Spatial and Temporal Variation of NO2 Vertical Column Densities (VCDs) over Poland: Comparison of the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations and the GEM-AQ Model Simulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. TROPOMI
2.2. The GEM-AQ Model
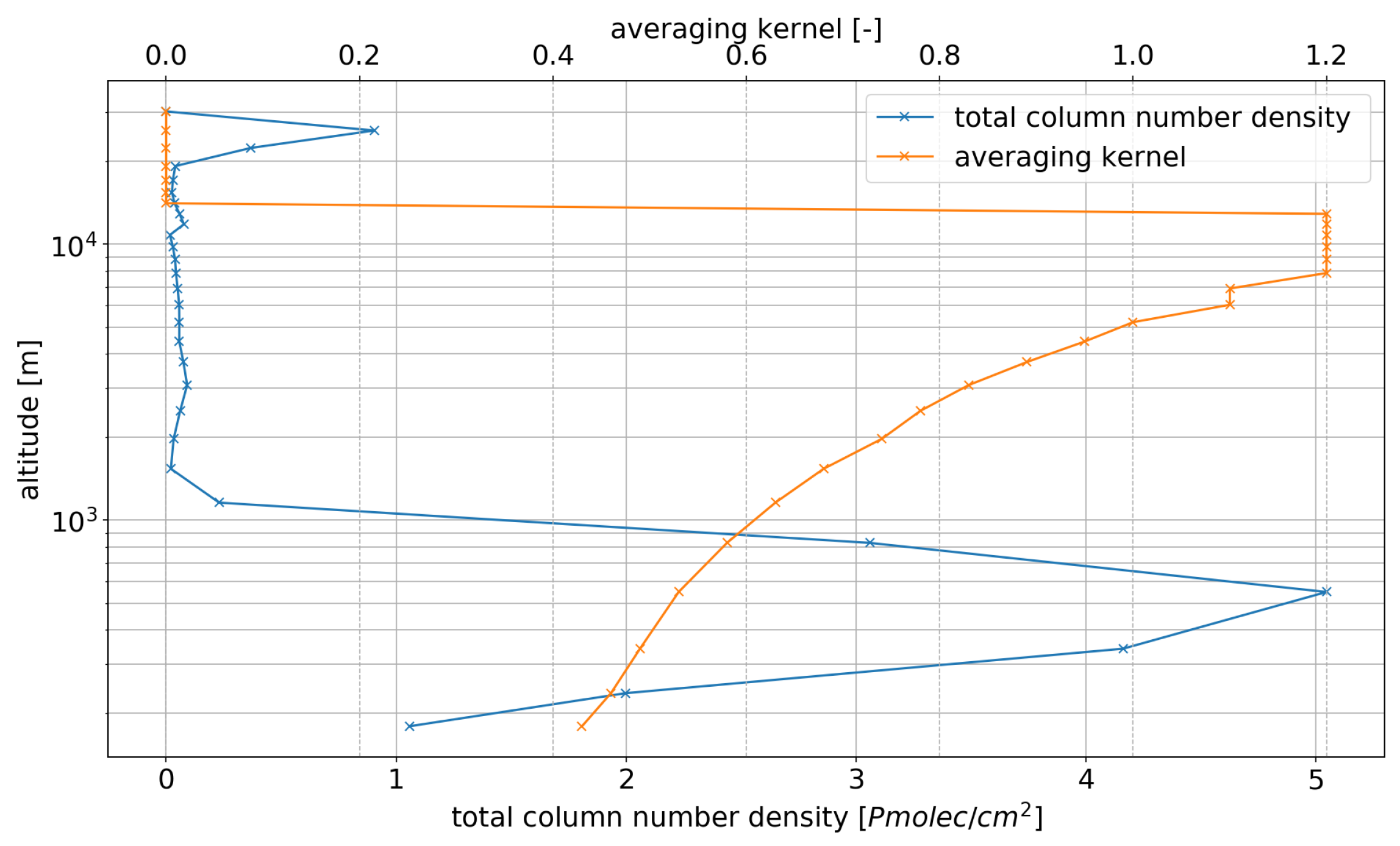
2.3. Boundary Layer Depth
2.4. Surface Observations
3. Results
3.1. Overall Performance
3.2. The Choice of qa_value
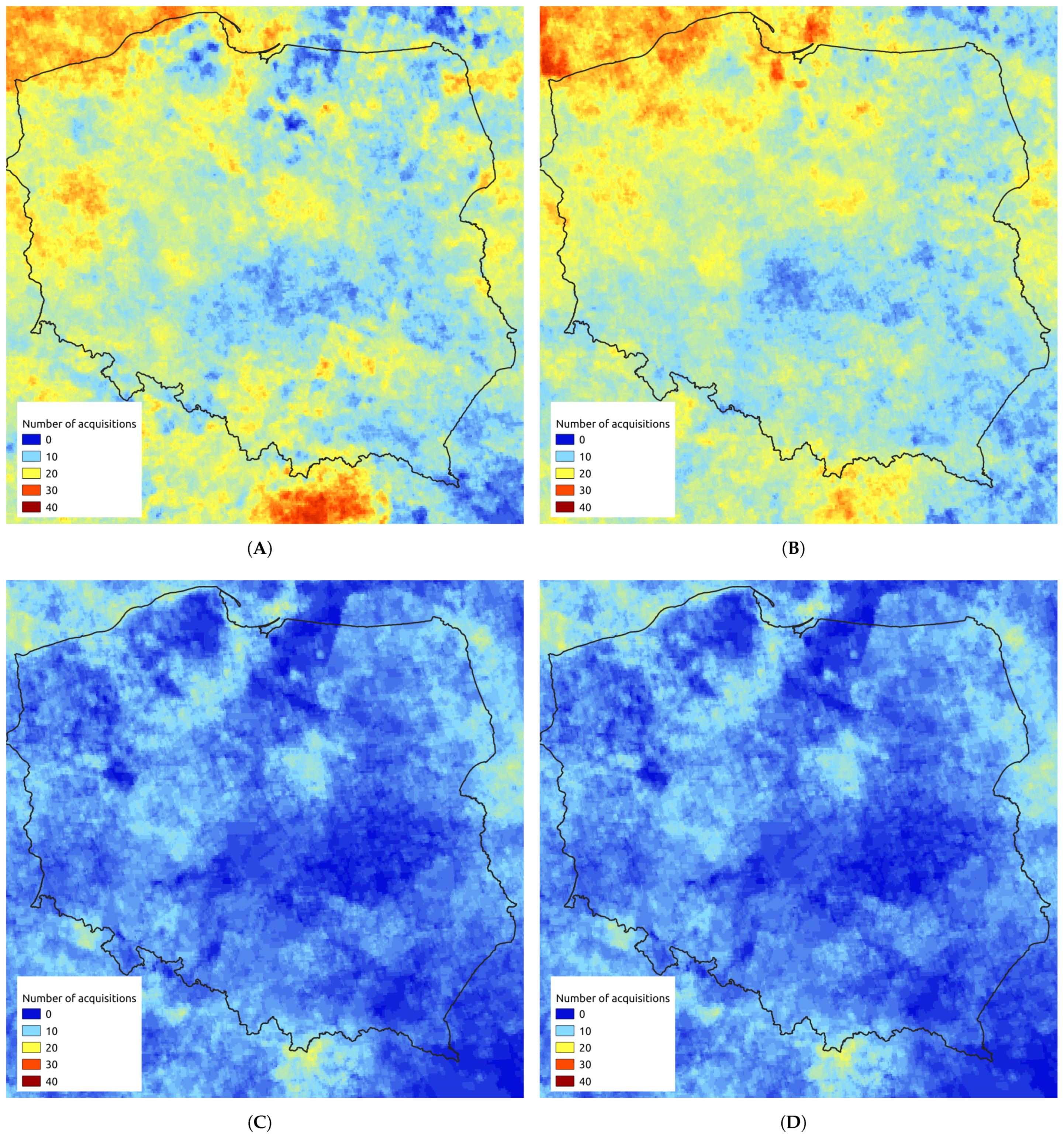
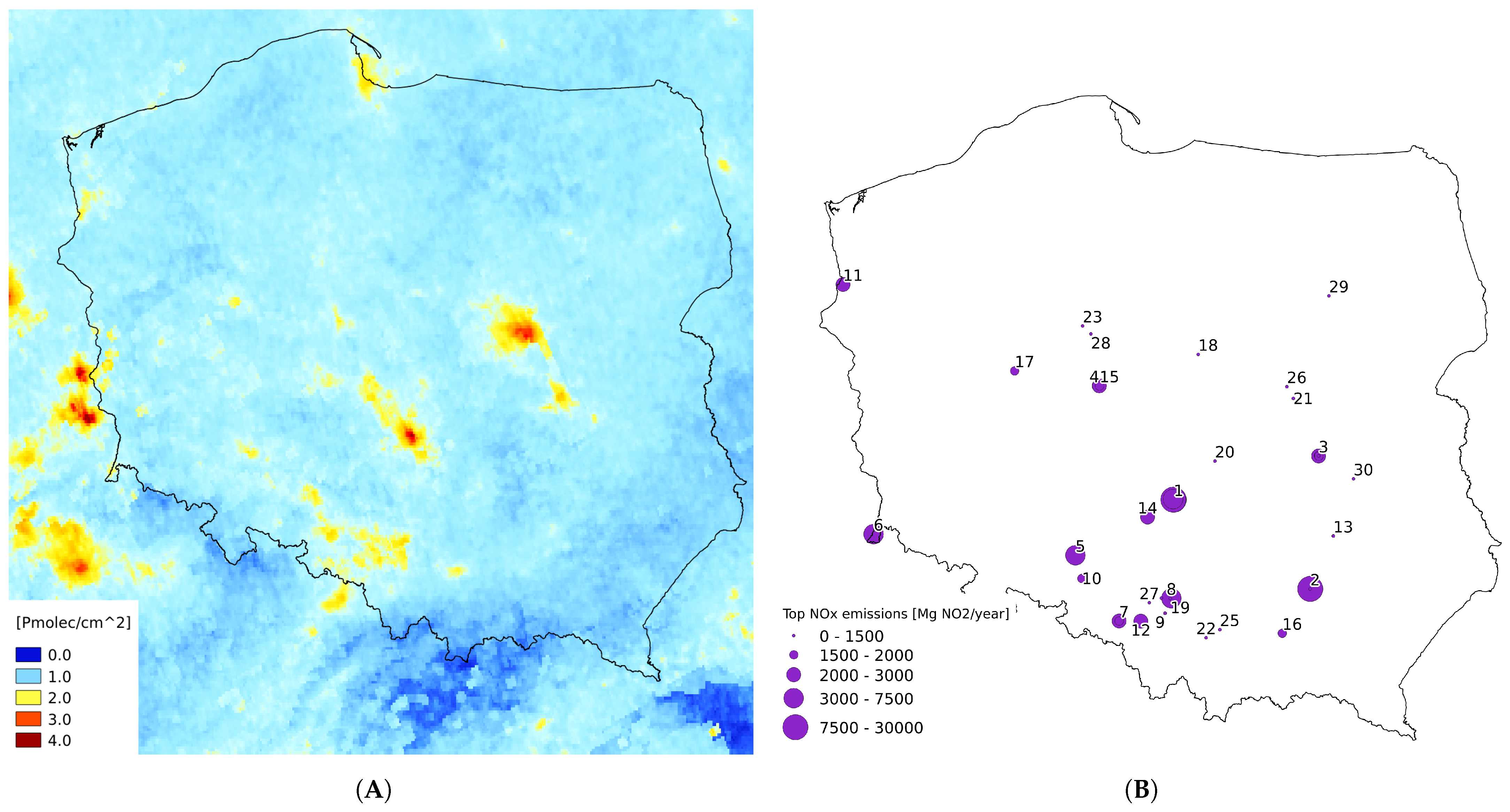
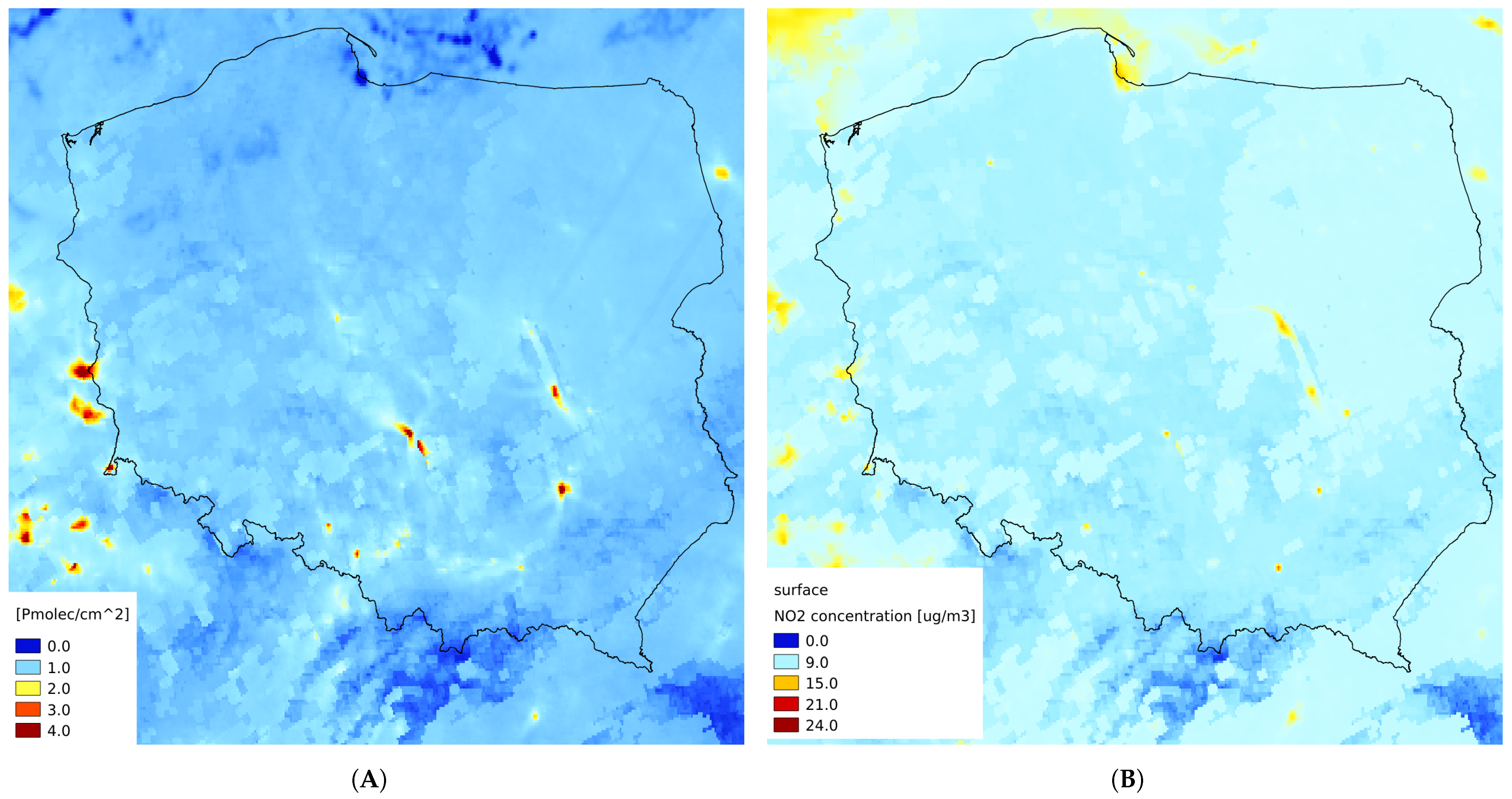
3.3. Spatial Distribution
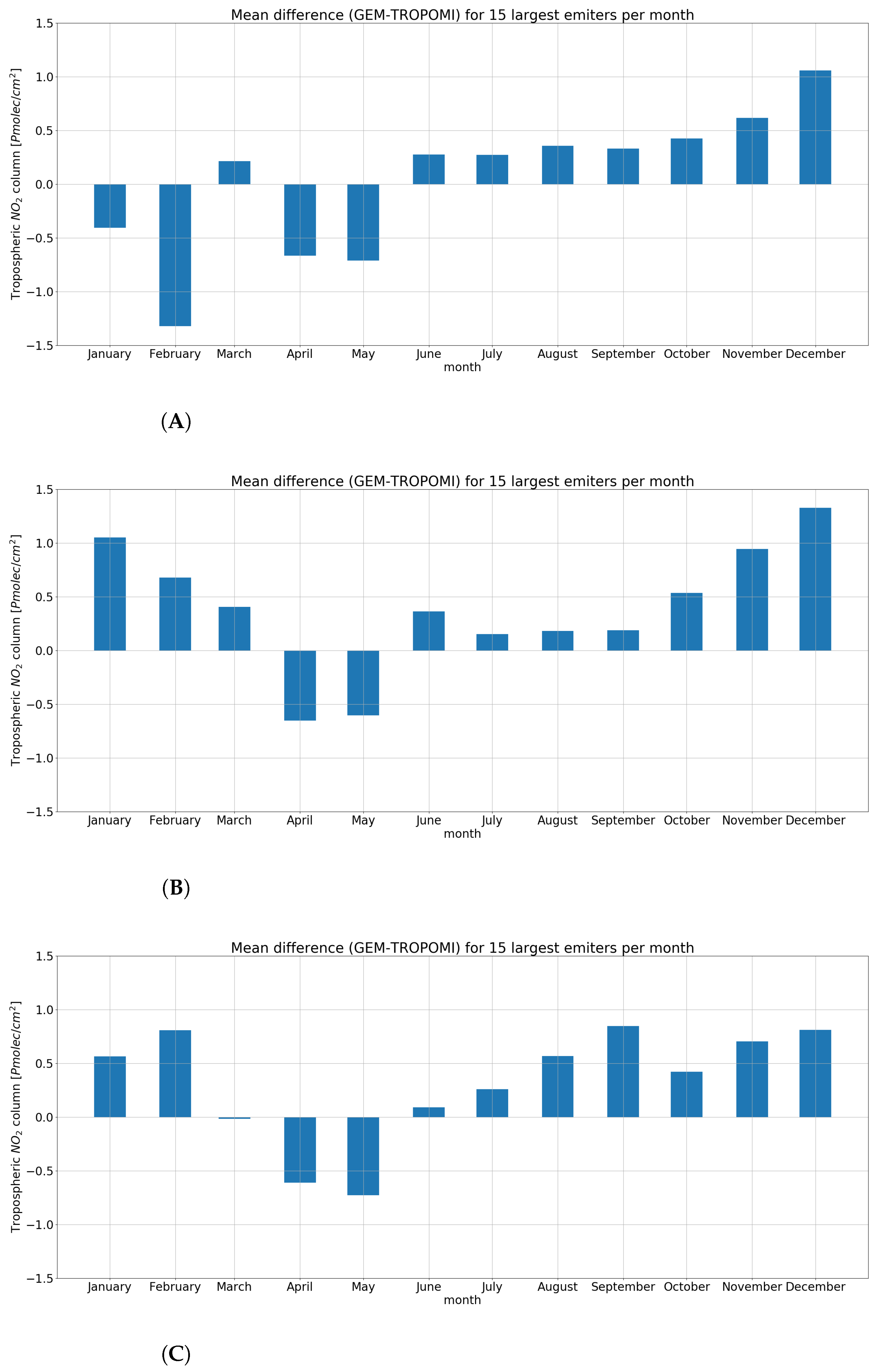
3.4. Temporal Comparison
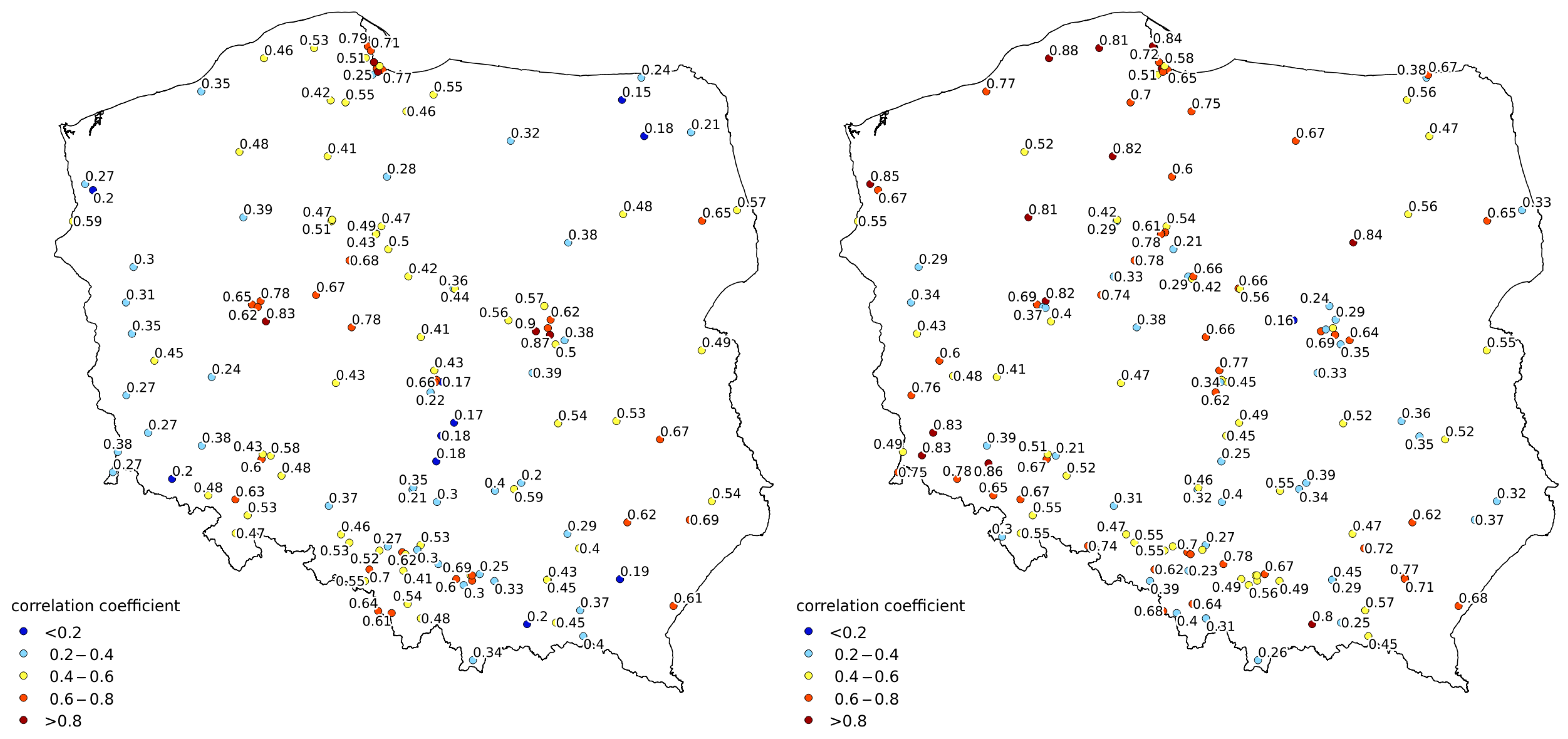
3.5. Relation to Near-Surface Concentration
4. Conclusions
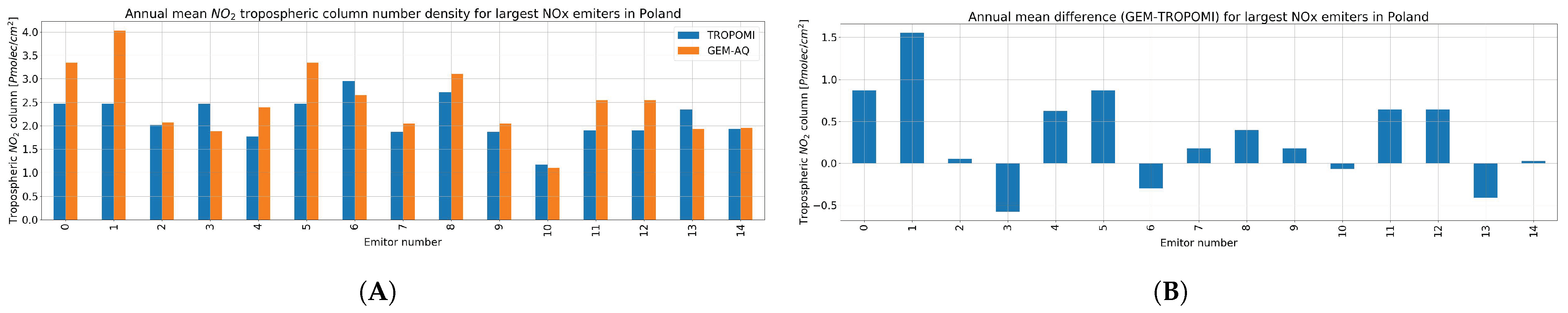
- In general, the GEM-AQ model tends to underestimate the tropospheric column number density, which may be caused by either too intense of mixing in the atmosphere, a sink of into further chemical processes (e.g., tropospheric ozone production), or too small of a background concentration.
- When looking at locations next to the largest point emitters in Poland, the GEM-AQ model and TROPOMI converge reasonably well. Minor differences should be explained by individual emission examination.
- The TROPOMI instrument does not correctly reproduce the annual temporal concentration pattern. It seems that cloud cover (thus qa_value threshold) and the number of satellite scenes averaged into a monthly average play an important role. Lowering the qa_value during the summer months improves the convergence between TROPOMI and GEM-AQ, while during the winter months, it acts oppositely.
- The relation between near-surface concentration and troposphere column number density can be parametrised using boundary layer depth as an additional explanatory variable.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Marinello, F. Spatial Variation of NO2 and Its Impact Factors in China: An Application of Sentinel-5P Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beloconi, A.; Vounatsou, P. Bayesian geostatistical modelling of high-resolution NO2 exposure in Europe combining data from monitors, satellites and chemical transport models. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curier, R.; Kranenburg, R.; Segers, A.; Timmermans, R.; Schaap, M. Synergistic use of OMI NO2 tropospheric columns and LOTOS–EUROS to evaluate the NOx emission trends across Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogen, R.; Rozanov, V.V.; Burrows, J.P. Ozone profiles from GOME satellite data: Algorithm description and first validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 8263–8280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, A.; Bovensmann, H.; Bracher, A.; Hrechanyy, S.; Rozanov, V.; Sinnhuber, M.; Stroh, F.; Burrows, J. NO2 and BrO vertical profile retrieval from SCIAMACHY limb measurements: Sensitivity studies. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 36, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valks, P.; Pinardi, G.; Richter, A.; Lambert, J.C.; Hao, N.; Loyola, D.; Van Roozendael, M.; Emmadi, S. Operational total and tropospheric NO2 column retrieval for GOME-2. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.R.; Valin, L.C.; Bucsela, E.J.; Wenig, M.O.; Cohen, R.C. Space-based Constraints on Spatial and Temporal Patterns of NOx Emissions in California, 2005–2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3608–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; de Foy, B.; Lamsal, L.N.; Streets, D.G.; Lu, Z.; Pickering, K.E.; Krotkov, N.A. The observed response of Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) NO2 columns to NOx emission controls on power plants in the United States: 2005–2011. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellanos, P.; Boersma, K.F. Reductions in nitrogen oxides over Europe driven by environmental policy and economic recession. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, B.N.; Lamsal, L.N.; Thompson, A.M.; Yoshida, Y.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Hurwitz, M.M.; Pickering, K.E. A space-based, high-resolution view of notable changes in urban NOx pollution around the world (2005–2014). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 976–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G. Satellite NO2 retrievals suggest China has exceeded its NO x reduction goals from the twelfth Five-Year Plan. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Nielsen, C.P.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; McElroy, M.B. Recent changes in particulate air pollution over China observed from space and the ground: Effectiveness of emission control. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7771–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruyter de Wildt, M.; Eskes, H.; Boersma, K.F. The global economic cycle and satellite-derived NO2 trends over shipping lanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. Long-term trends in NO2 columns related to economic developments and air quality policies from 1997 to 2016 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xie, Z. Global financial crisis making a V-shaped fluctuation in NO2 pollution over the Yangtze River Delta. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; Van Der A, R.; Boersma, K.; Van Roozendael, M.; De Smedt, I.; Kelder, H. Reductions of NO2 detected from space during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, G.K.; Dey, S.; Kaushal, H.; Lal, K. Tracking NO2 emission from thermal power plants in North India using TROPOMI data. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 259, 118514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidou, I.; Koukouli, M.E.; Segers, A.; Manders, A.; Balis, D.; Stavrakou, T.; van Geffen, J.; Eskes, H. Changes in Power Plant NOx Emissions over Northwest Greece Using a Data Assimilation Technique. Preprints 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, J.; Szeląg, M.E.; Ialongo, I.; Retscher, C.; Oda, T.; Crisp, D. Analyzing nitrogen oxides to carbon dioxide emission ratios from space: A case study of Matimba Power Station in South Africa. Atmos. Environ. X 2021, 10, 100110. [Google Scholar]
- Borsdorff, T.; García Reynoso, A.; Maldonado, G.; Mar-Morales, B.; Stremme, W.; Grutter, M.; Landgraf, J. Monitoring CO emissions of the metropolis Mexico City using TROPOMI CO observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15761–15774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, A.; Boersma, K.; Eskes, H.; Veefkind, J.; Van Geffen, J.; de Zeeuw, M.; van der Gon, H.D.; Beirle, S.; Krol, M. Quantification of nitrogen oxides emissions from build-up of pollution over Paris with TROPOMI. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; de Foy, B.; Griffin, D.; McLinden, C.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Eskes, H. Enhanced Capabilities of TROPOMI NO2: Estimating NO X from North American Cities and Power Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12594–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der A, R.J.; de Laat, A.T.J.; Ding, J.; Eskes, H.J. Connecting the dots: NO x emissions along a West Siberian natural gas pipeline. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Marais, E.A.; Vohra, K.; Zhu, L. Shipping Emissions in Rapidly Growing Seaports in Africa Determined with TROPOMI. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2020, Online, 1–17 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- McLinden, C.; Fioletov, V.; Griffin, D.; Dammers, E. High-Resolution Mapping of NOx Emissions from the Canadian Oil Sands from TROPOMI; EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts: Vienna, Austria, 2020; p. 3959. [Google Scholar]
- Tack, F.; Merlaud, A.; Iordache, M.D.; Pinardi, G.; Dimitropoulou, E.; Eskes, H.; Bomans, B.; Veefkind, P.; Van Roozendael, M. Assessment of the TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 product based on airborne APEX observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 615–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, L.M.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; Szykman, J.J.; Valin, L.C.; Janz, S.J.; Kowalewski, M.G.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; Cede, A.; Mueller, M.; et al. Evaluating Sentinel-5P TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 column densities with airborne and Pandora spectrometers near New York City and Long Island Sound. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6113–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitropoulou, E.; Hendrick, F.; Pinardi, G.; Friedrich, M.M.; Merlaud, A.; Tack, F.; De Longueville, H.; Fayt, C.; Hermans, C.; Laffineur, Q.; et al. Validation of TROPOMI tropospheric NO2 columns using dual-scan multi-axis differential optical absorption spectroscopy (MAX-DOAS) measurements in Uccle, Brussels. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 5165–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoelst, T.; Compernolle, S.; Pinardi, G.; Lambert, J.C.; Eskes, H.J.; Eichmann, K.U.; Fjæraa, A.M.; Granville, J.; Niemeijer, S.; Cede, A.; et al. Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5P TROPOMI NO2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ialongo, I.; Virta, H.; Eskes, H.; Hovila, J.; Douros, J. Comparison of TROPOMI/Sentinel-5 Precursor NO2 observations with ground-based measurements in Helsinki. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, K.; Eskes, H.; Dirksen, R.; Veefkind, J.; Stammes, P.; Huijnen, V.; Kleipool, Q.; Sneep, M.; Claas, J.; Leitão, J.; et al. An improved tropospheric NO2 column retrieval algorithm for the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1905–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorente, A.; Boersma, K.F.; Yu, H.; Dörner, S.; Hilboll, A.; Richter, A.; Liu, M.; Lamsal, L.N.; Barkley, M.; De Smedt, I.; et al. Structural uncertainty in air mass factor calculation for NO2 and HCHO satellite retrievals. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 759–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.E.; Boersma, K.F.; Le Sager, P.; Verstraeten, W.W. The high-resolution version of TM5-MP for optimized satellite retrievals: Description and validation. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 721–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Geffen, J.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.; Sneep, M.; Ter Linden, M.; Zara, M.; Veefkind, J.P. S5P TROPOMI NO2 slant column retrieval: Method, stability, uncertainties and comparisons with OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1315–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, B.U.; Lee, P. Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, D.; Griffin, D.; Zhao, X.; McLinden, C. High resolution mapping of nitrogen dioxide with TROPOMI: First results and validation over the Canadian oil sands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Geffen, J.; Eskes, H.; Boersma, K.; Maasakkers, J.; Veefkind, J. TROPOMI ATBD of the Total and Tropospheric NO2 Data Products (Issue 1.2. 0); Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI): De Bilt, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Niemeijer, S. ESA Atmospheric Toolbox; EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Volume 19, p. 8286. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, J.; Gravel, S.; Méthot, A.; Patoine, A.; Roch, M.; Staniforth, A. The operational CMC–MRB global environmental multiscale (GEM) model. Part I: Design considerations and formulation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1998, 126, 1373–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatram, A.; Karamchandani, P.; Misra, P. Testing a comprehensive acid deposition model. Atmos. Environ. (1967) 1988, 22, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, J.; Neary, L.; Struzewska, J.; McConnell, J.; Lupu, A.; Jarosz, J.; Toyota, K.; Gong, S.; Côté, J.; Liu, X.; et al. GEM-AQ, an on-line global multiscale chemical weather modelling system: Model description and evaluation of gas phase chemistry processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3255–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szymankiewicz, K.; Kaminski, J.W.; Struzewska, J. Interannual variability of tropospheric NO2 column over Central Europe—Observations from SCIAMACHY and GEM-AQ model simulations. Acta Geophys. 2014, 62, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaris, E.; Sotiropoulou, R.E.P.; Gounaris, N.; Andronopoulos, S.; Vlachogiannis, D. Effect of the Standard Nomenclature for Air Pollution (SNAP) categories on air quality over Europe. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dieudonné, E.; Ravetta, F.; Pelon, J.; Goutail, F.; Pommereau, J.P. Linking NO2 surface concentration and integrated content in the urban developed atmospheric boundary layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1247–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levenberg, K. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
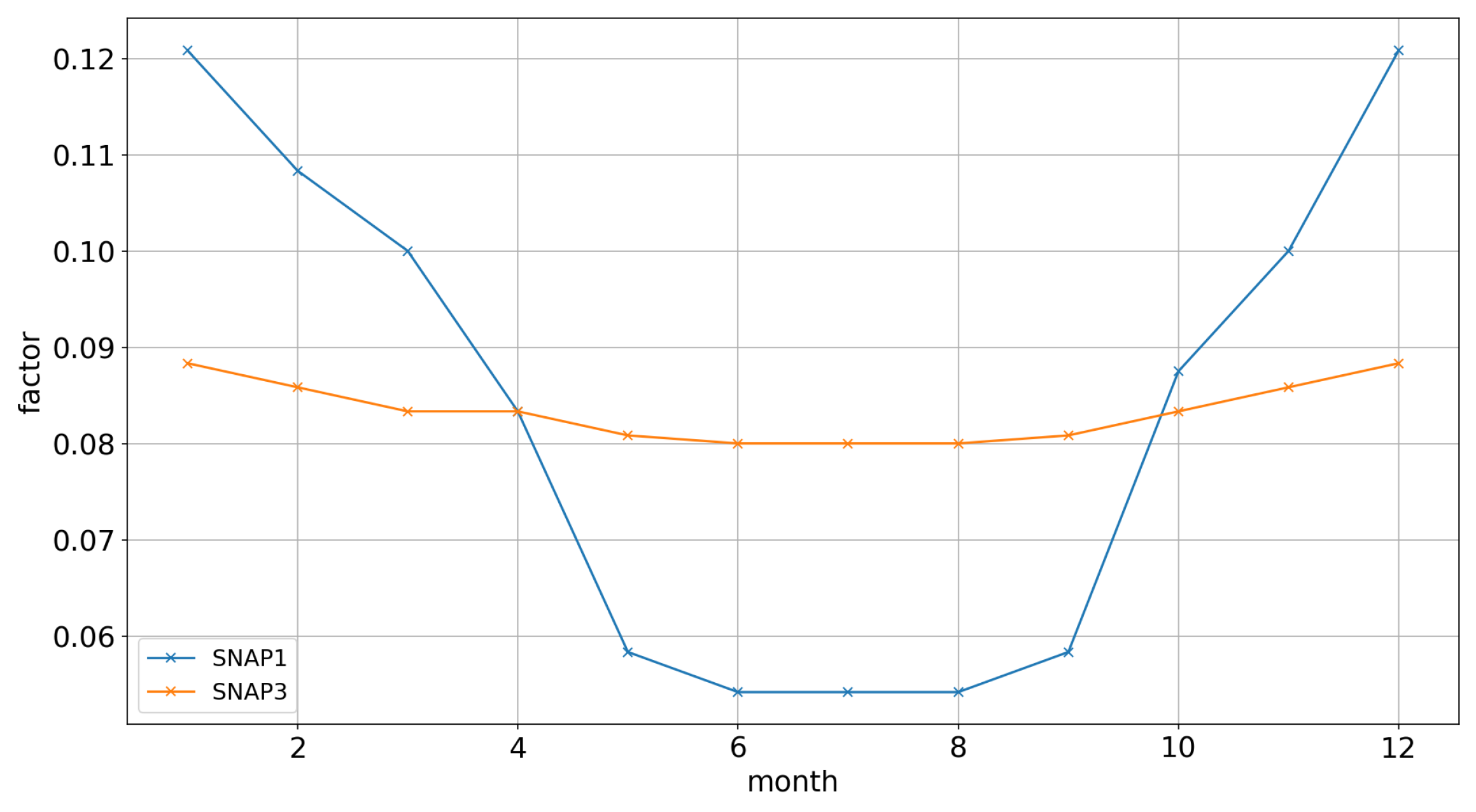
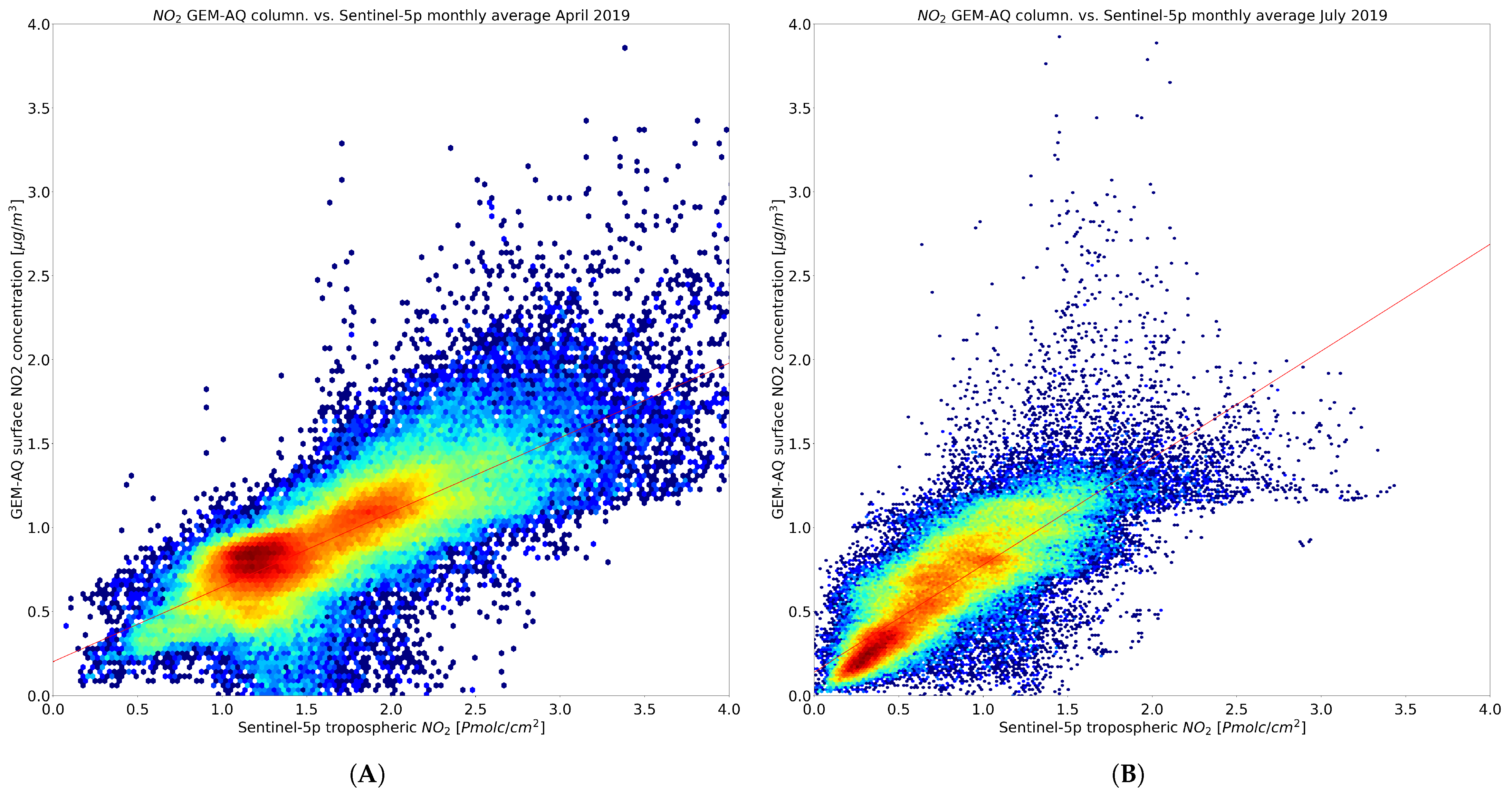
| Month | a | b | MSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1.4 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 1.29 |
| February | 0.92 | 0.3 | 0.36 | 0.67 |
| March | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.36 | 0.11 |
| April | 0.45 | 0.2 | 0.53 | 0.05 |
| May | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.06 |
| June | 0.51 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.04 |
| July | 0.64 | 0.14 | 0.66 | 0.04 |
| August | 0.59 | 0.15 | 0.45 | 0.04 |
| September | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.52 | 0.06 |
| October | 0.75 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 0.14 |
| November | 0.78 | 0.09 | 0.5 | 0.48 |
| December | 0.8 | 0.58 | 0.4 | 0.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawka, M.; Struzewska, J.; Kaminski, J.W. Spatial and Temporal Variation of NO2 Vertical Column Densities (VCDs) over Poland: Comparison of the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations and the GEM-AQ Model Simulations. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070896
Kawka M, Struzewska J, Kaminski JW. Spatial and Temporal Variation of NO2 Vertical Column Densities (VCDs) over Poland: Comparison of the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations and the GEM-AQ Model Simulations. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(7):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070896
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawka, Marcin, Joanna Struzewska, and Jacek W. Kaminski. 2021. "Spatial and Temporal Variation of NO2 Vertical Column Densities (VCDs) over Poland: Comparison of the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations and the GEM-AQ Model Simulations" Atmosphere 12, no. 7: 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070896
APA StyleKawka, M., Struzewska, J., & Kaminski, J. W. (2021). Spatial and Temporal Variation of NO2 Vertical Column Densities (VCDs) over Poland: Comparison of the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI Observations and the GEM-AQ Model Simulations. Atmosphere, 12(7), 896. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12070896






