Turbulence, Low-Level Jets, and Waves in the Tyrrhenian Coastal Zone as Shown by Sodar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
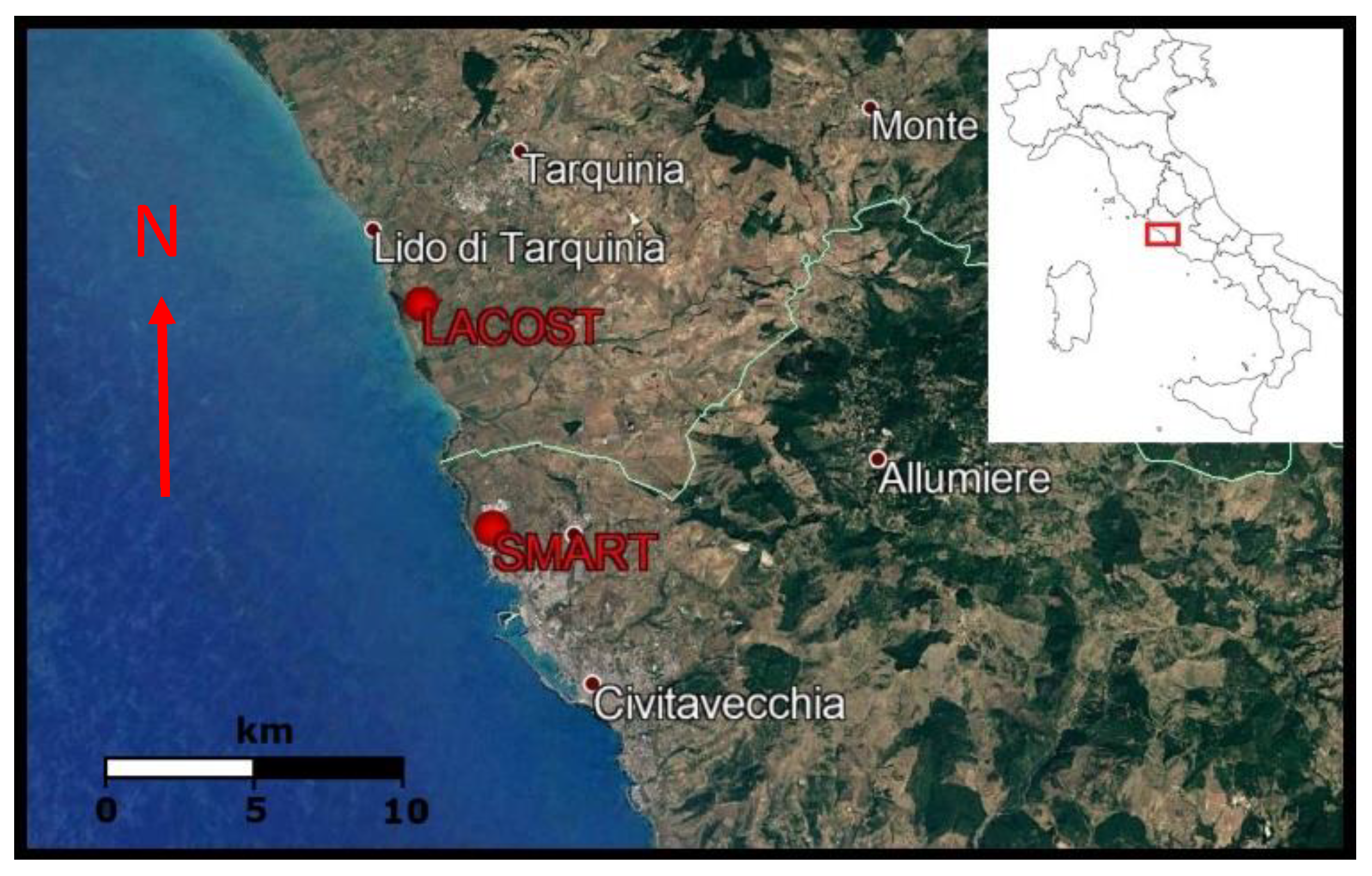
2.1. Site Location and Characterisation
2.2. Sodar Measurements
2.3. Other Measurements
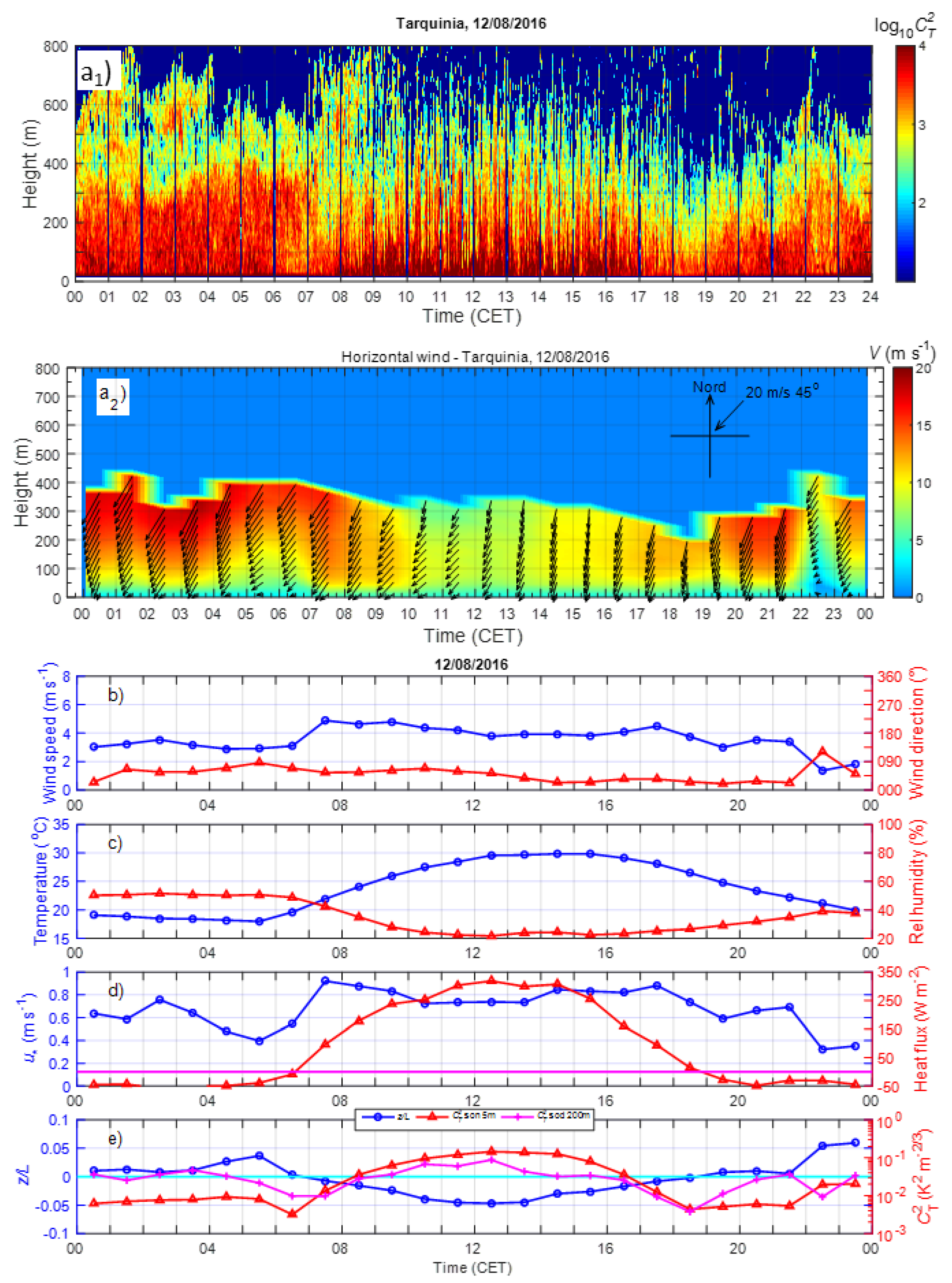
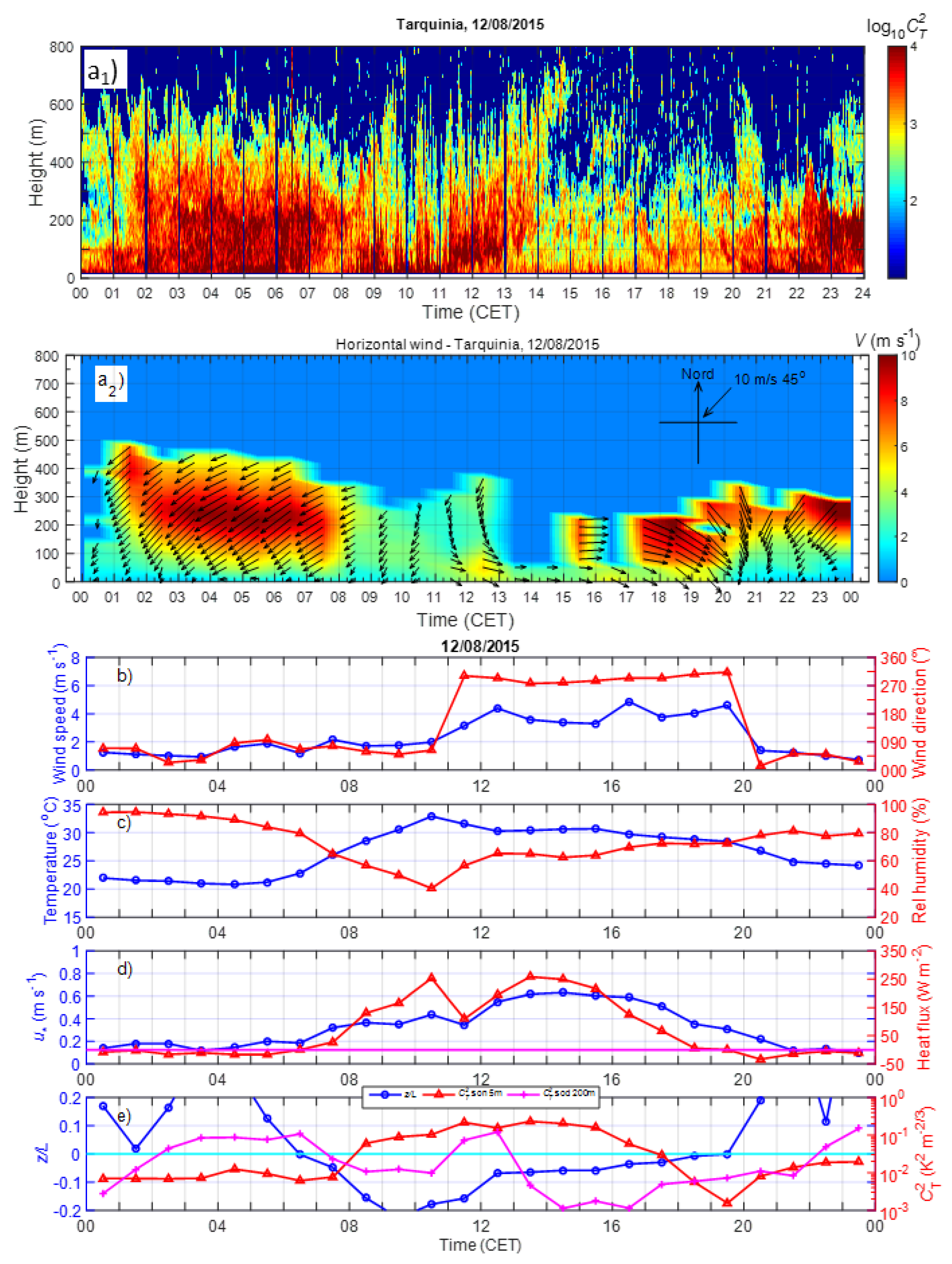
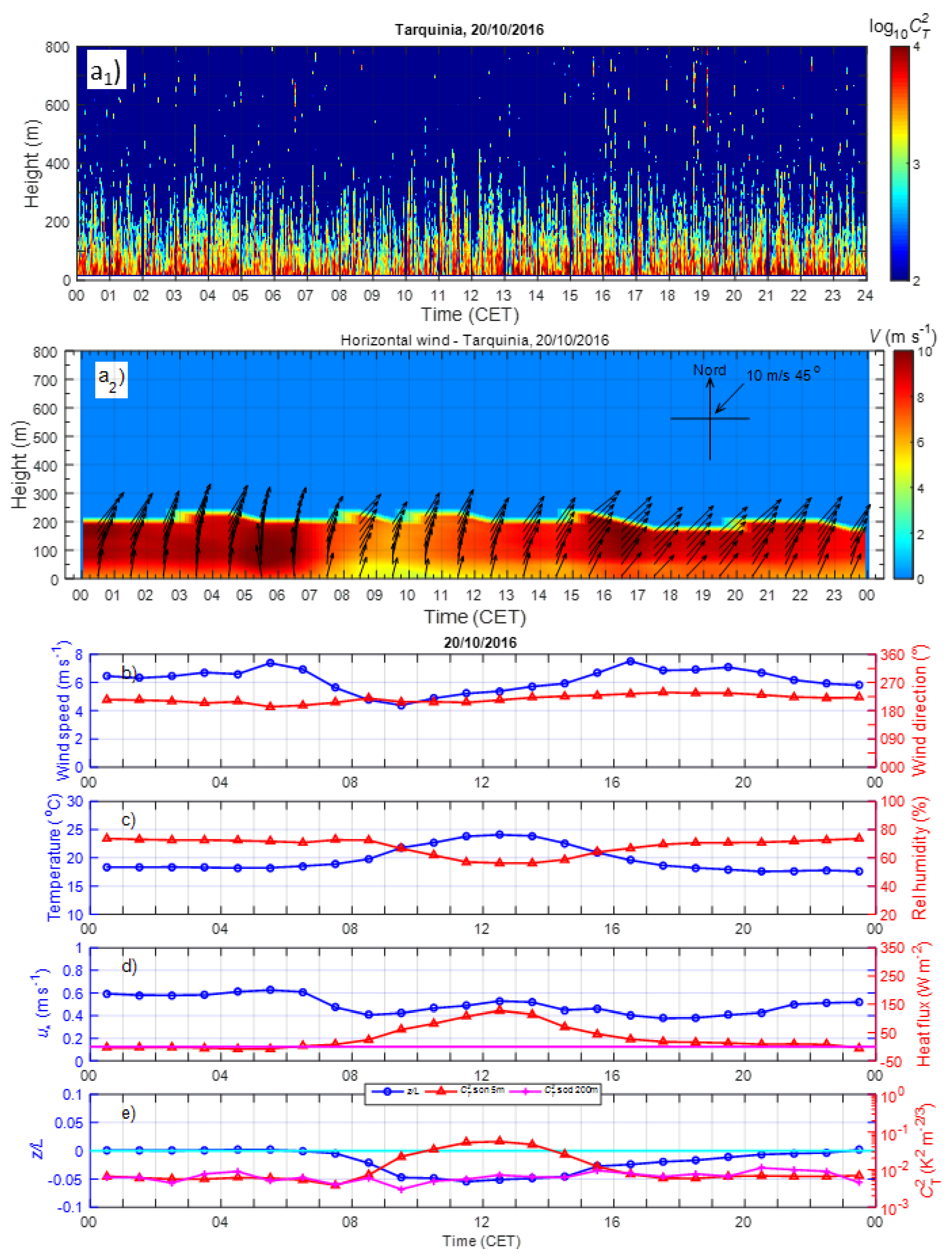
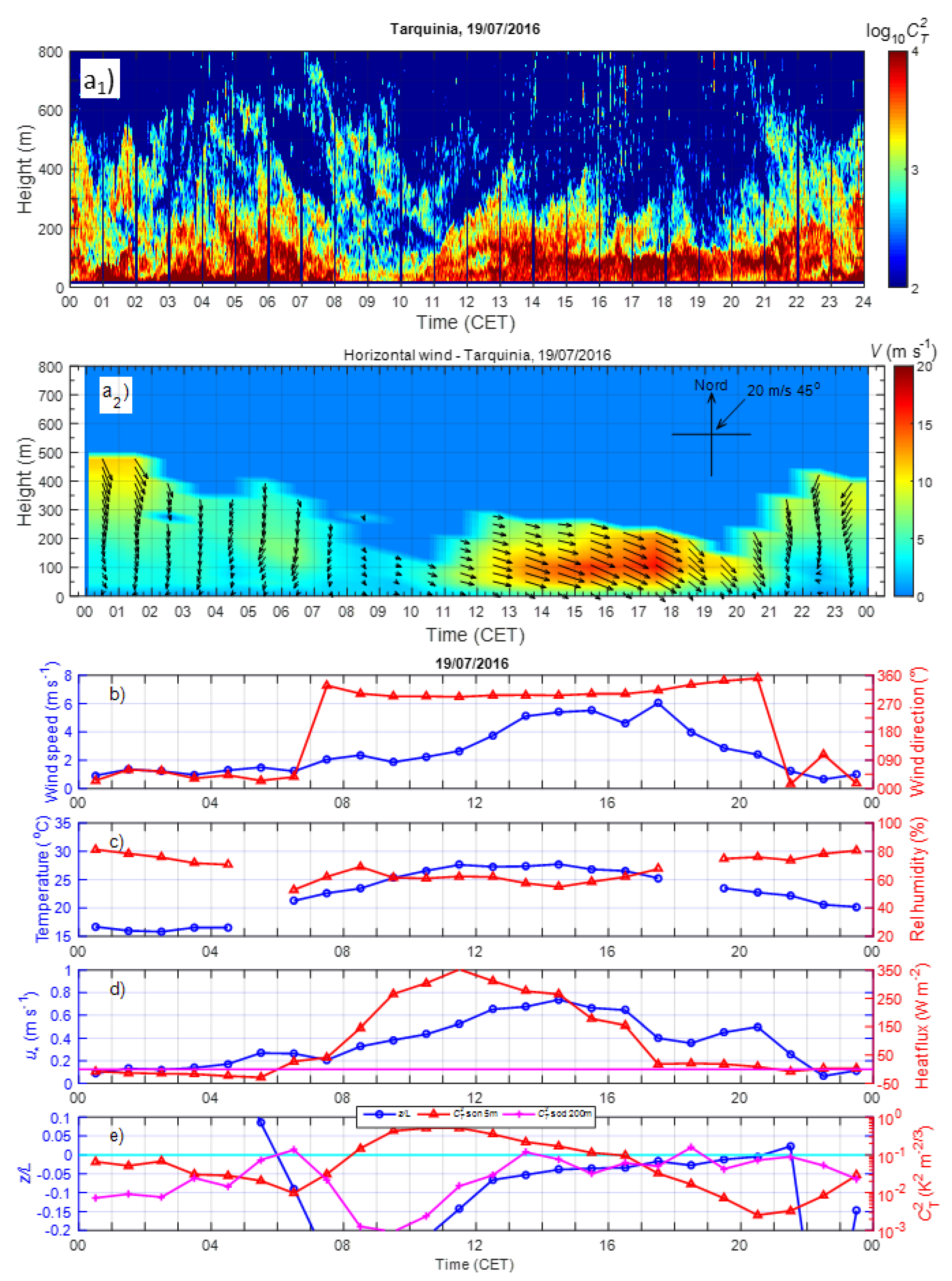
3. Results
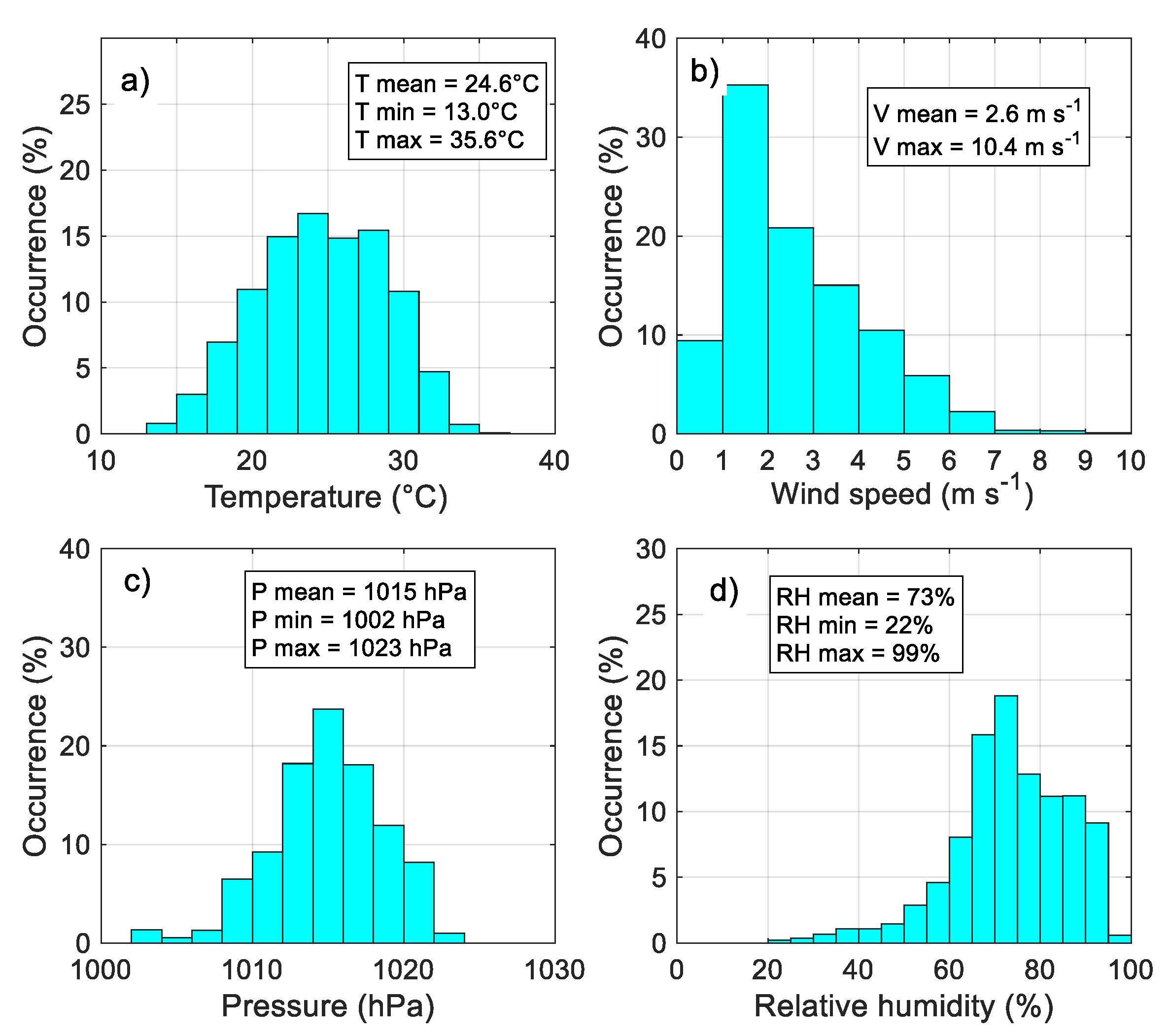
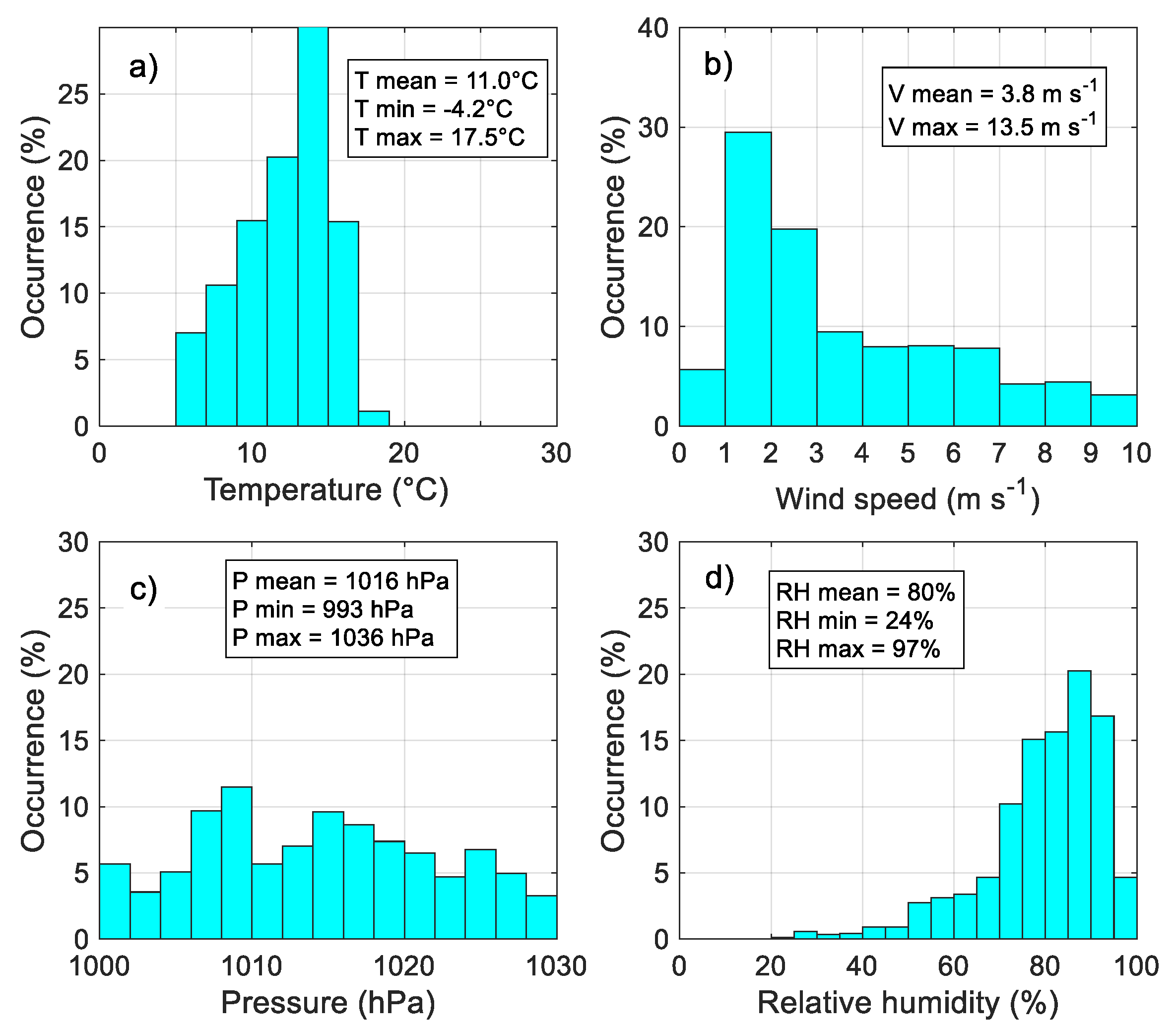
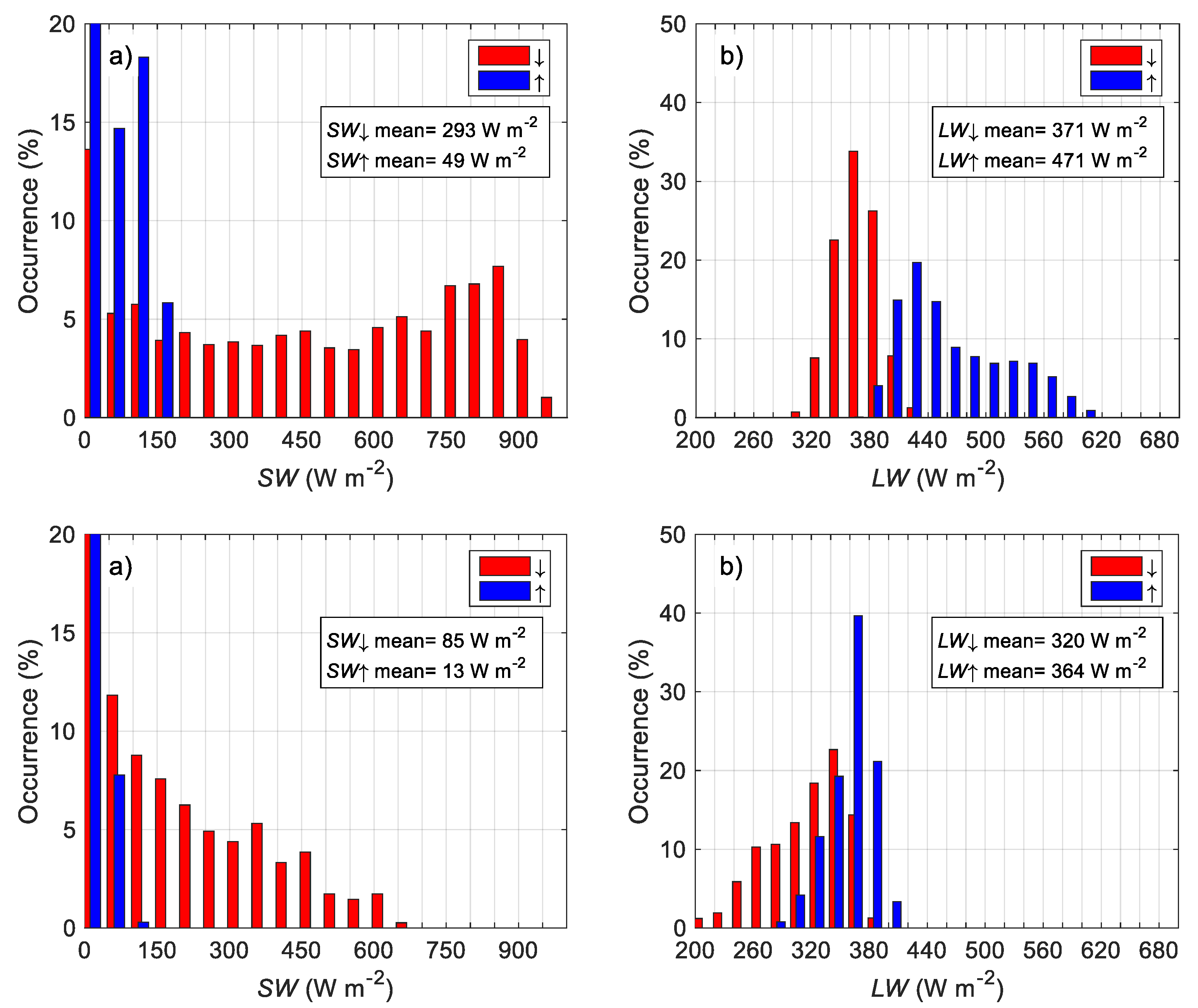
3.1. Statistics of the Principal Meteorological and Turbulent Parameters
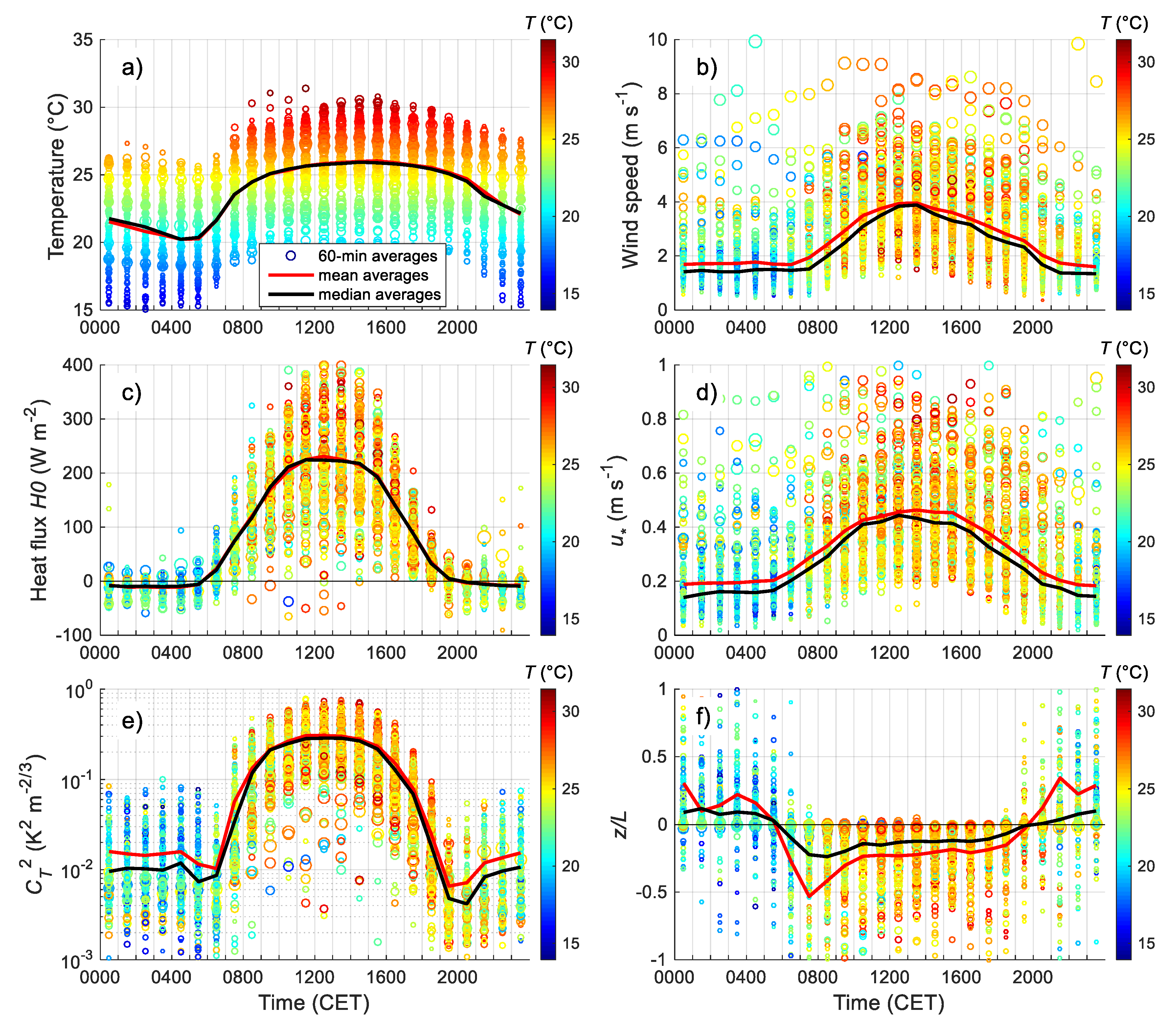
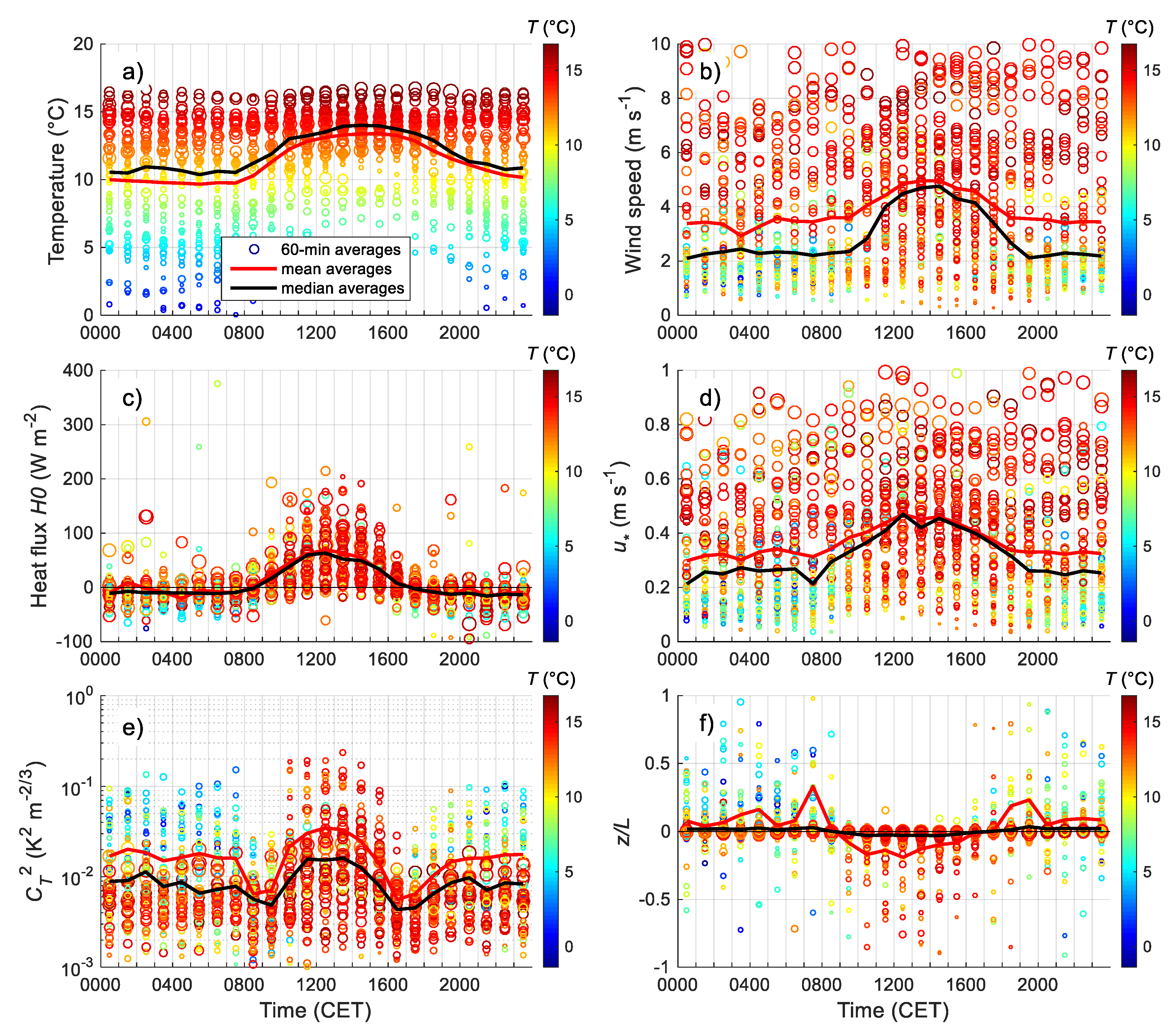
3.2. Diurnal Behaviour of the Meteorological and Turbulent Parameters
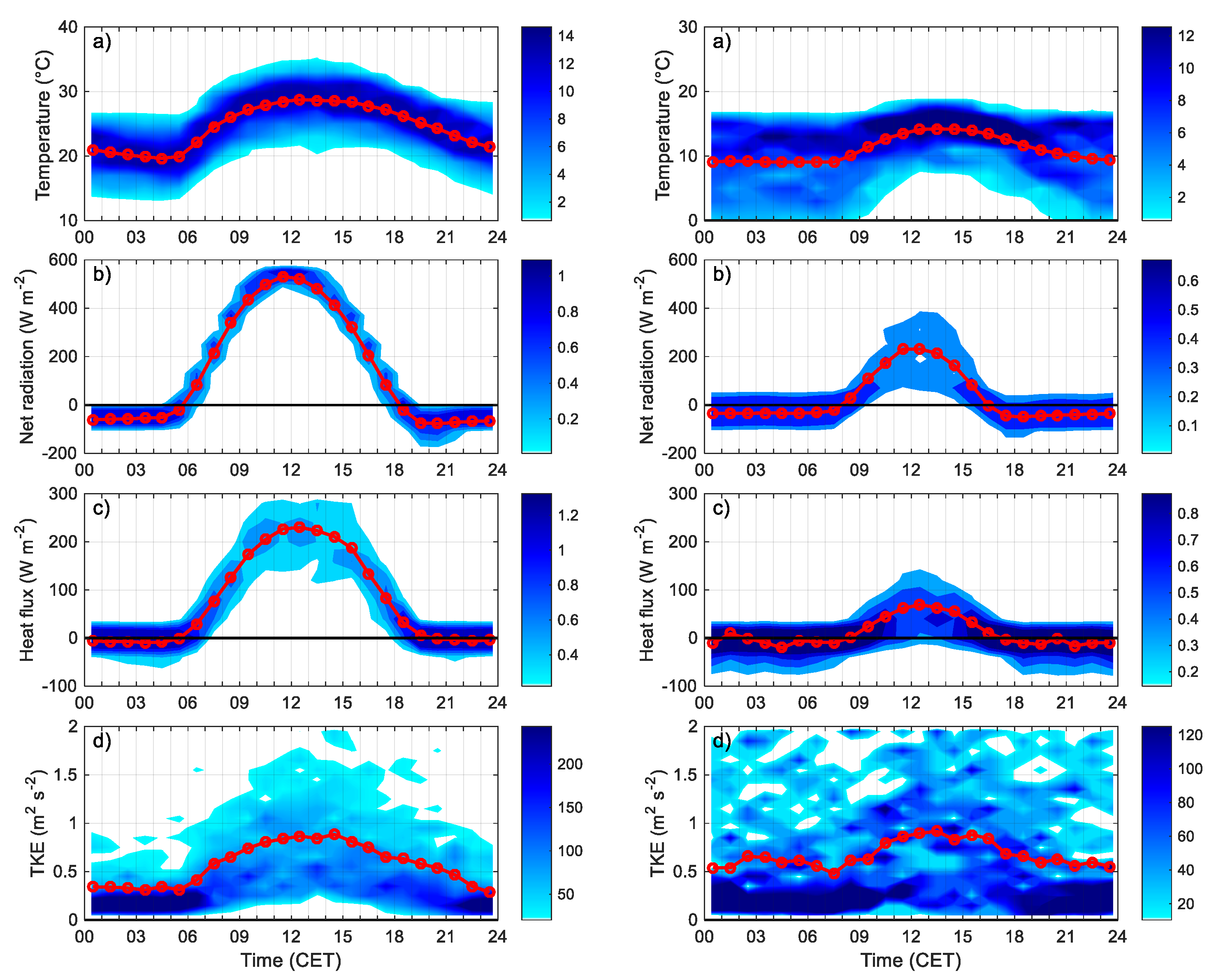
3.2.1. Daily Cycles of the Relevant Parameters in the Surface Layer
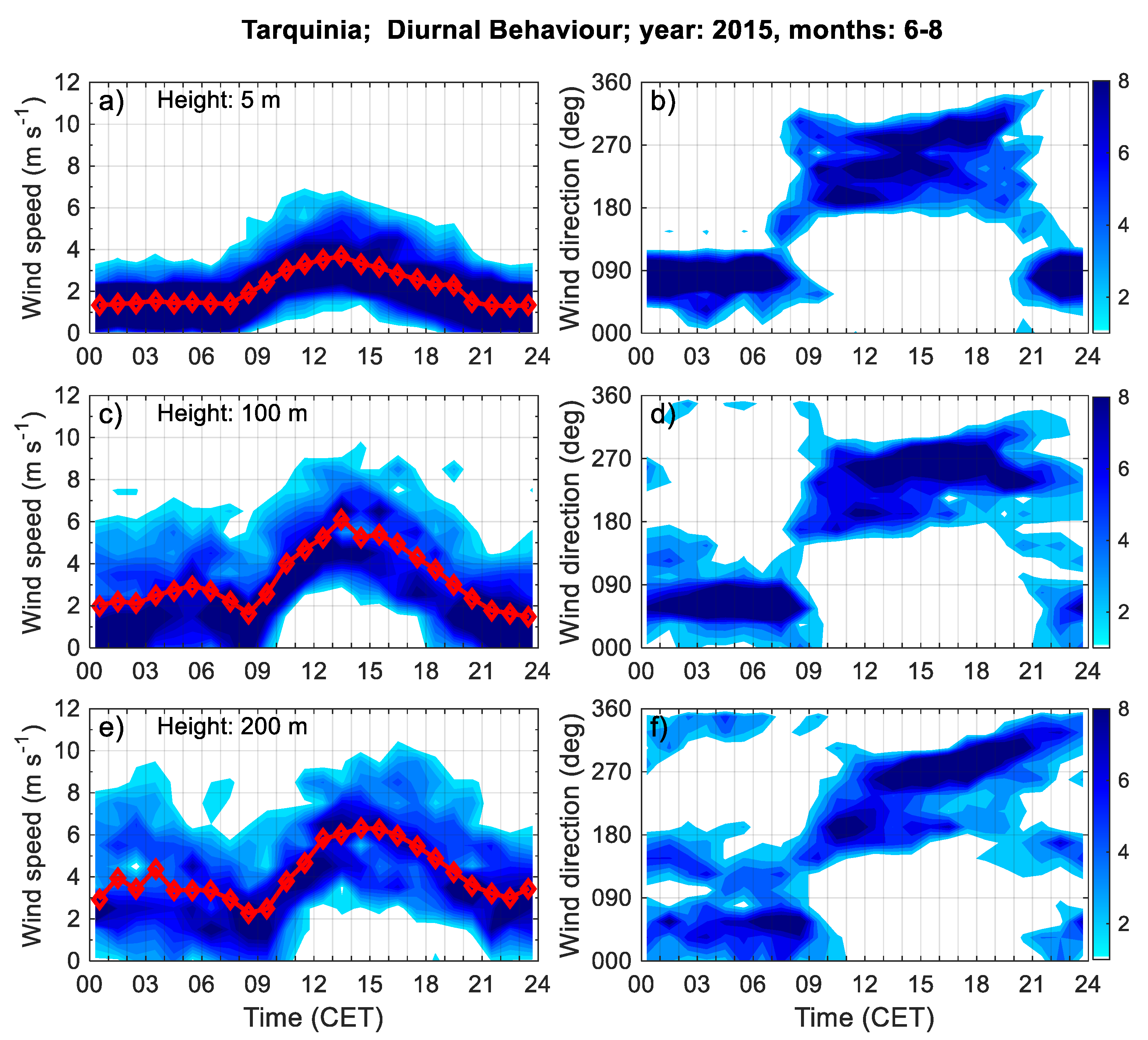
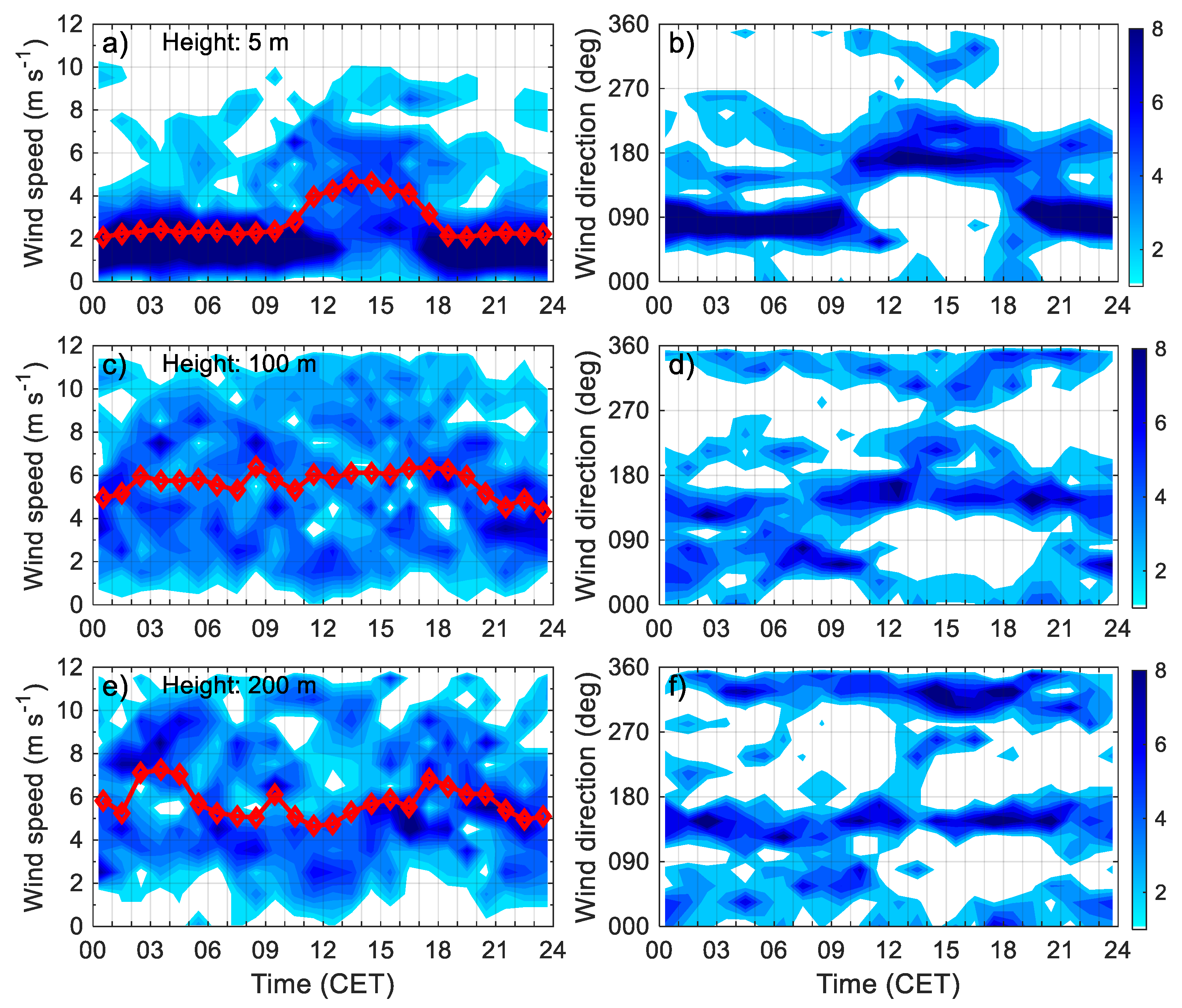
3.2.2. Diurnal Behaviour Patterns of the Wind Field from Sonic and Sodar Data
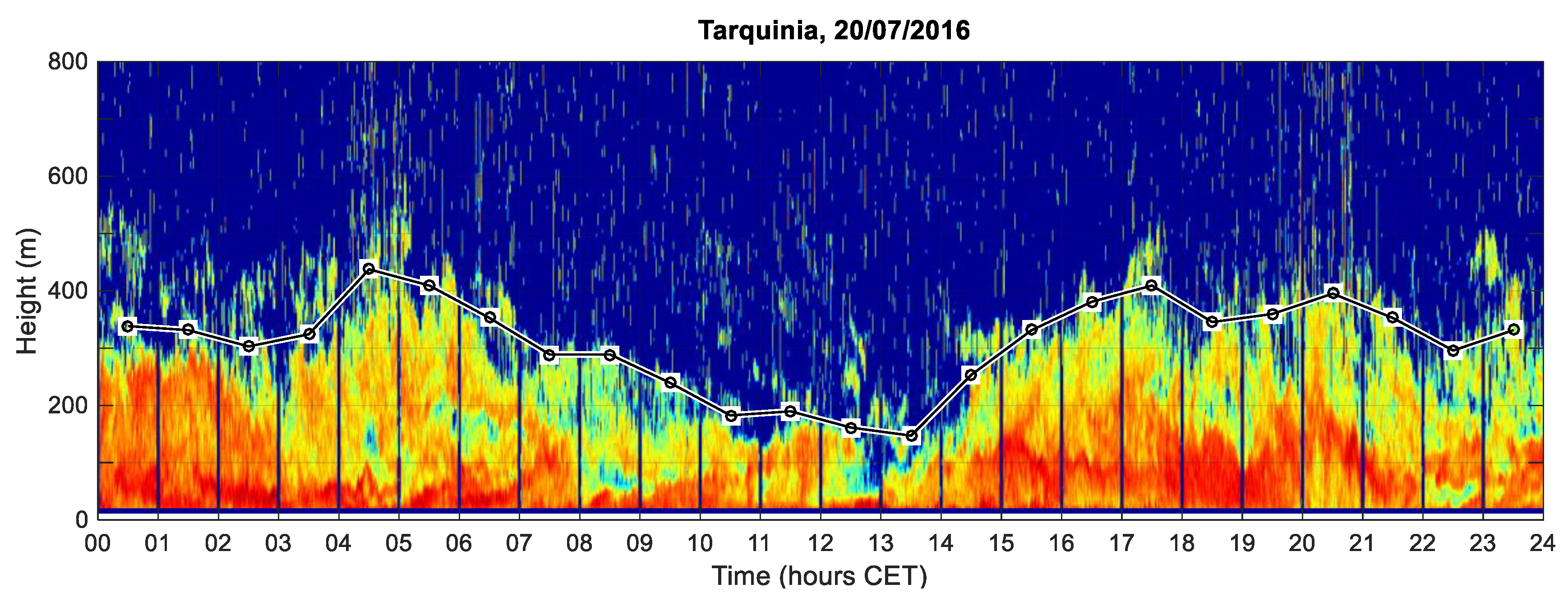
3.3. Temporal and Height Structure of Thermal Turbulence in the Coastal ABL
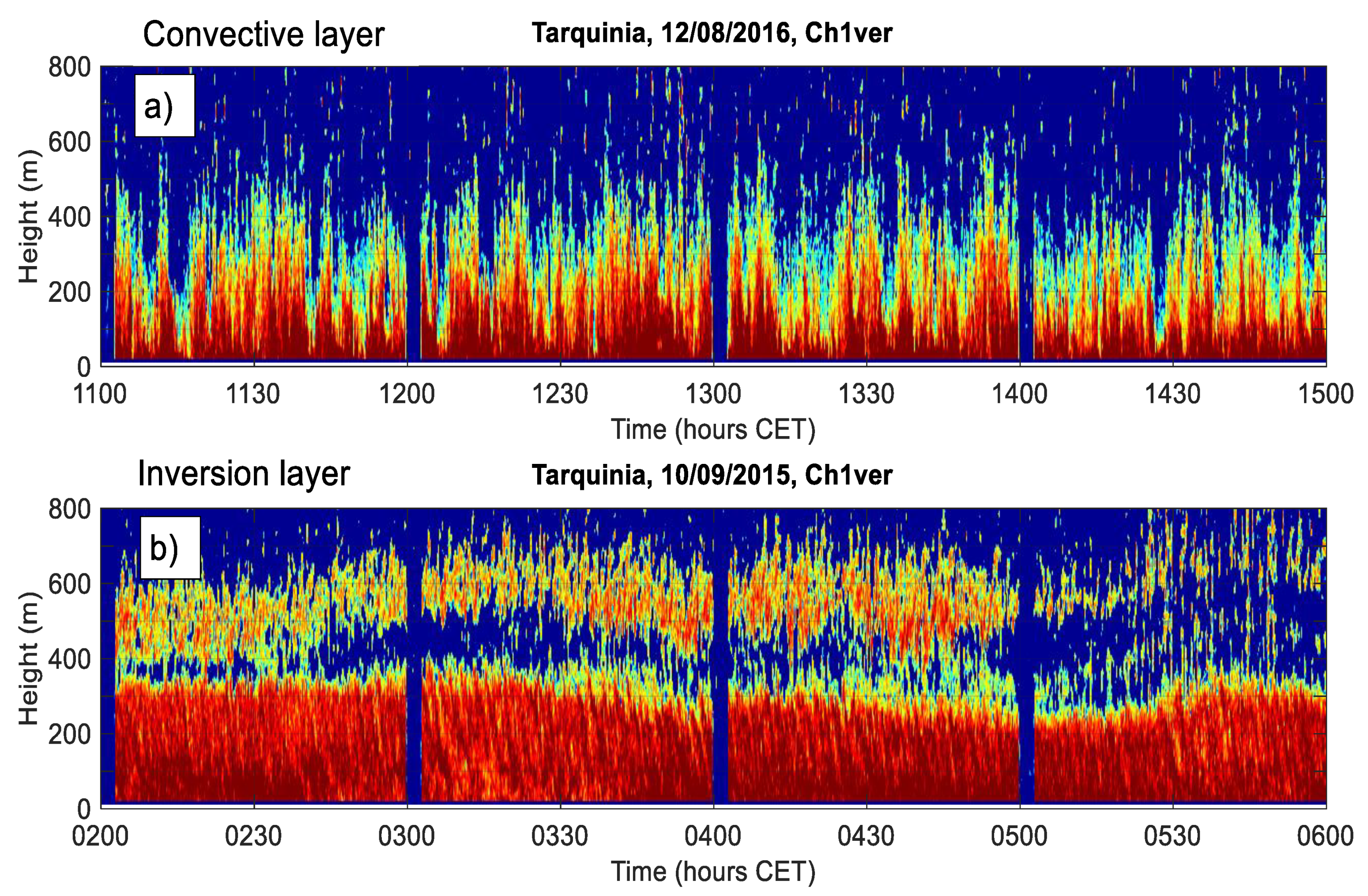
3.3.1. Prevailing Daily Regimes of the Coastal ABL
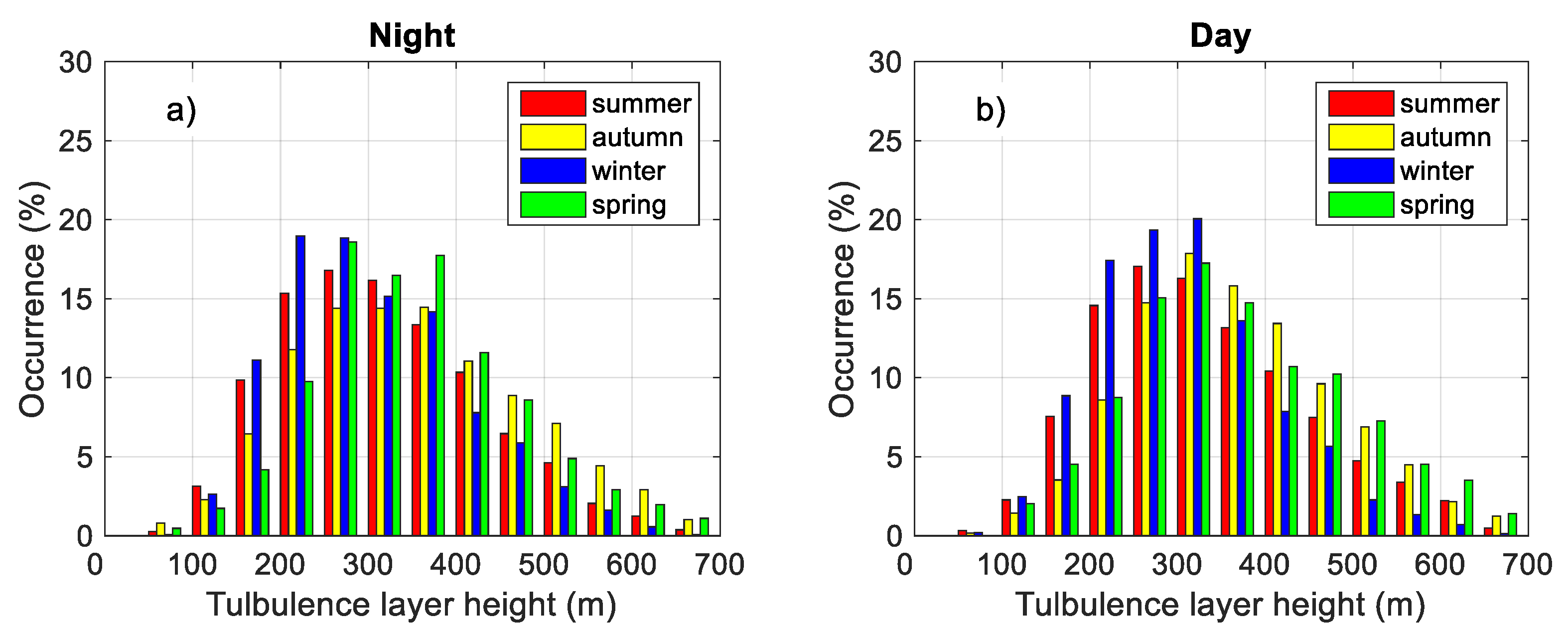
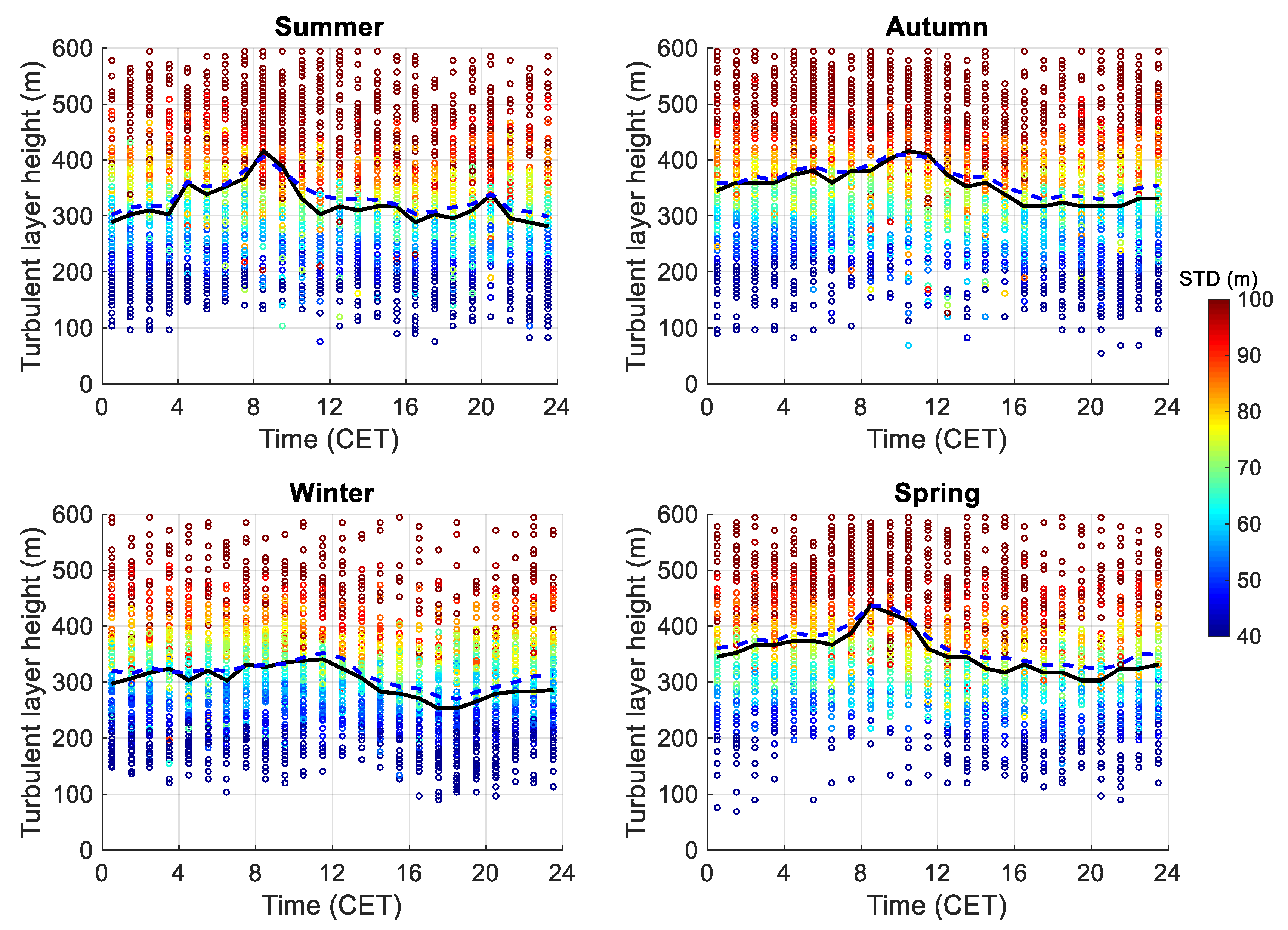
3.3.2. Statistics of the Turbulent Layer Height
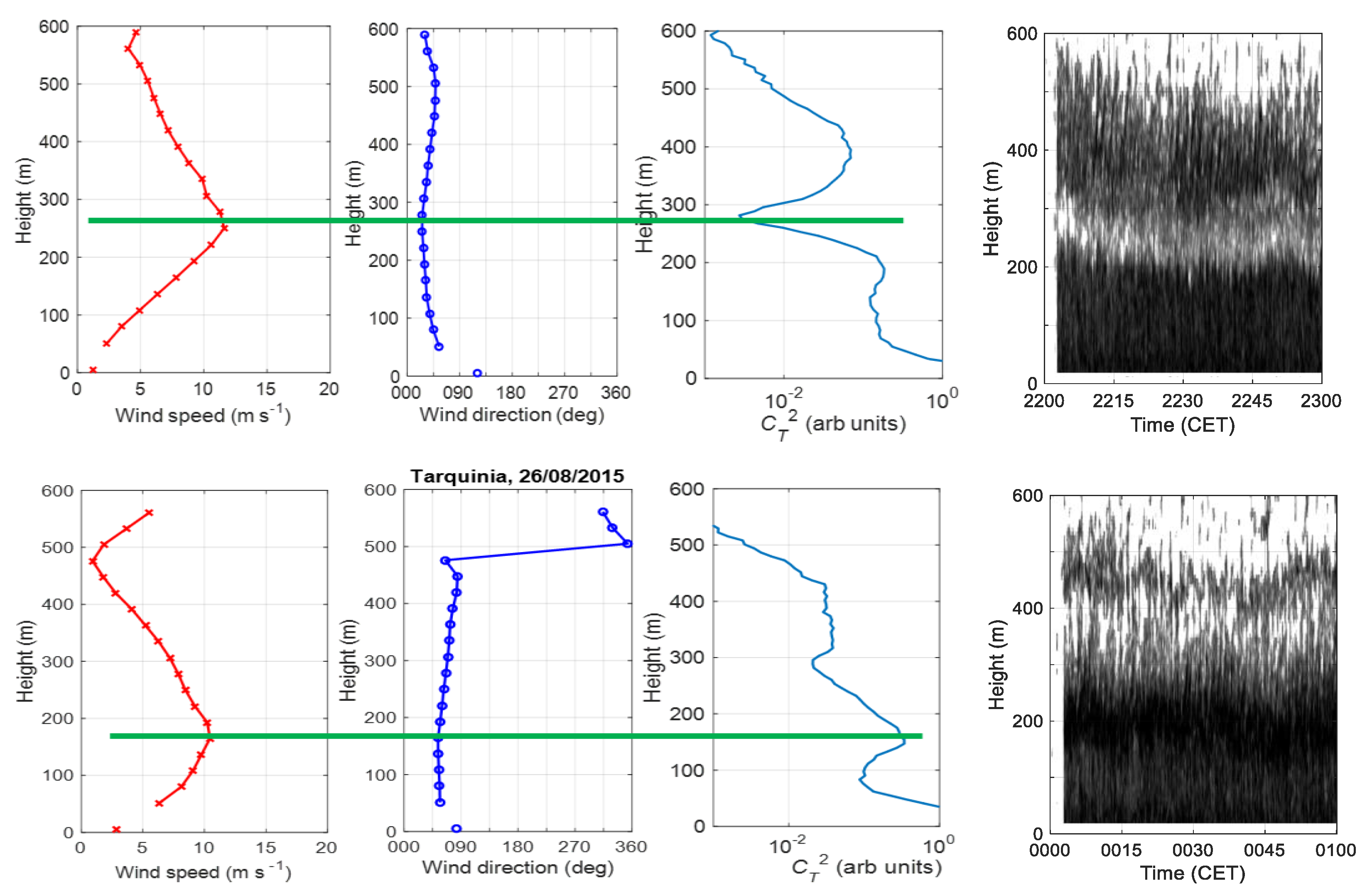
3.4. Description of LLJ Features
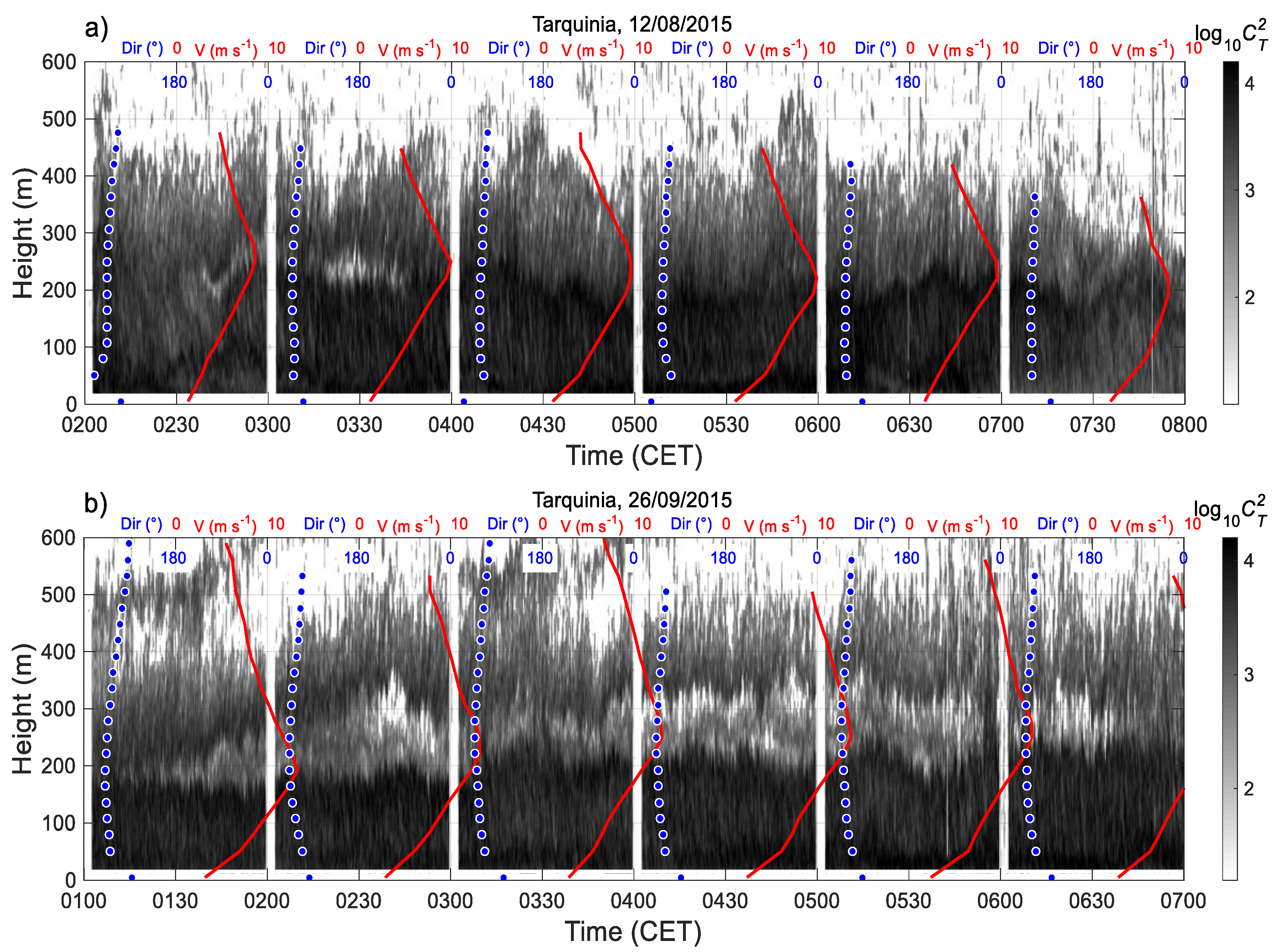
3.4.1. Examples of LLJs
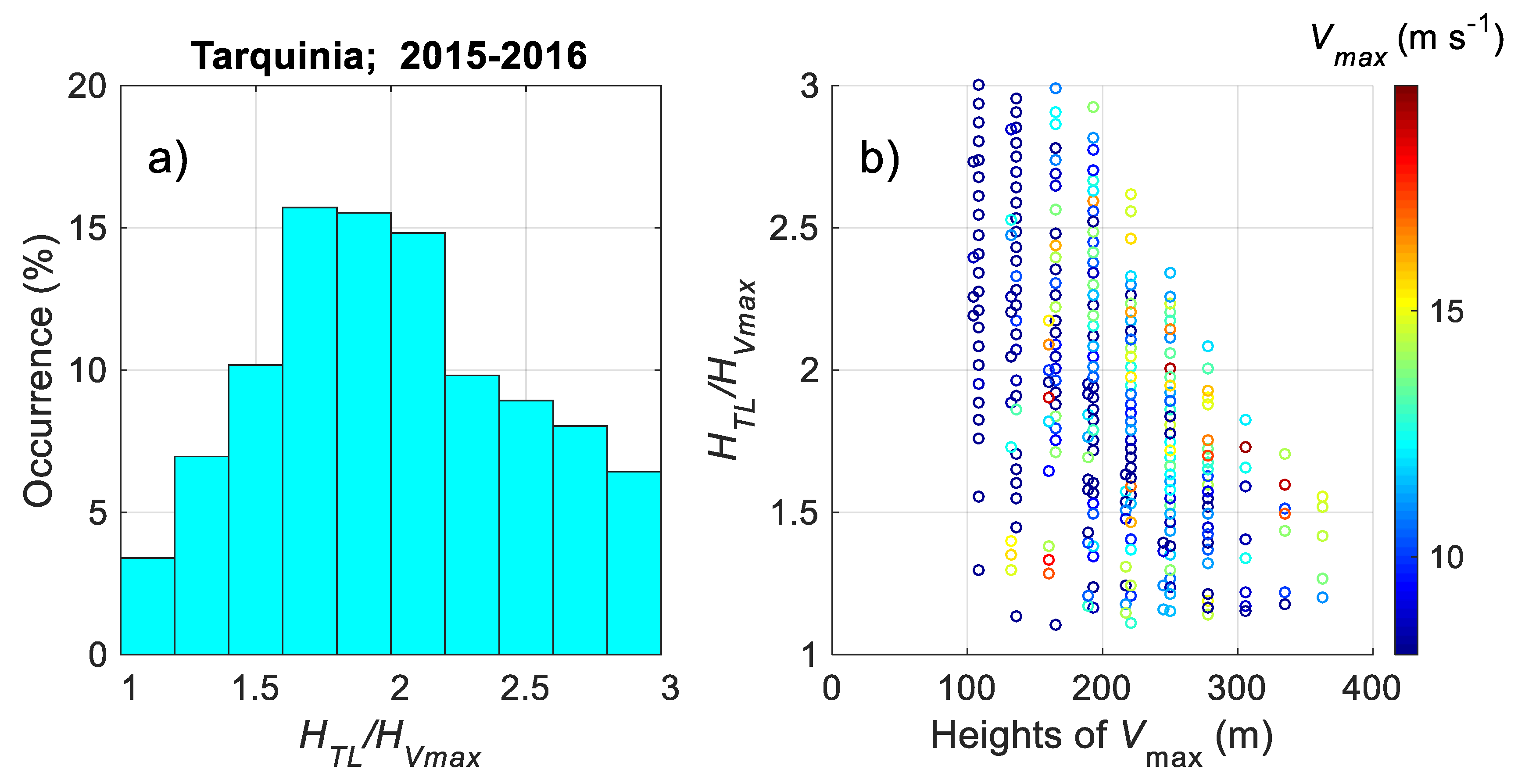
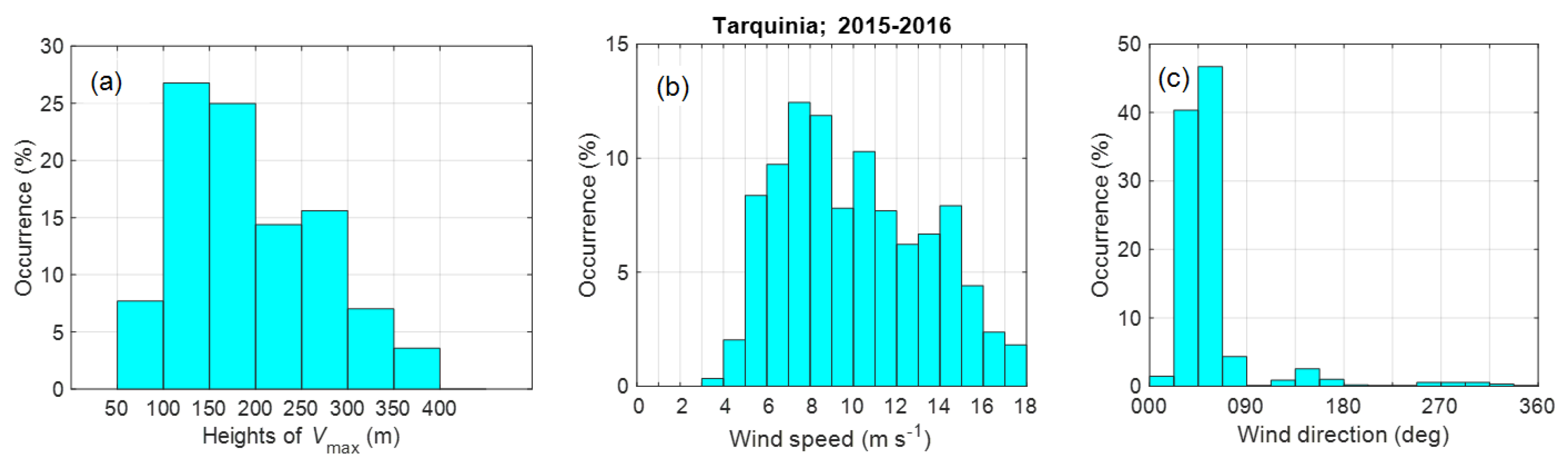
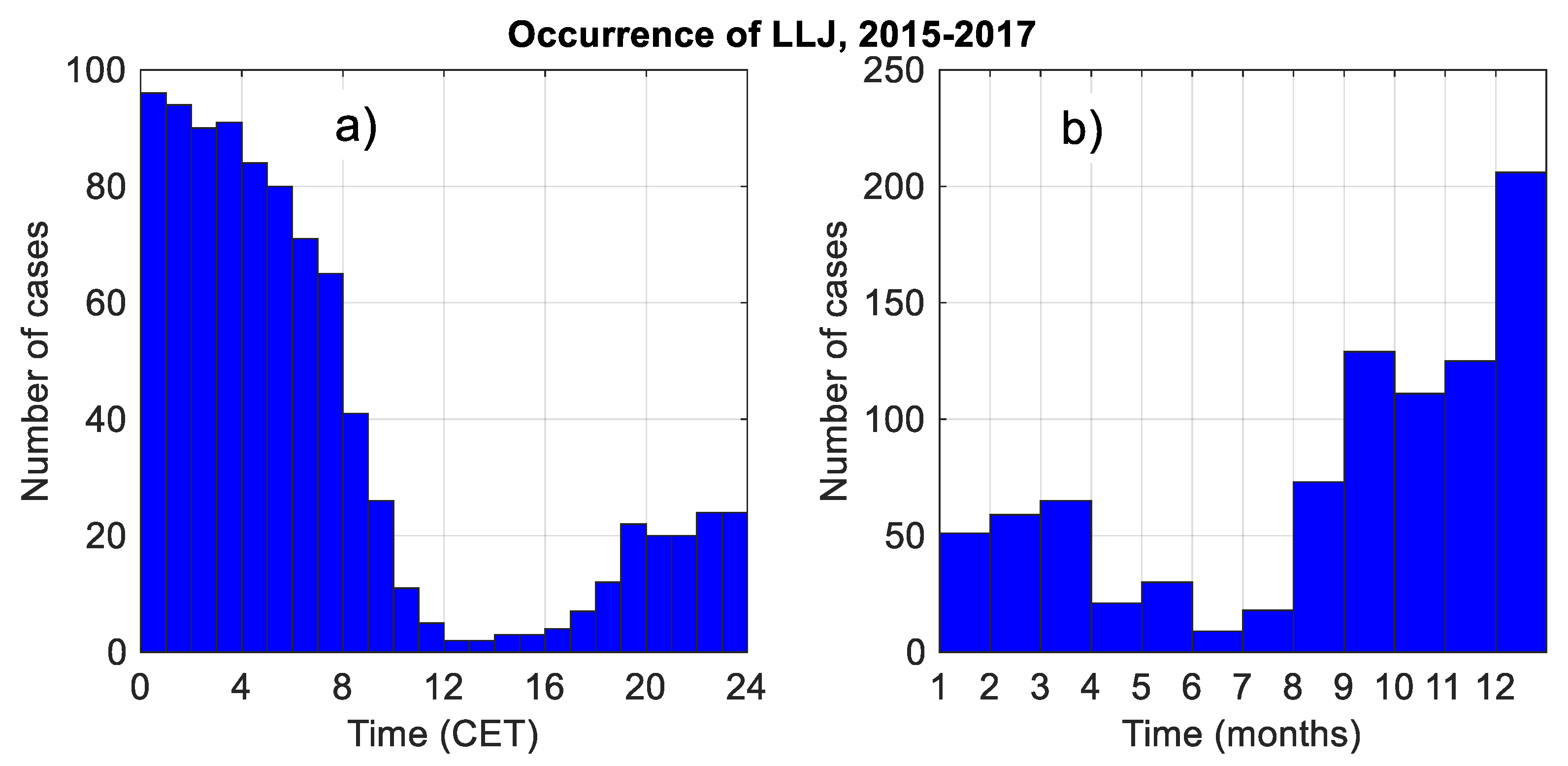
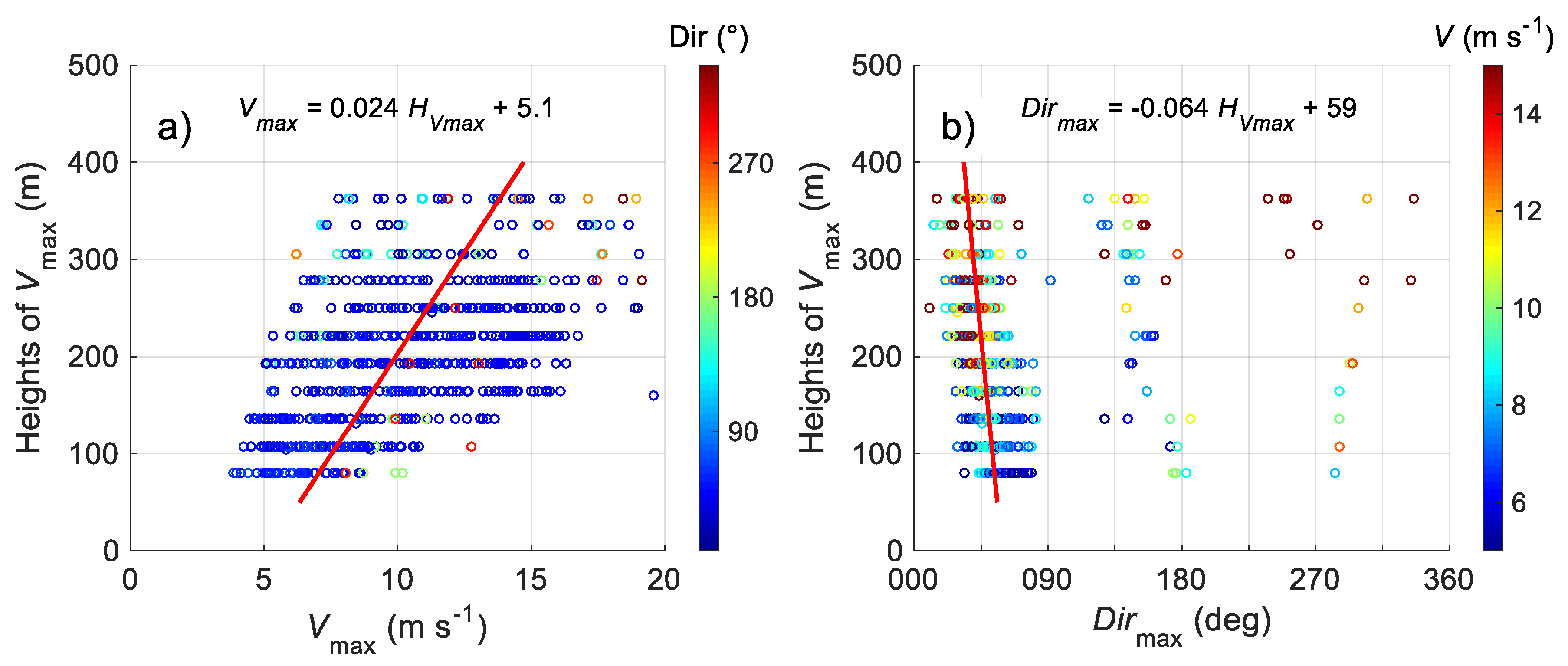
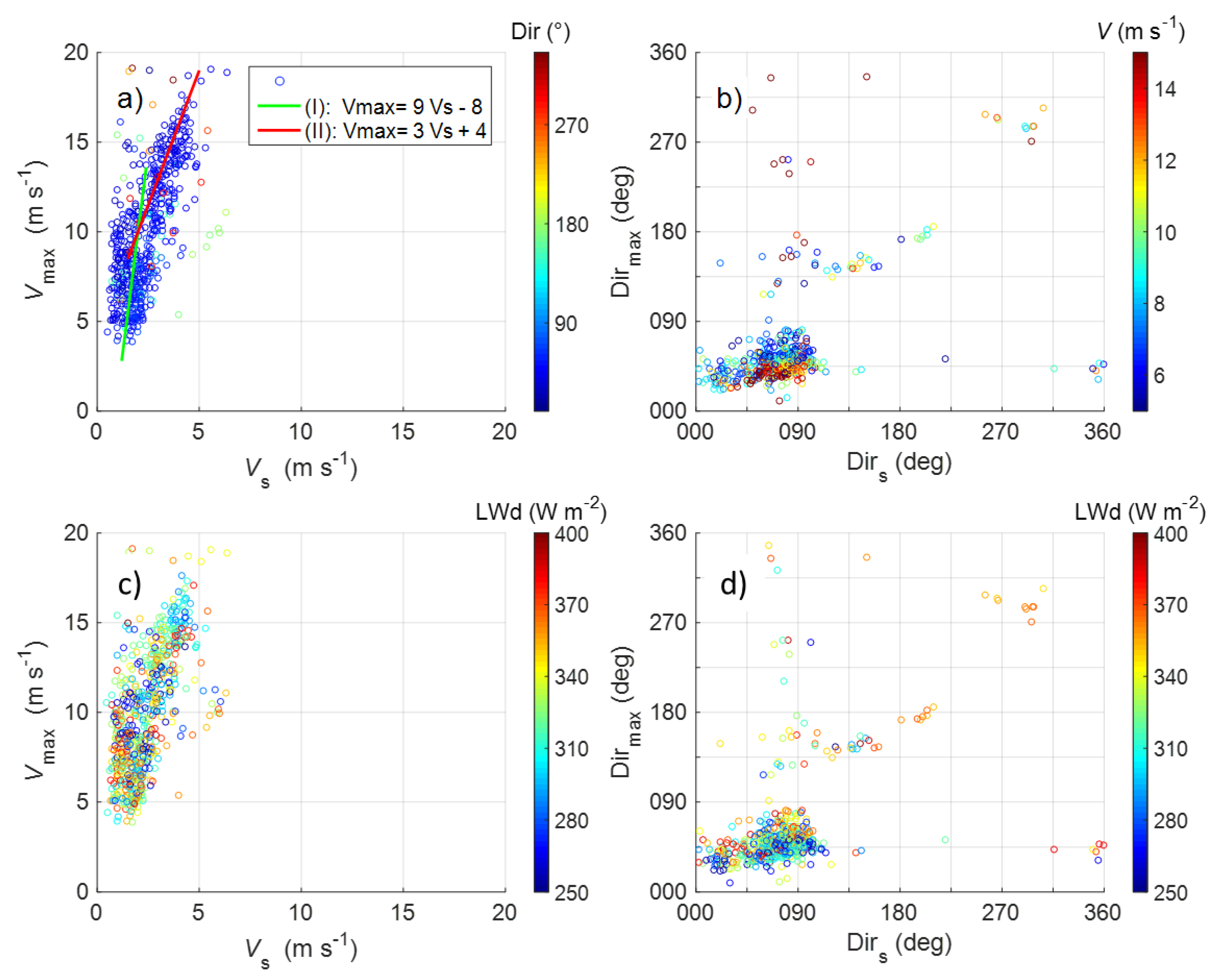
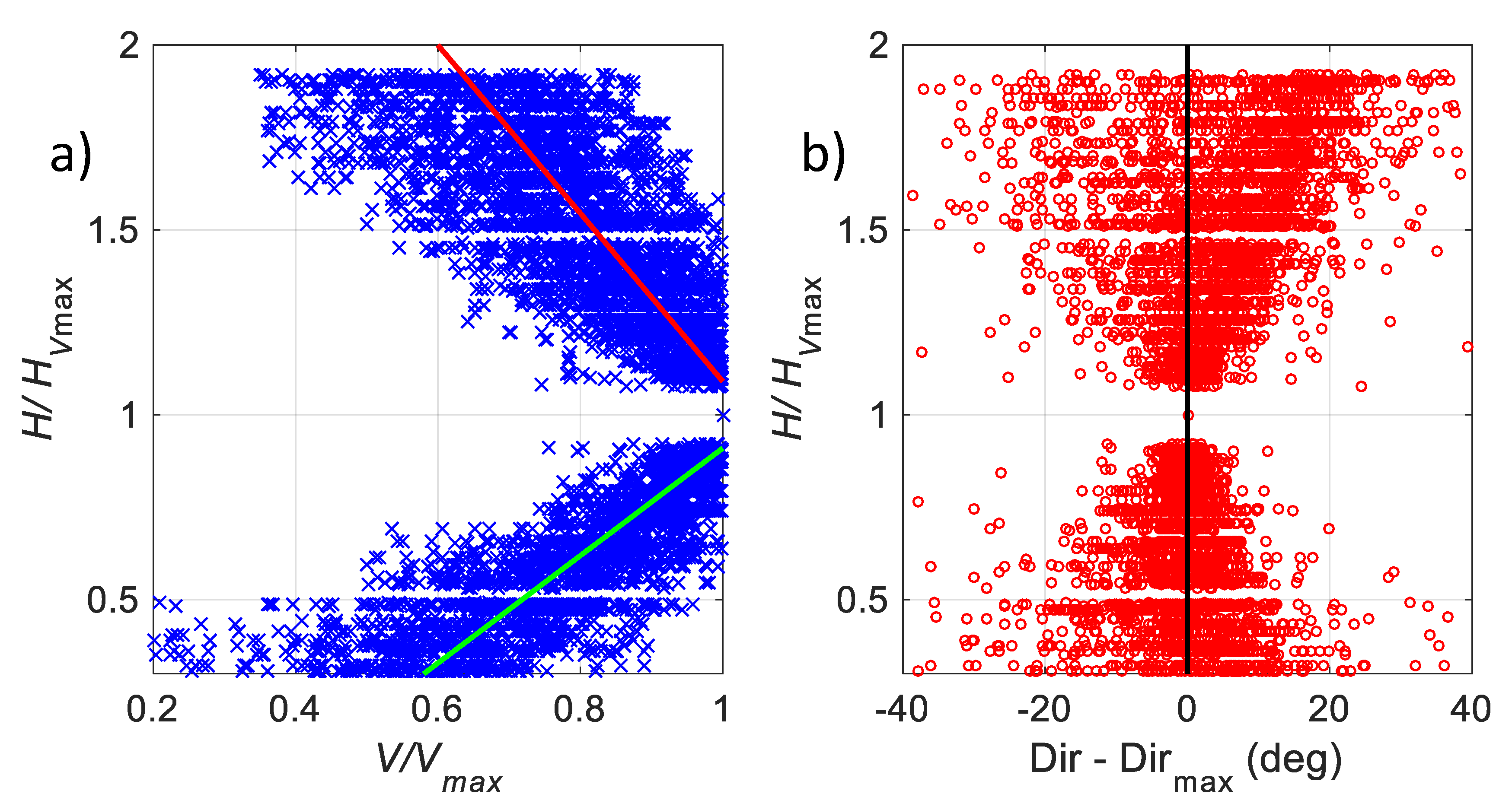
3.4.2. Statistics of LLJ Characteristics
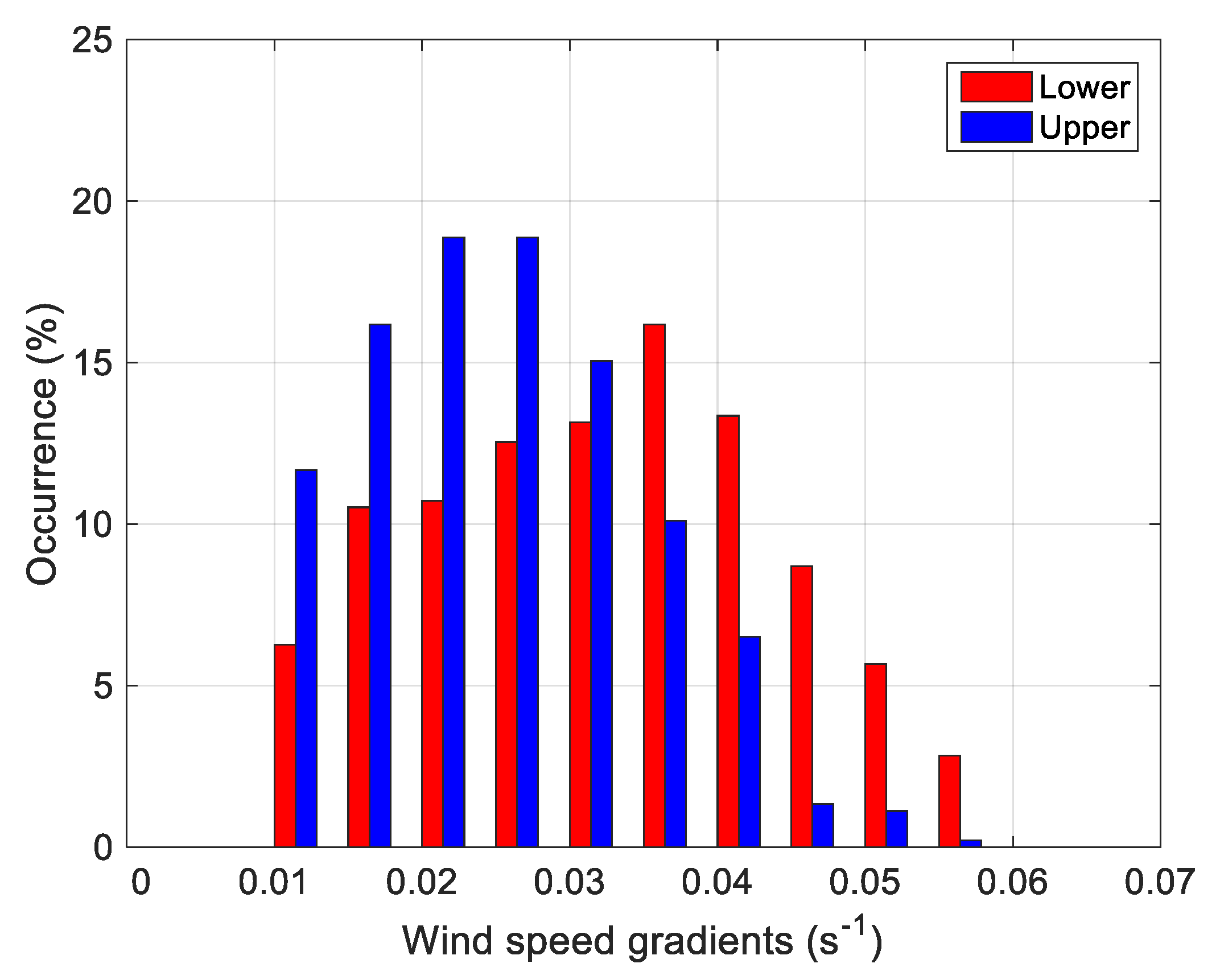
3.4.3. Wave-Like Structures in LLJs
4. Conclusions
- (i)
- The typical inland alternation of the nocturnal surface-based temperature inversion layer (with or without LLJ) and the convective-plume layer (capped by the inversion layer in the morning hours), as commonly experienced at inland sites;
- (ii)
- the presence of a surface-based temperature inversion layer during both night and day; and
- (iii)
- the presence of a convective-plume layer (either capped by the elevated inversion layer or without it) during both night and day.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sutton, O.G. Micrometeorology; Robert Krieger Pub. Co.: Huntington, NY, USA, 1977; p. 333. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.E. Sea Breeze and Local Winds; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 234. [Google Scholar]
- Emeis, S. Wind Energy Meteorology: Atmospheric Physics for Wind Power Generation; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wexler, R. Theory and observations of land and sea breezes. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1946, 27, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbs, D.J.; Physick, W.L. Sea-breeze observations and modelling: A review. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1992, 41, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, M. An investigation into the effect of the synoptic weather on sea breezes at Whitsand Bay, Cornwall. Weather 2011, 66, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y.; Arakawa, S.; Kimur, F.; Shirasaki, K.; Nagano, Y. Numerical study on the effects of mountains on the land and sea breeze circulation in the Kanto district. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 1981, 59, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cai, X.M.; Steyn, D.G. Modelling study of sea breezes in a complex coastal environment. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. Sea and lake breezes: A review of numerical studies. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2010, 137, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.J.; Dorling, S.R.; von Glasow, R.; Bacon, J. Modelling sea-breeze climatologies and interactions on coasts in the southern North Sea: Implications for offshore wind energy. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 141, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczak, J.M.; Gossard, E.E.; Neff, W.D.; Eberhard, W.L. Ground-based remote sensing of the atmospheric boundary layer: 25 years of progress. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 78, 321–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmis, C.G.; Papadopoulos, J.S.; Kalogiros, J.A.; Soilemes, A.T.; Asimakopoulos, N.D. Influence of background flow on evolution of Saronic Gulf sea breeze. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, D.; Ziomas, I.; Klemm, O.; Zerefos, C.S. Anatomy of the sea-breeze circulation in the Athens area under weak large-scale ambient winds. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2223–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melas, D.; Lavagnini, A.; Sempreviva, A.M. An investigation of the boundary layer dynamics of Sardinia island under sea-breeze conditions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prtnejak, M.T.; Grisogono, B. Sea/land breeze climatological characteristics along the northern Croatian Adriatic coast. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 90, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azorin-Molina, C.; Chen, D.A. Climatological study of the influence of synoptic-scale flows on sea breeze evolution in the Bay of Alicante (Spain). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 96, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.M.; Salvador, R.; Mantilla, E.; Artinano, B. Meteorology and photochemical air pollution in southern Europe: Experimental results from EC research projects. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cros, B.; Durand, P.; Cachier, H.; Drobinski, P.; Frejafon, E.; Kottmeier, C.; Perros, P.E.; Peuch, V.E.; Ponche, J.-L.; Robin, D.; et al. The ESCOMPTE program: An overview. Atmos. Res. 2004, 69, 241–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, M.M.; Estrela, M.J.; Sanz, M.J.; Mantilla, E.; Martín, M.; Pastor, F.; Salvador, R.; Vallejo, R.; Alonso, L.; Gangoiti, G.; et al. Climatic feedbacks and desertification: The Mediterranean model. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puygrenier, V.; Lohou, F.; Campistron, B.; Saïd, F.; Pigeon, G.; Bénech, B.; Serça, S. Investigation on the fine structure of sea breeze during ESCOMPTE experiment. Atmos. Res. 2005, 74, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estoque, M.A. The sea breeze as a function of the prevailing synoptic situation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1962, 19, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, B.W. Meso-Scale Atmospheric Circulations; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981; p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.L.; Zuckerberg, F.L.; Schaefer, J.T.; Rasch, G.E. Forecast problems: The meteorological and operational factors. In Mesoscale Meteorology and Forecasting; Ray, P.S., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1988; pp. 36–49. [Google Scholar]
- Jianmin, M. Numerical modeling of sea-breeze circulation over Cleveland Bay. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1997, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, C.V.; Venkatesan, R.; Somayaji, K.M.; Bagavath Singh, A. A numerical study of sea breeze circulation observed at a tropical site Kalpakkam on the east coast of India, under different synoptic flow situations. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 115, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petenko, I.; Mastrantonio, G.; Viola, A.; Argentini, S.; Coniglio, L.; Monti, P.; Leuzzi, G. Local circulation diurnal patterns and their relationship with large-scale flows in a coastal area of the Tyrrhenian Sea. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 139, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, A.P.; Petenko, I. Some aspects of the local atmospheric circulation in the Castelporziano Estate derived from sodar wind measurements. I. Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2015, 26, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colacino, M. Observations of a sea breeze event in the Rome area. Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Bilim. Ser. B 1982, 30, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantonio, G.; Viola, A.; Argentini, S.; Fiocco, G.; Giannini, L.; Rossini, L.; Abbate, G.; Ocone, R.; Casonato, M. Observations of sea breeze events in Rome and the surrounding area by a network of Doppler sodars. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1994, 71, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzzi, G.; Monti, P. Breeze analysis by mast and sodar measurements. Il Nuovo Cim. C. 1997, 20, 343–359. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, R.; Mastrantonio, G.; Argentini, S.; Santoleri, R.; Viola, A. A model-aided investigation of winter thermally driven circulation on the italian Tyrrhenian coast: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4777–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangia, C.; Martano, P.; Miglietta, M.M.; Morabito, A.; Tanzarella, A. Modelling local winds over the Salento peninsula. Meteorol. Appl. 2004, 11, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Calidonna, C.R.; Gullì, D.; Avolio, E.; Federico, S.; Feudo, T.L.; Sempreviva, A. One year of vertical wind profiles measurements at a Mediterranean coastal site of South Italy. Energy Procedia 2015, 76, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martano, P.; Mastrantonio, G.; Miglietta, M.; Moscatello, A.; Petenko, I.; Prodi, F.; Viola, A. Studio di Climatologia dei Sedimi Aeroportuali di Catania, Genova, Napoli, Reggio Calabria, Fiumicino, Malpensa, Olbia; Relazione Dell’attività Prevista Nella Lettera D’ordine, prot. GC/BDR/5007600/ 604 del 31 Dicembre 2004, ENAV O.d.A. 200401526; ISAC-CNR: Rome, Italy, 2005; p. 493. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Mastrantonio, G.; Viola, A.; Petenko, I.; Argentini, S.; Conidi, A.; Coniglio, L. Caratterizzazione della Circolazione Locale Mediante Analisi di Dati di Vento; Il Sistema Ambientale della Tenuta Presidenziale di Castelporziano, II Serie; “Scritti e Documenti” XXXVII; Accademia Nazionale delle Scienze detta dei Quaranta: Roma, Italy, 2006; pp. 13–49. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, W.D. Climatology of the low level jet. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, K.A.; Pardoe, C.W. Structure of low-level jet streams ahead of mid-latitude cold fronts. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1973, 99, 619–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, E.E.; Hooke, W.H. Waves in the Atmosphere; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Banta, R.M.; Newsom, R.K.; Lundquist, J.K.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Coulter, R.L.; Mahrt, L. Nocturnal low-level jet characteristics over Kansas during CASES-99. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2002, 105, 221–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Pichugina, Y.L.; Newsom, R.K. Relationship between low-level jet properties and turbulence kinetic energy in the nocturnal stable boundary layer. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M.; Mahrt, L.; Vickers, D.; Sun, J.; Balsley, B.B.; Pichugina, Y.; Williams, E.J. The very stable boundary layer on nights with weak low-level jets. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3068–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banta, R.M. Stable-boundary-layer regimes from the perspective of the low-level jet. Acta Geophys. 2008, 56, 58–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyulyukin, V.; Kouznetsov, R.; Kallistratova, M. The composite shape and structure of braid patterns in Kelvin-Helmholtz billows observed with a sodar. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 2704–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyulyukin, V.S.; Kallistratova, M.A.; Kouznetsov, R.D.; Kuznetsov, D.D.; Chunchuzov, I.P.; Chirokova, G.Y. Internal gravity-shear waves in the atmospheric boundary layer by the acoustic remote sensing data. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2015, 51, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallistratova, M.A.; Petenko, I.V.; Kouznetsov, R.D.; Kulichkov, S.N.; Chkhetiani, O.G.; Chunchusov, I.P. Sodar sounding of the atmospheric boundary layer: Review of studies at the Obukhov Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2018, 54, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorovich, E.; Gibbs, J.A.; Shapiro, A. Numerical study of nocturnal low-level lets over gently sloping terrain. J. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 74, 2813–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muschinski, A. Possible effect of Kelvin-Helmholtz instability on VHF radar observations of the mean vertical wind. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossard, E.E. Radar research on the atmospheric boundary layer. In Radar in Meteorology; Atlas, D., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 477–527. [Google Scholar]
- Gage, K.S. Radar observations of the free atmosphere: Structure and dynamics. In Radar in Meteorology; Atlas, D., Ed.; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 534–565. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, F.D.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Hines, J.R. A new frequency-modulated continuous wave radar for studying planetary boundary layer morphology. Radio Sci. 1995, 30, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, R.; Lyulyukin, V. Kelvin-Helmholtz billows at summertime katabatic flows in Antarctica. In Proceedings of the 17th ISARS, Aukland, New Zealand, 6–9 June 2014. Session 15. [Google Scholar]
- Lyulyukin, V.; Kallistratova, M.; Zaitseva, D.; Kuznetsov, D.; Artamonov, A.; Repina, I.; Petenko, I.; Kouznetsov, R.; Pashkin, A. Sodar observation of the ABL structure and waves over the Black Sea offshore site. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petenko, I.; Bucci, S.; Casasanta, G.; Cozzolino, M.; Kallistratova, M.; Sozzi, R.; Argentini, S. Low-level jets, turbulence and waves in the Tyrrhenian coastal zone as shown by sodar. In Proceedings of the 18th European Meteorological Society Annual Meeting, Budapest, Hungary, 3–7 September 2018; Available online: https://presentations.copernicus.org/EMS2018-453_presentation.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Simpson, J.E.; Britter, R.E. A laboratory model of an atmospheric mesofront. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 146, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, R.L.; Kurzeja, R.J. An observational and numerical study of the nocturnal sea-breeze. Part I: Structure and circulation. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 1577–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, T.W.; Tsuda, T.; Hashiguchi, H.; Fukao, S.R. Tropical sea-breeze circulation and related atmospheric phenomena observed with L-band boundary layer radar in Indonesia. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 78, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lapworth, A. Observations of atmospheric density currents using a tethered balloon-borne turbulence probe system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 126, 2811–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, R.S.; Keith, G.J. Occurrence of Kelvin–Helmholtz billows in sea breeze circulations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2007, 122, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Kawamura, T.; Ueda, H. A numerical study on sea/land breezes as a gravity current: Kelvin–Helmholtz billows and inland penetration of the sea-breeze front. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 1649–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Kawamura, T.; Ueda, H. A numerical study of nocturnal sea/land breezes: Prefrontal gravity waves in the compensating flow and inland penetration of the sea-breeze cutoff vortex. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Ogawa, S.; Iwasaki, T.; Wang, Z. A numerical study on the nocturnal frontogenesis of the sea breeze front. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 82, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantonio, G.; Fiocco, G. Accuracy of wind velocity determinations with Doppler sodar. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1982, 21, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Mastrantonio, G.; Viola, A.; Argentini, S. Mean vertical motions in the PBL measured by Doppler sodar: Accuracy, ambiguities. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1532–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.H.; Hall, F.F., Jr. Advances in atmospheric acoustics. Rev. Geophys. 1978, 16, 47–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarskii, V.I. The Effects of the Turbulent Atmosphere on Wave Propagation; Israel Program for Scientific Translations: Jerusalem, Israel, 1971; p. 472. [Google Scholar]
- Kallistratova, M.A. Experimental investigation of sound wave scattering in the atmosphere. Trudy Akad. Nauk SSSR Inst. Fiz. Atmos. 1962, 4, 203–256. [Google Scholar]
- Obukhov, A.M. Structure of the temperature field in a turbulent flow. Izv. Acad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Geogr. Geofiz. 1949, 13, 58–69. [Google Scholar]
- Coulter, R.L.; Wesely, M.L. Estimates of surface heat flux from sodar and laser scintillation measurements in the unstable boundary layer. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1980, 19, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Mousley, T.J.; Helmis, C.J.; Lalas, D.P.; Gaynor, J.E. Quantitative low-level acoustic sounding and comparison with direct measurements. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1983, 27, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, S.D.; Gur’yanov, A.E.; Kallistratova, M.A.; Petenko, I.V.; Singal, S.P.; Pahwa, D.R.; Gera, B.S. Simple method of calibration of conventional sodar antenna system. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.; Massman, W.; Law, B. Handbook of Micrometeorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kohsiek, W. Measuring CT2, CQ2 and CTQ in the unstable surface layer and the relations to the vertical fluxes of heat and moisture. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1982, 24, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Nertherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Carta, J.A.; Ramirez, P.; Velasquez, S. A review of wind speed probability distributions used in wind energy analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 933–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrich, F.; Kouznetsov, R.D.; Leps, J.P.; Lüdi, A.; Meijninger, W.M.L.; Weisensee, U. Structure parameters for temperature and humidity from simultaneous eddy-covariance and scintillometer measurements. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.R.; Kouznetsov, R.D.; Gierens, R.; Nordbo, A.; Järvi, L.; Kallistratova, M.A.; Kukkonen, J. On the temperature structure parameter and sensible heat flux over Helsinki from sonic anemometry and scintillometry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petenko, I.V.; Bedulin, A.N.; Shurygin, Y.A. Sodar observations of the ABL in ASTEX-91. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 81, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Türk, M. Frequency distributions of the mixing height over an urban area from SODAR data. Meteorol. Z. 2004, 13, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Civil Aviation Organization. Manual on Low-Level Wind Shear; Doc 9817, AN/449; International Civil Aviation Organization: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2005. [Google Scholar]


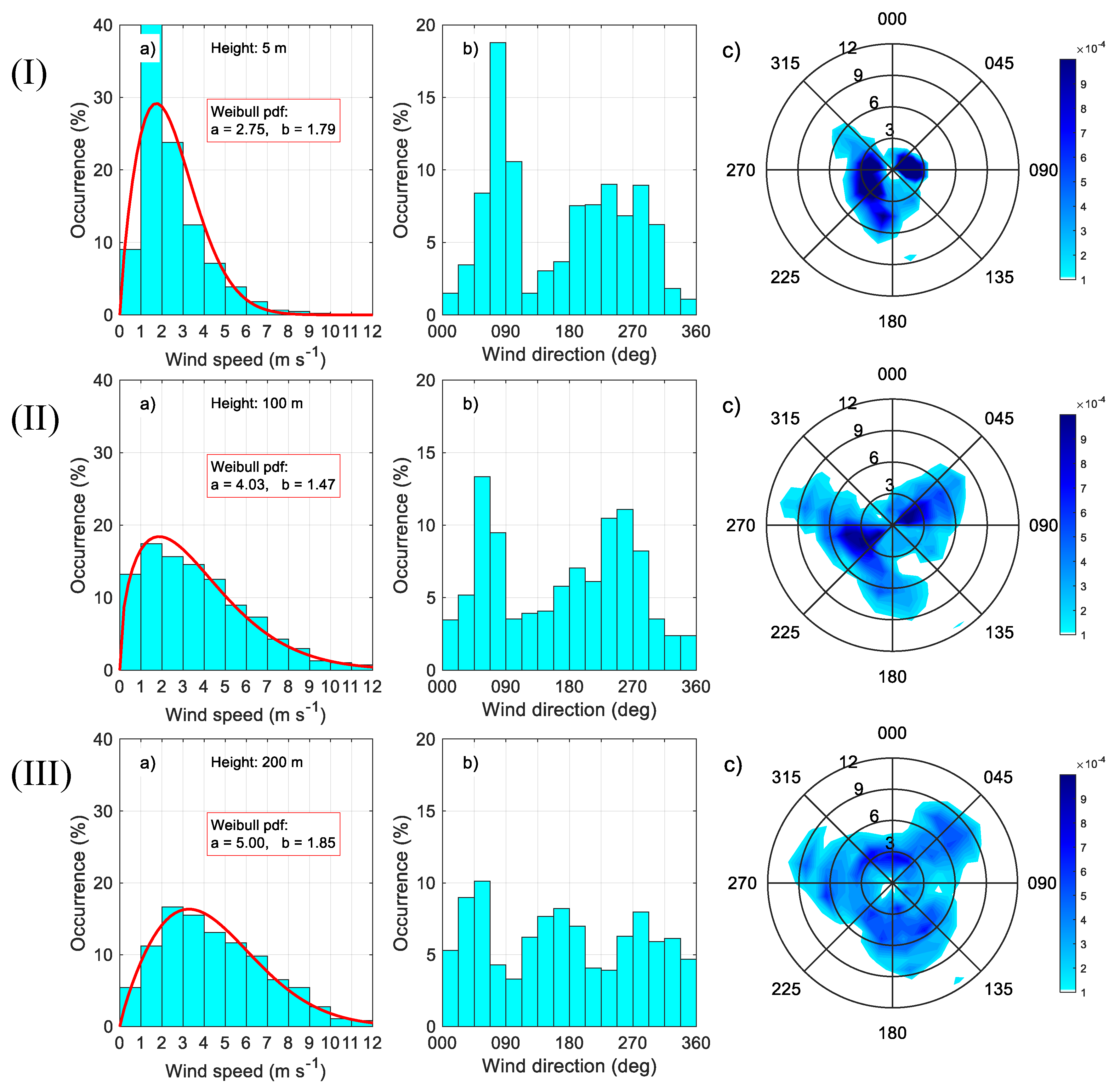
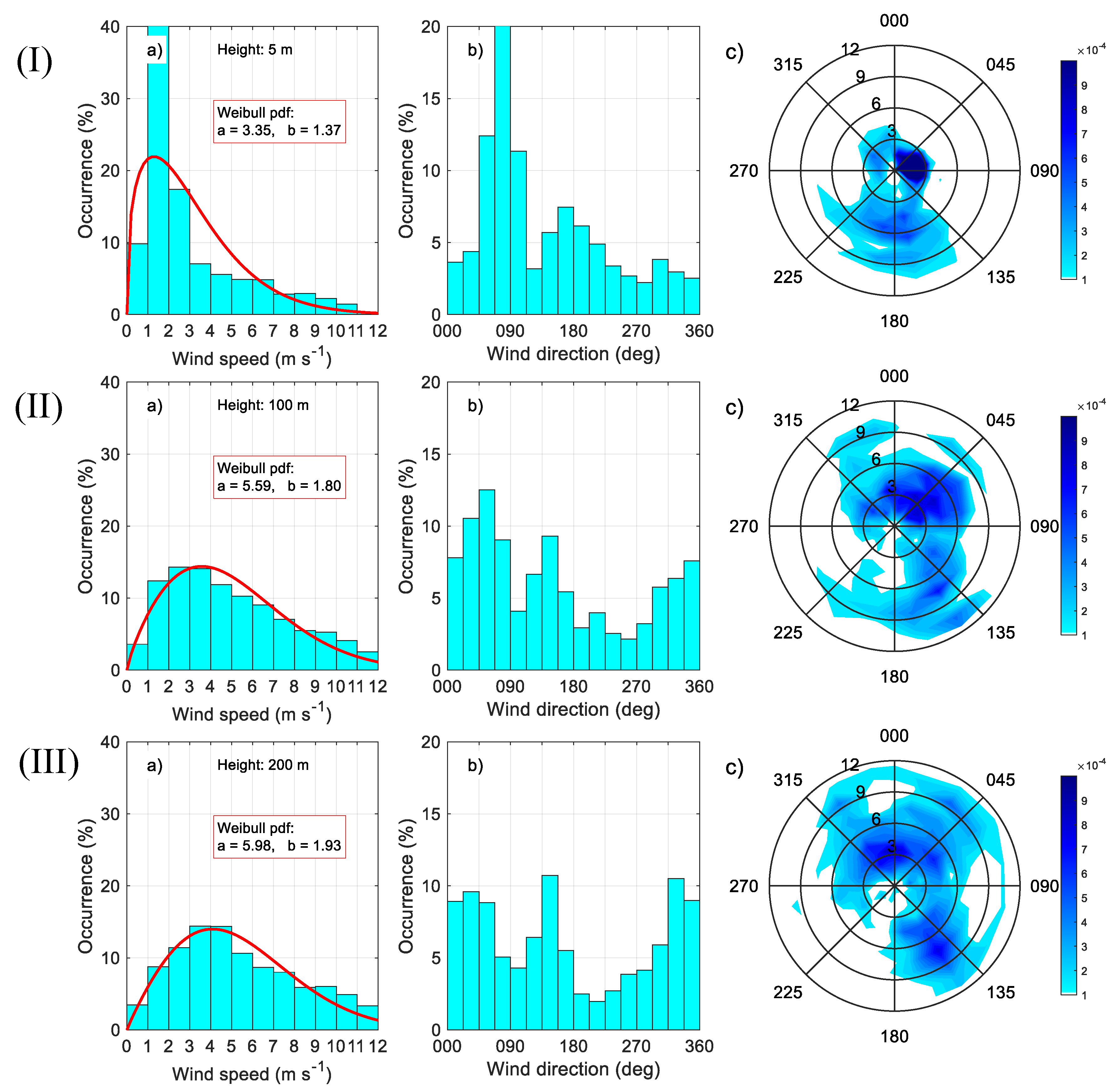
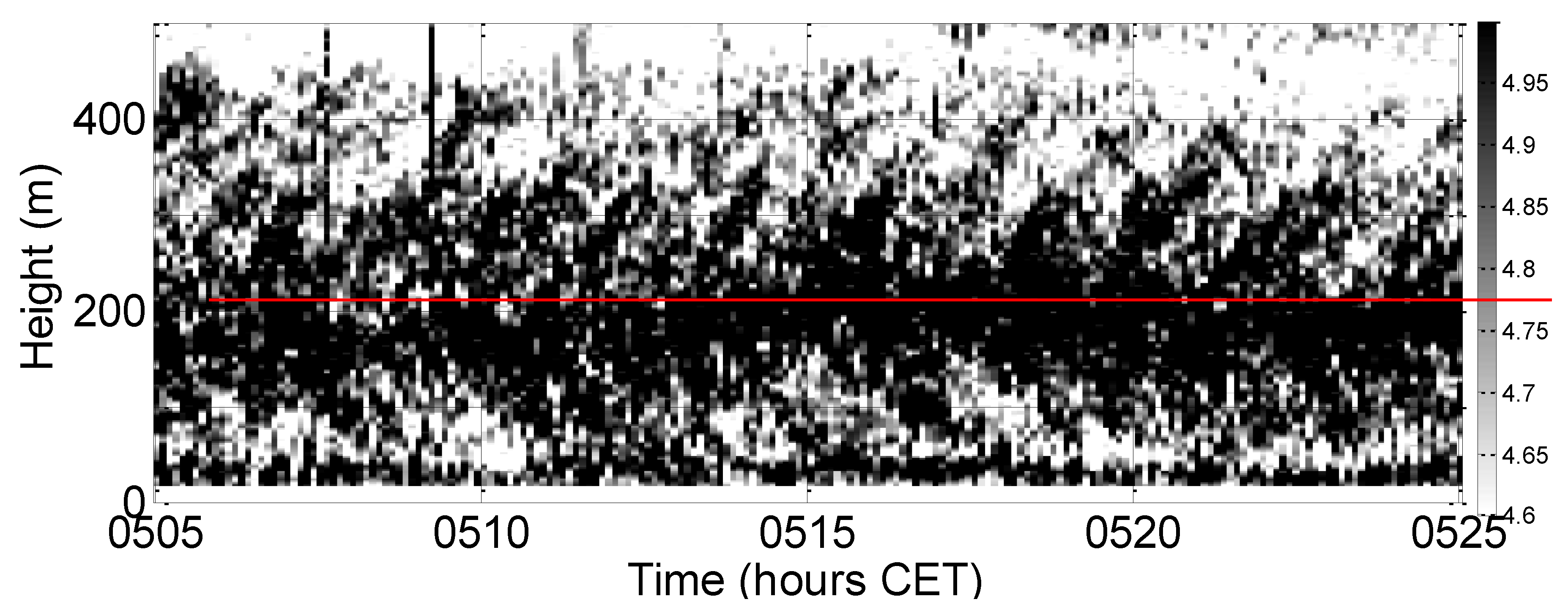
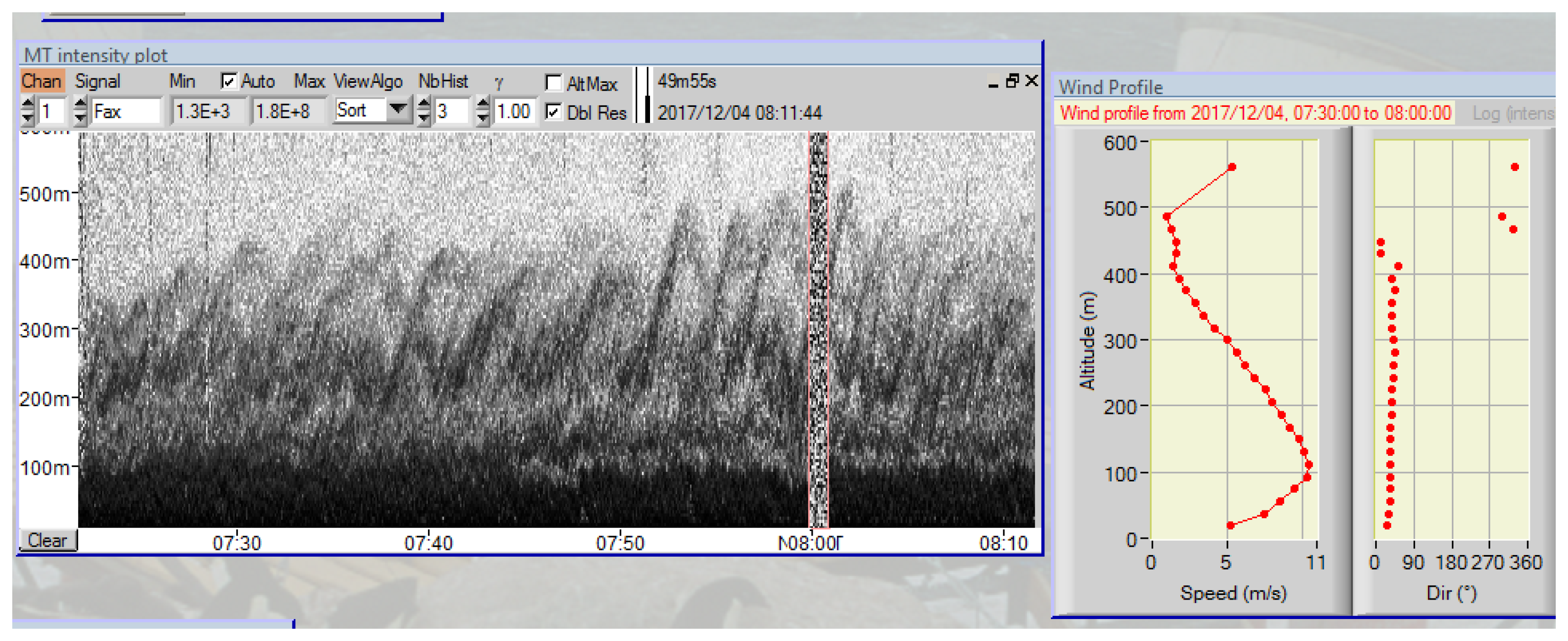
| Instrument | Type | Accuracy | Sampling Period (s) | Heights (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic anemometer | Metek USA-1 | Wind velocity 0.05 m s−1 Temperature 0.01 °C | 0.1 | 5.2 |
| Thermohygrometer | Vaisala HMP155 | T: 0.15 °C; RH: 1.5% | 60 | 1.8 |
| Net radiometer | Kipp & Zonen CNR1 | Daily sums: 10% | 60 | 1.6 |
| Barometer | Vaisala PTB110 | 0.3 hPa | 60 | 1.0 |
| Rain gage | Lastem C100A | 0.2 mm | 60 | 1.6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petenko, I.; Casasanta, G.; Bucci, S.; Kallistratova, M.; Sozzi, R.; Argentini, S. Turbulence, Low-Level Jets, and Waves in the Tyrrhenian Coastal Zone as Shown by Sodar. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010028
Petenko I, Casasanta G, Bucci S, Kallistratova M, Sozzi R, Argentini S. Turbulence, Low-Level Jets, and Waves in the Tyrrhenian Coastal Zone as Shown by Sodar. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010028
Chicago/Turabian StylePetenko, Igor, Giampietro Casasanta, Simone Bucci, Margarita Kallistratova, Roberto Sozzi, and Stefania Argentini. 2020. "Turbulence, Low-Level Jets, and Waves in the Tyrrhenian Coastal Zone as Shown by Sodar" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010028
APA StylePetenko, I., Casasanta, G., Bucci, S., Kallistratova, M., Sozzi, R., & Argentini, S. (2020). Turbulence, Low-Level Jets, and Waves in the Tyrrhenian Coastal Zone as Shown by Sodar. Atmosphere, 11(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010028








