Abstract
There is significant iron deposition in the oceans, approximately 14–16 Tg annually from mineral dust aerosols, but only a small percentage (approx. 3%) of it is soluble and, thus, bioavailable. In this work, we examine the effect of mineralogy, particle size, and surface area on iron solubility in pure mineral phases to simulate atmospheric processing of mineral dust aerosols during transport. Pure iron-bearing minerals common to Saharan dust were partitioned into four size fractions (10–2.5, 2.5–1, 1–0.5, and 0.5–0.25 µm) and extracted into moderately acidic (pH 4.3) and acidic (pH 1.7) leaching media to simulate mineral processing during atmospheric transport. Results show that, in general, pure iron-bearing clay materials present an iron solubility (% dissolved Fe/total Fe in the mineral) an order of magnitude higher than pure iron oxide minerals. The relative solubility of iron in clay particles does not depend on particle size for the ranges examined (0.25–10 μm), while iron in hematite and magnetite shows a trend of increasing solubility with decreasing particle size in the acidic leaching medium. Our results indicate that while mineralogy and aerosol pH have an effect on the solubilization of iron from simulated mineral dust particles, surface processes of the aerosol might also have a role in iron solubilization during transport. The surface area of clay minerals does not change significantly as a function of particle size (10–0.25 µm), while the surface area of iron oxides is strongly size dependent. Overall, these results show how mineralogy and particle size can influence iron solubility in atmospheric dust.
1. Introduction
Oceans are responsible for removing approximately one-third of anthropogenic CO2 from the Earth’s atmosphere [1]. Photosynthetic uptake by marine phytoplankton plays a key role in that removal. In many ocean regions, the rate of photosynthetic uptake is ultimately controlled by upwelling, which transfers nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, to the photic zone from deep waters. However, in some parts of the ocean, the concentration of these nutrients exceeds demand [2]. Iron—which is biologically essential but scarce in upwelled deep ocean water—is the limiting factor in these high nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC) regions, which dominate the Southern Ocean [3,4,5,6].
There are a variety of iron sources to the open ocean, depending on location. In remote ocean regions, such as the sub-Arctic, Southern Ocean, and equatorial Pacific Ocean, atmospheric mineral dust is a major source of iron, in addition to resuspension of coastal sediments, glacial melt, hydrothermal vents, sediment interactions, and volcanic activity [7,8,9]. In other ocean regions, atmospheric inputs from urban pollution, specifically oil and coal fly ash, can be a substantial source of iron [10,11].
Atmospheric mineral dust contains approximately 3% iron by mass and can undergo long range transport, resulting in an estimated 14–16 Tg of iron deposited into the oceans annually [7,12]. However, only a very small fraction of this iron is soluble (~2–4% of iron in clays and ~0.003% from iron (oxyhydr)oxides) [13]. The extent of iron dissolution in dust aerosols is controlled by particle composition (mineralogy), physical and chemical reactions during atmospheric transport, and the presence and mixing of more soluble (10–70%) anthropogenic iron with dust [14,15,16,17]. Modelling studies suggest that the long-range transport of aluminosilicate minerals specifically, which release nanoparticulate ferrihydrite and soluble iron, may provide an important source of bioavailable iron to remote ocean regions [18,19,20].
Insoluble iron in mineral aerosols can dissolve via three different mechanisms: (1) proton-promoted dissolution, where high proton concentrations disrupt Fe-O bonds in the crystal lattice [21,22]; (2) ligand-controlled dissolution, where organic acids form surface complexes with iron and detach to form soluble Fe(III) [23,24]; and (3) reductive dissolution, where Fe(III) forms soluble Fe(II) generally by photochemical reactions [23,25,26].
Although dust-bound iron can be found as both Fe(II) and Fe(III) [27], a majority of iron in dust is found in the oxidized Fe(III) state, which is substituted into aluminosilicate minerals and is present in (oxyhydr)oxides such as goethite and hematite [17,22]. Fe(II)(aq) can be produced by the dissolution of Fe(II) compounds or by the reduction of Fe(III) at the solid/liquid boundary layer [28]. The presence of organic ligands in atmospheric waters, most notably oxalate, increases the concentration of dissolved Fe(II) because these molecules can act as electron donors [29,30,31,32,33]. When included in model calculations, oxalate and photochemical redox cycling increased the dissolved iron fraction delivered to the open ocean by 75% [34]. Furthermore, Myriokefalitakis et al. (2015) found that in present day conditions, approximately 22% of the atmospheric iron dissolution flux is attributed to organic ligand-promoted dissolution [35]. The photochemical reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II), which then is rapidly reoxidized to Fe(III), is also a major source of Fe(II) [28,29,36,37].
The factors affecting the solubilization of iron during atmospheric transport of mineral dust need to be considered as aerosols are a large source of soluble iron to the open ocean. Three main processes likely to occur during atmospheric transport are: (1) aqueous phase processing (i.e., cloud and marine processing, changes in relative humidity, wetting, and drying cycles), (2) interactions with atmospheric gases (specifically anthropogenic contributions), and (3) photochemistry. Two other factors affecting iron solubilization during transport are related to the composition of the mineral dust: mineralogy, and particle size and surface area. In this work, simulated aqueous phase processing of pure mineral phases is examined as they relate to mineralogy and particle size/surface area. While particle size and surface area have been hypothesized to have a significant impact on iron solubility during transport, few laboratory studies have examined these parameters further [38,39,40,41], with most data coming from field measurements.
Size is a major factor in how far a mineral dust particle will travel in the atmosphere from its point of origin, and therefore, dictates the quantity deposited in the open ocean [42,43]. Dust particles can range from 0.200 μm to 100 μm in diameter, and particles smaller than 10 μm can be transported long distances, at times hundreds of kilometers, from their source [44]. This study focuses on particles ranging from 10 μm to less than 0.25 μm in diameter with a specific focus on particle sizes between 2.5 μm and 0.25 μm. Particles in this size range are mainly in the accumulation mode, which are most likely to be transported over long distances due to their atmospheric lifetimes and are in the range of particles that will become cloud condensation nuclei and will, therefore, undergo cloud processing [42].
Atmospheric dust typically contains quartz, feldspar, calcite, gypsum, illite, kaolinite, smectite, and hematite [45]. Pure illite, kaolinite, magnetite, hematite, and goethite are examined here as they are considered relevant iron bearing minerals [13,46,47,48]. Moderately acidic and acidic leaching media were used to examine aqueous atmospheric processing. The moderately acidic leaching medium (pH 4.3) was used to simulate cloud water, while the acidic leaching medium (pH 1.7) was used to simulate a marine aerosol solution.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
The moderately acidic leaching media (Table 1) was made from chemicals obtained from Sigma-Aldrich including glacial acetic acid (99.8%), sodium acetate (99.0%), formic acid (≥96%), sodium formate (99+%), and ammonium nitrate (99.999%). The acidic leaching media was prepared with sulfuric acid (10 N, Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and sodium chloride (≥99.5%, Fluka, Geneva, Switzerland).

Table 1.
Composition of extraction solutions in solubility experiments.
All plasticware was soaked overnight in a 10% nitric acid (OmniTrace, EMD) bath. Mineral extracts were filtered using polyethersulfone (PES) membrane filters (0.22 μm pore size, Millex, Millipore Corporation, Cork, Ireland). For inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) analysis, iron standards were made from a J. T. Baker iron standard (1000 ppm). For UV-Vis analysis, Fe(III) was reduced to Fe(II) with 5.5 mM hydroxylamine hydrochloride (99.999% metals basis, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and then complexed with 5.2 mM ferrozine solution (3-(2-Pyridyl)-5,6-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazine-4’,4”-disulfonic acid sodium salt, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). UV-VIS standards for Fe(II) and Fe(III) were made from ammonium iron(II) sulfate hexahydrate (minimum 99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and ammonium iron(III) sulfate dodecahydrate (minimum 99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), respectively [52].
2.2. Sample Preparation
Five pure mineral phases (kaolinite, illite, magnetite, goethite, and hematite) were obtained from Ward Life Sciences (kaolinite, illite, and goethite) and Fisher Scientific (hematite and magnetite). The samples were ground using a ceramic ball mill. The ground mineral phases were then resuspended using a laboratory set-up described in detail in Upadhyay et al. [53]. A cyclone was used to isolate particles less than 10 µm in diameter, and the PM10 was collected onto solvent cleaned/sonicated aluminum (Alfa Aesar Puratronic, 99.997% metals basis) substrates (25 mm) using a Sioutas Personal Cascade Impact Sampler (PCIS) (SKC Inc., Eighty Four, PA, USA), which size segregates the resuspended particles into 5 different size fractions: >2.5, 2.5–1.0, 1.0–0.5, 0.5–0.25, and <0.25 μm. Sample masses ranged from approximately 0.1 mg to 3 mg of deposited size-segregated mineral phases for the four largest size fractions: >2.5, 2.5–1.0, 1.0–0.5, and 0.5–0.25 μm. The last “catch” stage (<0.25 μm) was a 37 mm Teflon filter (Teflo, Pall Life Sciences, Port Washington, NY, USA), and the deposited sample mass was <0.1 mg. The flow rate of the resuspension system was 9 L min−1. Two extraction solutions, moderately acidic (pH 4.3) and acidic (pH 1–2) (Table 1), were chosen to represent the different acidic aqueous phases a particle might encounter during transport. Previous studies have reported that no additional iron is released in the extraction solutions after 100 min [52]. To ensure equilibrium in the extract solution, the aluminum substrates and Teflon “catch” stage were extracted into 8 mL of the two extraction solutions for 150 min. The pH of the solutions did not drift more than ±0.05 pH units throughout the course of the experiment. The extracts were then filtered through a polyethersulfone (PES) membrane filter (0.22 μm pore size, Millipore, Millex, Duluth, GA, USA) and subsequently aliquoted for analysis by ICP-MS for total soluble iron content and by UV-Vis for iron speciation measurements. Light exposure was limited by keeping the extracts covered with aluminum foil at all times. All resuspensions and wet-chemical analyses were performed in triplicate. In this manuscript, soluble iron is defined as iron that has passed through a 0.22 µm filter and has been analyzed by ICP-MS. UV-VIS spectroscopy is used to measure Fe2+ and Fe3+ in the filtrate.
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
SEM coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) (Phillips XL30 ESEM-FEG) was used to confirm the particle size distribution obtained by sampling with the PCIS. Two mineral phases representing the two classes of minerals investigated (clay and iron oxides) were examined using SEM. The bottom “catch” stage (<0.25 μm) could not be examined by SEM because gold and carbon sputter coatings disintegrated the Teflon filters.
2.4. Surface Area Measurements
Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Theory (BET) was applied using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 Surface Area and Porosity Analyzer to determine the surface area of kaolinite and magnetite at the following particle sizes: 10–2.5, 2.5–1.0, 1.0–0.5, and 0.5–0.25 µm. In BET, surface area is determined by the adsorption of N2 gas to the surface of the mineral [54]. The difference in mass before and after gas adsorption is proportional to the surface area.
2.5. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) Analysis
Filtrates were diluted with 0.32 M nitric acid and analyzed using a quadrupole ICP-MS (X Series 2, Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) for soluble iron content.
Illite and kaolinite have varying iron content [13], so the bulk ground minerals were digested using nitric and hydrofluoric acids in a CEM MARS5 oven in XP-1500 Teflon bombs (CEM, Matthews, NC, USA). The digestates were then dried down under laminar flow, diluted with 0.32 M nitric acid, and analyzed by ICP-MS to determine their total iron content [55]. The illite and kaolinite used in this work wwere determined to have a total iron content of 3.05% and 0.46%, respectively. The total iron content of hematite (Fe2O3), magnetite (Fe3O4), and goethite (FeOOH) was determined stoichiometrically.
2.6. UV-Vis Spectroscopy Analysis
To determine the Fe(II) content, 5.2 mM Ferrozine solution was added to the extracts. Ferrozine complexes the free Fe(II) producing a light pink color, so the absorbance can be measured by UV-Vis spectroscopy at a wavelength of 562 nm. To determine the total soluble iron content and subsequently the Fe(III) composition, 5.55 mM hydroxylamine hydrochloride was added to the extract before adding Ferrozine to reduce the Fe(III) to Fe(II) [56]. An example calibration curve used for UV-Vis analysis can be found in the Supplemental Materials (Figure S1).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Iron Dissolution of Minerals Extracted into Moderately Acidic and Acidic Leaching Media
Figure 1 shows the percent of iron that was soluble (i.e., sol Fe/total Fe × 100) when the size segregated mineral phases were extracted into a simulated cloudwater (pH 4.3) and a simulated marine aerosol (pH 1.7) leaching media. On average, the fraction of soluble iron (in the filtrate) was an order of magnitude greater in the clays, illite, and kaolinite, as compared to magnetite, hematite, and goethite. In the simulated cloudwater medium (pH 4.3), the average percentage of soluble Fe across all particles sizes was 1.3 ± 0.4% and 0.05 ± 0.04% for clays and iron (oxyhydr)oxides, respectively. In the marine aerosol leaching medium (pH 1.7) the average percentage of soluble Fe across all particles sizes was 8.3 ± 0.6% and 0.87 ± 0.05% for clays and iron (oxyhydr)oxides, respectively. The results of the solubility studies indicate that mineralogy greatly affects iron solubilization. These findings are in agreement with Journet and co-workers [13], who observed increased iron solubility in clays (~4%) as compared to iron (oxyhydr)oxides (<1%). Clay particles have been found to be the prevailing phase during long range transport of mineral dust; quartz, feldspars, and calcite are also prominent [46,47,57]. A comparison of aerosol samples collected in Bermuda (long range transport) and during the 2011 GEOTRACES Atlantic transect (Saharan air mass sampling) suggested that as the estimated travel time from the source increased, iron solubility generally increased [58], although no statistical correlation was observed. Longo and co-workers [58] attributed this trend to the decrease in pH during long atmospheric residence times, which after 15 days drops from approximately neutral to a pH less than 4.
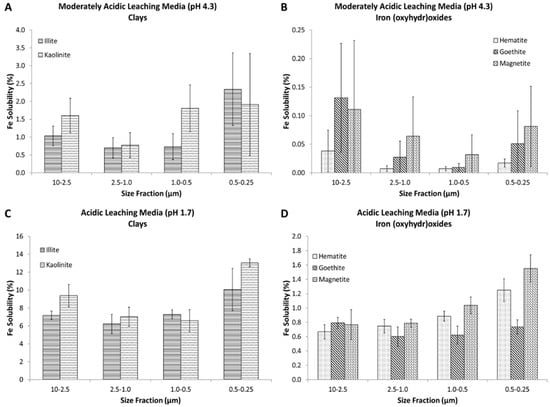
Figure 1.
Total soluble iron content (as a percentage, i.e., the iron that passes through a 0.22 µm filter/total iron in mineral × 100) of the extracted mineral samples into the moderately acidic leaching medium (A,B) and the acidic leaching medium (C,D) at the various size fractions. The graphs on the left show the two clay minerals (A,C), while the graphs on the right show the three iron (oxyhydr)oxide minerals (B,D), which are substantially less soluble. Concentrations were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Error bars are representative of the standard deviation of three replicate experiments.
Even though the weight percent of iron in clays (0.46% and 3.05% for kaolinite and illite, respectively) is much lower than in iron (oxyhydr)oxides (62.8%, 69.9%, and 72.3% for goethite, hematite, and magnetite, respectively), the iron in clays is much more soluble. This result is consistent with Cwiertny et al. [22], who found that although Saharan desert dust had lower iron content, it was more soluble than inland samples from Saudi Arabia that contained a higher mass fraction of iron oxides. In iron oxide minerals, iron is in strong Fe-O lattice bonds (Fe-O bond dissociation energy = 409 kJ·mol−1). Clays have nano-thin platelet layers, resulting in high surface area and, therefore, more reaction sites [59]. There are also differences in how the iron is bound in the crystal structure of clays. In clays, iron can “sit” in the interstitial layers as an impurity or can substitute in the crystal lattice for Mg, K, or Al [60,61,62].
As the pH of the extraction solution decreases, there is an increase in the fraction of solubilized iron across all mineral phases. When clays were extracted into a simulated cloudwater leaching medium (pH 4.3; Figure 1A), 0.70–2.3% of the iron in the clay was soluble, but when extracted into a marine aerosol leaching medium (pH 1.7; Figure 1C), the solubility increased to 6.2–13%. A similar trend is observed in iron oxides where the solubility increased from <0.2% to 0.60–1.6% when extracted into a simulated cloudwater (Figure 1B) and marine aerosol leaching medium (Figure 1D), respectively (t-test, p < 0.05). This is consistent with previous studies that showed an increase in iron solubility with a decrease in solution pH [22,63].
Goethite was investigated like other mineral phases, but showed a unique behavior. Unlike magnetite, there was no change in solubility observed as a function of particle size (Figure 1D). These findings challenge the importance of surface properties for these materials. As shown in previous literature, goethite presents different structures than hematite and magnetite. In fact, it is less spherical in shape and more rod-like, which may cause variations in the iron-solubilization mechanism, relative to hematite and magnetite. Specifically, in aqueous suspension, these rod-like structures tend to agglomerate. Rubasinghege et al. showed that decreasing pH from 2 to 1 caused micro-goethite to have higher solubility than nano-goethite [64]. This is unusual as nano-goethite has higher surface area than micro-goethite, but aggregation of nano-goethite at pH 1 (confirmed by TEM) reduces the reactive surface area, and appears to quench the dissolution of iron.
3.2. Effect of Particle Size on Iron Solubility
The effect of particle size and atmospheric processing on the solubility of iron from pure mineral phases that simulate mineral dust aerosols is examined. In the simulated cloudwater leaching medium (pH 4.3), at sizes greater than 0.25 μm, particle size does not appear to have an effect on iron solubility (Figure 1A,B). This is likely due to the low solubility of the iron in these minerals at this pH, which caused some measurements to be below the limit of quantification and could make changes in solubility difficult to observe. In this work, particle sizes smaller than 0.25 μm were collected, but because of very low mass loadings resulting in iron content below detection limit in many cases, the impact of solubility on particles sizes <0.25 μm was not investigated. Cartledge et al. performed gas phase processing experiments to examine the effect of particle size and sulfur dioxide exposure on iron solubility in a simulated cloud water buffer (pH > 4) [41]. That work showed that, especially in the smallest size fraction (0.5–0.25 μm), there does appear to be a trend of increasing solubility with decreasing particle size for goethite and hematite, but not for magnetite. Fe(II) and Fe(III) measurements were also made on the moderately acidic leaching media samples, although no obvious trends are observed as this relates to solubility (Figure S2).
In the marine aerosol leaching medium (pH 1.7), as particle size decreases, soluble iron increases for magnetite and hematite, especially between the largest and smallest size fractions, indicating that size and surface area of the particle could be one factor affecting iron solubility (Figure 1C,D). Baker and Jickells performed field studies examining the solubility of iron as a function of particle size [38]. They showed that iron solubility is an inverse function of mineral aerosol mass concentration, proposing that the surface area to volume ratio, or specific surface area, is a critical factor for solubility. They hypothesized that since smaller particles will likely have a larger fraction of their volume exposed, the iron solubility of fine aerosols as compared to coarse particles is greater. Sholkovitz et al. found a similar trend of increased soluble iron fractions with lower total iron content, as did other modelling studies [16,65]. In Sholkovitz et al., however, the increased soluble iron content was attributed to the high soluble iron fraction of combustion aerosols and the low soluble iron fraction of mineral dust aerosols (high total iron content).
3.3. Particle Size and Surface Area Measurements
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to verify the sample preparation process. SEM images for illite and magnetite particles are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. One of each type of mineral phase (clay and iron oxide) was chosen to be representative of the other minerals for the validation of the re-suspension protocol. The images show that the particles have the correct size distributions with minimal particle bounce; hence, separation using the PCIS was confirmed. There does appear to be some small particles “sitting” on top of the larger particles in the largest size fraction; however, this small particle adhesion was not considered to be an issue. These small particles may slightly increase the surface area of the larger particles, but the mass contribution of those small particles can be considered negligible and will not contribute significantly to the iron mass fraction. It was more important to ensure that no large particles were in the smallest size fraction, which is common in impaction methods from particle bounce between impaction stages. There were no large particles observed in the smallest size fractions and, hence, the sample preparation protocols were considered validated.
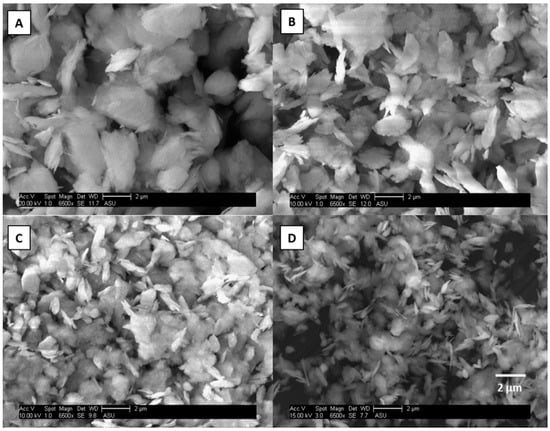
Figure 2.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images of illite particles at 10–2.5 (A), 2.5–1.0 (B), 1.0–0.5 (C), and 0.5–0.25 μm (D). The SEM images are shown at the same magnification, 6500 times, with a scale bar of 2 μm.
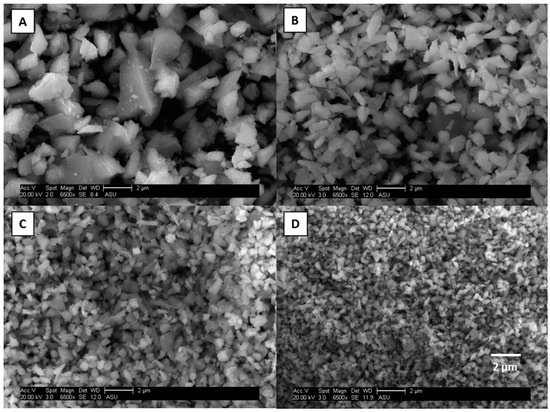
Figure 3.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images of magnetite particles at 10–2.5 (A), 2.5–1.0 (B), 1.0–0.5 (C), and 0.5–0.25 μm (D). The SEM images are shown at the same magnification, 6500 times, with a scale bar of 2 μm.
Surface area measurements of kaolinite and magnetite using BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) theory show differences between clays and iron oxides as particle size decreases. One of each category of mineral (clay and iron oxide) was chosen because their mineral structures are quite different. Surface area measurements were made on each set of particle sizes (10–2.5, 2.5–1.0, 1.0–0.5, and 0.5–0.25 μm) for kaolinite and magnetite. Table 2 shows that the surface area of kaolinite does not change with decreasing particle size while magnetite has a 3-fold increase in surface area with decreasing particle size. Figure 2A shows SEM images of the resuspended clay particles. It can be observed from these images that the clay minerals have a structure resembling stacked “plates” and contain many, large pores, which can be exposed to aqueous phase reactions. Figure 3B shows SEM images of resuspended magnetite particles. It can be observed that these iron oxide particles do not appear to have as many pores and are much more compact and geometric. The BET results for kaolinite suggest that since clays are already porous, changing their particle size does not significantly alter their surface area. Conversely, BET analysis of magnetite shows that since iron oxides are less porous, decreasing their particle size increases their surface area. In a simple spherical model, a 10-fold increase (approximation based on distribution of particles in each bin/size fraction going from 10 μm to 0.25 μm) in surface area would be expected. This shows the importance of making surface area measurements to account for pore volume instead of assuming spherical particles for an approximation of surface area.

Table 2.
Surface area measurements of kaolinite and magnetite made by the BET (Brunauer–Emmett–Teller) method.
To investigate the relationship of solubility and surface area, Figure 4 shows the soluble iron fraction in the moderately acidic (pH 4.3) and acidic (pH 1.7) leaching media normalized to surface area for magnetite and kaolinite, the two mineral phases for which there are BET measurements in this study. In the moderately acidic and acidic leaching media, when the soluble iron fraction is normalized to a particle surface area, there is no trend in normalized iron solubility between the size fractions. In this case, surface properties may influence the solubilization of iron for at least the two minerals that had surface area measurements available in this study. In a study by Journet and co-workers, the importance of aerosol mineralogy in atmospheric iron solubility was shown [13]. They asserted that solubilization was not a surface-controlled process, but instead a function of chemical composition of the aerosol. Our results confirm that mineralogical composition, in addition to aerosol pH, is the most important factor influencing iron solubility, but by size-fractionating the individual mineral phases, we also show that, in acidic conditions, solubility can be affected by mineral surface properties.
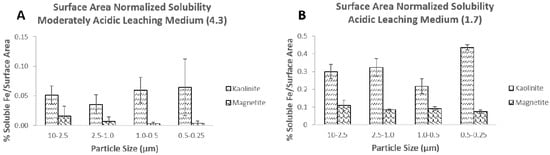
Figure 4.
Percent soluble iron normalized to surface area for magnetite and kaolinite in the moderately acidic (pH 4.3; (A)) and acidic (pH 1.7; (B)) leaching media. Error bars represent three replicate experiments for iron solubility experiments.
In summary, this work examined the effect of mineralogy, aerosol pH, and particle size/surface area on iron solubility. It was found that the largest factor examined in this study, affecting iron solubility during atmospheric transport, was mineralogy, with clays having higher solubility, 0.7–2.3% (moderately acidic leaching medium; pH 4.3) and 6.2–13% (acidic leaching medium; pH 1.7), overall than iron oxide minerals, <0.01–0.13% (moderately acidic leaching medium; pH 4.3) and 0.67–1.6% (acidic leaching medium; pH 1.7). Solution pH also plays a large role in iron solubility; as pH decreases, iron solubility in clays increases from an average of 1.4 to 8.3%, and in iron oxides from an average of 0.05 to 0.87% (averages include all size ranges). Both of these results are consistent with previous work in the literature. At lower pH environments, a trend of increasing iron solubility with decreasing particle size can be observed for hematite and magnetite; an increase from 0.67 to 1.2% and 0.77 to 1.6% between 10 and 0.25 μm was observed in the case of hematite and magnetite, respectively, similar to some modeling studies [66]. This observation is especially important given the fact that the pH of dust tends to decrease during transport in marine environments [67].
The solubilization of iron from clay minerals seems mostly unaffected by particle size. Surface area measurements taken in this work show greater changes in surface area as a function of particle size in iron oxides as compared to clays. Although the largest factors affecting solubility are aerosol or environmental pH and chemical composition, differences in surface area measurements between clays and iron oxide minerals could indicate that mineral surface properties are a factor affecting dissolution during atmospheric transport. The results from this work stress the inclusion of aerosol pH and mineralogy, which related to chemical composition and at a lesser extent, surface properties, in global biogeochemical models.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4433/11/5/533/s1, Figure S1: An example of a calibration curve used for UV-Vis measurements of Fe(II); Figure S2: Soluble iron fraction (as a percentage; i.e., dissolved iron/total iron in mineral × 100) and speciation of the size fractionated minerals.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D.A., B.J.M. and P.H.; methodology, A.R.M., B.J.M. and P.H.; investigation A.R.M., writing—original draft preparation, A.D.A., A.R.M. and P.H.; writing—review and editing, A.D.A., A.R.M., B.J.M., and P.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation, grant numbers AGS 0964810 and AGS 1206083.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Daniel Mieritz for providing BET measurements, Sisouk Phrasavath for his assistance with SEM imaging, and Kevin Shaffer for assistance with mineral resuspensions for BET measurement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Zeebe, R.E. History of Seawater Carbonate Chemistry, Atmospheric CO2, and Ocean Acidification. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2012, 40, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, R.T.; Chavez, F.P. Regulation of primary productivity rate in the equatorial Pacific. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1991, 36, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H. Glacial-interglacial CO2 change: The iron hypothesis. Paleoceanography 1990, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Barber, R.T.; Smetacek, V. Biogeochemical controls and feedbacks on ocean primary productivity. Science 1998, 281, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.K.; Doney, S.C.; Glover, D.M.; Fung, I.Y. Iron cycling and nutrient-limitation patterns in surface waters of the World Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Trop. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 463–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Myriokefalitakis, S.; Kanakidou, M.; Mahowald, N.M.; Scanza, R.A.; Hamilton, D.S.; Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.; Sarin, M.; Bikkina, S.; et al. Pyrogenic iron: The missing link to high iron solubility in aerosols. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jickells, T.D.; An, Z.S.; Andersen, K.K.; Baker, A.R.; Bergametti, G.; Brooks, N.; Cao, J.J.; Boyd, P.W.; Duce, R.A.; Hunter, K.A.; et al. Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate. Science 2005, 308, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, P.W.; Ellwood, M.J. The biogeochemical cycle of iron in the ocean. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, C.; Herckes, P.; Majestic, B.J.; Anbar, A.D. Source apportionment of aerosol iron in the marine environment using iron isotope analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5722–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.E.; Johnson, K. A model of the iron cycle in the ocean. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Laskin, A.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Gorski, C.A.; Scherer, M.M.; Grassian, V.H. Coal Fly Ash as a Source of Iron in Atmospheric Dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2112–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Fan, S.M.; Sarmiento, J.L. Aeolian iron input to the ocean through precipitation scavenging: A modeling perspective and its implication for natural iron fertilization in the ocean. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journet, E.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Caquineau, S.; Colin, J.-L. Mineralogy as a critical factor of dust iron solubility. Geophys. Res. Letters 2008, 35, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, P.Y.; Duvall, R.M.; Shafer, M.M.; Schauer, J.J. The origin of water soluble particulate iron in the Asian atmospheric outflow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Sarin, M.M.; Srinivas, B. Aerosol iron solubility over Bay of Bengal: Role of anthropogenic sources and chemical processing. Mar. Chem. 2010, 212, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholkovitz, E.R.; Sedwick, P.N.; Church, T.M.; Baker, A.R.; Powell, C.F. Fractional solubility of aerosol iron: Synthesis of a global-scale data set. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2012, 89, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, M.; Weber, R.J.; Lai, B.; Russell, A.; Ingall, E.D. Characterization of iron speciation in urban and rural single particles using XANES spectroscopy and micro X-ray fluorescence measurements: Investigating the relationship between speciation and fractional iron solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Xu, L. Response of acid mobilization of iron-containing mineral dust to improvement of air quality projected in the future. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 3441–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiswell, R.; Canfield, D.E. The iron biogeochemical cycle past and present. Geochem. Perspect. 2012, 1, 1–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzolo, J.A.; Barbosa, C.G.G.; Borillo, G.C.; Godoi, A.F.L.; Souza, R.A.; Andreoli, R.V.; Manzi, A.O.; Sá, M.O.; Alves, E.G.; Pöhlker, C.; et al. Soluble iron nutrients in Saharan dust over the central Amazon rainforest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2673–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spokes, L.J.; Jickells, T.D.; Lim, B. Solubilisation of aerosol trace metals by cloud processing: A laboratory study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 58, 3281–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiertny, D.M.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Hunter, G.J.; Laskin, A.; Scherer, M.M.; Grassian, V.H. Characterization and acid-mobilization study of iron-containing mineral dust source minerals. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, J.G.; Kraemer, S.M.; Teutsch, N.; Borer, P.M.; Halliday, A.N.; Kretzschmar, R. Iron Isotope Fractionation during Proton-Promoted, Ligand-Controlled, and Reductive Dissolution of Goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, J.R.; Cartledge, B.T.; Haynes, J.P.; York-Marini, R.; Robinson, A.L.; Drozd, G.T.; Goldstein, A.H.; Fakra, S.C.; Majestic, B.J. Water-soluble iron emitted from vehicle exhaust is linked to primary speciated organic compounds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertmann, U. Solubility and dissolution of iron oxides. Plant Soil 1991, 130, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Cwiertny, D.M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Scherer, M.M.; Grassian, V.H. Photoreductive dissolution of Fe-containing mineral dust particles in acidic media. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, P.; Dedik, A.N.; Ensling, J.; Weinbruch, S.; Weber, S.; Sinner, T.; Gutlich, P.; Ortner, H.M. Speciation of iron in atmospheric aerosol samples. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 2, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehkonen, S.O.; Siefert, R.L.; Erel, Y.; Webb, S.; Hoffmann, M.R. Photoreduction of iron oxyhydroxides in the presence of important organic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 2058–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzberger, B.; Laubscher, H. Reactivity of various types of iron (III) (hydr)oxides towards light-induced dissolution. Marine Chem. 1995, 50, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V.; Journet, E. Variability of dust iron solubility in atmospheric waters: Investigation of the role of oxalate organic complexation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6510–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Majestic, B.J.; Herckes, P. Solubility and speciation of atmospheric iron in buffer systems simulating cloud conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, R.; Desboeufs, K.V. Effect of atmospheric organic complexation on iron-bearing dust solubility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4895–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Grassian, V.H. Iron Dissolution of Dust Source Materials during Simulated Acidic Processing: The Effect of Sulfuric, Acetic, and Oxalic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10312–10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.S.; Meskhidze, N. Atmospheric dissolved iron deposition to the global oceans: Effects of oxalate-promoted Fe dissolution, photochemical redox cycling, and dust mineralogy. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myriokefalitakis, S.; Daskalakis, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Baker, A.R.; Nenes, A.; Kanakidou, M. Changes in dissolved iron deposition to the oceans driven by human activity: A 3-D global modelling study. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 3973–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedik, A.N.; Hoffman, P.; Ensling, J. Chemical characterization of iron in atmospheric aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 1992, 26A, 2545–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakaki, T.; Faust, B.C. Sources, sinks, and mechanisms of hydroxyl radical photoproduction and consumption in authentic acid continental cloud waters from Whiteface Mountain, New York: The role of the Fe (r) (r = II,III) photochemical cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 3487–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.R.; Jickells, T.D. Mineral particle size as a control on aerosol iron solubility. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooki, A.; Nishioka, J.; Ono, T.; Noriki, S. Size dependence of iron solubility of Asian mineral dust particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.S.; Landing, W.M.; Resing, J.A. Particle size and aerosol iron solubility: A high-resolution analysis of Atlantic aerosols. Mar. Chem. 2010, 120, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartledge, B.T.; Marcotte, A.R.; Herckes, P.; Anbar, A.D.; Majestic, B.J. The Impact of Particle Size, Relative Humidity, and Sulfur Dioxide on Iron Solubility in Simulated Atmospheric Marine Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7179–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald, N.; Albani, S.; Kok, J.F.; Engelstaeder, S.; Scanza, R.; Ward, D.S.; Fanner, M.G. The size distribution of desert dust aerosols and its impact on the Earth system. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buseck, P.R.; Adachi, K. Nanoparticles in the atmosphere. Elements 2008, 4, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claquin, T.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.J. Modeling the mineralogy of atmospheric dust sources. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 22243–22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaccum, R.A.; Prospero, J.M. Saharan aerosols over the tropical North Atlantic—Mineralogy. Mar. Geol. 1980, 37, 295–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.; Queralt-Mitjans, I.; Alarcón, M. Mineralogical composition of African dust delivered by red rains over northeastern Spain. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 21977–21996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Krom, M.D.; Jickells, T.D.; Bonneville, S.; Carslaw, K.S.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Baker, A.R.; Benning, L.G. Impacts on iron solubility in the mineral dust by processes in the source region and the atmosphere: A review. Aeolian Res. 2012, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.W.; Robinson, M.S.; McIlwraith, H.; Kingston, J.T.; Herckes, P. The Chemistry of Intercepted Clouds in Northern Arizona during the North American Monsoon Season. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 199, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Prospero, J.M.; Savoie, D.L.; Millero, F.J.; Zika, R.G.; Saltzman, E.S. Photoreduction of iron (III) in marine mineral aerosol solutions. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 9039–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dowd, C.D.; Hämeri, K.; Mäkelä, J.M.; Pirjola, L.; Kulmala, M.; Jennings, S.G.; Berresheim, H.; Hansson, H.C.; de Leeuw, G.; Kunz, G.L.; et al. A dedicated study of New Particle Formation and Fate in the Coastal Environment (PARFORCE): Overview of objectives and achievements. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majestic, B.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Shafer, M.M.; Turner, J.R.; Fine, P.M.; Singh, M.; Sioutas, C. Development of a Wet-Chemical Method for the Speciation of Iron in Atmospheric Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 2346–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, N.; Clements, A.L.; Fraser, M.P.; Sundblom, M.; Solomon, P.; Herckes, P. Size-differentiated chemical composition of re-suspended soil dust from the desert Southwest United States. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerlund, G. Determination of specific surface by the BET method. Matér. Constr. 1973, 6, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Majestic, B.J.; Prapaipong, P.; Herckes, P. Evaluation of polyurethane foam, polypropylene, quartz fiber, and cellulose substrates for multi-element analysis of atmospheric particulate matter by ICP-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stookey, L.L. Ferrozine—A New Spectrophotometric Reagent for Iron. Anal. Chem. 1970, 42, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Achterberg, E.P. Chemistry and mineralogy of clay minerals in Asian and Saharan dusts and the implications for iron availability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 15735–15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, A.F.; Feng, Y.; Lai, B.; Landing, W.M.; Shelley, R.U.; Nenes, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; Ingall, E.D. Influence of atmospheric processes on the solubility and composition of iron in Saharan dust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6912–6920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.Y.; Nousiainen, T. TEM analysis of the internal structures and mineralogy of Asian dust particles and the implications for optical modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 6619–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malden, P.J.; Meads, R.E. Substitution by iron in kaolinite. Nature 1967, 215, 844–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, J.H.; Cardile, C.M. Iron substitution in montmorillonite, illite, and glauconite by 57 Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy. Clays Clay Miner. 1987, 35, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahranowski, K.; Serwicka, E.M.; Stock, L.; Strycharski, P. On the possibility of removal of non-structural iron from kaolinite-group minerals. Clay Miner. 1993, 28, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, S.; Guieu, C. Dissolution of atmospheric iron in seawater. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubasinghege, G.; Lentz, R.W.; Park, H.; Scherer, M.M.; Grassian, V.H. Nanorod dissolution quenched in the aggregated state. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1524–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A. Atmospheric processing of combustion aerosols as a source of bioavailable iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Shi, Z. Delivery of anthropogenic bioavailable iron from mineral dust and combustion aerosols to the ocean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Prospero, J.M.; Millero, F.J.; Savoie, D.L.; Brass, G.W. The solubility of ferric iron in marine mineral aerosol solutions at ambient relative humidities. Mar. Chem. 1992, 38, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).