Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height and of the Wind Field over Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
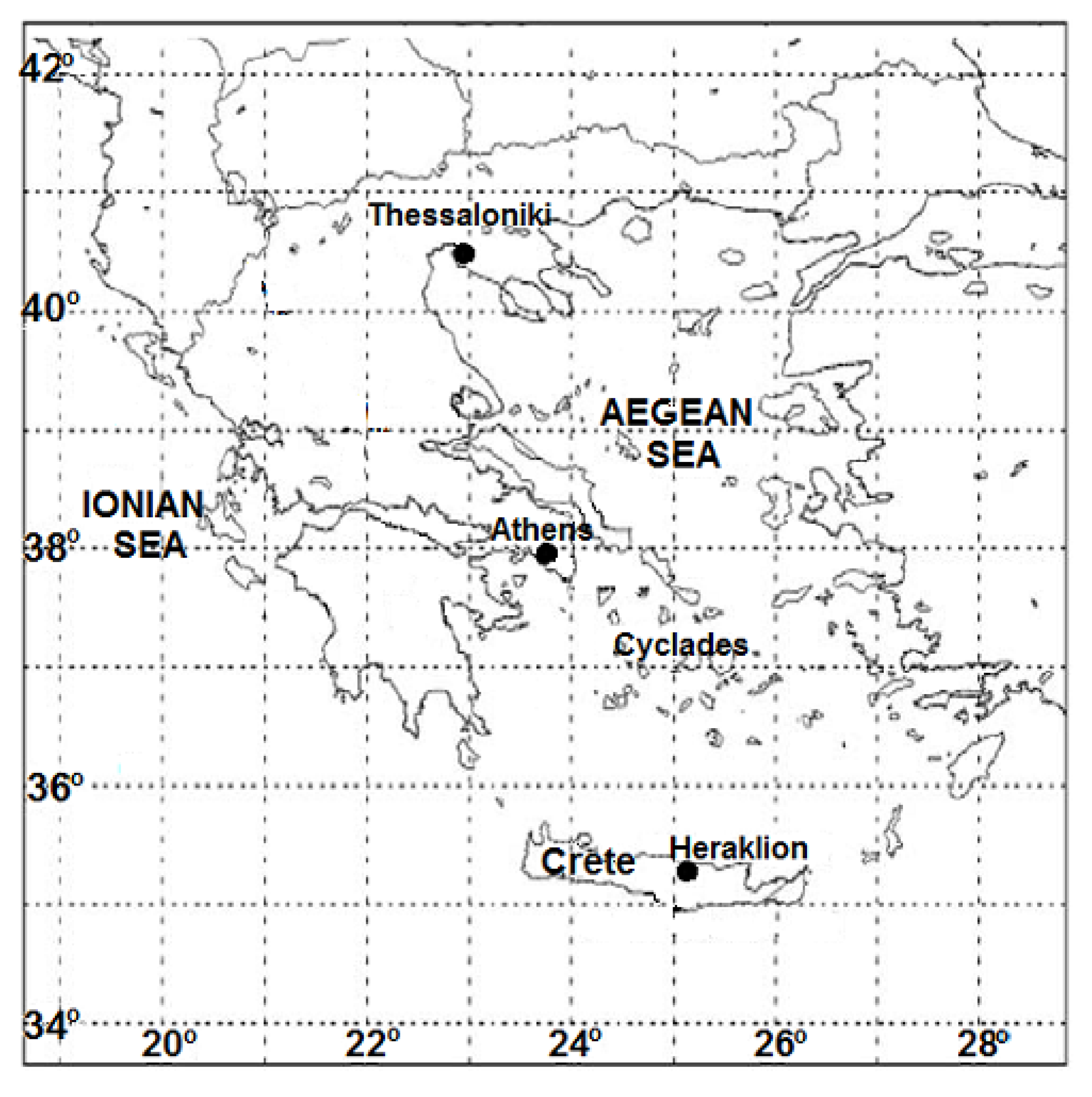
2.1. Data
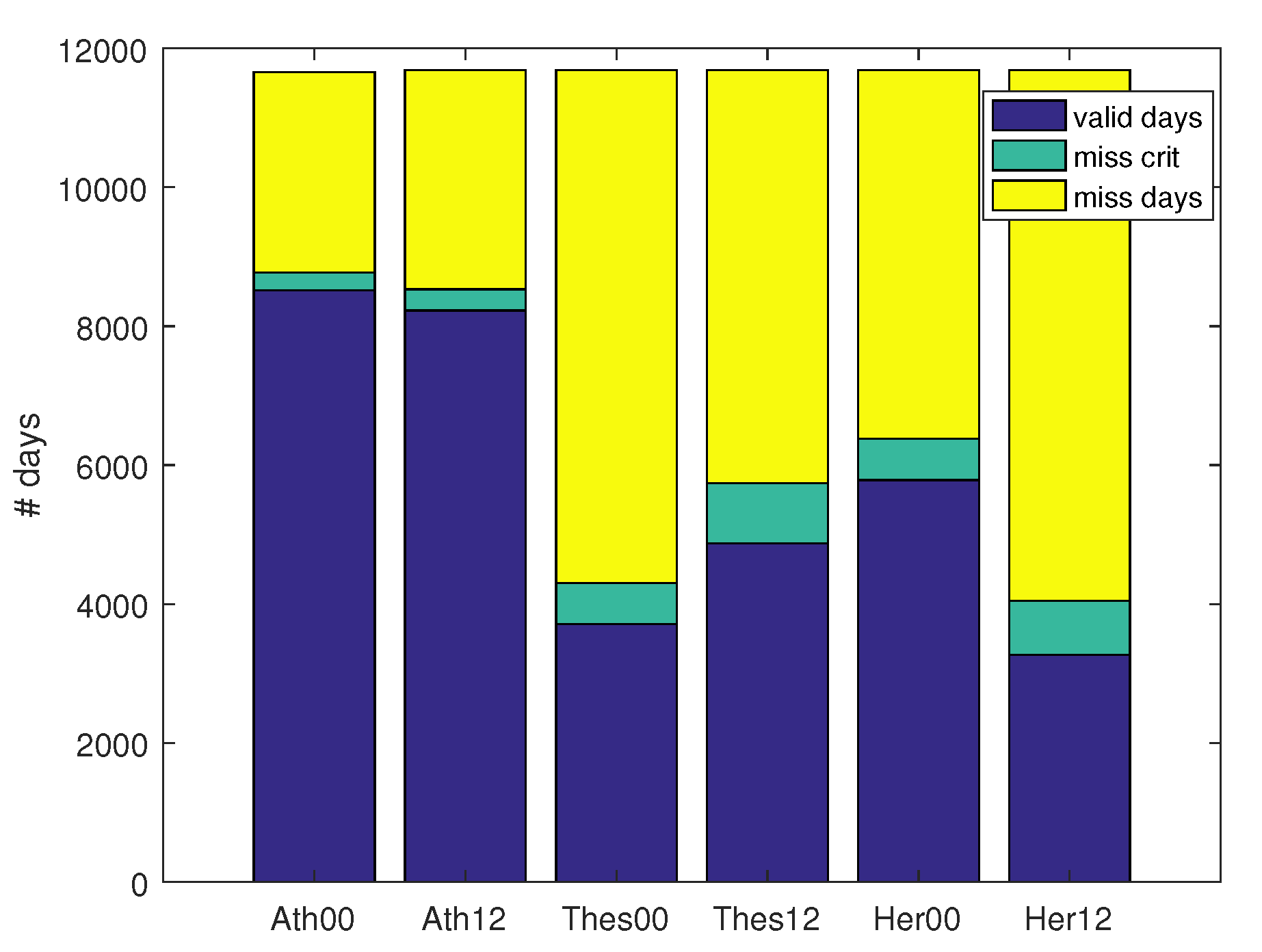
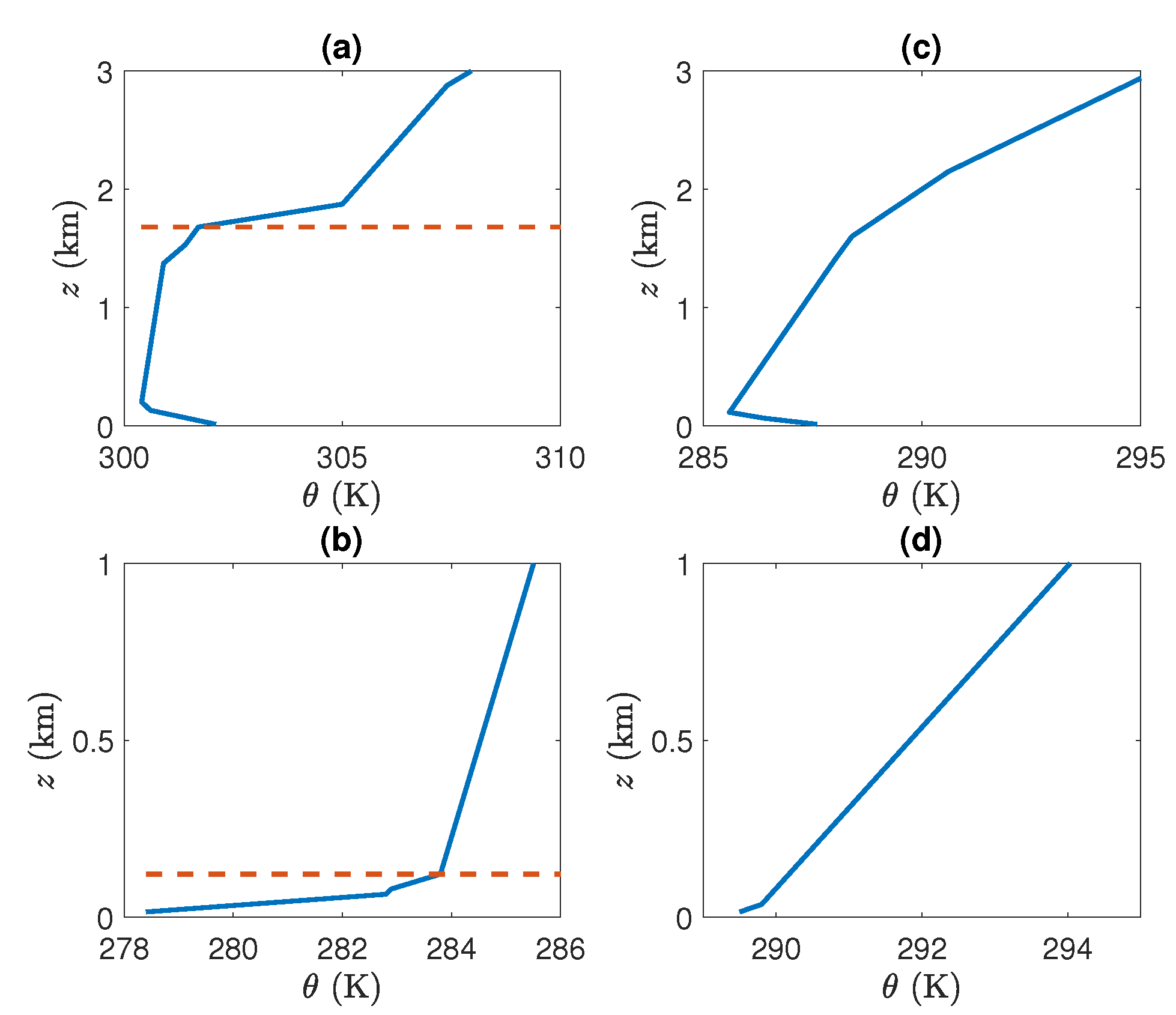
2.2. Methods Used to Determine the PBLH and Wind Turning
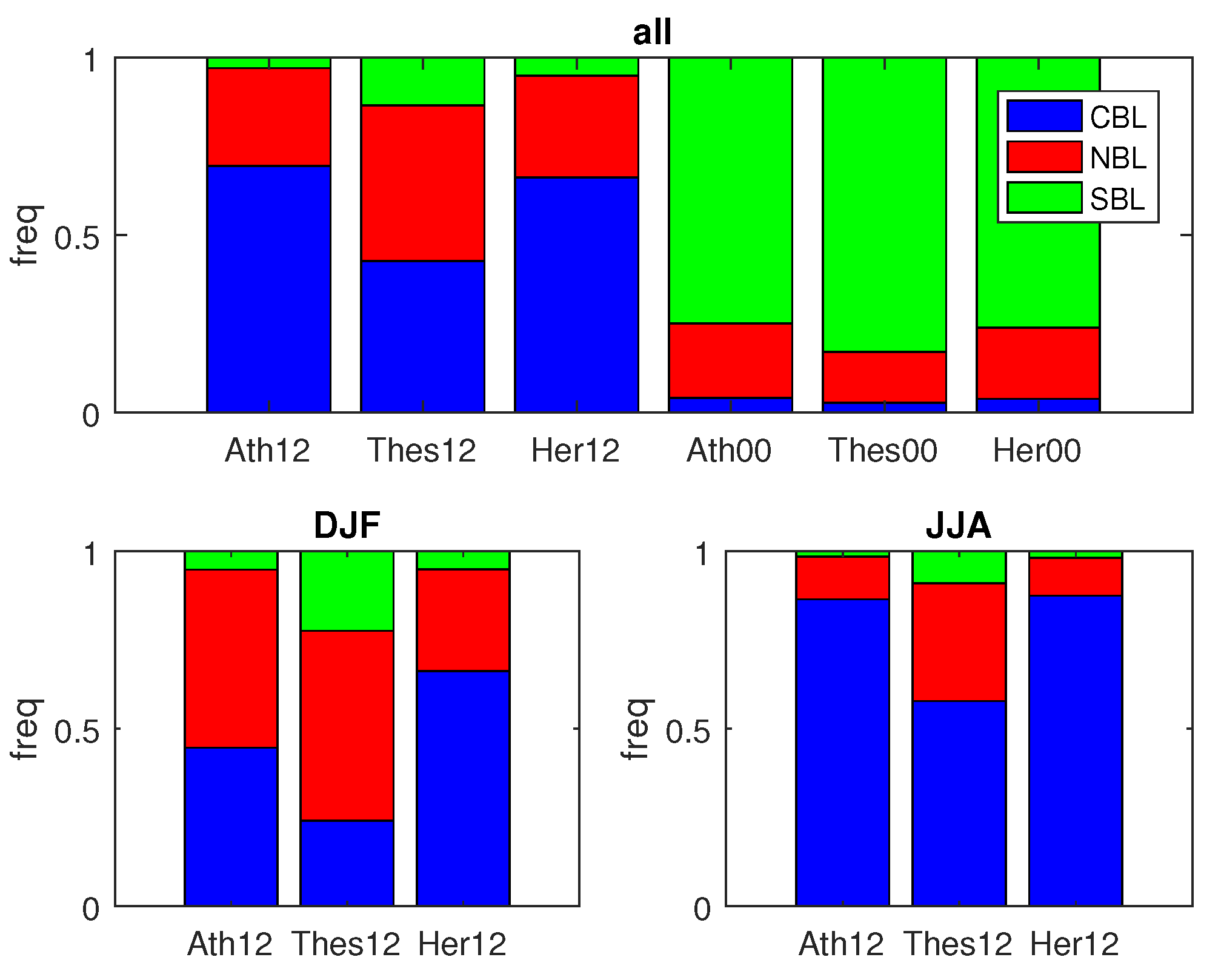
3. Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height
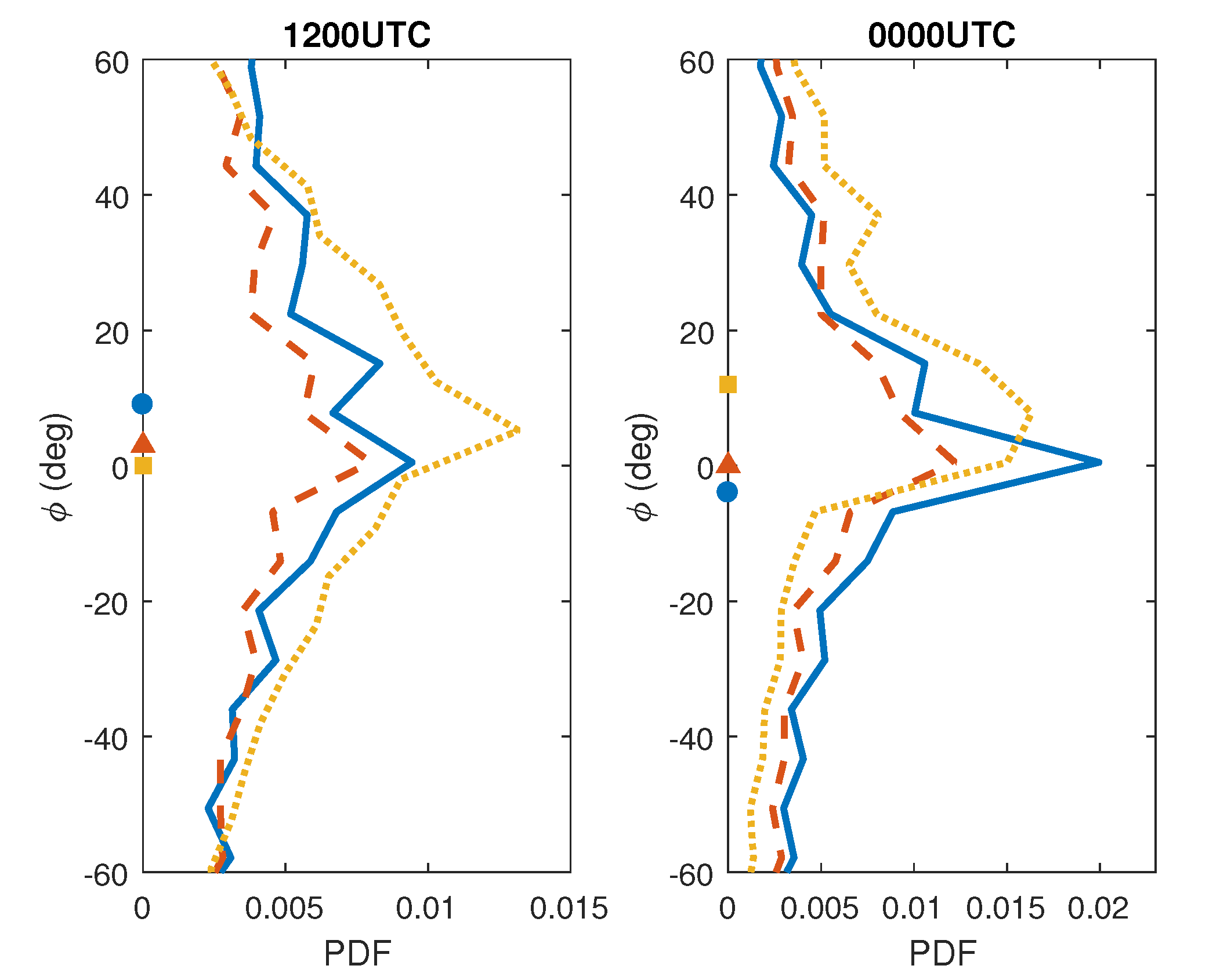
4. Climatology of the Wind in the Planetary Boundary Layer
5. Comparison to Results from Previous Studies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBL | Convective Boundary Layer |
| DJF | December January February |
| ECMWF | European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| HNMS | Hellenic National Meteorological Service |
| IGRA | Integrated Global Radiosonde Archive |
| JJA | June July August |
| NBL | Neutral Boundary Layer |
| PBL | Planetary Boundary Layer |
| PBLH | Planetary Boundary Layer Height |
| Probability Density Function | |
| SBL | Stable Boundary Layer |
| SPARC | Stratosphere-Troposphere Processes And their Role in Climate |
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Acad.: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; p. 666. [Google Scholar]
- Garratt, J.R. The Atmospheric Boundary Layer; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, A.; Schubert, W.H. Interaction of a cumulus cloud ensemble with the large scale envirnoment, part I. J. Atmos. Sci. 1974, 31, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Beyrich, F.; Gryning, S.E.; Joffre, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Tercier, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, B.A.; Hall, A.; Stevens, B. What controls the mean depth of the PBL? J. Clim. 2005, 18, 3157–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, R.J. Boundary-layer mechanisms in extratropical cyclones. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 133, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Gryning, S.E.; Hasager, C.B. Measurements and modelling of the wind speed profile in the marine atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2009, 129, 479–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Sun, J.; Blumen, W.; Delany, T.; Oncley, S. Nocturnal boundary-layer regimes. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1998, 88, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, A.; Floors, R.; Gryning, S.E. The Høvsøre TallWind-profile experiment: A description of wind profile observations in the atmospheric boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2014, 150, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floors, R.; Peña, A.; Gryning, S.E. The effect of baroclinicity on the wind in the planetary boundary layer. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 141, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, G.D.; Garratt, J.R. Evaluating models of the neutral barotropic planetary layer using integral measures. Part I: Overview. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2002, 104, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.M. A Diagnostic Study of the Planetary Boundary Layer over the Oceans; Technical Report, Paper 179; Department of Atmospheric Science, Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Estimating climatological planetary boundary layer heights from radiosonde observations: Comparison of methods and uncertainty analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melfi, S.H.; Spinhirne, J.D.; Chou, S.H. Lidar observations of vertically organized convection in the planetary boundary layer over the ocean. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1985, 24, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacesaria, V.; Marenco, F.; Balis, D.; Papayannis, A.; Zerefos, C. Lidar observations of the planetary boundary layer above the city of Thessaloniki, Greece. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1998, 21, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Hennemuth, B.; Lammert, A. Determination of the boundary layer height from radiosonde and lidar backscatter. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2006, 120, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrich, F. Mixing height estimation from sodar data—A critical discussion. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 3941–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Helmis, C.G.; Michopoulos, J. Evaluation of SODAR methods for the determination of the atmospheric boundary layer mixing height. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 85, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eresmaa, N.A.; Karpinnen, A.; Joffre, S.M.; Rasanen, J.; Talvitie, H. Mixing height determination by ceilometers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmis, C.G.; Sgouros, G.; Tombrou, M.; Schäfer, K.; Münkel, C.; Bossioli, E.; Dandou, A. A comparative study and evaluation of mixing-height estimation based on sodar-RASS, ceilometer data and numerical model simulations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2012, 145, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, X.Z. Observed diurnal cycle climatology of planetary boundary layer height. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5790–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrich, F.; Leps, J.P. An operational mixing height data set from routine radiosoundings at Lindenberg: Methodology. Meteorol. Z. 2012, 21, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Melas, D.; Amiridis, V.; Alexandri, G. Statistical analysis of boundary layer heights in a suburban environment. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2009, 104, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindvall, J.; Svensson, G. Wind turning in the atmospheric boundary layer over land. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 145, 3074–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryning, S.E.; Batchvarova, E. Parametrization of the depth of the entrainment zone above the daytime mixed layer. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 120, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzworth, G.C. Estimates of mean maximum mixing depths in the contiguous United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 1964, 92, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.E. Evaluation and model impacts of alternative boundary layer height formulation. Mon. Weather Rev. 1967, 95, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, A.J. Comparison of observed mixed layer depth to model estimates using observed temperature and winds, and MOS forecasts. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1981, 20, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.E.; Cavallo, S.M.; Coniglio, M.C.; Brooks, H.E. A Review of Planetary Boundary Layer Parameterization Schemes and Their Sensitivity in Simulating Southeastern U.S. Cold Season Severe Weather Environments. Weather Forecast. 2015, 30, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsom, R.K.; Banta, R.M. Shear-Flow Instability in the Stable Nocturnal Boundary Layer as Observed by Doppler Lidar during CASES-99. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrt, L.; Heald, R.C.; Lenschow, D.H.; Stankov, B.B.; Troen, I. An observational study of the structure of the nocturnal boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1979, 17, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.W. Determining the height of the nocturnal boundary layer. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1978, 17, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.S.; Keimig, F.T.; Diaz, H.F. Recent changes in the North American Arctic boundary layer in winter. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 8851–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, J.R. Observations in the nocturnal boundary layer. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1982, 22, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeldman, A.S. Some turbulence characteristics in stable atmospheric boundary layer flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 856–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vogelezang, D.H.P.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Evaluation and model impacts of alternative boundary layer height formulation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 81, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, J.W. On the stability of heterogenic shear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 1961, 10, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Engeln, A.; Teixeira, J. A planetary boundary layer height climatology derived from ECMWF reanalysis data. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 6575–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmboe, J. On the behavior of symmetric waves in stratified shear layer. Geofysiske 1962, 24, 67–113. [Google Scholar]
- Tombrou, M.; Dandou, A.; Helmis, C.; Akylas, E.; Angelopoulos, G.; Flocas, H.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Soulakellis, N. Model evaluation of the atmospheric boundary layer and mixed-layer evolution. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2007, 124, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, D.; Kokkalis, P.; Papayannis, A.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Argyrouli, A.; Tsaknakis, G.; Tzanis, C.G. Planetary boundary layer variability over Athens, Greece, based on the synergy of Raman lidar and radiosonde data: Application of the Kalman filter and other techniques. EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 176, 06007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houchi, K.; Stoffelen, A.; Marseille, G.J.; de Kloe, J. Comparison of wind and wind shear climatologies derived from high-resolution radiosondes and the ECMWF model. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D22123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ulden, A.P.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Estimation of atmospheric boundary layer parameters for diffusion applications. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1985, 24, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuma, M.; Iwamoto, S. Wind structure of the boundary layer over the Tropical Ocean. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1982, 60, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
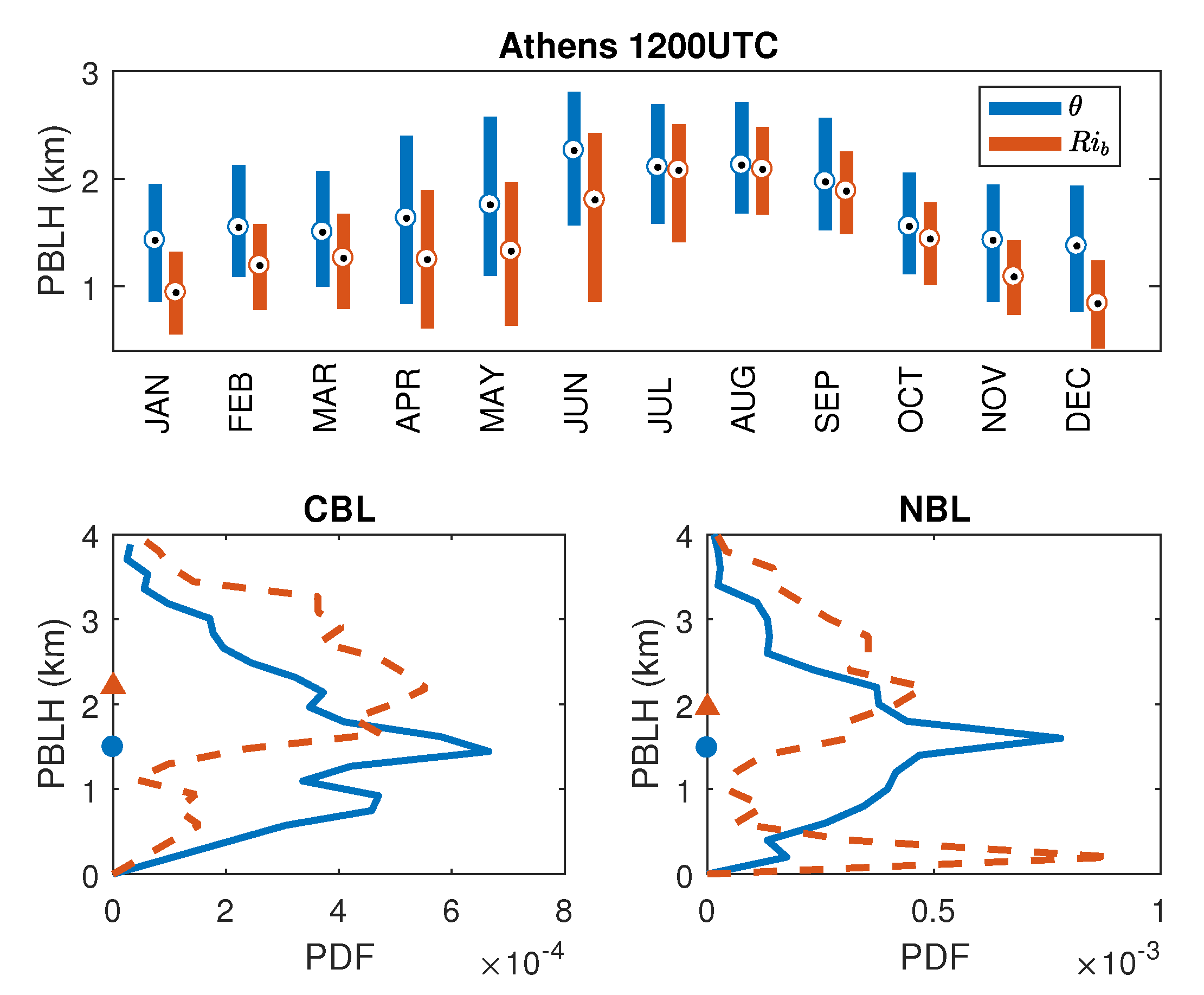
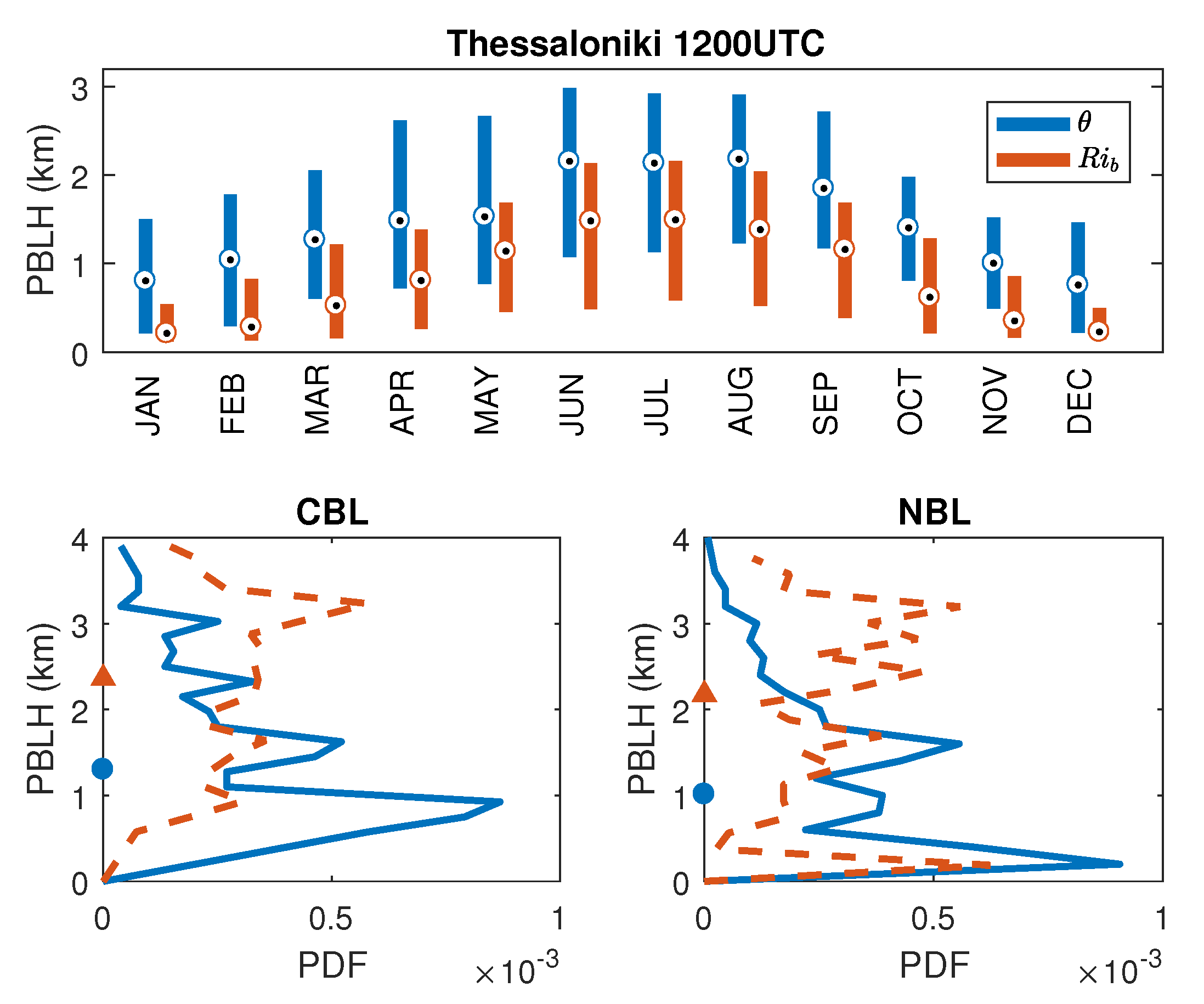
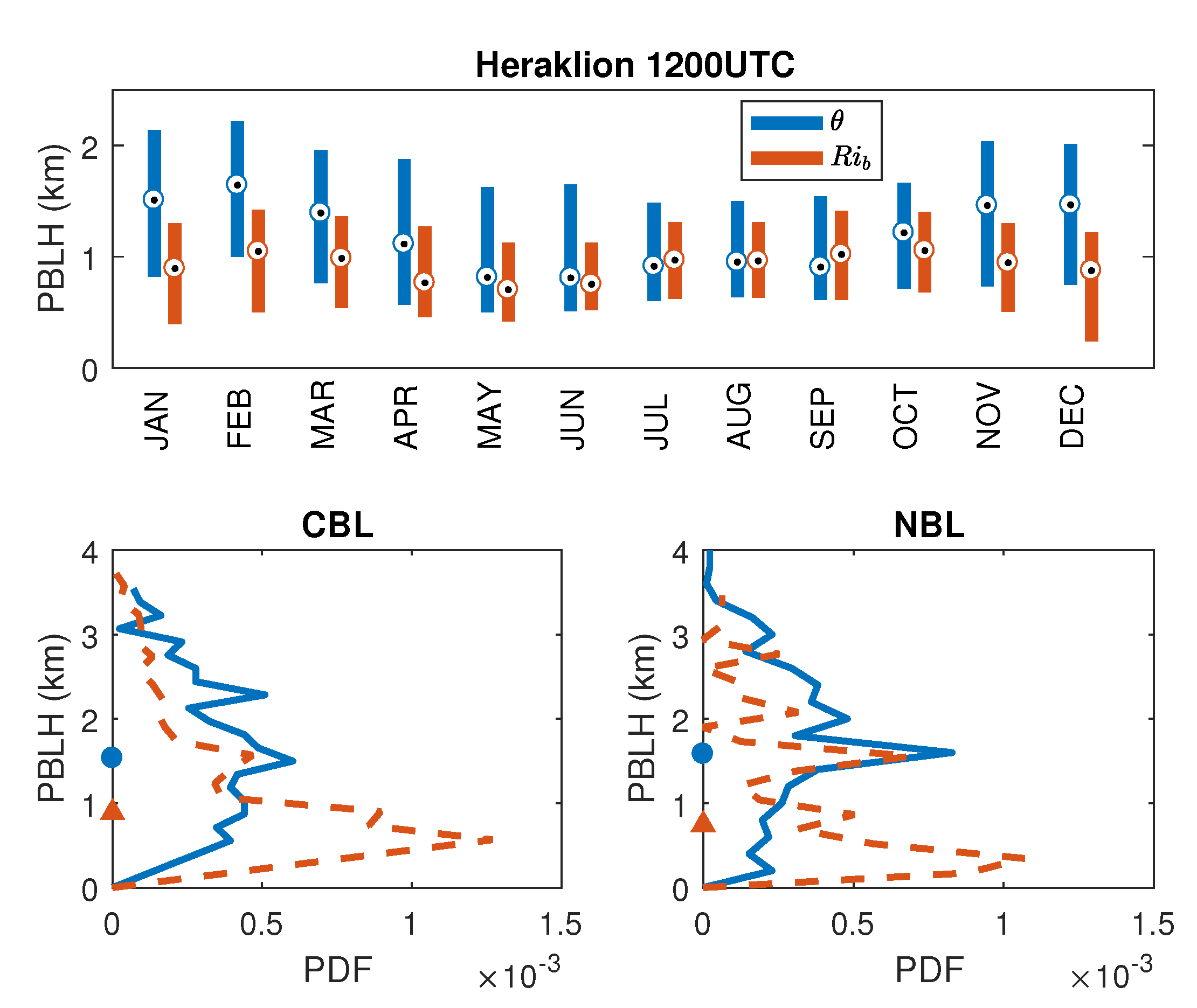

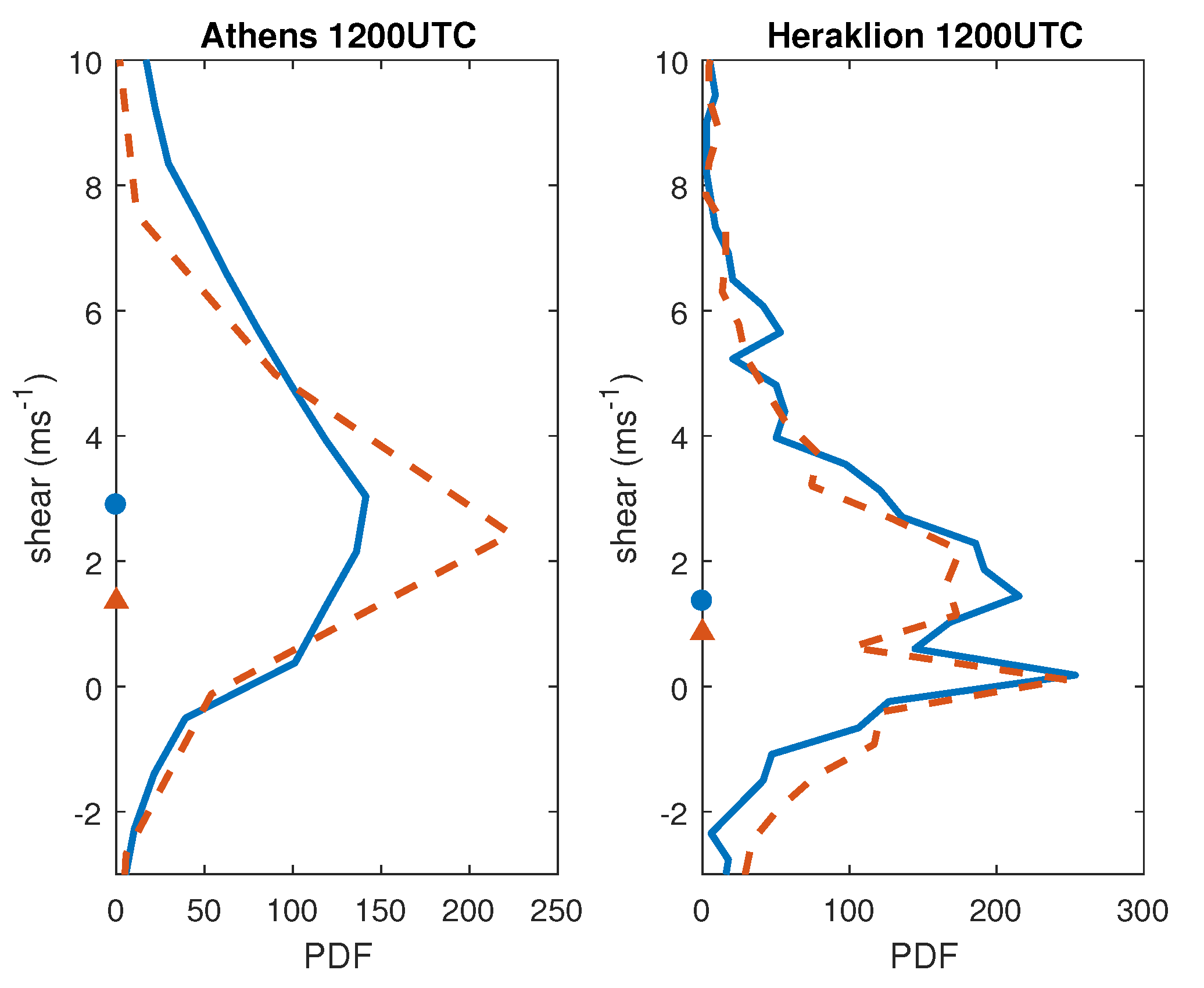
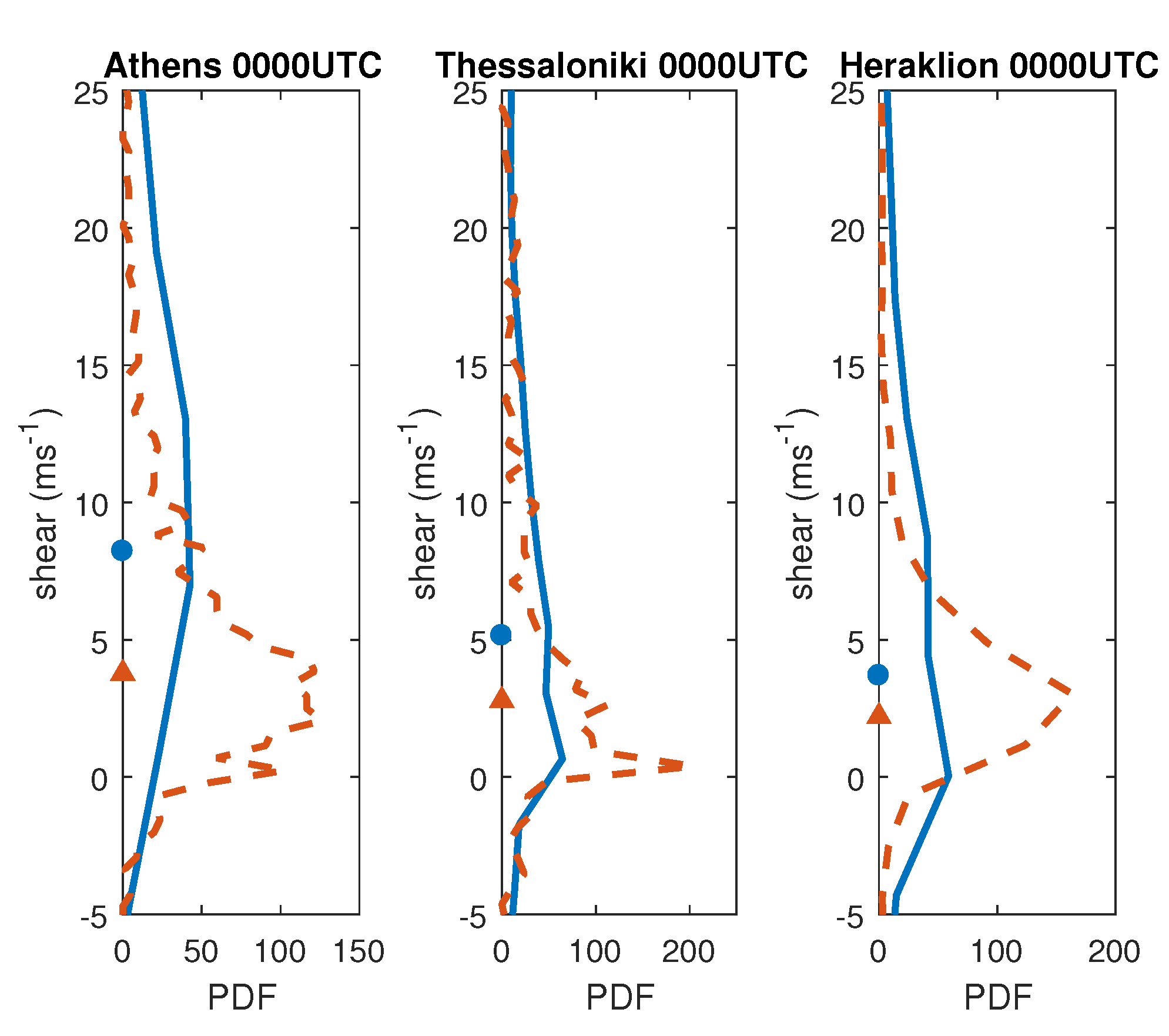
| Sounding | Gradient Method | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Athens 1200UTC | ||
| Athens 0000UTC | ||
| Thessaloniki 1200UTC | ||
| Thessaloniki 0000UTC | ||
| Heraklion 1200UTC | ||
| Heraklion 0000UTC |
| Study | Region | Duration | Instr./Method | PBLH 1200UTC | PBLH 0000UTC |
| Seidel et al. [21] | Europe | 24 years | sound./ | 1 km | 0.1 km |
| Asimakopoulos et al. [18] | Athens | 24 days (April) | sodar | 1.4 km | 0.2 km |
| Tombrou et al. [42] | Athens | 2 days (September) | sodar | 1.3 km | 0.3 km |
| Helmis et al. [20] | Athens | 7 days (September) | ceilometer | 1.8 km | 0.3 km |
| Alexiou et al. [43] | Athens | 5 years | LiDAR | km | km |
| Georgoulias et al. [25] | Thessaloniki | 2 years | sound./ | 1 km | 0.2 km |
| Santacesaria et al. [15] | Thessaloniki | 2 days (April) | LiDAR | 2 km | |
| Study | Region | Duration | Instr./Method | Angle | Shear |
| Lindvall & Svensson [26] | global | 40 years | sound./ | 15 deg | |
| Houchi et al. [44] | US | 10 years | sound. | 6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakas, N.A.; Fotiadi, A.; Kariofillidi, S. Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height and of the Wind Field over Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090910
Bakas NA, Fotiadi A, Kariofillidi S. Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height and of the Wind Field over Greece. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(9):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090910
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakas, Nikolaos A., Angeliki Fotiadi, and Sophia Kariofillidi. 2020. "Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height and of the Wind Field over Greece" Atmosphere 11, no. 9: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090910
APA StyleBakas, N. A., Fotiadi, A., & Kariofillidi, S. (2020). Climatology of the Boundary Layer Height and of the Wind Field over Greece. Atmosphere, 11(9), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11090910





