The Impacts of Aerosol Emissions on Historical Climate in UKESM1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Model
2.2. Experiments
2.3. ERF
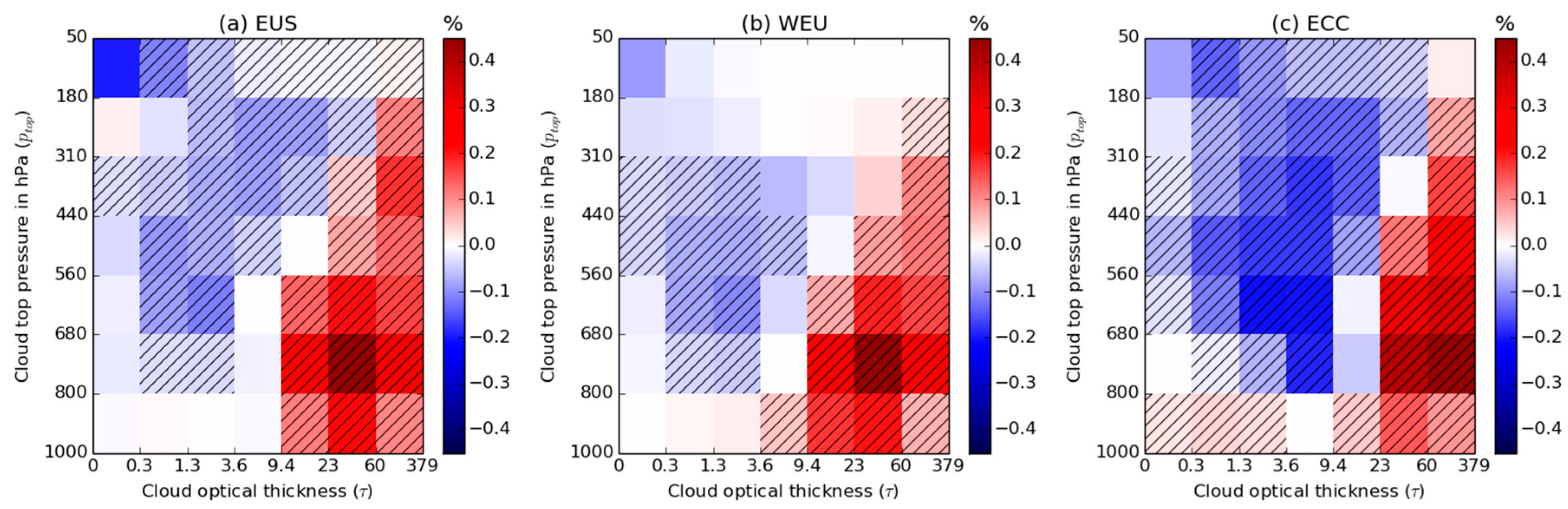
3. Results
3.1. Aerosol Optical Depth
3.2. ERFs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R.; Lacis, A.; Oinas, V. Global warming in the twenty-first century: An alternative scenario. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9875–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, V.; Crutzen, P.J.; Kiehl, J.T.; Rosenfeld, D. Aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 2001, 294, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, J.L.; Quaas, J.; Boucher, O.; Denvil, S.; Fairhead, L. Contrast in the effects on climate of anthropogenic sulfate aerosols between the 20th and the 21st century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 659–740. [Google Scholar]
- Feichter, J.; Roeckner, E.; Lohmann, U.; Liepert, B. Nonlinear aspects of the climate response to greenhouse gas and aerosol forcing. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2384–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Gong, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Lu, P.; Wei, X.; Che, H.; et al. Simulation of direct radiative forcing of aerosols and their effects on East Asian climate using an interactive AGCM-aerosol coupled system. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 38, 1675–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Kim, J.; Yum, S.S.; Lee, H.; Boo, K.-O.; Byun, Y.-H. Effects of anthropogenic and natural forcings on the summer temperature variations in east Asia during the 20th century. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J.; Penner, J.; Leaitch, R. Indirect effect of sulfate and carbonaceous aerosols: A mechanistic treatment. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 12193–12206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Roberts, D.L.; Woodage, M.J.; Johnson, C.E. Indirect sulphate aerosol forcing in a climate model with an interactive sulphur cycle. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 20293–20310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denman, K.L.; Brasseur, G. Couplings between Changes in the Climate System and Biogeochemistry. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis; Solomon, S., Qin, D., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tigor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 129–234. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.; Johns, T.; Gregory, J.; Tett, S. Climate response to increasing levels of greenhouse gases and sulfate aerosols. Nature 1995, 376, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Luo, Y. Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 2002, 297, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, P. Improvement of cloud microphysics in the aerosol-climate model BCC_AGCM2.0.1_CUACE/Aero, evaluation against observations, and updated aerosol indirect effect. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8400–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, O.; Randall, D.; Artaxo, P.; Bretherton, C.; Feingold, G.; Forster, P.; Kerminen, V.M.; Kondo, Y.; Liao, H.; Lohmann, U.; et al. Contribution of Working Group to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Clouds and Aerosols. In Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Doschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 616–617. [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman, N.H.A.; Frame, D.J.; Huntingford, C.; Lowe, J.A.; Smith, S.M.; Allen, M.R. The role of short-lived climate pollutants in meeting temperature goals. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Bond, T.C. Two hundred fifty years of aerosols and climate: The end of the age of aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Ruedy, R.; Sato, M.; Imhoff, M.; Lawrence, W.; Easterling, D.; Peterson, T.; Karl, T. A closer look at United States and global surface temperature change. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2001, 106, 23947–23963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipona, R.; Behrens, K.; Ruckstuhl, C. How declining aerosols and rising greenhouse gases forced rapid warming in Europe since 1980s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L02806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, J.; Boucher, O. Constraining the first aerosol indirect radiative forcing in the LMDZ GCM using POLDER and MODIS satelliete data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Qian, Y. Direct radiative forcing and regional climatic effects of anthropogenic aerosols over East Asia: A regional coupled climate-chemistry/aerosol model study. J. Geophy. Res. 2002, 107, D204439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Levy, R.C.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Mattoo, S.; Martins, J.V.; Ichobk, C.; Koren, I.; Yu, H.; et al. Global aerosol climatology from the MODIS satellite sensors. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D14S07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Radiative forcing and climate response. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 6831–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, K.P. The effects of human activity on radiative forcing of climate change: A review of recent developments. Glob. Planet Chang. 1999, 20, 205–225. [Google Scholar]
- Myhre, G.; Samset, B.H.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.; Berntsen, T.K.; Bian, H.; Bellouin, N.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; et al. Radiative forcing of the direct aerosol effect from AeroCom Phase II simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1853–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, S.C.; Bony, S.; Boucher, O.; Bretherton, C.; Forster, P.M.; Gregory, J.M.; Stevens, B. Adjustments in the forcing–feedback framework for understanding climate change. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 217–228. [Google Scholar]
- Forster, P.M.; Richardson, T.; Maycock, A.C.; Smith, C.J.; Samset, B.H.; Myhre, G.; Andrews, T.; Pincus, R.; Schulz, M. Recommendations for diagnosing effective radiative forcing from climate models for CMIP6. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12–460. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, W.; Lamarque, J.-F.; Schulz, M.; Boucher, O.; Eyring, V.; Hegglin, M.I.; Maycock, A.C.; Myhre, G.; Prather, M.J.; Shindell, D.; et al. AerChemMIP: Quantifying the effects of chemistry and aerosols in CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 585–607. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, D.; Baran, A.J.; Boutle, I.A.; Brooks, M.; Earnshaw, P.; Edwards, J.; Furtado, K.; Hill, P.; Lock, A.; Manners, J.; et al. The Met Office Unified Model Global Atmosphere 7.0/7.1 and JULES Global Land 7.0 configurations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 1909–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt, H.T.; Copsey, D.; Culverwell, I.D.; Harris, C.M.; Hill, R.S.R.; Keen, A.B.; McLaren, A.J.; Hunke, E.C. Design and implementation of the infrastructure of HadGEM3: The next-generation Met Office climate modelling system. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 223–253. [Google Scholar]
- Archibald, A.T.; O’Connor, F.M.; Abraham, N.L.; Archer-Nicholls, S.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Dalvi, M.; Folberth, G.A.; Dennison, F.; Dhomse, S.S.; Griffiths, P.T.; et al. Description and evaluation of the UKCA stratosphere-troposphere chemistry scheme (StratTrop vn 1.0) implemented in UKESM1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 13, 1223–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern, O.; Braesicke, P.; O’Connor, F.M.; Bushell, A.C.; Johnson, C.E.; Osprey, S.M.; Pyle, J.A. Evaluation of the new UKCA climate-composition model—Part 1: The stratosphere. Geosci. Model Dev. 2009, 2, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, F.M.; Johnson, C.E.; Morgenstern, O.; Abraham, N.L.; Braesicke, P.; Dalvi, M.; Folberth, G.A.; Sanderson, M.G.; Telford, P.J.; Voulgarakis, A.; et al. Evaluation of the new UKCA climate composition model. Part II. The troposphere. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 41–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, G.W.; Carslaw, K.S.; Spracklen, D.V.; Ridley, D.A.; Manktelow, P.T.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Pickering, S.J.; Johnson, C.E. Description and evaluation of GLOMAP-mode: A modal global aerosol microphysics model for the UKCA composition-climate model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2010, 3, 519–551. [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy, J.P.; Johnson, C.; Jones, C.; Povey, A.; Sellar, A.; Scott, C.E.; Turnock, S.T.; Woodhouse, M.T.; Abraham, L.N.; Andrews, M.; et al. Description and evaluation of aerosol in UKESM1 and HadGEM3-GC3.1 CMIP6 historical simulations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellar, A.; Jones, C.G.; Mulcahy, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Yool, A.; Wiltshire, A.; O’Connor, F.M.; Stringer, M.; Hill, R.; Palmieri, J.; et al. UKESM1: Description and Evaluation of the U.K. Earth System Model. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst. 2019, 11, 4513–4558. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.J.; Kramer, R.J.; Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Collins, W.; Sima, A.; Boucher, O.; Dufresne, J.-L.; Nabat, P.; Michou, M.; et al. Effective radiative forcing and adjustments in CMIP6 models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 9591–9618. [Google Scholar]
- Thornhill, G.D.; Collins, W.J.; Kramer, R.J.; Olivié, D.; O’Connor, F.; Abraham, N.L.; Bauer, S.E.; Deushi, M.; Emmons, L.; Forster, P.; et al. Effective Radiative forcing from emissions of reactive gases and aerosols—A multimodel comparison. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesly, R.M.; Smith, S.J.; Feng, L.; Klimont, Z.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Pitkanen, T.; Seibert, J.J.; Vu, L.; Andres, R.J.; Bolt, R.M.; et al. Historical (1750–2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emission Data System (CEDS). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 11, 369–408. [Google Scholar]
- Van Marle, M.J.E.; Kloster, S.; Magi, B.; Marlon, J.R.; Daniau, A.-L.; Field, R.D.; Arneth, A.; Forrest, M.; Hantson, S.; Kehrwald, N.M.; et al. Historic global biomass burning emissions for CMIP6 (BB4CMIP) based on merging satellite observations with proxies and fire models (1750–2015). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 3329–3357. [Google Scholar]
- Meinshausen, M.; Vogel, E.; Nauels, A.; Lorbacher, K.; Meinshausen, N.; Etheridge, D.M.; Fraser, P.J.; Montzka, S.A.; Rayner, P.; Trudinger, C.M.; et al. Historical greenhouse gas concentrations for climate modelling (CMIP6). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2057–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghan, S.J. Technical note: Estimating aerosol effects on cloud radiative forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9971–9974. [Google Scholar]
- Zelinka, M.D.; Andrews, T.; Forster, P.M.; Taylor, K.E. Quantifying components of aerosol-cloud-radiation interactions in climate models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7599–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, F.M.; Abraham, N.L.; Dalvi, M.; Folberth, G.A.; Griffiths, P.T.; Hardacre, C.; Johnson, B.T.; Kahana, R.; Keeble, J.; Kim, B.; et al. Assessment of pre-industrial to present-day anthropogenic climate forcing in UKESM1. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, B.; Zhou, T. Climate Effects of the Deep Continental Stratus Clouds Generated by the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2702–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philander, S.G.H.; Gu, D.; Lambert, G.; Li, T.; Halpern, D.; Lau, N.-C.; Pacanowski, R.C. Why the ITCZ Is Mostly North of the Equator. J. Clim. 1996, 9, 2958–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Y.; Mechoso, C.R. Links between Annual Variations of Peruvian Stratocumulus Clouds and of SST in the Eastern Equatorial Pacific. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 3305–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Su, H. Atmospheric responses to the redistribution of anthropogenic aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9625–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
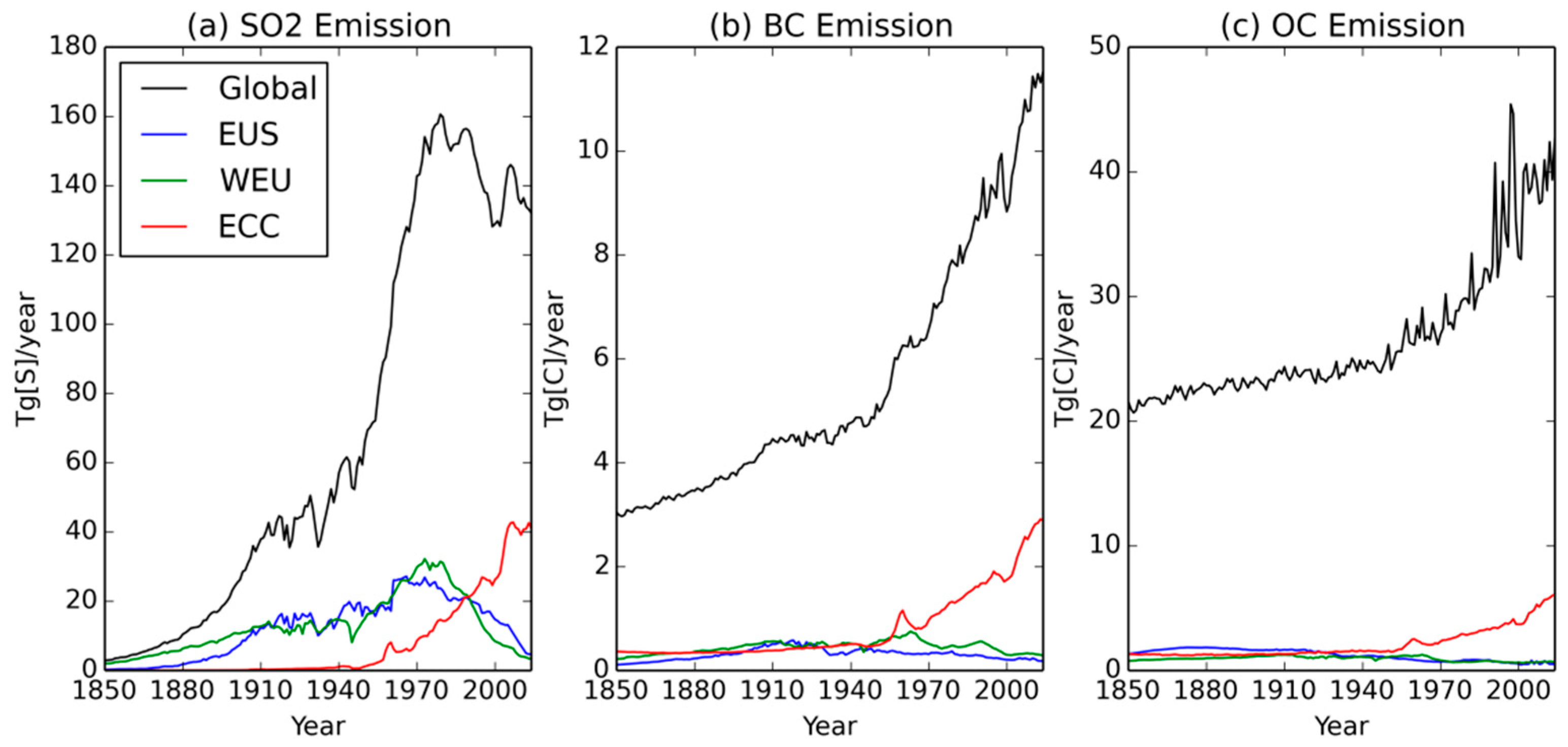
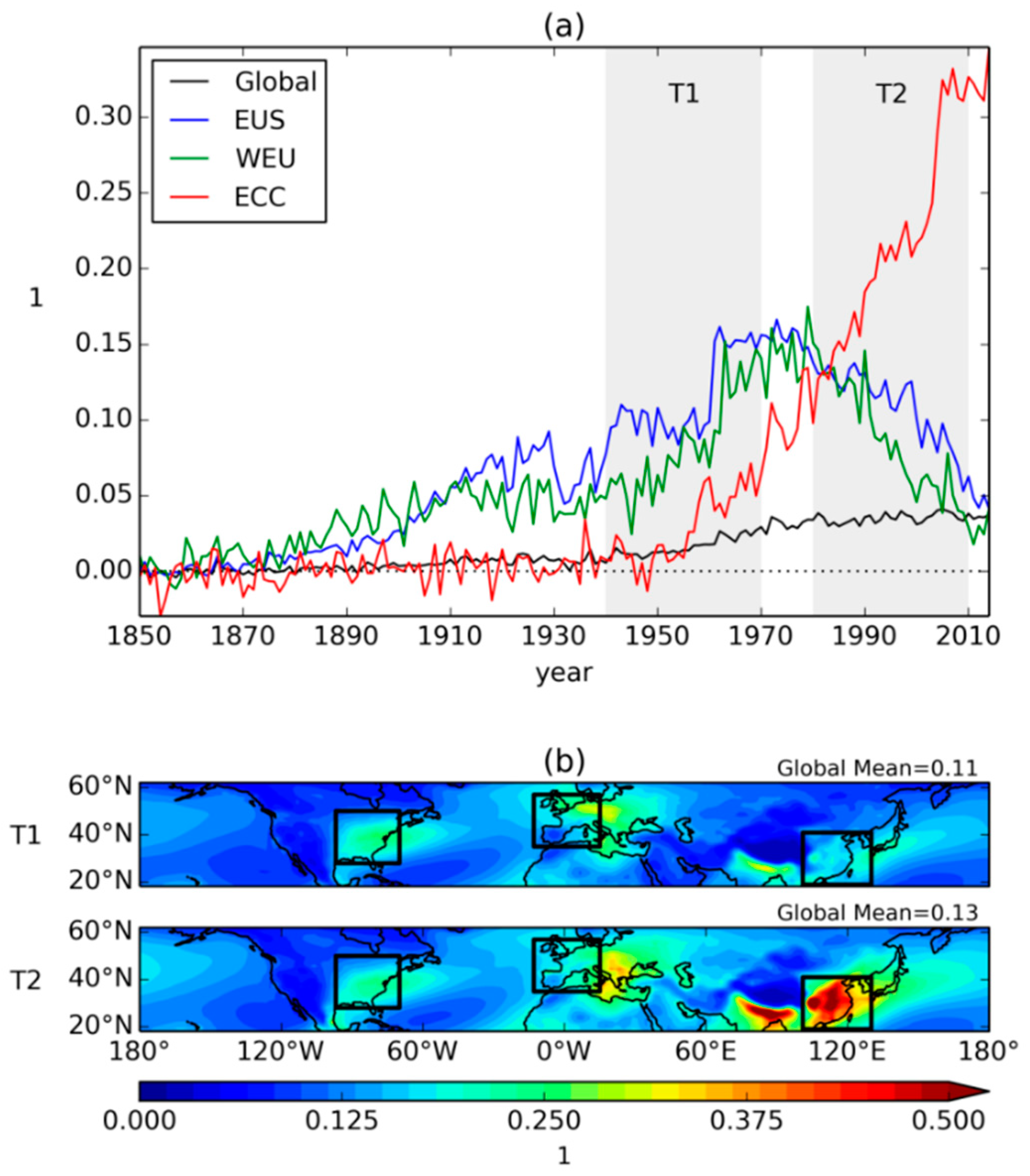


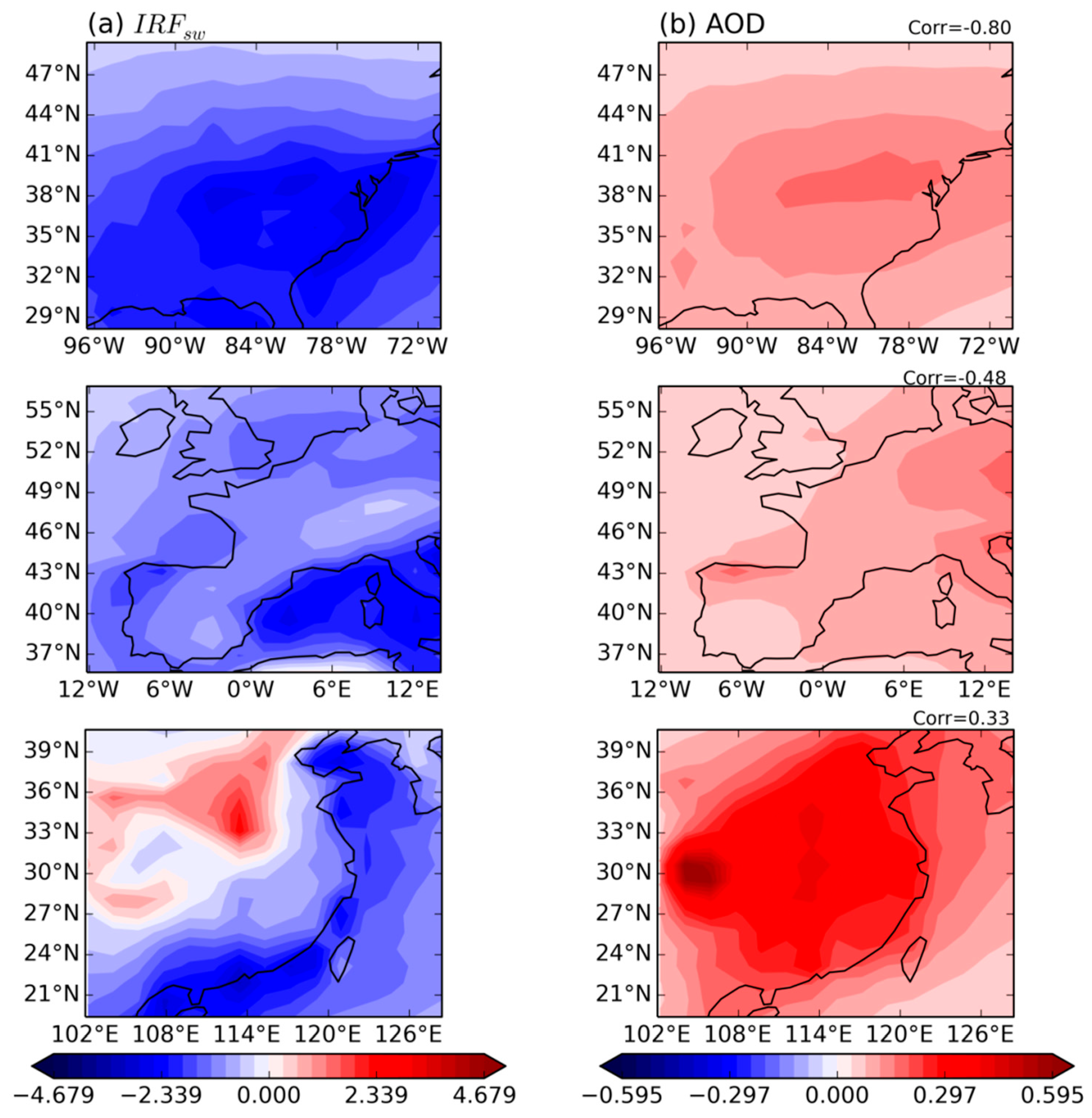
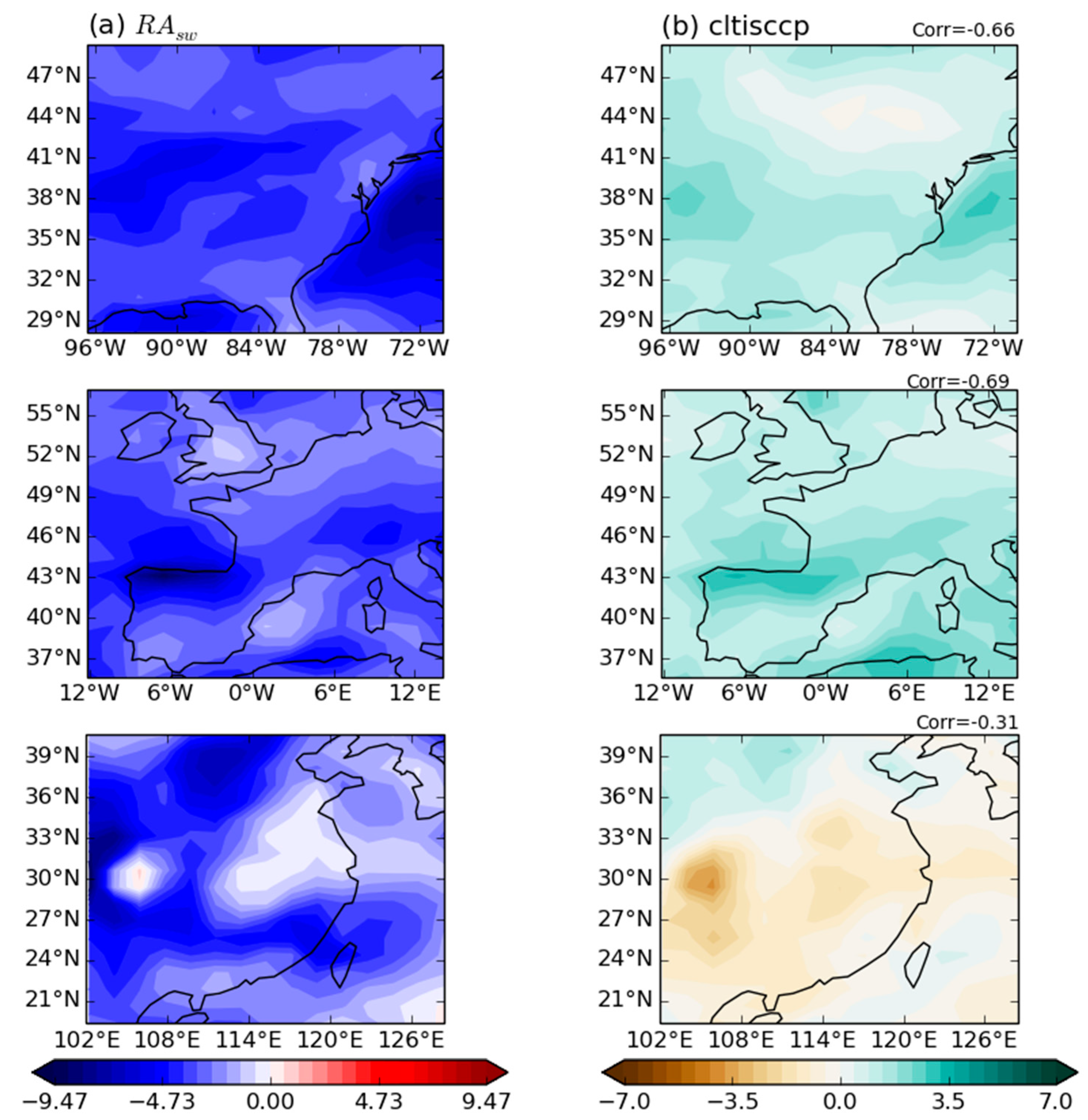
| Experiment ID | MIP | N2O | CH4 | Aerosol Precursors | Trop. O3 Precursors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| histSST | AerChemMIP | Hist | Hist | Hist | Hist |
| histSST-piAer | AerChemMIP | Hist | Hist | 1850 | Hist |
| piClim-control | CMIP6 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 |
| piClim-Aer | AerChemMIP | 1850 | 1850 | 2014 | 1850 |
| piClim-SO2 | AerChemMIP | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 (non-SO2) 2014 (SO2) | 1850 |
| piClim-BC | AerChemMIP | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 (non-BC) 2014 (BC) | 1850 |
| piClim-OC | AerChemMIP | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 (non-OC) 2014 (OC) | 1850 |
| sstClim | CMIP5 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 |
| sstClimAerosol | CMIP5 | 1850 | 1850 | 2000 | 1850 |
| RF Relative to PI | Glob | EUS | WEU | ECC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | ERF | −1.03 ± 0.05 | −5.04 ± 0.27 | −2.89 ± 0.37 | −2.34 ± 0.34 | |
| IRF | −0.16 ± 0.01 | −1.44 ± 0.09 | −0.92 ± 0.08 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | ||
| RA | 0.00 ± 0.02 | −0.46 ± 0.19 | 0.37 ± 0.15 | 0.08 ± 0.22 | ||
| −0.87 ± 0.04 | −3.14 ± 0.27 | −2.34 ± 0.40 | −2.52 ± 0.41 | |||
| T2 | ERF | −1.43 ± 0.05 | −4.57 ± 0.32 | −3.23 ± 0.38 | −3.87 ± 0.32 | |
| IRF | −0.30 ± 0.01 | −1.63 ± 0.06 | −1.23 ± 0.09 | −0.74 ± 0.08 | ||
| RA | 0.04 ± 0.03 | −0.00 ± 0.23 | 0.45 ± 0.17 | 0.12 ± 0.18 | ||
| −1.17 ± 0.03 | −2.94 ± 0.30 | −2.45 ± 0.40 | −3.24 ± 0.32 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, J.; Shim, S.; Kwon, S.-H.; Boo, K.-O.; Kim, Y.-H.; O’Connor, F.; Johnson, B.; Dalvi, M.; Folberth, G.; Teixeira, J.; et al. The Impacts of Aerosol Emissions on Historical Climate in UKESM1. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101095
Seo J, Shim S, Kwon S-H, Boo K-O, Kim Y-H, O’Connor F, Johnson B, Dalvi M, Folberth G, Teixeira J, et al. The Impacts of Aerosol Emissions on Historical Climate in UKESM1. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101095
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Jeongbyn, Sungbo Shim, Sang-Hoon Kwon, Kyung-On Boo, Yeon-Hee Kim, Fiona O’Connor, Ben Johnson, Mohit Dalvi, Gerd Folberth, Joao Teixeira, and et al. 2020. "The Impacts of Aerosol Emissions on Historical Climate in UKESM1" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101095
APA StyleSeo, J., Shim, S., Kwon, S.-H., Boo, K.-O., Kim, Y.-H., O’Connor, F., Johnson, B., Dalvi, M., Folberth, G., Teixeira, J., Mulcahy, J., Hardacre, C., Turnock, S., Woodward, S., Abraham, L., Keeble, J., Griffiths, P., Archibald, A., Richardson, M., ... Morgenstern, O. (2020). The Impacts of Aerosol Emissions on Historical Climate in UKESM1. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1095. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101095







