Abstract
As in other parts of the world, air pollution over West and Central Africa has major health and meteorological impacts. Air quality assessment and its possible sanitary impact have become essential even in medium-sized towns, therefore amplifying the need for easy-to-implement monitoring methods with low environmental impact. We present here the potential of magnetic methods to monitor air quality at street level in the medium-sized city of Maroua (northern Cameroon) affected by dust-laden desert winds. More than five hundred (544) samples of bark and leaves taken from Neem trees in Maroua were analyzed. Magnetic susceptibility, saturation remanence, and S-ratio were found to determine the concentration and nature of magnetic particles. They are dominated by magnetite-like particle signals as a part of particulate emissions due to urban activities, including both traffic, composed of a substantial proportion of motorcycles, and wood burning for food preparation. We show that both bark and leaves from Neem trees are adequate passive bio-recorders. The use of both enables different times and heights to be sampled, allowing for the high-resolution monitoring, in terms of spatialization, of various urban environments. Particle emissions require assessment and screening that could be carried out rapidly and efficiently by magnetic methods on bio-recorders, even in cities impacted by dust-laden wind.
1. Introduction
Atmospheric pollution resulting from urban traffic is now fully recognized as a major health issue in cities of any size (e.g., [1]). In recent decades, pollution by airborne particulate matter (PM) has been acknowledged as responsible for a growing range of health hazards leading to premature deaths [2,3,4,5]. Most of the health burden is likely related to chronic exposure to PM2.5 (i.e., airborne particles with aerodynamic dimensions less than 2.5 μm) (e.g., [6]). According to the WHO [7], 4.2 million deaths every year are attributed to exposure to ambient (outdoor) air pollution.
The rapid urbanization and population growth in African cities have resulted in a significant increase in the emission of pollutants in urban centers. Owili et al. [8] demonstrated that ambient PM2.5 is associated with under-five and maternal mortality in Africa. It is expected that anthropogenic emissions will triple (including traffic, biomass burning, and oil and mining industries) between 2000 and 2030 [9]. Recent observations in western African cities [10] indicate that the PM2.5 concentrations exceed the WHO recommendations by a factor of 3. Western African cities have specific fine particle sources that are either natural or anthropogenic. The fleet of light and heavy-duty vehicles is old and includes a large number of motorcycles. Motorcycles, specifically 2-stroke engines using a mix of oil and gasoline, emit more PM than cars [11]. It results in large emission factors of combustion aerosols [12]. Other specific sources, such as charcoal production, biomass burning, open stove and barbecue cooking, and waste burning, have a significant impact on air quality and health [13] in western African cities. On the other hand, aeolian mineral dust is also a large contributor to PM in the cities located downwind arid areas of the Sahel and the Sahara, such as the city of Maroua in northern Cameroon. In southern West Africa, the contribution of dust follows a seasonal cycle driven by monsoon and Harmattan flow alternations [14,15].
Over the last decade, environmental magnetism has proven its cost-effectiveness for the monitoring of atmospheric pollution [16]. Magnetic properties of pumped-air filters are related to the atmospheric PM2.5 [17] or the nitrogen oxides (NOX) concentrations [18]. Biocollectors-based environmental magnetism is a rapid and non-destructive way to monitor emitted particle dispersion in various environments ([16] and reference therein). Tree leaves or lichens and, to a lesser extent, tree bark, have been extensively used in recent years [1,19,20,21,22,23] as bio-monitors. Plant leaves, particularly tree leaves, can trap airborne particles, making them good passive monitors of ambient airborne pollution [24]. Tree leaves have been used as a bio-monitor for air pollution in many cities worldwide as well as in heavily polluted areas (see [25] for example) and with various plant species [26,27,28].
The rapid development of urban areas in West Africa raises a challenge in the deployment of air quality monitoring networks. Most of the largest conurbations, and moreover, medium-sized cities, are still not equipped with standard air quality monitoring devices. Biomagnetism is a promising tool to monitor particulate pollution spatial distribution in cities with scarce observations as it is based on easy-to-implement recorders with minimal costs [29]. Moreover, to date, environmental magnetism has not been tested to assess pollution in West and Central African cities, but it has the potential to facilitate simple and inexpensive monitoring. A particularity of the western African urban environments is that they are strongly affected by dust-laden winds, which dramatically impairs air quality. Besides sophisticated chemical speciation of PM, the use of magnetic methods on passive biocollectors could be implemented to reveal the impact of transported dust on local air quality.
To answer this question, we measured magnetic susceptibility and we used magnetic parameters to infer the mineralogy in order to monitor air pollution in Maroua, a medium-sized city of northern Cameroon. We used both leaves and bark from Neem trees that are naturally present in the city to track the dispersion of airborne particles related to anthropogenic activities. In addition, the results from isothermal remanent magnetizations (IRMs) and S-ratio measurements helped to distinguish between iron oxides blown by the wind and those derived for traffic, as well as to assess the resuspension processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The city of Maroua (10°35′ N, 14°18′ E) is located in the extreme northern area of Cameroon (Figure 1). This part of Cameroon has a Sudano-Sahelian climate characterized by an average temperature of 33 °C and an annual thermal amplitude of approximately 21 °C. The annual precipitation is approximately 800 mm. There are two contrasting climatic seasons: a short rainy season and a long dry season. The short rainy season starts in June and ends in October with a precipitation peak in August. The dry season, almost without any precipitation, extends from October to May. Between November and March, a frequent and intense wind, called Harmattan coming mostly from the North or Northeast, sweeps the region. Harmattan is a dry wind and often laden with dust particles coming from northern desertic regions.
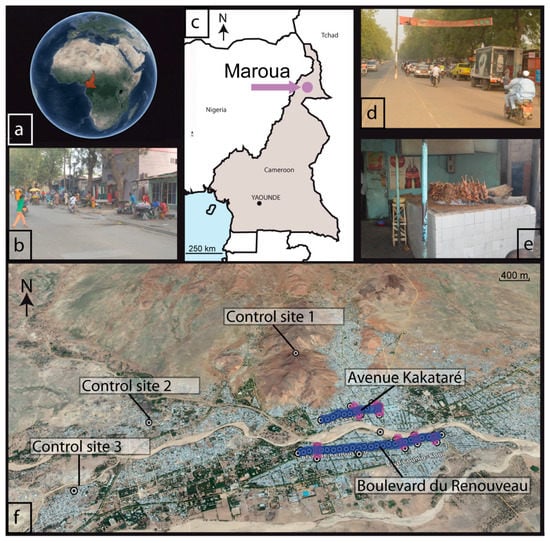
Figure 1.
Localization of sampling sites modified from @Google Earth (a,c,f) and photographs (@Daouda Dawai) illustrating anthropogenic activities in the streets of Maroua, Cameroon (b,d,e).
Maroua is built in the Diamare plain bordered on the West by the Mandara Mountains. Dominant soils in the region are vertisols and ferruginous soils derived from quaternary sediments. A few fersiallitic soils of low thickness are also present, mostly derived from Neoproterozoic metagabbros and metavolcanic and metasedimentary rocks surrounding the city (i.e., metavolcanic rocks, [30]).
With a population of approximately 400,000, Maroua is the fifth-most populated city in Cameroon. The main economic activities are services, trade, agriculture, and craft production. Industrial activity is virtually nonexistent. Cars and motorcycles, regularly used by the population for their daily journeys, are the major sources of anthropogenic airborne particle pollution in the city. In addition, wood burning and charcoal making, as in many other places in West Africa [12] can represent a source of particulate matter [10].
The sampling on the Neem trees was focused along the two main roads of Maroua, namely, “Boulevard du Renouveau” (D) (best known by the name of “Deux voies Domayo”) and “Avenue Kakataré” (or “Avenue du Marché”) (K). Several economic activities are concentrated on these two main roads, such as bars, restaurants, shops, joinery and street trading, thus draining important daily traffic. Boulevard du Renouveau and Avenue Kakataré are 2.60 km and 1.38 km long, respectively, and roughly east–west oriented. Located in the heart of Maroua, these two roads are separated by a distance of 0.6 to 0.9 km. Like most of the roads in Maroua, these roads are paved but locally degraded. They are planted with rows of Neem trees on their edges (Figure 1). Additional sampling was also realized in some adjacent streets (see Figure 1). Control sites correspond to three sites located in the peripheral districts of Maroua, namely, Doualaré (site 1), Palar (site 2) and Ouro-Tchédé (site 3). The control site of Doualaré is located north of the study area, ~1.5 km from Avenue Kataré and ~2.3 km from Boulevard du Renouveau. The control sites of Palar and Ouro-Tchédé neighborhoods, ~1.7 km apart from each other, are located west of the study areas. The control site of Palar is located ~3 km from Avenue Kakataré and ~2.7 km from Boulevard du Renouveau, whereas the control site of Ouro-Tchédé is located approximately ~4.1 km from Avenue Kakataré and ~3.6 from Boulevard du Renouveau.
The Neem (Azadirachta indica, A. Juss), a member of the Meliaceae family, is a tropical evergreen tree that originates from the Indian subcontinent. It is now valued worldwide as an important source of phytochemicals for use in human health and pest control. It is a hardy fast-growing small-to-medium-sized tree (7 to 15 m for mature specimens), with a straight trunk, wide and spreading branches and moderately thick, rough longitudinally fissured barks. It can tolerate high temperatures, as well as poor or degraded soil. It requires little water (450 to 1500 mm) and plenty of sunlight. The young leaves are reddish to purple, while the mature leaves are bright green, consisting of petiole, lamina, and the base that attaches the leaf to the stem and may bear two small lateral leaf-like structures known as stipules [31,32].
2.2. Sampling
A total of 435 leaf samples and 109 bark samples of Neem trees were collected from Boulevard du Renouveau, Avenue Kakataré, and adjacent streets (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Leaf and bark samples were also collected in the control sites far from the urban center, where traffic concentration is low (Figure 1). Site 1 is located in an almost uninhabited sector, and sites 2 and 3 are located in a semi-rural area.
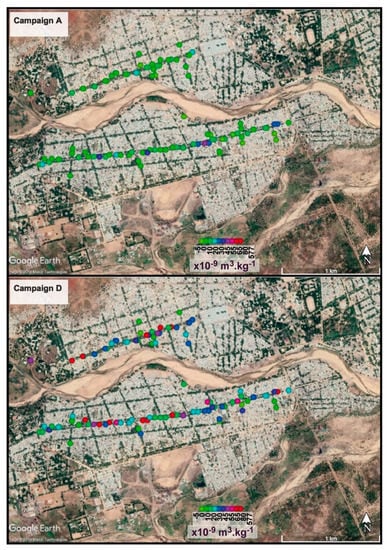
Figure 2.
Mass magnetic susceptibility obtained on leaves during campaigns A (mid-August) and D (end-December).
Samples were collected on trees on both sides of the roads at ~100 m spacing for leaves and 200 m spacing for bark. Four sampling campaigns were conducted on the same trees from August to December 2014 to monitor potential seasonal variability. The first (A) and second (B) sampling campaigns were carried out in mid-August and at the end of September, respectively, i.e., during the rainy season, while the last two (C and D) were completed during the dry season, in mid-November and at the end of December, respectively. The collection of bark was only performed during the first (A) (August) and third (C) (November) campaigns. Samples were collected using nonmagnetic packaging (paper or plastic). They were taken at different heights, between 1 and 1.5 meters from the ground for the bark and 1.5 and 2.5 meters for the leaves. These heights were chosen to represent the mean breathing exposure for pedestrians. Leaves were taken at the lowest possible level. During the rainy season, samplings were performed one or two days after the last precipitation.
The samples, unwashed, were dried for 3 to 4 days at constant temperature of 45 °C in a drying oven at the University of Maroua (Cameroon). The dried leaves and bark were subsequently crushed by hand.
2.3. Magnetic Measurements and Microscopic Observations
Magnetic measurements were carried out in the Geosciences Environnement Toulouse (GET) laboratory in France.
Bulk mass magnetic susceptibilities were measured for all samples using a KLY-3S Kappabridge (AGICO, Brno).
Isothermal remanent magnetizations (IRMs) were acquired for a total of 43 leaf and bark samples. IRMs were induced using a Pulse Magnetizer (Magnetic Measurements) and measured using a JR5 magnetometer (AGICO, Brno). The JR5 spinner magnetometer has a sensibility of 2.4 × 10−6 A/m (AGICO manual specification). Its use may prevent an accurate determination of the magnetization for very weak samples.
Reverse IRMs at 300 mT (IRM-300 mT) were acquired to calculate the S ratio, which is given by IRM-300 mT/SIRM [33].
IRM acquisition curves were obtained on 7 leaf and 7 bark samples. IRM acquisitions were analyzed using the curve-fitting program MAX UnMix [34] (available online at http://www.irm.umn.edu/maxunmix, accessed on 7 July 2021), based on analyses developed by [35,36,37]. This software uses skew-normal distributions that can be described with a mean coercivity (Bh), a dispersion parameter (DP, equivalent to one standard deviation in log-space), and a skewness factor (S). The magnetic mineralogy is interpreted from the range of coercivities derived from the IRM parameters.
Magnetic particles were investigated in situ by electron microscopy and imaged using a JEOL (JSM-6300 scanning electron microscope (SEM) housed at the GET laboratory (Toulouse, France) operating at 20 keV with an electron dispersive system (EDS) that allows for a rapid qualitative characterization of the chemical composition.
3. Results
3.1. Magnetic Content
Mass susceptibility (χ) is commonly used as a proxy for the concentration of magnetic minerals and mainly magnetite [22]. The three control area sites present “near-zero” susceptibility values between −5 and 5.3 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 (Figure 3), reflecting the dominance of the diamagnetism of the leaves and bark themselves as organic compounds.
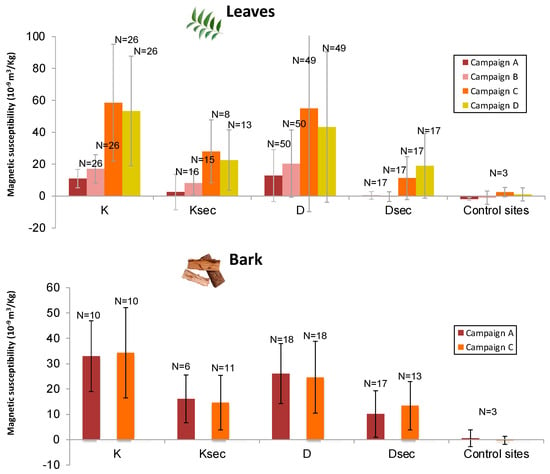
Figure 3.
Mean leaf and bark mass magnetic susceptibility values by sector and sampling campaign, showing the variations of magnetic susceptibility on leaves as a function of the season and the stability of the bark’s values. K is Avenue Kakataré and D, Boulevard du Renouveau. Ksec and Dsec refer to secondary streets crossing perpendicularly K and D, respectively (see Figure 1 and Figure 2 for localization). Error bars represent the standard deviation, N the number of data.
For downtown Maroua, considering all campaigns together, mass susceptibilities (χ) range between 42.5 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 and 577.4 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 for leaves and between 2.0 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 and 64.0 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 for bark samples (Figure 3). For both bark and leaves, magnetic susceptibility values are higher in the main streets than in their adjacent secondary streets.
Leaf χ values display high variability (Figure 2) depending on the street types (i.e., main or secondary roads) and the season (dry versus rainy). Overall, the χ values are significantly higher than those recorded in the control areas (Figure 3). Additionally, despite the high intrinsic variability observed (Figure 2 and Figure 3), leaf samples taken during the dry season give significantly higher χ values than those taken during the rainy season for a given road. Leaves taken during the dry season on the main streets show the highest recorded χ values up to 221 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 (discarding an extreme value of 577 × 10−9 m3 kg−1, probably reflecting uncontrolled contamination). Comparing main and secondary streets, for Kakataré Avenue, for example, a mean χ value of 58.5 ± 36.5 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 is recorded during campaign C (dry season) versus a mean value of 28.8 ± 19.7 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 for its secondary streets. During the wet season, leaves from Kakataré Avenue and its secondary streets display mean χ values of 11.00 ± 5.8 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 and 2.6 ± 11.2 × 10−9 m3 kg−1, respectively. Domayo Avenue displays a higher and more complex variability in magnetic susceptibility. Nevertheless, as for the Kataré Avenue, higher χ values are found during the dry season than during the rainy season. Magnetic susceptibilities are similarly greater on the main road than in the secondary street network independently of the season. It may be noted that leaves from the streets cutting Kakataré Avenue display greater χ values than those near Domayo Avenue. The χ values from the secondary streets intersecting Domayo Avenue present close-to-zero values in the same range as the control sites.
In contrast, bark χ values display similar values between the dry and wet seasons (Figure 3). For instance, the average values for Avenue K vary from 33.0 ± 14.0 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 for the wet season to 34.3 ± 17.8 × 10−9 m3 kg−1 for the dry season. Magnetic susceptibility values for bark are less influenced by climatic conditions. The mean χ values in the urban area are significantly higher than those in the control area (down to −0.3 ± 1.6 × 10−9 m3kg−1) for both the main and secondary streets (Figure 2 and Figure 3). Bark χ is greater for main avenues than secondary intersecting streets.
Isothermal remanent magnetization (IRM) is another parameter that can reflect the concentration of magnetic particles. Here, IRM@2T comprised between 3.52 × 10−5 and 1.13 × 10−3 Am2 kg−1 and between 4.26 × 10−5 and 3.18 × 10−4 Am2 kg−1 for the leaves and bark, respectively. IRM@2T and χ display linear correlations (Figure 4), indicating that IRM roughly reflects mainly the low to moderate coercivity magnetite-like content, at least for χ less than 120 × 10−9 m3 kg−1. However, IRM can also be influenced by the magnetic composition and grain size, as we will discuss in the next section. Due to the increase in the intensity of the measurable signal linked to the IRM@2T procedure, this parameter allows qualifying the number of magnetic minerals when χ is close to the limit of detection as in the control areas.
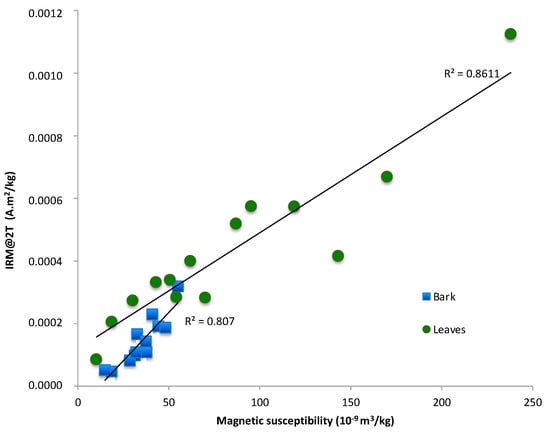
Figure 4.
Saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM) as a function of mass magnetic susceptibility depicting correlations for both leaves (green dots) and bark (blue squares).
In the two control sites measured, sites 2 and 3, IRMs@2T obtained on bark samples (2 samples) did not present any significant differences between the dry and wet seasons (Figure 5). In contrast, leaves show a relatively significant increase in magnetic content during the dry season (Figure 5). It can also be noted that the values of IRM@2T from control areas are two orders of magnitude lower than those from the urban area.

Figure 5.
Individual isothermal remanent magnetizations (IRMs) obtained at 2 T for control area site and by campaign. Bark does not present any significant difference between the dry and wet seasons, while leaves display an enhanced magnetic concentration during the dry season compared to the wet season.
3.2. Magnetic Characterization
The shape of the IRM acquisition curves reflects the magnetic mineralogy. The comparison of sites from the Avenue Kakatare/Domayo (12 samples) and one control site (site 3, 2 samples) indicates the presence of both moderate coercivity magnetic minerals (magnetite-type, including maghemite and Ti-magnetite) and high coercivity magnetic minerals (hematite/goethite) (Figure 6). We perform an analysis of the IRM acquisition curves [34] to better estimate the different components. The moderate coercivity component is characterized by a mean coercivity (Bh) between 44 and 80 mT, with the dispersion parameter (DP) decreasing from 0.49 to 0.39 while Bh increases. High DP (>0.45) could indicate the presence of a low and a moderate coercivity component. Accurate determination of low coercivity components is hampered by the fact that the acquisitions were performed with only 20 acquisition steps with the objective of identifying the presence of high coercivity minerals. The high coercivity component is difficult to extract because its Bh is sometimes greater than the maximum field applied (2 T). When reasonably identifiable, the high coercivity component displays Bh values superior to 2000 mT (see Figure 6), which probably corresponds to goethite [38,39,40] or fine-grained hematite [41].
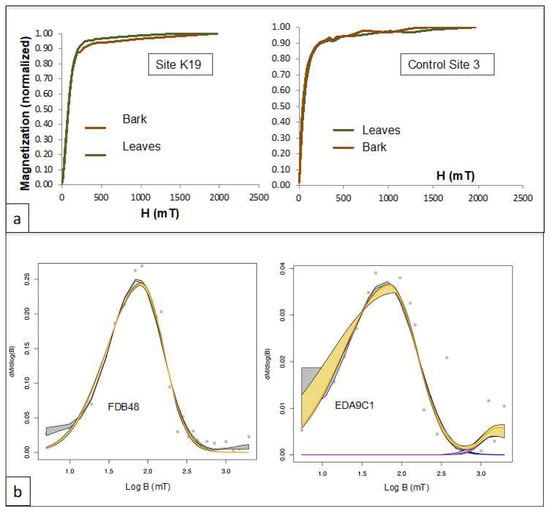
Figure 6.
Isothermal Remanent Magnetization. (a) IRM acquisition curves for samples from site K19 and the control site 3 taken during campaign C (mid-November). Curves do not saturate for fields up to 2T, indicating the presence of high coercivity minerals (goethite and/or hematite). At site K19, bark displays a higher contribution to the IRM of high coercivity minerals. (b) IRMs showing a high coercivity component in the side streets highlighted by the analysis of IRM components using the MaxUnmix program [34]. Shown in gray are the data, black is the spline, yellow is the fitting model, and pink and purple are components 1 and 2, respectively. Shaded areas of each color represent error envelopes of 95% confidence intervals.
The relative proportion of high coercivity versus moderate coercivity magnetic minerals varies as a function of sites and differs between leaves and bark. High coercivity minerals are slightly more represented in bark samples and in control areas. To further investigate this trend, we use the S-ratio, which is a sensitive parameter for estimation of the relative proportion of hematite and goethite versus magnetite in terms of magnetic remanence (see, for example, [42]). Values approaching 1 indicate the dominance of magnetite on the magnetic signal. In Maroua, this ratio varies from 0.79 to 0.98 for both leaves and bark. While this ratio indicates that the magnetite-like signal is preponderant, this ratio also evidenced the important abundance of hematite [42]. There is no identifiable difference between the dry and wet seasons. Figure 7 presents the mean S-ratio by sector and all campaigns combined. It shows that the high coercivity component increases toward zones with lower traffic, with the lowest values of S-ratio found in control areas sites (Figure 7). Bark samples present lower S-ratios than leaf samples at all sites. This indicates that their IRMs are influenced by both a moderate (magnetite-like) component and a high coercivity (hematite/goethite) component. Conversely, the hematite/goethite component is only detectable for leaves in the control areas. In the Maroua streets (main and secondary), the magnetite-like signature is dominant.
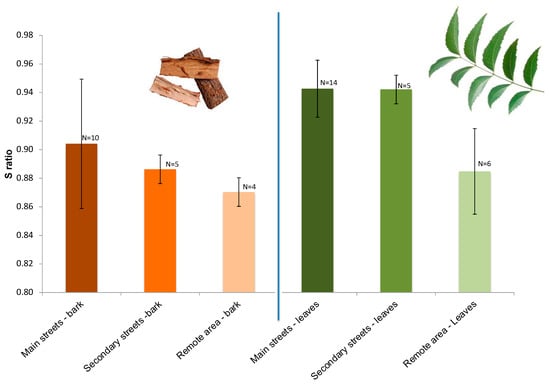
Figure 7.
Mean S-ratio (all campaigns together) for each site type. Error bars represent the standard deviation.
3.3. SEM Observation
We analyzed eight samples under the SEM comprising six leaves and two bark samples (Figure 8 and Figure 9). The observation of the PM content shows that large detrital particles (> to 10 microns) dominate (Figure 8a,b). They can form clusters on some leaves (Figure 8a). EDS spectra (Figure 8e,f and Figure 9b,d,f) reveal mainly Mg, Al, Ti, Si and Fe in these particles. Fe-rich particles are not very common and relatively small (<10 microns).
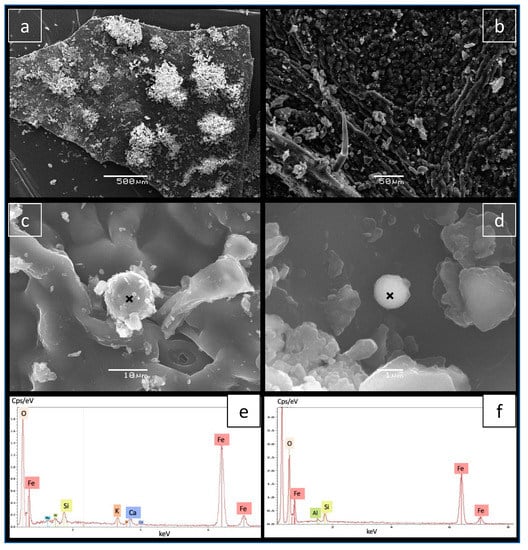
Figure 8.
SEM observations (a–d) and EDS spectra (e,f) acquired on the location marked by the cross on c and d, respectively. (a) Leaf from site D13 taken during campaign D. All others: leaf from site D48 taken during campaign D.
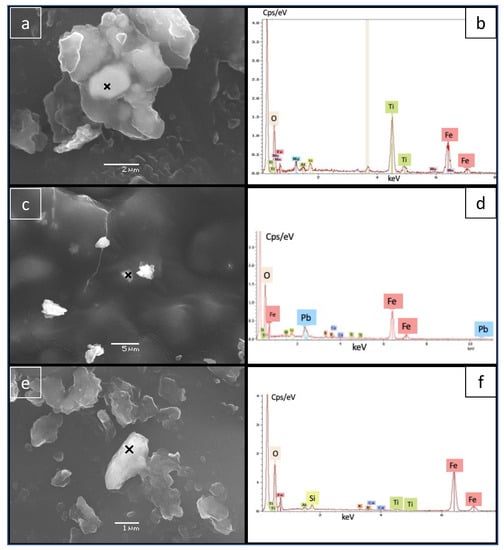
Figure 9.
SEM observations on a leaf from site D48 taken during campaign D (a,c,d) and respective EDS spectra (b,d,f) acquired on the location marked by the cross.
An apparently spherical magnetite (Figure 8c,d) that could be a typical spherule derived from combustion processes [43,44,45] is observed in sample DD48 from Domayo Avenue. This sample, taken during the dry season, displays a high magnetic susceptibility of 143 × 10−9m3kg−1. Apart from this occurrence, in all observed samples, Fe-oxides and non-spherical iron-rich particles are dominant, and magnetic spherules are almost absent. This indicates that non-exhaust emissions related to brakes and tyres prevail [46]. Figure 9e,g present irregular and platy Fe-rich particles. In some cases, Fe-rich particles are associated with Pb (Figure 9c,d). Although aeolian dust may occasionally contain Pb [47], this association clearly indicates an anthropogenic origin (see, e.g., [48,49]).
4. Discussion
4.1. Anthropogenic Pollution and Traffic-Related Particles
The aim of the approach presented here is to develop a method applicable to endemic tree species with an easy sampling of many biocollectors that can be applied in medium-sized cities where monitoring stations are sparse or nonexistent. We tested it for the city of Maroua, where different concentrations and types of magnetic airborne particles are found in the considered urban microenvironments (main, secondary roads and control areas) that can be tracked in the magnetic signal.
Control sites display mostly near-zero or negative χ values. Such values are attributed to the dominance of the diamagnetism of the leaves and bark themselves as organic compounds. They were chosen, far from anthropogenic sources (Figure 1), as witnesses of the lithic input. This lithic input exhibits a weak ferrimagnetic signal. Magnetic susceptibilities and hence magnetic particle contents increase toward zones with more human activities and traffic. This strongly suggests that most ferrimagnetic particles detected by magnetic susceptibility measurements originate from anthropic activities and not from wind-borne mineral dust.
Mineral dust transported over western Africa is known to be rich in iron oxides, mainly hematite and goethite [50,51,52]. Goethite seems to dominate in all regions [50,53,54], although magnetic methods may be more sensitive to hematite content [55]. In Maroua, the S-ratio results (see Figure 7) show increasing hematite/goethite proportion toward areas with less traffic, strongly suggesting that these minerals are part of the natural regional lithic dust component that can be wind-blown. The presence of iron-rich oxides incorporating Ti (Figure 9a,b) also indicates a lithic origin of some of the iron-rich particles, in accordance with the regional geology. However, their occurrence is very scarce in both bark and leaf samples (Figure 3), inducing only weak magnetic susceptibility. Therefore, observed variations in magnetic susceptibility are interpreted as reflecting mostly the anthropogenic contribution of the urban magnetic dust that masks the magnetic lithic fraction. This demonstrates that magnetic methods are a useful tool to monitor urban particulate pollution even in environments affected by Saharan dust and not only in megacities.
Traffic is the main source of magnetic particles in downtown Maroua, since neither industrial plants nor mining sites are present. Motorcycles represent an important part of circulating vehicles, as in other African cities. Particulate emissions from these vehicles are different from those of diesel engines, mainly due to the lubricating oil permanently added in two-stroke engines [56]. Two-stroke engines release a large amount of both particles and gases [57]. For instance, two-stroke motorcycles have been shown to emit more ultrafine particles (see a review in [58,59]). This could explain the large magnetic susceptibility values obtained in Maroua. Comparing the magnetic susceptibility data obtained on deciduous and evergreen leaves in some other cities, the values obtained in Maroua fall within the range of high traffic zones of diverse cities (see Table 1). However, variations occurring in the two main streets, especially very high magnetic susceptibility values near the eastern part of Domayo Avenue, require additional sources other than traffic to explain them. These values are found close to restaurants and shops with no evident traffic density variations compared to the rest of the avenue. This artisanal activity involves open stoves (sometimes giant) or other types of wood/coal burning (Figure 1) [10]. The burning of wood and coal in connection with cooking on an open stove next to the street (and trees) could represent an additional provider of magnetite particles, thus explaining the higher values. Indeed, coal generally contains a high Fe content [60], which results in a high iron oxide content in the fly ashes from coal combustion [17,61]. As the building material of the stove contains iron itself, it may also contribute to the magnetic particle load. Urban wood burning can release a substantial quantity of PM2.5 particles [13,62] containing magnetite [17,63]. For example, it has been shown that winter wood burning for indoor heating represents an important part of the total suspended particles in some North American cities [62].

Table 1.
Magnetic susceptibility values (in m3 kg−1) obtained on leaves in different cities. Env. is environment, Sus_min is the minimum magnetic susceptibility values, Sus_max is the minimum magnetic susceptibility values, Sus_mean is the mean magnetic susceptibility and Ref. is the reference.
SEM observations reveal that large amounts of detrital particles are trapped in both bark and leaves in all places from the control area to the busiest streets of Maroua. The occurrence of magnetic spherules, typical of traffic-related emissions, is very low compared to data on lichens and bark obtained from other cities [64,65]. However, if microscopic observations and detections of anthropogenic iron oxides are difficult due to the amount of mineral dust, magnetic measurements allow a clear determination of their relative amount.
4.2. Neem Bark and Leaves as Complementary Biocollectors
Climate and leaf types are known to affect the magnetic record on trees [19,28,66,67,68]. Neems are evergreen trees; thus, both bark and leaves can be considered permanent or at least with a lifespan greater than one year for the leaves. In Maroua, leaves and bark dissimilarly record both the ambient airborne particle content and the seasonality effect. The bark displays similar magnetic susceptibility values throughout the year, while for leaf records, low values are observed during the wet season and higher values are observed during the dry season. This observation is valid in all zones, from the busiest streets to the control areas. Thus, bark and leaves must be considered two different types of biocollectors: season-dependent for the leaves and season-independent for the bark.
As magnetic parameters reflect the concentration of magnetic particles, i.e., χ and IRM, data obtained from bark and leaves, cannot be directly compared. First, the time during which particles are collated on both biocollectors is probably different. Second, mass normalization does not compensate in the same way for each collector. The surface area per surface unit (or per mass unit), where magnetic particles can be trapped, is different for bark and leaves. Bark has surface rugosity and porosity, preventing important rain washing. This probably allows particles to be efficiently trapped. Particles trapped on the bark appear to have reached a stable balance over time between trapping and release, as evidenced by their relative stability throughout the year.
On leaves, the sequestration of particulate matter and, more specifically, of magnetic particulate matter, depends on their surface morphology [69]. For example, Kardel et al. [66] and Mitchell et al. [67] showed that hairy leaves trapped more magnetic particles than smoother leaves did. It has also been proposed that leaf structure or their waxy protective layer could incorporate part of the magnetic particulate matter [19,70], potentially accounting for up to half of the magnetic susceptibility signal [28].
In terms of temporal dynamics, Rodríguez-Germade et al. [68] described a constant gradual increase in PM concentrations on Platanus Hispanica tree leaves using magnetic parameters. Conversely, for Mitchell et al. [67], particles gradually accumulate on the surfaces of deciduous tree leaves until a dynamic equilibrium between particle deposition and particle loss is reached. This equilibrium is reached rapidly, on the order of 6 days, for birch and lime trees [67], whereas it is reached after 26 months for pine needles [71]. Neem leaves, being smooth and oily, probably combine particle entrapment in their foliar structure and dynamic equilibrium on the outer leaf surface.
Climatic variations are the most obvious candidate to explain differences in the leaf records between dry and wet seasons. During the rainy season, both the atmosphere and ground are washed by precipitation, meaning that the air contains fewer particles from the vehicles themselves and the resuspension phenomena [72]. The leaching of leaves during the wet season can also be invoked. Indeed, Rodríguez-Germade et al. [68] showed that meteorological conditions, particularly air humidity, control the relative influence of pollutants, lithic dust and biological effects on the magnetic record of tree leaves. The rain leaching of particles deposited on leaves has been described in various cities [28,68,73,74,75,76]. However, for evergreen trees, some authors argue that rainfall has little influence [28,77], such as pine needles [70,71], because magnetic particles are trapped in the wax layer that covers the leaf or are adsorbed by the leaf via the stomatal cavities [70]. In the case of the Neem leaves sampled in Maroua, the significant differences in magnetic grain content between the dry and wet seasons imply an observable washing effect of the heavy rains that spread throughout the region between July and September.
Using the IRM data, S-ratio and SEM observations, the ratio between the mineral dust component and the anthropogenic component can be compared between bark and leaves. Leaves appear to be dominated by traffic-related particles when taken near main and connected streets. They do not display a clear hematite/goethite component. Instead, they show magnetite-like particle dominance on the magnetic signal (as evidenced by the S-ratio). Conversely, bark always presents a small hematite/goethite component even in the busiest part.
The presence of this natural lithic dust fraction in the magnetic signal on the bark and not on the leaves can be due to the difference in the mean sampling height of each collector. Bark was sampled between 1 and 1.5 m away, while the height of leaf sampling was between 1.5 and 2.5 m. Bark can, therefore, be more impacted by a resuspension component. Maroua sidewalks and secondary roads are not always paved, and a substantial amount of lithic dust covers all surfaces (including main roads). Especially during the dry season, dust brought by both the wind and the traffic is deposited on the ground. Then, dust is resuspended by the wind itself and by the passing vehicles. The resuspension of dust in urban environments can significantly increase exposure to traffic-related particles [78]. For example, Meza-Figueroa et al. [79] have shown that in a medium-sized city of a Mexican state with a semi-arid climate, humidity is the controlling factor for the concentration of suspended particles, with the highest values occurring during the dry season. They emphasize the fact that the effect is maximum at the pedestrian level and that suspended particulate matter filter data must take that into account for the assessment of human exposure to traffic-related particles in a semi-arid climate. In our study, heights sampled by bark and leaves allow this exposure to be taken into account qualitatively, with the bark representing the pedestrian level.
Another explanation could be a difference in PM accumulation capacity of leaves and bark. Indeed, Xu et al. [80] showed that stem bark tends to accumulate a greater proportion of large particles compared to leaves. This could also explain the difference in the relationship between magnetic susceptibility and IRM@2T (Figure 2).
It is worth noting that both types of biocollectors, bark and leaves, indicate the same variations in magnetic particle concentrations related to anthropogenic activities across the city. This makes them both reliable for environmental studies. However, it should be kept in mind that collector types may induce a difference in recording due to the biocollectors specific trapping capacities (see [23,81]).
To compare the values obtained here with other cities and various leaf types, we compile data of magnetic susceptibility values obtained on leaves from different cities (Table 1, [27,28,68,70,71,77,82,83,84]. We report, when available, the lowest-highest individual value and mean values. Individual values and means are not directly comparable since they depend on the sampling strategy (trees from various distances of the road, areas of the city and exposure times). We choose to take the highest average provided by the authors. Sometimes this represents only a specific road section or only one of the sampling campaigns carried out.
It appears that the data obtained on persistent leaves are generally higher than those on deciduous leaves (Table 1). For example, in Rome, Moreno et al. [77] specifically compared the leaves of deciduous plane trees with those of Q. ilex, an evergreen oak species. They found that magnetic susceptibility values obtained on Q. ilex leaves were consistently higher on low/moderate and high traffic roads. Sant’Ovaia [84] made a similar comparison in Porto by sampling evergreen leaves of Nerium and deciduous leaves of Quercus spp. and Platanus spp. (plane tree). Oaks showed higher values than plane trees and Nerium did. The authors attributed these differences to the presence of trichomes. However, it can be noted that if the oaks and the plane trees are located in the central reservation of a busy road, the Nerium is located a few meters away at the edge of the same road, which hinders a direct comparison.
If we compare only data from deciduous leaves, magnetic susceptibility values obtained on Maroua’s leaves are in the same range as data obtained in Portugal (Porto, Braga and Valongo, [84]) and Nanjing (<8 M inhabitants, China, [85]) or Kathmandu [82] but lower than those measured in Rome [28,77]. While relatively isolated medium-sized African cities such as Maroua are not emission “hot spots”, such as large cities in West Africa and sub-Saharan Africa [86], our data imply that these cities display locally values comparable to the particulate emissions of some Asian or European cities. Monitoring air pollution is therefore also crucial, and more easy-to-implement methods, including biomonitoring with low environmental impact, as proposed here, must be developed and implemented.
5. Conclusions
This study illustrates that in a medium-sized African city such as Maroua, with a population of 400,000, anthropogenic activities can induce an important release of particles in the urban air, efficiently tracked by magnetic methods. We showed that magnetite-like particles can be used as a proxy for particulate emissions due to urban activities, including traffic and local handicrafts. While relatively isolated medium-sized African cities such as Maroua are not emission “hot spots”, such as large cities in West Africa and sub-Saharan Africa [86], our data imply that in these cities, local emissions from traffic and biomass combustion dominate over desert dust. The latter mainly consists of goethite, hematite and magnetite-like minerals present in the soil environment and carried by the wind.
We show that both bark and leaves from Neem trees are adequate passive biorecorders. The use of both enables different times and heights to be sampled. Neem trees are therefore good candidates for the low environmental impact monitoring of airborne particulate pollution because of their widespread occurrence in sub-arid to sub-humid regions. This study highlights that, in medium-sized cities in West and Central Africa, the health impact of particulate matter emissions, particularly related to wood burning and a large motorcycle fleet [8] remains to be assessed. Such emissions are contributing to the increased aerosol loads over West Africa known to have the potential to change the local climate [14]. Therefore, anthropogenic air emissions of medium-sized cities, including resuspension phenomena, require evaluation and screening that could be rapidly, efficiently and cost-effectively realized with environmental magnetic methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D., M.M. and S.R.; Data curation, D.D. and M.G.D.; Formal analysis, D.D., M.M., S.R. and J.-F.L.; Funding acquisition, M.M.; Investigation, S.R.; Methodology, D.D., M.M., S.R., J.-F.L. and L.D.; Writing—original draft, D.D., M.M. and S.R.; Writing—review & editing, D.D., M.M., S.R., J.-F.L., M.G.D. and L.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge support of the CNRS (Mission pour l’interdisciplinarité MI-CNRS –Osez l’interdisciplinarité–NanoEnvi project), of the AO OMP (Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées), of the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) grant number ANR-19-CE04-0008 through the BREATHE project and of the Belmont Forum “Pathways to sustainability”. DD was supported by a BEST fellowship of the Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Thierry Aigouy from the Géosciences Environnement Toulouse (GET) laboratory for his help with SEM observations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Marié, D.C.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Gogorza, C.S.G.; Navas, A.; Sinito, A.M. Vehicle-derived emissions and pollution on the road autovia 2 investigated by rock-magnetic parameters: A case study from Argentina. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2010, 54, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A. Acute Respiratory Effects of Particulate Air Pollution. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1994, 15, 107–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, N. Fine particles and human health—A review of epidemiological studies. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 149, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Air pollution and public health: Emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.; Chen, H.; Szyszkowicz, M.; Fann, N.; Hubbell, B.; Pope, C.A.; Apte, J.S.; Brauer, M.; Cohen, A.; Weichenthal, S.; et al. Global estimates of mortality associated with longterm exposure to outdoor fine particulate matter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9592–9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascal, M.; Corso, M.; Chanel, O.; Declercq, C.; Badaloni, C.; Cesaroni, G.; Henschel, S.; Meister, K.; Haluza, D.; Martin-Olmedo, P.; et al. Assessing the public health impacts of urban air pollution in 25 European cities: Results of the Aphekom project. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Owili, P.O.; Lien, W.H.; Muga, M.A.; Lin, T.H. The associations between types of ambient PM2.5 and under-five and maternal mortality in Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liousse, C.; Assamoi, E.; Criqui, P.; Granier, C.; Rosset, R. Explosive growth in African combustion emissions from 2005 to 2030. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djossou, J.; Léon, J.F.; Barthélemy Akpo, A.; Liousse, C.; Yoboué, V.; Bedou, M.; Bodjrenou, M.; Chiron, C.; Galy-Lacaux, C.; Gardrat, E.; et al. Mass concentration, optical depth and carbon composition of particulate matter in the major southern West African cities of Cotonou (Benin) and Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 6275–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Giechaskiel, B.; Pistikopoulos, P.; Fysikas, E.; Samaras, Z. Particle Emissions Characteristics of Different On-Road Vehicles. J. Fuels Lubr. 2003, 112, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Keita, S.; Liousse, C.; Yoboú, V.; Dominutti, P.; Guinot, B.; Assamoi, E.M.; Borbon, A.; Haslett, S.L.; Bouvier, L.; Colomb, A.; et al. Particle and VOC emission factor measurements for anthropogenic sources in West Africa. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Léon, J.F.; Liousse, C.; Guinot, B.; Yoboué, V.; Akpo, A.B.; Adon, J.; Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.S.H.; Li, L.; et al. Personal exposure to PM2.5 emitted from typical anthropogenic sources in southern West Africa: Chemical characteristics and associated health risks. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6637–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Evans, M.J.; Field, P.R.; Fink, A.H.; Liousse, C.; Marsham, J.H. The possible role of local air pollution in climate change in West Africa. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léon, J.F.; Barthélémy Akpo, A.; Bedou, M.; Djossou, J.; Bodjrenou, M.; Yoboué, V.; Liousse, C. PM2.5surface concentrations in southern West African urban areas based on sun photometer and satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, J.; Maher, B.A.; Muxworthy, A.R.; Wuyts, K.; Castanheiro, A.; Samson, R. Biomagnetic Monitoring of Atmospheric Pollution: A Review of Magnetic Signatures from Biological Sensors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6648–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.d.S.; Léon, J.-F.; Macouin, M.; Rousse, S.; da Trindade, R.I.F.; Proietti, A.; Drigo, L.; Antonio, P.Y.J.; Akpo, A.B.; Yoboué, V.; et al. PM2.5 Magnetic Properties in Relation to Urban Combustion Sources in Southern West Africa. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saragnese, F.; Lanci, L.; Lanza, R. Nanometric-sized atmospheric particulate studied by magnetic analyses. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagnotti, L.; Taddeucci, J.; Winkler, A.; Cavallo, A. Compositional, morphological, and hysteresis characterization of magnetic airborne particulate matter in Rome, Italy. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzola, L.C.; Muttoni, G.; Merlini, M.; Rotiroti, N.; Pagliardini, L.; Hirt, A.M.; Pelfini, M. Investigating distribution patterns of airborne magnetic grains trapped in tree barks in Milan, Italy: Insights for pollution mitigation strategies. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 210, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winkler, A.; Caricchi, C.; Guidotti, M.; Owczarek, M.; Macrì, P.; Nazzari, M.; Amoroso, A.; Di Giosa, A.; Listrani, S. Combined magnetic, chemical and morphoscopic analyses on lichens from a complex anthropic context in Rome, Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 1355–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, D.; Özdemir, Ö. Rock Magnetism: Fundamentals and Frontiers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Castañeda-Miranda, A.G.; Marié, D.C.; Gargiulo, J.D.; Lavornia, J.M.; Natal, M.; Böhnel, H.N. Fine air pollution particles trapped by street tree barks: In situ magnetic biomonitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A. Rain and dust: Magnetic records of climate and pollution. Elements 2009, 5, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordanova, D.; Petrov, P.; Hoffmann, V.; Gocht, T.; Panaiotu, C.; Tsacheva, T.; Jordanova, N. Magnetic Signature of Different Vegetation Species in Polluted Environment. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2010, 54, 417–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Chutia, B.M.; Patil, S.K. Monitoring of spatial variations of particulate matter (PM) pollution through bio-magnetic aspects of roadside plant leaves in an Indo-Burma hot spot region. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, B.A.; Mejía, V.; Goguitchaichvili, A.; Escobar, J.; Bayona, G.; Bautista, F.; Morales, J.C.; Ihl, T.J. Reconnaissance environmental magnetic study of urban soils, dust and leaves from Bogotá, Colombia. Stud. Geophys. Geod. 2013, 57, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szönyi, M.; Sagnotti, L.; Hirt, A.M. A refined biomonitoring study of airborne particulate matter pollution in Rome, with magnetic measurements on Quercus Ilex tree leaves. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Miranda, A.G.; Böhnel, H.N.; Molina-Garza, R.S.; Chaparro, M.A.E. Magnetic evaluation of TSP-filters for air quality monitoring. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsozué, D.; Nzeukou, A.; Azinwi, P. Genesis and classification of soils developed on gabbro in the high reliefs of Maroua region, North Cameroon 2017. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2017, 6, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbuewu, I.P.; Odoemenam, Y.U.; Obikaonu, H.O.; Opara, M.N.; Emenalom, O.O.; Uchegbu, M.C.; Okoli, I.C.; Esonu, B.O.; Iloeje, M.U. The growing importance of neem (Azadirachta indica A. Juss) in agriculture, industry, medicine and environment: A review. Res. J. Med. Plant 2011, 5, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forim, M.R.; Fernandes, D.S.M.F.; Fernandes, J.B.; Vieira, P.C. Processo de Obtenção de Nanopartículas Biopoliméricas Contendo Óleo e Extratos de Azadirachta Indica a. Juss (neem). Nanopartículas Biopoliméricas e Micropartículas em pó. BR102013021210-5 B1, 23 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.W.; Channell, J.E.T. Sedimentary Magnetism, Environmental Magnetism, and Magnetostratigraphy. Rev. Geophys. 1991, 29, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxbauer, D.P.; Feinberg, J.M.; Fox, D.L. MAX UnMix: A web application for unmixing magnetic coercivity distributions. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 95, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruiver, P.P.; Dekkers, M.J.; Heslop, D. Quantification of magnetic coercivity components by the analysis of acquisition curves of isothermal remanent magnetisation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2001, 189, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslop, D.; Dekkers, M.J.; Kruiver, P.P.; van Oorschot, I.H.M. Analysis of isothermal remanent magnetization acquisition curves using the expectation-maximization algorithm. Geophys. J. Int. 2002, 148, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, R. Characterization of individual rock magnetic components by analysis of remanence curves. 2. Fundamental properties of coercivity distributions. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Fillion, G. Field and temperature behavior of remanence in synthetic goethite: Paleomagnetic implications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1989, 16, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrajevitch, A.; Van der Voo, R.; Rea, D.K. Variations in relative abundances of goethite and hematite in Bengal Fan sediments: Climatic vs. diagenetic signals. Mar. Geol. 2009, 267, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itambi, A.C.; Von Dobeneck, T.; Dekkers, M.J.; Frederichs, T. Magnetic mineral inventory of equatorial Atlantic Ocean marine sediments off Senegal-glacial and interglacial contrast. Geophys. J. Int. 2010, 183, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, P.; Mathé, P.E.; Esteban, L.; Rakoto, H.; Bouchez, J.L.; Liu, Q.; Torrent, J. Non-saturation of the defect moment of goethite and fine-grained hematite up to 57 Teslas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, U.; Nowaczyk, N.R. Mineral magnetic properties of artificial samples systematically mixed from haematite and magnetite. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 175, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiteri, C.; Kalinski, V.; Rösler, W.; Hoffmann, V.; Appel, E. Magnetic screening of a pollution hotspot in the Lausitz area, Eastern Germany: Correlation analysis between magnetic proxies and heavy metal contamination in soils. Environ. Geol. 2005, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q.; Xue, Q.F. Magnetic properties as indicators of heavy metals pollution in urban topsoils: A case study from the city of Luoyang, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 171, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Blaha, U.; Appel, E.; Ghanashyam, N. Environmental magnetic approach towards the quantification of pollution in Kathmandu urban area, Nepal. Phys. Chem. Earth 2004, 29, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, A.; Contardo, T.; Vannini, A.; Sorbo, S.; Basile, A.; Loppi, S. Magnetic emissions from brake wear are the major source of airborne particulate matter bioaccumulated by lichens exposed in Milan (Italy). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grousset, F.E.; Biscaye, P.E. Tracing dust sources and transport patterns using Sr, Nd and Pb isotopes. Chem. Geol. 2005, 222, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.K.; Khoder, M.I. Chemical characteristics of atmospheric PM2.5 loads during air pollution episodes in Giza, Egypt. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, G. Characteristics of major elements and heavy metals in atmospheric dust in Beijing, China. J. Geochemical Explor. 2017, 176, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, P.; Caquineau, S.; Chevaillier, S.; Klaver, A.; Desboeufs, K.; Rajot, J.L.; Belin, S.; Briois, V. Dominance of goethite over hematite in iron oxides of mineral dust from Western Africa: Quantitative partitioning by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 12740–12754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, R.; Oldfield, F.; Williams, E. Mineral magnetic properties of surface soils and sands across four North African transects and links to climatic gradients. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrasoaña, J.C.; Pey, J.; Zhao, X.; Heslop, D.; Mochales, T.; Mata, P.; Beamud, E.; Reyes, J.; Cerro, J.C.; Pérez, N.; et al. Environmental magnetic fingerprinting of anthropogenic and natural atmospheric deposition over southwestern Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 261, 118568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, A.; Tsuno, H.; Kagi, H.; Kanai, Y.; Nomura, M.; Zhang, R.; Terashima, S.; Imai, N. Chemical compositions and XANES speciations of Fe, Mn and Zn from aerosols collected in China and Japan during dust events. Geochem. J. 2006, 40, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prietzel, J.; Thieme, J.; Eusterhues, K.; Eichert, D. Iron speciation in soils and soil aggregates by synchrotron-based X-ray microspectroscopy (XANES, μ-XANES). Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrasoaña, J.C.; Roberts, A.P.; Liu, Q.; Lyons, R.; Oldfield, F.; Rohling, E.J.; Heslop, D. Source-to-sink magnetic properties of NE saharan dust in Eastern Mediterranean marine sediments: Review and paleoenvironmental implications. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijkeboer, R.; Bremmers, D.; Samaras, Z.; Ntziachristos, L. Particulate matter regulation for two-stroke two wheelers: Necessity or haphazard legislation? Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etissa, D.; Mohr, M.; Schreiber, D.; Buffat, P.A. Investigation of particles emitted from modern 2-stroke scooters. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuurbier, M.; Willems, J.; Schaap, I.; van der Zee, S.; Hoek, G. The contribution of moped emissions to ultrafine and fine particle concentrations on bike lanes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.T.; Muttamara, S.; Laortanakul, P. Influence of benzene emission from motorcycle on Bangkok air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, H.O. Trace metal contents in barbeque (BBQ) charcoal products. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeda, A.; Zyrnicki, W. Application of sequential extraction and the ICP-AES method for study of the partitioning of metals in fly ashes. Microchem. J. 2002, 72, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, F.J.; Marshall, J.D.; Brauer, M. Intake fraction of urban wood smoke. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4701–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClean, R.G.; Kean, W.F. Contributions of wood ash magnetism to archaeomagnetic properties of fire pits and hearths. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1993, 119, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, M.A.E.; Lavornia, J.M.; Chaparro, M.A.E.; Sinito, A.M. Biomonitors of urban air pollution: Magnetic studies and SEM observations of corticolous foliose and microfoliose lichens and their suitability for magnetic monitoring. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 172, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Characterisation of airborne particulates and associated trace metals deposited on tree bark by ICP-OES, ICP-MS, SEM-EDX and laser ablation ICP-MS. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2626–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardel, F.; Wuyts, K.; Maher, B.A.; Hansard, R.; Samson, R. Leaf saturation isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM) as a proxy for particulate matter monitoring: Inter-species differences and in-season variation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5164–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.; Maher, B.A.; Kinnersley, R. Rates of particulate pollution deposition onto leaf surfaces: Temporal and inter-species magnetic analyses. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Germade, I.; Mohamed, K.J.; Rey, D.; Rubio, B.; García, Á. The influence of weather and climate on the reliability of magnetic properties of tree leaves as proxies for air pollution monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Wuyts, K.; Samson, R. Atmospheric net particle accumulation on 96 plant species with contrasting morphological and anatomical leaf characteristics in a common garden experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 202, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbat, M.; Lehndorff, E.; Schwark, L. Biomonitoring of air quality in the Cologne conurbation using pine needles as a passive sampler—Part I: Magnetic properties. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3781–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehndorff, E.; Urbat, M.; Schwark, L. Accumulation histories of magnetic particles on pine needles as function of air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 7082–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Paz, D.; Borge, R.; Vedrenne, M.; Lumbreras, J.; Amato, F.; Karanasiou, A.; Boldo, E.; Moreno, T. Implementation of road dust resuspension in air quality simulations of particulate matter in Madrid (Spain). Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzka, J.; Maher, B.A. Magnetic biomonitoring of roadside tree leaves: Identification of spatial and temporal variations in vehicle-derived particulates. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4565–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, G.; Gómez-Paccard, M.; Osete, M.L. The magnetic properties of particles deposited on Platanus x hispanica leaves in Madrid, Spain, and their temporal and spatial variations. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 382, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.; Maher, B.A. Evaluation and application of biomagnetic monitoring of traffic-derived particulate pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.K.; Pandey, S.K.; Tripathi, B.D. Monitoring of vehicles derived particulates using magnetic properties of leaves. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 120, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Sagnotti, L.; Dinarès-Turell, J.; Winkler, A.; Cascella, A. Biomonitoring of traffic air pollution in Rome using magnetic properties of tree leaves. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Allaban, M.; Gillies, J.A.; Gertler, A.W.; Clayton, R.; Proffitt, D. Tailpipe, resuspended road dust, and brake-wear emission factors from on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Figueroa, D.; González-Grijalva, B.; Del Río-Salas, R.; Coimbra, R.; Ochoa-Landin, L.; Moreno-Rodríguez, V. Traffic signatures in suspended dust at pedestrian levels in semiarid zones: Implications for human exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yu, X.; Mo, L.; Xu, Y.; Bao, L.; Lun, X. Atmospheric particulate matter accumulation on trees: A comparison of boles, branches and leaves. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, L.; Winkler, A.; Guttová, A.; Sagnotti, L.; Grassi, A.; Lackovičová, A.; Senko, D.; Loppi, S. Magnetic properties and element concentrations in lichens exposed to airborne pollutants released during cement production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 12063–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, P.; Blaha, U.; Appel, E. Magnetic susceptibility of dust-loaded leaves as a proxy of traffic-related heavy metal pollution in Kathmandu city, Nepal. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, S.; Khademi, H.; Cano, A.F.; Acosta, J.A. Biomagnetic monitoring of heavy metals contamination in deposited atmospheric dust, a case study from Isfahan, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ovaia, H.; Lacerda, M.J.; Gomes, C. Particle pollution—An environmental magnetism study using biocollectors located in northern Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Qian, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Leaf magnetic properties as a method for predicting heavy metal concentrations in PM2.5 using support vector machine: A case study in Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumbia, E.H.T.; Liousse, C.; Keita, S.; Granier, L.; Granier, C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Elguindi, N.; Law, K. Flaring emissions in Africa: Distribution, evolution and comparison with current inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 199, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).