in Estimating Typhoon-Related Heavy Rain. Water 2017, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. Rainfall Reinforcement Associated with Landfalling Tropical Cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 3541–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, O.S.; Samah, A.A.; Chenoli, S.N.; Subramaniam, K.; Ahmad Mazuki, M.Y. Extreme Rainfalls that Caused Devastating Flooding across the East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia during November and December 2014. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Lo, A.-K.; Wu, C.-C.; Hung, C.-W. Influence of Tropical Cyclones on the Estimation of Climate Variability in the Tropical Western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 2960–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.C.; Hsu, H.H.; Chou, C. Propagation and maintenance mechanism of the TC/sub-monthly wave pattern and TC feedback in the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 8591–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, T.J., Jr.; Davis, C.A. Diagnosing Forecast Errors in Tropical Cyclone Motion. J. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, A.V. Discrete-Time Signal Processing; Pearson Education India: Tamil, India, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Corbosiero, K.L.; Molinari, J. The Relationship between Storm Motion, Vertical Wind Shear, and Convective Asymmetries in Tropical Cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; He, H.Y.; Huang, M.C. A Comparison Analysis of the Large-Scale Circulations of the Two Typhoons Invaded the Western Part of South China. J. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 2005, 6, 110–113, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Malkus, J.; Riehl, H. On the dynamics and energy transformations in steady-state hurricanes. Tellus 1960, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Shen, X.; Zheng, X.; Shou, S. The numerical simulation of typhoon No. 200604 (Bilis) rainfall. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2009, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Dai, Y.; Chen, H. Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010130
Liu H, Wang L, Dai Y, Chen H. Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haoyu, Lijuan Wang, Yufan Dai, and Hong Chen. 2022. "Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun" Atmosphere 13, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010130
APA StyleLiu, H., Wang, L., Dai, Y., & Chen, H. (2022). Relationships between the Southwest Monsoon Surge and the Heavy Rainfall Associated with Landfalling Super Typhoon Rammasun. Atmosphere, 13(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13010130




