Evolution, Transport Characteristics, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in a Coastal City of China during 2015–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
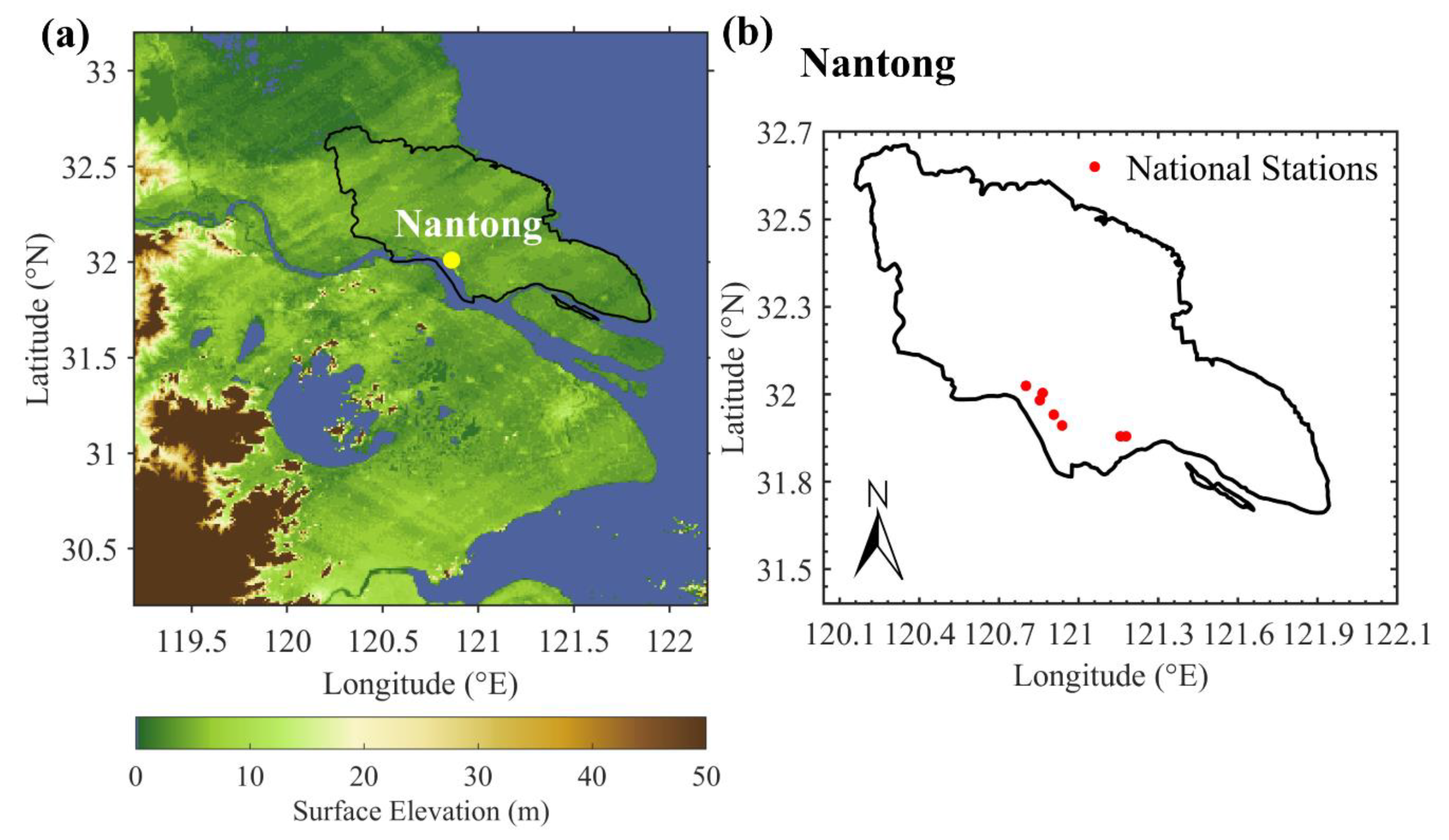
2.1. Site Location
2.2. Data and Analysis Methods
3. Results and Discussion
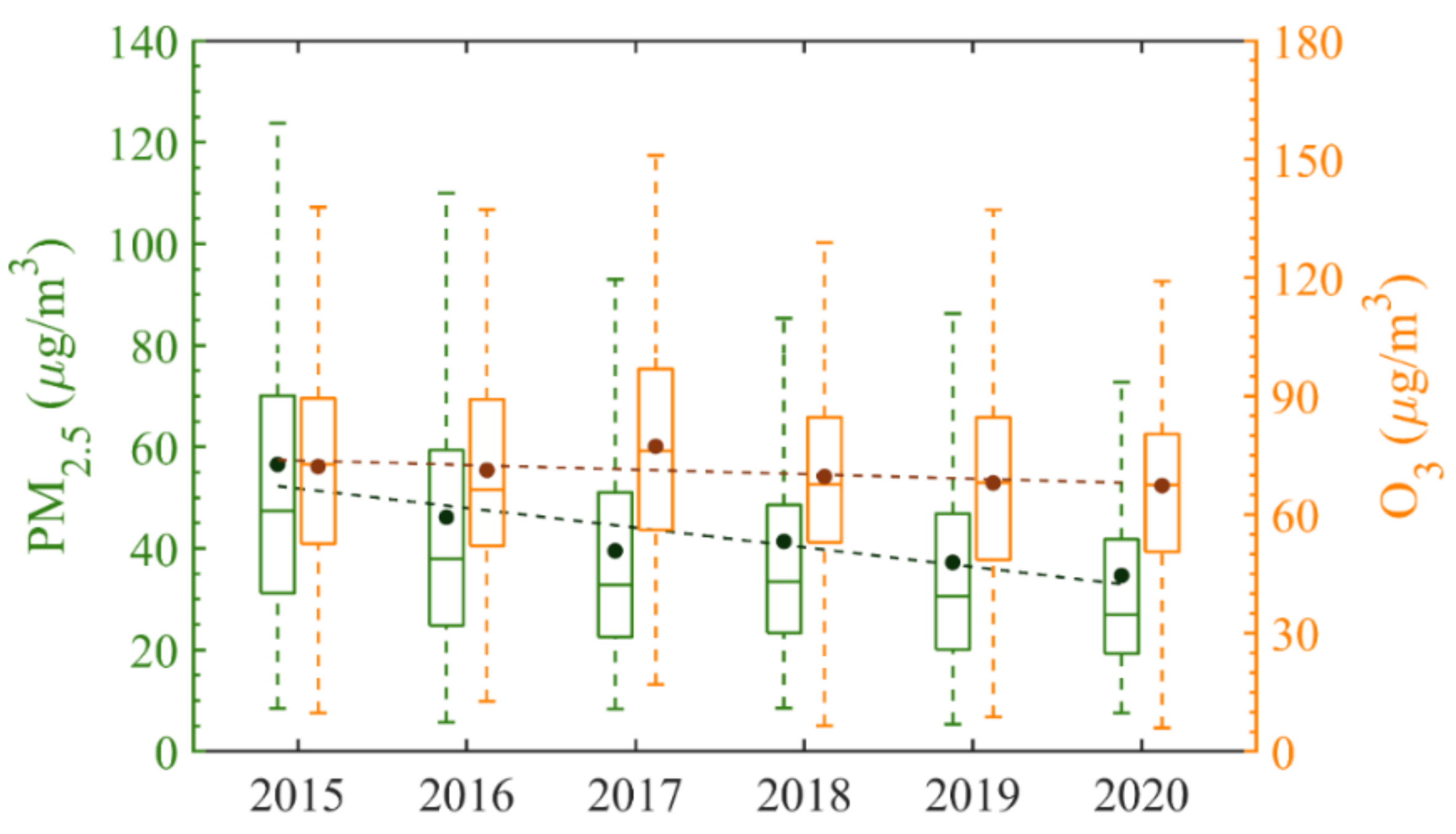
3.1. Evolution Characteristics of PM2.5 and O3
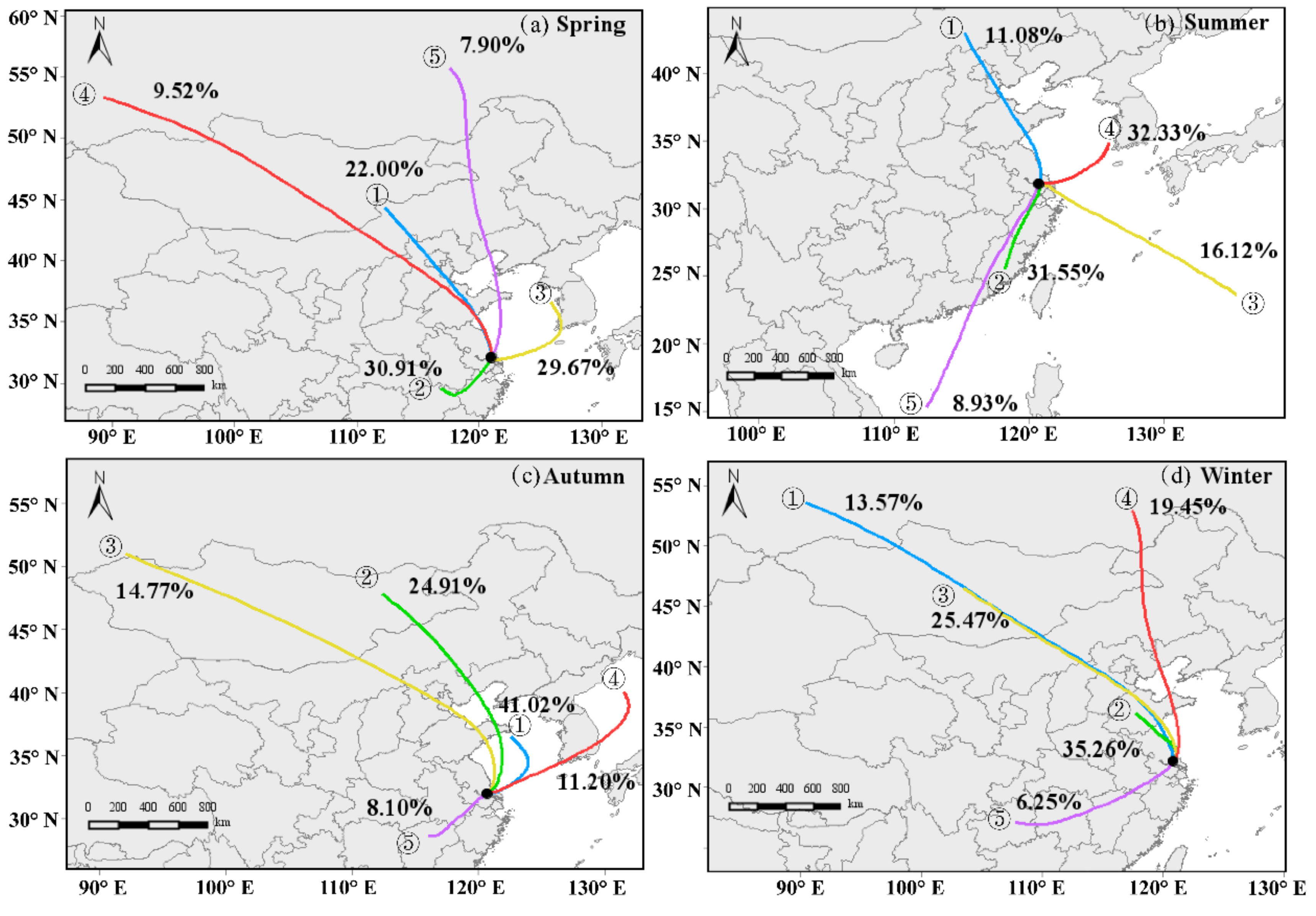
3.2. Transport Characteristics
3.3. PSCF and CWT Modeling of Source Regions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, G.J.; Duan, F.K.; Su, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Chang, D.; Pöschl, U.; et al. Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: The impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Bei, N.; Cao, J.; Huang, R.; Wu, J.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Tie, X.; et al. A possible pathway for rapid growth of sulfate during haze days in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silver, B.; Reddington, C.L.; Arnold, S.R.; Spracklen, D.V. Substantial changes in air pollution across China during 2015–2017. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 114012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Guo, H.; Hu, J.; Kota, S.H.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Responses of PM2.5 and O3 concentrations to changes of meteorology and emissions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, C.; Chan, P.W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, L. Tower observed vertical distribution of PM2.5, O3 and NOx in the Pearl River Delta. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 220, 117083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Dada, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Xie, C.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Cai, J.; Yao, L.; et al. A 3D study on the amplification of regional haze and particle growth by local emissions. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J. Progress of air pollution control in China and its challenges and opportunities in the ecological civilization era. Engineering 2020, 6, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, J.; Tao, W.; Yi, K.; Xu, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. Control of both PM2.5 and O3 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei and the surrounding areas. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 224, 117259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yin, D.; Yu, Y.; Kang, S.; Qin, D.; Dong, L. PM2.5 and O3 pollution during 2015–2019 over 367 Chinese cities: Spatiotemporal variations, meteorological and topographical impacts. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Tie, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, R.; Mao, X.; Zhou, G.; Chang, L. Long-term trend of O3 in a mega City (Shanghai), China: Characteristics, causes, and interactions with precursors. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Gong, K.; Wu, Z.; Chen, M.; Qin, M.; Huang, L.; Hu, J. Double high pollution events in the Yangtze River Delta from 2015 to 2019: Characteristics, trends, and meteorological situations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Zhao, T.; Cheng, X.; Gong, S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y. Inverse relations of PM2.5 and O3 in air compound pollution between cold and hot seasons over an urban area of east China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Bates, K.H. Anthropogenic drivers of 2013–2017 trends in summer surface ozone in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal distribution of ground-level ozone in China at a city level. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, W. Potential sources and formations of the PM2.5 pollution in urban Hangzhou. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Herrmann, E.; Nie, W.; Petäjä, T.; Kerminen, V.M. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, L.; Yao, C.; Xie, T.; Rao, L.; Lu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, S. Relationships between chemical elements of PM2.5 and O3 in Shanghai atmosphere based on the 1-year monitoring observation. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 95, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S. Relationship between summertime concurring PM2.5 and O3 pollution and boundary layer height differs between Beijing and Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, V.T.; Wang, T. Observational study of ozone pollution at a rural site in the Yangtze Delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 4947–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duan, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Yang, Y.; Cu, X. Spatiotemporal trends of PM2. 5 concentrations and typical regional pollutant transport during 2015–2018 in China. Urban Clim. 2020, 34, 100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, R.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Chen, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X. 2014: Origin of air pollution during a weekly heavy haze episode in Hangzhou, China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, J. Variation characteristics of atmospheric pollutants’ concentration and its relations with meteorological factors in Nantong City. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 9248–9254. [Google Scholar]
- Pongkiatkul, P.; Oanh, N.T.K. Assessment of potential long-range transport of particulate air pollution using trajectory modeling and monitoring data. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, B.A.; Kim, F.; Jeong, C.H.; Lee, D.W.; Hopke, P.K. Evaluation of the potential source contribution function using the 2002 Quebec forest fire episode. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3719–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigler, J.M.; Lee, X. Recent trends in anthropogenic mercury emission in the northeast United States. J. Geophy. Res. 2006, 111, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ji, D.; Wang, Y. Long-range transport and regional sources of PM2.5 in Beijing based on long-term observations from 2005 to 2010. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.; Lin, J. Transport pathways of PM10 during the spring in northwest China and its characteristics of potential dust sources. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhou, G. Analysis of characteristics and meteorological causes of PM2.5-O3 compound pollution in Shanghai. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2019, 37, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Draxler, R.R. TrajStat: GIS-based software that uses various trajectory statistical analysis methods to identify potential sources from long-term air pollution measurement data. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2009, 24, 938–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romshoo, S.A.; Bhat, M.A.; Beig, G. Particulate pollution over an urban Himalayan site: Temporal variability, impact of meteorology and potential source regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate PCB sources in Chicago. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, Y.F.; Xiao-Yun, W.U. Atmospheric compound pollution characteristics and the effects of meteorological factors in Jiangsu Province. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 2830–2839. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; et al. Air quality changes during the COVID-19 lockdown over the Yangtze River Delta Region: An insight into the impact of human activity pattern changes on air pollution variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitada, T.; Kitagawa, E. Numerical analysis of the role of sea breeze fronts on air quality in coastal and inland polluted areas. Atmos. Environ. 1990, 4, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, C.; Schipa, I.; Tanzarella, A.; Conte, D.; Marra, G.P.; Miglietta, M.M.; Rizza, U. A numerical study of the effect of sea breeze circulation on photochemical pollution over a highly industrialized peninsula. Meteorol. Appl. 2010, 17, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, N.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Feng, T.; Li, G. Impacts of sea-land and mountain-valley circulations on the air pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH): A case study. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

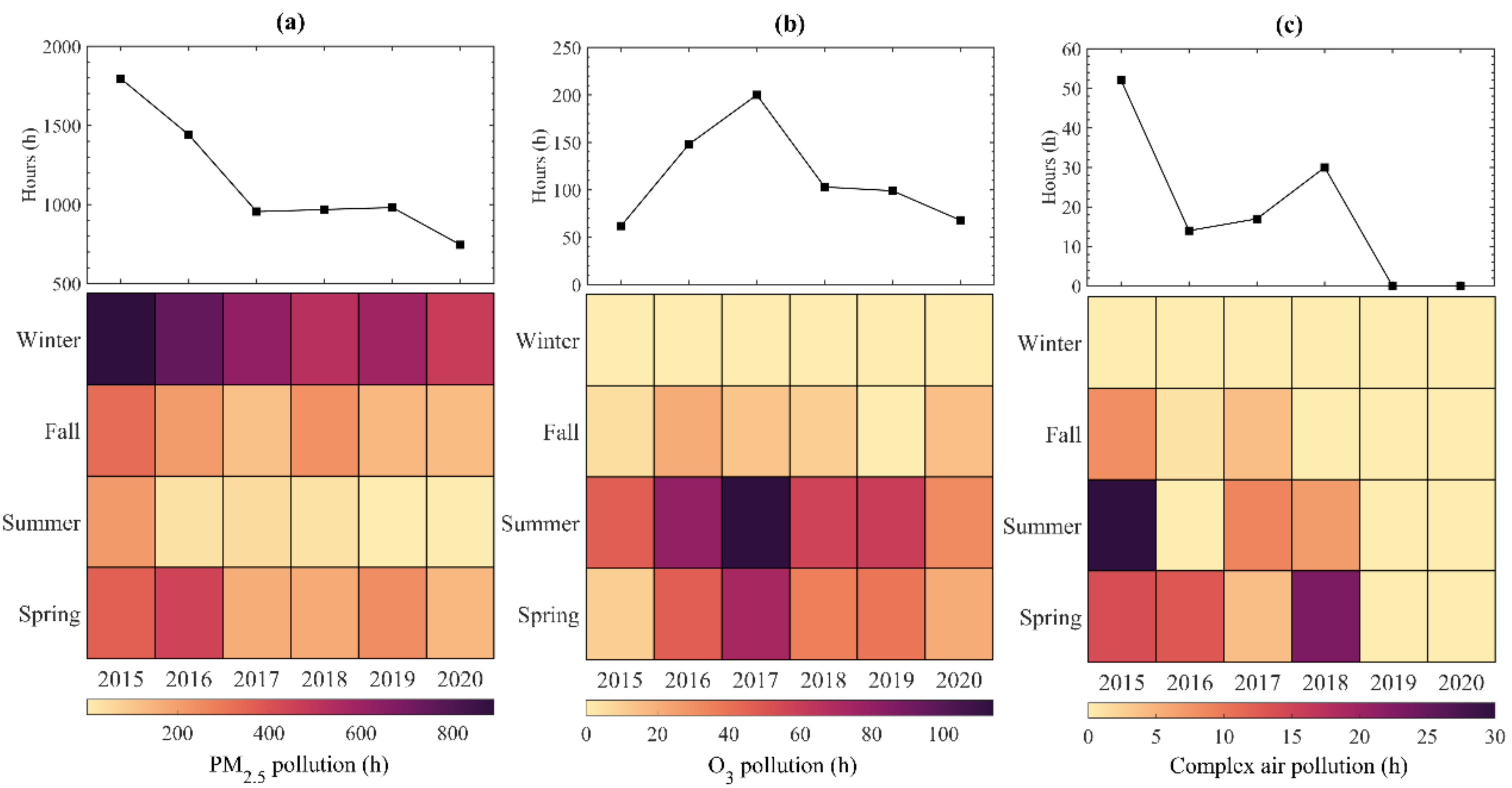
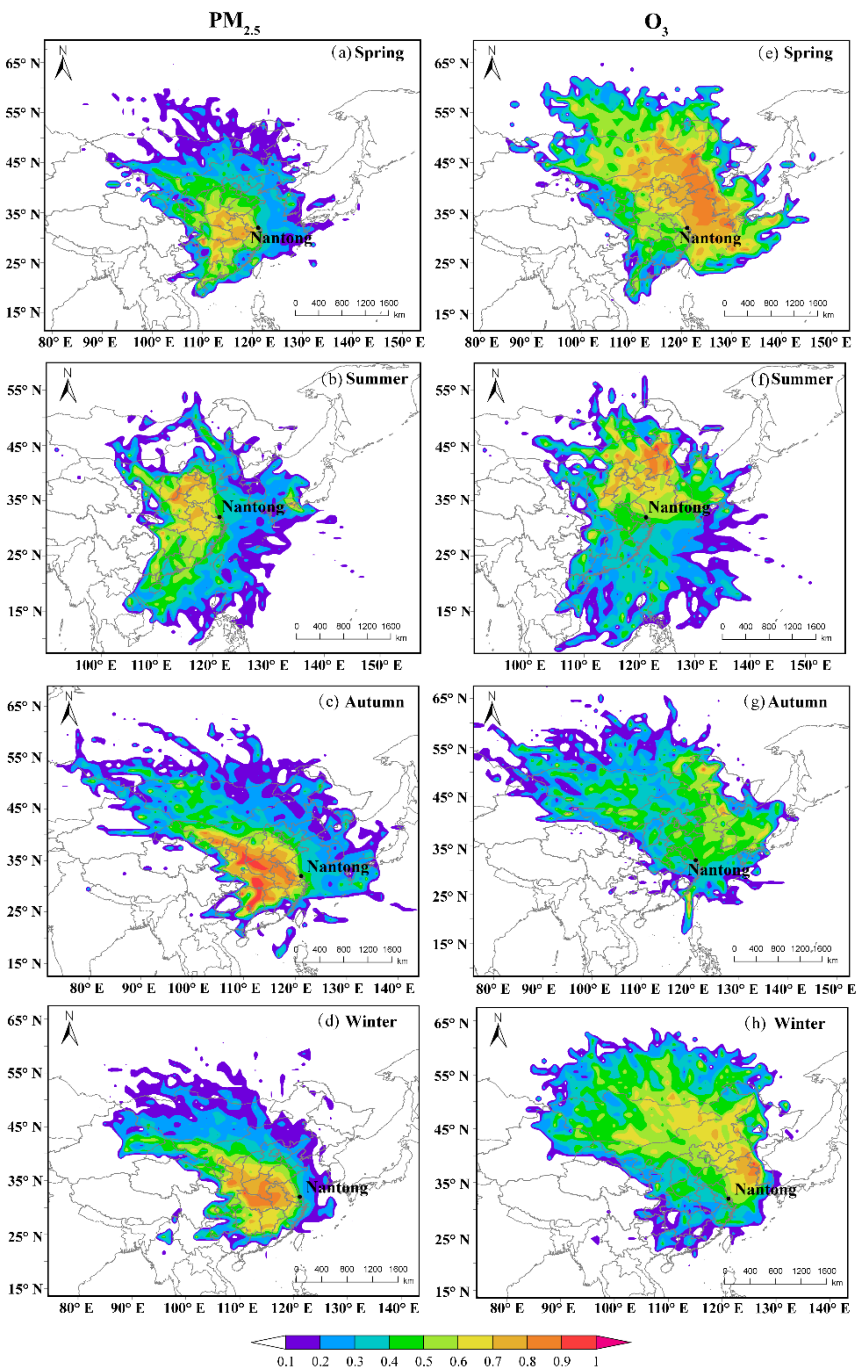
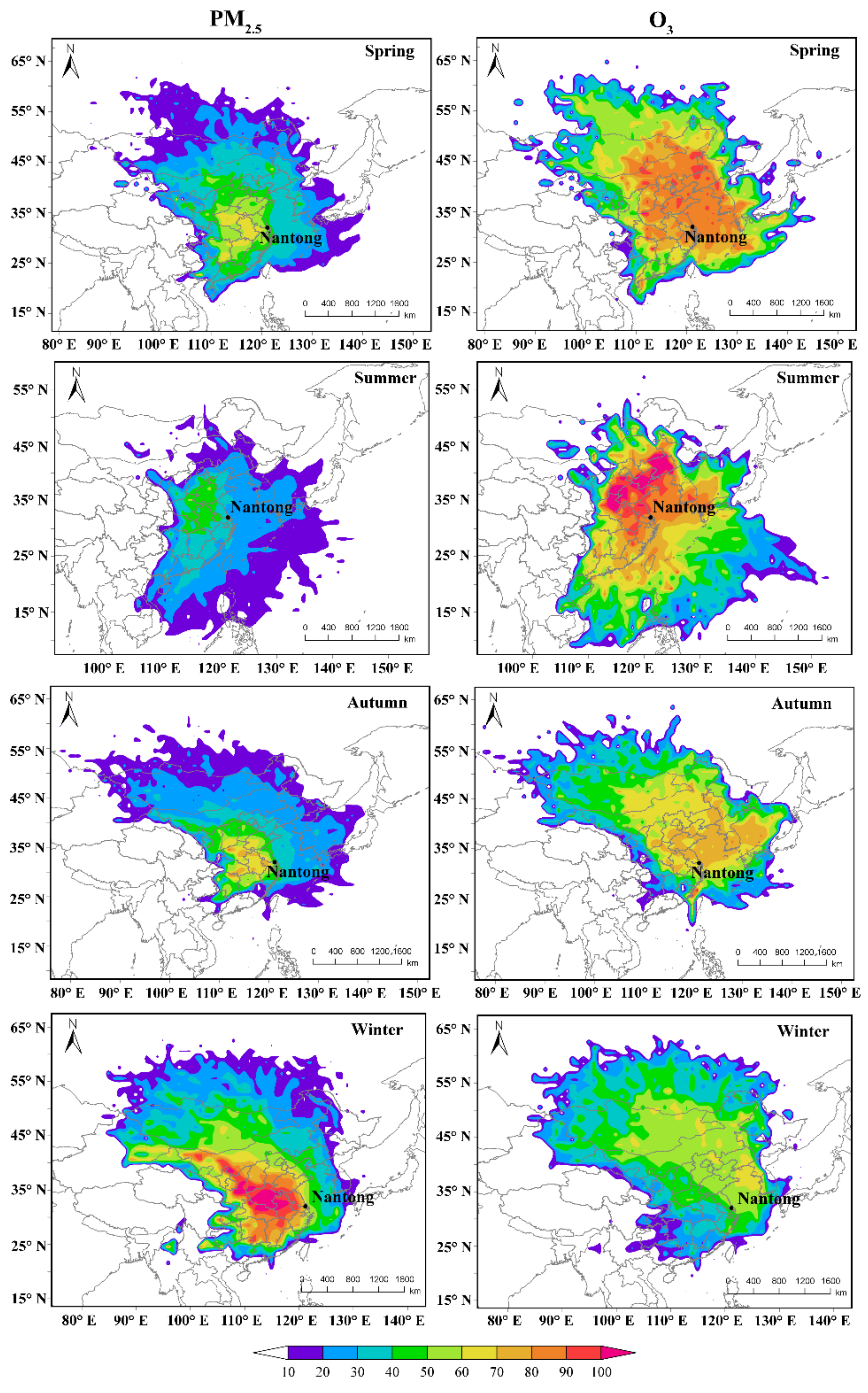
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (μg/m−3) | 43 | 29 | 36 | 62 |
| O3 (μg/m−3) | 62 | 78 | 70 | 52 |
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | lr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 56.5 ± 36.1 | 46.1 ± 29.3 | 39.5 ± 23.8 | 41.4 ± 28.8 | 37.2 ± 23.5 | 34.7 ± 24.0 | −3.9 |
| O3 | 72.2 ± 26.7 | 71.2 ± 28.1 | 77.3 ± 28.2 | 69.6 ± 25.2 | 68.0 ± 25.1 | 67.3 ± 22.1 | −1.2 |
| Season | Cluster | Ratio (%) | PM2.5 | O3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Std (μg/m−3) | P_Ratio (%) | Mean ± Std (μg/m−3) | P_Ratio (%) | |||
| Spring | 1 | 22.00 | 18.89 ± 30.50 | 30.61 | 87.00 ± 45.37 | 25.53 |
| 2 | 30.91 | 53.66 ± 31.22 | 46.62 | 77.14 ± 55.97 | 59.57 | |
| 3 | 29.67 | 35.84 ± 21.53 | 14.23 | 82.57 ± 36.82 | 8.51 | |
| 4 | 9.52 | 36.89 ± 26.87 | 7.47 | 80.04 ± 38.29 | 6.38 | |
| 5 | 7.90 | 26.95 ± 17.71 | 1.07 | 82.15 ± 28.27 | 0.00 | |
| Summer | 1 | 11.08 | 35.83 ± 24.43 | 26.76 | 101.6 ± 54.8 | 21.25 |
| 2 | 31.55 | 34.54 ± 20.02 | 38.03 | 82.02 ± 64.63 | 58.75 | |
| 3 | 16.12 | 16.77 ± 9.10 | 1.41 | 50.32 ± 37.50 | 2.50 | |
| 4 | 32.33 | 27.70 ± 17.77 | 29.58 | 84.34 ± 38.72 | 10.00 | |
| 5 | 8.93 | 25.31 ± 14.78 | 4.23 | 60.47 ± 51.53 | 7.50 | |
| Autumn | 1 | 41.02 | 38.35 ± 27.08 | 38.24 | 72.31 ± 40.45 | 46.67 |
| 2 | 24.91 | 33.27 ± 24.54 | 20.10 | 66.16 ± 34.76 | 26.67 | |
| 3 | 14.77 | 34.06 ± 25.93 | 11.27 | 59.31 ± 30.12 | 0.00 | |
| 4 | 11.20 | 25.38 ± 17.94 | 2.45 | 71.49 ± 31.81 | 0.00 | |
| 5 | 8.10 | 63.83 ± 42.20 | 27.94 | 60.15 ± 52.75 | 26.67 | |
| Winter | 1 | 13.57 | 50.48 ± 38.69 | 8.98 | 56.88 ± 25.32 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 35.26 | 77.40 ± 50.35 | 50.08 | 49.24 ± 30.17 | 0.00 | |
| 3 | 25.47 | 63.46 ± 45.72 | 25.27 | 50.98 ± 28.02 | 0.00 | |
| 4 | 19.45 | 37.37 ± 30.21 | 6.24 | 56.76 ± 23.30 | 0.00 | |
| 5 | 6.25 | 79.27 ± 39.00 | 9.44 | 32.57 ± 27.85 | 0.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, M.; Hu, A.; Chen, J.; Wan, B. Evolution, Transport Characteristics, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in a Coastal City of China during 2015–2020. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101282
Lv M, Hu A, Chen J, Wan B. Evolution, Transport Characteristics, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in a Coastal City of China during 2015–2020. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(10):1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101282
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Min, Anyong Hu, Jun Chen, and Bingcheng Wan. 2021. "Evolution, Transport Characteristics, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in a Coastal City of China during 2015–2020" Atmosphere 12, no. 10: 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101282
APA StyleLv, M., Hu, A., Chen, J., & Wan, B. (2021). Evolution, Transport Characteristics, and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 and O3 Pollution in a Coastal City of China during 2015–2020. Atmosphere, 12(10), 1282. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12101282






