Influence of Novaya Zemlya Bora on Sea Waves: Satellite Measurements and Numerical Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Bora Calendar
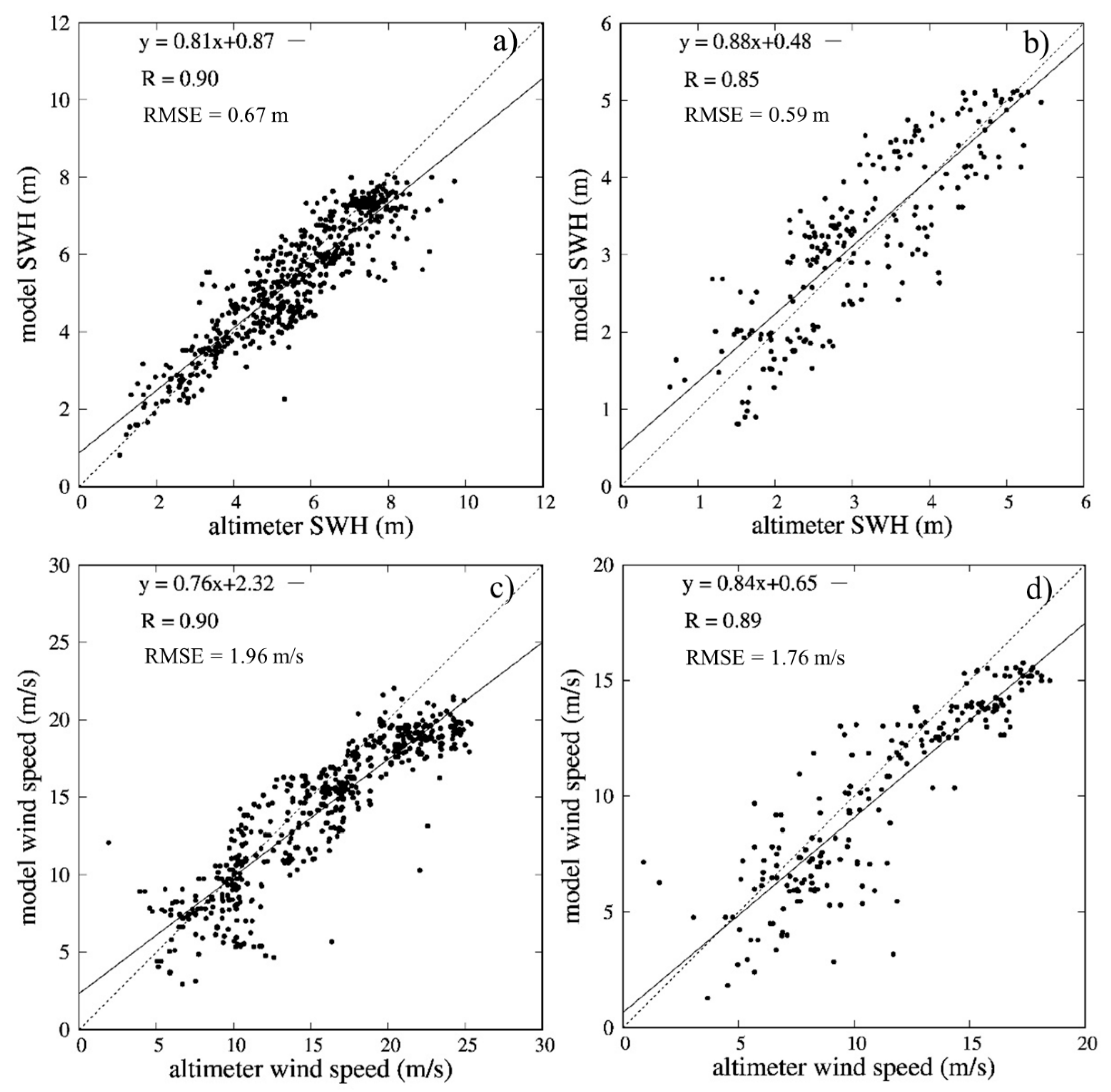
2.2. Satellite Altimetry
- -
- values with standard deviation of the altimeter SWH exceeding 0.4;
- -
- values with SWH lower than 0.3 m;
- -
- values with distance to the shore closer than 15 km; and
- -
- values with distance to the nonzero ice concentration closer than 10 km.
2.3. Wave Reanalysis
2.4. High-Resolution Wave Modeling
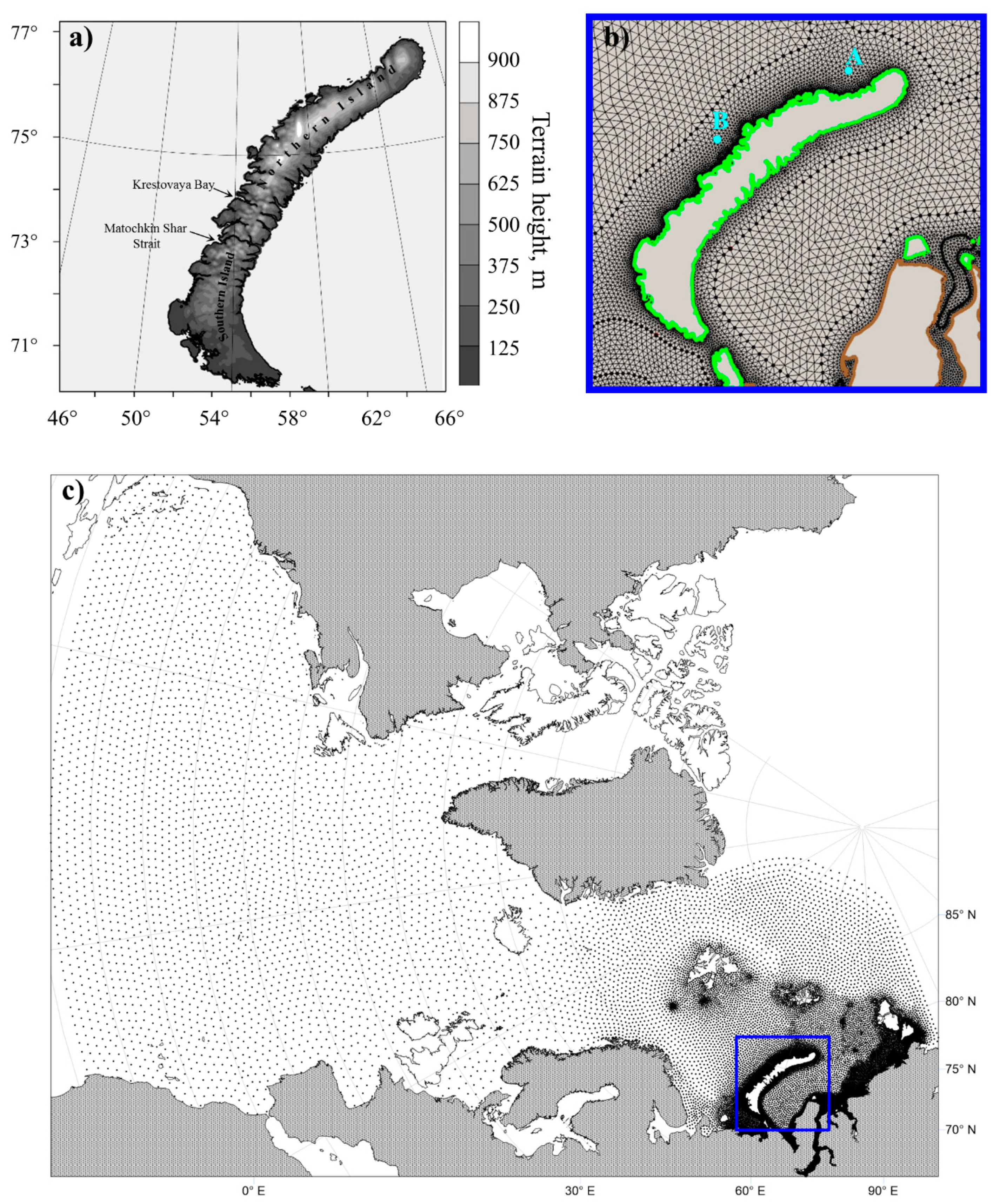
2.4.1. Model Configuration
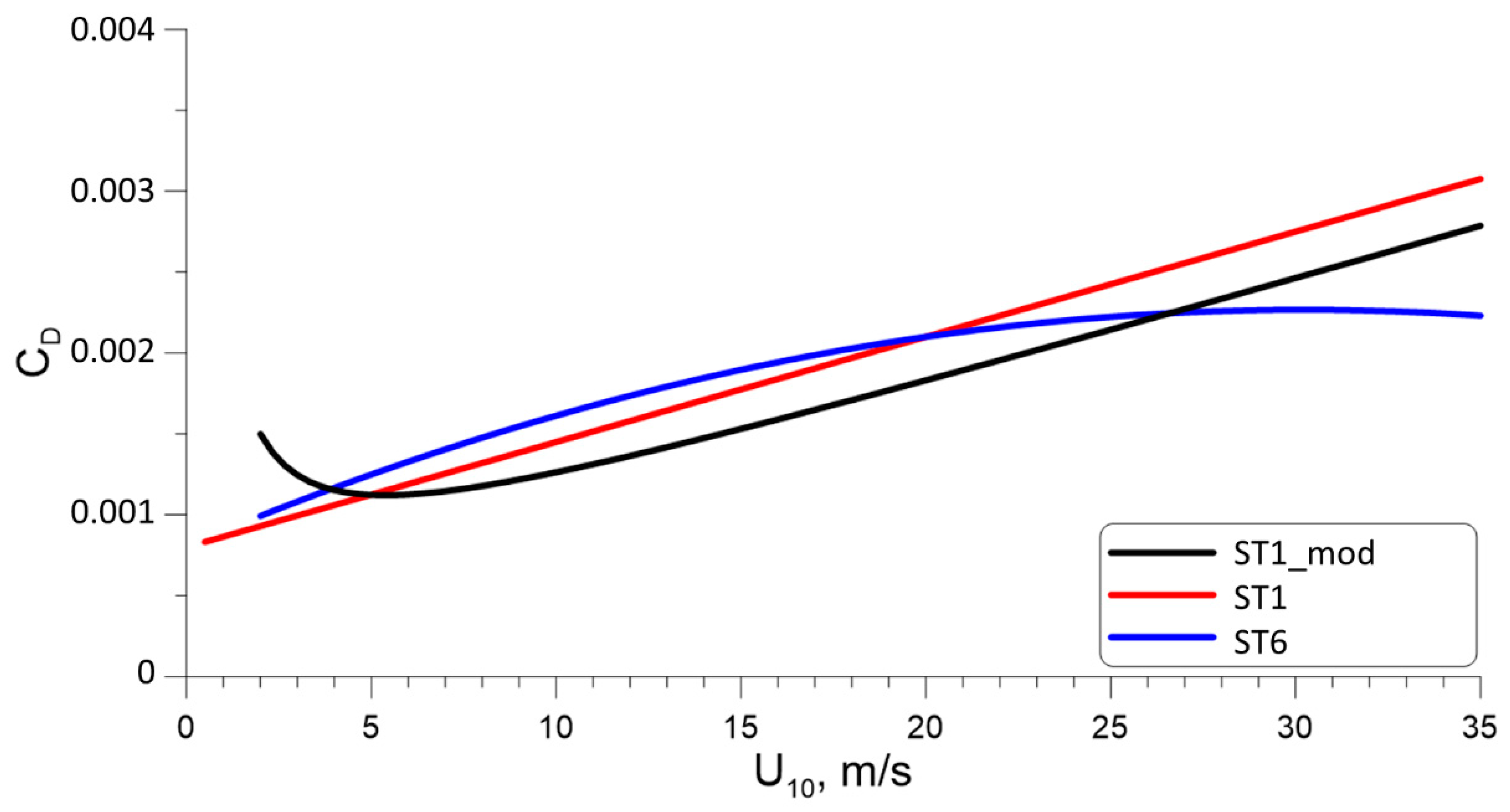
2.4.2. Experiments with Different Wind Input Parameterizations
3. Results
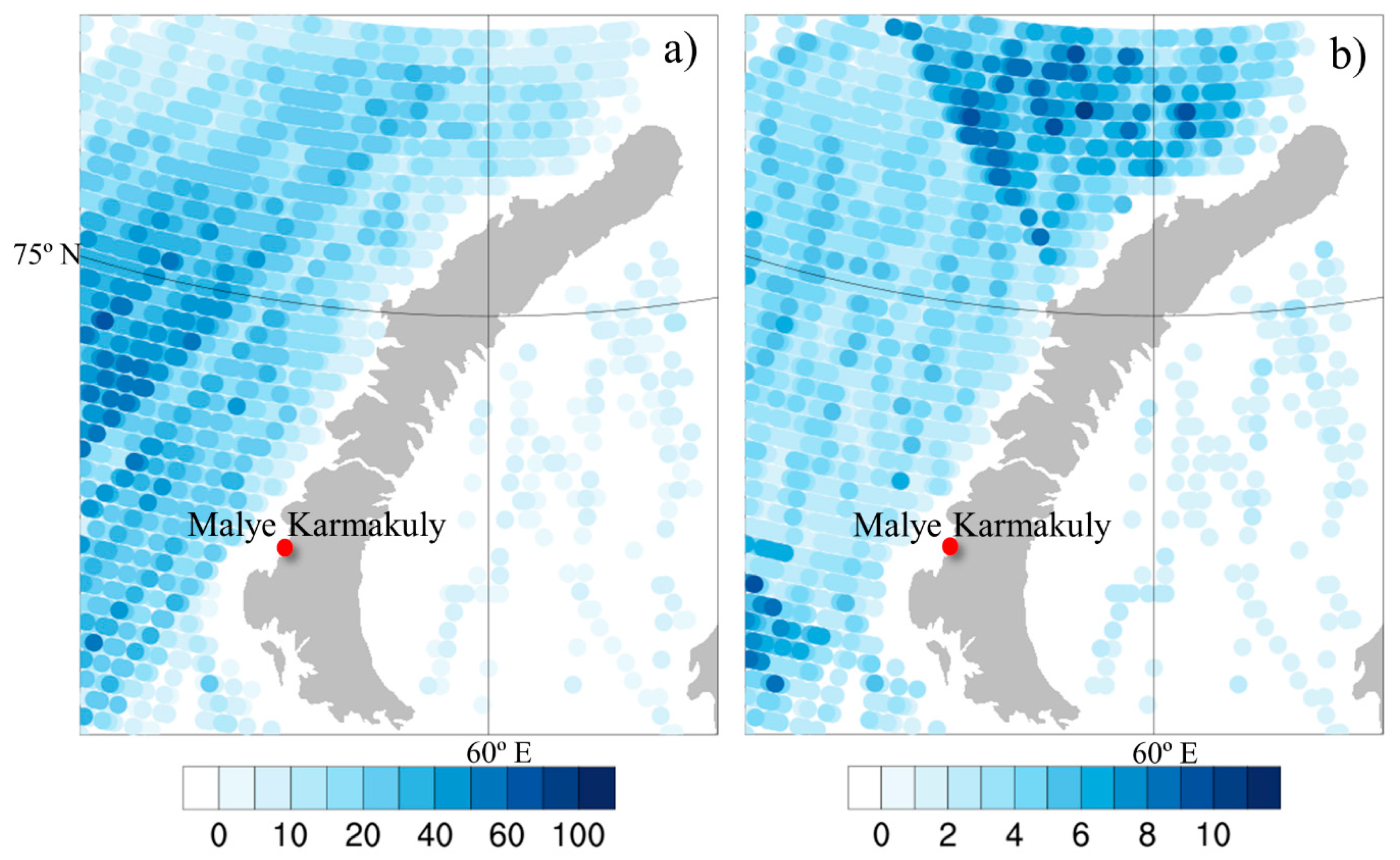
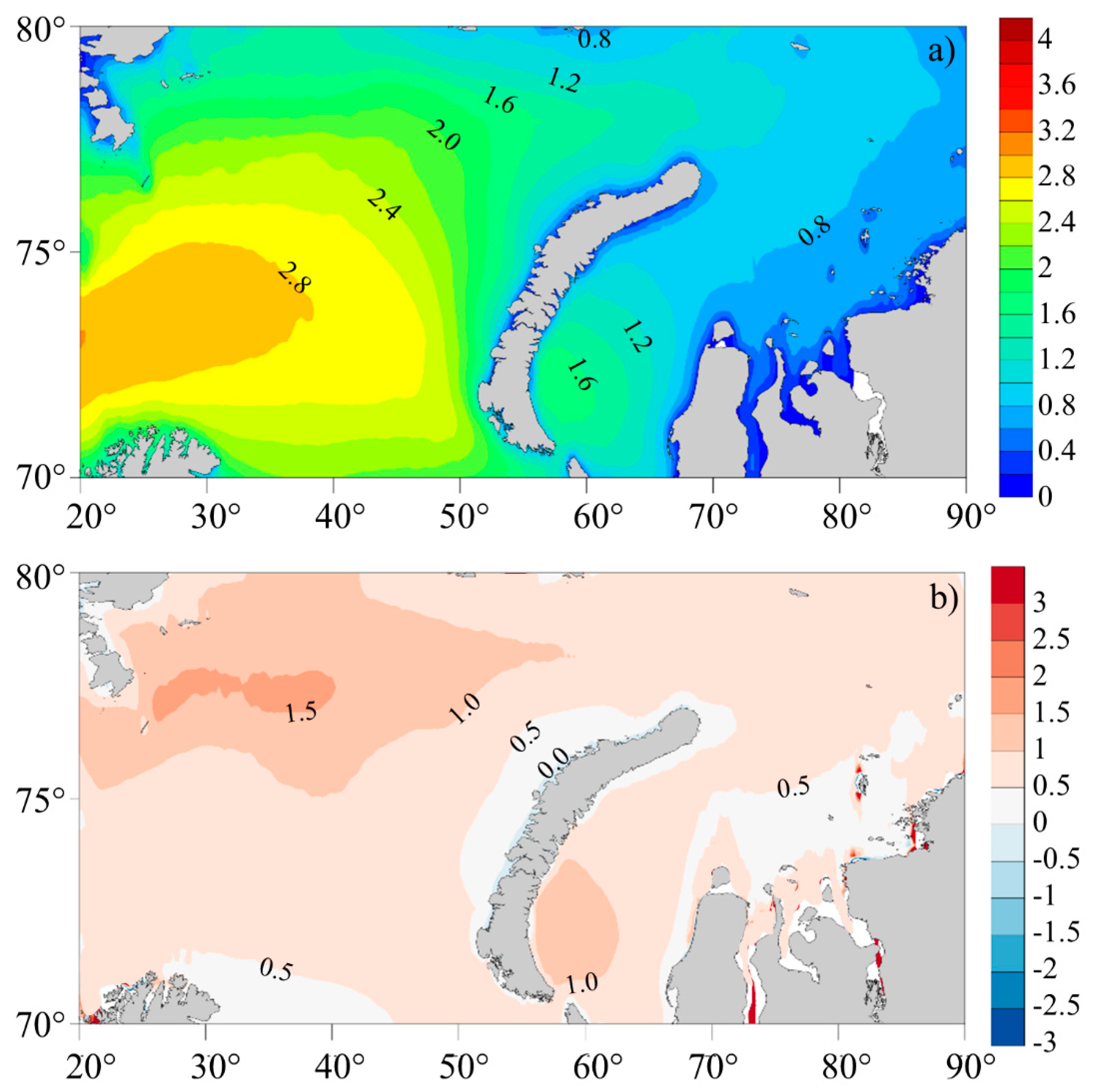
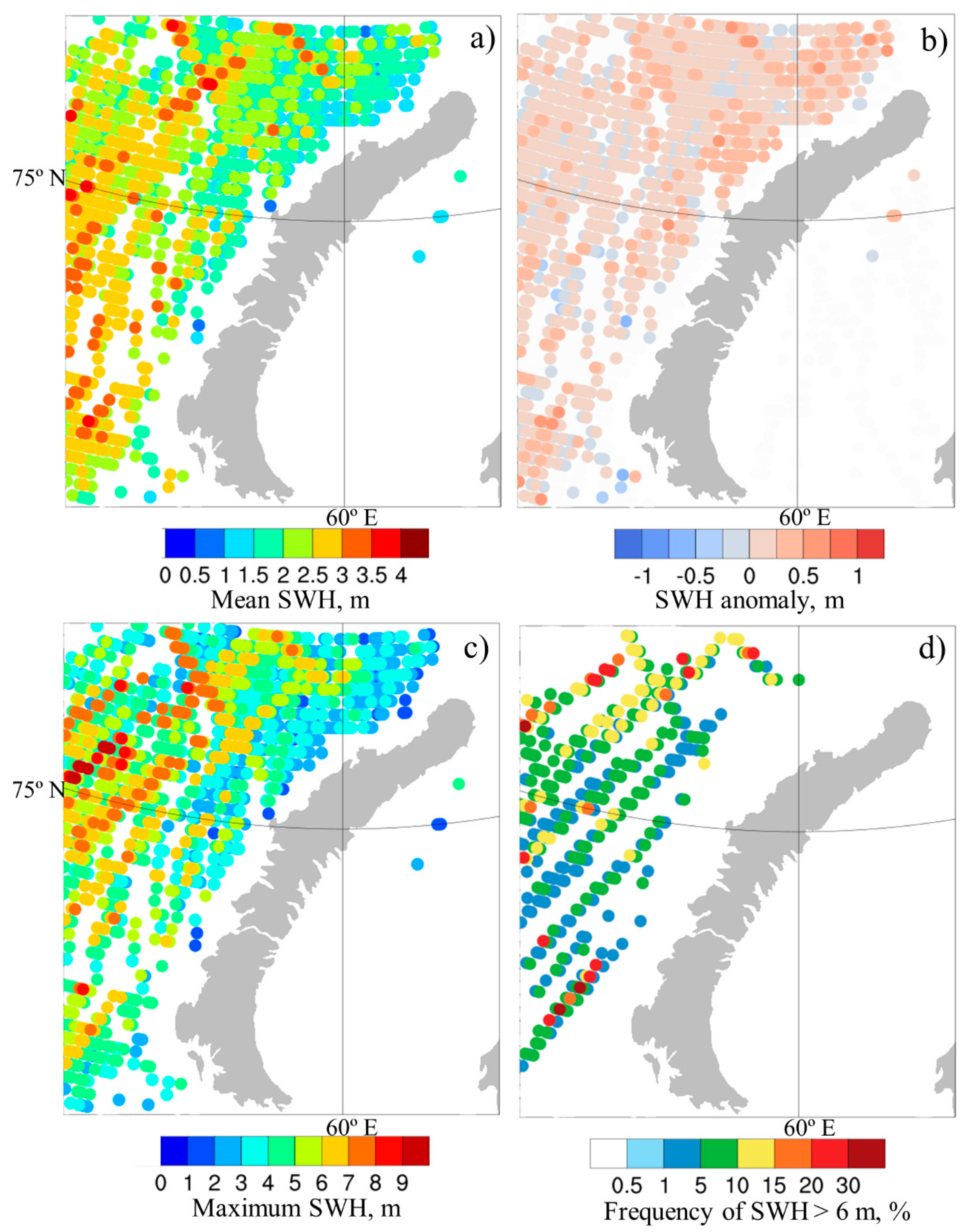
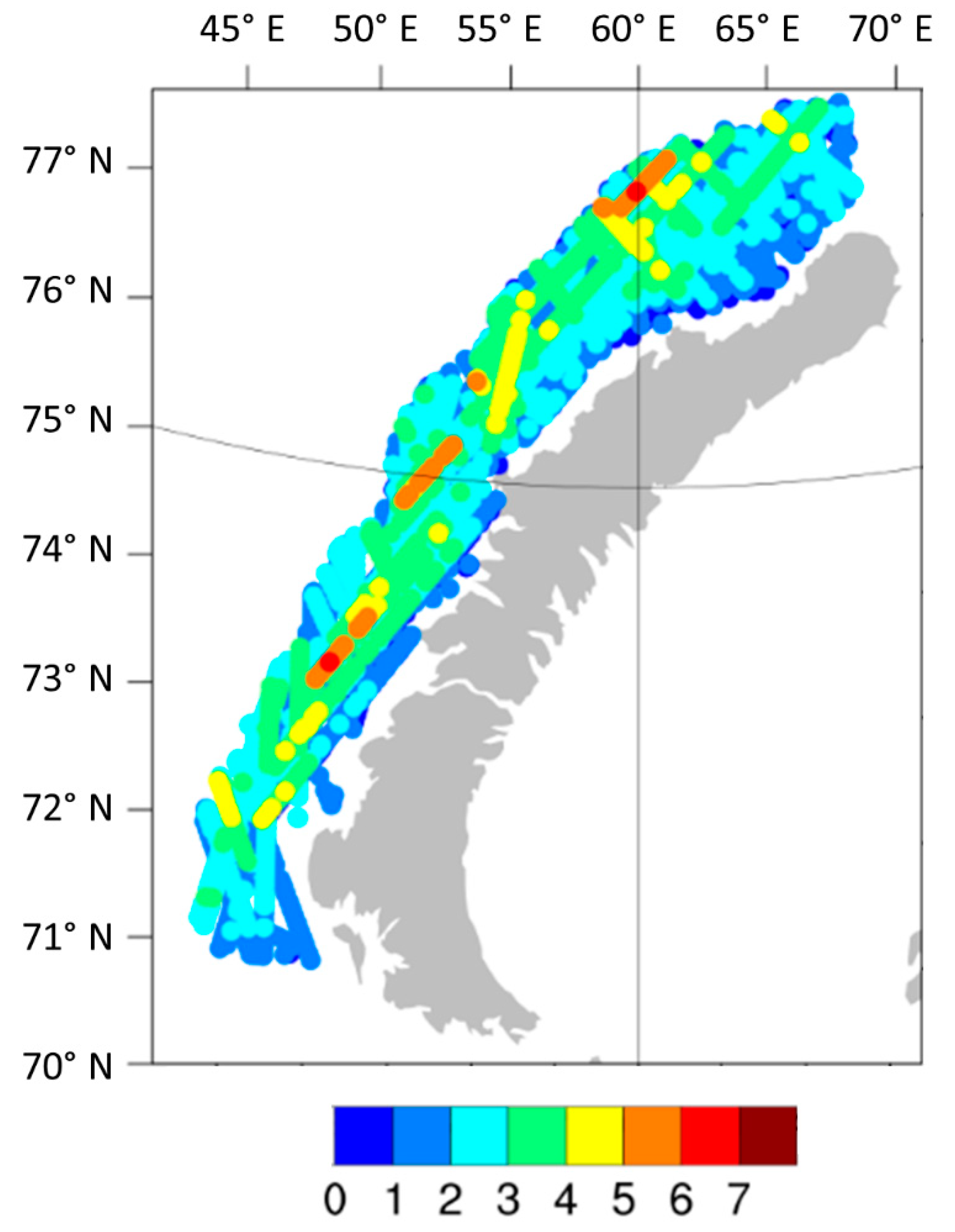
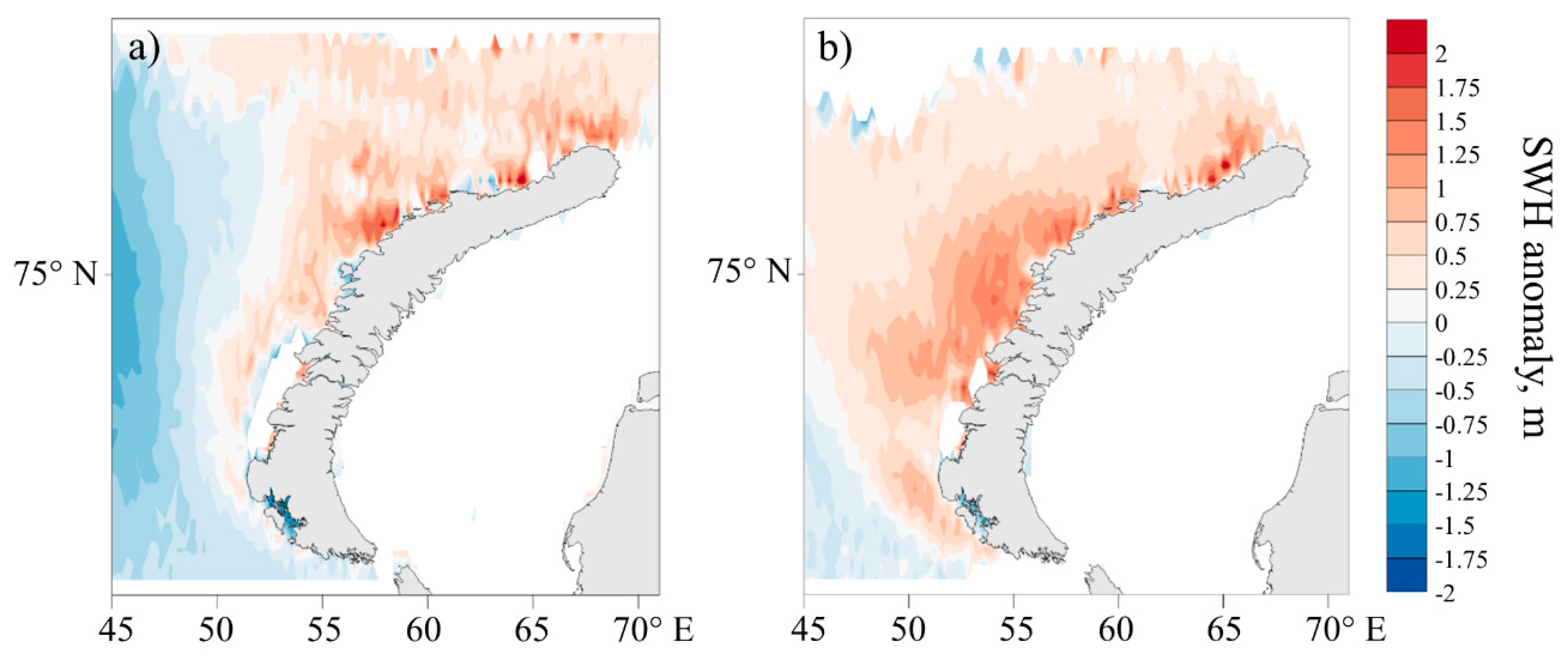
3.1. Statistics of Sea Waves during Bora
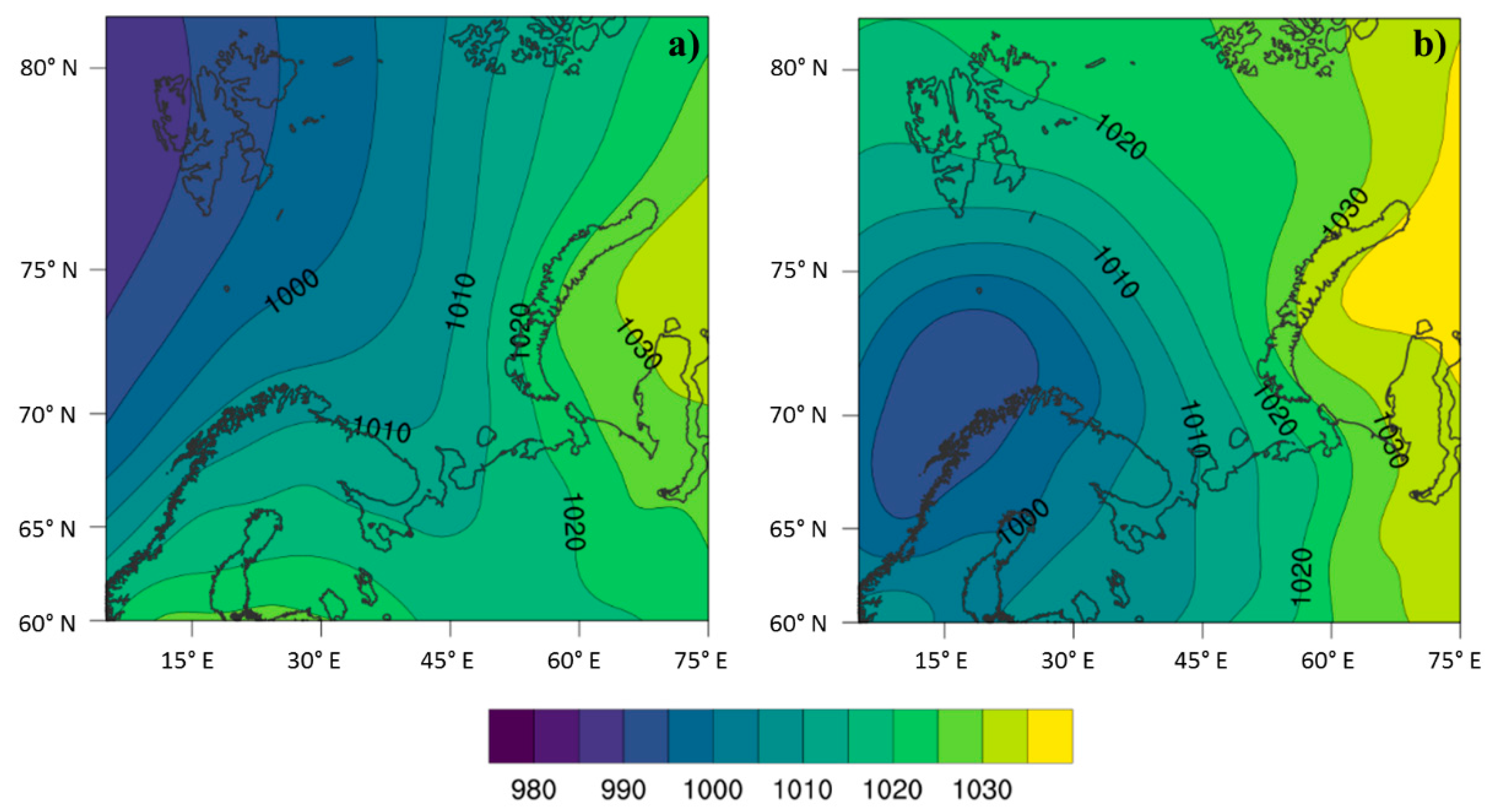
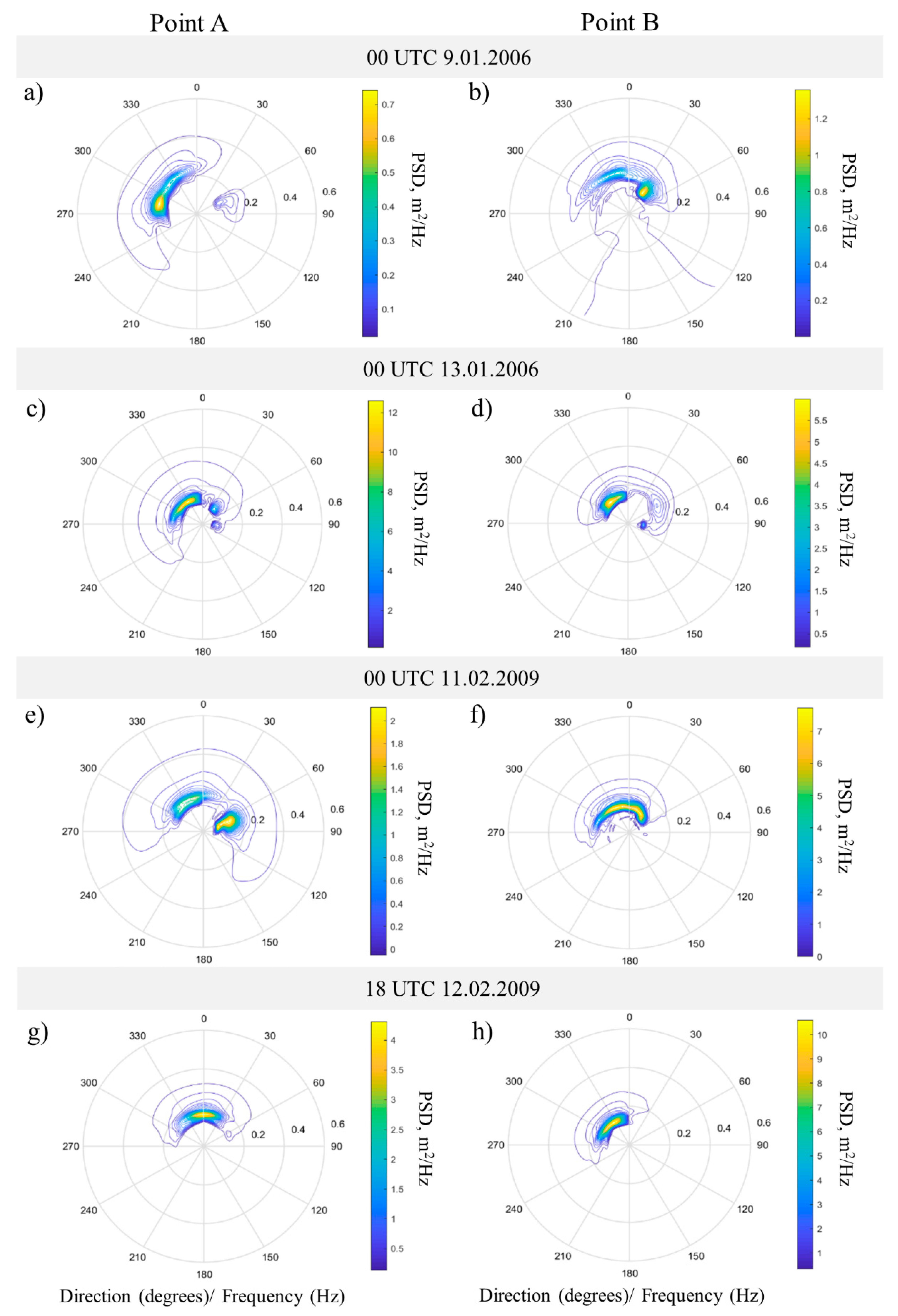
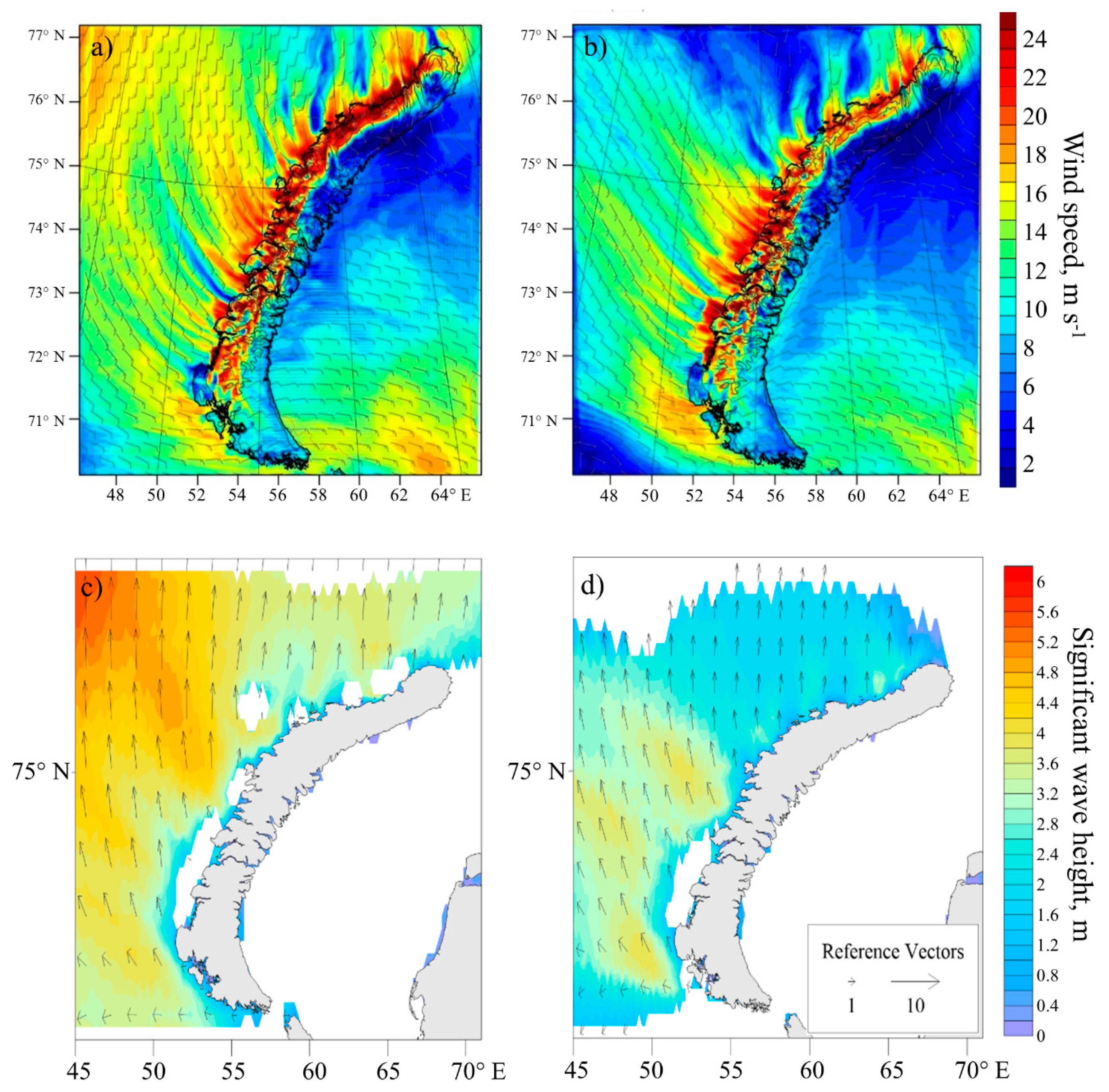
3.2. Case Studies: Two Bora Episodes
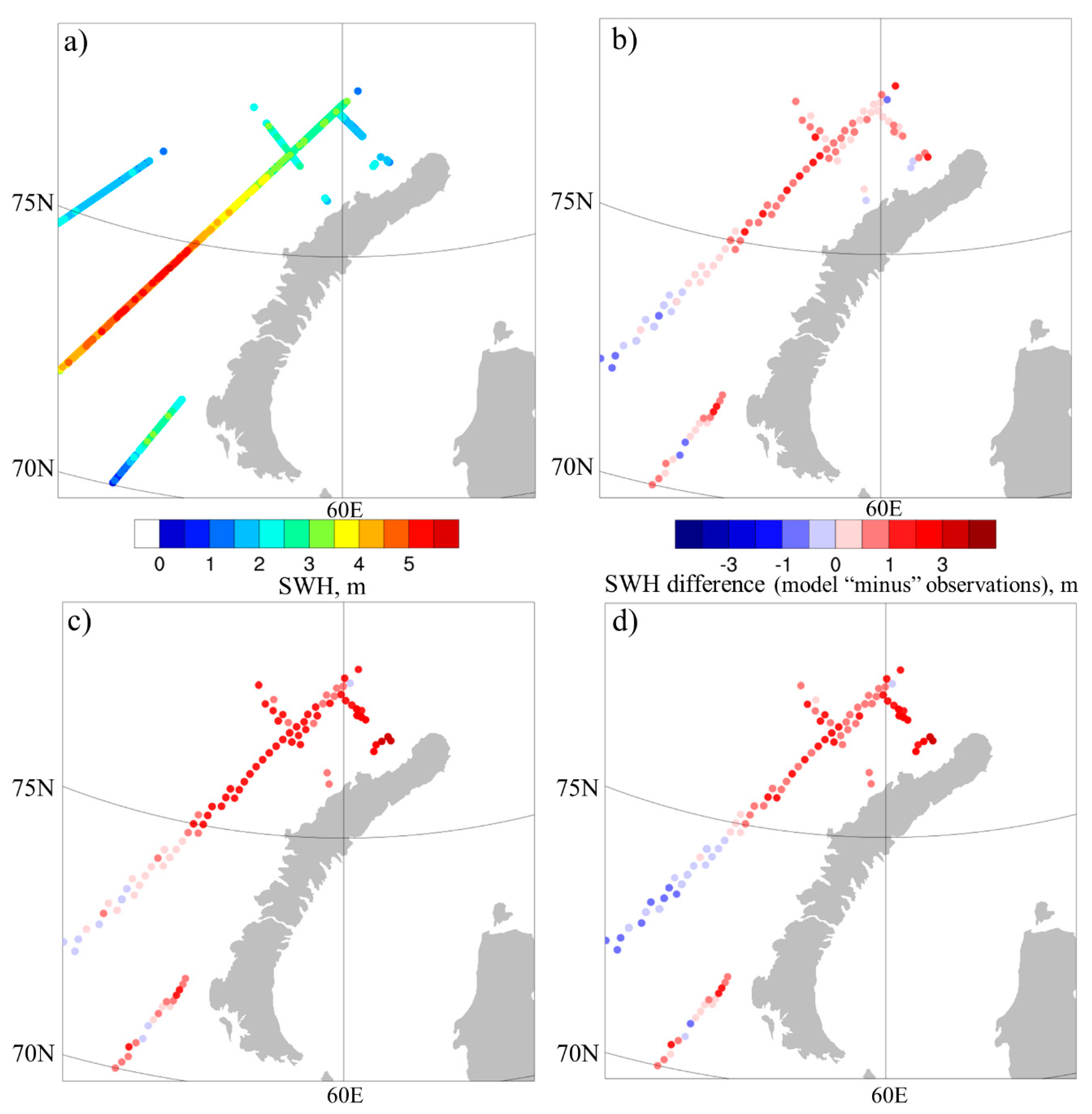
3.2.1. Model Verification
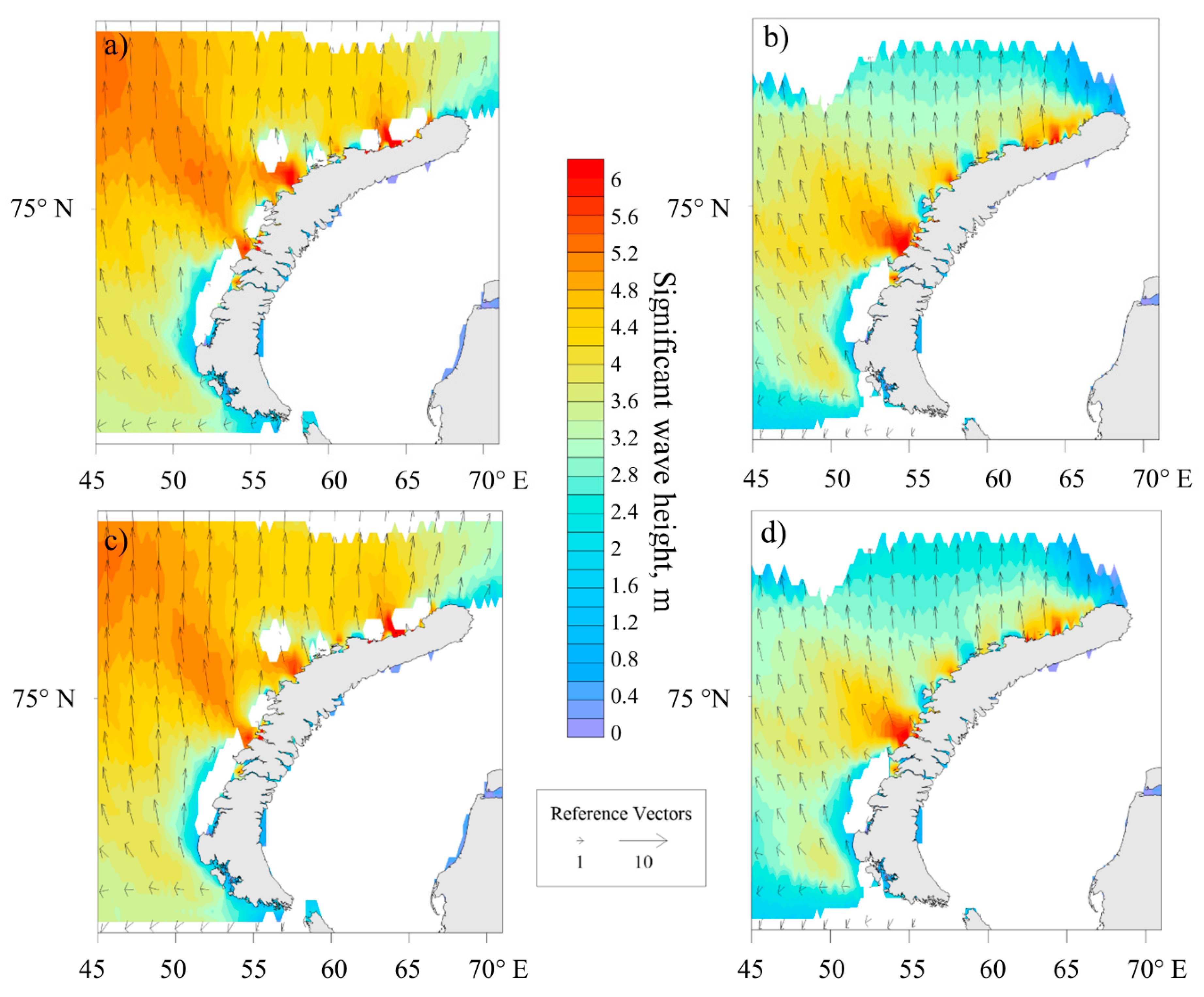
3.2.2. Bora and Sea Wave Evolution during the Episodes
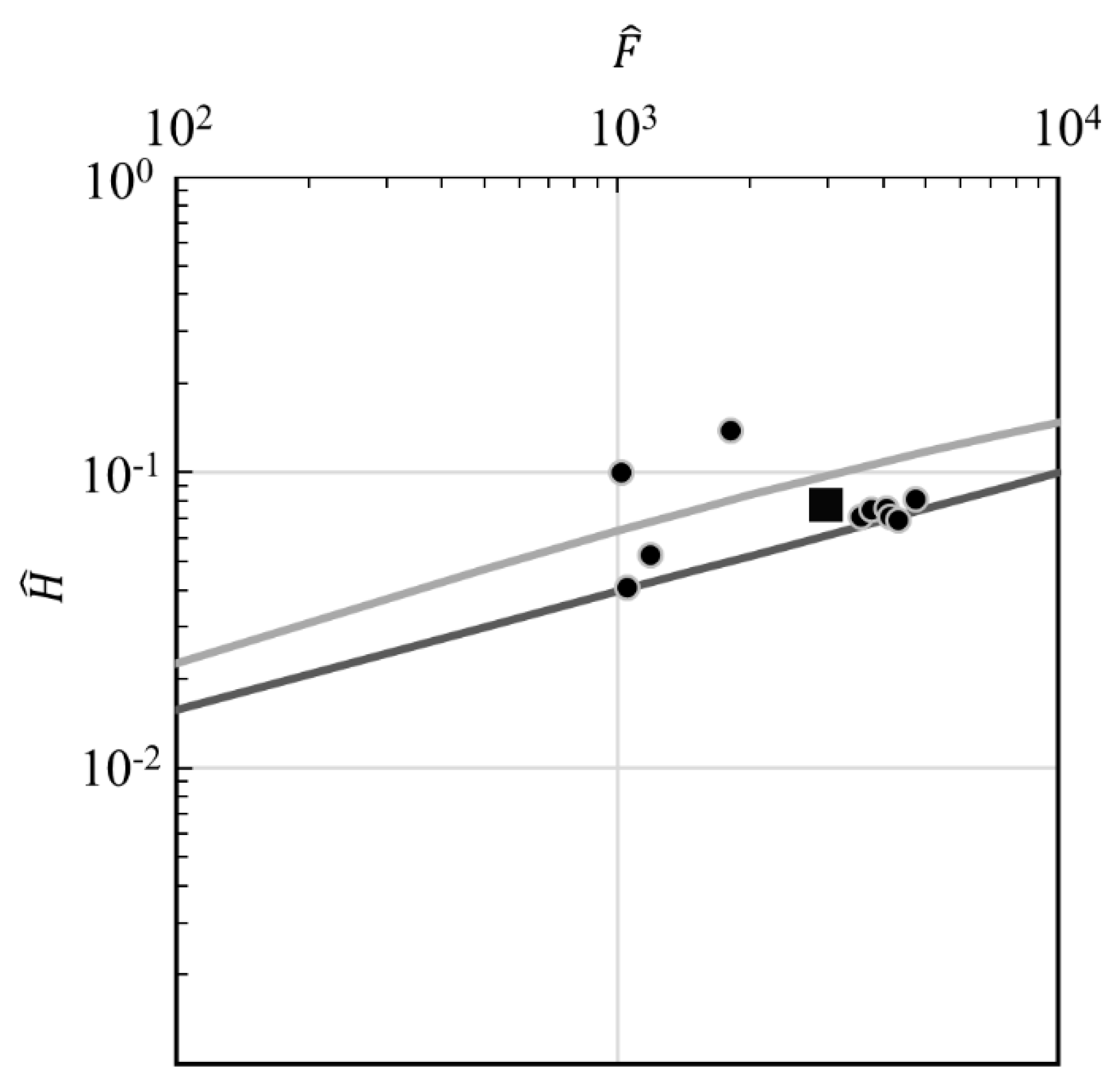
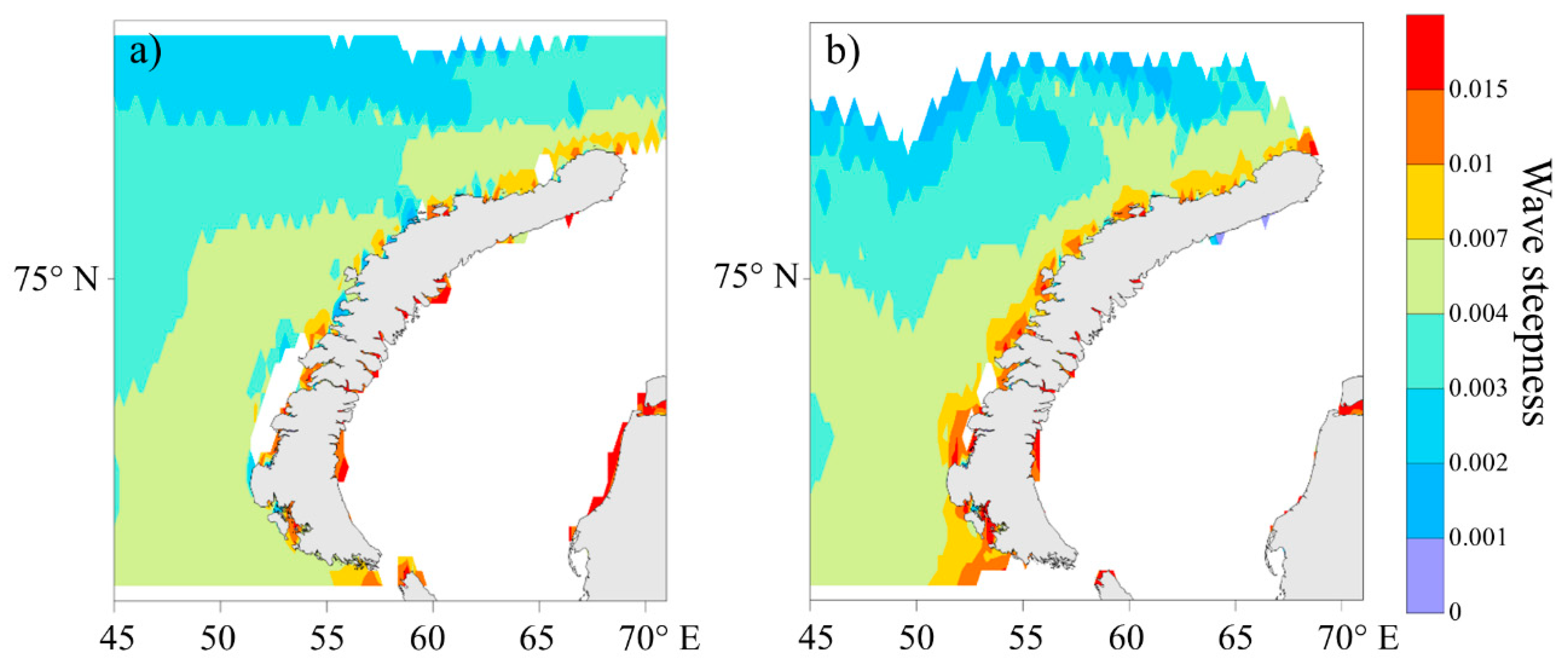
3.2.3. Features of Bora-Caused Waves
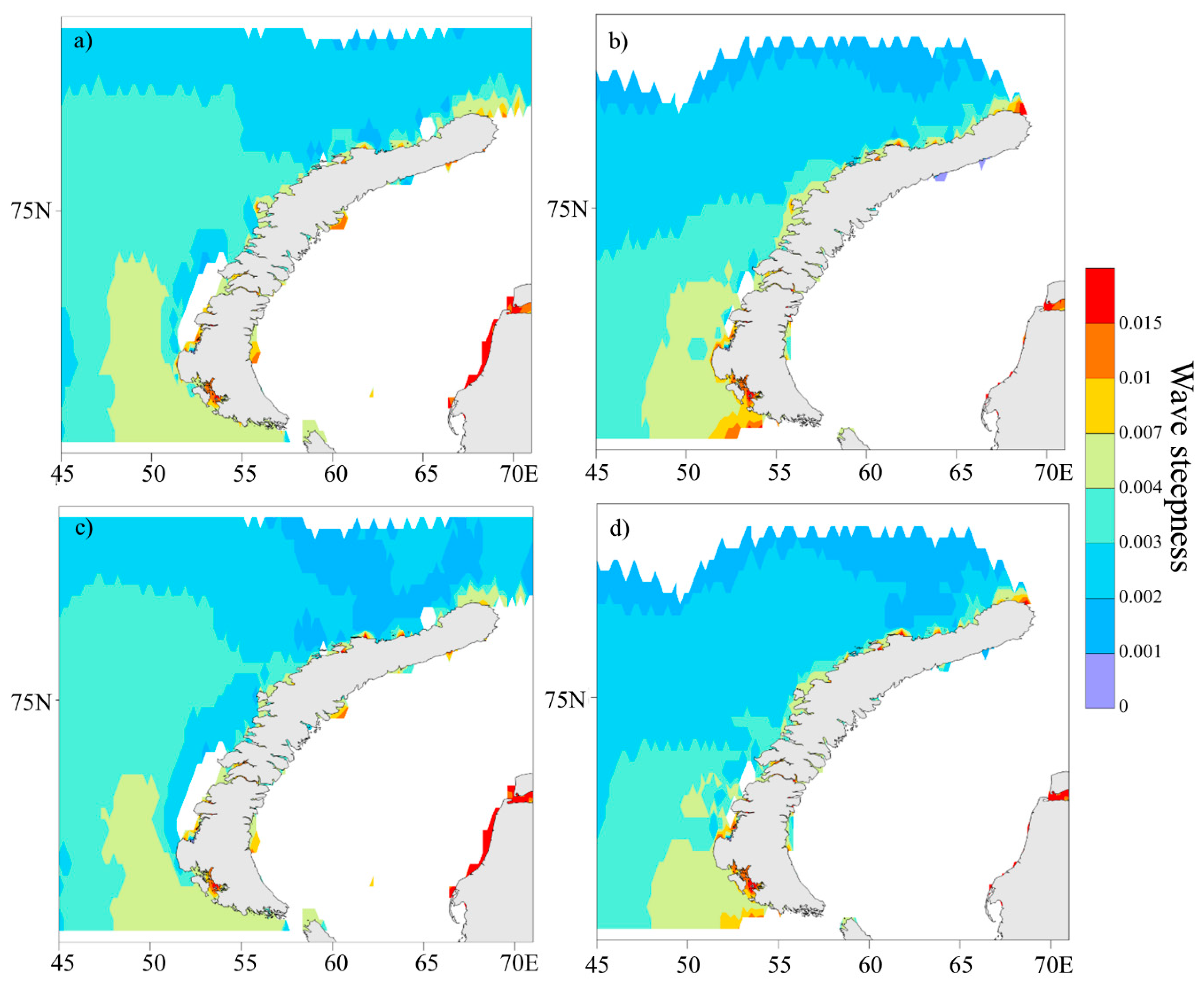
3.3. Impact of Wind Input Parametrizations on Modeling Results
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vize, V.Y. The Novaya Zemlya bora. Izv. Tsentr. Gidrometeorol. Byuro 1925, 5, 1–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shestakova, A.A.; Toropov, P.A.; Matveeva, T.A. Climatology of extreme downslope windstorms in the Russian Arctic. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2020, 28, 100256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, E.M.; Graversen, R.G. Weather situation during observed ship-icing events off the coast of Northern Norway and the Svalbard archipelago. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2019, 24, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastusiak, T. Northern Sea Route as a Shipping Lane; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 219. [Google Scholar]
- Buzin, I.V.; Glazovskiy, A.F. Icebergs of shokalsky glacier, Novaya Zemlya. Mater. Glaciol. Res. 2005, 99, 39–44. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Langodan, S.; Cavaleri, L.; Viswanadhapalli, Y.; Hoteit, I. The Red Sea: A natural laboratory for wind and wave modeling. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 3139–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toropov, P.A.; Myslenkov, S.A.; Shestakova, A.A. Numerical simulation of Novorossiysk bora and related wind waves using the WRF-ARW and SWAN models. Russ. J. Earth Sci. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakova, A.A.; Repina, I.A. Overview of strong winds on the coasts of the Russian Arctic seas. Ecol. Montenegrina 2019, 25, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryazgin, N.N.; Dementiev, A.A. Hazardous Meteorological Phenomena in the Russian Arctic; Gidrometeoizdat: Sankt-Petersburg, Russia, 1996; p. 150. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.W.K. The Novaya Zemlya Bora and its impact on Barents Sea air-sea interaction. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3462–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.Y. Novaya Zemlya Bora and Polar Cyclones Visible from Space in Radar and Optical Imagery. Issled. Zemli Kosm. 2016, 4, 9–22. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakova, A.A. The Novaya Zemlya bora: The downwind characteristics and the incomming flow structure. Arct. Antarct. 2016, 2, 86–98. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, V.V.; Komarovskaya, O.I. The Novaya Zemlya Bora: Analysis and Numerical Modeling. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2018, 54, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakova, A.A.; Moiseenko, K.B. Hydraulic regimes of flow over mountains during severe downslope windstorms: Novorossiysk bora, Novaya Zemlya bora, and Pevek Yuzhak. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2018, 54, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.W. Numerical prediction of ocean waves in the North Atlantic for December, 1959. Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z. 1965, 18, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkin, P.A.; Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Chapron, B. On wind wave development in the Arctic seas based on AltiKa altimeter measurements. Sovrem. Probl. Distancionnogo Zondirovaniya Zemli Kosm. 2017, 14, 179–192. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, P.; Grønås, S. Strongly stratified easterly flows across Spitsbergen. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2000, 52, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestakova, A.A.; Toropov, P.A.; Stepanenko, V.M.; Sergeev, D.E.; Repina, I.A. Observations and modelling of downslope windstorm in Novorossiysk. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2018, 83, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durran, D.R. Another look at downslope windstorms. Part I: The development of analogs to supercritical flow in an infinitely deep, continuously stratified fluid. J. Atmos. Sci. 1986, 43, 2527–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.Y. Local katabatic winds of the Russian Federation and their observation from space using SAR imagery. Issled. Zemli Kosm. 2019, 5, 15–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Kawamura, H. Wind-wave development under alternating wind jets and wakes induced by orographic effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RIHMI-WDC. Available online: http://meteo.ru/ (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Golubkin, P.A.; Kudryavtsev, V.N.; Chapron, B. Wind Waves in the Arctic Seas from Satellite Altimetry Data. Issled. Zemli Kosm. 2015, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribal, A.; Young, I.R. 33 years of globally calibrated wave height and wind speed data based on altimeter observations. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AODN. Available online: https://portal.aodn.org.au/ (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Janssen, P.; Abdalla, S.; Hersbsch, H.; Bidlot, J.-R. Error estimation of buoy, satellite, and model wave height data. J. Atm. Ocean. Tech. 2006, 24, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, C.; Bansal, S.; Krishnaveni, A.S.; Chacko, N.; Chowdary, V.M.; Dutta, D.; Rao, K.H.; Dutt, C.B.S.; Sharma, J.R.; Dadhwal, V.K. Evaluation of SARAL/AltiKa Measured Significant Wave Height and Wind Speed in the Indian Ocean Region. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2016, 44, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourrion, J.; Vandemark, D.; Bailey, S.; Chapron, B.; Gommenginger, G.P.; Challenor, P.G.; Srokosz, M.A. A two-parameter wind speed algorithm for Ku-band altimeters. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 2030–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkin, P.A.; Chapron, B.; Kudryavtsev, V.N. Wind Waves in the Arctic Seas: Envisat and AltiKa Data Analysis. Mar. Geod. 2014, 38, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, H.; Golubkin, P.; Chapron, B. Impact of the sea state on altimeter measurements in coastal regions. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.Y.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Lebedev, S.A.; Mityagina, V.I.; Ginzburg, A.I.; Sheremet, N.A. Complex Satellite Monitoring of the Russian Seas; IKI RAN: Moscow, Russia, 2011; p. 470. [Google Scholar]
- Myslenkov, S.A.; Markina, M.Y.; Arkhipkin, V.S.; Tilinina, N.D. Frequency of storms in the Barents Sea under modern climate conditions. Vestn. Mosk. Univ. Seriya 5 Geogr. 2019, 2, 45–54. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) 6-Hourly Products, January 1979 to December 2010; Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory: Boulder, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.-T.; Chuang, H.-Y.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myslenkov, S.A.; Markina, M.Y.; Kiseleva, S.V.; Stoliarova, E.V.; Arkhipkin, V.S.; Umnov, P.M. Estimation of Available Wave Energy in the Barents Sea. Therm. Eng. 2018, 65, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myslenkov, S.; Medvedeva, A.; Arkhipkin, V.; Markina, M.; Surkova, G.; Krylov, A.; Dobrolyubov, S.; Zilitinkevich, S.; Koltermann, P. Long-term statistics of storms in the Baltic, Barents and White Seas and their future climate projections. Geogr. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 11, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.; Cassano, J.J. The climatological distribution of extreme Arctic winds and implications for ocean and sea ice processes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7358–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, H.L. User Manual and System Documentation of WAVEWATCHIII Version 4.18.; Technical Note; NOAA; NWS; NCEP; MMAB: College Park, MD, USA, 2014; 302p. Available online: https://polar.ncep.noaa.gov/waves/wavewatch/manual.v4.18 (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Deng, X.; Featherstone, W.E.; Hwang, C.; Berry, P.A.M. Estimation of contamination of ERS-2 and POSEIDON satellite radar altimetry close to the coasts of Australia. Mar. Geod. 2002, 25, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASR v.2 Download Page. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds631.1/ (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Buckley, W.H. Extreme and climatic wave spectra for use in structural design of ships. Nav. Eng. J. 1988, 100, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natinal Data Buoy Center. Available online: https://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/wavecalc.shtml (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Polnikov, V.G.; Zilitinkevich, N.S.; Pogarskii, F.A.; Kubryakov, A.A. Comparative evaluation of accuracy of numerical wave models based on satellite altimetry data. Process. Geosredah 2017, 4, 700–709. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Wind-stress coefficients over sea surface from breeze to hurricane. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 9704–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repina, I.A.; Artamonov, A.Y.; Varentsov, M.I.; Kozyrev, A.V. Experimental study of the sea surface wind drag coefficient at strong winds. Morsk. Gidrofiz. Zhurnal 2015, 1, 53–63. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuznetsova, A.M.; Baydakov, G.A.; Papko, V.V.; Kandaurov, A.A.; Vdovin, M.I.; Sergeev, D.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I. Adjusting of wind input source term in WAVEWATCH III model for the middle-sized water body on the basis of the field experiment. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.M.; Dosaev, A.S.; Baydakov, G.A.; Balandina, G.N.; Sergeev, D.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I. Adjusting of the discrete interaction approximation (DIA) nonlinear source term in WaveWatchIII model to the conditions of the middle-sized reservoir. Process. Geosredah 2018, 3, 160–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.M.; Dosaev, A.S.; Baydakov, G.A.; Sergeev, D.A.; Troitskaya, Y.I. Adaptation of the Nonlinear Wave-Wave Interaction Parameterization for the Short Fetches Conditions in the Wave Prediction Model WAVEWATCH III. Izv. Ross. Akad. Nauk Fiz. Atmos. Okeana 2020, 56, 224–233. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, W.E.; Babanin, A.V.; Wang, D.W. Observation-consistent input and whitecapping dissipation in a model for wind-generated surface waves: Description and simple calculations. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 1329–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieger, S.; Babanin, A.V.; Rogers, W.E.; Young, I.R. Observation-based source terms in the third-generation wave model WAVEWATCH. Ocean Model. 2015, 96, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vledder, G.P.; Hulst, S.T.C.; McConochie, J.D. Source term balance in a severe storm in the Southern North Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2016, 66, 1681–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Rogers, W.E.; Babanin, A.V.; Young, I.R.; Romero, L.; Zieger, S.; Qiao, F.; Guan, C. Observation-based source terms in the third-generation wave model WAVEWATCH III: Updates and verification. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2019, 49, 489–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, R.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A. A note on nearshore wave features: Implications for wave generation. Prog. Oceanogr. 2006, 70, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoguchi, O.; Kawamura, H. Coastal wind jets flowing into the Tsushima Strait and their effect on wind-wave development. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.; Badulin, S.; Hwang, P.; Caulliez, G. Universality of sea wave growth and its physical roots. J. Fluid Mech. 2015, 780, 503–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO-No. 702. In Guide to Wave Analysis and Forecasting, 2nd ed.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1998; p. 159.
- Bidlot, J.R.; Holmes, D.J.; Wittmann, P.A.; Lalbeharry, R.; Chen, H.S. Intercomparison of the performance of operational ocean wave forecasting systems with buoy data. Weather Forecast 2002, 17, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunney, C.; Saulter, A. An ensemble forecast system for prediction of Atlantic–UK wind waves. Ocean Model. 2015, 96, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.K.; Yelland, M.J. The dependence of sea surface roughness on the height and steepness of the waves. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitajgorodskij, S.A.; Volkov, Y.A. On the roughness parameter of the sea surface and the calculation of turbulent momentum fluxes in the near-water layer of the atmosphere. Izv. SSSR Fizika Atmos. Okeana 1965, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, X. High-wind-speed evaluation in the Southern Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandu, I.; van Niekerk, A.; Shepherd, T.G.; Vosper, S.B.; Zadra, A.; Bacmeister, J.; Beljaars, A.; Brown, A.; Dörnbrack, A.; McFarlane, N.; et al. Impacts of orography on large-scale atmospheric circulation. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehama, T.; Sandu, I.; Beljaars, A.; van Niekerk, A.; Lott, F. Which orographic scales matter most for medium-range forecast skill in the Northern Hemisphere winter? J. Adv. Modeling Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 3893–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO-No. 471. In Guide to Marine Meteorological Services; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; p. 69.
| ST1 | ST6 | ST1_mod | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | |||
| Bias, m | −0.2 | −0.22 | −0.3 |
| RMSE, m | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.86 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 2009 | |||
| Bias, m | 0.1 | 0.73 | 0.39 |
| RMSE, m | 0.62 | 1.1 | 0.93 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.65 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shestakova, A.A.; Myslenkov, S.A.; Kuznetsova, A.M. Influence of Novaya Zemlya Bora on Sea Waves: Satellite Measurements and Numerical Modeling. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070726
Shestakova AA, Myslenkov SA, Kuznetsova AM. Influence of Novaya Zemlya Bora on Sea Waves: Satellite Measurements and Numerical Modeling. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(7):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070726
Chicago/Turabian StyleShestakova, Anna A., Stanislav A. Myslenkov, and Alexandra M. Kuznetsova. 2020. "Influence of Novaya Zemlya Bora on Sea Waves: Satellite Measurements and Numerical Modeling" Atmosphere 11, no. 7: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070726
APA StyleShestakova, A. A., Myslenkov, S. A., & Kuznetsova, A. M. (2020). Influence of Novaya Zemlya Bora on Sea Waves: Satellite Measurements and Numerical Modeling. Atmosphere, 11(7), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11070726






