Modeling Compact Intracloud Discharge (CID) as a Streamer Burst
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Positive Streamers
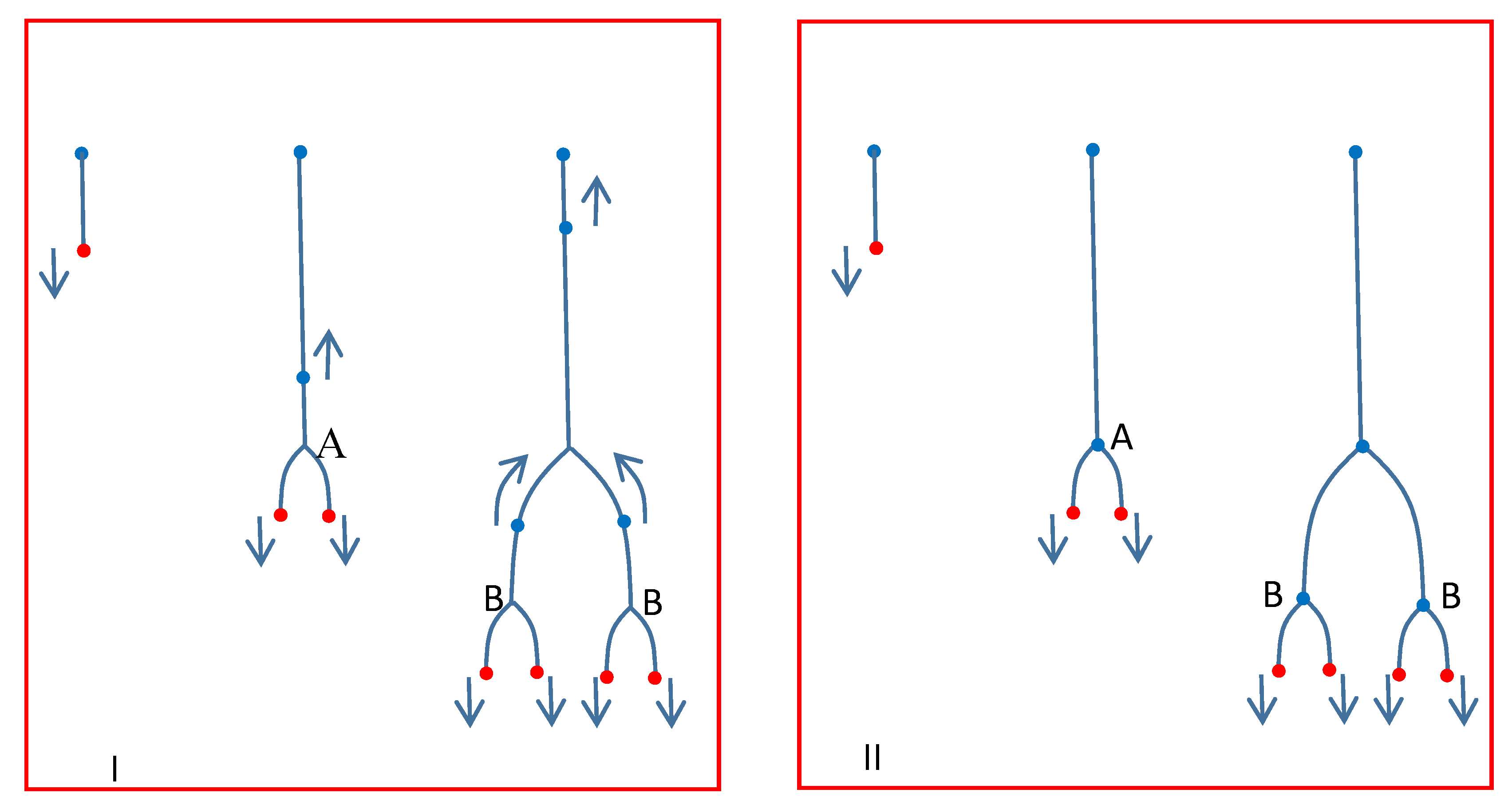
3. CID as a Streamer Burst and the Current Associated with the Streamers
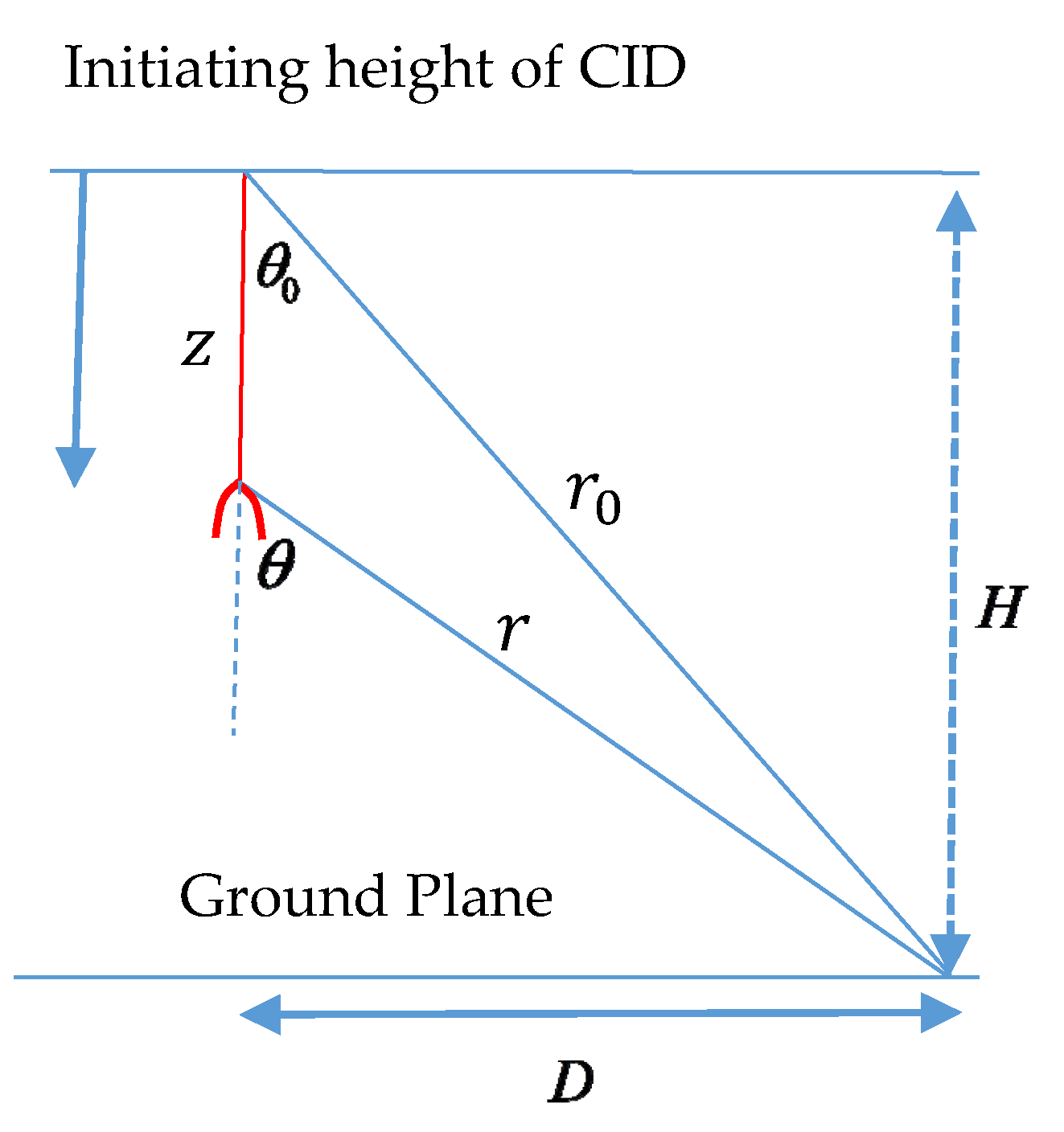
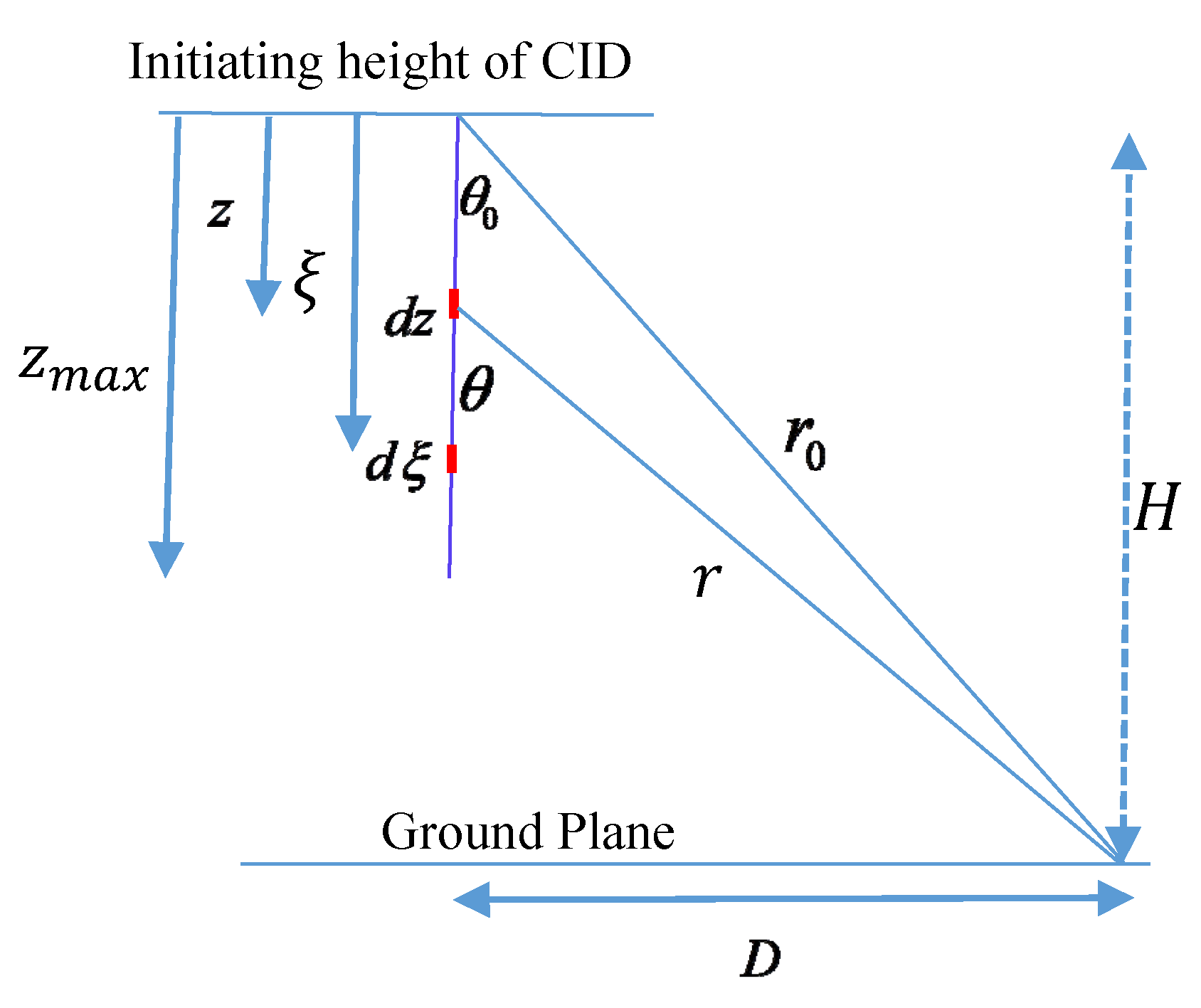
4. Radiation Field Generated by the Initiation and Branching of a Streamer Channel
5. Electric Field Generated by the Streamer Burst
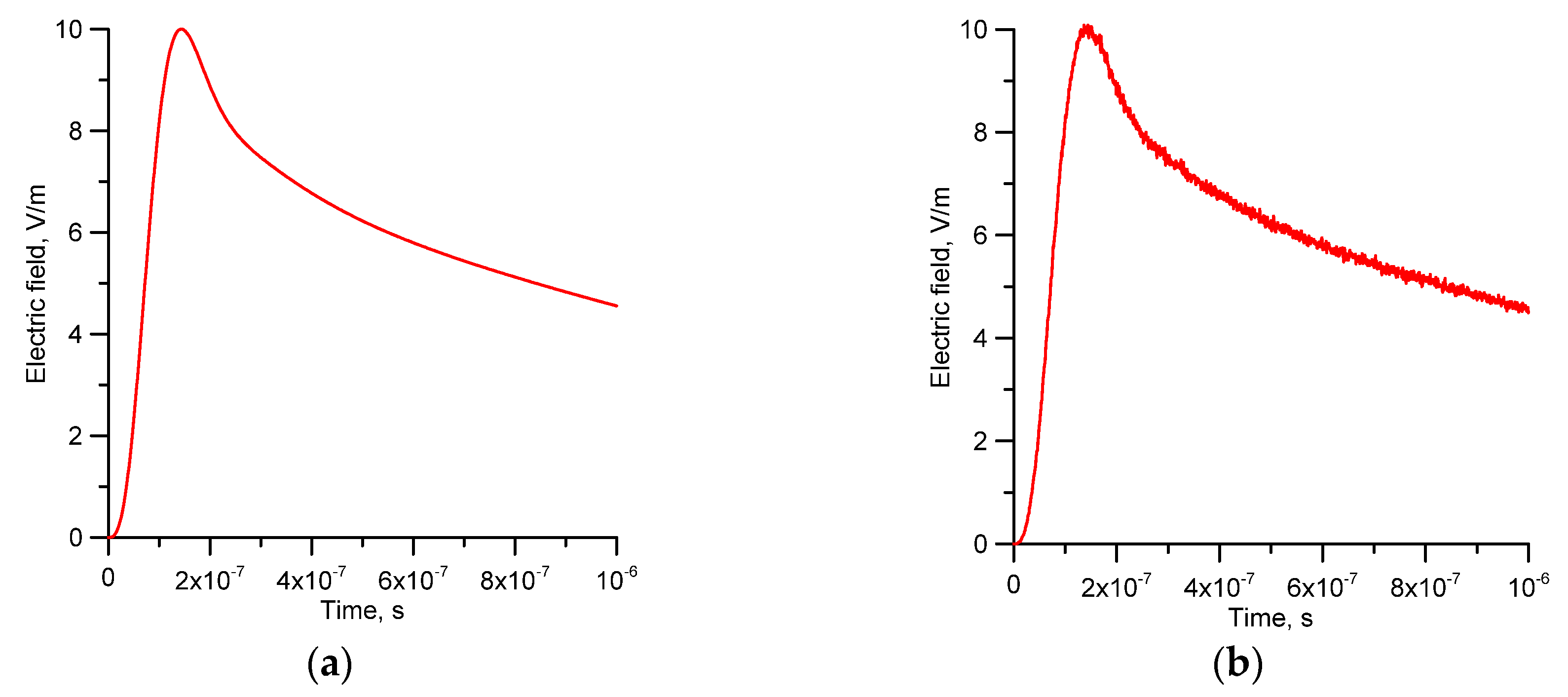
5.1. Radiation Field
5.2. Velocity Field Generated by the Streamer Burst
5.3. Static Field Generated by the Streamer Burst
6. Growth Parameters of Streamer Burst That Best Represent CID
7. Characteristics of the Streamer Bursts Giving Rise to NBPs
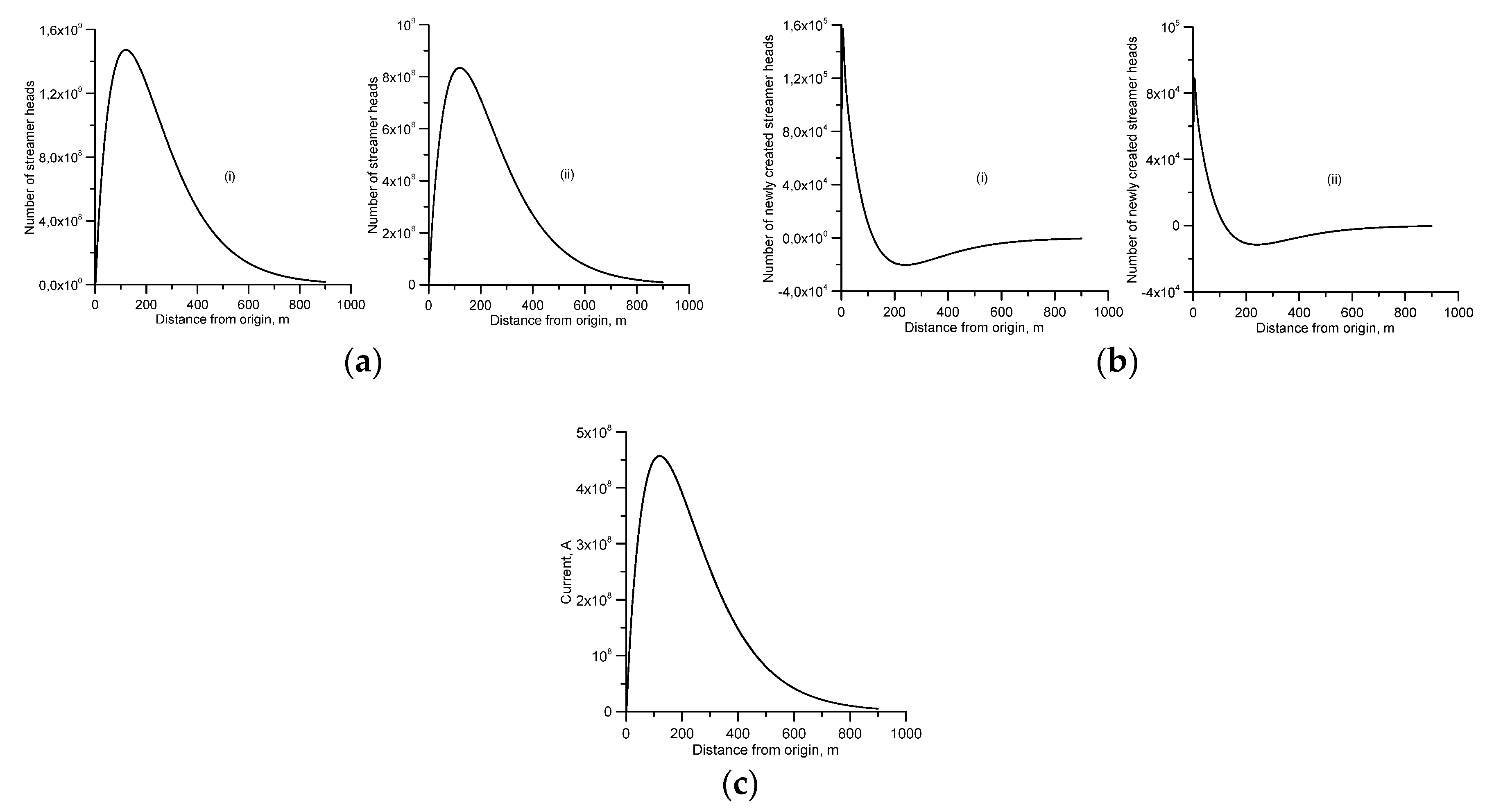
7.1. The Growth Rate of Streamer Heads and the Current
7.2. Charge Deposition in Space by the Streamer Burst
7.3. The Effect of Dispersion of the Backward Moving Current
7.4. Reasons for the Finer Features of the NBPs
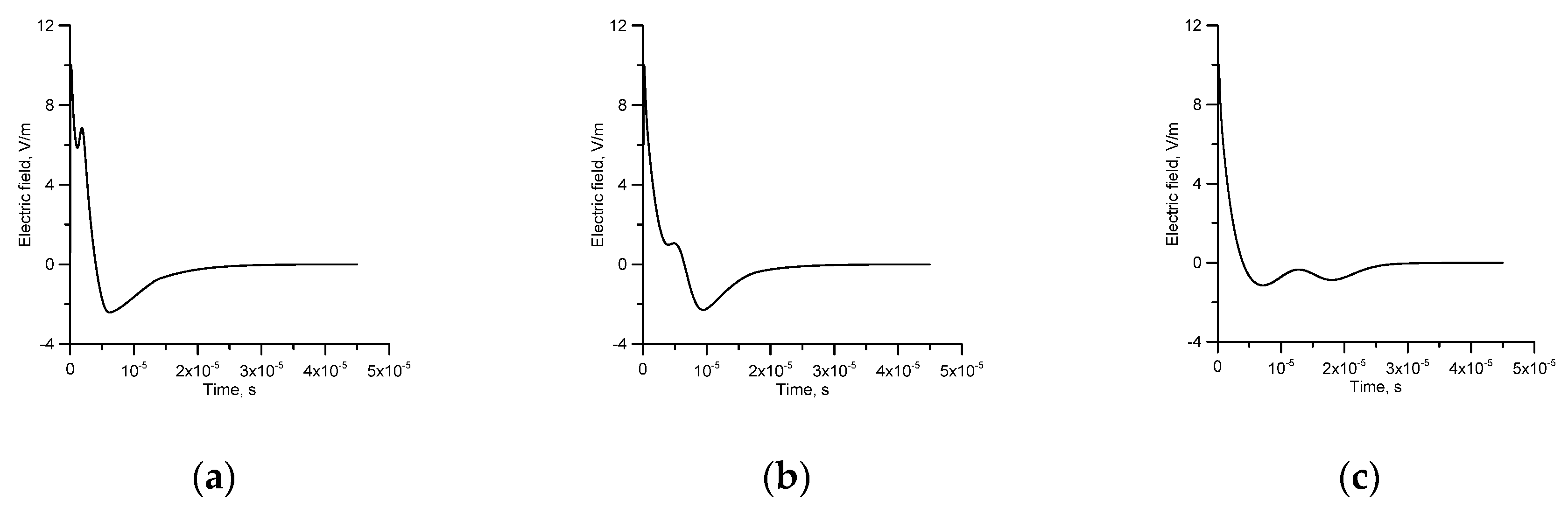
7.5. The Effect of the Random Nature of the Branching Process
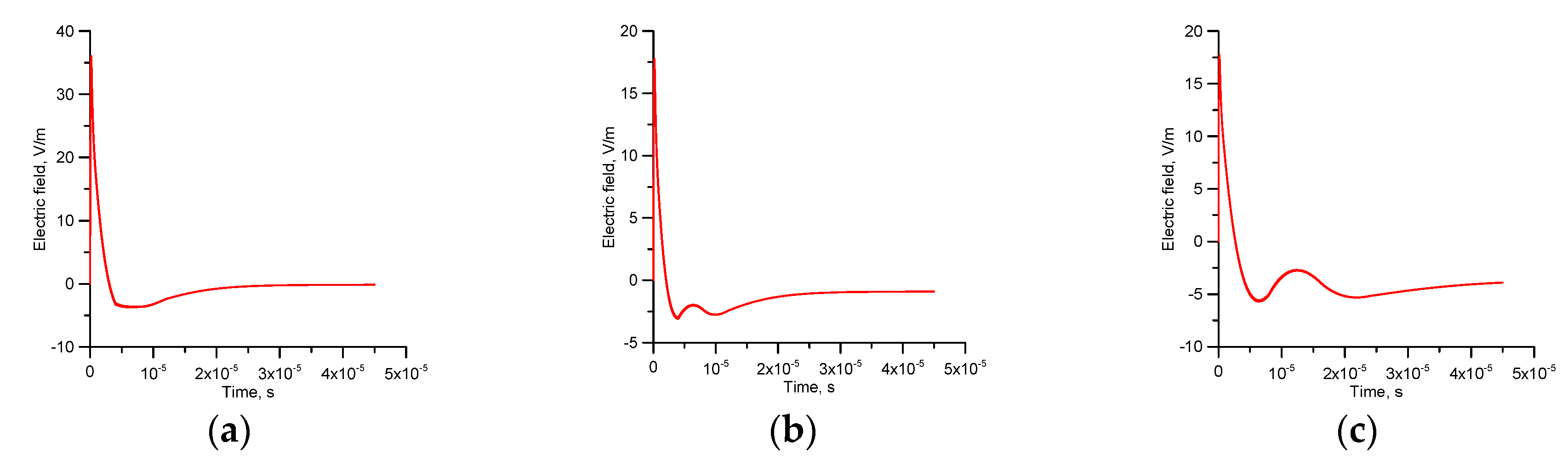
7.6. Field Signature as a Function of the Distance
8. Discussion
8.1. Streamer Initiation
8.2. Thermalization
8.3. Streamer Speed
8.4. A final Comment
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Vine, D.M. Sources of the strongest RF radiation from lightning. J. Geophys. Res. 1980, 85, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willett, J.C.; Bailey, J.C.; Krider, E.P. A class of unusual lightning electric field waveforms with very strong high-frequency radiation. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 16255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.; Shao, X.M.; Holden, D.N.; Rhodes, C.T.; Brook, M.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Stanley, M.; Rison, W.; Thomas, R.J. A distinct class of isolated intracloud lightning discharges and their associated radio emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 4189–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Rakov, V.A.; Tsalikis, D.; Cramer, J.A. On phenomenology of compact intracloud lightning discharges. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Rakov, V.A. Compact intracloud lightning discharges: 1. Mechanism of electromagnetic radiation and modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathne, S.; Marshall, T.C.; Stolzenburg, M.; Karunarathna, N. Observations of positive narrow bipolar pulses. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7128–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, S.; Marshall, T.; Karunarathne, S.; Stolzenburg, M. Electric field change and VHF waveforms of Positive Narrow Bipolar Events in Mississippi thunderstorms. Atmos. Res. 2020, 243, 105000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.F.R.; Rakov, V.A.; da Rocha, B.R.P. Classification of CIDs observed in Florida using the Lightning Detection and Waveform Storage System (LDWSS). In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Lightning Protection (XIV SIPDA), Natal, Brazil, 2–6 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Cooray, V.; Lundquist, S. Characteristics of the radiation fields from lightning in Sri Lanka in the tropics. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 6099–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.R.; Fernando, M.; Cooray, V. Narrow positive bipolar radiation from lightning observed in Sri Lanka. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, L.; Fernando, M.; Sonnadara, U.; Cooray, V. Characteristics of Narrow Bipolar Pulses observed from lightning in Sri Lanka. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2016, 138–139, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Fernando, M.; Baharudin, Z.A.; Cooray, V.; Ahmad, H.; Abdul Malek, Z. Characteristics of narrow bipolar pulses observed in Malaysia. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2010, 72, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.R.; Esa, M.R.M.; Cooray, V.; Baharudin, Z.A.; Hettiarachchi, P. Latitude dependence of narrow bipolar pulse emissions. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2015, 128, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V.; Cooray, G.; Marshall, T.; Arabshahi, S.; Dwyer, J.; Rassoul, H. Electromagnetic fields of a relativistic electron avalanche with special attention to the origin of lightning signatures known as narrow bipolar pulses. Atmos. Res. 2014, 149, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V.; Fernando, M.; Gunasekara, L.; Nanayakkara, S. Effects of Propagation of Narrow Bipolar Pulses, Generated by Compact Cloud Discharges, over Finitely Conducting Ground. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Funaki, T.; Yoshida, S.; Morimoto, T.; Ushio, T.; Kawasaki, Z. Discharge height of lightning narrow bipolar events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.R.F.; Rakov, V.A.; Rocha, B.R.P. Estimation of ionospheric reflection heights using CG and IC lightning electric field waveforms. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Lightning Protection (XIV SIPDA), Natal, Brazil, 2–6 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krehbiel, P.; da Silva, C.; Cummer, S. Continued mysteries of lightning studies. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Atmospheric Electricity, Nara, Japan, 17–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Medvedev, Y.V.; Zybin, K.P. New type discharge generated in thunderclouds by joint action of runaway breakdown and extensive atmospheric shower. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 329, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Zybin, K.P. Runaway Breakdown and the Mysteries of Lightning. Phys. Today 2005, 58, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, T.C.; Watson, S.S. Current propagation model for a narrow bipolar pulse. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, P.; Bochkov, E.I.; Kutsyk, I.M. Numerical simulation of compact intracloud discharge and generated electromagnetic pulse. Dokl. Earth Sci. 2015, 462, 569–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rison, W.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Stock, M.G.; Edens, H.E.; Shao, X.-M.; Thomas, R.J.; Stanley, M.A.; Zhang, Y. Observations of narrow bipolar events reveal how lightning is initiated in thunderstorms. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilles, J.N.; Liu, N.; Stanley, M.A.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Stock, M.G.; Dwyer, J.R.; Brown, R.; Wilson, J. Fast negative breakdown in thunderstorms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iudin, I.; Davydenko, S.S. Fractal model of a compact intracloud discharge. I. Features of the structure and evolution. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2015, 58, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydenko, S.S.; Iudin, D.I. Fractal model of a compact intracloud discharge. II. Specific features of electromagnetic emission. Radiophys. Quantum Electron. 2016, 59, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanasio, A.; Krehbiel, P.R.; da Silva, C.L. Griffiths and Phelps Lightning Initiation Model, Revisited. J. Geophys. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Dwyer, J.R.; Tilles, J.N.; Stanley, M.A.; Krehbiel, P.R.; Rison, W.; Brown, R.G.; Wilson, J.G. Understanding the radio spectrum of thunderstorm narrow bipolar events. J. Geophys. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.F.; Phelps, C.T. A model for lightning initiation arising from positive corona streamer development. J. Geophys. Res. 1976, 81, 3671–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimberti, I. The mechanism of long spark formation. J. Phys. Colloq. 1979, 40, 193–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briels, T.M.P.; Kos, J.; Winands, G.J.J.; van Veldhuizen, E.M.; Ebert, U. Positive and negative streamers in ambient air: measuring diameter, velocity and dissipated energy. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 234004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briels, T.M.P.; van Veldhuizen, E.M.; Ebert, U. Positive streamers in air and nitrogen of varying density: experiments on similarity laws. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 234008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les Renardières Group, L.R. Research on long gap discharges at Les Renardières. Electra 1972, 23, 53–157. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrov, N.L.; Bazelyan, E.M. Temperature and density effects on the properties of long positive streamer in air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 2873–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasco, P.V. Theoretical modeling of sprites and jets. In Sprites, Elves and Intense Lightning Discharges; Füllekrug, M., Mareev, E., Rycroft, M.J., Eds.; Nato Science Series; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cooray, V.; Cooray, G. The Electromagnetic Fields of an Accelerating Charge: Applications in Lightning Return-Stroke Models. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2010, 52, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, G.; Cooray, V. Electromagnetic fields of a short electric dipole in free space—Revisited. Prog. Electromagn. Res. Lett. 2012, 131, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V.; Cooray, G.; Rubinstein, M.; Rachidi, F. Generalized Electric Field Equations of a Time-Varying Current Distribution Based on the Electromagnetic Fields of Moving and Accelerating Charges. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eack, K.B. Electrical characteristics of narrow bipolar events, Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathne, S.; Marshall, T.C.; Stolzenburg, M.; Karunarathna, N. Electrostatic field changes and durations of narrow bipolar events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 10–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, S.; Liu, N.; Dwyer, J.R.; Rassoul, H.K. Streamer formation and branching from model hydrometeors in subbreakdown conditions inside thunderclouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3660–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, L.P.; Bochkov, E.I.; Neubert, T. The role of charged ice hydrometeors in lightning initiation. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2017, 154, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhn, C.; Chanrion, O.; Neubert, T. HighEnergy Emissions Induced by Air Density Fluctuations of Discharges. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 10, 5194–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinova, A.; Rutjes, C.; Ebert, U.; Buitink, S.; Scholten, O.; Trinh, G.T. Prediction of lightning inception by large ice particles and extensive air showers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.R. The initiation of lightning by runaway air breakdown. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L20808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, V. Mechanism of Electrical Discharges. In The Lightning Flash, 2nd ed.; Cooray, V., Ed.; IETPublishers: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]




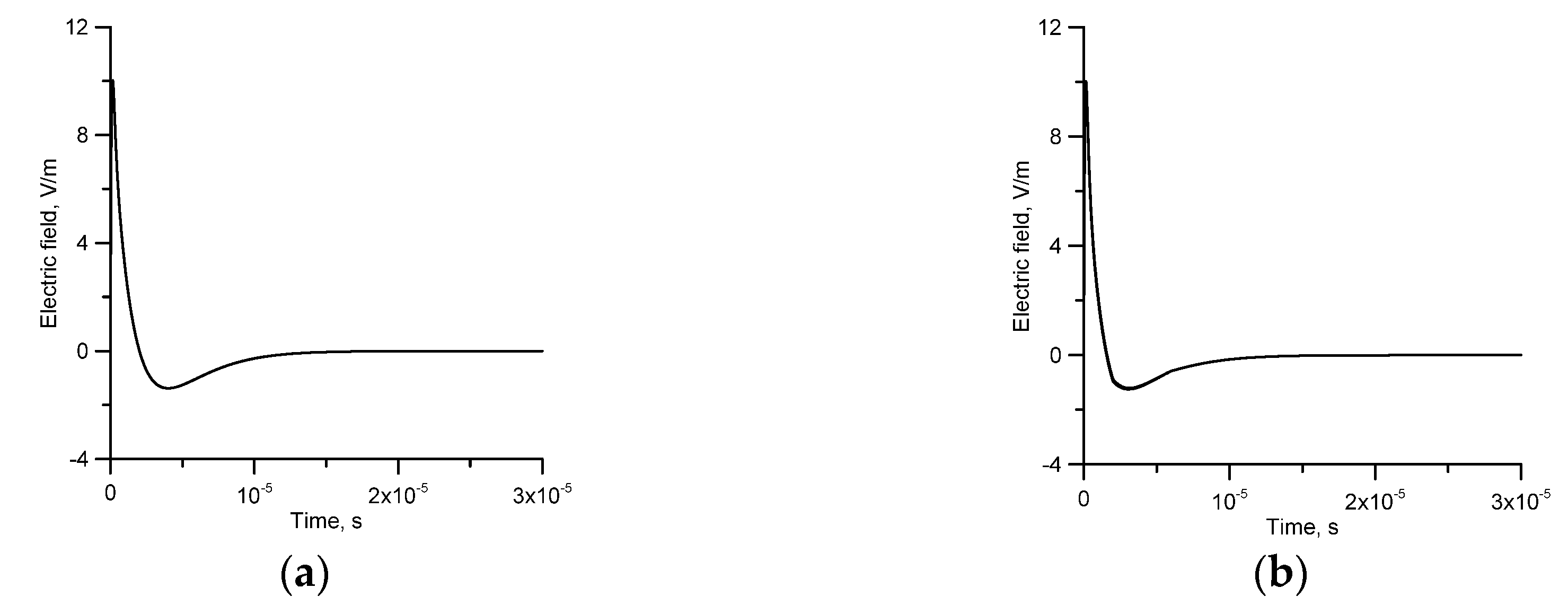








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cooray, V.; Cooray, G.; Rubinstein, M.; Rachidi, F. Modeling Compact Intracloud Discharge (CID) as a Streamer Burst. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050549
Cooray V, Cooray G, Rubinstein M, Rachidi F. Modeling Compact Intracloud Discharge (CID) as a Streamer Burst. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(5):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050549
Chicago/Turabian StyleCooray, Vernon, Gerald Cooray, Marcos Rubinstein, and Farhad Rachidi. 2020. "Modeling Compact Intracloud Discharge (CID) as a Streamer Burst" Atmosphere 11, no. 5: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050549
APA StyleCooray, V., Cooray, G., Rubinstein, M., & Rachidi, F. (2020). Modeling Compact Intracloud Discharge (CID) as a Streamer Burst. Atmosphere, 11(5), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11050549






