Integrating in situ Measurements and City Scale Modelling to Assess the COVID–19 Lockdown Effects on Emissions and Air Quality in Athens, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
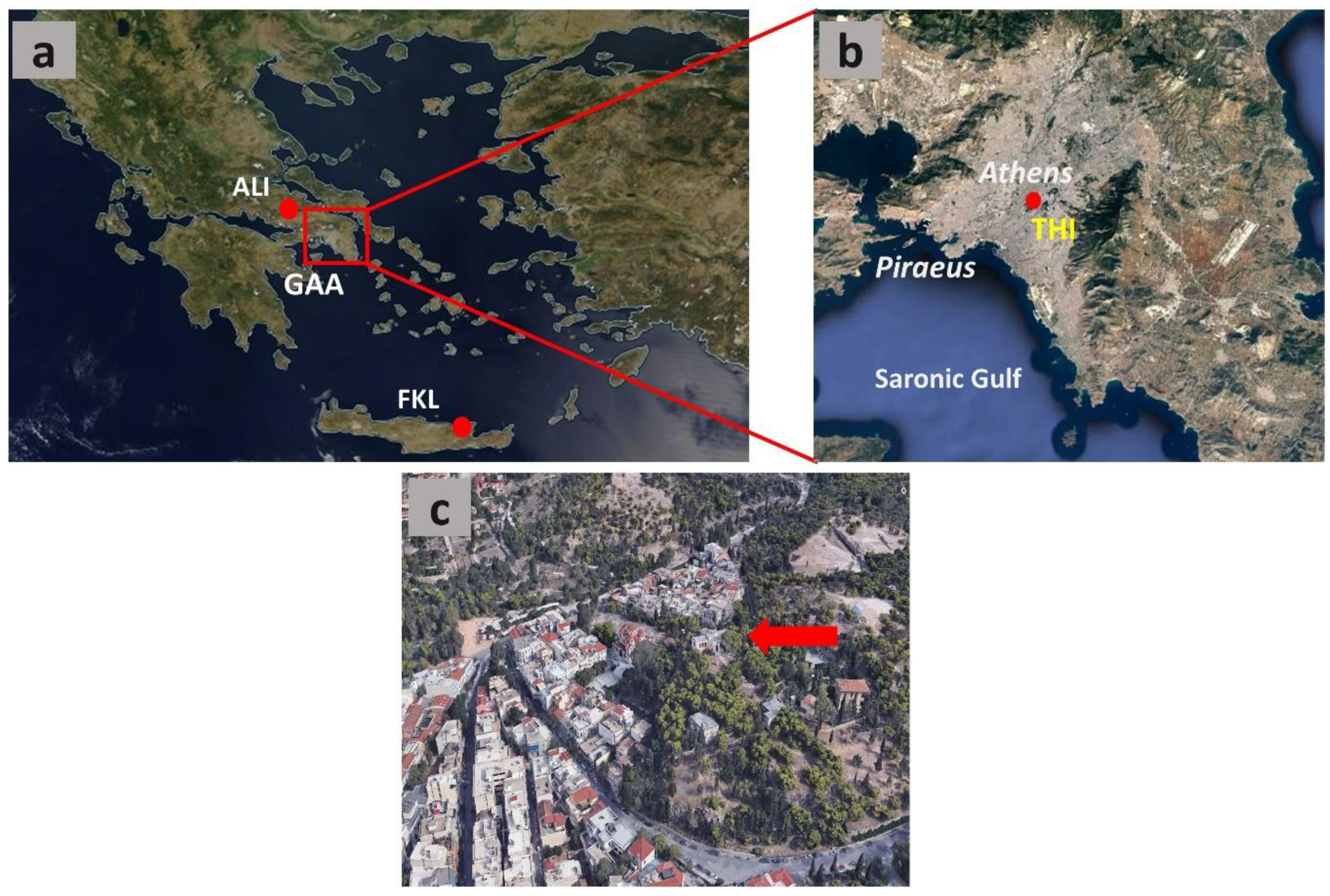
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Lockdown Measures in Greece and Selection of Study Periods
2.2. Sites and Measurement Periods
2.3. Measurements at the Central Site
2.4. Model Configuration and Setup
- 46% for road transport (urban congestion index in Europe)
- 35% for industry (change in coal consumption and/or steel production in China and USA, respectively)
- 85% in air transport (flight change in the Mediterranean countries of Italy and Spain)
- 2% in energy (change in the Greek power sector, based on daily electricity load)
2.5. Ancillary Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Representativeness and Influence of Meteorological Conditions
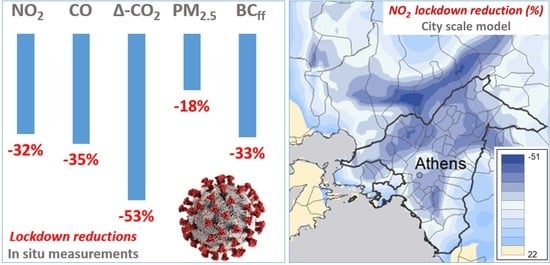
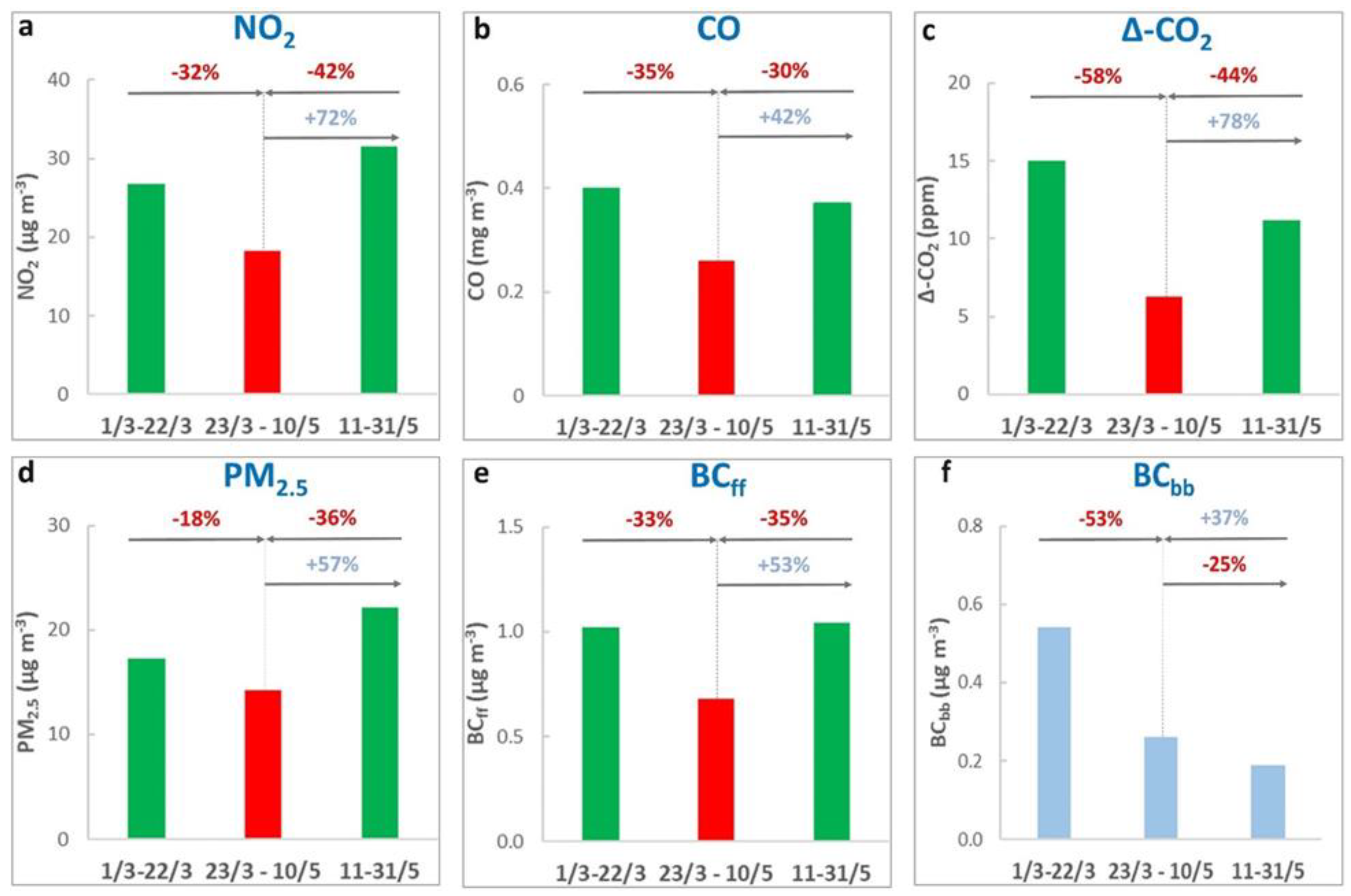
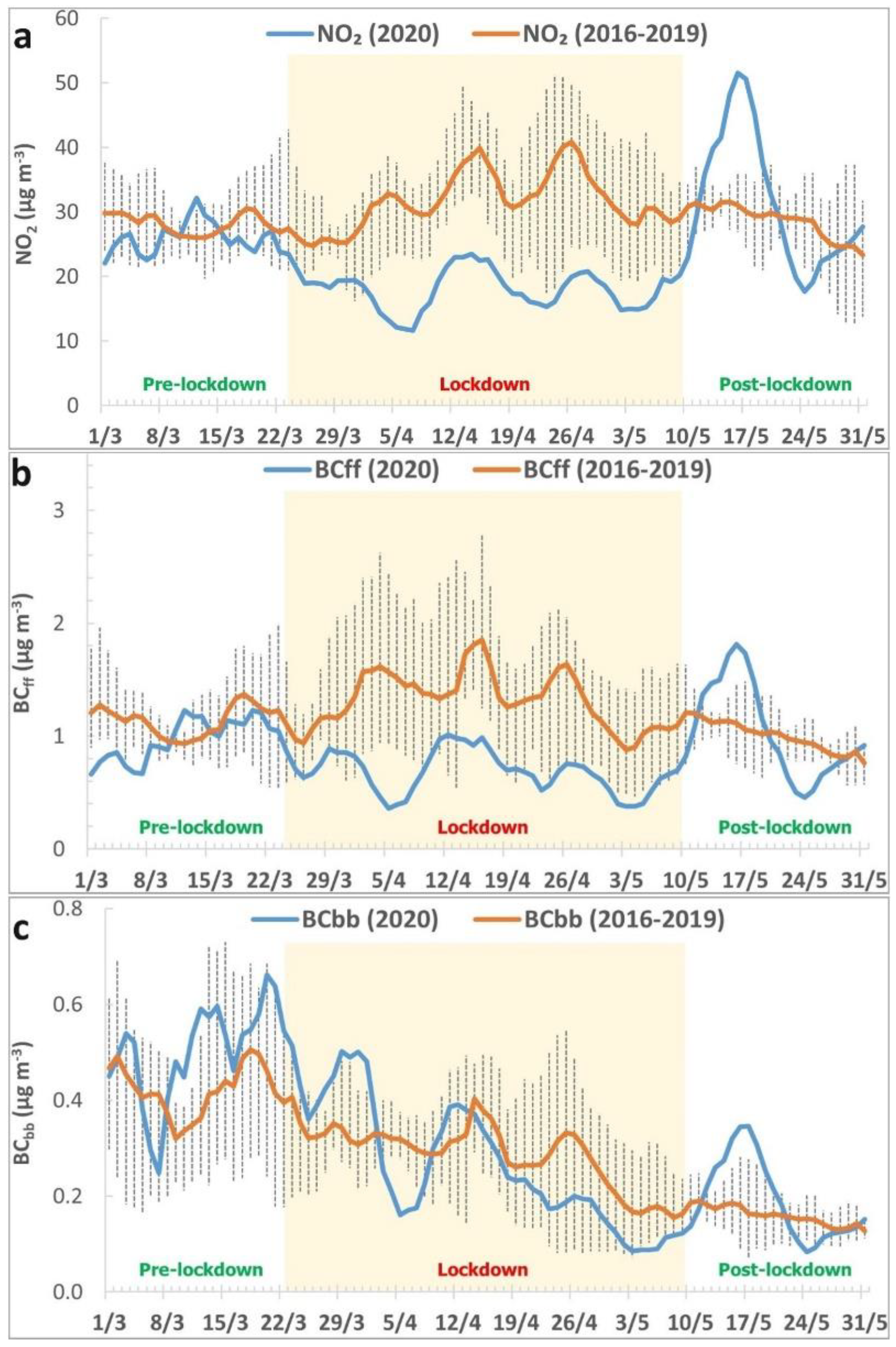
3.2. Changes of Ambient Pollutant Concentration Levels During the Lockdown Period
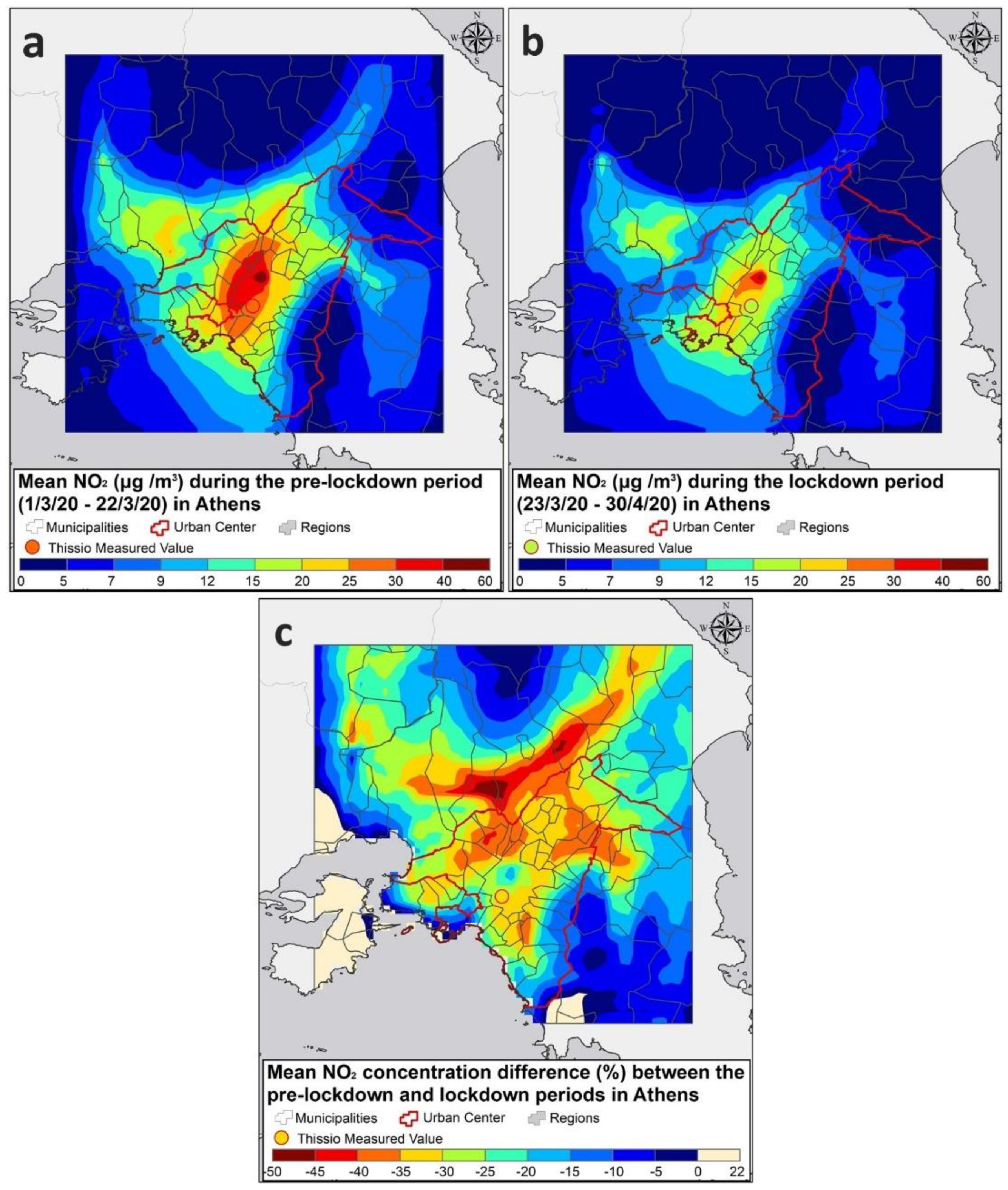
3.3. Estimated Changes in Emissions and Spatial Variability of Concentrations for NO2 During the Lockdown
3.4. Recovery of Ambient Pollutant Concentration Levels Following the Lift of Lockdown Measures
3.5. Changes in Concentration Levels in Comparison to Past Years
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Wu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Tong, Y.; Ren, R.; Leung, K.S.M.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamenidou, I.E.; Stavrianea, A.; Liava, C. Achieving a Covid–19 free country: Citizens preventive measures and communication pathways. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NPHO. Daily Report of Epidemiological Surveillance for Infections with the New COVID–19 Coronavirus. National Public Health Organization. 2020. Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/covid-gr-daily-report-20201024.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2020). (In Greek)
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID–19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Marquès, M.; Rovira, J. Influence of airborne transmission of SARS–CoV–2 on COVID–19 pandemic. A review. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tao, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Yuan, M.-L.; Liu, K.; Zhou, L.; Wei, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.-G.; et al. Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawska, L.; Cao, J. Airborne transmission of SARS–CoV–2: The world should face the reality. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doremalen, N.; Bushmaker, T.; Morris, D.H.; Holbrook, M.G.; Gamble, A.; Williamson, B.N.; Tamin, A.; Harcourt, J.L.; Thornburg, N.J.; Gerber, S.I.; et al. Aerosol and surface stability of SARS–CoV–2 as compared with SARS–CoV–1. N. Eng. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1564–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Long, X.; Salman, M. COVID–19 pandemic and environmental pollution: A blessing in disguise? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogen, Y. Assessing nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels as a contributing factor to coronavirus (COVID–19) fatality. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldasano, J.M. COVID–19 lockdown effects on air quality by NO2 in the cities of Barcelona and Madrid Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, J.D.; Ebisu, K. Changes in U.S. air pollution during the COVID–19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, T.; Jin, X. Effects of meteorological conditions and air pollution on COVID–19 transmission: Evidence from 219 Chinese cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, J.; Huang, F.; Cao, L. Association between short-term exposure to air pollution and COVID–19 infection: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Cui, K.; Young, L.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wan, S. Impact of the COVID–19 event on air quality in central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, M.; Anshika; Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Kota, S.H. Effect of restricted emissions during COVID–19 on air quality in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Pan, Y.; Tanaka, T. The short-term impacts of COVID–19 lockdown on urban air pollution in China. Nat. Sustain. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-J.; Kang, G.-U. Air quality variation in Wuhan, Daegu, and Tokyo during the explosive outbreak of Covid–19 and its health effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collivignarelli, M.C.; Abbà, A.; Bertanza, G.; Pedrazzani, R.; Ricciardi, P.; Carnevale Miino, M. Lockdown for CoViD–2019 in Milan: What are the effects on air quality? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; De Marco, A.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Paoletti, E.; Rodriguez, J.J.D.; Calatayud, V. Amplified ozone pollution in cities during the COVID–19 lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobías, A.; Carnerero, C.; Reche, C.; Massagué, J.; Via, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. Changes in air quality during the lockdown in Barcelona (Spain) one month into the SARS–CoV–2 epidemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Siour, G.; Mailler, S.; Pennel, R.; Cholakian, A. Impact of lockdown measures to combat Covid–19 on air quality over western Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaloulakou, A.; Mavroidis, I.; Gavriil, I. Compliance with the annual NO2 air quality standard in Athens. Required NOx levels and expected health implications. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratsea, M.; Liakakou, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Adamopoulos, A.; Tsilibari, E.; Gerasopoulos, E. The combined effect of reduced fossil fuel consumption and increasing biomass combustion on Athens’ air quality, as inferred from long term CO measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Cheristanidis, S.; Chaloulakou, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Mihalopoulos, N. Elemental composition and source apportionment of fine and coarse particles at traffic and urban background locations in Athens, Greece. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 1642–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Dumka, U.C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; et al. Long-term variability, source apportionment and spectral properties of black carbon at an urban background site in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 222, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demertzis, K.; Tsiotas, D.; Magafas, L. Modeling and forecasting the COVID–19 temporal spread in Greece: An exploratory approach based on complex network defined splines. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google. COVID–19 Community Mobility Report. Greece. Available online: https://www.gstatic.com/covid19/mobility/2020-05-25_GR_Mobility_Report_en-1.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Le Quéré, C.; Jackson, R.B.; Jones, M.W.; Smith, A.J.P.; Abernethy, S.; Andrew, R.M.; De-Gol, A.J.; Willis, D.R.; Shan, Y.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Temporary reduction in daily global CO2 emissions during the COVID–19 forced confinement. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiou, A.G.; Ziomas, I.C. Road traffic emissions impact on air quality of the Greater Athens Area based on a 20year emissions inventory. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. The new open Flexible Emission Inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area (FEI–GREGAA): Account of pollutant sources and their importance from 2006 to 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrekoussis, M.; Richter, A.; Hilboll, A.; Burrows, J.P.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Lelieveld, J.; Barrie, L.; Zerefos, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Economic crisis detected from space: Air quality observations over Athens/Greece. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosi, C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Lianou, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Multi-year chemical composition of the fine aerosol fraction in Athens, Greece, with emphasis on the contribution of residential heating in wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14371–14391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources and processes that control the submicron organic aerosol in an urban Mediterranean environment (Athens) using high temporal resolution chemical composition measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Bougiatioti, A.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Measuring the spatial variability of Black Carbon in Athens during wintertime. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 1405–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.; Flocas, H.A.; Lykoudis, S.; Petrakis, M. Analysis of mesoscale patterns in relation to synoptic conditions over an urban Mediterranean basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 1998, 59, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.; Kotroni, V.; Kallos, G. Analysis of climatological and air quality observations from Greater Athens Area. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourtziou, L.; Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Theodosi, C.; Zarbas, P.; Psiloglou, B.; Sciare, J.; Maggos, T.; Bairachtari, K.; Bougiatioti, A.; et al. Multi-tracer approach to characterize domestic wood burning in Athens (Greece) during wintertime. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panopoulou, A.; Liakakou, E.; Gros, V.; Sauvage, S.; Locoge, N.; Bonsang, B.; Psiloglou, B.E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Non Methane Hydrocarbons variability in Athens during wintertime: The role of traffic and heating. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16139–16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Brunner, D.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Changes in domestic heating fuel use in Greece: Effects on atmospheric chemistry and radiation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10597–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Michalopoulos, P.; Liakakou, E.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kalkavouras, P.; Fameli, K.M.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Field evaluation of low-cost PM sensors (Purple Air PA–II) under variable urban air quality conditions, in Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Weingartner, E.; Schmidhauser, R.; Gysel, M.; Baltensperger, U. A study of wood burning and traffic aerosols in an Alpine valley using a multi–wavelength Aethalometer. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinovec, L.; Mocnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rella, C.W.; Chen, H.; Andrews, A.E.; Filges, A.; Gerbig, C.; Hatakka, J.; Karion, A.; Miles, N.L.; Richardson, S.J.; Steinbacher, M.; et al. High accuracy measurements of dry mole fractions of carbon dioxide and methane in humid air. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 837–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.Y.; Laurent, O.; Guemri, A.; Philippon, C.; Wastine, B.; Rella, C.W.; Vuillemin, C.; Truong, F.; Delmotte, M.; Kazan, V.; et al. Comprehensive laboratory and field testing of cavity ring-down spectroscopy analyzers measuring H2O, CO2, CH4 and CO. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 89, 3867–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.; Physick, W.; Luhar, A. TAPM—A practical approach to prognostic meteorological and air pollution modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P. TAPM v. 4, Part 1: Technical Description; CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research Paper No. 25; CSIRO: Aspendale, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, P.J. An evaluation of several turbulence schemes for the prediction of mean and turbulent fields in complex terrain. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1997, 83, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.J.; Luhar, A.K. The Kwinana coastal fumigation study: III−meteorological and turbulence modelling on selected days. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2000, 94, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P. The Air Pollution Model (TAPM) Version 2. Part 1: Technical Description; CSIRO Atmospheric Research Technical Paper No. 55; CSIRO: Aspendale, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, P.; Manins, P.; Lee, S.; Boyle, R.; Ng, Y.L.; Dewundege, P. Year-long, high-resolution, urban airshed modelling: Verification of TAPM predictions of smog and particles in Melbourne, Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhar, A.K.; Hurley, P.J. Evaluation of TAPM, a prognostic meteorological and air pollution model, using urban and rural point-source data. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2795–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, M.; Walker, S.-E.; Solberg, S.; Ramacher, M.O.P. The Eulerian urban dispersion model EPISODE—Part 2: Extensions to the source dispersion and photochemistry for EPISODE–CityChem v1.2 and its application to the city of Hamburg. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 12, 3357–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ramacher, M.O.P.; Moldanová, J.; Matthias, V.; Karl, M.; Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Yaramenka, K.; Aulinger, A.; Gustafsson, M. The impact of ship emissions on air quality and human health in the Gothenburg area—Part 1: 2012 emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 20, 7509–7530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Ramacher, M.; Kakouri, A.; Speyer, O.; Karl, M.; Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Bailey, J. City scale air pollution modelling and high resolution exposure mapping of an urban hotspot in the Eastern Mediterranean. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2020, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 December 2019. A13Q-3154. [Google Scholar]
- Ramacher, M.O.P.; Karl, M. Integrating modes of transport in a dynamic modelling approach to evaluate population exposure to ambient NO2 and PM2.5 pollution in urban areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerimray, A.; Baimatova, N.; Ibragimova, O.P.; Bukenov, B.; Kenessov, B.; Plotitsyn, P.; Karaca, F. Assessing air quality changes in large cities during COVID–19 lockdowns: The impacts of traffic-free urban conditions in Almaty, Kazakhstan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaloulakou, A.; Kassomenos, P.; Grivas, G.; Spyrellis, N. Particulate matter and black smoke concentration levels in central Athens, Greece. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elminir, H.K. Dependence of urban air pollutants on meteorology. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chate, D.M.; Pranesha, T.S. Field studies of scavenging of aerosols by rain events. J. Aerosol Sci. 2004, 35, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founda, D.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Pierros, F.; Kalimeris, A.; Petrakis, M. Observed and projected precipitation variability in Athens over a 2.5 century period. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2013, 14, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Papakosta, D.; Karakatsani, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Chaloulakou, A. Ozone exposure assessment for children in Greece: Results from the RESPOZE study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581–582, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, G.; Chaloulakou, A.; Samara, C.; Spyrellis, N. Spatial and temporal variation of PM10 mass concentrations within the greater area of Athens, Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrys, J.; Eeftens, M.; Heinrich, J.; Ampe, C.; Armengaud, A.; Beelen, R.; Bellander, T.; Beregszaszi, T.; Birk, M.; Cesaroni, G.; et al. Variation of NO2 and NOx concentrations between and within 36 European study areas: Results from the ESCAPE study. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Effect of lockdown amid COVID–19 pandemic on air quality of the megacity Delhi, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, G.; Siciliano, B.; França, B.B.; da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. The impact of COVID–19 partial lockdown on the air quality of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, L.Y.K.; Urban, R.C. COVID–19 pandemic: Impacts on the air quality during the partial lockdown in São Paulo state, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarian, S.; Unnthorsson, R.; Richter, C. Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 on CO2 emission in the world. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioli, B.; Toscano, P.; Lugato, E.; Matese, A.; Miglietta, F.; Zaldei, A.; Vaccari, F.P. Methane and carbon dioxide fluxes and source partitioning in urban areas: The case study of Florence, Italy. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 164, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagakis, S.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Spyridakis, N.; Feigenwinter, C.; Vogt, R. Eddy Covariance measurements and source partitioning of CO2 emissions in an urban environment: Application for Heraklion, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 201, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueref–Remy, I.; Dieudonné, E.; Vuillemin, C.; Lopez, M.; Lac, C.; Schmidt, M.; Delmotte, M.; Chevallier, F.; Ravetta, F.; Perrussel, O.; et al. Diurnal, synoptic and seasonal variability of atmospheric CO2 in the Paris megacity area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3335–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources of atmospheric aerosol from long-term measurements (5 years) of chemical composition in Athens, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriou, K.; Grivas, G.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Assessing the contribution of regional sources to urban 1 air pollution by applying 3D–PSCF modeling. Atmos. Res. 2021, 248, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Amiridis, V.; Kazadzis, S.; Kokkalis, P.; Eleftheratos, K.; Andreae, M.O.; Andreae, T.W.; El-Askary, H.; Zerefos, C.S. Three-year ground based measurements of aerosol optical depth over the Eastern Mediterranean: The urban environment of Athens. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Urrego, D.; Rodríguez-Urrego, L. Air quality during the COVID–19: PM2.5 analysis in the 50 most polluted capital cities in the world. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.D. Air pollution in Ontario, Canada during the COVID–19 State of Emergency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Zhang, A. Does lockdown reduce air pollution? Evidence from 44 cities in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Tombrou, M.; Russell, A.G.; Karanasiou, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Dandou, A. Implementation of road and soil dust emission parameterizations in the aerosol model CAMx: Applications over the greater Athens urban area affected by natural sources. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouli, M.-E.; Skoulidou, I.; Karavias, A.; Parcharidis, I.; Balis, D.; Manders, A.; Segers, A.; Eskes, H.; van Geffen, J. Sudden changes in nitrogen dioxide emissions over Greece due to lockdown after the outbreak of COVID–19. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, I.; Chaloulakou, A. Long-term trends of primary and secondary NO2 production in the Athens area. Variation of the NO2/NOx ratio. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6872–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, B.; Dantas, G.; da Silva, C.M.; Arbilla, G. Increased ozone levels during the COVID–19 lockdown: Analysis for the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Short-term exposure to ambient air quality of the most polluted Indian cities due to lockdown amid SARS–CoV–2. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Ji, D.; Maenhaut, W.; Gao, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Levels and sources of hourly PM2.5-related elements during the control period of the COVID–19 pandemic at a rural site between Beijing and Tianjin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEA. Healthy Environment, Healthy Lives: How the Environment Influences Health and Well-Being in Europe; European Environmental Agency EEA Report No 21\2019; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/healthy-environment-healthy-lives (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Jenkin, M.E.; Clemitshaw, K.C. Ozone and other secondary photochemical pollutants: Chemical processes governing their formation in the planetary boundary layer. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 34, 2499–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzianastassiou, N.; Katsoulis, B.D.; Antakis, B. Extreme nitrogen oxide and ozone concentrations in Athens atmosphere in relation to meteorological conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 127, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remoundaki, E.; Kassomenos, P.; Mantas, E.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Tsezos, M. Composition and mass closure of PM2.5 in urban environment (Athens, Greece). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 13, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangari, S.; Hill, D.T.; Charette, A.T.; Mirowsky, J.E. Air quality changes in New York City during the COVID–19 pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCESD. Greece: State of the Environment Report; National Center for the Environment and Sustainable Development (NCESD): Athens, Greece, 2020; pp. 33–34. Available online: https://ekpaa.ypeka.gr/ektheseis/soer-2018 (accessed on 23 September 2020).
- Zambrano-Monserrate, M.A.; Ruano, M.A. Has air quality improved in Ecuador during the COVID–19 pandemic? A parametric analysis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Kong, S.; Chen, N.; Yan, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, B.; Xu, K.; Cao, W.; Ding, Q.; Lan, B.; et al. Significant changes in the chemical compositions and sources of PM2.5 in Wuhan since the city lockdown as COVID–19. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Fu, X.; Bartelli, D.; Smith, L. Insignificant impact of the “stay-at-home” order on ambient air quality in the Memphis Metropolitan Area, U.S.A. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grivas, G.; Athanasopoulou, E.; Kakouri, A.; Bailey, J.; Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kalkavouras, P.; Bougiatioti, A.; Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Ramonet, M.; et al. Integrating in situ Measurements and City Scale Modelling to Assess the COVID–19 Lockdown Effects on Emissions and Air Quality in Athens, Greece. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111174
Grivas G, Athanasopoulou E, Kakouri A, Bailey J, Liakakou E, Stavroulas I, Kalkavouras P, Bougiatioti A, Kaskaoutis DG, Ramonet M, et al. Integrating in situ Measurements and City Scale Modelling to Assess the COVID–19 Lockdown Effects on Emissions and Air Quality in Athens, Greece. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(11):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111174
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrivas, Georgios, Eleni Athanasopoulou, Anastasia Kakouri, Jennifer Bailey, Eleni Liakakou, Iasonas Stavroulas, Panayiotis Kalkavouras, Aikaterini Bougiatioti, Dimitris G. Kaskaoutis, Michel Ramonet, and et al. 2020. "Integrating in situ Measurements and City Scale Modelling to Assess the COVID–19 Lockdown Effects on Emissions and Air Quality in Athens, Greece" Atmosphere 11, no. 11: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111174
APA StyleGrivas, G., Athanasopoulou, E., Kakouri, A., Bailey, J., Liakakou, E., Stavroulas, I., Kalkavouras, P., Bougiatioti, A., Kaskaoutis, D. G., Ramonet, M., Mihalopoulos, N., & Gerasopoulos, E. (2020). Integrating in situ Measurements and City Scale Modelling to Assess the COVID–19 Lockdown Effects on Emissions and Air Quality in Athens, Greece. Atmosphere, 11(11), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11111174