Differences in the Evolution of Pyrocumulonimbus and Volcanic Stratospheric Plumes as Observed by CATS and CALIOP Space-Based Lidars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
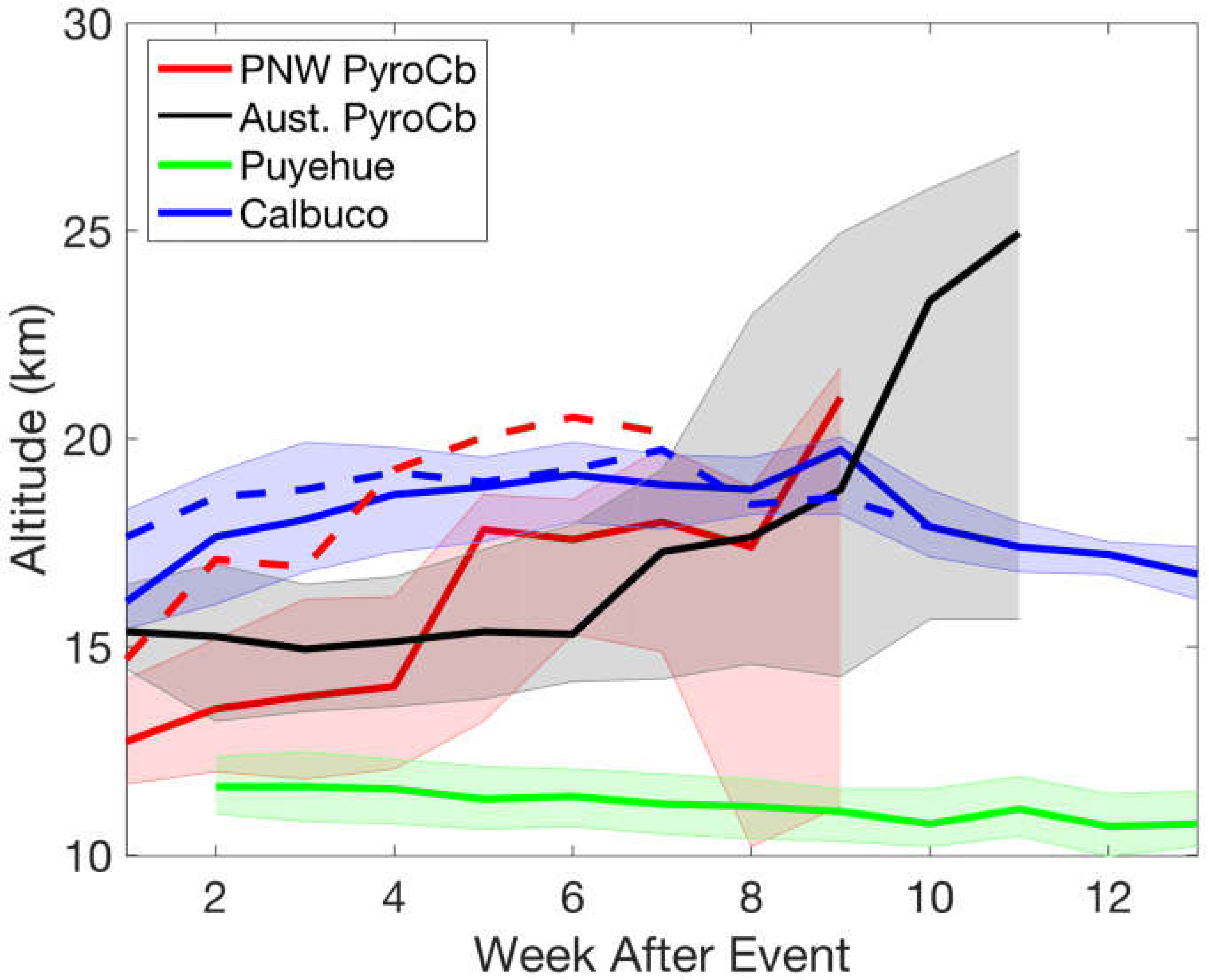
3.1. Plume Altitude Evolution
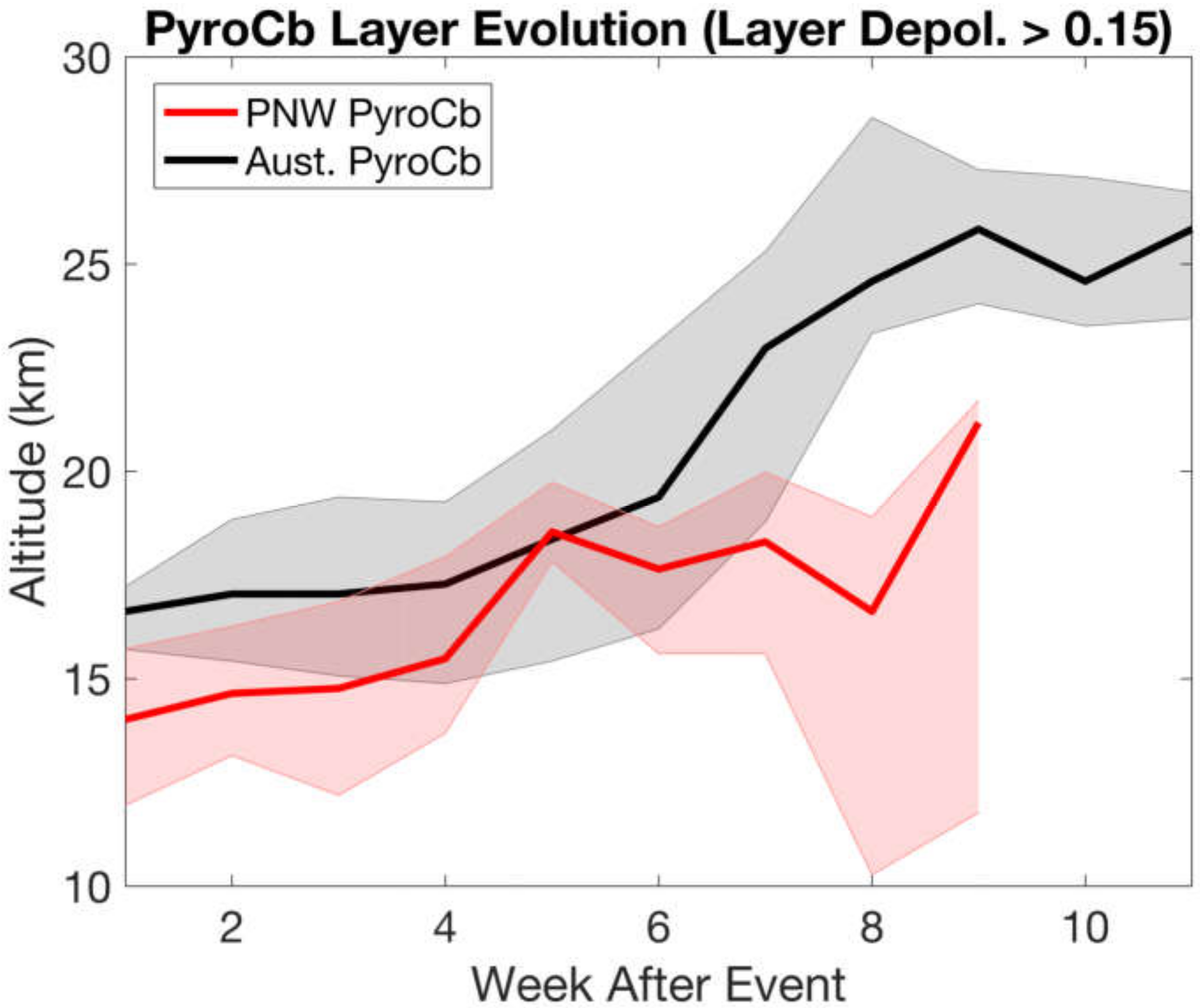
3.1.1. Pyrocb Events
3.1.2. Volcanic Events
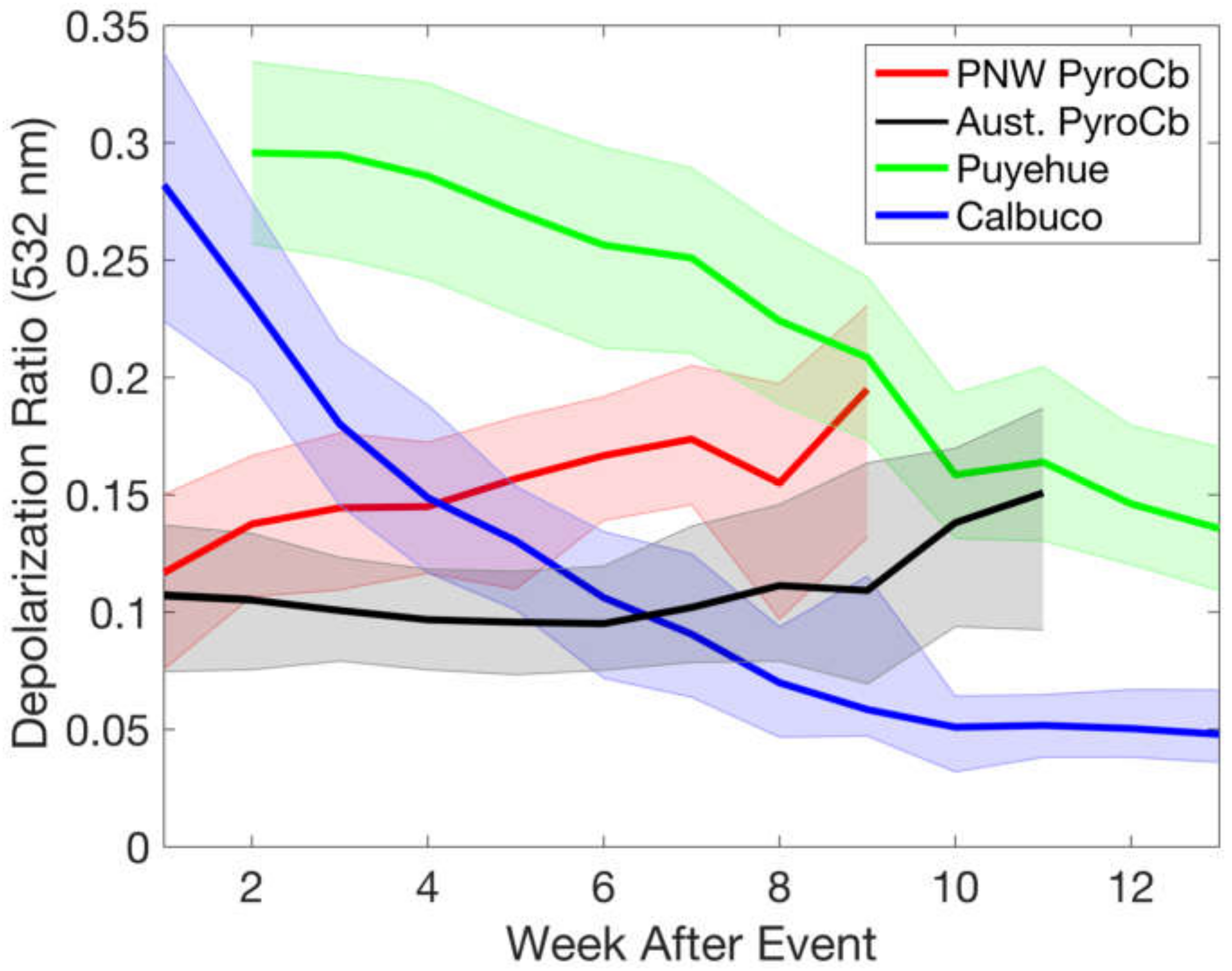
3.2. Aerosol Optical Evolution
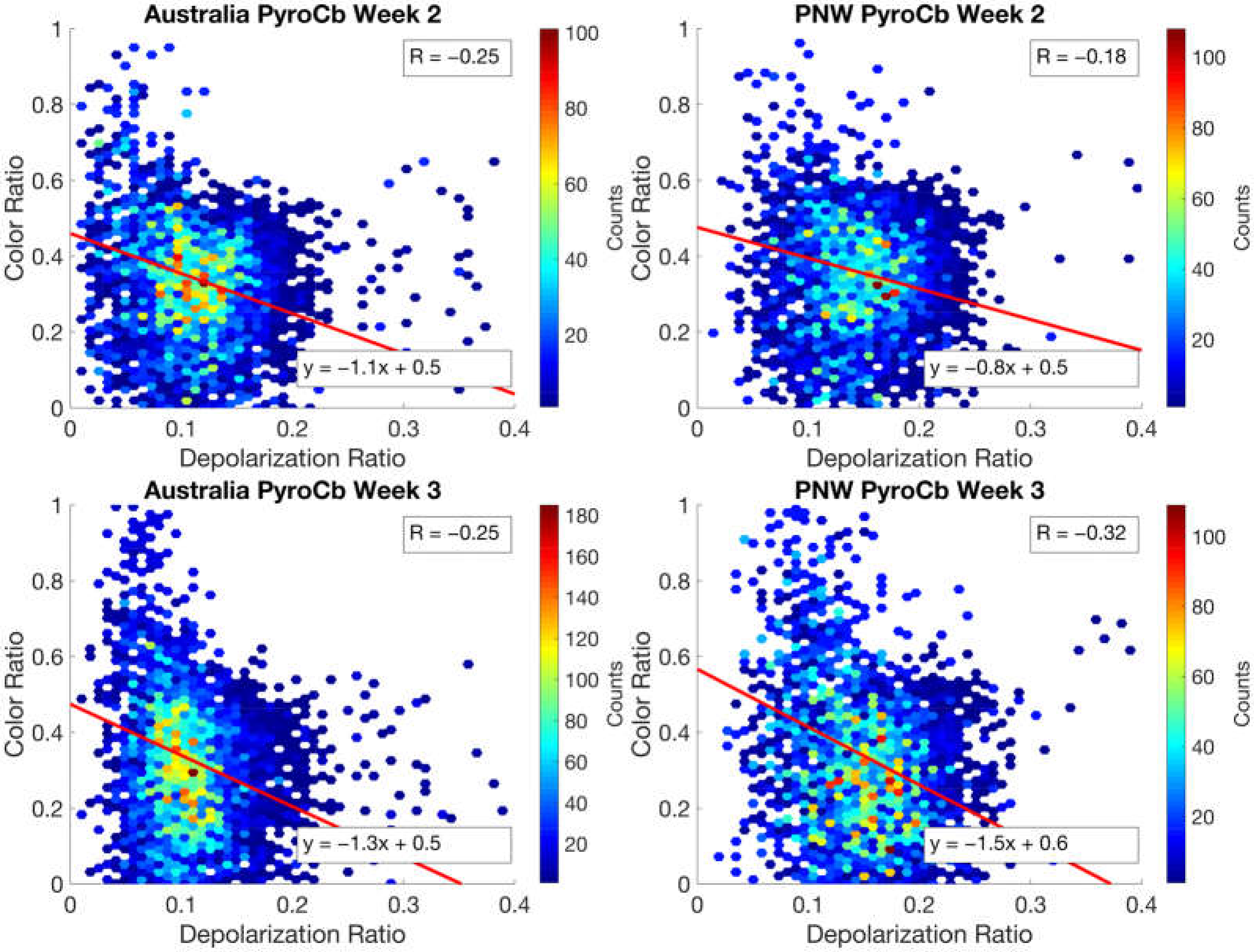
3.2.1. Pyrocb Events
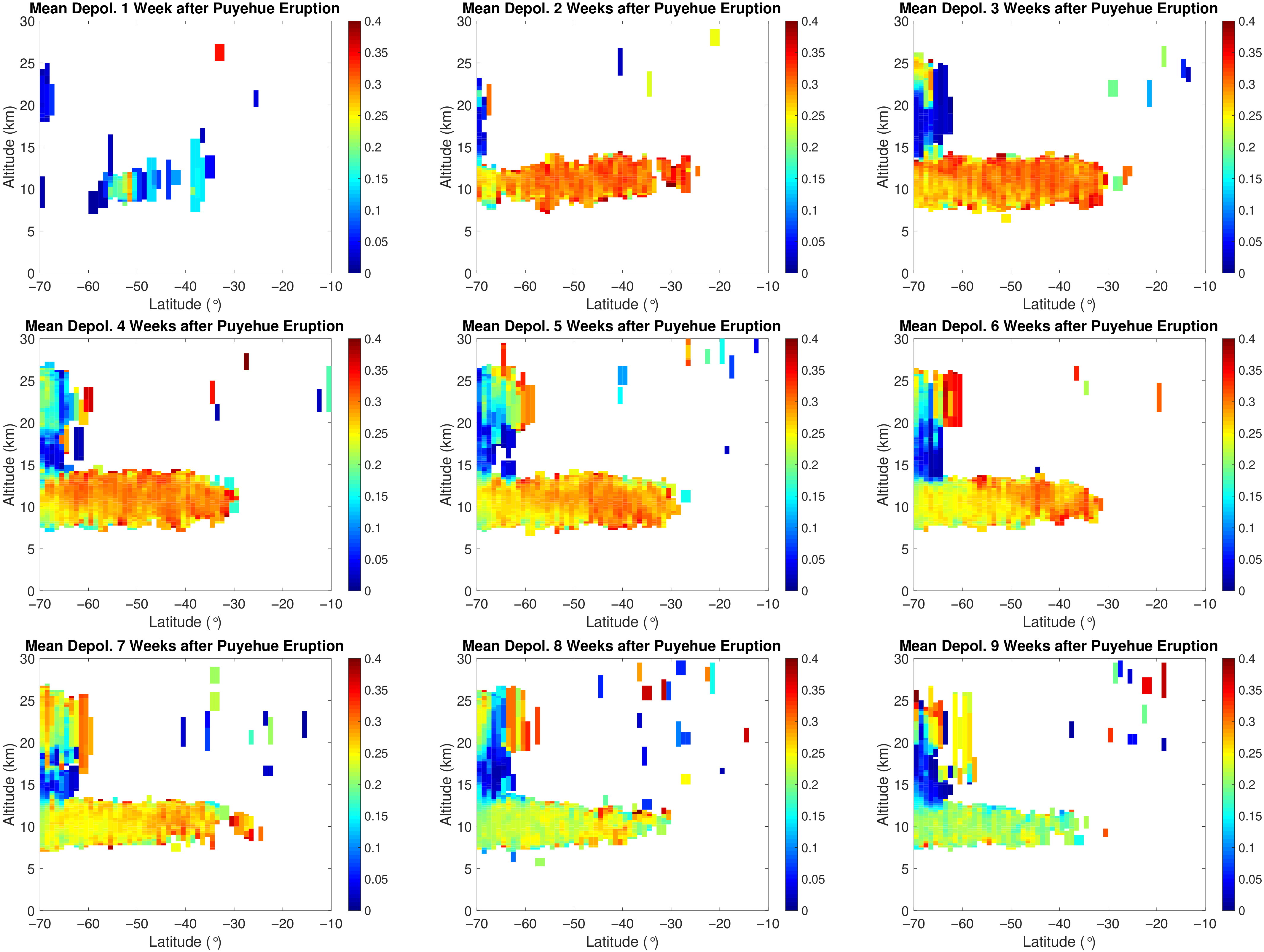
3.2.2. Volcanic Events
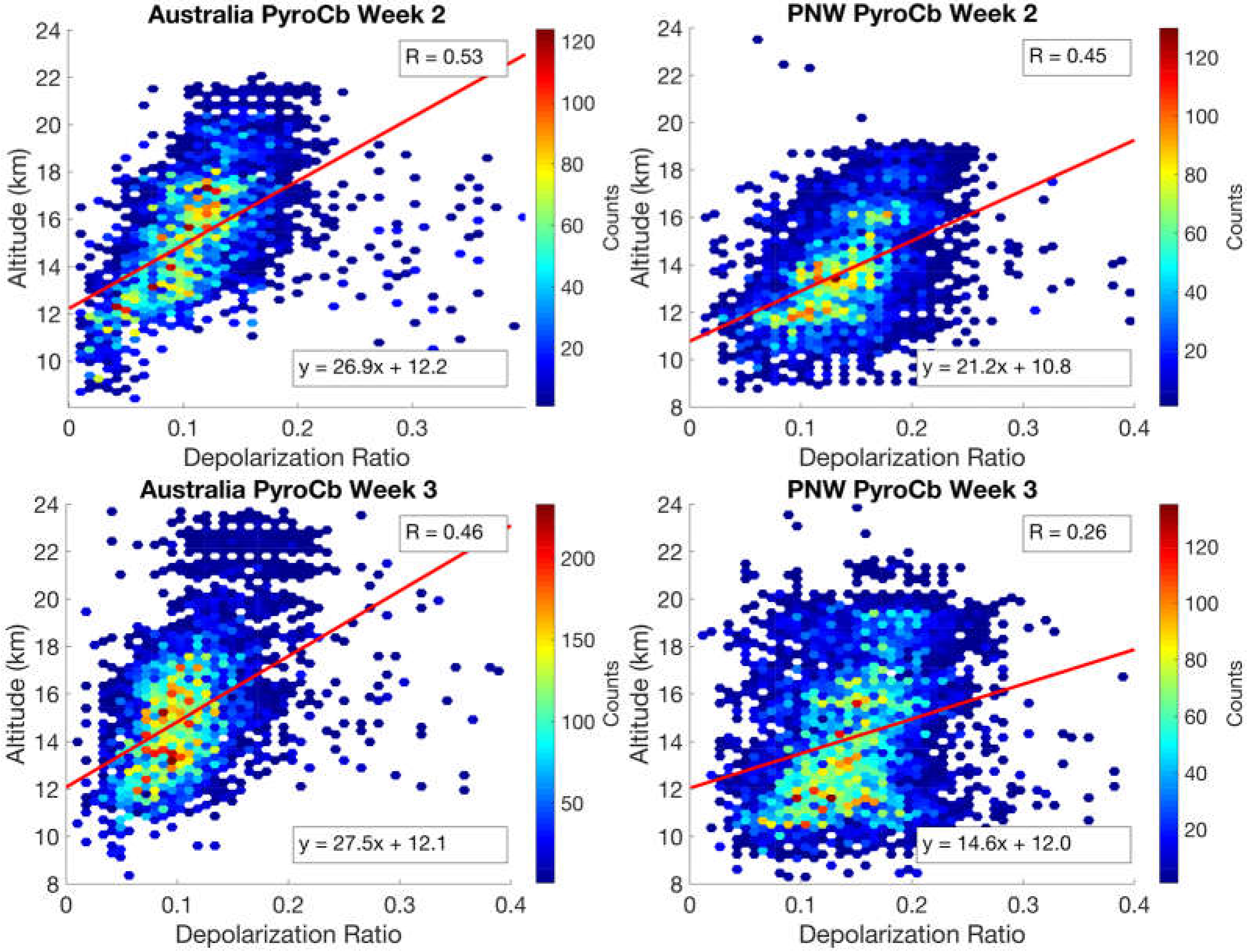
4. Discussion
Explaining the Depolarization Patterns in the Pyrocb Plumes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. GEOS Model and Sensitivity to Including Dust within Smoke on Depolarization Ratios
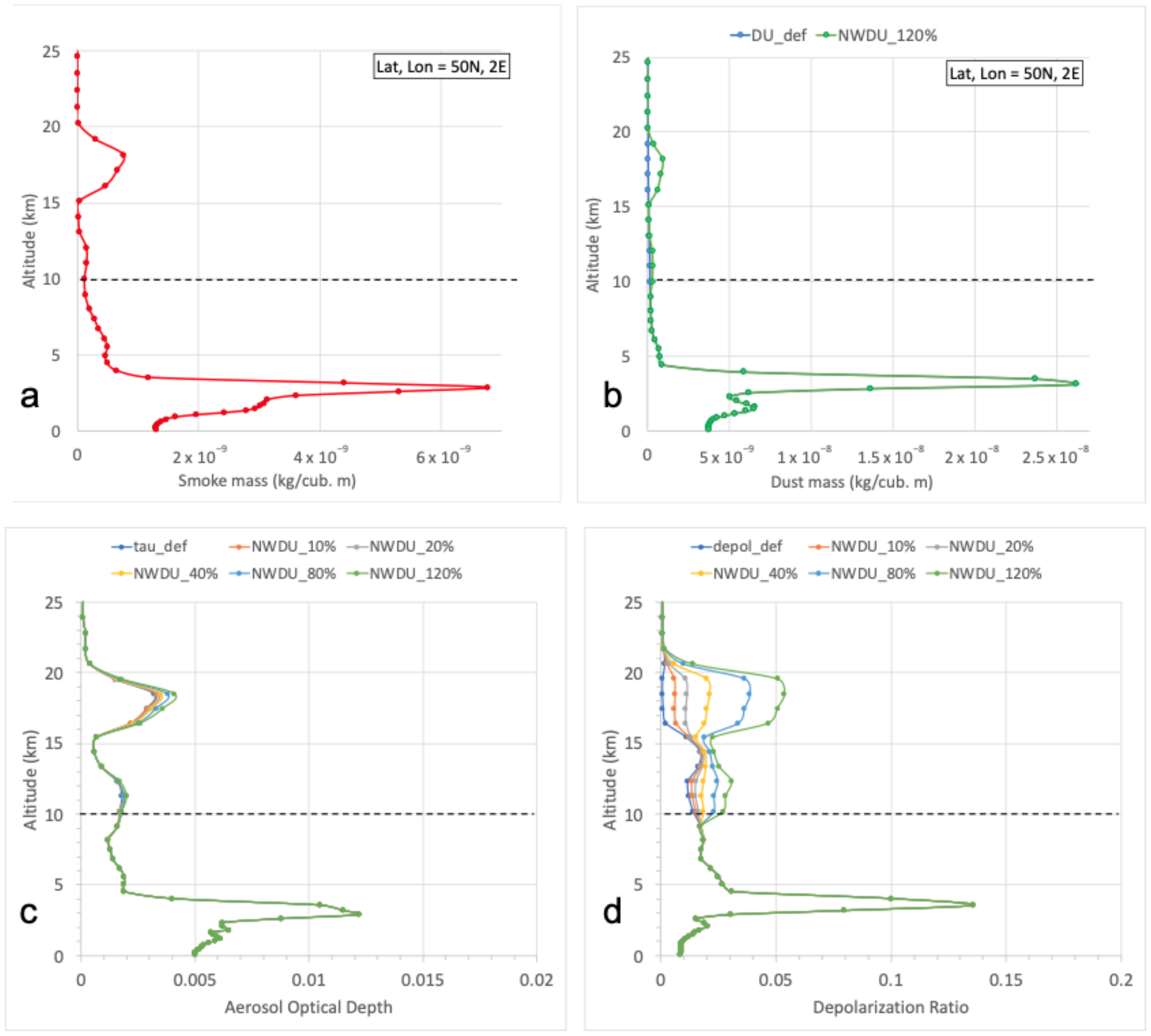
Appendix B. Zonal Averages of CALIOP Layer-Integrated Depolarization Ratios
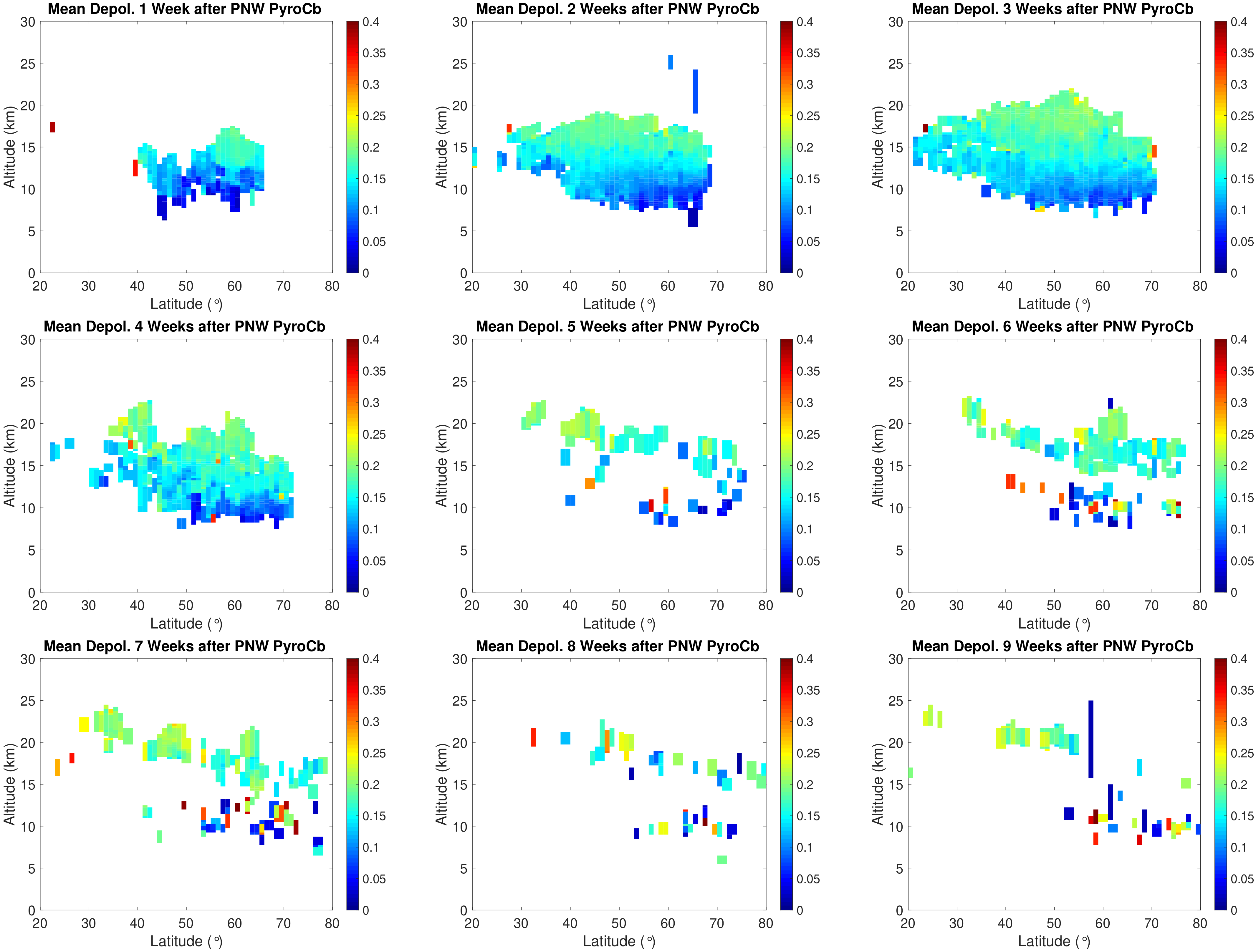
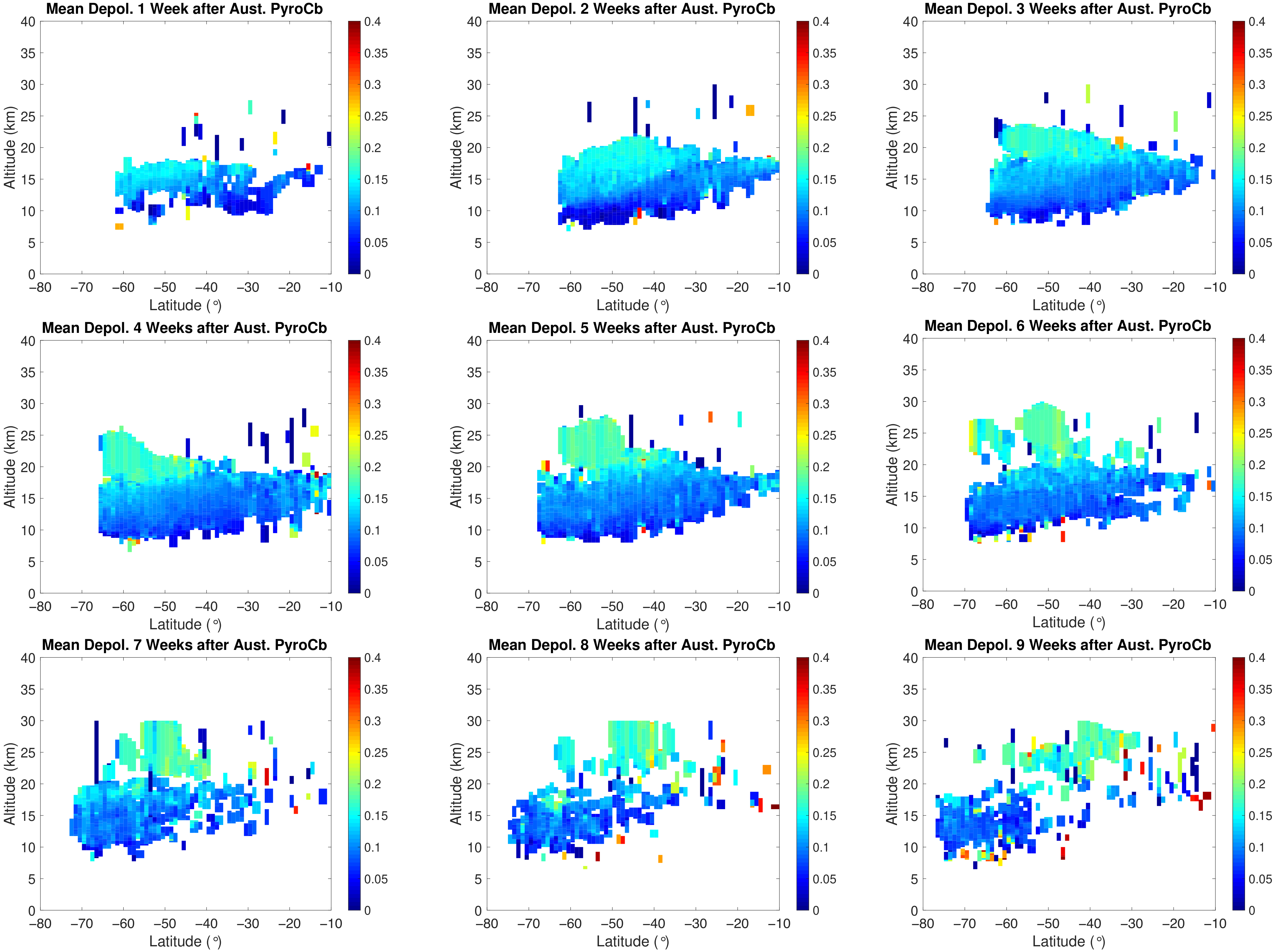
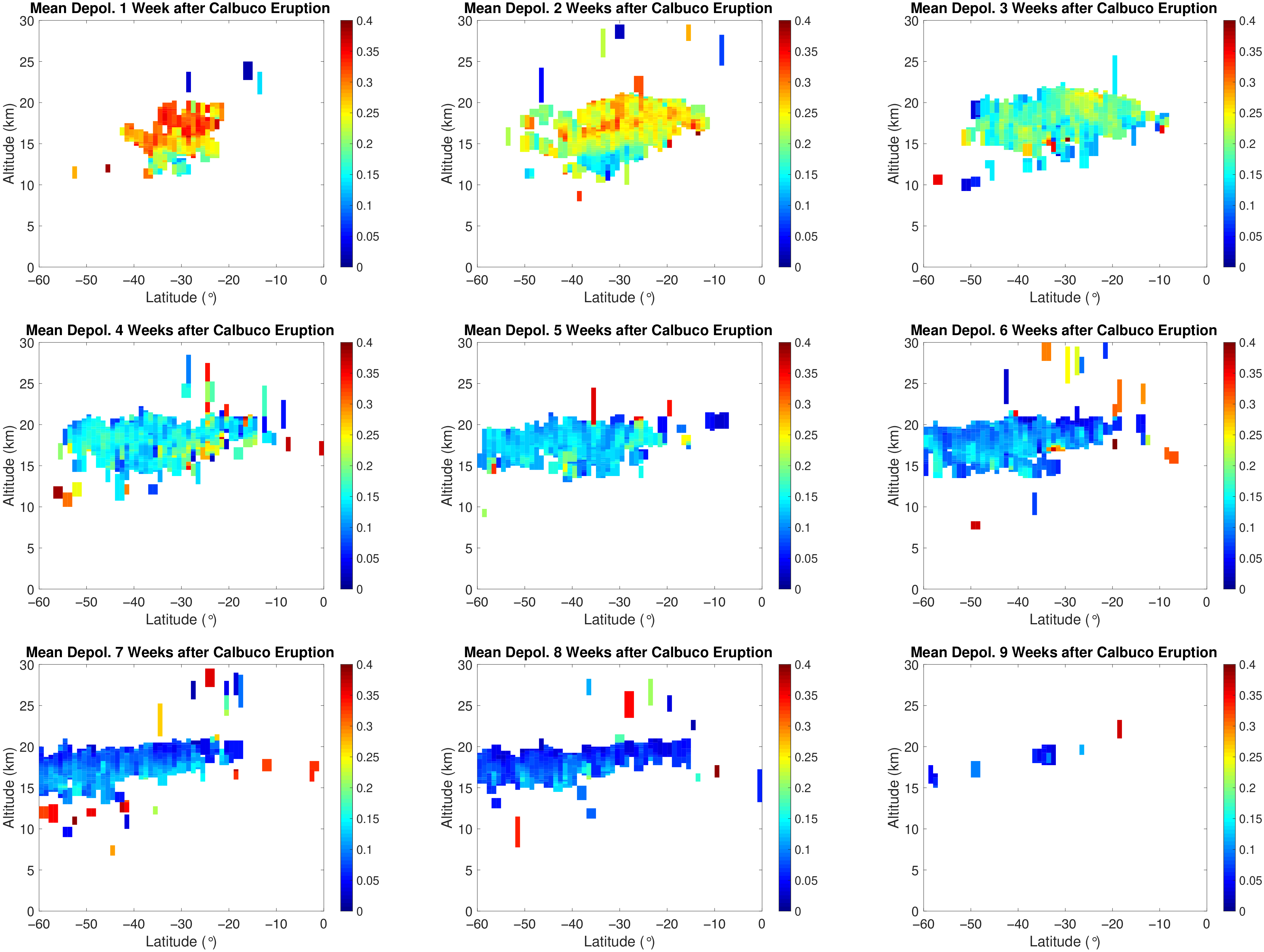
References
- Deshler, T. A review of global stratospheric aerosol: Measurements, importance, life cycle, and local stratospheric aerosol. Atmos. Res. 2008, 90, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremser, S.; Thomason, L.W.; Hobe, M.V.; Hermann, M.; Deshler, T.; Timmreck, C.; Toohey, M.; Stenke, A.; Schwarz, J.P.; Weigel, R.; et al. Stratospheric aerosol—Observations, processes, and impact on climate. Rev. Geophys. 2016, 54, 278–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Lindsey, D.T.; Servranckx, R.; Yue, G.; Trickl, T.; Sica, R.; Doucet, P.; Godin-Beekmann, S. The Untold Story of Pyrocumulonimbus. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, D.A.; Campbell, J.R.; Hyer, E.J.; Fromm, M.D.; Kablick, G.P.; Cossuth, J.H.; DeLand, M.T. Wildfire-driven thunderstorms cause a volcano-like stratospheric injection of smoke. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christian, K.; Wang, J.; Ge, C.; Peterson, D.; Hyer, E.; Yorks, J.; McGill, M. Radiative Forcing and Stratospheric Warming of Pyrocumulonimbus Smoke Aerosols: First Modeling Results With Multisensor (EPIC, CALIPSO, and CATS) Views from Space. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10061–10071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Toon, O.B.; Bardeen, C.G.; Zhu, Y.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Portmann, R.W.; Thornberry, T.D.; Gao, R.S.; Davis, S.M.; Wolf, E.T.; et al. Black carbon lofts wildfire smoke high into the stratosphere to form a persistent plume. Science 2019, 365, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Wang, J.; Carn, S.; Yang, K.; Ginoux, P.; Krotkov, N. Satellite-based global volcanic SO2 emissions and sulfate direct radiative forcing during 2005–2012. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3446–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labitzke, K.; McCormick, M.P. Stratospheric temperature increases due to Pinatubo aerosols. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohneiser, K.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Seifert, P.; Barja, B.; Jimenez, C.; Radenz, M.; Teisseire, A.; Floutsi, A.; Haarig, M.; et al. Smoke of extreme Australian bushfires observed in the stratosphere over Punta Arenas, Chile, in January 2020: Optical thickness, lidar ratios, and depolarization ratios at 355 and 532 nm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8003–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablick III, G.P.; Allen, D.R.; Fromm, M.D.; Nedoluha, G.E. Australian PyroCb Smoke Generates Synoptic-Scale Stratospheric Anticyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, A.T.; Young, S.A.; Siems, S.T.; Manton, M.J. Lidar ratios of stratospheric volcanic ash and sulfate aerosols retrieved from CALIOP measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8599–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumphrey, H.C.; Santee, M.L.; Livesey, N.J.; Schwartz, M.J.; Read, W.G. Microwave Limb Sounder observations of biomass-burning products from the Australian bush fires of February 2009. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6285–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, V.J.B.; Kahn, R.A. Assessing the altitude and dispersion of volcanic plumes using MISR multi-angle imaging from space: Sixteen years of volcanic activity in the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 337, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, V.J.B.; Kahn, R.A. Karymsky volcano eruptive plume properties based on MISR multi-angle imagery and the volcanological implications. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3903–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.J.; Yorks, J.E.; Scott, V.S.; Kupchock, A.W.; Selmer, P.A. The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS): A technology demonstration on the International Space Station. In Proceedings of the Lidar Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring XV International Society for Optics and Photonics, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–13 August 2015; p. 96120A. [Google Scholar]
- Yorks, J.E.; McGill, M.J.; Palm, S.P.; Hlavka, D.L.; Selmer, P.A.; Nowottnick, E.P.; Vaughan, M.A.; Rodier, S.D.; Hart, W.D. An overview of the CATS level 1 processing algorithms and data products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4632–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorks, J.E.; Palm, S.P.; McGill, M.J.; Hlavka, D.L.; Hart, W.D.; Selmer, P.A.; Nowottnick, E.P. CATS Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Level 1 and Level 2 Data Products; Technical Report; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ginoux, P. Effects of nonsphericity on mineral dust modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laat, A.T.J.d.; Zweers, D.C.S.; Boers, R.; Tuinder, O.N.E. A solar escalator: Observational evidence of the self-lifting of smoke and aerosols by absorption of solar radiation in the February 2009 Australian Black Saturday plume. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bègue, N.; Vignelles, D.; Berthet, G.; Portafaix, T.; Payen, G.; Jégou, F.; Benchérif, H.; Jumelet, J.; Vernier, J.P.; Lurton, T.; et al. Long-range transport of stratospheric aerosols in the Southern Hemisphere following the 2015 Calbuco eruption. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 15019–15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.P.; Hair, J.W.; Kahnert, M.; Ferrare, R.A.; Hostetler, C.A.; Cook, A.L.; Harper, D.B.; Berkoff, T.A.; Seaman, S.T.; Collins, J.E.; et al. Observations of the spectral dependence of linear particle depolarization ratio of aerosols using NASA Langley airborne High Spectral Resolution Lidar. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13453–13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarig, M.; Ansmann, A.; Baars, H.; Jimenez, C.; Veselovskii, I.; Engelmann, R.; Althausen, D. Depolarization and lidar ratios at 355, 532, and 1064 nm and microphysical properties of aged tropospheric and stratospheric Canadian wildfire smoke. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11847–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaykin, S.M.; Godin-Beekmann, S.; Hauchecorne, A.; Pelon, J.; Ravetta, F.; Keckhut, P. Stratospheric Smoke With Unprecedentedly High Backscatter Observed by Lidars Above Southern France. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I.; Dlugach, J.M.; Liu, L. Linear depolarization of lidar returns by aged smoke particles. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 9968–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.S.; Hobbs, P.V. Physical and optical properties of young smoke from individual biomass fires in Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32013–32030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablick, G.; Fromm, M.; Miller, S.; Partain, P.; Peterson, D.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lambert, A.; Li, Z. The Great Slave Lake PyroCb of 5 August 2014: Observations, Simulations, Comparisons With Regular Convection, and Impact on UTLS Water Vapor. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12332–12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.V.; Hobbs, P.V.; Weiss, R.E.; Artaxo, P. Sphericity and morphology of smoke particles from biomass burning in Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32051–32057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molod, A.; Takacs, L.; Suarez, M.; Bacmeister, J. Development of the GEOS-5 atmospheric general circulation model: Evolution from MERRA to MERRA2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Todling, J.; Bacmeister, J.; Takacs, L.; Liu, H.C.; Gu, W.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Koster, R.D.; Gelaro, R.; et al. The GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System—Documentation of Versions 5.0.1, 5.1.0, and 5.2.0; Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, M.; Ginoux, P.; Kinne, S.; Torres, O.; Holben, B.N.; Duncan, B.N.; Martin, R.V.; Logan, J.A.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Tropospheric Aerosol Optical Thickness from the GOCART Model and Comparisons with Satellite and Sun Photometer Measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Dubovik, O.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Sinyuk, A.; Streets, D.G. Light absorption by pollution, dust, and biomass burning aerosols: A global model study and evaluation with AERONET measurements. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 3439–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarco, P.; Silva, A.D.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T. Online simulations of global aerosol distributions in the NASA GEOS-4 model and comparisons to satellite and ground-based aerosol optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarco, P.R.; Gassó, S.; Ahn, C.; Buchard, V.; Silva, A.M.d.; Torres, O. Simulation of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument aerosol index using the NASA Goddard Earth Observing System aerosol reanalysis products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4121–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds: The Software Package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colarco, P.R.; Nowottnick, E.P.; Randles, C.A.; Yi, B.; Yang, P.; Kim, K.M.; Smith, J.A.; Bardeen, C.G. Impact of radiatively interactive dust aerosols in the NASA GEOS-5 climate model: Sensitivity to dust particle shape and refractive index. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 753–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowottnick, E.P.; Colarco, P.R.; Welton, E.J.; da Silva, A. Use of the CALIOP vertical feature mask for evaluating global aerosol models. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 3647–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Colarco, P.R.; Oman, L.; Taha, G.; Torres, O. Pyrocumulonimbus Events over British Columbia, 2017: The Long-term Transport and Radiative Impacts of Smoke Aerosols in the Stratosphere. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 4–8 May 2020. (online). [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christian, K.; Yorks, J.; Das, S. Differences in the Evolution of Pyrocumulonimbus and Volcanic Stratospheric Plumes as Observed by CATS and CALIOP Space-Based Lidars. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101035
Christian K, Yorks J, Das S. Differences in the Evolution of Pyrocumulonimbus and Volcanic Stratospheric Plumes as Observed by CATS and CALIOP Space-Based Lidars. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(10):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101035
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristian, Kenneth, John Yorks, and Sampa Das. 2020. "Differences in the Evolution of Pyrocumulonimbus and Volcanic Stratospheric Plumes as Observed by CATS and CALIOP Space-Based Lidars" Atmosphere 11, no. 10: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101035
APA StyleChristian, K., Yorks, J., & Das, S. (2020). Differences in the Evolution of Pyrocumulonimbus and Volcanic Stratospheric Plumes as Observed by CATS and CALIOP Space-Based Lidars. Atmosphere, 11(10), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11101035





