The Impact of a Hydroelectric Power Plant on a Regional Climate in Portugal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
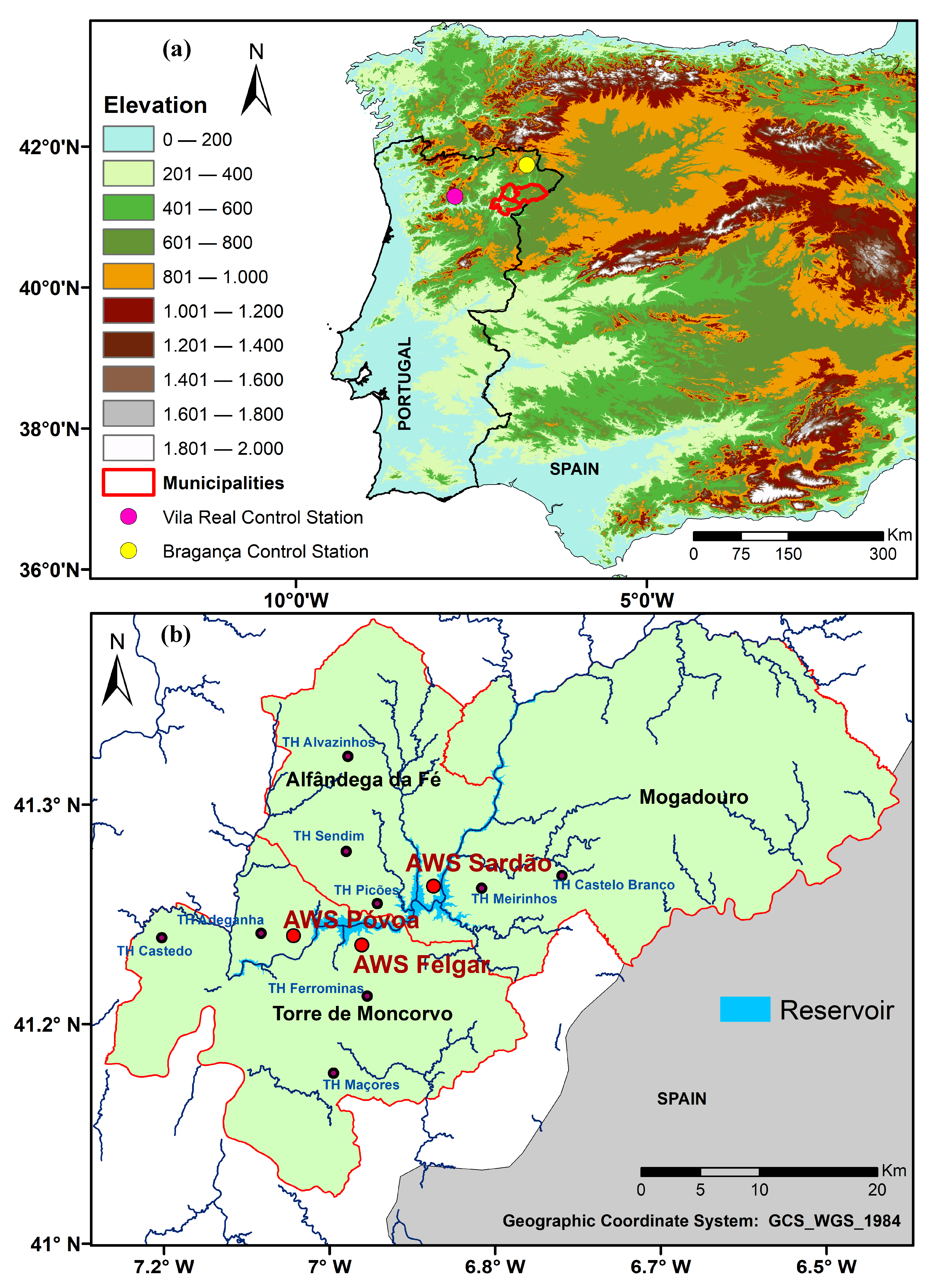
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Meteorological Network Stations
| Station Name | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°W) | Elevation (m amsl) | Parameters * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS Póvoa | 41.23 | 7.03 | 466 | T/RH/P/WS/WD/SR/ST |
| AWS Felgar | 41.22 | 6.97 | 457 | T/RH/P/WS/WD/SR/ST |
| AWS Sardão | 41.27 | 6.89 | 321 | T/RH/P/WS/WD/SR/ST |
| TH Ferrominas | 41.18 | 6.96 | 704 | T/RH |
| TH Maçores | 41.13 | 6.99 | 658 | T/RH |
| TH Adeganha | 41.23 | 7.06 | 485 | T/RH |
| TH Castedo | 41.23 | 7.16 | 609 | T/RH |
| TH Meirinhos | 41.27 | 6.84 | 506 | T/RH |
| TH Alvazinhos | 41.37 | 6.79 | 593 | T/RH |
| TH Sendim | 41.30 | 6.98 | 481 | T/RH |
| TH Picões | 41.25 | 6.95 | 437 | T/RH |
| TH Castelo Branco | 41.27 | 6.76 | 580 | T/RH |
2.3. Validation of Collected Data
2.4. Control Meteorological Station
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Climate Characterization
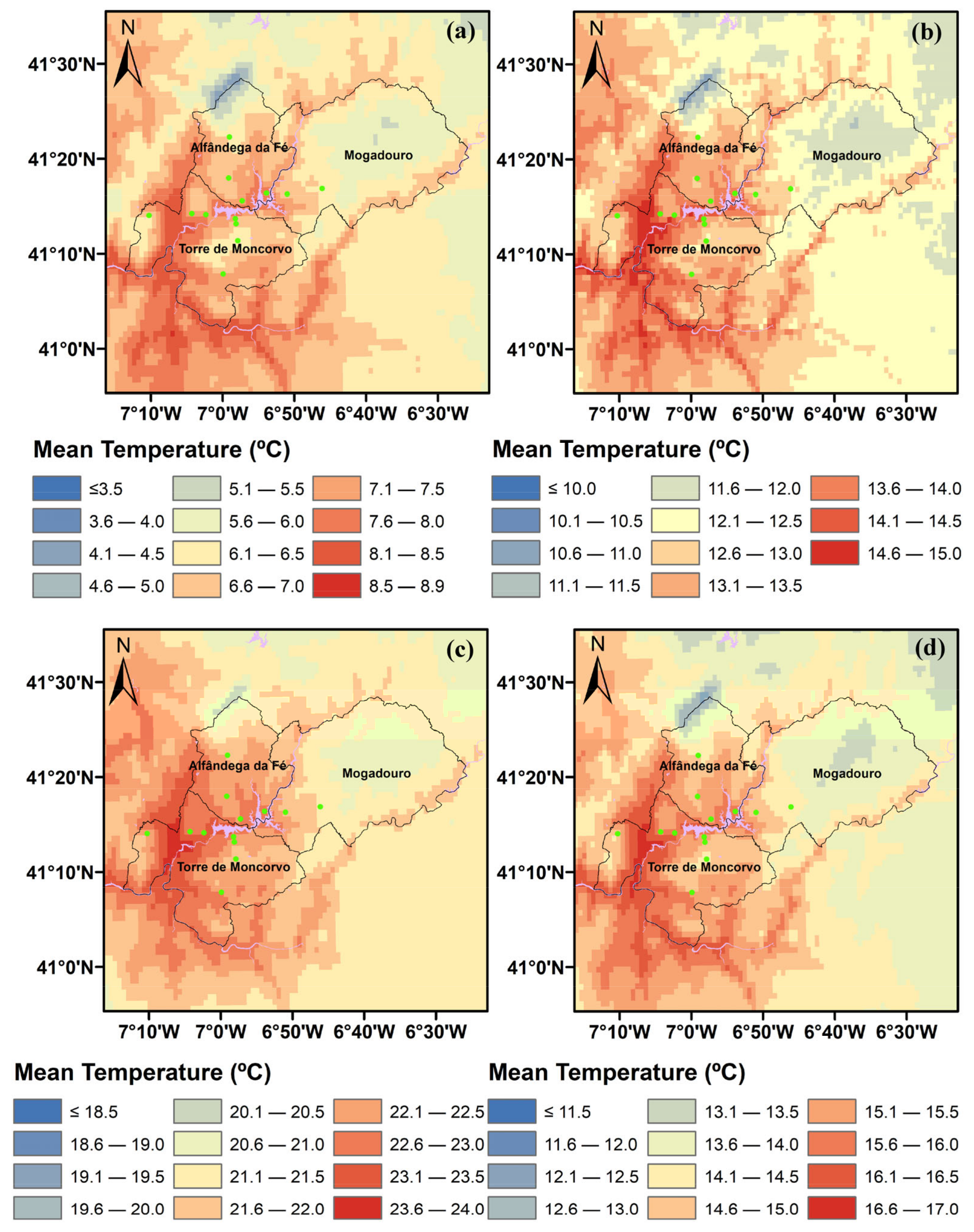
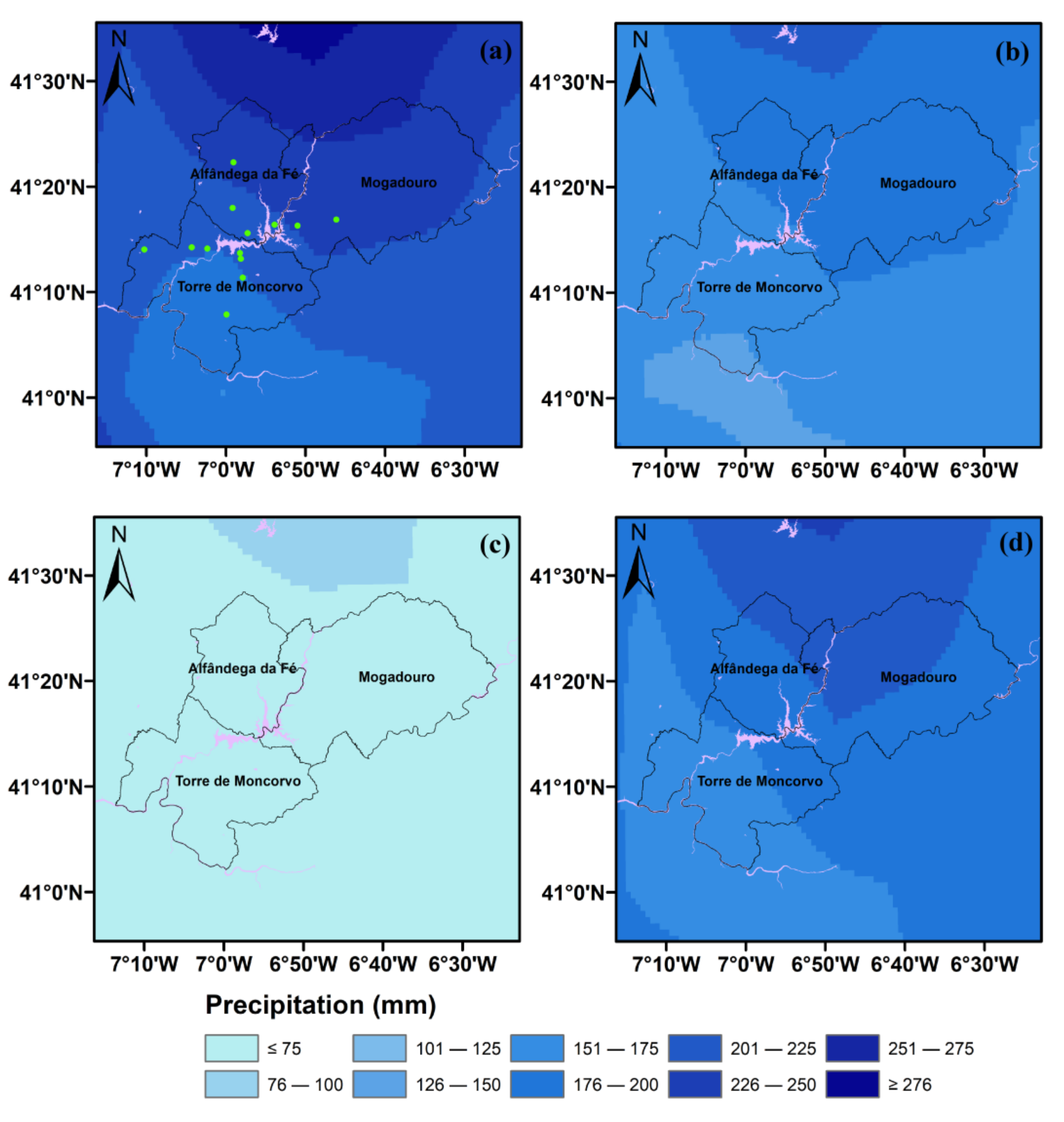
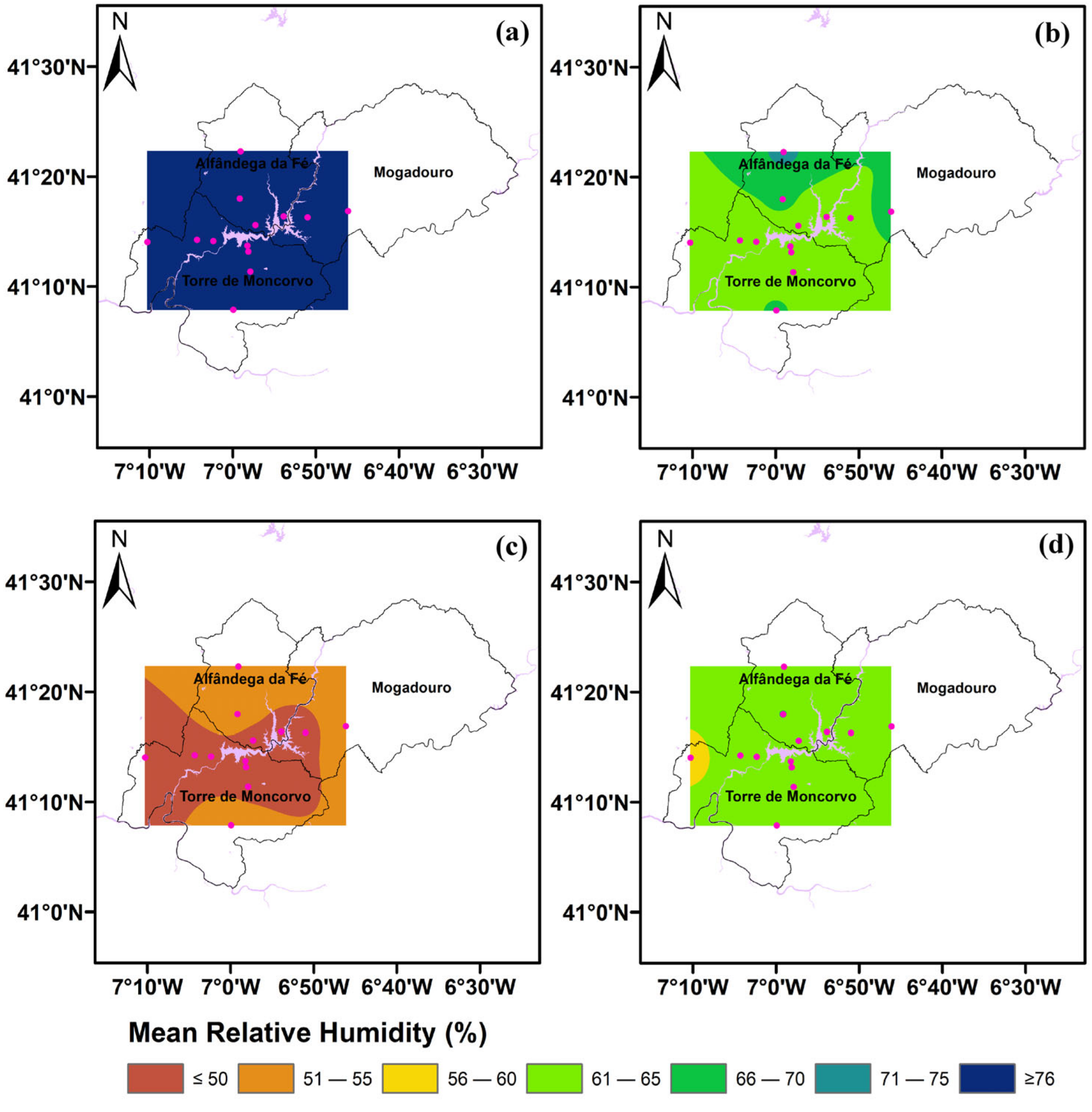
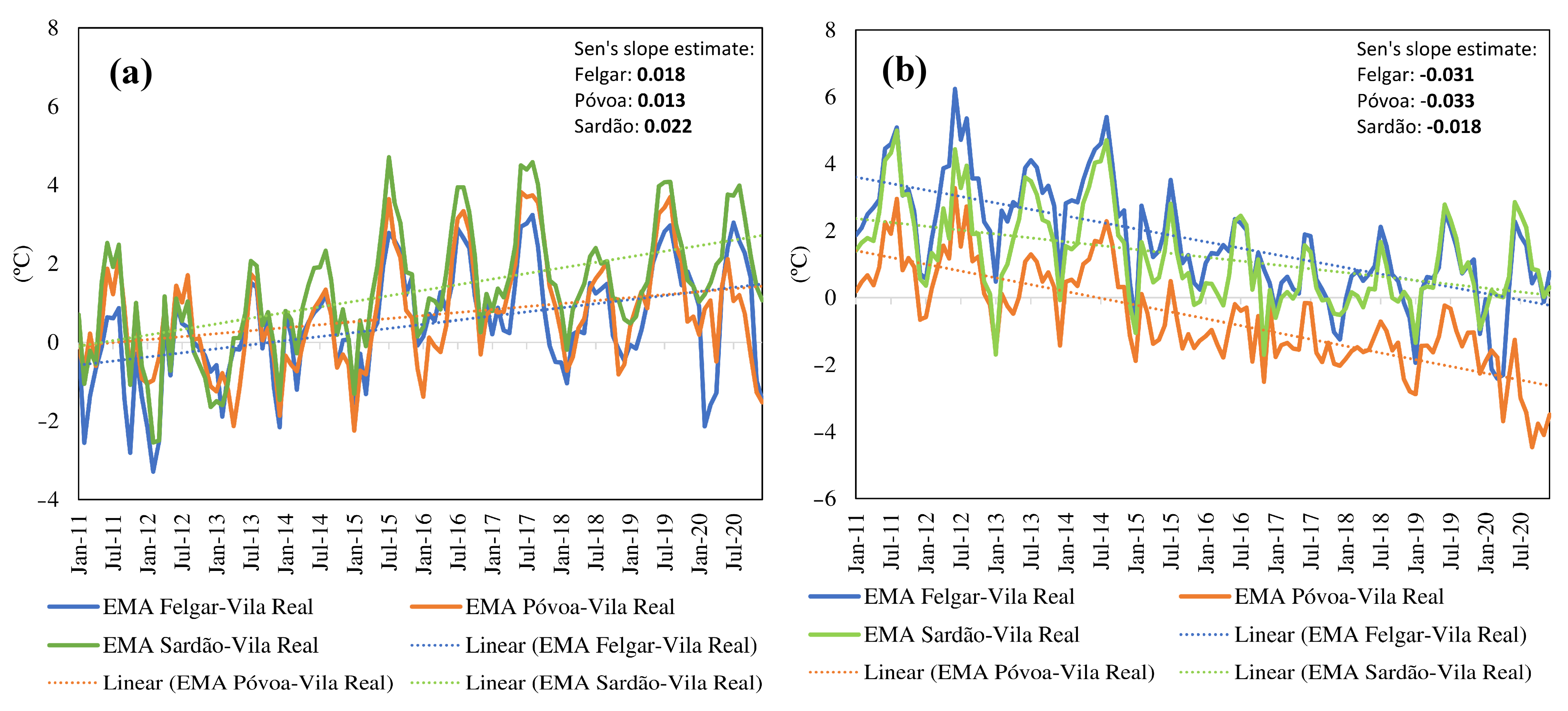
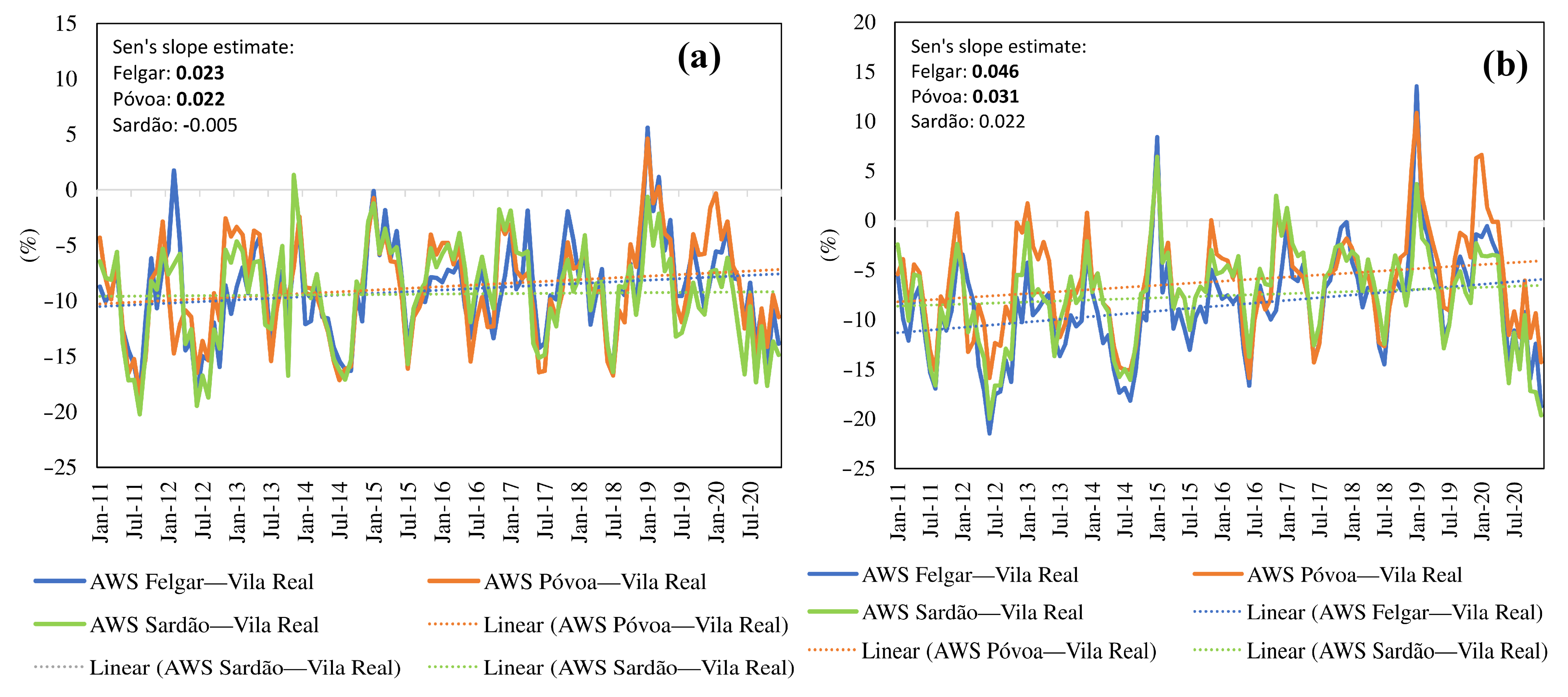
3.2. Daily Trends
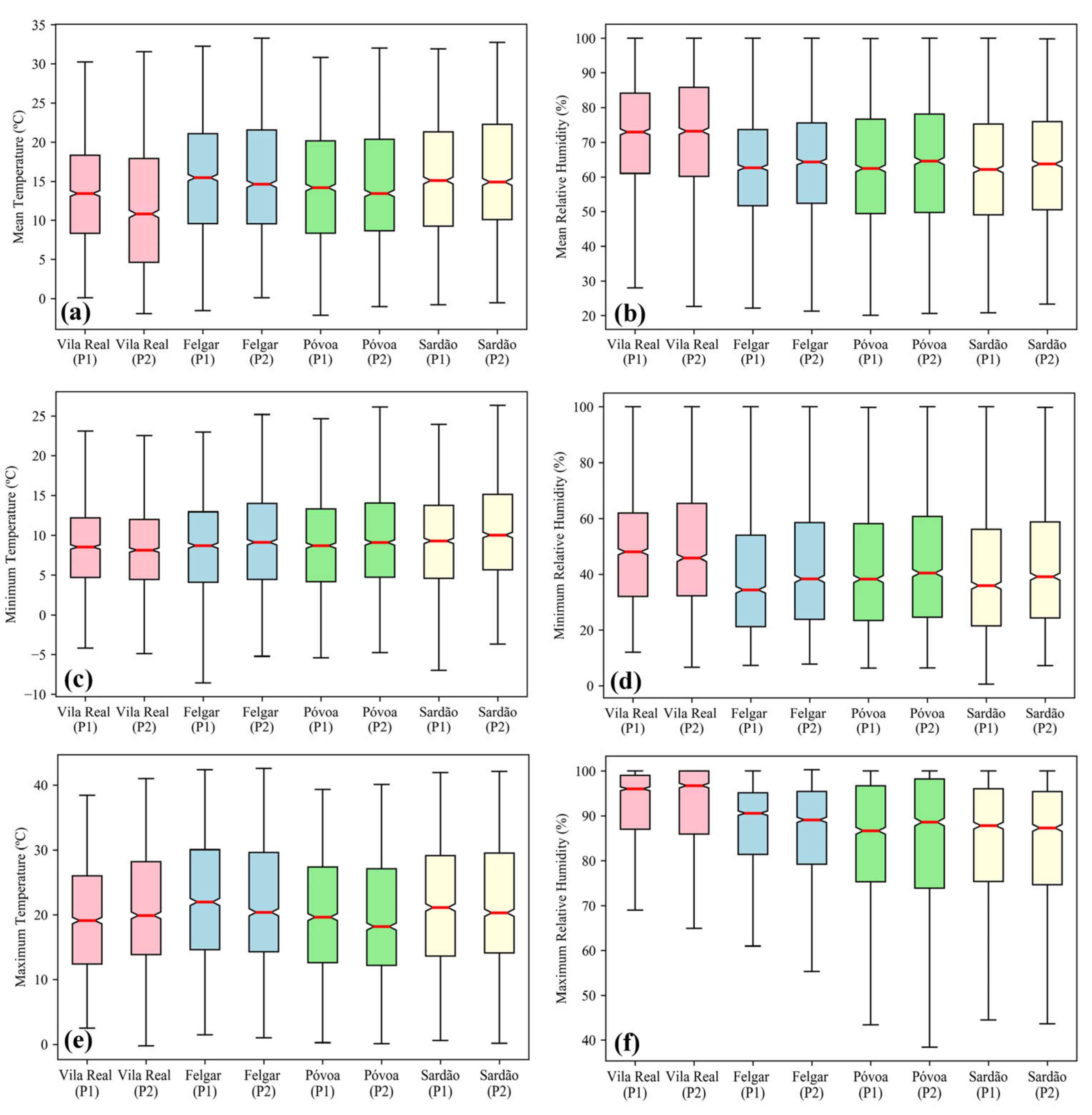
3.3. Anomaly Trends
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elagib, N.A.; Basheer, M. Would Africa’s Largest Hydropower Dam Have Profound Environmental Impacts? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8936–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.N. Energy Revolutions: A Story of the Three Gorges Dam in China. In Climate Change and Economics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bayazıt, Y. The Effect of Hydroelectric Power Plants on the Carbon Emission: An Example of Gokcekaya Dam, Turkey. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, F.M.; Abraham, N.L.; Dalvi, M.; Folberth, G.A.; Griffiths, P.T.; Hardacre, C.; Johnson, B.T.; Kahana, R.; Keeble, J.; Kim, B. Assessment of Pre-Industrial to Present-Day Anthropogenic Climate Forcing in UKESM1. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 1211–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, R.B.; Berntsen, T.K.; Myhre, G.; Tanaka, K.; Kvalevåg, M.M.; Hoyle, C.R. Anthropogenic Radiative Forcing Time Series from Pre-Industrial Times until 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11827–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kum, G. The Influence of Dams on Surrounding Climate: The Case of Keban Dam. Gaziantep Univ. J. Soc. Sci. 2016, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gyau-Boakye, P. Environmental Impacts of the Akosombo Dam and Effects of Climate Change on the Lake Levels. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2001, 3, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.; Fraga, H.; Fonseca, A.; Santos, J.A. Climate Projections for Precipitation and Temperature Indicators in the Douro Wine Region: The Importance of Bias Correction. Agronomy 2021, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Santos, J.A. High-Resolution Temperature Datasets in Portugal from a Geostatistical Approach: Variability and Extremes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2018, 57, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Fonseca, A.; Fraga, H.; Jones, G.V.; Santos, J.A. Bioclimatic Conditions of the Portuguese Wine Denominations of Origin under Changing Climates. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Santos, M.; Santos, J.A. Hydrological and Flood Hazard Assessment Using a Coupled Modelling Approach for a Mountainous Catchment in Portugal. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Santos, J.A. A New Very High-Resolution Climatological Dataset in Portugal: Application to Hydrological Modeling in a Mountainous Watershed. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 109, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Santos, J.A. Predicting Hydrologic Flows under Climate Change: The Tâmega Basin as an Analog for the Mediterranean Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Fonseca, A.; Fragoso, M.; Santos, J.A. Recent and Future Changes of Precipitation Extremes in Mainland Portugal. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 137, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; ASantos, J.; Varandas, S.G.; Monteiro, S.M.; Martinho, J.L.; Cortes, R.; Cabecinha, E. Current and Future Ecological Status Assessment: A New Holistic Approach for Watershed Management. Water 2020, 12, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Fonseca, A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Water Quality in Lis River, Portugal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7125–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, J.; Fonseca, A.; Vilar, V.J.P.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Water Quality Modelling of Lis River, Portugal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.; Botelho, C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Vilar, V.J.P. Global Warming Effects on Faecal Coliform Bacterium Watershed Impairments in Portugal. River Res. Appl. 2015, 31, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Vilar, V.J.P. Integrating Water Quality Responses to Best Management Practices in Portugal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tata, L.R.R. Biodiversity Impact Assessment of Two Large Dam Projects in India under Long Term Multi-Scenarios Simulation. Impact Assess. Proj. Apprais. 2021, 39, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Pal, S.; Talukdar, S.; Mandal, I. Impact of Wetland Fragmentation Due to Damming on the Linkages between Water Richness and Ecosystem Services. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 50266–50285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk-Woźniak, E.; Krztoń, W.; Górnik, M. Synergistic Impact of Socio-Economic and Climatic Changes on the Ecosystem of a Deep Dam Reservoir: Case Study of the Dobczyce Dam Reservoir Based on a 30-Year Monitoring Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, D.; Kishtawal, C.; Tripathi, S.; Govindaraju, R.S. Observational Evidence That Agricultural Intensification and Land Use Change May Be Reducing the Indian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takata, K.; Saito, K.; Yasunari, T. Changes in the Asian Monsoon Climate during 1700–1850 Induced by Preindustrial Cultivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9586–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degu, A.M.; Hossain, F.; Niyogi, D.; Pielke, R., Sr.; Shepherd, J.M.; Voisin, N.; Chronis, T. The Influence of Large Dams on Surrounding Climate and Precipitation Patterns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlet, A.F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Effects of Climate Change on Hydrology and Water Resources in the Columbia River Basin 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 1597–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, H.; Yang, D.; Hou, A. Causal Effects of Dams and Land Cover Changes on Flood Changes in Mainland China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 2705–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, N.S.; Wood, A.W.; Voisin, N.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Palmer, R.N. The Effects of Climate Change on the Hydrology and Water Resources of the Colorado River Basin. Clim. Chang. 2004, 62, 337–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussi, G.; Darby, S.E.; Whitehead, P.G.; Jin, L.; Dadson, S.J.; Voepel, H.E.; Vasilopoulos, G.; Hackney, C.R.; Hutton, C.; Berchoux, T. Impact of Dams and Climate Change on Suspended Sediment Flux to the Mekong Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Huang, G.; Piwowar, J.M.; Zhou, X.; Zhai, Y. Risk of Hydrological Failure under the Compound Effects of Instant Flow and Precipitation Peaks under Climate Change: A Case Study of Mountain Island Dam, North Carolina. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 125305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluixá-Sanmartín, J.; Escuder-Bueno, I.; Morales-Torres, A.; Castillo-Rodríguez, J.T. Accounting for Climate Change Uncertainty in Long-Term Dam Risk Management. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, G. Quantifying the Individual Contributions of Climate Change, Dam Construction, and Land Use/Land Cover Change to Hydrological Drought in a Marshy River. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, J. Hydrologic Impacts of Cascade Dams in a Small Headwater Watershed under Climate Variability. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.L.; Jin, J.; Tsang, C.-F. Local Climate Sensitivity of the Three Gorges Dam. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correia, M.F.; da Silva Dias, M.A.F.; da Silva Aragão, M.R. Soil Occupation and Atmospheric Variations over Sobradinho Lake Area. Part Two: A Regional Modeling Study. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2006, 94, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, L. Meteorological Climate Change Effect of the Ataturk Dam in Turkey at Eastern Anatolia. Mater. Geoenviron. 2006, 53, 467. [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg, C.H.; Zhou, X. Impact of the Construction of a Large Dam on Riparian Vegetation Cover at Different Elevation Zones as Observed from Remotely Sensed Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 32, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, F.C.; Fernandes, M.R.; Martins, M.J.; Ferreira, M.T. Effects of a Large Irrigation Reservoir on Aquatic and Riparian Plants: A History of Survival and Loss. Water 2019, 11, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.M.B.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Cortes, R.M.V.; Varandas, S.G.P.; Jesus, J.J.B.; Pacheco, F.A.L. Integrative Assessment of River Damming Impacts on Aquatic Fauna in a Portuguese Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.J.; Pedroso, N.M.; Ferreira, J.P.; Matos, H.M.; Sales-Luís, T.; Pereira, Í.; Baltazar, C.; Grilo, C.; Cândido, A.T.; Sousa, I.; et al. Assessing Dam Implementation Impact on Threatened Carnivores: The Case of Alqueva in SE Portugal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 142, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, C.; Contente, J.; Santos, J.A. Climate Change Projections of Aridity Conditions in the Iberian Peninsula. Water 2021, 13, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Contente, J.; Santos, J.A. Climate Change Projections of Dry and Wet Events in Iberia Based on the WASP-Index. Climate 2021, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Fonseca, A.; Santos, J.A. Are Land Use Options in Viticulture and Oliviculture in Agreement with Bioclimatic Shifts in Portugal? Land 2021, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation; Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Klein Tank, A.M.G.; Wijngaard, J.B.; Können, G.P.; Böhm, R.; Demarée, G.; Gocheva, A.; Mileta, M.; Pashiardis, S.; Hejkrlik, L.; Kern-Hansen, C. Daily Dataset of 20th-century Surface Air Temperature and Precipitation Series for the European Climate Assessment. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 22, 1441–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, H.E. Rank Correlation and Population Models. J. R. Stat. Society Ser. B Methodol. 1950, 12, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revadekar, J.V.; Hameed, S.; Collins, D.; Manton, M.; Sheikh, M.; Borgaonkar, H.P.; Kothawale, D.R.; Adnan, M.; Ahmed, A.U.; Ashraf, J.; et al. Impact of Altitude and Latitude on Changes in Temperature Extremes over South Asia during 1971–2000. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, J.D.; Chakraborti, S. Nonparametric Statistical Inference: Revised and Expanded; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 0203911563. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, J.A.; Corte-Real, J.; Leite, S.M. Weather Regimes and Their Connection to the Winter Rainfall in Portugal. Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 25, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AWS | TG | TX | TN | HRG | HRX | HRN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Felgar | 0/0.10 | −1/0 | 1/0 | 1/0.04 | 0/0.57 | 1/0 |
| Póvoa | −1/0 | −1/0 | 1/0 | 0/0.06 | 0/0.56 | 1/0.02 |
| Sardão | 0/0.36 | −1/0 | 1/0 | 0/0.88 | 0/0.08 | 0/0.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonseca, A.; Santos, J.A. The Impact of a Hydroelectric Power Plant on a Regional Climate in Portugal. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111400
Fonseca A, Santos JA. The Impact of a Hydroelectric Power Plant on a Regional Climate in Portugal. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(11):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111400
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonseca, André, and João A. Santos. 2021. "The Impact of a Hydroelectric Power Plant on a Regional Climate in Portugal" Atmosphere 12, no. 11: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111400
APA StyleFonseca, A., & Santos, J. A. (2021). The Impact of a Hydroelectric Power Plant on a Regional Climate in Portugal. Atmosphere, 12(11), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12111400







