Abstract
In spite of the obvious climate changes effects on the Carpathian Basin hydrographic nets fish fauna, studies on their potential refuge habitats in drought periods are scarce. Multiannual (2016–2021) research of fish in some streams located in the Saxon Villages area during hydrological drought periods identified, mapped, and revealed the refuge aquatic habitats presence, management needs, and importance for fish diversity and abundance for small rivers. The impact of increasing global temperature and other human activities induced hydrologic net and habitats alteration, decreased the refuge habitats needed by freshwater fish, diminished the fish abundance, and influenced the spatial and temporal variation in fish assemblage structure in the studied area. The sites more than one meter in depth in the studied lotic system were inventoried and all 500 m of these lotic systems were also checked to see what species and how many individuals were present, and if there is was difference in their abundance between refuge and non-refuge 500 m sectors. The scarce number of these refuges due to relatively high soil erosion and clogging in those basins and the cumulative effects of other human types of impact induced a high degree of pressure on the fish fauna. Overall, it reduced the role of these lotic systems as a refuge and for reproduction for the fish of downstream Târnava Mare River, into which all of them flow. Management elements were proposed to maintain and improve these refuges’ ecological support capacity.
1. Introduction and Background
Water, the fundamental factor of initiation, persistence, and evolution of life on Earth is ever-present; it influences everything and is a key to comprehending the universe in general [1,2], including the biodiversity structure, distribution, and ecological state [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. In this framework, the relevance of small water bodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services is not negligible [12,13].
Climate change is one of the most known crises to all-encompassing environmental, economic, social, and human health conditions [14,15,16,17] modern human have ever challenged [18]. The simulations conducted using global climate models uncover that the most important factors that induce this planetary phenomena are natural (variations in solar radiation, volcanic activity, and aerosol concentrations) and anthropogenic (fluctuation in the content of the atmosphere due to human actions); only the amassing effect of the two factors can provide a reason for the transformations noticed in the world average temperature in the last century and a half [19,20], despite the fact that this is only a small part of the extent of fluctuations in climatic parameters, even including the planet ocean level [21].
It is accepted that inland water conditions are closely connected with weather and atmospheric temperature fluctuations, so climate change may have forceful direct and indirect effects on freshwater biota [22].
The most recent IPCC Climate Report, “Code Red for Humanity”, emphasizes undeniable proofs accompanying the reality that warming has sped up in recent decades; the planet warming is affecting all regions on Earth, and additional heating is anticipated for the next century. Many of the modifications becoming irreversible climate impacts will certainly exacerbate [23]. Another effect of climate change is the alteration of hydrologic cycles; with rising intensity and frequency of extreme events such as droughts, this scenario could influence freshwater biota, generating changes in phenology, life cycles, and dispersion areas, and even the extinction of sensitive species [24]. Accelerated climate change is estimated to influence the biodiversity of huge areas forcefully, with changes in the presence and distribution of numerous species, the decline of the taxonomic richness, and the vanishing of entire ecosystems [25]. There is much proof that global warming is threatening the biodiversity of our planet, including fish [26,27,28,29,30,31,32], a significant taxonomic group under permanent high global human-impact threats and risks [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45].
In this global warming scenario, freshwater ecosystems are highly vulnerable and their communities could experience significant impacts. Some new research highlights that freshwater biodiversity has declined quicker than both marine and terrestrial [46].
Due to the fact that in the above-mentioned recent United Nations report that the researched Carpathian area will be characterized by heat waves and severe drought periods [46], and the freshwater biota is under a accentuated risk in general, the aim of this study was to provide information about the state of the local fish species refuge habitats in the context of climate change and human impact effects.
Climate change forecasts for Europe are not an exception and it is clear that air temperatures will rise because of the impact of human activities on the atmosphere [47,48,49]. The predictions are also clear that the contemporary precipitation regime will be modified and altered and will vary from one area to another beyond the normal known seasonal patterns, with drought episodes becoming accentuated [50], and severe and even extreme climatic crisis are anticipated [51].
The climate system heating is unquestionable due to the relatively uninterrupted long-term warming trend since the mid-20th century, which may be correlated with anthropogenic influence [52,53,54].
Drought is an effect-dependent phenomenon [55], and considerable human impact is at least partly culpable for the harshness of the contemporary frequent and persistent drought episodes [56] generating a very intricate hydro-climatic risk affecting the natural and anthropogenic systems [57]. More than that, the heat wave magnitude is projected to rise everywhere in future [58].
Climate change-associated issues are some of the most contentious scientific issues of the present day. At this time of the climate change situation, the temperature increases all around [54], even in unanticipated ranges on Earth [59,60,61,62,63], and drought, decreasing altered flows on streams, which is a significant driver for aquatic ecosystems’ ecological status [64], aquatic biodiversity [65], and even their potential economic use [66,67] appear and remains even in what are considered “safe” geographical areas. From this viewpoint, the Carpathian Basin was considered, bringing their synergic effects together with other human impact types that could also have consequences on functional traits of aquatic assemblages in terms of the abundance and distribution of their species [68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75].
Carpathian Basin climate change trends exceed the Earth warming rate since the 1950s of the last century through rising temperature and precipitation and drier spring, summer, and autumn seasons [76,77,78,79]. For example, in the last century, a 0.8 °C increase in surface temperature and a 60–80 mm decrease in precipitation were registered [80].
In the last decades, the Carpathian Basin has experienced very persistent and accentuated droughts, a trend connected with climate change, inducing remarkable drying in this region, particularly in the summer, in the chiefly exposed south-eastern sectors that have had environmental and socio-economic effects [81].
In the general climate change circumstances, the Carpathian Basin and its valuable biosphere are considered to be very sensitive. Drought is one of the important climate-related detrimental natural phenomena, and it has been appearing with increasing frequency, severity, and extent in the last decades [82,83].
The causes of fast expansion of the drought in the South-Eastern Carpathian basin are: the rise of the yearly average temperature by 0.3 °C, the rise in number of tropical days (>30 °C), the diminishing of winter days (<0 °C), the diminishing of precipitation, and the lessening of runoff. As results: reduced inflows to aquatic ecosystems, decreased stream-flows in a most of basins, reduced recharge of groundwater, high repetitiveness and period of the drying up of lotic systems (principally those smaller than 500 km2), and the stream flow drought which has arisen more often since 2000 [84,85].
Climate changes disturb ecosystems and cause potential threats and risks regarding their natural products and services; in these circumstances, human society should anticipate and adapt in time to these major global challenges [60].
The ephemeral and small lotic systems are the most abundant and hydrologically dynamic of all freshwater ecosystems, existing across most of our planet, including rivers in alpine and hilly zones as well as temperate regions [86,87,88].
The Carpathian Mountains’ geographic typical features (i.e., form, orientation, latitude, and altitude) were and are essential elements which played a key driving role concerning the fish species’ presence, dispersion, evolution, and their populations’ ecological status [89]. In the recent climate change pattern for the hydrological nets, is the drought a new game changer in the Carpathian area? What will be the effect of this type of change on small lotic low-flow systems’ habitats and their fish populations, which are already under high stress from human impact? How can we be proactive and identify such risk hotspots and how can we design proper management plans for these threatened lotic systems in order to diminish these climate-induced negative effects?
This research intended to deal with several local case studies of small lotic systems based on which similar areas can benefit by the proposed habitats and fish population risk assessment, monitoring, and management elements. Such a research-targeted area, the so-called “Saxon Villages” area/Southern Transylvania Tableland, in South-East Transylvania (Romania), is one of these types of identified areas where climate change can lead to great pressures both on the water-related habitats and biodiversity.
The research area is located in the arena-like Transylvanian Depression. Encircled by the South-Eastern Carpathians, the middle Târnava Mare River basin sector is located in the central-south part of the Transylvanian Plateau, particularly in the central Târnave Plateau, populated by more than seven million people [90], and its lotic systems are under both historical and modern diverse human-impact negative effects [91,92,93].
The geological basis is under a deep Neogene bed, formed by the southern segment of the Central Transylvanian massif, composed of crystalline schists, over which were accumulated Miocene, Pliocene, and Quaternary soft structures. The interfluvial areas are topped by dispersed Sarmatian marls-clays, sands, and tuffs. The most frequent is the Pliocene (Pannonian) structure, characterized by marl-clays and sands [94,95,96,97,98].
From the geomorphologic viewpoint, the base of the researched area was the river meadow suspended above the Târnava Mare riverbed and the lower terraces, creating transversely fragmented hilly surfaces. The energy relief is lessened, with a maximum of 100 m, and the regular fragmentation degree is 05–07 km/km2 [94,95,96,97,98].
The climatic regime, connected with the sector of the hilly area with a moderate-continental climate, is defined by warm summers with rather low precipitation, and winters with warmer periods. The circulation of the atmosphere is characterized by the high frequency of western and north-western temperate-oceanic air masses, chiefly in summer. Less often, south-west and south Mediterranean air masses appear, and northern Arctic masses less often. The annual average temperatures lie between +8 °C and +9 °C, with absolute values of +37 °C and −32 °C. The average July temperatures vary between +18 °C and +20 °C, and those of January between −3 °C and −4 °C. The atmospheric precipitation has an annual quantity of 500–700 mm [94,95,96,97,98].
In the study area of the Târnava River basin, the torrential character of the superficial flow has high maximum flows in rainy periods and common minimum low-flows, with run-dry during drought [94,95,96,97,98]. In the field activities, in the August months of the 2016–2021 study period, the drought and heat waves kept the general trend of the last decades; moreover, the years 2019 and 2020 were the hottest years since 1961 [99,100,101,102,103].
The studied lotic systems, Dupuş (5 km length, 10 km2 basin surface, 0.024 m3/s multiannual flow—2016–2021), Biertan (17 km, 58 km2, 0.124 m3/s), Valchid (16 km, 56 km2, 0.120 m3/s), Laslea (22 km, 111 km2, 0.345 m3/s), Mălâncrav (14 km, 41 km2, 0.100 m3/s), and Felţa/Florești (9.6 km, 17 km2 0.041 m3/s) belong to the southern Târnava Mare Basin. This basin’s aquatic and riverine habitats and associated biodiversity are under the influence of the impacts of multiple and diverse human activities [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113].
The rather new extended-heat summers and warmer winters increased the temperature of rivers, decline snowpack, and the accessibility water and its related resources to riverine human communities. In addition, the present higher human pressure, contrasting with the traditional past environmentally friendly practices of natural resources use, on water resources finally induced a decrease in water quality and quantity.
Recurrently, the accent of drought-connected effects are pushed onto human-centric water resources and agricultural, socioeconomic, and migration aspects due to the related economic losses and social tension [114,115,116,117], and avoiding the related and primary triggering features of droughts, namely the meteorological and hydrological elements.
This study addressed some of the ecological dimensions of frequent and prolonged droughts, and their lasting structural effects on some aquatic habitats and their fish communities, which are communities with high relevance for the studied lotic systems’ ecological status under climate change/drought seasons’ constant pressure.
The human indirect (climate changes/drought) and direct influence (water overuse, water pollution, habitats fragmentation and destruction, scarcity of refuge habitats, wetland and riverine areas mismanagement, stimulating over sedimentation, etc.) are key aspects of understanding many of the drought effects on the researched lotic systems.
Other objectives of this study were to reveal some landscape (geographical, cultural, and natural heritage) values and traditional best-practices loss effects in the new climatic change situation and to identify new threats and the different types of human impact affecting some lotic system fish fauna, based upon specially designed scientific research. In the beginning of the twenty-first century, the human-nature relationship is far from balanced and with significant and variable negative effects on the biodiversity, including the whole Danube Basin [118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133], to which the studied area belongs.
It is very likely that the tendency of climate change in the twenty-first century will be very much alike that of the end of the twentieth century, manifested by rising values of extreme maximum temperatures and heat waves [76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]; this reiterates the need for applied studies by identification of problems and proposals of integrated management plans for the ecological support systems for human society and its enterprises.
This study had as a main aim to identify and map the lotic refuges in drought periods, and also the sectors where these should be rehabilitated or made. Adjacent monitoring and management elements were proposed for the studied lotic systems’ natural processes recovery. It must be highlighted that no such research approach regarding the south-east Carpathians small rivers fish refuge habitats has previously been realized.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was based on a fish samples assessment, from 2016 to 2021, in summer drought periods, at five rivers, on every 500 m sector, in the west of the Saxon Villages area (Figure 1). The sites more than one meter in depth in the studied lotic systems were measured and inventoried, walking in all the riverbeds length. The near downstream 500 m-long stretches of these lotic systems were also checked to see what fish species and how many individuals thereof are present, and if there is a difference in their abundance between refuge and non-refuge 500 m sectors. The fish numbers in the identified refuge habitats (lotic habitats with a depth of minimum one meter and a length of maxim 10 m) were compared with the near downstream 500 m-long lotic sector fish number of individuals and presented. The major method limitation is that it is relatively cronophagous; the river’s entire length should be walked by the researchers through the riverbed.
Figure 1.
The study area location on the South-Eastern Carpathians basin (Romania).
The sampling highlights the presence of aquatic refuge habitats and fish communities’ richness in and near the refuge habitats.
During the drought season, field studies concerning the habitats were carried out on Dupuş, Biertan, Valchid, Laslea, Mălâncrav, and Felţa/Florești rivers (Figure 2).
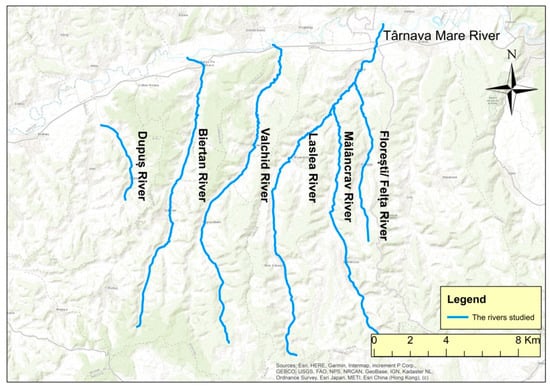
Figure 2.
The studied lotic systems.
The fish assemblages’ survey presented, through time/on effort (one hour/500 m), these quantitative samplings, which were gathered with a hand-net.
For the fish communities’ quantitative structure, the used description was: the individuals’ number in the unit of time/effort unit—average value for the samples of the same station, for six years of the study, on each identified refuge habitat and its downstream near-500-m sector.
The sampled fish were identified, counted, and released immediately back into their natural habitats. Different habitat characteristics data (refuge depth, banks description, land use, substrate, banks height, minor riverbed width, GPS coordinates, vegetation, and human impact) were collected (Table A1, Table A2, Table A3, Table A4, Table A5 and Table A6).
This research proposed some in situ adapted management elements for the recovery, at least partially, of the previous ecologic status of the lotic systems’ habitats in the area and of their associated fish species communities.
3. Results
3.1. Dupuş River
Based on the field inventory, on the Dupuș River, only one refuge was identified with a depth of 150 cm (i.e., Figure 3), and the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 4) had different depths between 10 to 80 cm.

Figure 3.
Dupuş River refuge habitat.
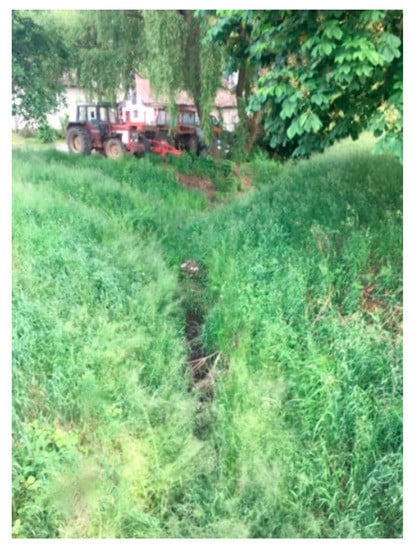

Figure 4.
Dupuş River non-refuge sector.
In the Dupuș River, three fish species have permanent populations: Gobio gobio (Linnaeus, 1758) (9 total caught individuals), Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (6), and Squalius cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) (3).
The ratio between the total number of fish between the refuge habitat of maximum 10 m length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sector of 500 m length was two to one.
The single identified refuge habitat is present in the lower third of the river (Scheme A1) revealing the drought-related risks for the biodiversity in at least two thirds of the river sectors.
Given the shallow depth of the Dupuș River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, the building of artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m is proposed. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 12 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A1).
3.2. Biertan River
Based on the field inventory, on the Biertan River, only three refuges were identified with a depth of 100–120 cm (i.e., Figure 5); the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 6) had different depths between 5 and 100 cm.
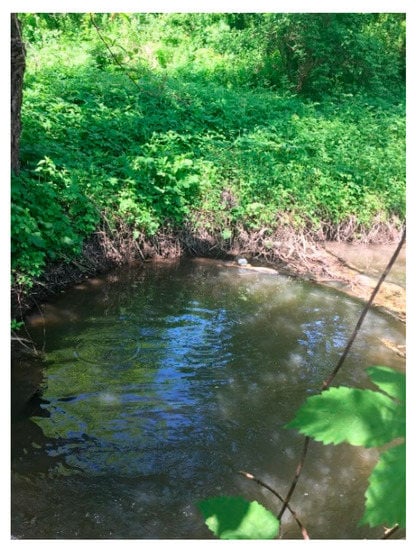

Figure 5.
Biertan River refuge habitat.
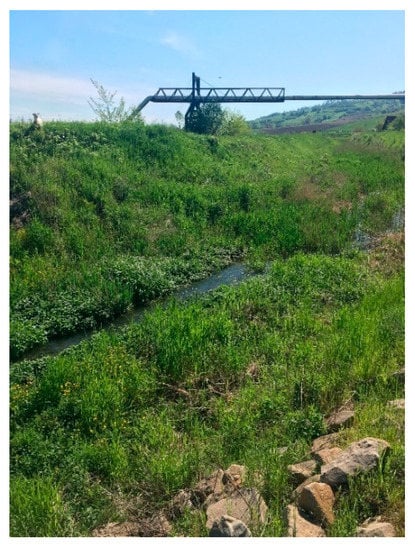

Figure 6.
Biertan River non-refuge sector.
In the Biertan River, 11 fish species have permanent populations: Squalius cephalus (Linnaeus 1758) (total caught individuals 21), Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus 1758) (7), Alburnoides bipunctatus (Bloch 1782) (20), Chondrostoma nasus (Linnaeus 1758) (8), Gobio gobio (Linnaeus 1758) (19), Barbus barbus (Linnaeus 1758) (9), Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (23), Carassius gibelio (Bloch 1782) (5), Barbatula barbatula (Linnaeus 1758) (11), Sabanejewia romanica (Băcescu 1943) (31), and Sabanejewia aurata (De Filippi 1863) (14).
The ratio between the number of fish between the refuge habitats of maximum 10 m in length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sectors of 500 m length was six to one.
The identified refuge habitats are present only in the lower one-fifth sector of the river (Scheme A2), revealing the drought-related risks for the biodiversity in four-fifths of the river sectors.
Given the shallow depth of the Biertan River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, it is proposed to build artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 34 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A2).
3.3. Valchid River
Based on the field inventory, on the Valchid River, 27 refuge habitats were identified with a depth of 100–160 cm (i.e., Figure 7); the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 8) had different depths between 5 and 100 cm.
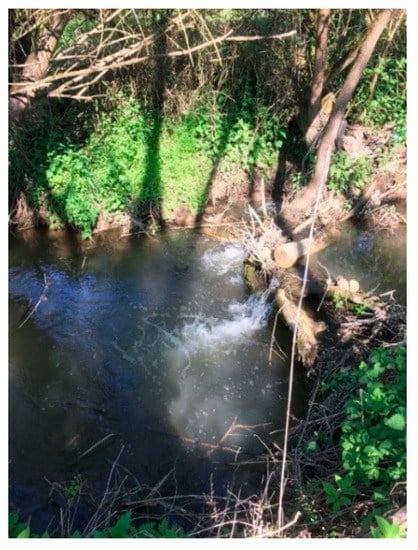

Figure 7.
Valchid River refuge habitat.
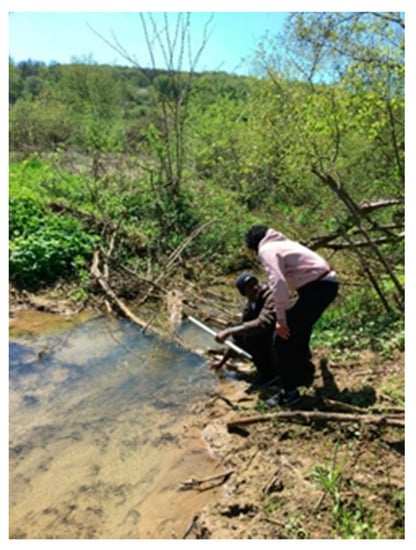

Figure 8.
Valchid River non-refuge sector.
In the Valchid River, 10 fish species have permanent populations: Squalius cephalus (Linnaeus 1758) (total caught individuals 28), Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus 1758) (6), Alburnoides bipunctatus (Bloch 1782) (22), Chondrostoma nasus (Linnaeus 1758) (3), Gobio gobio (Linnaeus 1758) (26), Barbus barbus (Linnaeus 1758) (3), Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (30), Barbatula barbatula (Linnaeus 1758) (19), Sabanejewia romanica (Băcescu 1943) (20), and Sabanejewia aurata (De Filippi 1863) (19).
The ratio between the number of fish and the refuge habitats of maximum 10 m in length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sectors of 500 m length was seven to one.
Refuge habitats are present in four-fifths of the lower and middle parts of the river, and should be extended to the upper part and multiplied so that at every 500 m there is at least one.
Given the general depth of the Valchid River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, the building of artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m is proposed. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 17 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A3).
3.4. Laslea River
Based on the field inventory, on the Laslea River, only four refuge habitats were identified with a depth of 100–120 cm (i.e., Figure 9); the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 10) had different depths between 5 and 120 cm.
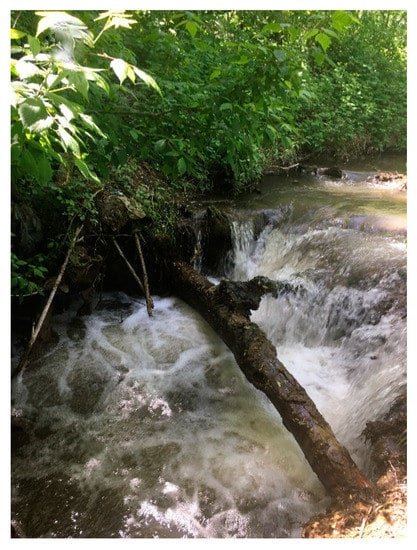

Figure 9.
Laslea River refuge habitat.
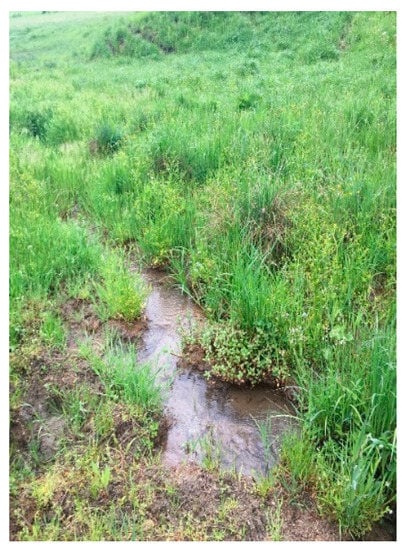

Figure 10.
Laslea River non-refuge sector.
In the Laslea River, seven fish species have permanent populations: Alburnus alburnus (Linnaeus 1758) (total caught individuals 9), Chondrostoma nasus (Linnaeus 1758) (8), Gobio gobio (Linnaeus, 1758) (40), Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (42), Barbatula barbatula (Linnaeus 1758) (44), Sabanejewia romanica (Băcescu 1943) (60), and Sabanejewia aurata (De Filippi, 1863) (31).
The ratio between the number of fish between the refuge habitats of maximum 10 m in length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sectors of 500 m length was 12 to 1.
Refuge habitats are rarely present on two-thirds of the lower and middle parts of the river, and should be extended to the upper part of it and also multiplied so that at every 500 m there is at least one.
Given the general depth of the Laslea River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, it is proposed to build artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 37 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A4).
3.5. Mălâncrav River
Based on the field inventory on the Mălâncrav River, only three refuge habitats were identified with a depth of 100–110 cm (i.e., Figure 11); the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 12) had different depths between 10 and 100 cm.
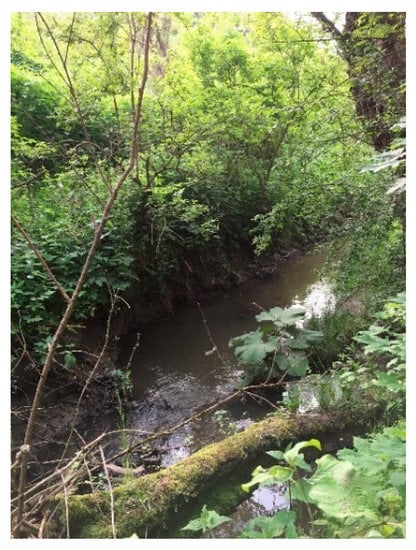

Figure 11.
Mălâncrav River refuge habitat.
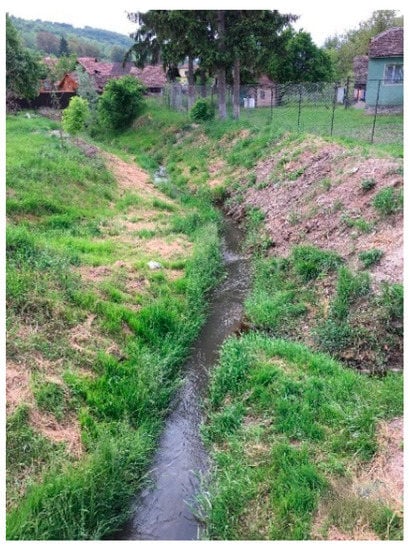

Figure 12.
Mălâncrav River non-refuge sector.
In the Mălâncrav River, four fish species have permanent populations: Squalius cephalus (Linnaeus 1758) (total caught individuals 12), Gobio gobio (Linnaeus, 1758) (8), Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (22), and Barbatula barbatula (Linnaeus 1758) (13).
The ratio between the number of fish between the refuge habitats of maximum 10 m in length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sectors of 500 m length was four to one.
Refuge habitats are rarely present throughout the length of the river, but should be more numerous, with at least one every 500 m.
Given the general depth of the Mălâncrav River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, the building of artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m is proposed. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 21 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A5).
3.6. Felţa River
Based on the field inventory on the Felţa/Floreşti River, only two refuge habitats were identified with a depth of 100 cm (i.e., Figure 13)’ the other non-refuge sectors (i.e., Figure 14) had different depths between 10 and 100 cm.
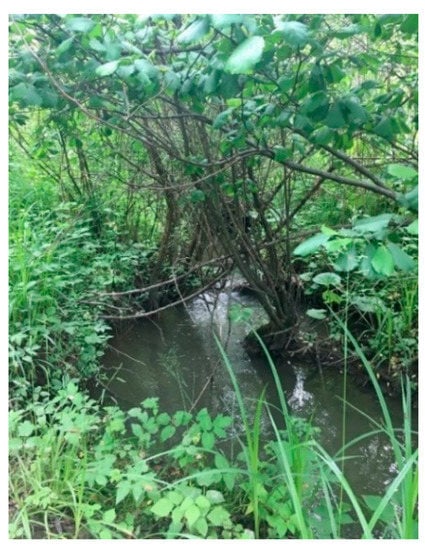

Figure 13.
Felţa River refuge habitat.
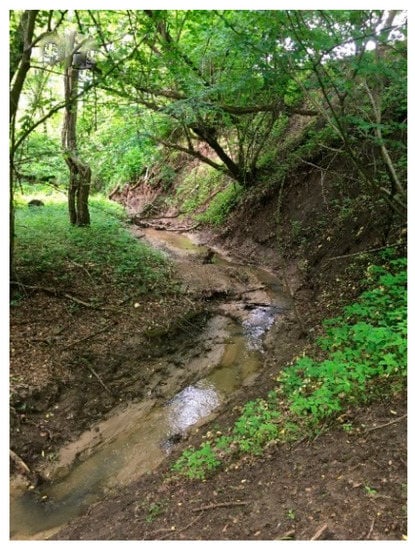

Figure 14.
Felţa River non-refuge sector.
In Felţa/Floreşti River 3 fish species have permanent populations: Squalius cephalus (Linnaeus 1758) (total caught individuals 14), Gobio gobio (Linnaeus, 1758) (24), and Barbus meridionalis Risso 1827 (10).
The ratio between the number of fish between the refuge habitats of maximum 10 m length and the adjacent/downstream non-refuge sectors of 500 m in length was three to one.
The only two identified refuge habitats were in the lower third of the river (Scheme A6), revealing the drought related risks for the biodiversity in at least two middle and upper-third sectors of the river.
Given the general depth of the Felţa River and the vulnerabilities that occur for fish during periods of drought, the building of artificial refuges for fish from about 500 to 500 m is proposed. In total, it would be necessary to build a number of 12 such refuges with a depth of at least one meter (Scheme A6).
4. Discussion
4.1. Identified Ecological State Elements
Practically all fish species have a definite range of habitat preference delineated by abiotic attributes such as substrate, depth, velocity, floods, temperature, dissolved oxygen, etc. [134,135,136,137,138,139,140,141]. The spawning periods of fish also differ with respect to such distinct ecological elements as stagnant or running water, as well as altitude, temperature, quality of water, and etc. A fundamental property of fecundity is its raise during the development of the fish; a big fish produces more eggs than a small one [142,143]. If no relative large habitats, including refuge-type habitats, exist, no large fish can exist, and consequently reduced fecundity of fish populations can appear in the rivers.
As stream discharge lessens, decreasing water quantitative and qualitative characteristics may exceed resilience limits, pushing fish to search for and use refuge habitats. These can be characterized as sites where the adverse effects of disruption are absent or reduced than in more damaged sectors. For example, as discharge diminishes, the fish species which prefer riffles leave and search for refuge in pools. In these general circumstances, it is self-evident that the refuge habitats play a critical role in reducing the disruptive effects of drought in terms of individual endurance of fish and population survival. However, the quality of the pools varies in relation with many elements such as abiotic suitability, trophic opportunities, predation risks, etc.
Drought drying is a critical disruption circumstance in many small streams creating irregular or isolated lotic habitats [144]. We assessed and found that, based on the ratio between the fish numbers in refuge habitats and in the near lotic sectors, the remaining pools act as needed refuge habitats, especially during drought episodes.
In the researched area, there are two fish species of conservative interest, namely Barbus meridionalis Riso, 1827 and Sabanejewia aurata (De Filipi, 1863). The barbels, Ord. Cypriniformes; Fam. Cyprinidae are influenced by stream habitat quality such as, for example, drought periods [145]. Barbus meridionalis species terra typica is the Mureş River basin to which the studied Târnava River tributaries belong. This fish is a bottom-dweller, relatively fresh, cool, and well saturated with oxygen water species. It prefers hard substrate [134]. The loaches, Ord. Cypriniformes; Fam. Cobitidae are also influenced by the streams’ habitat quality, inclusive of drought effects [146]. Sabanejewia aurata is a mainly nocturnal, demersal, freshwater, bottom-feeder species. The sand presence in the riverbed is an important habitat precondition, with individuals spending extended periods in the sand. Its presence in muddy or silted areas is rare. It needs a quite warm water temperature especially in the summer season, but not over 20 °C [134].
When habitat characteristics match the favored range, anticipated fish species will appear in good abundance [147]. The first fact, which was observed in the research in the field, was that in hydrological drought periods, the number of fish was higher in the identified refuge habitats, a critical aspect for fish conservation, in contrast with transitional lotic sectors and especially in riffles, which are usually the first habitats to dewater at low flows. It is clear that the pools offer refuge from the most negative effects of drought (i.e., isolations and stranding of fish). Specifying a niche is equivalent to defining habitat conditions [148,149] that allow a species to remain in space and time. That is why proper habitats in general and especially the highly needed refuge habitats should be identified, characterized, and inventoried for considering present-future climate changes.
Together with flow fluctuations and low flow prolonged periods, a second stressor which can be important for the fish communities’ deteriorated ecological status is the temperature, which can differ among river sectors with refuge habitats bordered by dense riparian vegetation and sectors with no such refuge habitats and no or rare vegetation. These sectors are exposed to the sun heat and have a higher temperature and evaporation rate; in consequence, both the water’s quality and quantity decrease.
The rise in frequency and magnitude of hydrological droughts has quantitative and qualitative negative effects, lowering the refuge habitats’ surface and volume, the lateral connectedness between rivers and floodplains, the longitudinal connectedness, and the quality of water. Drought also impacts the relative habitat availability (i.e., ratio of pools to riffles), reproduction sectors and activities, and diminishes the trophic base support surfaces. The shallow habitats may dry pools, decreasing them in dimension, but still hold water for longer after the surface flow ends. Drought also intensifies density-dependent biotic interactions such as competition and predation, as fish are congested into a smaller volume of water.
A fall in fish numbers among refuge-sampled habitats goes along with descending discharge and growth in the sampled refuge habitat areas.
Over the course of the summer low-flow period, numbers of fish in the sampled non-refuge habitats were lower in comparison with the refuge habitat, indicating degradation in abiotic and biotic conditions linked with drought.
Interest and struggle are increasing on improving environments that are human-dominated [150]. In this study, the skewed natural fish communities’ structure, or even disappearance/local extinction of some fish species on some studied lotic systems sectors, had complex causes, among which climate change and human impact synergy in these basins can play a central role, inducing as a mitigation measure the completion of the needed refuge habitats proposed herein.
The traditional land and water use best practices in the studied area, i.e., lotic systems with natural courses, using the phreatic rather than the river water for household needs, thick riverine natural vegetation (especially Alnus incana, Telekia speciosa, and Chrysosplenium alternifolium Erika Schneider-Binder in verbis), terraces with vineyards with anti-erosional effects on slopes, full coverage with forests on the tops of the hills, soft agricultural practices in small family farms in lowland areas, raising of cows, etc., were replaced by new, modern activities with negative effects on the environment.
The traditional best practices related with the land and water use were replaced by new ones which are aggressive with the aquatic environment: habitat fragmentation with riverbed barriers with no fish ladders or passages; aquatic lotic habitats over sedimentation due to improper riverine forestry and agricultural area use; the riverine vegetation destruction on some sectors reduces their capacity to retain sediments carried down by floods from the basin; overgrazing mainly with sheep and, to a lesser degree, with cows also induces sediment mobilization in the basin; the relatively big riverine industrial farms and the small family farms overflowing their animal manure direct into the river without any cleaning treatment; household water and solid waste overflows without any treatment; the lotic natural courses being affected in some sectors by modifications of the course, banks, and riverine habitats; the escape of alien fish from adjacent fish farms/ponds, etc.
All these quantitative shortages in refuge habitats and the qualitative problems induce significant pressure on fish fauna in the context of climate change and should be addressed with specific in situ adapted management measures.
The shortage of refuge habitats did not allow the presence of proper conditions for fish related first to the needed hard and coarse sand substrata due to fine sediments and mud over sedimentation and clogging, and second with water temperature and oxygenation due to the rising of water temperature and decreasing of oxygenation in lotic sectors not protected by riverine vegetation, exposed to direct sun heat, without refuges, and which are shallow.
Human activities in drought conditions, which synergically induces erosion regularly, deliver massive quantities of fine sediments into streams and rivers, forming large static bodies of sediment known as sand slugs, which smother in-stream habitat, alter community structures, and decrease biodiversity [151,152,153]. Based on our findings of such droughts plus a high variety of human impacts in the studied area, a strategic basin management should be designed and put into action to accomplish effective and viable aquatic refuge habitats used for the associated fish communities. Correct protection of the fish populations should rely on the protection of their environment through integrated management, which should solve the following identified problems: riparian zones were reduced on the surface or removed by the agriculture expansion and destructive agriculture works, lessening river shading and raising aquatic habitat temperatures and decreasing water oxygenation; severe sedimentation problems due to basin erosion, channel cuttings and strong weather water runoff raised by the insufficiency or absence in some sectors of riparian vegetation; accentuated erosion and sedimentation issues that develop from a lack of riparian vegetation along long sectors of river corridors and which can lead to gravel bed siltation, critical to the insectivorous fish species; disturbed hydrologic regimes in some sectors by water over extraction and use; the man-made stream barriers which have repercussions on the ability of fish to move among refuge habitats; lasting inputs of pollutants; habitat loss-induced native fish species decline; stream sectors channelization and isolation from their alluvial plain, important for cyprinids; habitat deficit easing fish overcrowding circumstances, which lead to occurrences and outbreaks of diseases; etc.
Based on the biological and ecological characteristics of the two sampled fish species of conservative interest and on the identified problems in relation with this species throughout the six years of monitoring activities, some management directions can be highlighted so that basin managers can have the key information and recommendations needed to preserve a good quantitative and qualitative conservation status of the local water resources and fish populations in synergic climate change and anthropogenic impact conditions.
Drought is a natural disruption including aquatic ecosystems in terms of physical and chemical water quality, increased fish death rates, and decreased fish birth rates and/or expanding migration rates, and can be an important factor in destruction of aquatic communities; for fish to remain in affected lotic systems, they must have refuge from interfering factors. Refuges’ dimension, commonness, and connectedness play an important role in fish populations’ ecological status and persistence. Population dynamics of fish using refuges during drought are best modeled by modified source-sink dynamics, but such dynamics are likely to change with spatial scale [154,155,156,157,158].
For the studied lotic systems, habitats, and their fish populations ecological status recovery, as a part of “a best practice” management of the researched area, relatively numerous new refuge habitats should be created and properly managed: nine times more than the existing number on the Dupuş River, 10 times more on the Biertan River, 0.4 times more on the Valchid River, 10 times more on the Laslea River, eight times more on the Mălâncrav River, and six times more on the Felţa River. Among all of these rivers, the Valchid River state reveals a potential good status to be reached by all lotic systems in the area. We can understand now how this area’s conditions were in the past, and why, in some localities, coat of arms waterfowls were present (Erika Schneider-Binder in verbis).
A complex, integrated, and permanent monitoring system should be implemented in the studied area, based on the fact that the physic-chemical and biological variables can show and anticipate the human impact actions and climate change effects on lotic systems’ basin ecologic status and perspectives [159]. For the efficiency of the proposed monitoring activities, people with appropriate fish-related taxonomic skills should be involved [160].
The torrential nature of the superficial flow in the studied lotic ecosystem basins set off high maximum flows especially in rainy periods and minor flows, with very low-flow episodes, during drought periods of the year [98], periods which are more numerous and longer under the present climate changes. The researched area’s geomorphologic processes are of high amplitude, have a high frequency, and an intensity of manifestation that confers on them a risk character on the local geomorphosystems [151], especially in the relatively new appearance of climate change effects, including on the refuge habitats of fish.
Sediment motion, flow, amassing, and clogging are influential phenomena in lotic habitats and their associated fish communities due to their significance for: riverbed features, river channel morphology and stability, and refuge habitats availability and quality. In the studied area, the sediment entrainment, transport, and deposition induced a significant refuge habitat loss with associated fish communities, decreasing living conditions. This situation is stimulated especially in the climate change context of change in flow regime, respectively, the diminishing of the water flow in the drought periods, through affecting entrainment, transport, and deposition processes. Changes in the frequency, duration, and magnitude of flows competent to move the pre-existent bed materials have significance for substrate character formation and maintenance. For example, if riffles are not sufficiently flushed on a regular enough basis, fine sediment deposits amass in the interstices among the gravels and rocks, lowering or even removing the interstitial micro-habitats. Over the longer term, the hydrographical net substrate is buried, depth sectors/refuge habitats are clogged, and some disappear, and all of this leads to the loss of a natural series of river sectors along with the refuge habitats. Reductions in the frequency, duration, and magnitude of flows sufficient for transporting tributary sediment inputs further downstream have significance for river channels sedimentology and morphology, as sediment bars tend to expand, including in the confluence areas with tributaries, reducing fish access and mobility to long sectors of habitats and their resources.
The geomorphologic balance adjustment and sustenance in the studied area can be dealt with in an anthropic way by a set of measures for the prevention and diminishing of the effects of geomorphologic risk processes, but the witnessing of their manifestation remains for long periods, and needs a reconversion of the lands and a realistic management of the soil and sediments in the resilience limits of the area [151].
4.2. Fish Fauna Refuge Habitats Management Elements Proposals
It must be highlighted that no such research approach regarding the south-east Carpathians small rivers fish refuge habitats was previously realized.
Appropriate basin management measures should begin from the following elements: water is part of the environment and for that reason, different users can adapt only to the surplus quantity that is naturally available from rivers. In nature, there is more water in riverine systems than is needed for support of the riverine ecosystems; if the main features of the natural flow regime can be identified and adequately maintained in a changed flow regime, then the valuable biota should be preserved.
The management measures should mostly include: basin soil stabilization and conservation, slopes and tributaries erosion diminishing measures, treatment of point sources, etc.
The silting of deep stream habitats is a natural physical phenomenon which cannot be avoided, but by understanding the effects of hydro-morphological pressure due to a lack of basin sediment management, mitigation of this situation’s effects on fish refuge habitats can be obtained based on basin sediment management measures: buildups of sediments could be managed by physical intervention like mechanical raking or excavation; restoration of more natural levels of sediment inputs reduce the demand imposed on streams to transport and rework elevated sediment loads; creating outside-of-river-beds storage ponds in which, through some mobile diversion dams, the high-flow period water will be channeled for the deposition of sediments before they can clog the refuge habitats; and all the torrent and soil erosion control works in the basin should be carried out.
Numerous forestry management measures can be useful for basin sediment management: the forest stands’ vertical and horizontal structure should be as close as possible to its natural model (multi-layers, groups, and patches) in order to reduce soils being destabilized because of slope characteristics, loss of moisture, loss of large canopy cover, loss of root strength, and etc.; permanent watercourses will be protected by commercial intervention with a minimum 50-m-wide stripe on both sides of the watercourse. It is important to keep and respect the natural dynamics of habitats (i.e., reed beds, sedges and forests), together with their necromass (i.e., died wood), in banks (i.e., major/minor riverbed and alluvial terraces) and in water. The cross-over, in accidental or extraordinary cases when it cannot be avoided, will be made over the shortest distance on installations adopted to keep the water clean and soil erosion at a minimum; riparian forest and the natural bushy and grassy, local vegetation and flora will be strictly protected; any timber harvesting or transport activity is recommended to take place on a frozen substrate, covered by snow and/or ice and on well-maintained forestry roads with a layer of mineral aggregates on top of the road; the network of forestry roads must be optimally dimensioned for maximum efficiency with the minimum amount of damage; existing roads should be preserved and maintained in order to avoid or minimize erosion, sediment transport, and accumulation in the area; building of new forestry roads should be avoided; ecologically friendly, low-impact logging technologies (oxen, horses, cableway-skidders) are always preferred; timber will not be removed from forests during or after precipitation while the soil is moist; skid-roads will always be designed, built, and monitored in order to avoid soil-erosion as much as possible, ensure the protection of permanent and temporary watercourses, and protect remaining trees; sensitive areas like potential land-slide zones, talus, cliffs, steep slopes, etc., will be identified, protected (excepted from logging), and monitored; it will be prohibited to store timber (even for short periods of time) in the riverbed, on its banks, and on the minimum 50-m-wide protection stripes adjacent to both perennial and ephemeral waterways. All the vegetation within the protection belts shall remain intact; intervention cuttings will be applied in openings with a diameter up to a tree height, from which the old trees can be completely removed; timber harvesting will not exceed 10% of the volume of the stand (exceptions can be allowed in special accidental situations, for example windfalls and/or snowfalls, etc.), and the harvest volume will be correlated with the condition of the stand, the dynamics of natural regeneration, and with assigned conservation requirements; logging techniques will be adopted to minimize the level of injuries to the remaining trees and soil; if there are stands in which the natural regeneration is very difficult or stands are affected by calamities, replanting or direct sowings will be carried out using only seminological material of local origin or, if not possible, from identical ecotypes; timber harvesting access corridors should run parallel to the lotic and lentic ecosystems; pioneer species will not be extracted as they are important for soil improvement; illegal logging will be controlled with the aim of eradicating illegitimate logging activities; during logging and timber transport activities, sediment traps will be installed on the main watercourses (with around 500 m distance between them), and will be cleaned as often as necessary, with their evacuation/transport in areas that do not influence the degree of sedimentation in waterways; construction/monitoring/maintenance of drainage ditches for liquid and sediment flows from the transport routes designed to manage excessive and rapid precipitation events that are characteristic of the mountain area; installation of sediment traps (with around 500 m distance between them) on ditches used to evacuate liquids from the transport routes, cleaned as often as necessary, with the anticipation that the proposed sediment traps will stop, or at least diminish, the potential of these channels’ networks to be an unwanted sediment delivery system directly to downstream water bodies; leafy branches and debris left over from the logging will be placed on remaining stumps; full reforestation of the watershed with canopy projection over 0.8 (to reduce the kinetic energy of raindrops on the soil surface, surface runoff from precipitation, air currents, solar radiation, and minimize large temperature differences, etc.) and a subsequent forest management regime; excluding human activity in the riverbed of watercourses and preserving permanent or temporary riparian wetlands as natural sediment traps during periods of increased precipitations and high flows; the construction of new bridges, if needed, should not narrow the waterway to avoid increasing water speed and its capacity for erosion and sediment transport to downstream sectors; ecological restoration of sediment deposits formed at high waters in the riparian areas by fixing sediments or planting on sedimentary areas will prevent sediments from moving downstream in subsequent episodes of high flows; efforts should be made to favor existing flora, undergrowth, shrubs, and the herbaceous bed; it is acceptable to intervene with sowing or planting in critical areas; leaving the stumps in situ; and controlling waste management [152,153].
Sediment management in watersheds is necessary for their water quality, but indirectly, sediments are also the sources of other problems. Sediments are not unmixed and can be adhered to or can bear pollutants. To prevent such situations, various measures can be enforced: monitoring tributary torrents, slopes, and banks, etc., specifically those prone to accidental or permanent erosion; in sectors with accidental erosion, its effects can be drop off with blankets, sandbags, gravel bags, rugs, plastic materials barricades, etc., until the ecological state is secured through ecological rehabilitation and reconstruction; development of dense, vegetated fencerows, due to their function as sediment traps; banning the extraction of mineral resources in the basin; banning damming or regulating riverbeds, with the exception of debris basins, settling ponds, and other similar structures which can catch and retain sediments, which should then be frequently cleaned up; banning burning vegetation and trimmings; banning grazing and watering domestic animals in the forest; in pastoral lands, grazing will be organized to prevent the destruction of flora, soil compaction and the onset of erosion phenomena and will even be banned in sensitive seasons or sectors; a ban on the substitution forests and pastures with intensive agriculture lands; small-scale family farms are preferable to big-scale, industrial farms; and natural water filtration sectors and retention ponds should be protected and created and largely used in localities and in opposition solid sectors, growth runoff, and the transportation of sediments should be reduced, particularly hard sectors linked with the construction of buildings and roads infrastructure [152,153].
The general indiscipline with the dispositions commanding the wastewater management and the deficiency of dilution is one of the main causes for some of the researched sectors’ environmental bad situations. In this circumstance some management elements are suggested: rising water use performance through general use of contour meters and trustworthy transport pipelines; the development of a hazardous waste site assessment and monitoring unit; the protected lotic sectors must be big and abundant enough to admit the river natural self-cleaning processes to work; the lotic ecosystems must be used like ecological capital seeking to decrease the costs for water cleaning technologies and low-cost fish protein for local consumers.
The present hydrotechnical works’ impact should be reduced following some main management directions: increasing the river assimilative capacity thorough its restoration activities; revitalization of the traditions for land protection and use; avoiding the impact of wetland loss; and restoration of sectors of typical lotic ecosystems.
The riverine land exploitation should follow some main directions in this respect: determining the policies for cultivation of multi-year cultures; rehabilitation of the riverine forest corridor, hoping also in areas where the forest and other ecosystems in contact can be allowed to evolve according to natural dynamics; prohibiting access to the upper parts of the catchment areas so that spontaneous perennial vegetation could regenerate in good conditions and limit erosion damages; and rotating sylviculture and grazing (diminishing forestry, agriculture, and livestock impacts) with regard to seasonal conditions, especially on the river adjacent areas.
To sustain the protection of the conservative interest fish species and their habitats, their shelters should to be protected from all man-related aggression; the fact that proper protection is a useful help to the economic development of the rural communities should be highlighted; and complementarily should exist between human society’s development and conservation.
The collector river, The Târnava Mare River, which belongs, together with some of its tributaries, to the Natura 2000 Sighişoara-Târnava Mare protected area, cannot be properly managed if its tributaries are not in the ecological state to offer permanent refuge habitats for fish reproduction, development at early growing stages, feeding, and refuge in periods of accidental pollution and high flows.
The elements of the design used for the management of these river basins management can be followed as a general suggested model for other similar Carpathian Basin river basins of conservation interest facing similar environmental issues.
5. Conclusions
The global increasing temperature and other human activities impact induced the hydrologic net and habitats alteration, with a decrease of needed refuge habitats for freshwater fish, diminishing the fish distribution and abundance in the studied area.
In the new climate change scenario, an ongoing pattern in the context of the already-present human impact stress, especially the small hydrological nets, their lotic refuge habitats, and associated fish fauna are under a significant increasing environmental and anthropogenic risk due to an accentuated, new game changer, the drought/low flows, even in what have been, until recently, considered safe geographical areas like the Carpathian Basin.
New proactive special in situ adapted assessment, monitoring, and management integrated systems should be designed and implemented in such risky, potential hot spots to prevent and mitigate these present and future negative effects for the conservation and restoration of fish communities.
Poor water and land use imposed long-term effects on natural lotic systems, namely a change in the physical structure and substratum cover of fish habitat and the fish themselves. This is due to the human-induced, increase in fine sediment clogging in the refuge habitats of fish, which had an adverse effect on them, a process in a continuous acceleration due to climate change-induced diminishing of liquid flow on streams.
A composite model of climatic and anthropogenic induced threats and pressures of the researched river basins has significantly jeopardized the ecological status of its fish. As indirect (climate changes) and direct (various human activities in the basin) human impact affects the lotic habitats, they have become, in some sectors, critically altered or degraded, and the fish populations of conservative interest, and others, have been affected.
For the studied lotic systems’ fish populations ecological status recovery, relatively numerous new refuge habitats for fish should be created: nine times more than the existing number on the Dupuş River, 10 times more on the Biertan River, 0.4 times more on the Valchid River, 10 times more on the Laslea River, eight times more on the Mălâncrav River, and six times more on the Felţa River.
The habitat managers are required to specifically monitor the extent to which the changes in physical structures and cover for fish refuge habitats will affect these fish populations in the future, and a key management element should be the refuge habitats’ proper management and the creation of others.
The proposed fish refuge habitat monitoring and the creation of new ones should increase the fish survival rate and the recovery of species populations experiencing climate change-induced environmental disturbance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B. and A.C.-B.; methodology, D.B., A.S., K.C., S.B. and A.C.-B.; software, A.S.; validation, D.B. and A.C.-B.; formal analysis, D.B., A.S., K.C., S.B. and A.C.-B.; investigation, D.B., A.S. and A.C.-B.; resources, D.B., A.S. and A.C.-B.; data curation, D.B. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B., A.S., K.C., S.B. and A.C.-B.; writing—review and editing, D.B. and A.C.-B.; visualization, D.B., A.S., K.C., S.B. and A.C.-B.; supervision, A.C.-B.; project administration, D.B.; funding acquisition, A.C.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. The first and the last authors have equal contributions.
Funding
The APC was funded by Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Applied Ecology Research Center, and Hasso Platner Foundation research action LBUS-RC 2020-01-12.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Acknowledgments
The project was financed by Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Applied Ecology Research Center, and Hasso Platner Foundation research action LBUS-RC 2020-01-12. The first and the last authors thank to their students (Ceauşu M., Tchoumta R. and Nagapin S.) for their active involvement in the field activities. Last but not least the authors thank for the editorial English language support to Baumgartel D., writer/editor in Lausanne, Switzerland, and to Atmosphere journal editors and reviewers support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Dupuş River Habitat Characteristics.
Table A1.
Dupuş River Habitat Characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1D0 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 70 | 46°10′46.0″ N 24°28′20.6″ E | Lush vegetation and branches in the riverbed | |
| AD1 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°10′41.6″ N 24°28′39.2″ E | 100 m upstream accumulation lake with fish, probably holiday house, rush, floodplain | |
| A1D2 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | + | 100 | 46°10′36.6″ N 24°28′57.3″ E | Downstream 100 m from the lake, lush vegetation, plastic wastes |
| A1D3 | R | 150 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 120 | 46°10′24.9″ N 24°29′06.6″ E | Meander, sheep farm, metal, plastic, textile waste | |
| A1D4 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Grassland | Oozy | 0.5 | 60 | 46°10′24.9″ N 24°29′06.7″ E | Lush vegetation | |
| A1D5 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°10′11.0″ N 24°29′18.1″ E | Bridge, furniture waste | |
| A1D6 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 50 | 46°10′00.0″ N 24°29′27.0″ E | Rush | |
| A1D7 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Sandy | 2 | + | 60 | 46°09′51.5″ N 24°29′32.6″ E | Sheep farm |
| A1D8 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°09′38.8″ N 24°29′41.1″ E | Rush, Plastic wastes | |
| A1D9 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 40 | 46°09′25.5″ N 24°29′37.6″ E | Wool waste, construction (brick, tile), at the entrance in Dupus village | |
| A1D10 | M | 15 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 30 | 46°09′15.7″ N 24°29′41.7″ E | Minor riverbed with grass vegetation | |
| A1D11 | M | 15 | Shrub layer | In locality | Sandy | 2 | 35 | 46°09′06.3″ N 24°29′43.7″ E | ||
| A1D12 | M | 15 | Shrub layer | In locality | Sandy | 1.5 | 35 | 46°08′54.9″ N 24°29′36.7″ E | ||
| A1D13 | M | 15 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 35 | 46°08′47.3″ N 24°29′25.8″ E | At the exit of the village, branches in the riverbed | |
| A1D14 | M | 10 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 20 | 46°08′38.3″ N 24°29′23.3″ E | Rush, cattle farm, close to the river source |

Table A2.
Biertan River Habitat Characteristics.
Table A2.
Biertan River Habitat Characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2B0 | R | 75 | Arboreal layer and grass | Arable | Oozy | 5 | + | 200 | 46°12′50.3″ N 24°32′04.7″ E | Confluence with Tarnava Mare (close to the road and railway |
| A2B1 | R | 35 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°12′51.3″ N 24°32′04.1″ E | ||
| A2B2 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 200 | 46°12′45.4″ N 24°32′08.0″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B3 | R | 60 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′46.3″ N 24°32′17.4″ E | Waste metal, plastic, textiles | |
| A2B4 | R | 55 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′46.0″ N 24°32′17.5″ E | Rush, polystyrene, plastic waste | |
| A2B5 | R | 55 | Grass layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 300 | 46°12′44.4″ N 24°32′23.9″ E | Concreted banks, near the railway bridge | |
| A2B6 | M | 25 | Grass layer | Pasture | Oozy, concreted | 3 | 400 | 46°12′42.3″ N 24°32′30.1″ E | Banks and bed of the river concreted on a length of 30 m | |
| A2B7 | R | 40 | Grass layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°12′42.3″ N 24°32′30.8″ E | Reeds, gardens | |
| A2B8 | R | 60 | Grass layer | Arable and In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′40.5″ N 24°32′40.3″ E | Entrance to Saros on Tarnave | |
| A2B9 | R | 35 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′40.5″ N 24°32′40.5″ E | In the village, Saros on Tarnave, drenate banks, stone nets | |
| A2B10 | R | 65 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′32.7″ N 24°32′46.8″ E | Sewer holes, untreated wastewater, plastic waste, manure dumps | |
| A2B11 | R | 60 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | + | 100 | 46°12′27.9″ N 24°32′45.7″ E | Sewer holes, untreated wastewater, plastic waste, manure dumps |
| A2B12 | R | 50 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°12′22.5″ N 24°32′44.6″ E | Discharge of wastewater, traces and smell of detergents | |
| A2B13 | R | 100 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 100 | 46°12′18.2″ N 24°32′41.8″ E | Discharge of wastewater | |
| A2B14 | R | 45 | Grass layer and shrub | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 100 | 46°12′18.2″ N 24°32′41.8″ E | Plastic waste, rush | |
| A2B15 | R | 40 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | + | 100 | 46°12′09.0″ N 24°32′39.7″ E | |
| A2B16 | R | 60 | Grass layer | In locality and pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | + | 100 | 46°12′07.7″ N 24°32′39.2″ E | Pumping from the river for irrigation |
| A2B17 | R | 55 | Grass layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′58.0″ N 24°32′40.9″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B18 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′52.7″ N 24°32′37.9″ E | ||
| A2B19 | R | 70 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 200 | 46°11′52.1″ N 24°32′38.6″ E | |
| A2B20 | R | 90 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°11′45.2″ N 24°32′39.0″ E | Sector with meanders and fallen trees in the minor riverbed | |
| A2B21 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°11′42.0″ N 24°32′31.3″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B22 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′42.2″ N 24°32′31.1″ E | Hard to reach, twigs | |
| A2B23 | R | 65 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′36.1″ N 24°32′32.7″ E | ||
| A2B24 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′28.4″ N 24°32′30.9″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B25 | R | 95 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′28.2″ N 24°32′30.7″ E | Fallen branches in the minor riverbed, many nettles, traces of deer crossing | |
| A2B26 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°11′25.6″ N 24°32′31.3″ E | Meandered sector, with high meanders, low flow speed | |
| A2B27 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′21.4″ N 24°32′35.1″ E | Meandering, bridge crossing | |
| A2B28 | R | 25 | Shrub layer | Arable and grass | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°11′14.2″ N 24°32′30.0″ E | ||
| A2B29 | R | 80 | Shrub layer | Arable and grass | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°13′16.6″ N 24°33′01.7″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B30 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable and grass | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°13′16.6″ N 24°33′01.7″ E | ||
| A2B31 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable and grass | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°11′06.7″ N 24°32′32.4″ E | Large meanders, sheepfold without animals probably present by cows | |
| A2B32 | R | 45 | Grass layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°11′09.3″ N 24°32′27.3″ E | Floodplain | |
| A2B33 | R | 40 | Grass layers and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 5.5 | 150 | 46°13′16.9″ N 24°33′01.8″ E | ||
| A2B34 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°13′16.9″ N 24°33′01.8″ E | ||
| A2B35 | R | 55 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°10′55.1″ N 24°32′26.5″ E | ||
| A2B36 | R | 70 | Shrub layer | Arable and grassland | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°10′44.7″ N 24°32′27.1″ E | ||
| A2B37 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable and grassland | Oozy | 3 | 200 | 46°10′44.7″ N 24°32′27.1″ E | ||
| A2B38 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 5 | 200 | 46°10′31.2″ N 24°32′21.1″ E | ||
| A2B39 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 6 | 150 | 46°10′31.2″ N 24°32′21.1″ E | Landslide, denuded shore, meander, poultry farm across the street | |
| A2B40 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 5 | 200 | 46°13′05.2″ N 24°32′42.2″ E | Wildly | |
| A2B41 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable and grassland | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°13′04.3″ N 24°32′58.4″ E | ||
| A2B42 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°09′51.7″ N 24°32′06.1″ E | Wildly | |
| A2B43 | R | 60 | Grass layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°09′58.3″ N 24°32′07.8″ E | Plastic waste, fallen trees in the minor riverbed | |
| A2B44 | R | 60 | Grass layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°09′49.0″ N 24°32′04.1″ E | ||
| A2B45 | M | 20 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Arable and pasture | Rocky | 2 | 150 | 46°09′47.4″ N 24°32′04.6″ E | Construction and plastic waste, possible sheep farm, traces of wool on branches | |
| A2B46 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°09′33.3″ N 24°31′56.4″ E | ||
| A2B47 | R | 45 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 4.5 | 200 | 46°09′16.1″ N 24°31′47.1″ E | Wild, hard to reach, closed by shrub vegetation | |
| A2B48 | R | 65 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 200 | 46°09′10.1″ N 24°31′43.9″ E | ||
| A2B49 | R | 45 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 200 | 46°09′04.2″ N 24°31′40.7″ E | Steep banks | |
| A2B50 | R | 120 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°08′58.6″ N 24°31′37.1″ E | Many plastics waste, twig dam, cloudy water | |
| A2B51 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°08′39.2″ N 24°31′24.6″ E | ||
| A2B52 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′32.7″ N 24°31′20.5″ E | ||
| A2B53 | R | 35 | Grass layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′34.5″ N 24°31′21.8″ E | ||
| A2B54 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′32.7″ N 24°31′20.5″ E | ||
| A2B55 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′18.4″ N 24°31′26.8″ E | In the village, bridge under construction, river channeled through pipes | |
| A2B56 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′05.3″ N 24°31′14.8″ E | ||
| A2B57 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°08′05.3″ N 24°31′14.8″ E | ||
| A2B58 | R | 35 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′04.3″ N 24°31′09.2″ E | ||
| A2B59 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′02.8″ N 24°31′05.1″ E | ||
| A2B60 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°07′59.3″ N 24°31′01.5″ E | ||
| A2B61 | R | 35 | Shrub layer | Arable and grassland | Oozy | 1.5 | 100 | 46°07′13.8″ N 24°29′59.2″ E | ||
| A2B62 | R | 30 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°06′59.2″ N 24°29′41.8″ E | ||
| A2B63 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°06′46.8″ N 24°29′30.3″ E | Twigs in the minor riverbed | |
| A2B64 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°06′47.4″ N 24°29′29.7″ E | Underarm clay | |
| A2B65 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°06′31.7″ N 24°29′06.8″ E | Cow farm | |
| A2B66 | R | 35 | Grassy layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 55 | 46°06′29.2″ N 24°29′05.4″ E | ||
| A2B67 | R | 35 | Grass layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°06′23.8″ N 24°28′57.0″ E | ||
| A2B68 | R | 30 | Grass layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°06′13.2″ N 24°29′00.5″ E | ||
| A2B69 | M | 25 | Grass layer | In locality and Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 55 | 46°06′10.2″ N 24°29′00.3″ E | ||
| A2B70 | M | 25 | Grass layer | In locality and Arable | Oozy | 1 | - | 55 | 46°05′56.7″ N 24°28′48.7″ E | Green water, eutrophication |
| A2B71 | M | 25 | Grass layer | In locality and Arable | Oozy | 1 | 55 | 46°05′59.0″ N 24°28′52.5″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A2B72 | M | 15 | Grass layer | In locality and Arable | Oozy | 55 | 46°05′58.1″ N 24°28′52.3″ E | Discharges of domestic water directly into the river | ||
| A2B73 | M | 20 | Grass layer and arboreal | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 55 | 46°05′37.7″ N 24°28′35.9″ E | Discharge of domestic water directly into the river | |
| A2B74 | M | 15 | Grass layer | In locality and arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 55 | 46°05′35.5″ N 24°28′35.4″ E | ||
| A2B75 | M | 15 | Grass layer and shrub | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 55 | 46°05′14.4″ N 24°28′37.7″ E | ||
| A2B76 | R | 35 | Grass layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°04′60.0″ N 24°28′34.8″ E | Plastic and electronic waste | |
| A2B77 | M | 15 | Grass layer | Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 50 | 46°05′00.7″ N 24°28′31.3″ E | Wetland, rush | |
| A2B78 | M | 5 | Arboreal layer | Pasture and Forest | 0.5 | - | 46°04′27.5″ N 24°28′40.2″ E | Spring area |

Table A3.
Valchid River habitat characteristics.
Table A3.
Valchid River habitat characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3V0 | R | 60 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 5 | + | 300 | 46°13′10.7″ N 24°35′52.9″ E | Valchid confluence with Tarnava Mare, near to the road |
| A3V1 | R | 35 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 1 | + | 200 | 46°13′13.0″ N 24°35′48.9″ E | |
| A3V2 | R | 51 | Concreted banks | Pasture and arable | 3 | 200 | 46°13′12.1″ N 24°35′51.9″ E | River channeled on a portion of 5 m, upstream banks and concrete riverbed, road, railway | ||
| A3V3 | R | 27 | Concreted banks | Arable | 4 | 800 | 46°13′12.0″ N 24°35′52.1″ E | Succession of concrete thresholds of about 60 cm | ||
| A3V4 | R | 45 | Grassy layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 250 | 46°13′08.5″ N 24°35′56.7″ E | Boulder Dam | |
| A3V5 | R | 100 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 200 | 46°13′08.2″ N 24°35′59.1″ E | ||
| A3V6 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 6 | + | 200 | 46°13′07.1″ N 24°36′01.3″ E | |
| A3V7 | R | 100 | Grassy and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4.5 | + | 200 | 46°13′06.6″ N 24°36′05.0″ E | |
| A3V8 | R | 120 | Grassy layer, Exposed shore, without trees | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°13′06.3″ N 24°36′08.8″ E | Low flow rate | |
| A3V9 | R | 130 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°13′02.8″ N 24°36′07.0″ E | ||
| A3V10 | M | no refuges, fleeting | Grassy layer and denuded banks | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°12′58.2″ N 24°36′07.2″ E | ||
| A3V11 | R | 110 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 200 | 46°13′34.4″ N 24°37′52.6″ E | ||
| A3V12 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 200 | 46°12′53.9″ N 24°36′04.9″ E | ||
| A3V13 | R | 85 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°12′53.6″ N 24°36′05.9″ E | ||
| A3V14 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 250 | 46°12′47.6″ N 24°36′04.9″ E | ||
| A3V15 | R | 150 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 250 | 46°12′45.5″ N 24°36′03.8″ E | Cloudy water | |
| A3V16 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 200 | 46°12′45.6″ N 24°36′03.8″ E | ||
| A3V17 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°12′43.3″ N 24°36′03.4″ E | Beaver dam | |
| A3V18 | R | 102 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′43.0″ N 24°36′03.4″ E | ||
| A3V19 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 200 | 46°12′42.3″ N 24°36′04.1″ E | |||
| A3V20 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′37.1″ N 24°36′03.9″ E | Household waste (plastic, pet, cardboard, textiles) | |
| A3V21 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 200 | 46°13′25.7″ N 24°36′36.1″ E | ||
| A3V22 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Gravel, ballast | 2 | 150 | 46°12′39.4″ N 24°36′10.3″ E | ||
| A3V23 | M | Shallow depth | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Gravel, ballast | 2 | 150 | 46°12′39.4″ N 24°36′10.3″ E | ||
| A3V24 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 100 | 46°12′24.3″ N 24°36′01.0″ E | ||
| A3V25 | R | 65 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 100 | 46°12′20.4″ N 24°36′03.3″ E | ||
| A3V26 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 100 | 46°13′06.9″ N 24°36′26.9″ E | Secondary arm | |
| A3V27 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°13′16.9″ N 24°36′32.1″ E | ||
| A3V28 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°13′22.3″ N 24°36′34.8″ E | ||
| A3V29 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°13′29.4″ N 24°36′38.5″ E | Foam stain of 1 m2, waste (pet, bran), fallen trees | |
| A3V30 | R | 160 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′10.1″ N 24°35′48.5″ E | ||
| A3V31 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°12′06.2″ N 24°35′47.1″ E | Low flow rate, 50 cm course width | |
| A3V32 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°12′05.3″ N 24°35′43.7″ E | Low flow rate, course width of 50 cm, forest | |
| A3V33 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°12′03.3″ N 24°35′41.9″ E | ||
| A3V34 | R | 90 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°12′01.7″ N 24°35′40.3″ E | ||
| A3V35 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 180 | 46°11′59.9″ N 24°35′38.7″ E | ||
| A3V36 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 220 | 46°11′57.6″ N 24°35′34.7″ E | ||
| A3V37 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable | 200 | 46°11′55.7″ N 24°35′30.0″ E | Sheepfold | |||
| A3V38 | R | 130 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°11′55.7″ N 24°35′29.7″ E | Sheepfold | |
| A3V39 | R | 130 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | + | 180 | 46°11′56.6″ N 24°35′30.9″ E | |
| A3V40 | R | 75 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | + | 150 | 46°11′52.7″ N 24°35′20.9″ E | Sheepfold, culvert, in the summer the level drops by half, minimum flow provided almost all the time, in 2020 much weaker flow than so far in 2021 |
| A3V41 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | + | 46°11′49.5″ N 24°35′17.9″ E | ||
| A3V42 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 150 | 46°11′49.5″ N 24°35′18″ E | |
| A3V43 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 180 | 46°11′46.8″ N 24°35′15.6″ E | |
| A3V44 | R | 85 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 50 | 46°11′38.3″ N 24°35′09.4″ E | |
| A3V45 | R | 75 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°11′38.3″ N 24°35′10″ E | No human settlements, only three sheep farms | |
| A3V46 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 46°11′34.0″ N 24°34′58.6″ E | Many twigs in the water | ||
| A3V47 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°11′29.8″ N 24°35′04.7″ E | Waste (plastic, cardboard, electro-household) | |
| A3V48 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′19.7″ N 24°35′02.1″ E | ||
| A3V49 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°11′14.8″ N 24°35′04.7″ E | Waste (plastic) | |
| A3V50 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°11′14.8″ N 24°35′04.7″ E | ||
| A3V51 | R | 180 | Arboreal layer | Arable, orchard | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°11′14.8″ N 24°35′04.7″ E | ||
| A3V52 | R | 175 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 46°11′14.0″ N 24°35′08.4″ E | |||
| A3V53 | R | 150 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°10′57.6″ N 24°35′09.5″ E | ||
| A3V54 | R | 160 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 200 | 46°10′57.2″ N 24°35′09.6″ E | Dam of twigs | |
| A3V55 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 46°10′58.9″ N 24°35′08.1″ E | |||
| A3V56 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 46°10′54.5″ N 24°35′07.2″ E | |||
| A3V57 | R | 109 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1.5 | 170 | 46°10′45.1″ N 24°35′10.2″ E | Cattle farm | |
| A3V58 | R | 57 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°10′42.7″ N 24°35′07.7″ E | Waste, we are approaching human settlements | |
| A3V59 | R | 110 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 120 | 46°10′38.9″ N 24°35′07.4″ E | ||
| A3V60 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable, In locality | Oozy | 2 | 110 | 46°10′35.1″ N 24°35′06.0″ E | ||
| A3V61 | R | 115 | Arboreal layer | Arable, In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°10′28.2″ N 24°35′06.7″ E | Behind the houses, gardens | |
| A3V62 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy/ Gravel | 1.5 | 160 | 46°10′23.1″ N 24°35′05.6″ E | ||
| A3V63 | M | 5 | Grassy layer | In locality | Oozy/ Gravel | 0.5 | 100 | 46°10′11.9″ N 24°34′58.0″ E | ||
| A3V64 | R | 25 | Grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.8 | 150 | 46°10′09.2″ N 24°34′55.8″ E | ||
| A3V65 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 100 | 46°10′09.2″ N 24°34′55.8″ E | ||
| A3V66 | R | 27 | Grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 1.5 | 150 | 46°09′59.7″ N 24°34′48.1″ E | ||
| A3V67 | R | 80 | Grassy and arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°10′00.4″ N 24°34′50.2″ E | ||
| A3V68 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 150 | 46°09′52.0″ N 24°34′44.1″ E | ||
| A3V69 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 120 | 46°09′52.0″ N 24°34′44.1″ E | ||
| A3V70 | R | 130 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 120 | 46°08′20.8″ N 24°33′02.6″ E | ||
| A3V71 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 120 | 46°09′39.0″ N 24°34′40.5″ E | ||
| A3V72 | R | 110 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 5 | 120 | 46°08′13.2″ N 24°32′53.4″ E | Fallen trees in the water | |
| A3V73 | R | 100 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 150 | 46°09′16.6″ N 24°34′16.8″ E | ||
| A3V74 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 110 | 46°08′15.2″ N 24°32′55.9″ E | ||
| A3V75 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 110 | 46°08′18.9″ N 24°32′57.7″ E | ||
| A3V76 | R | 130 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′15.1″ N 24°32′55.8″ E | ||
| A3V77 | R | 65 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′12.8″ N 24°32′52.7″ E | ||
| A3V78 | R | 70 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°09′08.4″ N 24°34′08.1″ E | ||
| A3V79 | M | 25 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°08′41.8″ N 24°33′26.1″ E | ||
| A3V80 | R | 80 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 120 | 46°08′41.8″ N 24°33′26.1″ E | ||
| A3V81 | R | 85 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°08′14.6″ N 24°32′55.1″ E | ||
| A3V82 | M | 60 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°08′25.3″ N 24°33′09.3″ E | ||
| A3V83 | R | 70 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 120 | 46°08′18.1″ N 24°32′59.7″ E | |
| A3V84 | R | 95 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 100 | 46°08′16.5″ N 24°32′57.5″ E | ||
| A3V85 | R | 50 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 110 | 46°08′15.3″ N 24°32′56.0″ E | ||
| A3V86 | R | 120 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°08′34.9″ N 24°33′15.8″ E | Wood dam | |
| A3V87 | M | 30 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 50 | 46°08′26.0″ N 24°33′06.8″ E | Construction waste (rubble, brick, plastic and paper packaging) | |
| A3V88 | R | 100 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 120 | 46°08′16.3″ N 24°32′56.9″ E | ||
| A3 A3V89 | R | 55 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°08′09.4″ N 24°32′55.8″ E | ||
| V90 | R | 60 | Shrub and grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 120 | 46°08′01.3″ N 24°32′54.4″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A3V91 | R | 40 | Shrub and grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°07′53.7″ N 24°32′51.6″ E | Denuded banks | |
| A3V92 | M | 25 | Shrub and grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°07′56.0″ N 24°32′50.3″ E | L bank denuded | |
| A3V93 | M | 25 | Shrub and grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 100 | 46°07′50.6″ N 24°32′51.8″ E | Denuded banks, trees cut off from the shore, the banks have undergone works... | |
| A3V94 | R | 45 | Shrub and grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°07′44.1″ N 24°32′46.4″ E | ||
| A3V95 | M | 30 | Shrub and grassy layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 50 | 46°07′20.3″ N 24°32′57.3″ E | ||
| A3V96 | R | 45 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 50 | 46°07′20.1″ N 24°32′57.4″ E | ||
| A3V97 | R | 35 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | + | 50 | 46°07′20.1″ N 24°32′57.4″ E | Plastic waste |
| A3V98 | R | 80 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 100 | 46°07′19.0″ N 24°32′58.8″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A3V99 | R | 80 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°07′19.0″ N 24°32′58.8″ E | Cutting trees on the shore, in summer almost dry sector (shepherd) | |
| A3V100 | M | 10 | Grassy layer | Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 40 | 46°06′57.4″ N 24°32′58.5″ E | ||
| A3V101 | M | 5 | Grassy layer and shrub | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 40 | 46°06′47.0″ N 24°33′29.9″ E | ||
| A3V102 | M | 5 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 4 | 30 | 46°06′35.4″ N 24°33′21.0″ E | We approach the spring, the river branches into several streams, low flow, wetland | |
| A3V103 | M | 5 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 20 | 46°06′23.9″ N 24°33′37.6″ E | Near the spring, unidentified refuges, plastic waste, forest road |

Table A4.
Laslea River Habitat Characteristics.
Table A4.
Laslea River Habitat Characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4L0 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 5 | + | 200 | 46°13′53.1″ N 24°40′29.8″ E | Confluence of Laslea with Tarnava Mare |
| A4L1 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 5 | 200 | 46°13′53.2″ N 24°40′29.5″ E | ||
| A4L2 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 5 | 200 | 46°13′53.2″ N 24°40′29.5″ E | Significant ripisilva vegetation, meadow, hard to reach | |
| A4L3 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Pasture and arable | Oozy | 3 | 200 | 46°13′39.4″ N 24°40′24.3″ E | ||
| A4L4 | R | 30 | Concreted banks | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 46°13′22.7″ N 24°40′13.3″ E | Concreted banks | ||
| A4L5 | M | 10 | Concreted banks | Arable | Concreted | 4 | 500 | 46°13′23.2″ N 24°40′13.4″ E | Banks and bed concreted on a portion of 100 m | |
| A4L6 | R | 35 | Shrub and grassy layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 46°13′16.6″ N 24°40′14.9″ E | |||
| A4L7 | R | 120 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°13′15.3″ N 24°40′15.9″ E | Dam of twigs, plastic waste, rubble, and packaging waste constructions | |
| A4L8 | M | 25 | Shrub and grassy layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°13′15.3″ N 24°40′15.9″ E | Concrete banks on a portion of 10 m | |
| A4L9 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 150 | 46°13′11.5″ N 24°40′12.2″ E | Meander, plastic waste | |
| A4L10 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 100 | 46°13′04.1″ N 24°40′07.2″ E | Rubber, plastic waste | |
| A4L11 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 70 | 46°12′59.7″ N 24°40′05.7″ E | Angus cows farm, denuded banks, bathing cows | |
| A4L12 | R | 45 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°12′53.2″ N 24°40′03.3″ E | Plastic waste, polystyrene | |
| A4L13 | R | 45 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°12′44.4″ N 24°39′57.3″ E | Angus cows farm, denuded banks, bathing cows, passers-by | |
| A4L14 | R | 35 | Grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 50 | 46°12′25.6″ N 24°39′26.4″ E | ||
| A4L15 | M | 25 | Grassy layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°12′25.5″ N 24°39′26.5″ E | ||
| A4L16 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 50 | 46°12′06.6″ N 24°39′16.9″ E | ||
| A4L17 | R | 30 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°11′59.2″ N 24°39′14.4″ E | At the exit of Laslea, branches and grasses fallen into the water | |
| A4L18 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°11′56.3″ N 24°39′01.7″ E | Meandering, branches, and grasses fallen into the water | |
| A4L19 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°11′46.1″ N 24°38′47.5″ E | Plastic waste, polystyrene, nettles | |
| A4L20 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°11′46.1″ N 24°38′47.5″ E | Sheep farm, riverbed closed with electric fence on a portion of 500 m | |
| A4L21 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°11′30.5″ N 24°38′33.3″ E | Waste plastics, meanders | |
| A4L22 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°11′29.1″ N 24°38′30.7″ E | Twigs fallen into the water | |
| A4L23 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°11′28.8″ N 24°38′24.1″ E | Meandering | |
| A4L24 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°10′47.0″ N 24°37′41.9″ E | ||
| A4L25 | R | 55 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 150 | 46°10′45.9″ N 24°37′38.9″ E | Sheep farm, low flow, branches fallen into the water | |
| A4L26 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°10′35.5″ N 24°37′20.7″ E | ||
| A4L27 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°10′26.4″ N 24°37′04.7″ E | ||
| A4L28 | R | 60 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 60 | 46°10′17.2″ N 24°36′54.1″ E | ||
| A4L29 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°10′17.3″ N 24°36′54.4″ E | Waste from plastic, rubble, wood, textiles | |
| A4L30 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°09′51.9″ N 24°36′37.8″ E | Entrance to Roandola, hard to reach, a lot of vegetation, mostly nettles, large quantities of plastic waste, polystyrene, textiles, furniture, electronic, manure storage, animal manure... | |
| A4L31 | R | 45 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 60 | 46°09′52.9″ N 24°36′51.8″ E | Household waste | |
| A4L32 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 4 | 60 | 46°09′44.1″ N 24°36′19.1″ E | Meandering, household waste, many nettles, lush vegetation | |
| A4L33 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 100 | 46°09′12.1″ N 24°35′59.4″ E | Meander, passing animals, sheep farm, municipal waste | |
| A4L34 | R | 40 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 80 | 46°09′03.6″ N 24°35′55.0″ E | Lush vegetation, hard to reach, confluence with Malancrav | |
| A4L35 | R | 100 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 70 | 46°08′53.6″ N 24°35′47.8″ E | Lush vegetation, hard to reach, gas pipe passes over the riverbed, municipal waste | |
| A4L36 | M | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 70 | 46°08′53.6″ N 24°35′48.1″ E | Lush vegetation | |
| A4L37 | R | 35 | Grassy and shrub layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°08′33.3″ N 24°35′48.0″ E | The left bank is close to the hill, the coast, the steep bank, the rush, and the floodplain | |
| A4L38 | R | 60 | Grassy and shrub layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | + | 60 | 46°08′04.4″ N 24°35′50.0″ E | Lush vegetation, floodplain |
| A4L39 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°07′37.4″ N 24°35′53.0″ E | ||
| A4L40 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 70 | 46°07′37.4″ N 24°35′53.0″ E | Lush vegetation, nettles | |
| A4L41 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°06′54.8″ N 24°36′01.1″ E | ||
| A4L42 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°06′33.4″ N 24°36′22.6″ E | Plastic waste, branches fallen into the water | |
| A4L43 | R | 40 | Grassy and shrub layer | In locality and Arable | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°06′18.2″ N 24°36′22.6″ E | Reservoir | |
| A4L44 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 60 | 46°06′07.1″ N 24°36′27.9″ E | 200 m upstream of the lake, forest road, rush, wetland | |
| A4L45 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 60 | 46°05′56.8″ N 24°36′32.4″ E | Rush, wetland | |
| A4L46 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°05′54.1″ N 24°36′32.5″ E | Cow farm | |
| A4L47 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°05′51.1″ N 24°36′33.6″ E | Rush, wetland | |
| A4L48 | R | 20 | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°05′46.5″ N 24°36′34.1″ E | |||
| A4L49 | R | 20 | Grassy and shrub layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°05′40.8″ N 24°36′34.3″ E | ||
| A4L50 | R | 15 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 30 | 46°05′39.7″ N 24°36′35.9″ E | Close to the spring | |
| A4L51 | R | 10 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 20 | 46°05′35.4″ N 24°36′36.3″ E | Nearby spring |

Table A5.
Mălâncrav River Habitat Characteristics.
Table A5.
Mălâncrav River Habitat Characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5M0 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°11′23.4″ N 24°38′20.6″ E | ||
| A5M1 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°10′57.3″ N 24°38′30.8″ E | ||
| A5M2 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°10′16.4″ N 24°38′40.7″ E | Bridge, lush vegetation, ripisilva | |
| A5M3 | R | 90 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 60 | 46°10′07.1″ N 24°38′39.0″ E | ||
| A5M4 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 5 | 200 | 46°09′50.9″ N 24°38′36.2″ E | Ripisilva 50 m high | |
| A5M5 | R | 110 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 5 | 250 | 6°09′09.7″ N 24°38′27.0″ E | Cow farm, plastic waste | |
| A5M6 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 4 | 250 | 46°08′57.3″ N 24°38′32.0″ E | Bank close to the hill, steep, logging, plastic waste | |
| A5M7 | R | 50 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°08′20.9″ N 24°38′19.7″ E | Lush vegetation, floodplain | |
| A5M8 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 70 | 46°08′20.7″ N 24°38′19.7″ E | Bank close to the hill, steep, logging, plastic waste | |
| A5M9 | R | 110 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 4 | 150 | 46°07′53.3″ N 24°38′22.9″ E | Meandering, lush vegetation, floodplain | |
| A5M10 | R | 80 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Rocky | 3 | 100 | 46°07′33.5″ N 24°38′40.6″ E | Pass, construction waste | |
| A5M11 | R | 75 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 100 | 46°07′33.5″ N 24°38′40.6″ E | ||
| A5M12 | M | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°07′06.0″ N 24°38′54.4″ E | ||
| A5M13 | M | 35 | Shrub layer | Arable | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°06′23.9″ N 24°39′02.0″ E | Municipal waste | |
| A5M14 | R | 75 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 100 | 46°05′53.3″ N 24°39′25.2″ E | Entrance to Malancrav village, foam water, smell of detergents, sheep farm | |
| A5M15 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°05′49.0″ N 24°39′34.7″ E | ||
| A5M16 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 80 | 46°05′41.9″ N 24°39′50.7″ E | ||
| A5M17 | M | 25 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°05′41.4″ N 24°40′06.3″ E | Municipal waste | |
| A5M18 | R | 110 | Shrub layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 2 | 70 | 46°05′42.0″ N 24°40′27.6″ E | At the exit of Malancrav, the pig farm, Roma community, large quantities of waste, meandered | |
| A5M19 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 60 | 46°05′43.8″ N 24°40′40.0″ E | Sheep farm | |
| A5M20 | R | 30 | Shrub layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 1 | 60 | 46°05′42.7″ N 24°40′53.1″ E | ||
| A5M21 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 1 | 40 | 46°05′40.6″ N 24°40′59.0″ E | ||
| A5M22 | M | 20 | Shrub layer | Arable and pasture | Oozy | 1 | 30 | 46°05′36.8″ N 24°41′08.1″ E | Nearby spring |

Table A6.
Floreşti/Felţa River Habitat Characteristics.
Table A6.
Floreşti/Felţa River Habitat Characteristics.
| Station Code | R-Refuge/M-Downstream Refuge Sector | Refuge Depth (cm) | Banks Description | Land Use | Substrate | Banks Height (m) | Fish Presence | Minor Riverbed Width (cm) | GPS Coordinates | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A6F0 | R | 60 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 100 | 46°12′03.9″ N 24°39′16.1″ E | ||
| A6F1 | R | 60 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 5 | 100 | 46°12′02.5″ N 24°39′20.3″ E | Municipal waste, at the exit of Laslea | |
| A6F2 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 5 | 100 | 46°11′58.1″ N 24°39′23.2″ E | ||
| A6F3 | R | 95 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°11′42.9″ N 24°39′31.7″ E | Cow farm, hop plantation | |
| A6F4 | R | 40 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°11′28.5″ N 24°39′39.6″ E | ||
| A6F5 | R | 100 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°11′03.9″ N 24°39′43.3″ E | Municipal waste, hop plantation, lush vegetation, burdock | |
| A6F6 | R | 45 | Shrub layer and arboreal | Arable | Oozy | 1 | 70 | 46°10′41.1″ N 24°39′55.8″ E | ||
| A6F7 | R | 100 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 100 | 46°10′23.7″ N 24°40′04.4″ E | Meandering, lush vegetation | |
| A6F8 | R | 35 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 80 | 46°10′22.7″ N 24°40′03.7″ E | ||
| A6F9 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 80 | 46°10′05.7″ N 24°40′02.7″ E | ||
| A6F10 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable | Oozy | 0.5 | 60 | 46°10′03.0″ N 24°40′00.4″ E | 100 m upstream chalet, bed closed with electric wire | |
| A6F11 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°09′52.6″ N 24°39′53.7″ E | Plastic waste, twigs in the riverbed, cattle | |
| A6F12 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°09′52.6″ N 24°39′53.7″ E | ||
| A6F13 | R | 30 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°09′40.8″ N 24°39′45.5″ E | Meandering | |
| A6F14 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 70 | 46°09′27.1″ N 24°39′37.8″ E | ||
| A6F15 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 60 | 46°09′19.5″ N 24°39′36.8″ E | Farm cattle, twigs in the riverbed, passing cows | |
| A6F16 | R | 60 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 60 | 46°09′01.3″ N 24°39′31.1″ E | ||
| A6F17 | R | 25 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 1.5 | 80 | 46°08′47.4″ N 24°39′30.6″ E | Lush vegetation | |
| A6F18 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy | 46°08′36.0″ N 24°39′36.2″ E | ||||
| A6F19 | M | 25 | Arboreal layer | In locality | Oozy | 1 | 50 | 46°08′23.9″ N 24°39′35.3″ E | Cemetery | |
| A6F20 | R | 65 | Shrub layer | In locality | Oozy | 0.5 | 50 | 46°08′21.7″ N 24°39′38.0″ E | ||
| A6F21 | R | 40 | Shrub layer | Arable | Clayey | 0.5 | 70 | 46°08′18.6″ N 24°39′41.0″ E | At the exit of the village, construction waste, branches in the riverbed | |
| A6F22 | R | 45 | Arboreal layer | Arable and Pasture | Oozy | 0.5 | 60 | 46°08′15.9″ N 24°39′43.7″ E | Cattle farm | |
| A6F23 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 50 | 46°08′15.8″ N 24°39′43.9″ E | Step from twigs and trunk, meander, farm cows | |
| A6F24 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 4 | 60 | 46°08′06.0″ N 24°39′50.0″ E | ||
| A6F25 | M | 15 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 5 | 50 | 46°08′00.8″ N 24°39′51.0″ E | Steep banks, lush vegetation | |
| A6F26 | M | 15 | Shrub layer | Pasture | Oozy | 4 | 35 | 46°07′55.2″ N 24°39′49.9″ E | ||
| A6F27 | M | 15 | Shrub and arboreal layer | Pasture | Rocky | 4 | 35 | 46°07′50.5″ N 24°39′50.1″ E | Plastic waste | |
| A6F27 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Forest | Rocky | 6 | 20 | 46°07′46.6″ N 24°39′49.8″ E | Logging | |
| A6F28 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Forest | Rocky | 5 | 25 | 46°07′41.6″ N 24°39′51.8″ E | Logging | |
| A6F29 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 25 | 46°07′35.1″ N 24°39′52.2″ E | ||
| A6F30 | M | 20 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 3 | 25 | 46°07′31.8″ N 24°39′52.4″ E | ||
| A6F31 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 20 | 46°07′26.4″ N 24°39′52.9″ E | Cattle farm | |
| A6F32 | M | 15 | Arboreal layer | Pasture | Oozy | 2 | 15 | 46°07′20.2″ N 24°39′53.4″ E | Nearby spring |
Appendix B
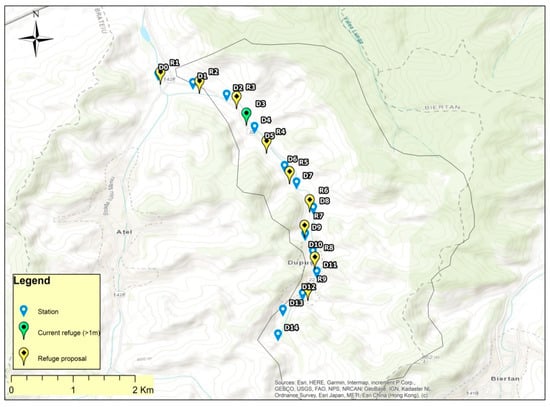
Scheme A1.
Dupuş River—present refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.

Scheme A2.
Biertan River—refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.
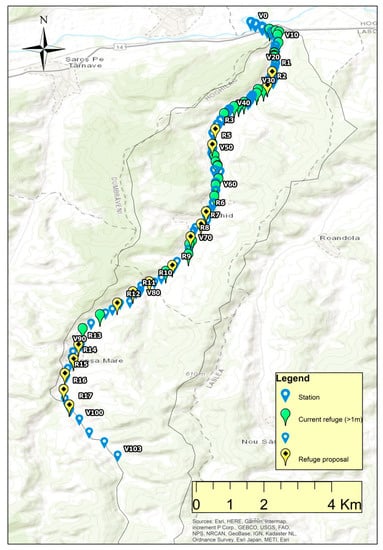
Scheme A3.
Valchid River—refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.
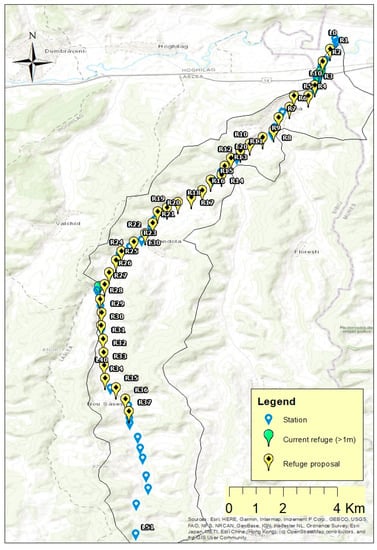
Scheme A4.
Laslea River—refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.
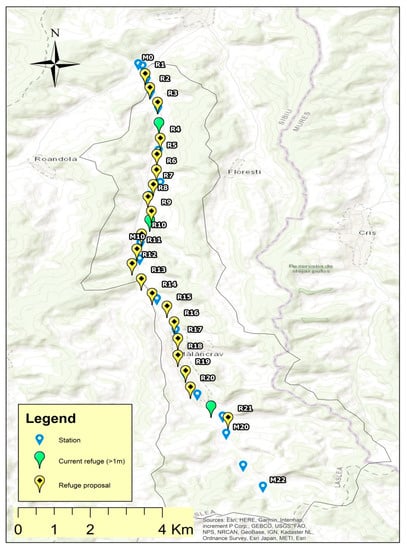
Scheme A5.
Mălâncrav River—present refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.
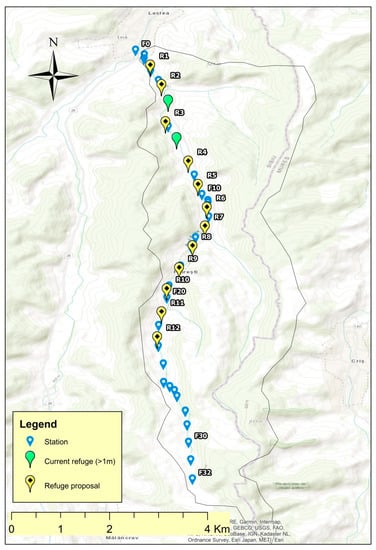
Scheme A6.
Felţa River—refuge habitats and proposals for new refuge to be created.
References
- Maruyama, S.; Ikoma, M.; Genda, H.; Hirose, K.; Yokohama, T.; Santosh, M. The naked planet earth: Most essential pre-requisite for the origin and evolution of life. Geosci. Front. 2013, 4, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharuk, W.; Goncharuk, V.V. Water is everywhere. It holds everything a key to understanding the universe. D. I. Mendeleev’s law is the prototype of the universe constitution. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2019, 41, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, R.M. Biological diversity: Differences between land and sea. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1994, 343, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Benton, M.J. Biodiversity on land and in the sea. Geol. J. 2001, 36, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, C.; Bloesch, J.; Coman, A. Water pollution in the Mureş Catchment and its impact on the aquatic communities (Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2008, 6, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, C.; Tittensor, D.P.; Adl, S.; Simpson, A.G.B.; Worm, B. How many species are there on Earth and in the ocean? PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, 1001127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, K.; Geerat, G.; Vermeij, J.; Wainwright, P.C. Biodiversity in water and on land. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R900–R903. [Google Scholar]
- Barinova, S.S. Empirical model of the functioning of aquatic ecosystems. Int. J. Oceanogr. Aquac. 2017, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S. On the classification of water quality from an ecological point of view. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sender, J.; Maślanko, W.; Różańska-Boczula, M.; Cianfaglione, K. A new multi-criteria method for the ecological assessment of lakes: A case study from the transboundary biosphere reserve ‘West Polesie’ (Poland). J. Limnol. 2017, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cianfaglione, K. Plant landscape and models of french atlantic estuarine systems. Extended summary of the doctoral thesis. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2021, 23, 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, J.; von Fumetti, J.S.; Kelly-Quinn, M. The importance of small water bodies for biodiversity and ecosystem services: Implications for policy makers. Hydrobiologia 2017, 793, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekárik, L.; Čejka, T.; Čiamporovà-Zatovičovà, Z.; Darolovà, A.; Illèsovà, D.; Illyová, M.; Pastuchovà, Z.; Gatial, E.; Čiampor, F. Multidisciplinary evaluation of the function and importance of the small water reservoirs: The biodiversity aspect. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2009, 8, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Agenţia Europeană de Mediu (AEM). Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/ro/themes/climate/about-climate-change (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Treut, L.; Somerville, R.; Cubasch, U.; Ding, Y.; Mauritzen, C.; Mokssit, A.; Peterson, T.; Prather, M.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; et al. Historical overview of climate change science. Earth 2007, 43, 93–127. [Google Scholar]
- Heaviside, C. Understanding the impacts of climate change on health to better manage adaptation action. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, V.; Waite, T.D. Climate change and human health—The links to the UN landmark agreement on disaster risk reduction. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Security Council. Available online: https://www.un.org/press/en/2021/sc14445.doc.htm (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC-53 BIS). Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/ (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Mann, M.E.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K. Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries. Nature 1998, 392, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krassilov, V.; Barinova, S. Sea level—Geomagnetic polarity correlation as consequence of rotation geodynamics. Earth Sci. 2013, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bates, B.C.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Wu, S.; Palutikof, J.P. Climate change and water. In Technical Paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Secretary-General Meetings Coverage and Press Releases. Available online: https://www.un.org/press/en/2021/sgsm20847.doc.htm (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Fenoglio, S.; Bo, T.; Cucco, M.; Mercalli, L.; Malacarne, G. Effects of global climate change on freshwater biota: A review with special emphasis on the Italian situation. Ital. J. Zool. 2010, 77, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenning, J.C.; Kerr, J.; Rahbek, C. Predicting future shifts in species diversity. Ecography 2009, 32, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, I.; Sykes, M.T.; Berry, P.M.; Thuiller, W.; Piper, J.M.; Nigmann, U. MACIS: Minimization of and adaptation to climate change impacts on biodiversity. GAIA—Ecol. Per. Sci. Soc. 2009, 17, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero, J.C. Changes in the Euro-Atlantic fish species composition resulting from fishing and ocean warming. Ital. J. Zool. 1998, 65, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Jones, G.P.; Pratchett, M.S.; Williams, A.J. Climate change and the future for coral reef fishes. Fish Fish. 1998, 9, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomi, T.; Nagasaka, M.; Fukuda, T.; Hagihara, H. Shifting of the life cycle and life-history traits of the fall webworm in relation to climate change. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1998, 125, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balletto, E.; Barbero, F.; Casacci, L.P.; Cerrato, C.; Patricelli, D.; Bonelli, S. L’Impatto dei Cambiamenti Climatici Sulle Farfalle Italiane; XVIII Convegno Gruppo Per l’Ecologia di Base G. Gadio: Alessandria, Italy, 2008; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pounds, J.A.; Fogden, P.L.; Campbell, J.H. Biological response to climate change on a tropical mountain. Nature 1999, 398, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, A.H.; Balcombe, S.R.; Wilson, G.A.; Thoms, M.C.; Marschall, J.C. Spatial and temporal variation in fish assemblage structure in isolated waterholes during the 2001 dry season of an arid-zone river, Cooper Creek, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2005, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubcov, N.; Zubcov, E.; Schlenk, D. The dynamics of metals in fish from Nistru and Prut rivers (Moldova). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2008, 6, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev, M.; Botev, I. Assessment of the ecological status of some Bulgarian rivers from the Aegean Sea Basin based on both environmental and fish parameters. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2008, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Momeu, L.; Battes, K.; Battes, K.; Stoica, I.; Avram, A.; Cîmpean, M.; Pricpe, F.; Ureche, D. Algae, macroinvertebrate and fish communities from the Arieş River catchment area (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2009, 7, 149–180. [Google Scholar]
- Trichokva, T.; Stefanov, T.; Vassilev, M.; Zivcov, M. Fish species diversity in the rivers of the north-west Bulgaria. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2009, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jeeva, V.; Kumar, S.; Verma, D.; Rumana, S. River fragmentation and connectivity problems in Gange River of upper Himalayas: The effect on the fish communities (India). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2011, 12, 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Florea, L.; Strătilă, S.D.; Costache, M. The assessment of community interest fish species from protected area ROSCI0229. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2014, 16, 73–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosai, A.S. Illegal fishing in southern Mannar Island coastal area (Sri Lanka). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2015, 17, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnood, Z.; Khoshnood, R. Effect of industrial wastewater on fish in Karoon River. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2015, 17, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rumana, H.S.; Jeeva, V.; Kumar, S. Impact of the low head dam/barrage on fisheries—A case study of Giri River of Yamuna Basin (India). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2015, 17, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Del Monte-Luna, P.; Lluch-Belda, D.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Lluch-Cota, S.; Villalobos-Ortiz, H. Approaching the potential of world marine fish. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2015, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwo, I.O.; Olopade, O.A.; Bamidele, N.A. Heavy metal concentration in eight fish species from Epe Lagoon (Nigeria). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2019, 21, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kar, D. Wetlands and their fish diversity in Assam (India). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2019, 21, 47–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.M. Predation by nonnative Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum, 1792), on the native biota from freshwater environment of the Central Andes (Argentina). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2019, 23, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, M. Prospects for biodiversity. Science 2003, 302, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, B. In Verbis, 11 August 2021. Available online: https://www.digi24.ro/stiri/actualitate/romania-in-raportul-cod-rosu-pentru-umanitate-expert-meteo-vom-avea-valuri-de-caldura-precipitatii-intense-si-seceta-1629497 (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014, Synthesis Report. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/syr/ (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Lupo, A.R.; Kononova, N.K.; Semenova, I.G.; Lebedeva, M.G. A comparison of the characteristic drought during the late 20th and early 21st centuries over Eastern Europe, Western Russia and Central North America. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellström, E.; Nikulin, G.; Hanson, U.; Strandberg, G.; Ullerstig, A. 21st century changes in the European climate: Uncertainties derived from an ensemble of regional climate model simulations. Tellus A 2010, 63, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.K.; Beldring, S. Climate change effects on spatiotemporal patterns of hydroclimatological summer droughts in Norway. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1205–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfaglione, K.; Chelli, S.; Campetella, G.; Wellstein, C.; Cerivellini, M.; Ballelli, S.; Lucarini, D.; Canullo, R.; Jentsch, A. European grasslands gradient and the resilience to extreme climate events: The SIGNAL project in Italy. In Climate Gradients and Biodiversity in Mountains of Italy; Pedrotti, F., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Brönnimann, S. Early twentieth-century warming. Nature 2009, 2, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitus, S.; Antonov, J.I.; Wang, J.; Delworth, T.L.; Dixon, K.W.; Broccoli, A.J. Anthropogenic warming of Earth’s climate system. Science 2001, 292, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B. The impracticality of a universal drought definition. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 117, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC 2012. Summary for policymakers. In Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Stocker, D., Qin, D.J., Dokken, K.L., Ebi, M.D., Mastrandrea, K.J., Mach, G.-K., Plattner, S.K., Allen, M.T., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Stahle, D.W. Anthropogenic megadrought, human-driven climate warming worsens an otherwise moderate drought. Science 2020, 368, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Pulwarty, R.S. (Eds.) Drought as hazard: Understanding the natural and social context. In Drought and Water Crises; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gerald, A.M.; Washington, W.M.; Arblaster, J.M.; Hu, A.; Teng, H.; Tebaldi, C.; Sanderson, B.N.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Conley, A.J.; Strand, W.G.; et al. Climate system response to external forcings and climate change projections in CCSM4. J. Clim. 2007, 25, 3661–3683. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D.; Joy, M.; Olosutean, H.; Afanasyev, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Natural and anthropogenic driving forces as key elements in the Lower Danube Basin‒South-Eastern Carpathians‒North-Western Black Sea coast area lakes, a broken stepping stones for fish in a climatic change scenario? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Barinova, S. Cladocera from the sediment of high Arctic lake in Svalbard. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2021, 23, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cianfaglione, K. On the potential of Quercus pubescens willd and other species of Quercus in the camerino syncline (central Italy). In Warm-Temperate Deciduous Forests around the Northern Hemisphere; Box, E., Fujiwara, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wellstein, C.; Cianfaglione, K. Impact of extreme drought and warming on survival and growth characteristics of different provenences of juvenile Quercus pubescens willd. Folia Geobot. 2014, 49, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, A. The challenge of providing environmental flow rules to sustain river ecosystems. Ecol. Appl. 2006, 16, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H. Basic principles and ecological consequences of altered flow regimes for aquatic biodiversity. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Garrote, L. Influence of hydrological based environmental flow methods on flow alteration and energy production in a run-of-river hydropower plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Bejarano, M.D.; Garrote, L. Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—Current status and future prospects on the brink of energy transition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 142, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, G.-O.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Florescu, I.E.; Burcea, A.; Dudu, A.; Georgescu, S.E.; Costache, M. Molecular markers reveal reduced genetic diversity in Romanian populations of Brown Trout, Salmo trutta L., 1758 (Salmonidae). Acta Zool. Bulg. 2016, 68, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Marić, S.; Stanković, D.; Wazenbök, J.; Šanda, R.; Erös, T.; Takács, A.; Specziár, A.; Sekulić, A.; Sekulić, N.; Bănăduc, D.; et al. Phylogeography and population genetics of the European mudminnow (Umbra krameri) with a time-calibrated phylogeny for the family Umbridae. Hydrobiologia 2017, 792, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Olosutean, H.; Bănăduc, D. Influence of environmental variables on the structure and diversity of ephemeropteran communities: A case study of the Timiş River, Romania. Acta Zool. Bulg. 2016, 68, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Didenko, A.; Guti, G.; Bănăduc, D. Telestes souffia (Risso, 1827) species conservation at the eastern limit of range—Vişeu River basin, Romania. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2018, 16, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Marić, S.; Gabor, G.; Didenko, A.; Rey Planellas, S.; Bănăduc, D. Hucho hucho (Linnaeus, 1758): Last natural viable population in the Eastern Carpathians—Conservation elements. Turk. J. Zool. 2019, 43, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcea, A.; Boeraş, I.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Bănăduc, D.; Matei, C.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Adding the Mureş River Basin (Transylvania, Romania) to the list of hotspots with high contamination with pharmaceuticals. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Burcea, A.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Berg, V.; Lyche, J.L.; Bănăduc, D. Bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants in the gonads of Barbus barbus (Linnaeus, 1758). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 201, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Cianfaglione, K.; Akeroyd, J.R.; Cioca, L.-I. Proposed environmental risk management elements in a Carpathian valley basin, within the Roşia Montană European historical mining area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholy, J.; Pongracz, R. Regional analysis of extreme temperature and precipitation indices for the Carpathian Basin from 1946 to 2001. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 57, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholy, J.; Pongracz, R.; Torma, C.; Pieczka, I.; Kards, I.; Hunyady, A. Analysis of regional climate change modeling experiments for the Carpathian Basin. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2009, 1, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüzselyi, I.; Bartholy, J.; Horányi, A.; Piecza, I.; Pongrácz, R.; Szabó, P.; Szépszó, G.; Torma, C.S. The future climate characteristics of the Carpathian Basin based on a regional climate model mini-ensemble. Adv. Sci. Contrib. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2011, 29, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bartholy, J.; Pongracz, R. Analysis of precipitation conditions for the Carpathian Basin based on extreme indices in the 20th century and climate simulations for 2050 and 2100. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2010, 35, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakonczai, J. Effects and Consequences of Global Climate Change in the Carpathian Basin. In Climate Change—Geophysical Foundations and Ecological Effects; Intechopen: London, UK, 2011; pp. 297–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mezösi, G.; Blanka, V.; Ladányi, Z.; Bata, T.; Udrea, P.; Frank, A.; Burghard, C. Expected mid- and long-term changes in drought hazard for the south-eastern Carpathian Basin. Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 11, 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Sábitz, J.; Pongrácz, R.; Bartholy, J. Estimated changes of drought tendency in the Carpathian Basin. Hung. Geogr. Bull. 2014, 63, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Antofie, T.; Barbosa, P.; Bihari, Z.; Lakatos, M.; Szalai, S.; Szentimrey, T.; Vogt, J. An overview of drought events in the Carpathian Region in 1961–2010. Adv. Sci. Res. 2013, 10, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antofie, T.; Naumann, G.; Spinoni, J.; Vogt, J. Estimating the water needed to end the drought or reduce the drought severity in the Carpathian region. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, C. Action Plan for Water Scarcity and Drought in Romania. Water Resources Management Directorate. Available online: https://www.icpdr.org/main/sites/default/files/08_CONSTANTIN_Climate_Change_Romania_Action_Plan.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Larned, S.T.; Datry, T.; Arscott, D.B.; Tockner, K. Emerging concepts in temporary-river ecology. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 717–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupa, E.G.; Barinova, S.S.; Romanova, S.M. Ecological mapping in assessing the impact of environmental factors on the aquatic ecosystem of the Arys River Basin, South Kazakhstan. Diversity 2019, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarenko, P.M.; Bilous, O.P.; Kryvosheia-Zakharova, O.M.; Lilitska, H.H.; Barinova, S. Diversity of algae and cyanobacteria and bioindication characteristics of the alpine lake nesamovyte (Eastern Carpathians, Ukraine) from 100 years ago to the present. Diversity 2021, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, G.-O.; Dudu, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Burcea, A.; Ureche, D.; Nechifor, R.; Georgescu, S.E.; Costache, M. Genetic analysis of populations of brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) from the Romanian Carpathians. Aquat. Living Resour. 2019, 32, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D. The Transylvanian Water Tower through history. Danub. News 2015, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Burcea, A.; Mihuţ, C.-M.; Bănăduc, D. The benthic trophic corner stone compartment in POPs transfer from abiotic environment to higher trophic levels—Trichoptera and Ephemeroptera pre-alert indicator role. Water 2021, 13, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costea, G.; Push, M.T.; Bănăduc, D.; Cosmoiu, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. A review of hydropower plants in Romania: Distribution, current knowledge, and their effects on fish in headwater streams. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 54, 111003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D.; Bucşa, C. Watersheds Management (Transylvania/Romania): Implications, Risks, Solutions, Strategies to Enhance Environmental Security in Transition Countries, NATO Science for Peace and Security Series Series C-Environmental Security; Springer: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 225–238. ISSN 1971-4668. [Google Scholar]
- Mac, I. Subcarpaţii Transilvăneni Dintre Mureş şi Olt; Academic Press: Bucureşti, Romania, 1972; p. 156. [Google Scholar]
- Oancea, D.; Velcea, V. Geografia României, III, Carpaţii şi Depresiunea Transilvaniei; Academic Press: Bucharest, Romania, 1987; p. 647. [Google Scholar]
- Posea, G.R. Geomorfologia României; Fund România de Mâine: Bucharest, Romania, 2002; p. 444. [Google Scholar]
- Dobros, V. Aspects concerning the liquid flow in Târnava Mică River hydrographic basin (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dobros, V. Aspects concerning the superficial liquid flow in the Târnava Mare River middle hydrographic basin (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2007, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Raport Annual 2016 Administraţia Naţională de Meteorologie, Bucureşti, România; Meteo Romania: Bucureşti, Romania, 2016; pp. 1–154.
- Raport Annual 2017 Administraţia Naţională de Meteorologie, Bucureşti, România; Meteo Romania: Bucureşti, Romania, 2017; pp. 1–80.
- Raport Annual 2018 Administraţia Naţională de Meteorologie, Bucureşti, România; Meteo Romania: Bucureşti, Romania, 2018; pp. 1–181.
- Raport Annual 2019 Administraţia Naţională de Meteorologie, Bucureşti, România; Meteo Romania: Bucureşti, Romania, 2019; pp. 1–220.
- Raport Annual 2020 Administraţia Naţională de Meteorologie, Bucureşti, România; Meteo Romania: Bucureşti, Romania, 2020; pp. 1–170.
- Drăgulescu, C. The Hydrophilous and Hygrophilous Flora and Vegetation of Târnave rivers. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Mountford, O.J.; Akeroyd, J.R. A biodiversity assessment of the saxon villages region of Transylvania. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cupșa, D. Preliminary note on the aquatic Oligochaeta from the Târnave rivers. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Sîrbu, I. The freshwater mollusks from the Târnava rivers basin (Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Study regarding Târnava Mare and Târnava Mică rivers (Transylvania, Romania) stonefly (Insecta. Plecoptera) larvae communities. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Târnava Mare River (Romania) ecological assessment, based on the benthic macroinvertebrates communities. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, S.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Aspects concerning Târnava Mare and Târnava Mică rivers (Transylvania, Romania) caddis fly (Insecta. Trichoptera) larvae communities. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Momeu, L.; Péterfi, L.Ş. The structure of Diatom communities inhabiting the Târnava Mică and Târnava Mare rivers. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D. Fish associations—Habitats quality relation in the Târnave rivers (Transylvania, Romania) ecological assessment. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2005, 2, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D. Benthic macro-invertebrate and fish communities of some southern Târnava Mare River tributaries (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2007, 4, 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Yuan, S.; Quiring, S.M. Evaluation of six indices for monitoring agricultural drought in the south-central United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, C.; Mueller, V. Drought and population mobility in rural Ethiopia. World Dev. 2012, 40, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolle, J. Historical case studies of famines and migrations in the West African Sahel and their possible relevance now and in the future. Popul. Environ. 2015, 37, 181–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, S.K.; Wolfe, D.W.; DeGaetano, A.; Benner, R. Anatomy of the 2016 drought in the Northeastern United States: Implications for agriculture and water resources in humid climates. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Binder, E. The habitats along the upper danube in germany and changes to them induced by human impacts. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cianfaglione, K.; Pedrotti, F. Italy in the Danube geography: Territory, landscape, environment, vegetation, fauna, culture, Human management and outlooks for the future. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 87–118. [Google Scholar]
- Adámek, Z.; Jurajdová, Z.; Janáč, M.; Zahrádková, S.; Němejcová, D.; Jurajda, P. The response of fish assemblages to human impacts along the lower stretch of the Rivers Morava and Dyje (Danube River Basin, Czech Republic). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 135–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ćaleta, M.; Mustafić, P.; Zanella, D.; Buj, I.; Marčić, Z.; Mrakovčić, M. Human impact on the Dobra River (Croatia). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Dekić, R.; Ivanc, A.; Ćetković, D.; Lolić, A. Anthropogenic impact and environmental quality of different tributaries of the River Vrbas (Bosnia and Hertzegovina). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 169–214. [Google Scholar]
- Guti, G. Assessment of long-term changes in the Szigetköz Floodplain of the Danube River. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 215–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ðikanović, V.; Nikčević, M.; Mićković, B.; Hegediš, A.; Mrdak, D.; Pešić, V. Anthropogenic pressures on watercourses of the Danube River Basin in Montenegro. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 241–256. [Google Scholar]
- Lenhardt, M.; Snederevac-Lalić, M.; Hegediš, A.; Skorić, S.; Cvijanović, G.; Višnjić-Jeftić, Ž.; Djikanović, V.; Jovičić, K.; Jaćimović, M.; Jarić, I. Human impacts on fish fauna in the Danube River in Serbia: Current status and ecological implications. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 257–280. [Google Scholar]
- Mišiková Elexová, E.; Makovinská, J. Assessment of the aquatic ecosystem in the slovak stretch of the Danube River. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Maślanko, W.; Ferencz, B.; Dawidek, J. State and changes of natural environment in polish part of the Danube River Basin Poland. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 301–326. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasyev, S.; Lyashenko, A.; Iarochevitch, A.; Lietytska, O.; Zorina-Sakharova, K.; Marushevska, O. Pressures and impacts on ecological status of Surface Water Bodies in Ukrainian part of the Danube River Basin. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 327–359. [Google Scholar]
- Bakiu, R. Drina River (Sava’s Tributary of Danube River) and Human Impact in Albania. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 359–380. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, V.; Slavevska-Stamenkovic, V.; Ristovska, M.; Stojov, V.; Marić, S. Characteristics of the Danube Drainage area in the Republic of Macedonia. In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 381–392. [Google Scholar]
- Snigirova, A.; Bogatova, Y.; Barinova, S. Assessment of river-sea interaction in the Danube Nearshore Area (Ukraine) by Bioindicators and Statistical Mapping. Land 2021, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenderov, L.; Trichkova, T. Long-term changes in the ecological conditions of the Iskar River (Danube River Basin, Bulgaria). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 393–424. [Google Scholar]
- Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Bănăduc, D. Human impact effects on Târnava Mare Basin aquatic biodiversity (Transylvania, Romania). In Human Impact on Danube Watershed Biodiversity in the XXI Century. Geobotany Studies (Basics, Methods and Case Studies); Bănăduc, D., Curtean-Bănăduc, A., Pedrotti, F., Cianfaglione, K., Akeroyd, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 425–437. [Google Scholar]
- Bănărescu, P.M.; Bănăduc, D. Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC) fish species (Osteichthyes) on the Romanian territory. Acta Ichtiologica Romanica 2007, 2, 43–78. [Google Scholar]
- McEwan, A.J.; Joy, M.K. Responses of three PIT-tagged native fish species to floods in a small, upland stream in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 47, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bănăduc, D.; Oprean, L.; Bogdan, A. Fish species of community interest management issues in Natura 2000 site Sighişoara-Târnava Mare (Transylvania, Romania). Rev. Econ. 2011, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Smederevac-Lalic, M.M.; Kalauzi, A.J.; Regner, S.B.; Lenhardt, M.B.; Naunovic, Z.Z.; Hegedis, A.W. Prediction of fish catch in the Danube River based on long-term variability environmental parameters and catch statistics. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 609, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanenko, D.; Afanasyev, S.; Vasenko, A.G. Review and status of fisheries and aquaculture in the Dnipro region in relation to biodiversity conservation. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2005, 40, 42–53. [Google Scholar]
- Didenko, A.V. Gobiids of the Dneprodzerzhinsk Reservoir (Dnieper River, Ukraine): Distribution and habitat preferences. Acta Ichthyologica Piscatoria 2013, 43, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askeyev, A.; Askeyev, O.; Yanybaev, N.; Askeyev, I.; Monakhov, M.; Marić, S.; Hulsman, K. River fish assemblages along an elevation gradient in the eastern extremity of Europe. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2017, 100, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapci-Kotori, L.; Vavalidis, T.; Zogaris, D.; Šanda, R.; Vukic, J.; Geci, D.; Ibrahimi, H.; Bilalli, A.; Zogaris, S. Fish distribution patterns in the White Drin (Drini I Bardhë) river, Kosovo. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2020, 421, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolsky, G.V. Theory of fish population dynamics as the biological background for rational exploitation and management of fishery resources. J. Appl. Ecol. 1970, 7, 660–662. [Google Scholar]
- Erdoğan, Z.; Torcu Koç, H.; Özdemir, F. Reproductive biolgy of the Tigris Scraper, Capoeta umbla (Heckel, 1843) population living in Solhan Creek of Murat River (Bingöl, Turkey). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2021, 23, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, S.W.; Magoulick, D.D. Refuge habitats for fishes during seasonal drying in an intermittent stream: Movement, survival and abundance of three minnow species. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Paterna, F.J.; Miñnano, P.A.; Torralva, M. Habitat quality affects the condition of Barbus sclateri in Mediterranean semi-arid streams. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2003, 67, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo-Yeon, P.; Chanyang, S.J.-H.L.; Jong-Suk, K. Ecological drought monitoring through fish habitat-based flow assessment in the Gam river basin of Korea. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105830. [Google Scholar]
- Pulliam, H.R. On the relationship between niche and distribution. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 3, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, M.B.; Haifeng, J. A habitat model for fish communities in large streams and small rivers. Int. J. Ecol. 2012, 2012, 962071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirzel, A.H.; Le Lay, G. Habitat suitability modeling and niche theory. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.; Bernhardt, E.; Chornesky, E.; Collins, S.; Dobson, A.; Duke, C.; Gold, B.; Jacobson, R.; Kingsland, S.; Kranz, R.; et al. Ecology for a crowded planet. Science 2004, 304, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costea, M. Characteristics of the relief from the Central-Eastern part of the Târnavelor Plateau, with reference to present modeling and the associate geomorphologic risk (Transylvania, Romania). Transylv. Rev. Ecol. Res. 2007, 4, 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Stăncioiu, P.T.; Lazăr, G.; Tudoran, G.M.; Candrea Bozga, Ş.B.; Predoiu, G.; Şofletea, N. Habitate Forestiere de Interes Comunitar Incluse în Proiectul Life 05/NAT/RO/000176: Habitate Prioritare Alpine, Subalpine şi Forestiere din România, Măsuri de Gospodărire; Universităţii Transilvania din Braşov: Braşov, România, 2008; pp. 1–184. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Bănăduc, D.; Voicu, R.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A. Sediments as factor in the fate of the threatened endemic fish species Romanichthys valsanicola Dumitrescu, Bănărescu and Stoica, (Vâlsan River basin, Danube Basin). Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2021, 22, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kareiva, P.; Watts, S.; McDonald, R.; Boucher, T. Domesticated nature: Shaping landscapes and ecosystems for human welfare. Science 2007, 316, 1866–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, N.R.; Lake, P.S. Ecological restoration and large-scale ecological disturbance: The effects of drought on the response by fish to a habitat restoration experiment, restoration ecology. J. Soc. Ecol. Rest. 2005, 13, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoulick, D.D.; Kobza, R.M. The role of refugia for fishes during drought: A review and synthesis. Freshw. Biol. 2003, 48, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoulick, D.D.; Dekar, M.P.; Hodges, S.W.; Scott, M.K.; Rabalais, M.R.; Bare, C.M. Hydrologic variation influences stream fish assemblage dynamics through flow regime and drought. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, F.; Găldean, N. Ecological taxonomy: A basic tool for biodiversity conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1997, 12, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.C.; Lobegeiger, J.S.; Starkey, A. Risks to fish populations in Dryland Rivers from the combined threats of drought and instream barriers. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopper, G.W.; Gido, B.; Pennock, C.A.; Hedden, S.C.; Frenette, B.D.; Barts, N.; Hedden, C.K.; Lindsey Bruckerhoff, A. Nowhere to swim: Interspecific responses of prairie stream fishes in isolated pools during severe drought. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).