Abstract
Equivalent black carbon (EBC) was measured with a seven-wavelength Aethalometer (AE-31) in the Urumqi River Valley, eastern Tien Shan, China. This is the first high-resolution, online measurement of EBC conducted in the eastern Tien Shan allowing analysis of the seasonal and hourly variations of the light absorption properties of EBC. Results showed that the highest concentrations of EBC were in autumn, followed by those in summer. The hourly variations of EBC showed two plateaus during 8:00–9:00 h local time (LT) and 16:00–19:00 h LT, respectively. The contribution of biomass burning to EBC in winter and spring was higher than in summer and autumn. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) showed an inverse relationship with EBC concentrations, suggesting that the reduction of the PBLH leads to enhanced EBC. The aerosol optical depths (AOD) over the Urumqi River Valley, derived from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data and back trajectory analysis, showed that the pollution from Central Asia was more likely to affect the atmosphere of Tien Shan in summer and autumn. This suggests that long-distance transported pollutants from Central Asia could also be potential contributors to EBC concentrations in the Urumqi River Valley, the same as local anthropogenic activities.
1. Introduction
Black carbon (BC) has attracted worldwide attention in the past few decades because of its complex climate and environmental significance [1]. The source of BC is the incomplete combustion of fossil and biomass fuels (natural and anthropogenic) [2]. BC absorbs solar radiation and alters cloud formation processes in the atmosphere, and is estimated to be the second most significant contributor to global warming [3,4,5]. BC emissions are often transported far from their source, impacting the lifetime in the atmosphere from several days to weeks. Because of its ability to strongly absorb solar radiation, BC can immensely reduce surface albedo after being deposited on the cryosphere, which may accelerate snow and ice melting [6,7,8]. BC not only impacts global climate but also has adverse effects on human health [9]. Therefore, it is essential to understand the physical and optical characteristics of BC in the atmosphere.
Previous measurements of equivalent black carbon (EBC) in China were mainly concentrated in urban sites and a few suburbs, and indicated strong anthropogenic sources [10,11,12,13]. However, similar measurements are particularly scarce in remote regions, especially in snow-covered areas. Such studies have investigated EBC in different remote regions. These studies have played a key role in determining the seasonal and hourly variation, potential source contribution areas, and optical properties of EBC. For example, Zhao et al. [14] used an Aethalometer (AE-31) to derive the EBC concentrations in Qilian Shan and suggested that the average background concentration of EBC varied between 18 ng/m3 and 72 ng/m3 with the highest in summer and the lowest in autumn. Wang et al. [15] derived the EBC in the Ranwu area of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and revealed that the EBC average concentration was 413 ng/m3 from November 2012 to January 2013 decreasing to 139 ng/m3 from February to June 2013.
Tien Shan in northwestern China is a crucial region with many glaciers that are a vital water resource for the population and the ecosystem in the central Asia region. The glaciers in Tien Shan have shown accelerated retreating in recent decades [16]. Compared with the glaciers on the TP, the glaciers in the Tien Shan are more vulnerable to human activities because of their lower elevations and more populated surroundings [17]. Several previous studies have shown that BC deposited on the glaciers would modify the albedo of snow and accelerate glacier melt in Tien Shan [18,19,20]. Tien Shan has relatively weaker local emissions and can be an ideal site to monitor regional environmental changes and evaluate various impacts from human activities [21]. However, Tien Shan is significantly perturbed by both neighboring BC emissions and dust activities in central Asia. Previous studies have suggested that the emissions from Xinjiang and Central Asia, transported by westerlies, could be the most important source of BC measured in Tien Shan [21]. Therefore, the monitoring of BC in Tien Shan is necessary and fundamental not only for its local environmental impact but also for its climatic significance.
Here, a high temporal resolution data of EBC in Tien Shan derived from aethalometer measurement (Model AE-31) are presented. The primary objective of this study is to analyze the seasonal and hourly variations of EBC and to understand its possible sources. The result will help to better understand the impact of EBC on the local environmental and climate in this remote area of western China.
2. Experimental Site and Methodology
2.1. Site Description
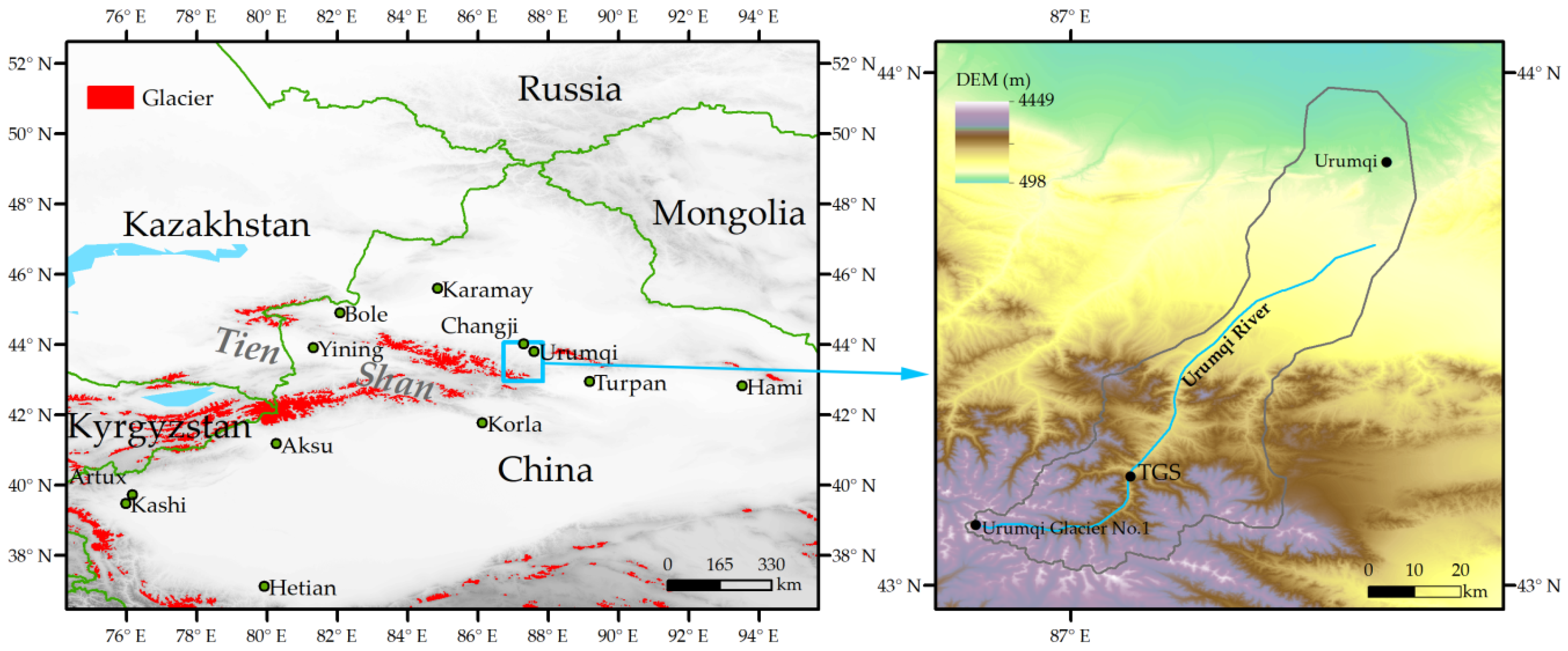
The study area was located in the Urumqi River Valley, eastern Tien Shan, China. This area is dominated by westerly winds in a dry and cold climate. The observation site was located at Tianshan Glaciological Station, hereby “TGS” (43.21° N, 87.12° E, 2130 m a.s.l), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China (Figure 1). The TGS was built in 1958 and provides the longest glaciological and climatological monitoring record among Chinese glaciers. TGS is approximately 100 km southwest of the city of Urumqi (the Capital of the Xinjiang Autonomous Region). There are relatively light anthropogenic emissions due to traffic and tourist activities at a distance of a few to tens of kilometers away. The study site is most frequently affected by the local emissions and those from sources further away transported by westerly winds [21].
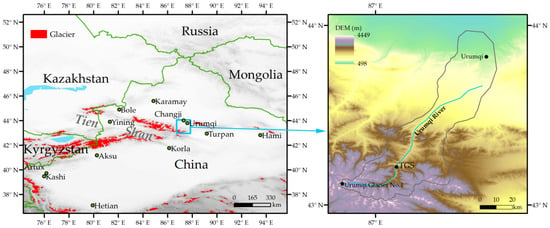
Figure 1.
Location map of the Tienshan Glaciological Station (TGS).
Meteorological parameters, i.e., relative humidity (RH), temperature, precipitation, wind speed and direction have been recorded by an automatic weather station (AWS) at the TGS. The daily average temperature in summer is the highest (average value: 13.6 °C), the average temperature is only −9.8 °C in winter, and the average temperature in spring and autumn is 2.5 °C and 1 °C respectively. The annual precipitation (362 mm), occurring mainly in summer, accounts for 55% of the yearly total. Precipitation was scarce in autumn and winter, accounting for only 15% of the yearly total. During the study period, daily average wind speeds were 1.6 m/s in spring, 1.4 m/s in summer, 1.2 m/s in autumn, and 0.8 m/s in winter.
2.2. Instrument and Data Analysis
Near-real-time continuous measurement were made from August 2016 to July 2017 using a seven -wavelength Aethalometer model AE31 (Magee Scientific®, Berkeley, CA, USA, = 370, 470, 520, 590, 660, 880, and 950 nm). The flow rate was 3.9 LPM, with sample made every five minutes. The air sampling inlet without cutoff was at a height of ~2 m above the ground. The optical attenuation-detecting technique is used in the aethalometer. The Aethalometer does not measure BC directly, rather an “equivalent black carbon” (EBC) [22] is derived from the light attenuation of the aerosol particles that are deposited on a filter strip. The EBC is estimated a wavelength-dependent specific mass absorption cross-section (MAC) to convert the attenuation to EBC. Regularly calibrations and flow check of the instrument were carried out to maintain the data reliability and accuracy [23]. This instrument was calibrated in 2016 by the manufacturer, Magee Technologies™. The 880 nm channel is considered as the standard channel for EBC estimates since EBC is the principle absorber of light at that wavelength. A MAC value of 16.6 m2 g–1(given by manufacturer) was used to determine the EBC at 880 nm as used by previous authors [23,24,25]. Because of the small quantity of absorptive dust and its weakly absorptive nature compared to EBC, we presumed that the main reason of adsorption at 880 nm is EBC, so the possible adsorption of dust is ignored.
In this study, the data sets were analyzed and processed through three-sigma filter and data points beyond three-sigma levels in the hourly mean were considered as outliers. Extremely high or negative values were also excluded. The filtered data is then averaged over an hour and used for further analysis. Using this data processing procedure, we deleted about 2.1% of the data. A similar data screening procedure of EBC is described elsewhere [26]. As mentioned above, certain steps are taken to correct the EBC; however, the accuracy of this technique still has an uncertainty of 20% [27].
2.3. Calculation of Optical Properties
The aerosol absorption coefficient α(λ) was obtained by using the following equations:
where α(λ) is aerosol absorption coefficient, λ is the wavelength, 14,625/λ is the specific attenuation cross section (m2g–1) [27], which is 16.6 m2g–1 at 880 nm. C is the multiple scattering uncertainty factor, which depends on the filter paper and apparatus and R is the correction factor for minimizing the inherent uncertainty associated with the Aethalometer, arising from multiple scattering of light in the filter matrix and the change in the optical path length because of successive aerosol loading [28]. Because C and R depend on unavailable data, such as different aerosol type (fresh/aged), chemical composition, and scattering coefficient, this study cannot characterize the uncertainty of EBC data due to scattering and shadowing effects. Hence, C = 2.14 (for quartz filter) and R = 1 was adopted in this study [29].
In order to know the spectral changes in the aerosol light absorption properties, we calculated the AAE in the present study with the following equations:
where AAE is the absorption Ångström exponent. AAE is a measure of the strength of the spectral variation in aerosol light absorption. Earlier investigators have reported that EBC originating from fossil fuel combustion, has an AAE varying inversely with wavelength [30].
2.4. Calculation of Biomass-Burning Fraction
In this study, a two-component model is used to determine the contribution of biomass burning and fossil fuel to the total EBC [31]. The AAEff and AAEbb can be calculated for two observed absorption coefficients at two different wavelengths (λ1, λ2), based on the absorption dependency of different particles:
where α(λ)ff is the fossil fuel fraction of α(λ), and α(λ)bb is the biomass burning fraction of α(λ). Gogoi et al. [32] have shown that AAE = 2 for biomass smoke aerosols, while AAE = 1 for mostly fossil fuel emissions. The accurate estimation of source apportionment of BC is also based on the selection of source-specific AAEs. However, AAEff and AAEbb are highly variable depending on fuel type, aerosol aging and combustion conditions [33]. Kirchstetter et al. [29] have shown that the aerosols produced from biomass burning with values of AAE = 2 and those from fossil fuel burning with value of AAE were close to 1. Sandradewi et al. [30] have shown that AAEs of 1.1 for traffic and 1.8–1.9 for wood burning calculated from the light absorption at 470 and 950 nm.
The two-component model assumes that α(λ) at a specific wavelength can be expressed as the sum of biomass burning and fossil fuel burning fractions [34]:
The portion of EBC from biomass burning (BB (%)) was obtained with the following equations:
EBC fractions were obtained with the following equations:
EBCff were calculated as
It is worth noting that estimating the contribution of biomass combustion in this manner is not strictly a contribution of biomass combustion, but non-fossil fuels and lensing effect [35].
2.5. Analysis of PBLH
To study the hourly variation of EBC, variations in the planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) over the study area were investigated. We obtained information from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website (ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives/gdas1) for the Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) data set which gives the boundary layer height for every three hours 00:00, 03:00, 06:00, 09:00, 12:00, 15:00, 18:00, and 21:00 UTC, with a spatial resolution of 1° × 1°. The data are available at http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready.php. The data in the latitude-longitude grid of 43.21° N and 87.12° E cover the observation site. To compare the data sets, we calculated the PBLH at the same hourly intervals of EBC.
2.6. Air Mass Trajectory Model
Since Tien Shan is a high-elevation and sparsely inhabited region, local emissions are rather weak compared to emissions from their neighboring regions. To determine the potential long-distance transport pathways of air masses reaching TGS, five-day backward air-mass trajectories are calculated using the Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory (HYSPLIT) model and the National Centre for Environmental Prediction (NCEP/NCAR) GDAS dataset [36]. We obtained a total of 365 daily trajectories averaged from 6-h trajectories, which can be grouped into three clusters via the built-in clustering tool in the model. We also calculated the median trajectory for each cluster. More details of the cluster analysis are available in Dumka et al. [37].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal Variations of EBC
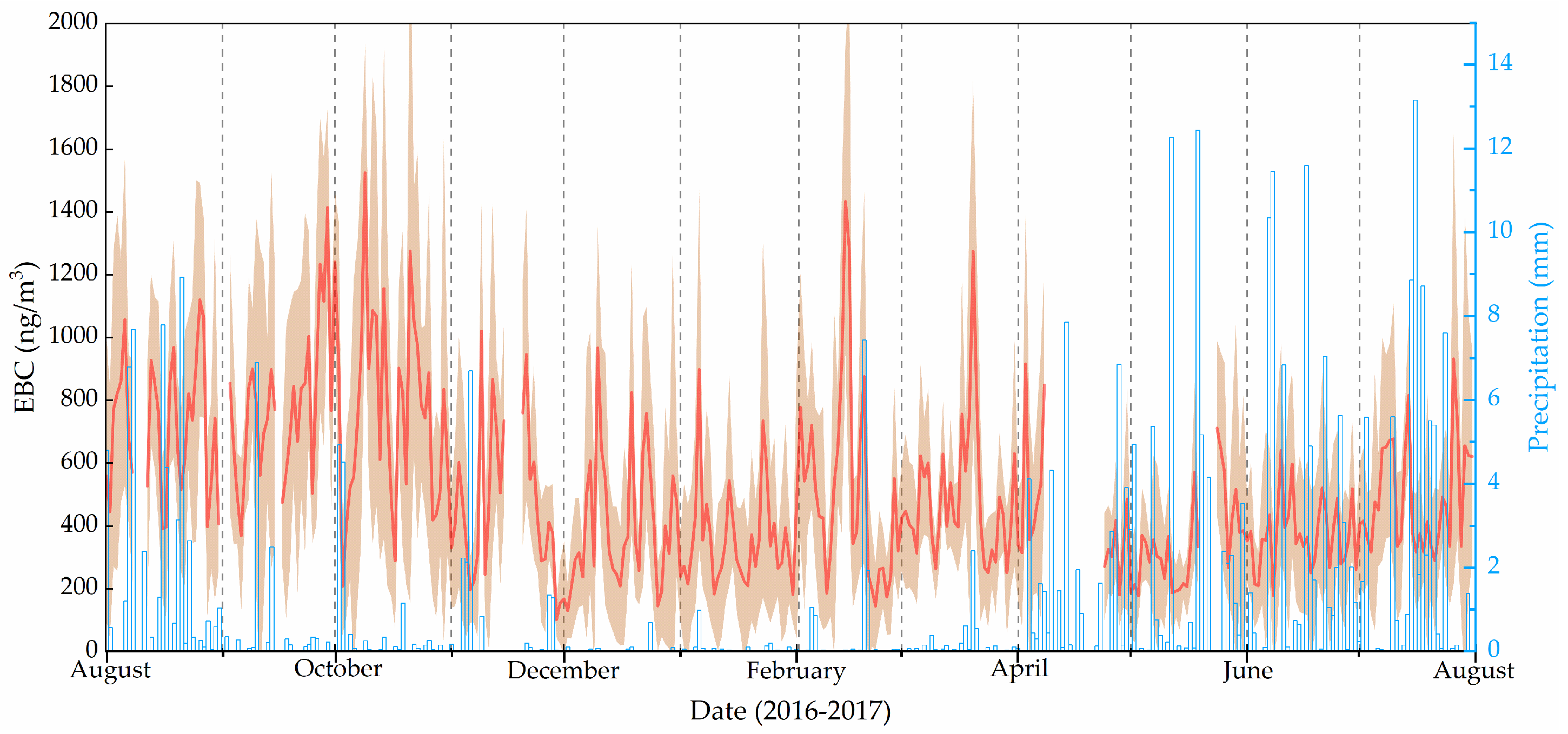
The daily mean concentrations of EBC at TGS from August 2016 to July 2017 are shown in Figure 2. Daily mean EBC is in the range of 102–1525 ng/m3 with a mean of 520 ng/m3 during the study period. The highest daily EBC concentration (1525 ng/m3) occurred on 9 October 2016, while the lowest (102 ng/m3) was on 29 November 2016. The highest value observed was due to a series of pollution events. For example, the daily averaged EBC concentration was higher than 1100 ng/m3 from 8 October to 12 October. The lowest values observed may be related to frequent snowfall acting as a significant scavenging factor. Compared with rainfall, snowfall has a stronger influence of the removal of aerosols, and hence, it took longer for the EBC concentration to recover to the average concentration after snowfall events than after rainfall [38]. Different from some studies at remote site (e.g., Qilian Shan), the daily mean concentrations of EBC at TGS was significantly higher because of the relative lower elevation and more BC emission around the sampling site [14].
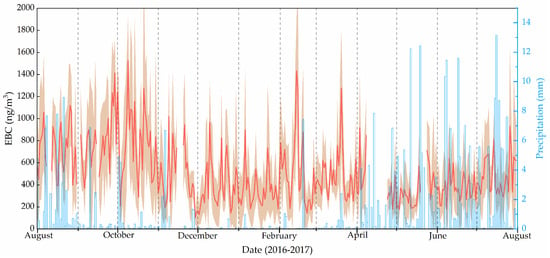
Figure 2.
The daily mean EBC concentrations observed at TGS. The shaded area indicates the ±1σ standard deviation.
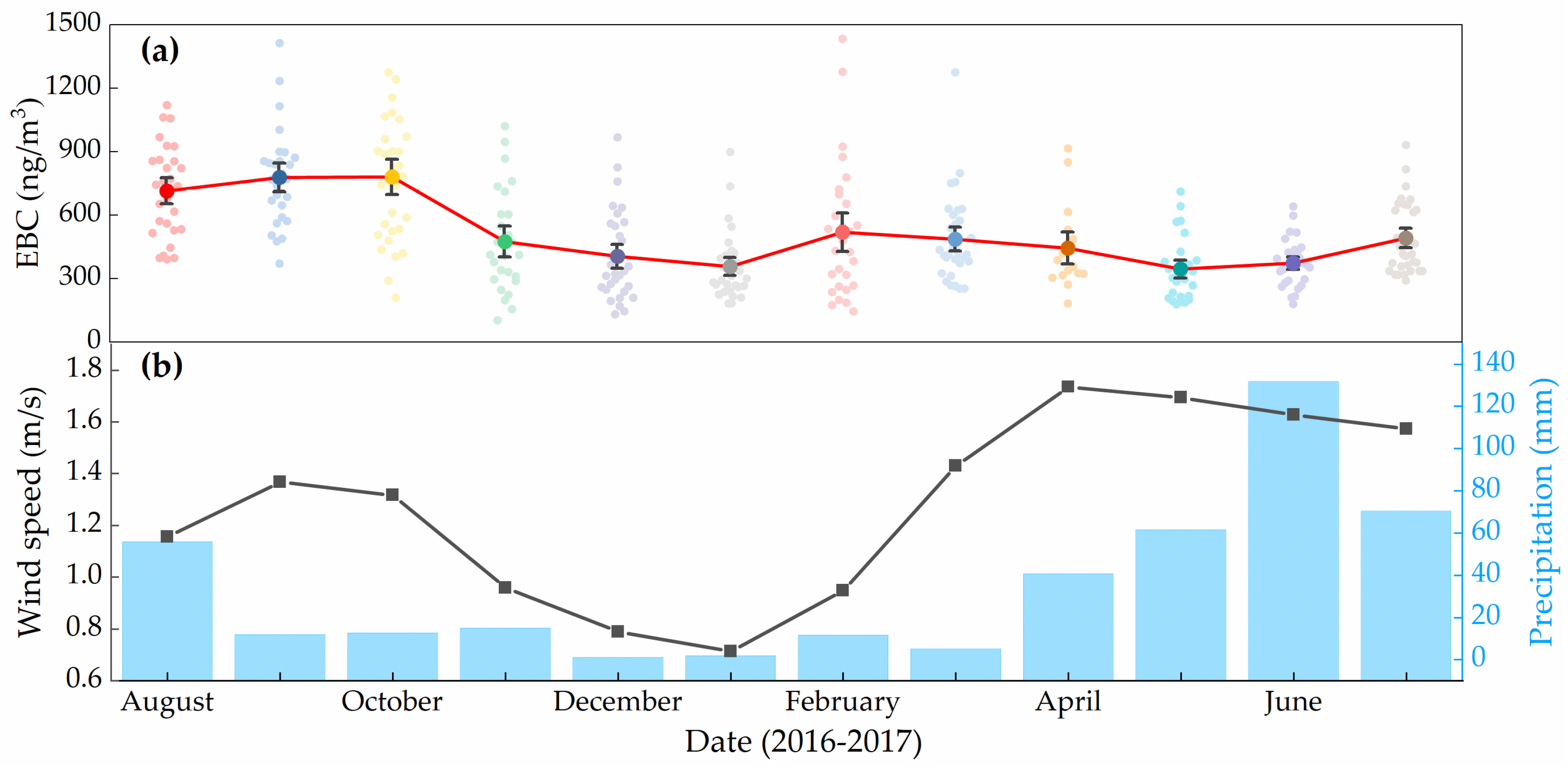
The monthly mean of the concentrations of EBC ranged from 344–805 ng/m3. The highest (805 ng/m3) was observed in October 2016, and the lowest (344 ng/m3) in May 2017. The highest concentration might be related to the active of local residents (cooking and heating) and traffic, and relatively drier weather. The lowest average concentration in May could be attributed to more precipitation and higher wind speed. The precipitation days in May 2017 reached 18 days, and the precipitation on 12 May and 19 May 2017, exceeded 12 mm. In addition, the average wind speed in May was 1.7 m/s, second only to April. As the wind speed increased, the dispersion and dilution of BC in the atmosphere also accelerated.
The seasonally averaged EBC concentrations during the study period are 425, 536, 686, and 427 ng/m3 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively. The autumn season has the highest mean EBC concentration, followed by summer, winter, and spring. This seasonal variation was mainly related to long-distance transport and meteorological conditions. Our observation site is closer to the Urumqi Glacier No. 1 and records of BC in snow and ice has proved this seasonal change. Xu et al. 2012 [18] has measured the BC concentration in snow samples and showed the BC concentration were autumn > summer > spring > winter. The high EBC concentrations in autumn could be attributed to meteorological conditions such as low wind speeds and less precipitation (Figure 3). On the other hand, TGS was a remote site with a low local EBC concentration; it may be related to long-distance transmission by westerly flow. Compared with autumn, the EBC concentration in summer is lower, which may be due to the frequent precipitation events, accounting for 60% of the yearly total. Precipitation can remove BC, which greatly reduces the concentrations. The low EBC concentration in winter may be related to the temperature inversion layer during the winter. Previous studies found that there was a strong inversion at 1000–2400 m a.s.l in winter, which hinders the spread of pollutants to higher altitudes [39] and traps them within the boundary layer. Therefore, although the air pollution in the Urumqi city is particularly heavy during the winter, the atmosphere environment in the Urumqi River Valley is still relatively clean. The presence of the inversion layer prevents the pollutants from spreading to higher altitudes. In addition, the road neighboring the measurement site was covered with snow, which greatly reduced local traffic emissions.
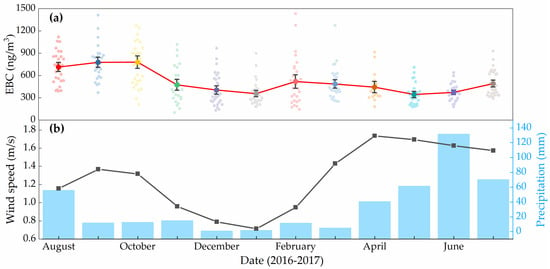
Figure 3.
The monthly mean (a) EBC concentrations, (b)wind speed and precipitation observed at TGS.
The EBC at TGS has clear seasonal cycles, however, the trends are different from those reported in Urumqi and other northern urban/rural sites of China, where consistently higher EBC values were observed in winters and lower in summers. A reasonable explanation of the difference could be that direct biofuel burning (heating, cooking, etc.,) of urban residents in the winter induces higher EBC concentrations [10,13]. For example, in Urumqi city, which is only 100 kilometers northeast of TGS, the average concentration of EBC was as high as 123,700 ng/m3 in winter, while in summer and autumn was only 3840 ng/m3 [40]. The seasonal variations of EBC at TGS are similar to those observed at the Muztagata [41] and Mt. Waliguan [42] sites, showing higher EBC concentrations in autumn and summer, lower in spring and winter. These sites are relatively remote and have fewer human activities, and the main human activities were dominated by traditional agriculture and animal husbandry.
3.2. Hourly Variations of EBC
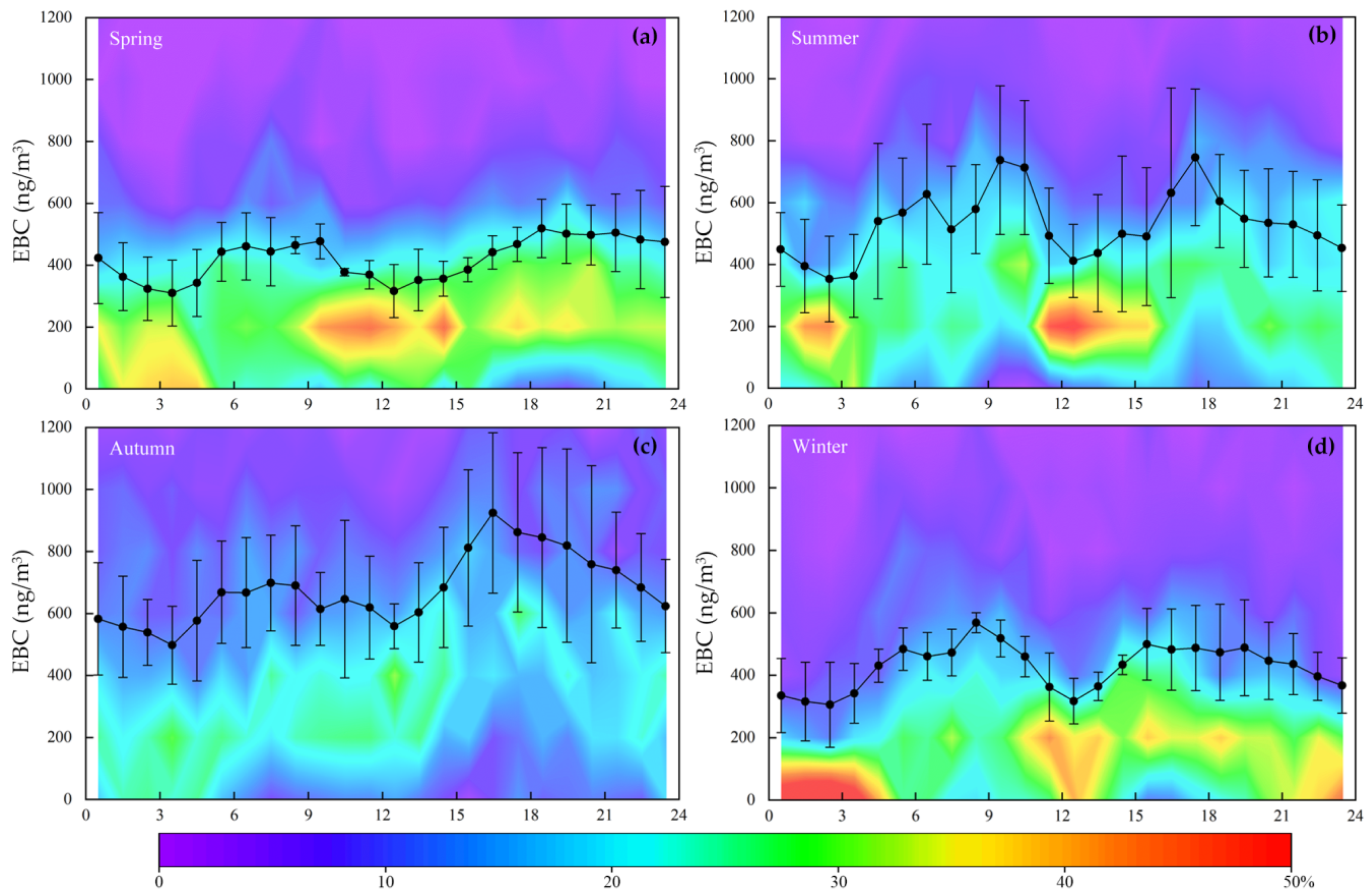
Studying the hourly variations of EBC is a useful approach to understand the effects of mesoscale atmospheric processes and human activities on BC [37]. Figure 4 shows the seasonal mean hourly variations of EBC concentrations at TGS. During all seasons, the hourly variations showed a similar pattern. There are two prominent features: one is at 08:00–09:00 local time (LT) and the other is at 16:00–19:00 LT. The EBC concentration rises sharply between 06:00 and 08:00, and thereafter decreases gradually till 12:00, rising again after 15:00 and remaining high from 16:00–19:00. The morning and evening maxima in concentration during the autumn were higher than the other seasons, probably because of the meteorological conditions such as low wind speeds and less precipitation.
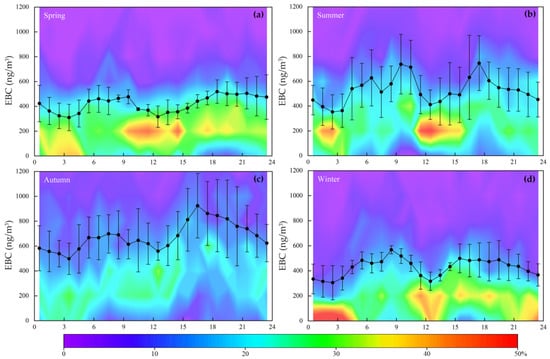
Figure 4.
Hourly variations of EBC concentrations during four seasons. The black line represents the average EBC concentration, while the color map shows the frequency distribution of EBC (200 ng/m3 per bin).
This hourly variation is linked to atmospheric boundary layer dynamics and winds (see Section 3.4 and Section 3.5). The peak concentration that appears at 8:00–9:00 might be related to the influence of local emissions (e.g., residential heating, traffic), for which we do not have correlating evidence. The peak concentration that appeared at time 16:00–19:00 was related to the decrease in the boundary layer depth and the wind speed decreases. The low wind speed at night is not conducive to the dispersion of pollutants, resulting in the accumulation of pollutants in the near-surface layer, and generally higher concentrations during this period. The minimum values of concentration appear between 1:00 and 3:00, when air temperatures are a minimum and there is no solar radiation, atmospheric turbulence can occur. This process can influence the transport and dispersion of EBC as well as hourly variation. The other minimum value of concentration occurred between 12:00 and 13:00. This is the time period of maximum boundary layer height and wind speed, leading to dispersion and dilution.
There is an inverse relationship between PBLH and BC. With the decrease of PBLH in the early morning, the EBC concentration began to rise. When the PBLH decreased to the minimum, the EBC concentration reached the maximum. The main reason is that the reduction of the PBLH leads to a smaller volume of air for the same number of particles and hence increases the relative concentration. Investigations of the relationship between PBLH and pollution show that PBLH has a significant impact on the concentration of all pollutants not just the BC [43,44].
Similar hourly variation was observed at other locations, such as Ranwu and Muztagh Ata Mountain [15,45]. Wang et al. [15] showed the hourly variation of EBC concentration at Ranwu with a peak shortly after sunrise and a decrease before noon. The rise in the concentration in the evening hours is likely a result of the same dynamics as observed at TGS.
3.3. Absorption Properties of EBC
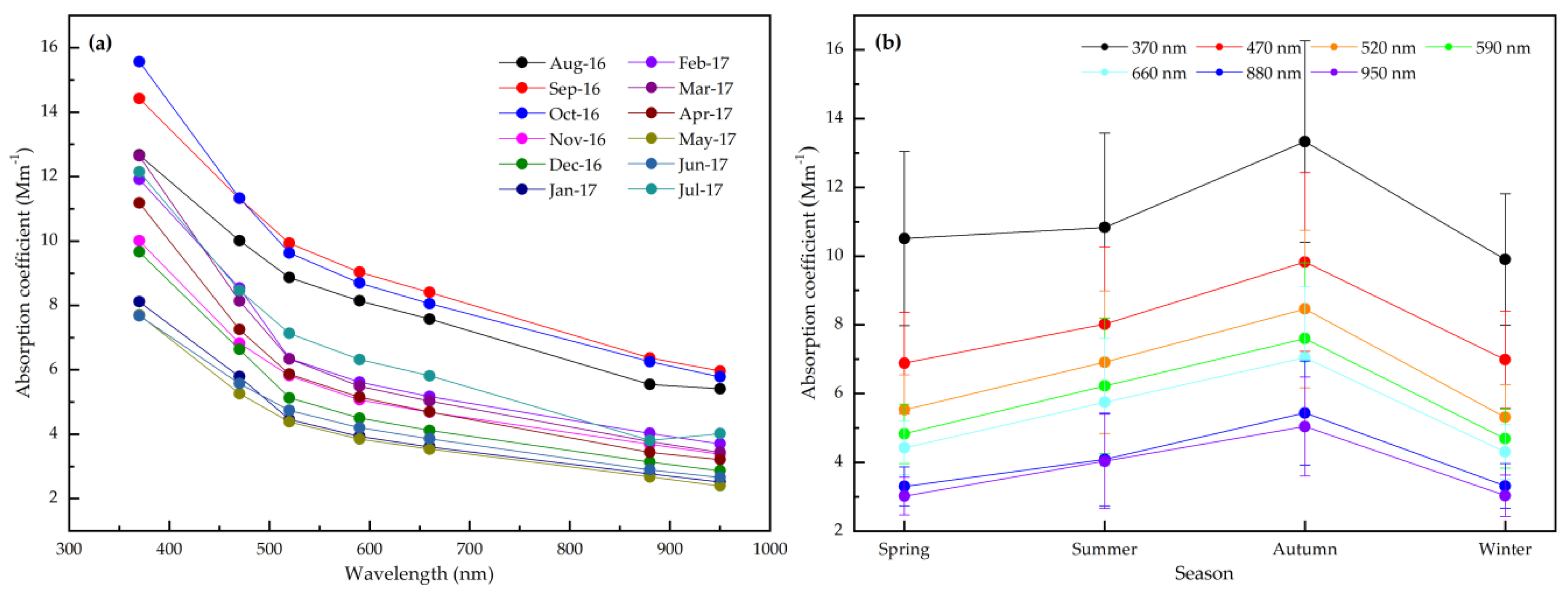
The spectral and seasonal mean variations of the absorption coefficient are shown during the study period (Figure 5). As expected, the α(λ)880nm decreases with the increase in wavelength. The monthly averages ranged from 2.67 to 6.37 Mm–1 for α(λ)880nm with an average value of 4.03 ± 1.31 Mm−1. The seasonal averages were 3.3 ± 0.6, 4.1 ± 1.3, 5.4 ± 1.5, 3.3 ± 0.6 Mm–1 for α(λ)880nm in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively (Figure 5b). Under favorable meteorological conditions, aerosol accumulation including light-absorbing components increases and removal efficiency decreases, resulting in stronger aerosol absorption in autumn. Overall, the presence of a strong absorbing component may lead to higher α(λ) at shorter wavelengths.
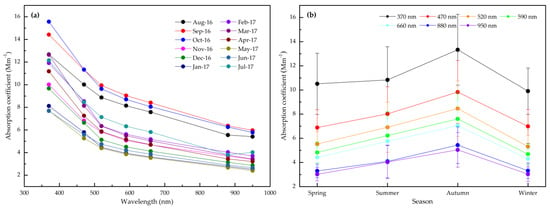
Figure 5.
The spectral (a) and seasonal (b) mean of the absorption coefficients.
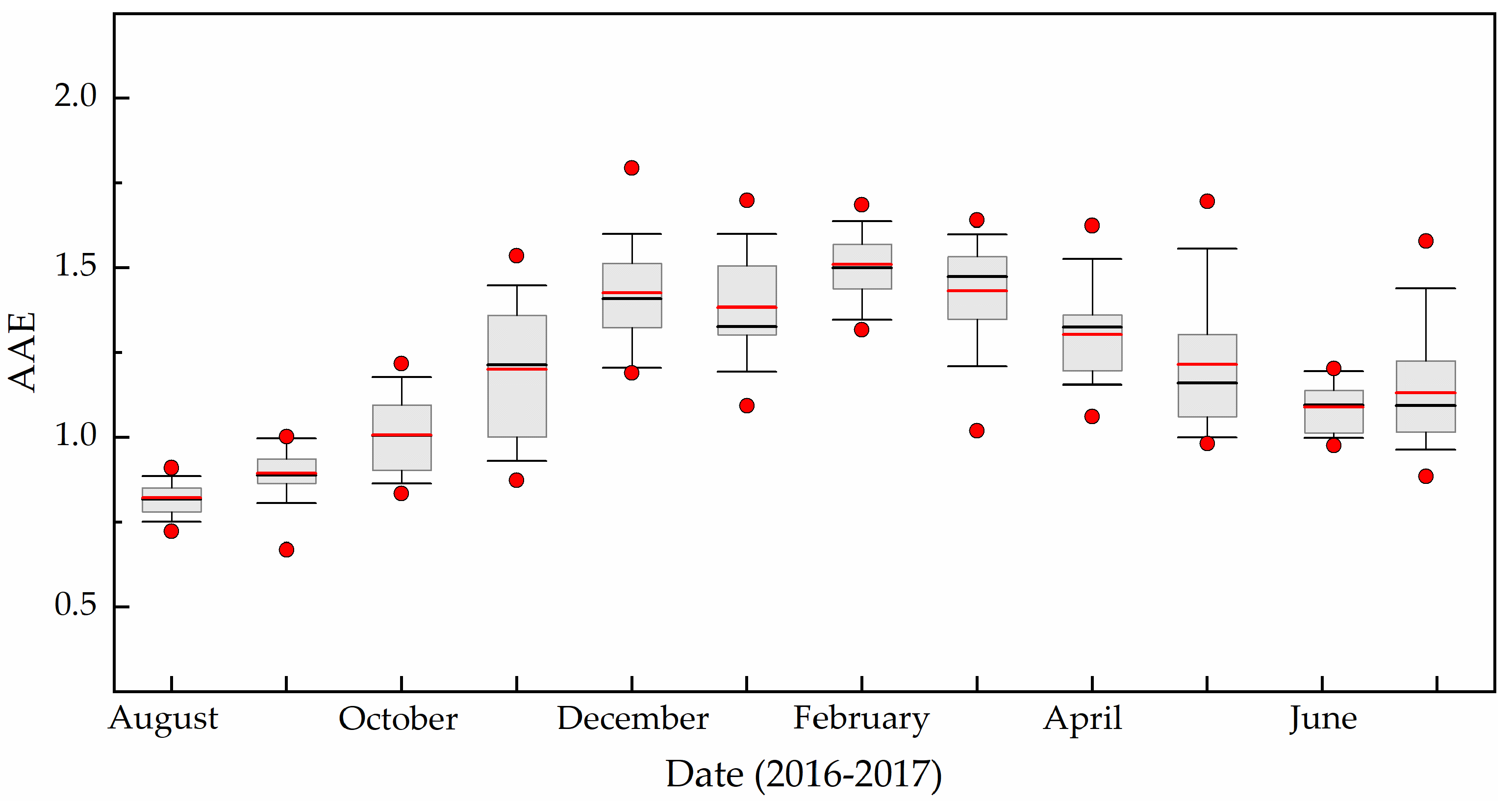
As previously discussed, previous studies have shown that the AAE can be used to distinguish between those aerosols originating from fossil fuel and those from biomass fuel combustion [30,46,47]. The AAEs were calculated at the visible wavelength (470–660 nm). Monthly average AAEs at TGS are shown in Figure 6. The AAE ranged from 0.82 to 1.51, with an average of 1.2. The highest AAE was 1.51 in February, indicating the high contribution from biomass burning. The lowest AAE was 0.82 in August, suggesting that fossil fuel contribution was most dominant, which mainly associated with locally and freshly emitted BC. The AAEs in summer (1.01) and autumn (1.03) were close to 1, the AAE values in winter (1.44) and spring (1.32) are significantly higher than 1. The higher value observed in winter and spring was due to lensing and additional sources of absorption (e.g., brown carbon aerosols, dust aerosols, and sulfate aerosols) mixed with the BC and increased the AAE [48,49]. An AAE value between 1 and 2 could be indicative of aerosol of mixed sources, that is, fossil and biomass fuels. Therefore, fossil-fuel emissions are the main source of BC at TGS, but the contribution of biomass burning to BC in winter and spring was higher than in summer and autumn.
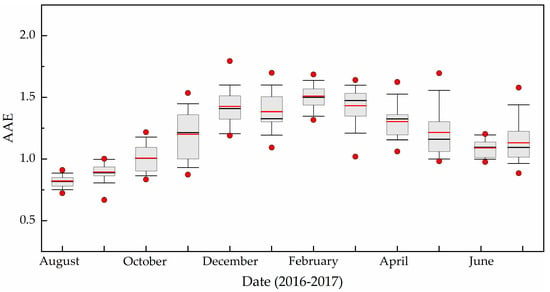
Figure 6.
Monthly variation of AAE during the study period.
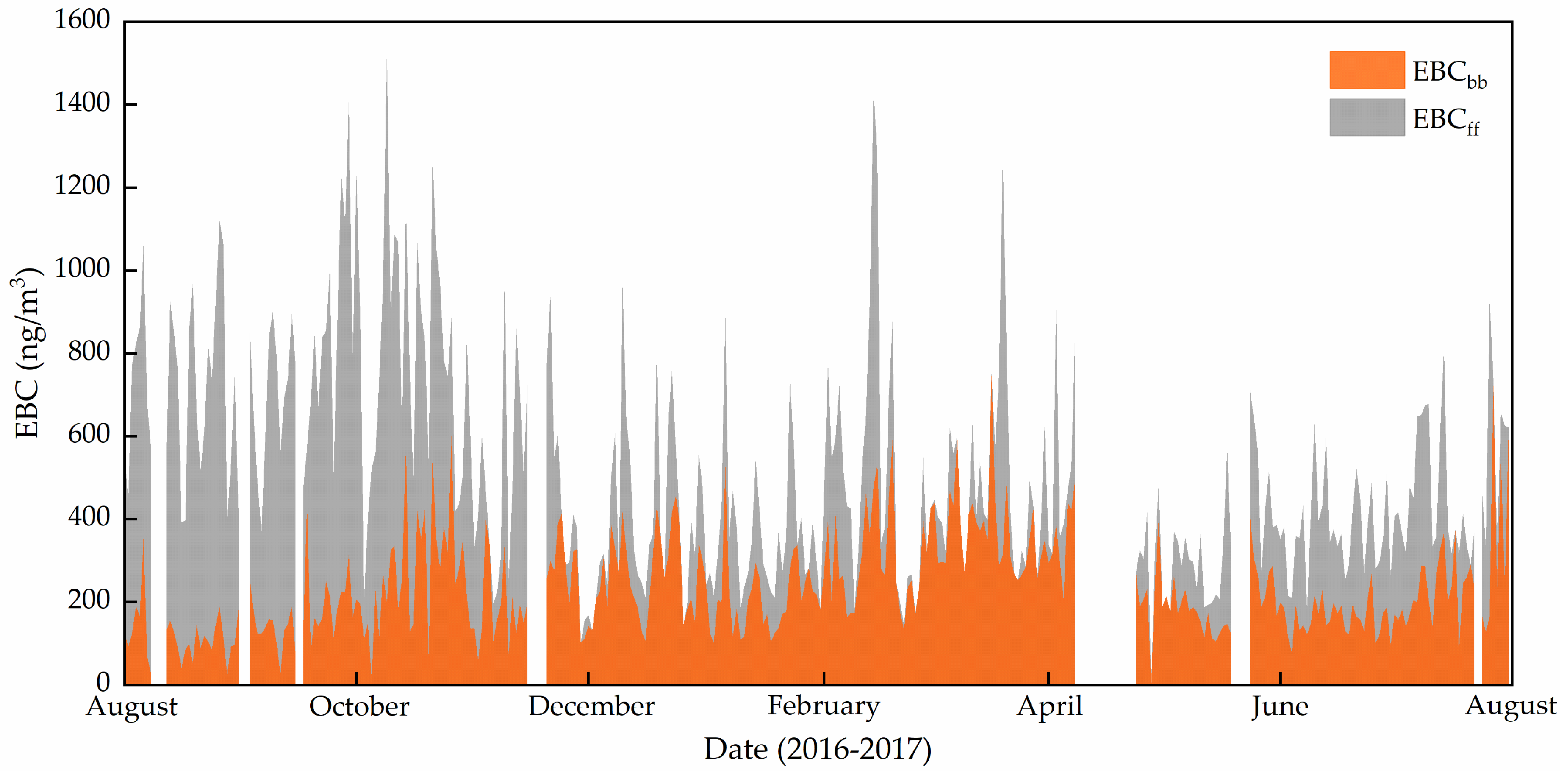
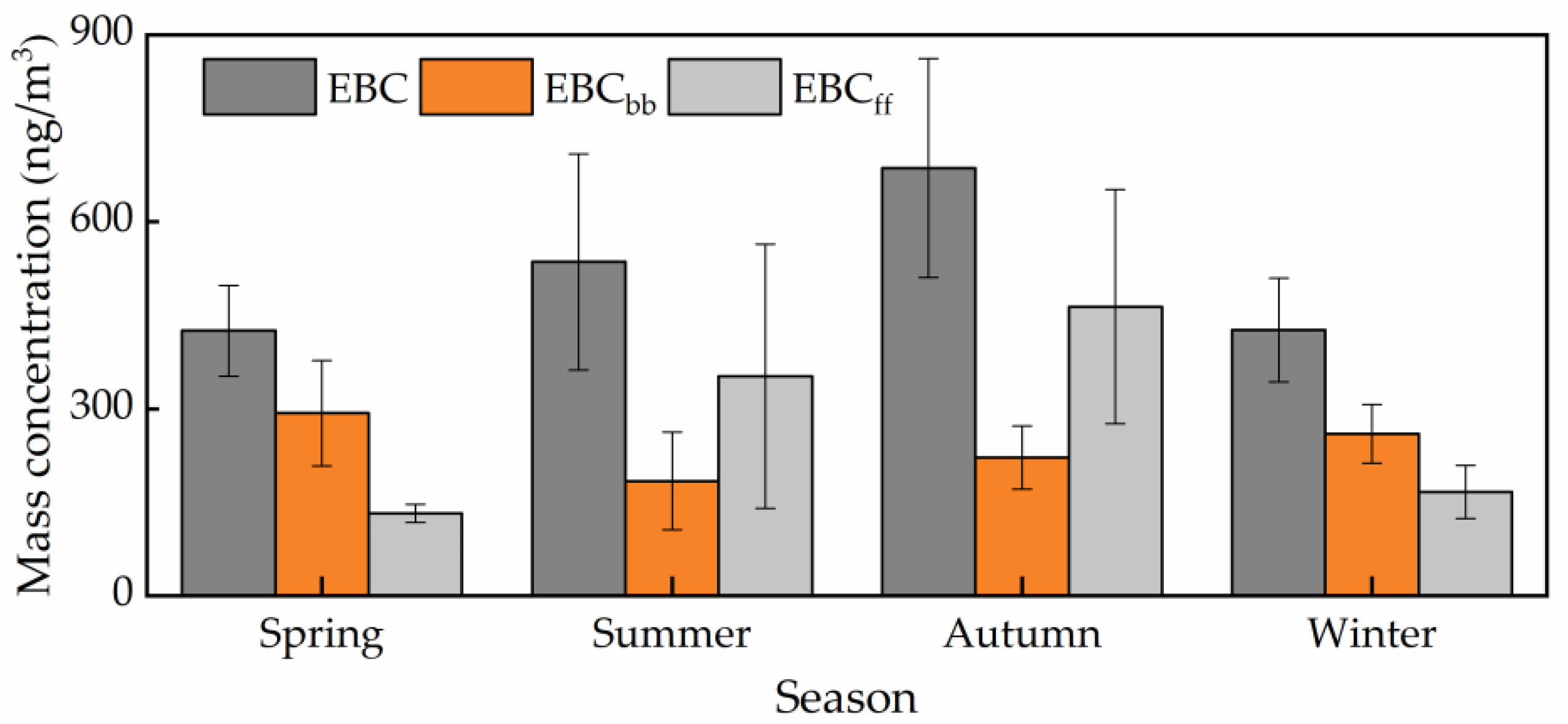
Figure 7 shows the daily average concentrations of EBCff and EBCbb at TGS during the study period. The average daily EBCff concentration was 278 ± 256 ng/m3, and EBCbb was 238 ± 125 ng/m3. The seasonally averaged EBCff concentrations are 127, 345, 464, and 167 ng/m3 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively (Figure 8). The highest EBCff appeared in autumn, followed by summer, due to the local emission and long-distance transport. Previous studies have shown that fine particles (d < 1 μm) in the precipitation also significantly increased during September to October 2003 in Urumqi River Valley, which was inferred to be caused by anthropogenic activities [50]. The seasonally averaged EBCbb concentrations are 293, 184, 222, and 260 ng/m3 in spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively. The high EBCbb at TGS during spring and winter might be due to the amount of biomass burnings. Therefore, fossil fuel combustion is dominant in summer and autumn, and biomass fuel is dominant in winter and spring.
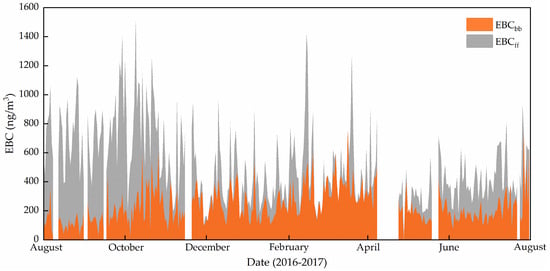
Figure 7.
The daily mean concentrations of EBCff and EBCbb.
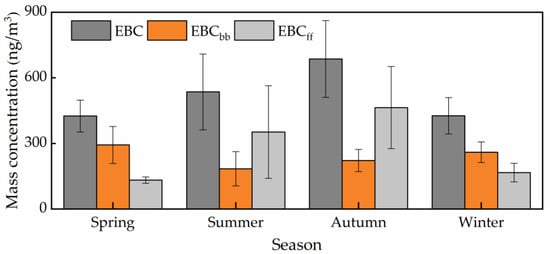
Figure 8.
Seasonal variation of EBC, EBCbb, and EBCff.
3.4. Effect of Wind on the Variation of EBC
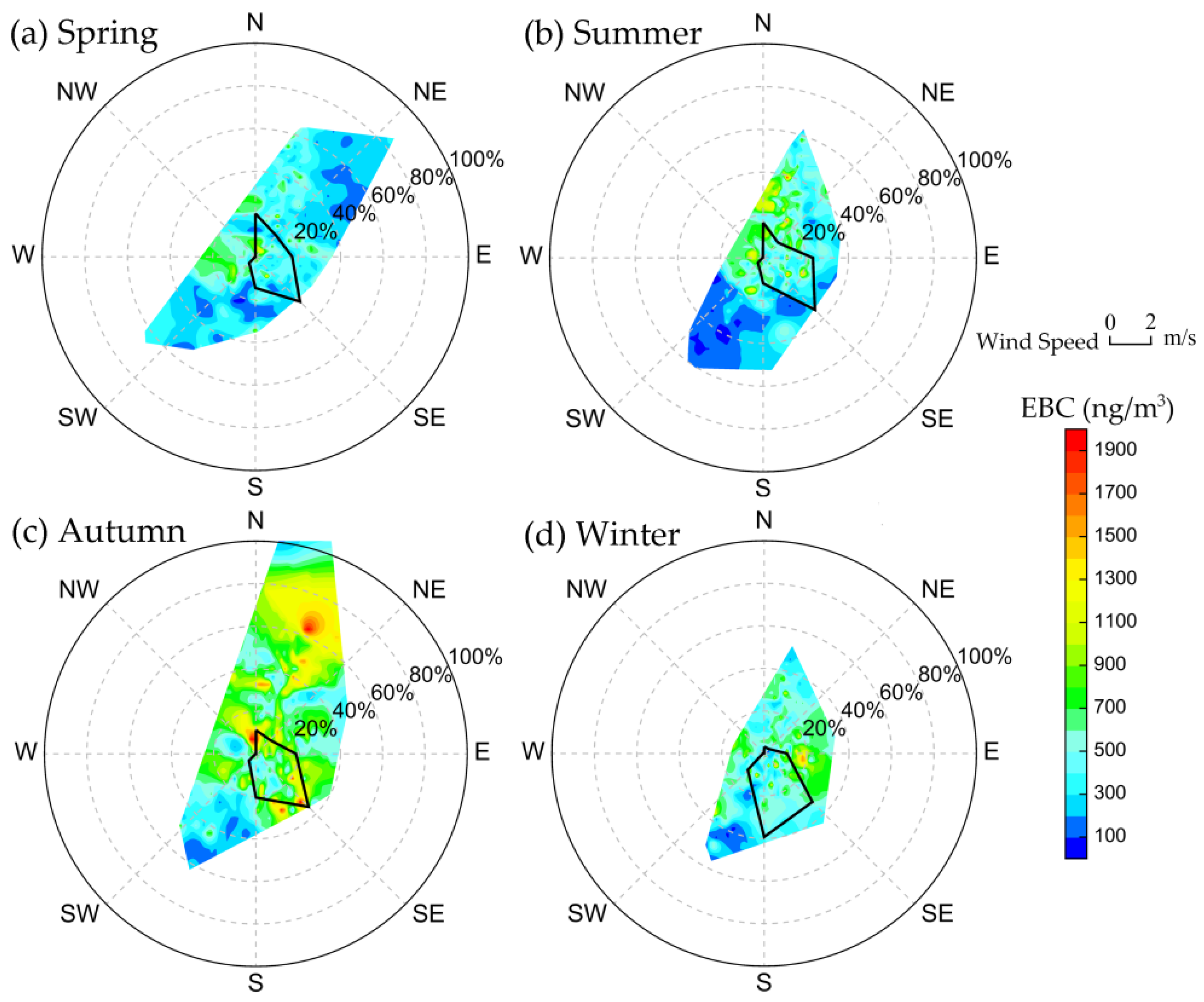
The prevailing westerly flow at TGS depends on the general atmospheric circulation and seasonal climate. Figure 9 shows the relationship between EBC and winds at TGS. When the wind speed was less than 2 m/s, the EBC was significantly higher in concentration, which was associated with the poor dispersion conditions. When the wind speed was greater than 2 m/s, the concentrations of EBC decreased. When the wind speed was greater than 4 m/s, the concentrations were generally smaller than 250 ng/m3 due to the strong dispersion. The variations of wind speeds and BC concentrations indicate that EBC could be largely due to local emissions, but higher wind speeds in autumn are also likely to transport EBC from farther away sources.
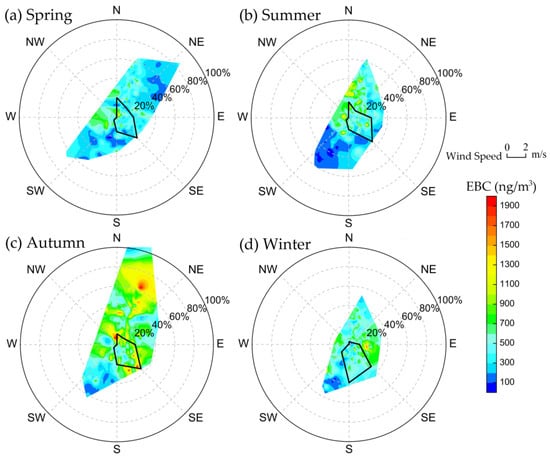
Figure 9.
The relationship of average EBC concentration and winds in (a) Spring; (b) Summer; (c) autumn; (d) winter. Concentrations of EBC are given by the color bar. The frequency of wind direction is shown by the black line.
3.5. EBC Potential Sources
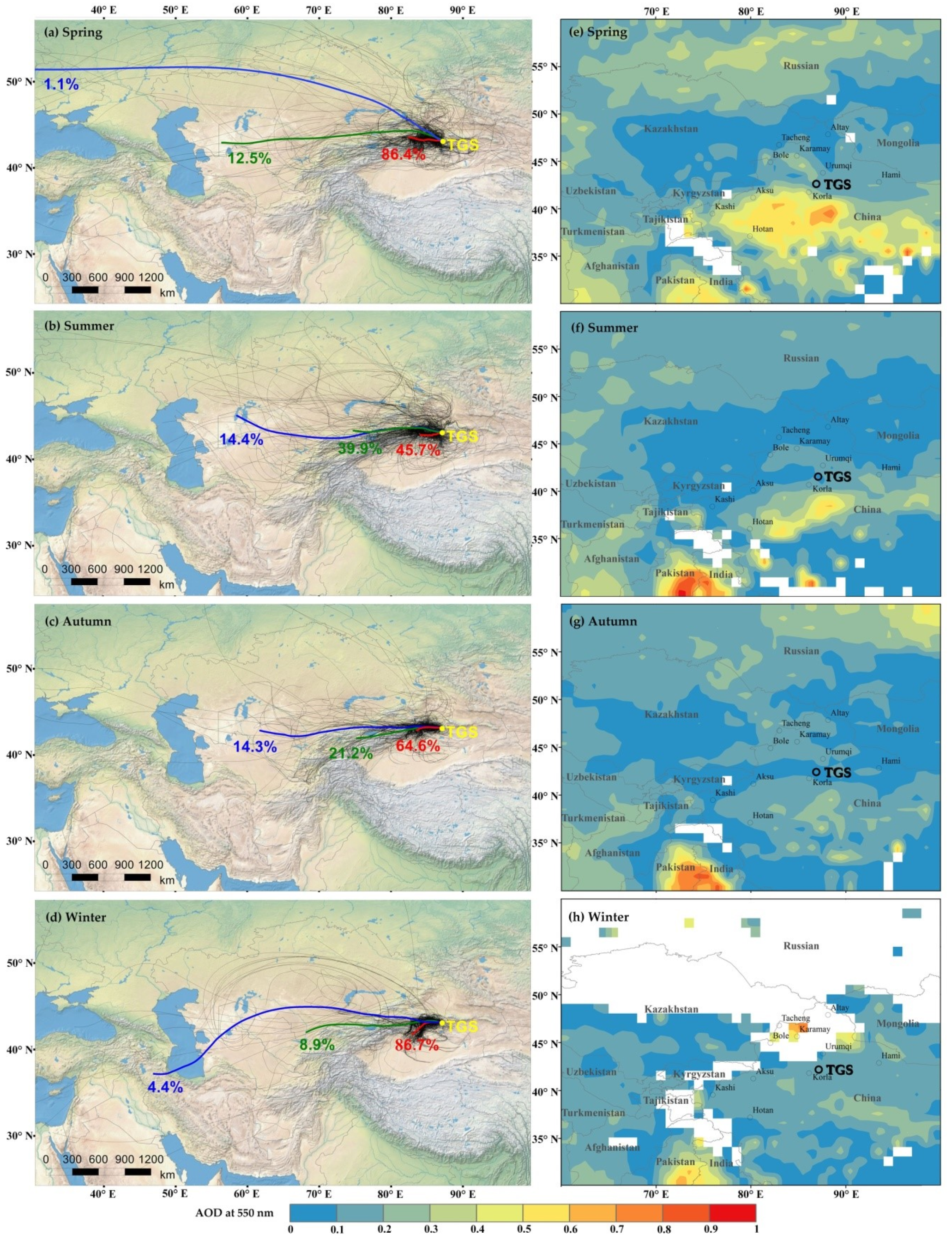
Figure 10a–d shows that there are three possible pathways for air masses to arrive at TGS from their distant sources. In addition, we use aerosol optical depth (AOD) at 550 nm retrieved from Aqua MODIS data with a spatial resolution of 1° × 1° as another method to identify the potential sources of BC from August 2016 to July 2017. The area-averaged maps of the AOD at 550 nm including the TGS site and its surroundings (20° N–40° N, 70° E–100° E) are shown in Figure 10e–h. Notably, in this study, the AOD was not a direct manifestation of the EBC concentration, and the accuracy of the satellite derived AOD was considerably uncertain.
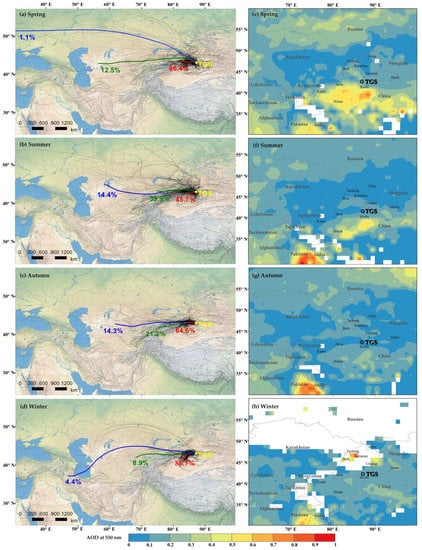
Figure 10.
The 5-day backward air-mass trajectories calculated by the HYSPLIT model ending at TGS including the percentages of each cluster trajectories in: (a) spring, (b) summer, (c) autumn, (d) winter, and area-averaged maps of aerosol optical depths (AOD) including TGS site and its surroundings in: (e) spring, (f) summer, (g) autumn, (h) winter.
The cluster analysis suggests air masses over the sampling site are mostly from Xinjiang for both spring (86.4%) and winter (86.7%). In summer, air masses are largely contributed by those from the Xinjiang (45.7%) and Central Asia (39.9%). In autumn, air masses are largely contributed by those from the Xinjiang (64.6%), followed by Central Asia (21.2%), which is more susceptible to long-distance transmission from Central Asia.
The higher AOD was in northern Xinjiang during spring, largely attributed to emissions of dust particles over the Taklimakan Desert. The higher AOD was in the city of Xinjiang during winter, which was due to the winter heating in the city. The higher AOD was in the northern part of South Asia and northern Xinjiang in summer, while the higher AOD was in the northern part of South Asia in autumn. The monthly average of AOD at TGS (average value: 0.09) are generally much smaller than surrounding areas, such as northern parts of South Asia and the Taklimakan Desert.
Combined with trajectory analysis and seasonal changes, we found that the pollution from Central Asian is more likely to affect the atmosphere of Tien Shan in summer and autumn. This is also one of the important reasons for higher concentrations of EBC in summer and autumn. In addition, the values of AOD during spring may be partly due to the influence of long-range transported dust aerosols, which make the EBCbb reach the highest in spring. Although there is a large amount of anthropogenic activities in the north to the Urumqi River valley, the EBC in the Urumqi River Valley remains at a low level. Therefore, the EBC concentration in the Urumqi River Valley is likely to be affected by the westerly and circular winds from the surrounding area. In addition, the pollution from Central Asia can change the concentrations of EBC at TGS during summer and autumn in a short period of time.
4. Conclusions
Tien Shan in northwestern China is a key region where many glaciers exist. Tien Shan has relatively weak local emissions, which makes it an ideal choice to monitor regional-background concentrations of EBC and evaluate various impacts caused by human activities. The monitoring of EBC as an air pollutant in Tien Shan is necessary and fundamental not only for its environmental reasons but also for its climatic significance. In this study, EBC was derived from measurements of optical attenuation with a seven-wavelength Aethalometer (AE-31) in the Urumqi River Valley, eastern Tien Shan, China. Results showed that the average daily EBC concentration was 520 ng/m3, fluctuating between 102 ng/m3 and 1525 ng/m3. The highest concentration of EBC was in autumn (686 ng/m3), followed by that in summer (536 ng/m3), and winter (427 ng/m3), and spring (425 ng/m3). There was a strong correlation between EBC concentration and meteorology. The higher concentration was more associated with the wind speed smaller than 2 m/s. The variations of wind speed and EBC concentrations indicated that EBC could be largely due to short-range emissions, while higher wind speeds in summer and autumn brought pollutants from farther upwind. The hourly variations of EBC showed plateaus from 8:00-9:00 LT and 16:00-19:00 LT with seasonal variations, associated with local traffic emissions and meteorological factors. The planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) showed an inverse relationship with EBC, indicating that the reduction of the PBLH can cause EBC enrichment near the ground. The average AAE was 1.2, suggesting that fossil-fuel emissions were the main source of EBC in the Urumqi River Valley, and the contribution of biomass burning to BC in winter and spring was higher than summer and autumn. The aerosol optical depths (AOD) derived from the MODIS data over the Tianshan Glaciological Station (TGS) and trajectory analysis showed that the pollution from Central Asian was more likely to affect the atmosphere of Tien Shan in summer and autumn. This suggests that long-distance transport of pollutants from Central Asia could be significant contributors to BC measured in the Urumqi River Valley.
Author Contributions
Data curation, X.Z.; formal analysis, X.Z.; funding acquisition, Z.L.; investigation, J.M.; methodology, F.W.; software, X.Z.; writing—original draft, X.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (2019QZKK0201), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Class A)(XDA20060201;XDA20020102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41761134093;41471058) and The SKLCS founding (SKLCS-ZZ-2020).
Acknowledgments
We thank the staffs working in the Tianshan Glaciological Station for helping collect data. We also gratefully thank the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC WG1 AR5. 2013. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1 (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Short-term effects of controlling fossil-fuel soot, biofuel soot and gases, and methane on climate, Arctic ice, and air pollution health. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, A.S.; Pandithurai, G.; Safai, P.D.; Dipu, S.; Lee, D.I. On the contribution of black carbon to the composite aerosol radiative forcing over an urban environment. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3066–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, S.G.; Wiscombe, W.J. A Model for the Spectral Albedo of Snow. II: Snow Containing Atmospheric Aerosols. J. Atmos. Sci. 1980, 37, 2734–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanner, M.G.; Zender, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Rasch, P.J. Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D11202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Xiao, C.; Xu, X.; Ding, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, W. Widespread albedo decreasing and induced melting of Himalayan snow and ice in the early 21st century. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordukhovich, I.; Wilker, E.; Suh, H.; Wright, R.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Black carbon exposure, oxidative stress genes, and blood pressure in a repeated-measures study. Environ. Health PERSP 2009, 117, 1767–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Hao, J. Black carbon at a roadside site in Beijing: Temporal variations and relationships with carbon monoxide and particle number size distribution. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Cheng, T.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Leng, C.; Zhang, D.; Du, J. Characteristics and relevant remote sources of black carbon aerosol in Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2014, 135, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.S.; Li, L.; Pang, B.; Xue, P.; Wang, L.L.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, Y.S. Characterization of black carbon in an urban-rural fringe area of Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Tie, X.; Cao, J.; Li, N.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, C.; Long, X.; Li, J.; Feng, T.; et al. Seasonal variation and four-year trend of black carbon in the Mid-west China: The analysis of the ambient measurement and WRF-Chem modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Ming, J.; Xiao, C.D.; Sun, W.J.; Qin, X. A preliminary study on measurements of black carbon (EBC) in the atmosphere of northwest Qilian Shan. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, B.Q.; Wang, N.L.; Cao, J.J.; Tie, X.X.; Wang, H.L.; Zhu, C.S.; Yang, W. Two distinct patterns of seasonal variation of airborne black carbon over Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, P. Long-range terrestrial laser scanning measurements of annual and intra-annual mass balances for Urumqi Glacier No. 1, eastern Tien Shan, China. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2361–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Xiao, C.D.; Cachier, H.; Qin, D.H.; Qin, X.; Li, Z.Q.; Pu, J.C. Black carbon (EBC) in the snow of glaciers in west China and its potential effects on albedos. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Cao, J.; Joswiak, D.R.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; He, J. Post-depositional enrichment of black soot in snow-pack and accelerated melting of Tibetan glaciers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Xiao, C.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Grey Tienshan Urumqi Glacier No.1 and light-absorbing impurities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9549–9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmale, J.; Flanner, M.; Kang, S.; Sprenger, M.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Schwikowski, M.; Farinotti, D. Modulation of snow reflectance and snowmelt from Central Asian glaciers by anthropogenic black carbon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Qin, D.; Kang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Qin, X. Individual particles of cryoconite deposited on the mountain glaciers of the Tibetan Plateau: Insights into chemical composition and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; et al. Recommendations for reporting “black carbon” measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.D.A. 2005. Available online: https://www.psi.ch/sites/default/files/import/lac/ProjectAddonCatcosOperationsEN/Aethalometer_book_2005.07.02.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2015).
- Beegum, S.N.; Moorthy, K.K.; Babu, S.S.; Satheesh, S.K.; Vinoj, V.; Badarinath, K.V.S.; Safai, P.D.; Devara, P.C.S.; Singh, S.; Vinod Dumka, U.C.; et al. Spatial distribution of aerosol black carbon over India during pre-monsoon season. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Manchanda, R.K.; Sinha, P.R.; Sreenivasan, S.; Moorthy, K.K.; Suresh Babu, S. Temporal variability and radiative impact of black carbon aerosol over tropical urban station hyderabad. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 105, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, T.S.; Hooda, R.K.; Lihavainen, H.; Hyvarinen, A.P.; Sharma, V.P.; Viisanen, Y. Atmospheric aerosols at a regional background Himalayan site-Mukteshwar, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4753–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begam, G.R.; Vachaspati, C.V.; Ahammed, Y.N.; Kumar, K.R.; Babu, S.S.; Reddy, R.R. Measurement and analysis of black carbon aerosols over a tropical semi-arid station in Kadapa, India. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaud Coen, M.; Weingartner, E.; Apituley, A.; Ceburnis, D.; Fierz-Schmidhauser, R.; Flentje, H.; Henzing, J.S.; Jennings, S.G.; Moerman, M.; Petzold, A.; et al. Minimizing light absorption measurement artifacts of the Aethalometer: Evaluation of five correction algorithms. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prévôt, A.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.; Lanz, V.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using aerosol light absorption measurements for the quantitative determination of wood burning and traffic emission contributions to particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsson, J.; Eriksson, A.C.; Elbæk Nielsen, I.; Berg Malmborg, V.; Ahlberg, E.; Andersen, C.; Lindgren, R.; Nystrom, R.; Nordin, E.Z.; Brune, W.H.; et al. Impacts of combustion conditions and photochemical processing on the light absorption of biomass combustion aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14663–14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.M.; Babu, S.S.; Moorthy, K.K. Radiative effects of absorbing aerosols over northeastern India: Observations and model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 1132–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, Y.; Shaik, D.S.; Mitra, D.; Chandola, H.C.; Babu, S.S.; Chauhan, P. Black carbon aerosol quantification over north-west Himalayas: Seasonal heterogeneity, source apportionment and radiative forcing. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 257, 113446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draxler, R.; Hess, G. An overview of the HYSPLIT_4 modelling system for trajectories. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Schnaiter, M.; Linke, C.; Möhler, O.; Naumann, K.H.; Saathoff, H.; Wagner, R.; Schurath, U.; Wehner, B. Absorption amplification of black carbon internally mixed with secondary organic aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumka, U.C.; Moorthy, K.K.; Kumar, R.; Hegde, P.; Sagar, R.; Pant, P.; Singh, N.; Babu, S.S. Characteristics of aerosol black carbon mass concentration over a high altitude location in the Central Himalayas from multi-year measurements. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, Q.; Bey, I. Pollution transport efficiency toward the Arctic: Sensitivity to aerosol scavenging and source regions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Kang, E.S.; Liu, C.H. The Climate Features of Tianshan Urumqi River Valley. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1994, 16, 333–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.T.; Liu, X.C.; He, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhao, K.L. Pollution Characteristics and Source of Black Carbon Aerosols in Urumqi in Winter. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2014, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Shen, Z.X.; An, Z.S. Black carbon relationships with emissions and meteorology in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wen, Y.P.; Zhou, L.X.; Qi, D.L.; Zheng, M. Observational study of black carbon in clean air area of western China. Q. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 10, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty, R.; Moosmuller, H.; Chen, L.W.A.; Lewis, K.; Arnott, W.; Mazzoleni, C.; Dubey, M.; Wold, C.; Hao, W.; Kreidenweis, S. Brown carbon in tar balls from smoldering biomass combustion. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6363–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Sun, T.L.; Zeng, L.W.; Yu, G.H.; Luan, S.J. Black carbon aerosol characterization in a coastal city in south china using a single particle soot photometer. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 51, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielonen, T.; Arola, A.; Komppula, M.; Kukkonen, J.; Koskinen, J.; De Leeuw, G.; Lehtinen, K.E.J. Comparison of CALIOP level 2 aerosol subtypes to aerosol types derived from AERONET inversion data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.S.; Cao, J.J.; Xu, B.Q.; Huang, R.J.; Wang, P.; Ho, K.F.; Shen, Z.X.; Liu, S.X.; Han, Y.M.; Tie, X.X.; et al. Black carbon aerosols at Mt. Muztagh Ata, a high-altitude location in the western Tibetan plateau. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, P.S.; Ahmed, T.; Kar, A.; Rehman, I.H.; Ramanathan, V. Link between local scale EBC emissions in the Indo-Gangetic Plains and large scale atmospheric solar absorption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Global distribution and climate forcing of carbonaceous aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 110, D11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, V.B. Association between atmospheric circulation patterns and firn-ice core records from the Inilchek glacierized area, central Tien Shan, Asia. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovec, L.; Gregorič, A.; Zotter, P.; Wolf, R.; Bruns, E.A.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Petit, J.E.; Favez, O.; Sciare, J.; Arnold, I.J.; et al. The filter-loading effect by ambient aerosols in filter absorption photometers depends on the coating of the sampled particles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1043–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Brook, J.R.; Cachier, H.; Chow, J.; Gaudenzi, A.; Lu, G. Light absorption and thermalmeasurements of black carbon in different regions of Canada. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, AAC-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).