Abstract
The diurnal temperature range (DTR) is considered a signature of observed climate change, which is defined as the difference between the maximum (Tmax) and minimum temperatures (Tmin). It is well known that the warming rate of mean temperature is larger at high elevations than at low elevations in northeast China. However, it is still uncertain whether DTR trend is greater at high elevations. This study examined the spatiotemporal variation in DTR and its relationship with elevation in northeast China based on data from 68 meteorological stations from 1961 to 2015. The results show that there was a significant declining trend (0.252 °C/decade) in DTR from 1961 to 2015 due to the fact that Tmin increased at a faster rate than Tmax. Seasonally, DTR in northeast China showed a decreasing trend with the largest decrease rate in spring (−0.3167 °C/decade) and the smallest decrease rate in summer (−0.1725 °C/decade). The results of correlation analysis show that there was a significant positive correlation between the annual DTR trend and elevation in northeast China. This is due to the fact that increasing elevation has a significant warming effect on Tmax. Seasonally, there were significant positive correlations between the DTR trend and elevation in all seasons. The elevation gradient of DTR trend was the greatest in winter (0.392 °C/decade/km) and the lowest in autumn (0.209 °C/decade/km). In spring, summer, and autumn, increasing elevation has a significant warming effect on Tmax, leading to a significant increase of the DTR trend with increasing elevation. However, in winter, increasing elevation has a significant cooling effect on Tmin, resulting in a significant increase of the DTR trend with increasing elevation.
1. Introduction
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report (AR5), the global climate has warmed by about 0.74 °C in the last century [1]. The intensified warming contributes to a series of extreme climate events, such as droughts, floods, and heat and cold waves [2]. Diurnal temperature range (DTR), defined as the difference between the maximum temperature (Tmax) and the minimum temperature (Tmin), is a meteorological indicator related with global and regional climate change. Furthermore, it provides more information on climate change than mean temperature due to its relationship with Tmax and Tmin and its sensitivity to radiation energy balance change [3,4,5,6]. Therefore, DTR is considered as an important indicator and is receiving much more attention in regional and global scale in recent times [7,8,9,10]. Previous studies have reported that DTR changes were not uniform globally, which was attributed to complicated interactions of local climatic and anthropogenic factors [11,12]. In most parts of world, it is reported that DTR decreased with individual rate, such as in Bangladesh [13], Australia [14], and United States [15]. However, an increase of DTR was reported in India [16]. Because DTR change is different indifferent regions, investigating the DTR change at regional scale is necessary for understanding the global climate change.
Northeast China is located at the highest latitude and in the coldest region in China, and it is one of the most significant warming regions in China [17,18]. Furthermore, northeast China is one of the biggest grain production bases in China, accounting for approximate 20% of China’s total grain production. Grain production strongly depends on temperature during the growing season [19,20]. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the spatial and temporal long-term temperature change in northeast China. Many scholars have studied the variation of temperature in northeast China. Mwagona et al. [21] found that Tmin increased at a faster rate than Tmax, leading to the decrease of DTR in northeast China. Shen et al. [22] obtained similar results using data from meteorological stations. Based on Earth System Model’s low-warming simulations released by the National Center for Atmosphere research, Hu et al. [23] found DTR will decease at a rate of −0.4 °C/decade (−1.5 °C/decade) under the 1.5 °C (2.0 °C) warming scenario. According to data from meteorological stations, Sun et al. [24] found the mean, maximum, and minimum temperatures exhibited increasing trends from 1951 to 2014. Recently, most studies have focused on the horizontal distribution of temperature change. Northeast China includes Changbai Mountain, Da and Xiao Xing’anling Mountains, Songnen Plain, and Sanjiang Plain, which leads to significant differences in elevation. The complexity of topography further causes temperature change to be far from uniform [25,26,27]. It is reported that high-elevation regions have warmed at a faster rate than low-elevation ones in East Asia [28]. For example, Liu et al. [29] found that the Tmin trend magnitude is more prominent at high elevation than that at low elevation in the Tibetan Plateau, especially in winter and spring. Thakuri et al. [30] found that the observed positive elevation-dependent warming for Tmax until 2566 m could be related to the reduced number of rainy days in Nepal from 1976 to 2015. Dong et al. [31] investigated the relationship between temperature trend and elevation by dividing China into three subregions and found the temperature trend changed with elevation. Xu et al. [32] confirmed that the elevation dependency of warming was most significant in winter, followed by spring, summer, and winter in Hengduan Mountain. Dimri et al. [33] used three different regional climate models to assess the probable future changes in Tmax and Tmin and confirmed that the insignificant increase of the Tmax trend and the significant decrease of the Tmin trend with elevation resulted in a significant increase of the DTR trend magnitude with elevation in winter. However, few studies have studied the relationship between the temperature trend and elevation in northeast China. Thus, it is necessary to understand the impact of elevation on DTR change, which is used for understanding climate change in mountain regions.
In this study, we collected data from 68 meteorological stations in northeast China from 1961 to 2015. By analyzing the monthly observation data, we examined the spatial and temporal changes of DTR and its relationship with elevation. Finally, we analyzed the plausible mechanisms that can explain the relationships between temperature trends and elevation.
2. Method and Data
Data used in this study included monthly Tmax, Tmin, and sunshine duration (SD) and station elevation, provided by the National Meteorological Information Center, China Meteorological Administration (NMIC/CMA). During the study period, the same standards and instrumentation were used for all meteorological stations. According to the standard of no more than 2% missing data, 68 meteorological stations were selected to investigate the climate change in northeast China from 1961 to 2015. Figure 1 shows the distribution of the 68 meteorological stations in northeast China. The elevation of these meteorological stations varies from 3 to 1017 m (Figure 2). In the aspects of climate condition, northeast China is characterized by a cool-temperate continental monsoon climate with long winter and short warm summer [34,35,36]. The annual average temperature gradually increases from approximately −1 °C in the northeast to 6 °C in the south. The annual precipitation in northeastChinagradually increasesfrom about 400 mm in the west to 1000 mm in the east. The precipitation in northeast China is mainly concentrated in summer [37].
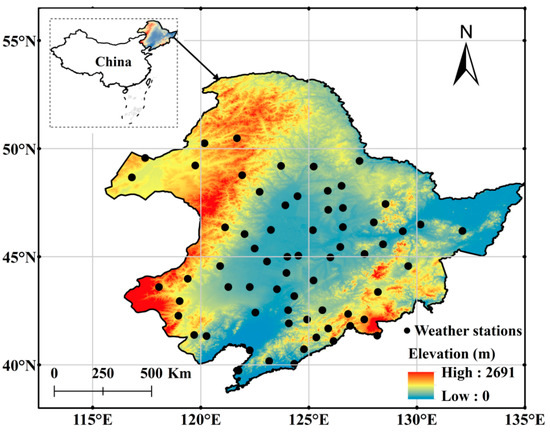
Figure 1.
Geographical distribution of the 68 meteorological stations in northeast China.
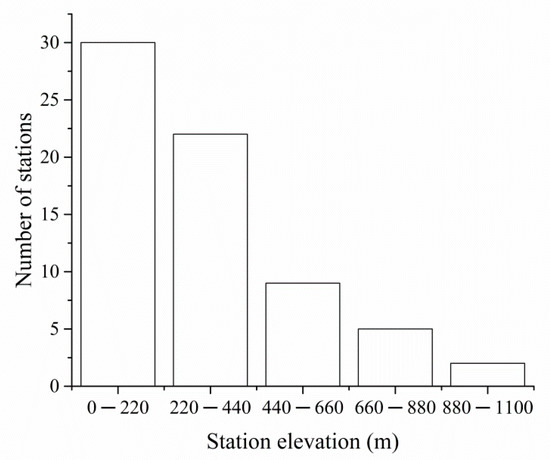
Figure 2.
The numberof meteorological stations at different elevations.
The data processing was described in our previous study [22]. We used the method proposed by Wang and Gaffen [38] to assure the quality and consistency of data. To supply the missing data, linear interpolation and stepwise were used. The method used to fill the data gaps cannot affect the results in analyzing climate change. The missing data accounted for less than 0.35% of the total records. According to filled data and raw data, we calculated the means and trends, respectively. It was found that the difference between the two datasets was insignificant. In this study, gap-filled data were used because the missing data mainly concentrated in the early years.
The trend in annual and seasonal Tmax, Tmin, DTR, and SD were analyzed quantitatively by linear regression. The magnitude of change for Tmax, Tmin, DTR, and SD were determined by the tenfold slope. The altitude gradient of temperature tendency rate was also estimated by linear regression, shown by Equation (1).
where y is warming rate; ele is elevation at each station; and k0 and k1 are regression coefficients. The coefficient k1 represents the altitude gradient. The correlation coefficient was applied to determinate the relationship between elevation and the trends of climate factors (DTR, Tmax, Tmin, and SD). The correlation coefficient was also used to determine the relationship between the trend of SD and the trend of temperature (DTR, Tmax, and Tmin). Finally, t-test was used for significance test. The trend was considered to be statistically significant when p < 0.05.
y = k0 + k1ele
The seasons include spring, summer, autumn, and winter in this study. Spring is from March to May, summer is from June to August. autumn is from September to November, and winter is from December to February.
3. Results
3.1. Temperature Characteristics
The analysis results of the annual temperature trend in northeast China are shown in Figure 3. Annual Tmax and Tmin in northeast China increased significantly from 1961 to 2015. Annual Tmax showed a warming trend (0.209 °C/decade), and 94% of stations reached the 95% level of significance (Table 1). Annual Tmin trend increased by 0.454 °C/decade, and all stations reached 95% level of significance (Table 1). Although annual Tmax and Tmin increased significantly from 1961 to 2015, the trend of Tmin was larger than that of Tmax, which led to a significant decreasing trend of DTR in northeast China. Annual DTR decreased significantly at a rate of −0.252 °C/decade, and 91% of stations reached the 95% level of significant (Table 1).
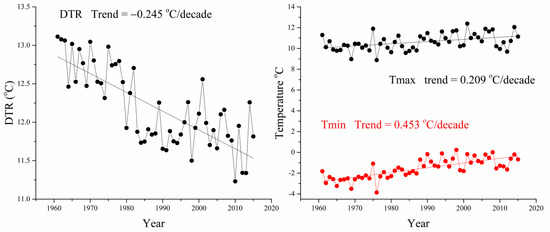
Figure 3.
Time series of annual mean DTR, Tmax, and Tmin in northeast China from 1961 to 2015. The solid lines represent the linear fit.

Table 1.
Number of stations that reach the significant level (p < 0.05).
Considering the seasonal characteristics, DTR in northeast China decreased significantly in all seasons, exceeding 95% level of significance (Table 2). The decrease of DTR was higher in spring and winter than that in summer and autumn. Tmin deceased significantly, but Tmax showed an insignificant change during spring and winter. As a result, DTR decreased significantly at greater rates during spring and winter. Tmax and Tmin increased significantly during summer and autumn, exceeding the 95% level of significance. Warming rates of Tmin were greater than those of Tmax. Therefore, DTR decreased significantly at slower rates during summer and autumn. On the other hand, we also found that the increases of Tmax and Tmin were the greatest in winter (0.5261 and 0.2298 °C/decade).

Table 2.
Seasonal trends (°C/Decade) of Tmax, Tmin, and DTR in northeast China from 1961 to 2015.
3.2. Relationship between Temperature and Elevation
Elevation is one of the factors influencing the distribution of temperature trend. Therefore, for the distribution of DTR trend, we mainly analyzed the influence of elevation on temperature trend. The correlation coefficient was used to estimate the relationship between temperature and elevation.
The results of correlation analysis are shown in Figure 4. There was a significant positive correlation between annual Tmax trend and elevation in northeast China (Figure 4a). This indicated that increasing elevation had a warming effect on Tmax. By contrast, a negative correlation between the annual Tmin trend and elevation was found (Figure 4b), although it was not significant. These results lead to a significant positive correlation between the DTR trend and elevation. This result confirms those of previous studies that increasing elevation is positively correlated with DTR [30,39]. When the elevation increased 1000 m, the DTR tendency rate increased by 0.293 °C/decade in northeast China.
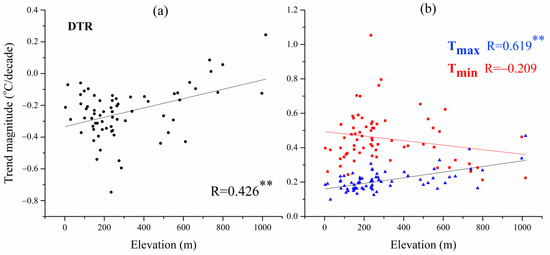
Figure 4.
The relationship between elevation and (a) annual DTR, (b) annual Tmax, and (b) annual Tmin trends in the northeast China during 1961–2015. ** Significant at p < 0.01.
To further prove the influence of elevation on temperature, we calculated the correlation coefficient between temperature trends and elevations during different seasons. The analysis results of the relationship between seasonal trend and elevation is shown in Table 3. Similar to the results of annual analysis, there were significant positive relationships between the DTR trend and elevation in all seasons in northeast China. Significant positive correlations between the Tmax trend and elevation were found in spring, summer, and autumn. This indicated that increasing elevation had a warming effect on Tmax during spring, summer, and autumn. However, the relationship between the Tmin trend and elevation was not significant in spring, summer, and autumn. It resulted in a significant positive correlation between the DTR trend and elevation in spring, summer, and autumn. Therefore, increasing elevation had a warming effect on DTR. In winter, the results of correlation analysis show that there was a significant negative correlation between the Tmin trend and elevation in northeast China. This indicated that increasing elevation had a cooling effect on Tmin. However, we found no significant correlation between the Tmax trend and elevation. This also led to a significant positive correlation between the DTR trend and elevation. Therefore, increasing elevation also had a warming effect on DTR in winter. The greatest altitude gradient of the DTR trend occurred in winter. With the elevation increasing 1000 m, DTR tendency rate increased by 0.392 °C/decade. The lowest altitude gradient of DTR trend occurred in autumn. When the elevation increased 1000 m, the DTR tendency rate increased by 0.209 °C/decade.

Table 3.
Relationships between elevation and the Tmax, Tmin, and DTR trends in northeast China. “R” represents the correlation coefficient, while“slope” represents the altitude gradient of temperature.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
DTR in northeast China decreased significantly at a rate of −0.209 °C/decade from 1961 to 2015. This result is lower than the result of Shen et al. [22] (−0.273 °C/decade from 1962 to 2011). This is probably caused by the different study period. In this study, Tmin increased at a faster rate than Tmax from 1961 to 2015. The change of DTR is mainly caused by the asymmetry of the Tmax and Tmin trends. Some research has found that Tmin is rising more quickly than Tmax in China [22], which is consistent with our result. A similar pattern was also observed in Bangladesh [13]. However, different from what was observed in Nepal, the Tmax trend was greater (0.45 °C/decade) than the Tmin trend (0.09 °C/decade), leading to significant increasing trend of DTR from 1976 to 2015 (0.34 °C/decade) [30]. Kattel et al. [40] also found that the increasing trend of Tmax was greater than that of Tmin on the southern of slope of the Himalayas. This is possibly due to the fact that, different from northeast China, other factors may influence the trends of temperature change.
Previous studies found that only the warming rate of Tmin was the greatest in winter (from 1950 to 1993) [5]. However, Vose et al. [10] found that Tmax and Tmin in the Northern Hemisphere showed the greatest changes in winter (from 1950 to 2004). This indicated that Tmax increased at a faster rate after 1990 in the Northern Hemisphere, and the Northern Hemisphere was experiencingthe great warming in winter. At the regional scale, Ding et al. [41] also pointed out that northern China experienced the greatest warming in winter. Shen et al. [22] examined the spatiotemporal variation in temperature in China based on meteorological stations and found that the magnitudes of change for Tmax and Tmin were the greatest in winter. The results from this study (i.e., the greatest increase of Tmax and Tmin in winter) are consistent with those in previous studies. On the other hand, although the magnitudes of change for Tmax and Tmin were the greatest in winter, the decreasing trend of DTR was the greatest in spring. This is due to the fact that the greatest difference between the trend of Tmax and the trend of Tmin occurred in spring.
4.2. Possible Causes for Elevation-Dependent DTR Trend
In this study, we found that the annual and seasonal DTR trends were significantly positively correlated with elevation in northeast China. This is possibly due to the fact that solar radiation and greenhouse gases are elevation-dependent. Solar radiation affects the energy between daytime and nighttime, which has a larger effect on Tmax than Tmin [42,43]. Solar radiation increases with increasing elevation, resulting in a warming temperature at high elevations compared to at low elevations. Therefore, solar radiation has a warming effect on temperature at high elevation. On the other hand, greenhouse gases influence temperature by absorbing longwave radiation [44]. Different from solar radiation, greenhouse gas concentrations decrease with increasing elevation, resulting in a warming temperature at low elevations compared to at high elevation. Therefore, greenhouse gases have a cooling effect on temperature at high elevation.
As shown in Figure 4, elevation was significantly positively correlated with the annual Tmax trend and insignificantly correlated with the annual Tmin trend in northeast China. As mentioned above, the warming effect caused by solar radiation could be the dominant factor. Sunshine duration worked as a proxy for analyzing the relationship between solar radiation and elevation [45,46]. The results of correlation analysis indicate that the annual trend of sunshine duration was significantly correlated with elevation and the annual trend of Tmax (Figure 5 and Table 4). Furthermore, there was a significant correlation between the annual Tmax trend and elevation. These indicated that increasing elevation had a warming effect on Tmax due to the warming effect of solar radiation. Due to the insignificant correlation between the annual Tmin trend and elevation, increasing elevation had a warming effect on DTR.
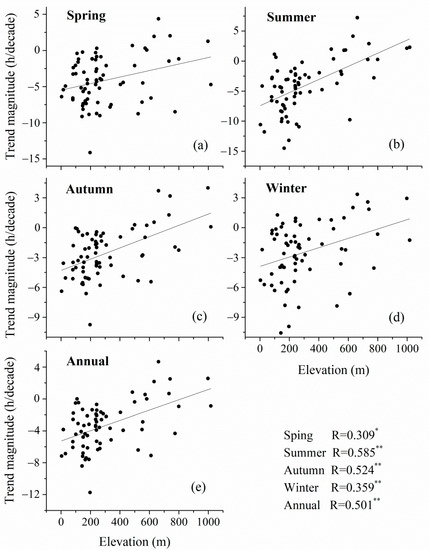
Figure 5.
The relationship between the sunshine duration trend and elevation at seasonal (a–d) and annual (e) scales in northeast China during 1961–2015. “SD” represents sunshine duration. * Significant at p < 0.05, ** Significant at p < 0.01.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficient between the trend of SD and the trends of Tmax, Tmin, and DTR at annual and seasonal scales in northeast China during 1961–2015.
During spring, summer, and autumn, similar to the results of the annual analysis, the warming effect caused by solar radiation is the dominant factor to cause the elevation-dependent DTR trend. In summer, we found that the correlation between the Tmax trend and elevation was the most significant. This is due to the fact that solar radiation is the strongest in summer, which has the strongest warming effect (Table 4). The greenhouse gas concentration is the lowest in summer, which has the weakest cooling effect. The correlation between trend of solar radiation and elevation was the most significant in summer, leading to the most significant correlation between the Tmax trend and elevation in summer. On the other hand, we also found a weak correlation between the Tmin trend and elevation in summer (Table 4). This could be due to the fact that the increase of temperature during daytime can be extended to nighttime [22]. There was significant negative correlation between the Tmin trend and elevation in winter. Different from other seasons, the cooling effect caused by greenhouse gases could be a dominant factor. As anthropogenic activities are gradually intensifying, greenhouse gas emissions are highest in winter [47]. The greenhouse gas concentration at low elevation is much greater than that at high elevation in winter [48], indicating that the warming trend at low elevation is relatively greater as compared with at high elevation. The cooling effect caused by greenhouse gases was greater than the warming effect caused by solar radiation. Therefore, there was significant negative correlation between the Tmin trend and elevation in winter. On the other hand, the warming effect caused by solar radiation may be relatively weaker during daytime than the cooling effect caused by greenhouse gases, leading to insignificant correlation between the Tmax trend and elevation in winter. As a consequence, similar to in other seasons, we also found increasing elevation had a warming effect in DTR.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we examined the DTR trend and its relationship with elevation in northeast China from 1961 to 2015 by using available data recorded from 68 meteorological stations. The results show that Tmax and Tmin in northeast China increased significantly at rates of 0.209 and 0.454 °C/decade, respectively. As a result, DTR in northeast China decreased significantly at a rate of 0.252 °C/decade from 1961 to 2015. This is due to the fact that the increase of Tmin is faster than the increase of Tmax. At the seasonal scales, the increase rates of Tmin were greater than those of Tmax in all seasons, leading to a significant decrease of DTR in all seasons. The decrease rates of DTR were the greatest in spring (−0.317 °C/decade) and the lowest in summer (−0.173 °C/decade). Tmax increased insignificantly in spring and summer, but significantly in summer and autumn. By contrast, Tmin increased significantly in all seasons.
Tmax tendency rate increased significantly with increasing elevation, leading to significant increase of the DTR trend with increasing elevation at the annual scale. Seasonally, it was also found that the DTR trend increased significantly with increasing elevation. The greatest elevation gradient of the DTR trend occurred in winter (0.392 °C/decade/km). The lowest elevation gradient of the DTR trend occurred in spring (0.209 °C/decade/km). In spring, summer, and autumn, the elevation-dependent DTR trend increased significantly with increasing elevation. However, in winter, the elevation-dependent DTR trend decreased significantly with an increase of elevation. Solar radiation increased with increasing elevation, which had a warming effect on temperature. The greenhouse gas concentration deceased with increasing elevation, which had a cooling effect on temperature. The warming and cooling effects may cancel each other out, resulting in significant correlation between the DTR trend and elevation at the annual and seasonal scales.
Author Contributions
Y.Z and X.S. conceived and designed the framework. Y.Z. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. X.S. and G.F. contributed to the writing and review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National KeyR&DProgramofChina (2019YFC0409101), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41971065), Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2019235), and Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences, CAS (ZDBS-LY-7019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; He, Z.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, X.; Li, J. Recent changes in daily climate extremes in an arid mountain region, a case study in northwestern China’s Qilian Mountains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganza, K.; Karoly, D.J.; Arblaster, J.M. Diurnal temperature range as an index of global climate change during the twentieth century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, B. Geographical distribution of changes in maximum and minimum temperatures. Atmos. Res. 1995, 37, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterling, D.R.; Horton, B.; Jones, P.D.; Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Parker, D.E.; Salinger, M.J.; Razuvayev, V.; Plummer, N.; Jamason, P.; et al. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 1997, 277, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Hondula, D.M.; Sharif, H. Examining the diurnal temperature range enigma: Why is human health related to the daily change in temperature? Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.; Michaelides, S.; Pashiardis, S.; Alpert, P. Long term changes in diurnal temperature range in Cyprus. Atmos. Res. 1999, 51, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F. Spatial and temporal variability of daily temperature in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 112, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Wang, L.; Shen, X.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X. Climatology and trends of air and soil surface temperatures in the temperate steppe region of North China. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, R.S.; Easterling, D.R.; Gleason, B. Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe: An update through 2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 277, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Jiang, M.; Lu, X. Marshland Loss Warms Local Land Surface Temperature in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, T.R.; Kukla, G.; Razuvayev, V.N.; Changery, M.J.; Ouayle, R.G.; Richard, R.; Helm, J.; Easterling, D.R.; Fu, C.B. Global warming: Evidence for asymmetric diurnal temperature change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 2253–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Harun, S.B.; Katimon, A. Changes in Diurnal Temperature Range in Bangladesh during the Time Period 1961–2008. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, N.; Lin, Z.; Torok, S. Trends in the diurnal temperature range over Australia since 1951. Atmos. Res. 1995, 37, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, R.G.; Rogers, J.C. U.S. Diurnal Temperature Range Variability and Regional Causal Mechanisms, 1901–2002. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 7216–7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Kumar, K.K.; Pant, G.B. Diurnal asymmetry of surface temperature trends over India. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J. Recent progress in studies of climate change in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 958–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ren, G.; Zwiers, F.; Hu, T. Contribution of urbanization to warming in China. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Schlenker, W.; Costa-Roberts, J. Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science 2011, 333, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, E. The effects of past climate change on the northern limits of maize planting in Northeast China. Clim. Chang. 2013, 117, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwagona, P.C.; Yao, Y.; Shan, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y. Trend and abrupt regime shift of temperature extreme in Northeast China, 1957–2015. Adv. Meteorol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Li, G.; Wu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yu, P.; Zhou, D. Spatiotemporal change of diurnal temperature range and its relationship with sunshine duration and precipitation in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 13163–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, G.; Li, Z. Changes in extreme low temperature events over Northern China under 1.5 °C and 2.0 °C warmer future scenarios. Atmosphere 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, P.; Ren, G.; Ren, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xue, X. A remarkable climate warming hiatus over Northeast China since 1998. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, N.C.; Lundquist, J.D. Temperature trends at high elevations: Patterns across the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwala, I.; Miller, J.R. Climate change in mountains: A review of elevation-dependent warming and its possible causes. Clim. Chang. 2012, 114, 527–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountain Research Initiative EDW Working Group. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Chen, A.; Ciais, P.; Li, Y.; Li, L.Z.X.; Vautard, R.; Zhou, L.; Yang, H.; Huang, M.; Piao, S. Regional air pollution brightening reverses the greenhouse gases induced warming-elevation relationship. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 4563–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, L.; Yin, Z.-Y. Elevation dependency of recent and future minimum surface air temperature trends in the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2009, 68, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakuri, S.; Dahal, S.; Shrestha, D.; Guyennon, N.; Romano, E.; Colombo, N.; Salerno, F. Elevation-dependent warming of maximum air temperature in Nepal during 1976–2015. Atmos. Res. 2019, 228, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Huang, G.; Qu, X.; Tao, W.; Fan, G. Temperature trend–altitude relationship in China during 1963–2012. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 122, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jia, Y.; Peng, H.; Niu, C.; Liu, J. Temperature and precipitation trends and their links with elevation in the Hengduan Mountain region, China. Clim. Res. 2018, 75, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimri, A.P.; Kumar, D.; Choudhary, A.; Maharana, P. Future changes over the Himalayas: Maximum and minimum temperature. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 162, 212–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Varis, O. Climate Change in China. Ambio 2001, 30, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. Observed changes in precipitation on the wettest days of the year in China, 1960–2000. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Henderson, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. Spatiotemporal change in China’s climatic growing season: 1955–2000. Clim. Chang. 2009, 99, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Shen, B.; Gao, Z.; Sui, B.; Bai, L.; Wang, S.-H.; An, G.; Li, J. The impacts of moisture transport of East Asian Monsoon on summer precipitation in Northeast China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 24, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.L.; Gaffen, D.J. Late-Twentieth-Century Climatology and Trends of Surface Humidity and Temperature in China. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2833–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N. Temporal and spatial characteristics of precipitation and temperature in Punjab, Pakistan. Water 2019, 11, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, D.B.; Yao, T. Recent temperature trends at mountain stations on the southern slope of the central Himalayas. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 122, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Detection, causes and projection of climate change over china: An overview of recent progress. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 24, 954–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, F.; Sun, G.; Guo, A. Solar dimming and its impact on estimating solar radiation from diurnal temperature range in China, 1961–2007. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 101, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-L.; Li, G.-S. Evaluation of support vector machine for estimation of solar radiation from measured meteorological variables. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipona, R.; Behrens, K.; Ruckstuhl, C. How declining aerosols and rising greenhouse gases forced rapid warming in Europe since the 1980s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L02806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanhill, G.; Cohen, S. Solar radiation changes in the United States during the twentieth century: Evidence from sunshine duration measurements. J. Clim. 2004, 18, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Dickinson, R.E.; Wild, M.; Liang, S. Atmospheric impacts on climatic variability of surface incident solar radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 9581–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, L.; Zou, L. Detecting human influence on the temperature changes in Central Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 4553–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Yin, Y.Y.; Huang, G.H.; Huang, Y.F. Uncertainty Analysis for Distribution of Greenhouse Gases Concentration in Atmosphere. J. Environ. Inform. 2004, 3, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).