Abstract
Sunshine duration is an important indicator of the amount of solar radiation received in a region and an important input parameter for the study of atmospheric energy balance, climate change, ecosystem evolution, and social sustainability. Currently, extrapolation and interpolation of data from meteorological stations are the most common methods used to calculate sunshine duration on a regional scale. However, it is difficult to obtain high precision sunshine duration in areas lacking ground observation or where sunshine duration is highly heterogeneous on the ground. In this paper, a new method is proposed to estimate sunshine duration with hourly total cloud amount (CTA) data from sunrise to sunset derived from the Fengyun-2G geostationary meteorological satellite (FY-2G). This method constructs a new index known as daytime mean total cloud coverage amount and provides quadratic equations relating daytime mean total cloud coverage amount to relative sunshine duration in different seasons. The method was validated with ground observation data for 2016 from 18 meteorological stations in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Qinghai Province, China. For individual stations, the coefficient of determination (R2) between estimated and measured sunshine was at least 0.894, the RMSE (root mean square error) was 0.977 h/day or less, the MAE (mean absolute error) was 0.824 h/day or less, the RE (relative error) was 0.150 or lower, and the value of d was 0.963 or greater, which validated that the proposed method can effectively predict daily sunshine duration. These equations can also provide higher precision estimates of regional-scale sunshine duration. This was demonstrated by comparing, for the entire study region, the spatial distribution of sunshine duration estimated from season-based equations with results from three different interpolation methods based on ground observations. Overall, the study confirms that total cloud amount measures from a geostationary satellite can be used to successfully estimate sunshine duration.
1. Introduction
Sunshine duration refers to the length of time the sun is illuminating the earth’s surface. More formally, it is defined as the sum of the time periods in which direct solar irradiance reaches or exceeds 120 W/m2. It is an important indicator of the amount of solar radiation received in a region [1] and also an important input parameter in many applications, such as estimation of global solar radiation [2], atmospheric energy balance [2], the thermal loads on buildings, yield planning in agriculture, ecosystem process models, hydrological models, biophysical models [3], and determination of the health of humans and animals [4]. Consequently, the accurate estimation of sunshine duration is important, especially for climate change, ecosystems evolution, and social sustainability.
Researchers began ground observation work to measure sunshine duration more than a century ago [5], and almost all countries/regions are still using field observations. The main measurement methods are direct measurement with sunshine duration recorders, the pyrheliometric method using direct irradiance from a pyrheliometer, and pyranometric algorithms using the global irradiance from a pyranometer [6,7,8]. However, these methods can only obtain sunshine duration at a site representing a limited area. When used to obtain regional sunshine duration, multiple sets of measurement equipment and higher frequency observations are required, which are time-consuming and labor-intensive and, therefore, expensive [9]. Consequently, extrapolation and interpolation methods are often used to calculate regional sunshine duration based on data from a limited number of field sites [10,11,12]. However, the accuracy of the estimates from these methods is dependent upon the number and spatial distribution of the sites. Since existing sites are generally not evenly distributed spatially, the values of sunshine duration obtained from these methods can have high degrees of spatial uncertainty [13], particularly in regions where there are few or no ground observations. This is especially true for developing countries where measurement networks for sunshine duration are often sparse due to various geographic and financial limitations [14].
Several alternative methods have been proposed to estimate sunshine duration on a regional scale. These include the sunshine duration percentage empirical method, relative sunshine duration statistical models, and remote sensing empirical models. Sunshine duration percentage methods include the astronomical sunshine percentage method and the geographic sunshine percentage method [9,10,15,16,17], but both overly rely on the accuracy of the assimilation of radiation data. Relative sunshine duration statistical models derive estimates from multiple variables including elevation from digital elevation models (DEMs), the amount of clouds observed at ground stations, clearness indices, air pollution indices (API), precipitation, wind speed, and surface incoming direct radiation [6,10,13,18,19]. However, these do not take into account changes in the attributes of the clouds. Instead, they simply build an artificial neural network model or statistical equation relating sunshine duration to these variables [10,18,19,20], and are more often used to estimate monthly rather than daily sunshine duration.
Remote sensing empirical models estimate sunshine duration directly or indirectly by establishing the relationship between sunshine duration, or relative sunshine duration, and cloud attributes. Cloud attributes mainly include cloud type and cloud cover. Cloud type-based sunshine duration estimation usually constructs an empirical equation directly between sunshine duration and a combination of different cloud types [9,13,19], or establishes an empirical relationship between relative sunshine hours and different cloud types [21]. However, the same cloud type in a region may differ in thickness, coverage, and amount, which all affect sunshine duration. In addition, there is no fixed relationship between relative sunshine duration and different cloud types in different regions at different times [21]. Therefore, it is difficult to estimate sunshine duration accurately based on these methods. Cloud cover-based sunshine duration estimation is mainly based on a polar orbiting satellite or geostationary satellite data using parameters such as cloud pixel reflectance, solar zenith angle, solar elevation, and sky transmission factors. These are used to estimate a daily mean cloud cover index and an empirical equation is then constructed between this index and sunshine duration data from ground observation to estimate sunshine duration at the regional scale [14,22,23,24,25,26]. Unfortunately, each satellite data source has significant limitations. The limited transit times of the polar orbiting satellites do not generate a representative daily mean cloud cover index. Although geostationary meteorological satellites have more daily transit data and can provide information about cloud cover per hour, or even shorter time intervals, the daily mean cloud cover index generated from the data is not the key parameter affecting sunshine duration. The fundamental determinant of sunshine duration is the total amount of cloud cover between sunrise and sunset [5,9,13].
This paper investigates a new method to derive sunshine duration from geostationary meteorological satellite data on temporal variation in the total amount of cloud coverage. The method analyses the relationship between the temporal and spatial variation in total cloud coverage amount between sunrise and sunset derived from China’s Fengyun-2G geostationary meteorological satellite and relative sunshine duration calculated from ground station observations. This is used to build a new index of daytime mean total cloud coverage amount as a means for deriving daily sunshine duration at the regional scale. The estimated sunshine duration values from the proposed method are validated with independent ground observation data for 2016 from meteorological stations in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Western China, and the spatial distribution of these satellite-derived sunshine duration estimates is compared with the results of different interpolation methods applied to ground station data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Datasets
The Three-River Headwaters Region (TRHR) comprises the headwaters of the Yellow, Yangtze, and Lancang rivers in the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of southern Qinghai Province, China, from 31°39′ N to 36°16′ N and 89°24′ E to 102°23′ E (Figure 1). It is known as the “Asia water tower” due to the multiple large rivers originating in the region [27,28]. The total land area is over 350,000 km2 and elevations range from 3450 m to 6621 m with an average of more than 4000 m. The area is characterized by a cold and dry climate with average annual temperatures below 10 °C and annual precipitation varying between 262.2 mm·year−1 and 772.8 mm·year−1 from the west to the southeast. The main vegetation type is alpine grassland, including meadow and steppe [29]. Natural ecosystems in the region are relatively fragile and highly sensitive to climate change [30], which causes serious disturbances to the structure and function of these ecosystems and poses a threat to ecosystem security [31]. The high heterogeneity of the Three-River Headwaters Region provides a rigorous test of the method proposed in this paper as well as preliminary results for future climate change research in the region.
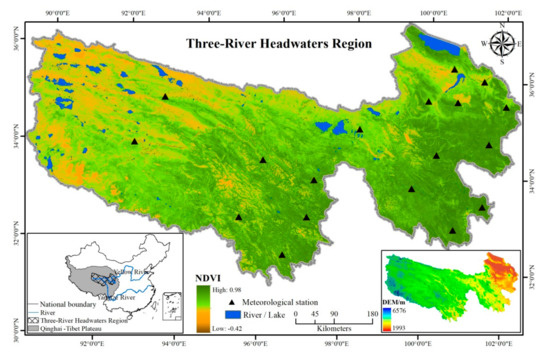
Figure 1.
Location of the study area including 18 meteorological stations and digital elevation model data (DEM).
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Data and Pre-Processing Methods
Sunshine Duration Observation Data
Data from 18 meteorological stations covering the Three-River Headwaters Region were collected from the Chinese National Meteorological Bureau (Figure 1 and Table 1). The sites have different physiographic characteristics (mountains and plains), with generally fewer stations in the central and western regions and more in the east. A standard six-element meteorological observation system is installed at each station and the observation data includes daily sunshine duration, daily maximum and minimum temperature, daily average air pressure, daily average air humidity, daily average wind speed, and daily rainfall. The sunshine duration data based on the photoelectric digital sunshine meter used in the study were from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2018 and can be downloaded from the website: http://data.cma.cn/en. There is no missing measurement of sunshine duration data at all stations and quality control of the data was performed by the Chinese National Meteorological Information Centre [9].

Table 1.
Station names, numbers, and coordinates.
Geostationary Meteorological Satellite Total Cloud Amount Data
The geostationary meteorological satellite data used in this paper is from the Fengyun 2G geostationary meteorological satellite (FY-2G), which is the fifth operational vehicle of the first-generation geostationary meteorological satellite system operated by the Chinese National Satellite Meteorological Centre. It was launched on 31 December 2014 and is located above the equator at 105° E at an altitude of 35,800 km. Its purpose is to obtain visible light cloud data during the daytime, day and night infrared clouds, and water and gas distribution information. Stretched-Visible and Infrared Spin-Scan Radiometer (S-VISSR) and Space Environmental Monitors (SEM) are the two main payloads on FY-2G. The visible and infrared spin-scan radiometers have a visible channel with a resolution of 1.25 km and four infrared channels with a resolution of 5 km. The total cloud amount data is one of the products of the Stretched-Visible and Infrared Spin-Scan Radiometer (S-VISSR) [32].
The hourly total cloud amount product (CTA) for the same time period as the ground sunshine data was downloaded from the Chinese National Satellite Meteorological Centre website (http://satellite.nsmc.org.cn/PortalSite/Default.aspx?currentculture=en-US). Quality control of the data was also performed by the Chinese National Satellite Meteorological Centre. Since the downloaded data is in a flat image file format, a companion geographic lookup table (GLT) file was also downloaded and used to place the cloud data in a suitable geographic projection for the target area [32].
The cloud total amount data is based on the radiation transfer equation. The irradiation quantity received on the satellite under parallel atmospheric conditions can be expressed as:
where Ac is the total cloud amount, Iclr is the irradiation quantity of the clear-sky pixel, and Icld is the irradiation quantity of the complete cloud-covered pixel. From the above equation, the total cloud amount can be obtained by the equation below [33].
In fact, the emissivity of the cloud has been considered in the process of calculating the cloud total amount based on Equation (2), and retains the spatial resolution of the original observation pixel. At the same time, the irradiation quantity can be converted to reflectance for visible channels and to bright temperature for the infrared channels [33]. Therefore, the cloud total amount of the pixel at a given time is actually similar to the calculation of the cloud cover index for a pixel at a given time in the radiation equation Cano proposed [22].
2.2.2. Modeling Sunshine Duration
Estimation of Sunshine Duration
A relationship certainly exists between relative sunshine duration and both the total cloud amount from satellite data, or cloud cover observed from meteorological stations. However, the accuracy of sunshine duration depends on the total cloud amount or cloud cover between sunrise and sunset rather than on average total cloud amount or average cloud cover during the day and night. Since the FY-2G total cloud amount data is similar to the calculation of the cloud cover index commonly used by other researchers, if the relationship between relative sunshine duration and FY-2G total cloud amount data can be established, then actual sunshine duration can be calculated based on the maximum possible sunshine duration.
Assume that the following equation describes the relationship between relative sunshine hours and the total cloud amount between sunrise and sunset.
where n is sunshine duration, N is maximum possible sunshine duration, and f(fccom) is a function representing total cloud coverage amount between sunrise and sunset.
Maximum possible sunshine duration depends on the latitude of the site and the solar declination angle, and can be computed by the equation below [34].
where ψ is the latitude of location in the range −90 ≤ ψ ≤ +90 and δ is the solar declination given by the equation below.
where n is the number of days in the year starting from 1 January.
Therefore, if the functional equation (f(fccom)) is determined, then Equations (3)–(5) can be combined to estimate the sunshine duration on a regional scale based on the FY-2G total cloud amount data.
Function for Total Cloud Amount between Sunrise and Sunset (f(fccom))
As mentioned in the previous section, sunshine duration is fundamentally dependent upon the total cloud coverage amount between sunrise and sunset. We propose a new index and daytime mean total cloud coverage amount (fccom) to characterize the magnitude of the effect of daytime total cloud amounts on sunshine duration. Each pixel of daytime mean total cloud coverage amount (fccom) can be calculated from the following relation.
where fi is the pixel value of FY-2G hourly total cloud amount from sunrise to sunset, j and k are the times of sunrise and sunset, respectively, and i is a time series that ranges between sunrise and sunset at the local time. The sunrise and sunset times can be calculated from the geographic latitude and earth decline based on the day of the year. The value of daytime mean total cloud coverage amount is between 0 and 1.
Accordingly, using Equation (6), the daytime mean total cloud coverage amount (fccom) at each meteorological station can be estimated based on the FY-2G satellite hourly total cloud amount data from sunrise to sunset. Correspondingly, relative sunshine duration can be calculated using maximum possible sunshine duration (Equations (4) and (5)) and measured sunshine duration data at each meteorological station.
By fitting the data between estimated daytime mean total cloud coverage amount (fccom) and calculated relative sunshine duration at each meteorological station, a function for total cloud amount between sunrise and sunset (f(fccom)) can be constructed, which is shown below.
where a1, a2, a3, am, b1, b2, b3, bm, and c are regression coefficients to be determined. A generic polynomial form is used to allow for a non-linear relationship.
2.2.3. Model Performance Assessment
Many statistical methods, including the coefficient of determination (R2), mean absolute error (MAE), root mean square error (RMSE), relative error (RE), and modified index of agreement (d) were proposed by Willmott [35], are chosen to assess proposed sunshine duration method performance [36] to show the agreement between the measured value and estimated value. These parameters are defined as follows [35,36].
In the above equations, Oi is the actual measurement, Pi is its estimate, is the mean measurement, is the mean of the estimates, and n is the sample size. Colaizzi et al. [37] and Liu et al. [38] suggest that a model performs well if the MAE (Equation (9)) is less than 50% of the measured standard deviation, and there are few outliers when the RMSE (Equation (10)) is not greater than 50% of the MAE. Additionally, the higher the value of d is (Equation (12)), the better the model performance is [37].
3. Results
Figure 2 gives the statistics for the relationships between the daily daytime mean total cloud coverage amount ((fccom), from the satellite data) and measured relative sunshine duration (from ground observations) for all 18 meteorological stations in the study region from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2018. Since a nonlinear relationship appears to exist between daytime mean total cloud coverage amount and relative sunshine duration, which is a quadratic model rather than a linear model that better fits the data. The coefficients a1, a2, a3, am, b1, b2, b3, bm, and c for Equation (7) were obtained by the least square method using Statistical Product and Service Solutions (SPSS) and Origin statistical analysis tools. The optimal fit coefficients over the entire Three-River Headwaters Region are shown in the equation below, which rewrites Equation (7) in a specified format.
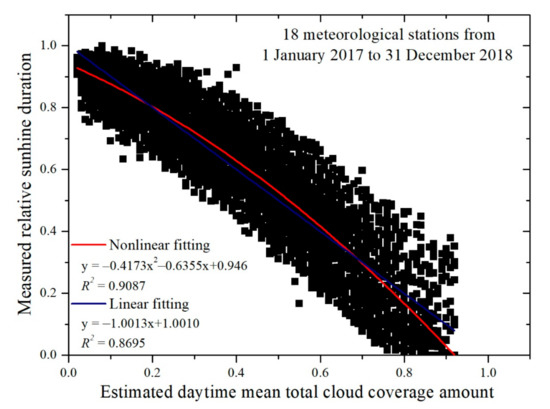
Figure 2.
Relationship between estimated daytime mean total cloud coverage amount and measured relative sunshine duration for 18 meteorological stations from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2018.
Fitting the data over annual periods, as in Figure 2, may obscure likely seasonal variation in cloud coverage and its relation to sunshine. Consequently, Figure 3 shows the relationship between daytime mean total cloud coverage amount (fccom) and relative sunshine duration for each of the four major seasons (spring, summer, autumn, and winter) for all 18 meteorological stations for the years 2017 and 2018. As with the annual data, a nonlinear relationship is evident, especially in the spring and the winter. Consequently, quadratic models rather than linear models better fit the data. Based on the least square method using SPSS and Origin statistical analysis tools, the optimal fit coefficients (a1, a2, a3, am, b1, b2, b3, bm, and c) for Equation (7) are shown below for each season.
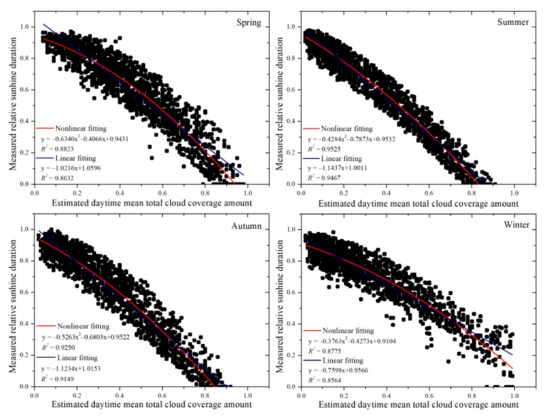
Figure 3.
Relationship between daytime mean total cloud coverage amount and relative sunshine duration for 18 meteorological stations by season for 2017 and 2018.
By combining Equations (6) and (13) for the annual data for 2017 and 2018, or Equations (6) and (14) for the seasonal data for these years, relative sunshine duration can now be estimated for other years from the daily geostationary meteorological satellite hourly total cloud amount data. Accordingly, Figure 4 and Table 2 relate estimated daily relative sunshine duration (from the satellite data) and measured daily relative sunshine duration (from ground data) for 1 January through 31 December, 2016 at the 18 meteorological stations in the Three-River Headwaters Region, using both the annual and the seasonal data fitting equations. The coefficients of determination (R2) from Equations (13) and (14) were both greater than 0.880 indicating a strong correlation between estimated and measured daily relative sunshine duration. In addition, the difference between the RMSE and MAE from Equations (13) and (14) were less than 30% of the MAE, which shows there are very few outliers in the estimated daily relative sunshine duration.
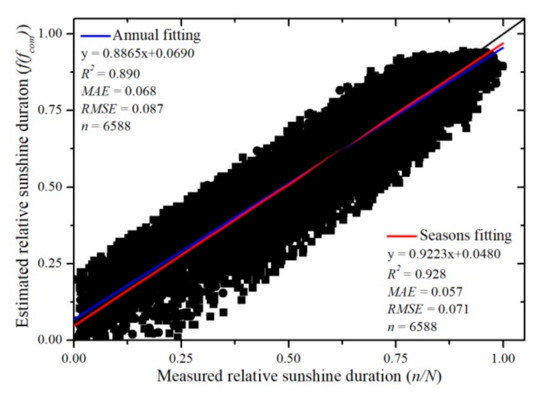
Figure 4.
Comparison of estimated daily relative sunshine duration by Equations (13) and (14), and measured daily relative sunshine duration at the 18 meteorological stations for 2016.

Table 2.
Statistics for the estimation of relative sunshine duration at 18 meteorological stations daily from 1 January to 31 December, 2016 over the Three-River Headwaters region.
In addition, the seasonal equations provide more accurate predictions than the annual equation. In Figure 4 and Table 2, which pool observations for the entire year, the d values using Equation (14) are larger than the value based on Equation (13). The RE measures are less than the value based on Equation (13), which indicates the relative sunshine duration calculated using the seasonal Equations (14) are better than those calculated using the annual Equation (13). Using these same measures, Figure 5 and Table 3 also suggest the seasonal equations are more accurate, especially in the spring and winter.
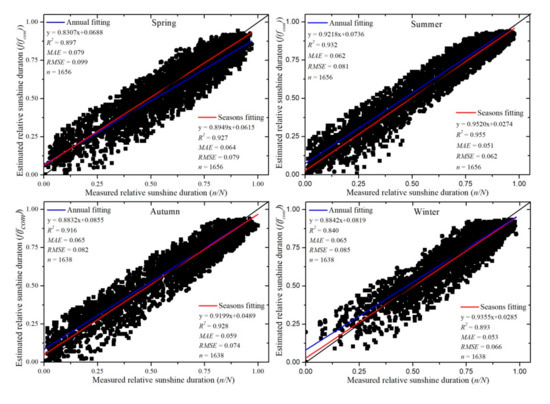
Figure 5.
Comparisons of estimated daily relative sunshine duration by Equations (13) and (14), and measured daily relative sunshine duration at the 18 meteorological stations by season in 2016.

Table 3.
Statistics for the estimation of relative sunshine duration at all 18 meteorological stations daily by season in 2016.
Table 4 shows the statistical performance of the proposed method for estimating sunshine duration for each meteorological station separately. For the seasonal Equations (14), the coefficient of determination (R2) range from 0.894 to 0.951, which indicates a strong correlation between measured sunshine duration and estimated sunshine duration at all stations. The RMSE value range is from 0.779 to 0.977 h/day, and the MAE value range is from 0.583 to 0.824 h/day. The RMSE at all stations is never greater than 40% of MAE, which suggests there are few outlying, inaccurate estimates of sunshine duration, according to Colaizzi [37]. The RE was lower than 0.150 at all stations, which implies good performance, according to Cai [36]. The value of d is greater than 0.960 at all stations, which, again, demonstrates good performance of the method. Figure 6 demonstrates visually that using the seasonal equations (red lines) rather than a single annual equation (blue lines) to estimate daily sunshine duration provides a better estimate since the red lines are generally closer than the blue lines to the perfect fit line shown in black.

Table 4.
Statistics for the estimation of daily sunshine duration (h) at each of the 18 meteorological stations daily in 2016.

Figure 6.
Validation of the measured sunshine duration and estimated sunshine duration for individual meteorological stations in the Three-River Headwaters region in 2016.
Using the FY-2G satellite data, the proposed method for estimating sunshine duration can be applied at any geographic location over Three-River Headwaters region. Accordingly, the estimated results can be compared with spatial distributions from typical interpolation methods based on data from meteorological stations. For these comparisons, four typical days were selected from different seasons in 2016 and the 18 stations in the Three-River Headwaters region were used as the base for the interpolations. In Figure 7, the first column shows the spatial distribution of sunshine duration estimated using Equation (14) from the proposed model, with the subsequent columns showing results from interpolations using, respectively, IDW (inverse distance weighting with exponent 2), Kriging (ordinary and exponential), and the spline method.
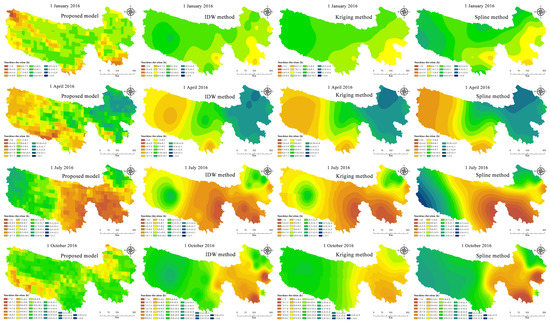
Figure 7.
Spatial distribution of sunshine duration estimated by the proposed model (first column), Inverse distance weighted interpolation (IDW) method (second column), Kriging method (third column), and spline method (fourth column) in different seasons of 2016 over the Three-River Headwaters region.
The maps from the interpolation methods show low values for sunshine duration in the south-eastern region for 1 January, in the southern and western regions for 1 April, in the central and eastern regions for 1 July, and in the north-central region for 1 October. These are consistent with the spatial distribution results from the proposed method, even though there are differences in specific value ranges. However, topography can reduce the values of direct solar irradiance below 120 W/m2. Thus, there would be no registration of sunshine duration. This is not reflected in any of the results. Thus, the estimates lack precision. In addition, there are large differences between the spatial distributions of sunshine duration from the different interpolation methods in the west region on 1 January, the south-western region on 1 April, the west region on 1 July, and the south-western region on 1 October compared with the spatial distribution of sunshine duration for those days by the proposed method in this paper. These results are most likely a consequence of the relatively few meteorological stations in the west and their absence in the south-western portion of the Three-River Headwaters region (Figure 1). No interpolation method can produce accurate results without data from meteorological stations. This suggests that the proposed method in this paper, which is not reliant on stations in a given geographic area, has a higher potential than interpolation methods for producing more accurate representations of the spatial distribution of sunshine duration.
4. Discussion
In this paper, a new method was proposed to estimate sunshine duration based on hourly total cloud amount data between sunrise and sunset from the FY-2G geostationary meteorological satellite. This method constructs a new index, daytime mean total cloud coverage amount, and provides a quadratic equation relating this index to relative sunshine duration in different seasons. Combined with data for maximum possible sunshine duration, these equations can estimate regional scale sunshine duration in different seasons with higher precision than traditional methods. Parameters of quadratic equations were estimated using point-scale daily observation data from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2018 for 18 meteorological stations and verified using corresponding data for 2016. For individual stations, the coefficient of determination (R2) between estimated and measured sunshine was at least 0.894, the RMSE was 0.977 or less, the MAE was 0.824 or less, the RE was 0.150 or lower, and the value of d was 0.963 or greater, which demonstrates that pixel-level satellite-derived estimates can accurately estimate point-based ground measurements. This enables the proposed method to estimate daily sunshine duration at the pixel scale with high precision over an entire region. The effectiveness of this was demonstrated in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Western China by comparing results from the new method with those from several different interpolation methods derived from ground station data.
Unlike some other methods, the proposed method does not depend on an extensive network of meteorological ground stations even though some ground data is needed for initial model calibration. The goal of the method is to more accurately and quickly estimate sunshine duration using only FY-2G hourly total cloud amount data. It does not rely on polar satellite data. Even though its resolution is relatively high, the number of satellite transits per day is limited, which makes it difficult to obtain daytime details. Nor does it depend on meteorological station observation data other than for initial calibration. Since the 1970s, more countries have launched more meteorological satellites, usually with data products that include hourly total cloud amount data. Consequently, the proposed method has the potential to estimate sunshine duration or radiation data for climate change and radiation balance research on a global scale in the long-term.
Previous researchers found that there is a linear or non-obvious non-linear relationship between relative sunshine duration and mean cloud cover or cloud types during the day and night [14,21,25], while the proposed method in this paper showed that a significant non-linear relationship exists between relative sunshine duration and daytime mean total cloud coverage amount, especially for the spring and winter seasons. Consequently, using seasonal-based equations for estimation provides estimates more consistent with ground observation data. Similarly, the use of daytime mean total cloud coverage amount in this paper, rather than the average total cloud coverage amount during the day and night, is the more appropriate choice. Figure 8 shows the relationships between measured daily relative sunshine duration for the 18 meteorological stations for 2017 and 2018 and the average total cloud coverage amount during the day and night calculated based on Equation (6) with parameters j and k set to 0 and 23, respectively. It is apparent that the relationship, either linear or non-linear, is relatively weak, with correlation coefficients less than 0.6. Sunshine duration is mainly affected by differences in the total cloud coverage amount between sunrise and sunset. The differences in total cloud coverage amount at night will not affect sunshine duration. Since the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) defines sunshine duration as the number of hours for which the direct solar irradiance is above 120 W/m2, while the direct solar irradiance at night is significantly less than 120 W/m2. In addition, compared with the sunshine duration estimation method based on hourly cloud classification of geostationary meteorological satellite [9] (name, cloud classification-based method). The maximum value of R2 between the sunshine duration estimate based on seasonal-based equations proposed in this paper and the sunshine duration measured is 0.951. Except for the tuotuohe station, the R2 value of all other ground stations is greater than 0.900, and the RMSE value range is from 0.779 to 0.979 h/day, while the range value of R2 for the cloud classification-based method is from 0.850 to 0.925 h/day, and the RMSE value range is from 1.105 to 1.626 h/day. This indicates that the proposed method in this paper is better than the cloud classification-based method due to the same cloud type in a region that may differ in total cloud amount.
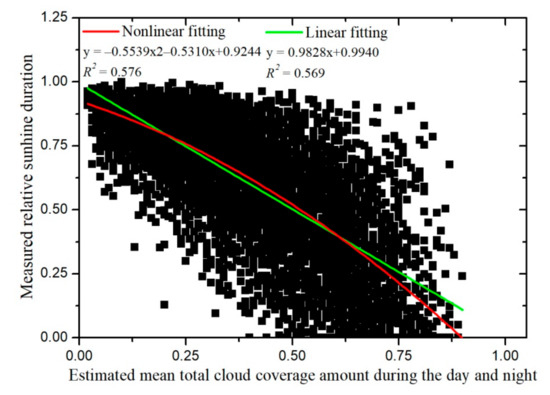
Figure 8.
Relationship between average total cloud coverage amount during the day and night and measured relative sunshine duration for 18 meteorological stations from 1 January 2017 to 31 December 2018.
Spatial interpolation methods based on meteorological stations for determining sunshine duration across a region require relative uniformity across the region or a dense network of observation stations. The Three-River Headwaters Region has clear topographic variability as well as relatively few meteorological stations, which are also unevenly distributed. Consequently, no matter the interpolation method used, an accurate representation of the spatial distribution of sunshine duration is almost impossible to achieve using ground-based methods. Furthermore, due to the effects of topography, some areas or some stations have low direct solar irradiance. Thus, real sunshine durations are relatively low. This leads to lower correlations between the measured sunshine duration and the estimated sunshine duration, as shown in the results for the Tuotuohe and Qingshuihe stations. Additionally, a remotely sensed image describes the sunshine duration value for discrete geo-referenced area-scaled pixels. For FY-2G cloud amount data, the pixel value represents the average sunshine duration over a 5 km × 5 km area. Meteorological station measurements of in-situ sunshine duration are a point value, which significantly differs from the area covered by a pixel. In addition, due to the scale effect caused by the difference in spatial resolution, some small clouds may not be recorded by the satellite data, given its 5-km resolution. Yet, it may reduce direct solar irradiance to below 120 W/m2 on the ground, which impacts sunshine duration data at a meteorological station. Therefore, some outliers would be expected in Figure 4 and Figure 5, where area-based estimated sunshine duration is compared with point-based measured sunshine duration.
The proposed method is empirically based. Although there is a clear relationship between daytime mean total cloud coverage amount and sunshine duration, the coefficients in Equation (7) are empirically derived. They need to be fitted based on least square or other methods using meteorological station data. Their specific values in Equation (14) are optimal only for the Three-River Headwaters Region. They must be recalibrated using sunshine duration data from local meteorological stations when the proposed method is applied in other regions. Similarly, sunshine duration will also be affected by the geographical latitude and time of year. They are zero in polar regions in the winter. All these factors need to be considered in the future development of sunshine duration datasets. If done appropriately, such datasets could provide independent information to improve, or even replace, the interpolation of station-based sunshine duration data provided by data service organizations or meteorological departments, as well as expand geographic coverage to areas underserved by meteorological stations. This could substantially enhance the ability to conduct global and related research.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, a new method was proposed to estimate sunshine duration based on hourly total cloud amount data between sunrise and sunset from China’s FY-2G geostationary meteorological satellite. The method constructs a new index, daytime mean total cloud coverage amount, and provides parameter estimates for quadratic equations relating this index to relative sunshine duration in different seasons. The estimated sunshine duration from the proposed method was validated with ground observation data for 2016 from 18 meteorological stations in the Three-River Headwaters Region of Western China. The validation results show that the coefficient of determination (R2) between estimated and measured sunshine was at least 0.894, the RMSE was 0.977 h/day or less, the MAE was 0.824 h/day or less, the RE was 0.150 or lower, and the value of d was 0.963 or greater for all stations, which illustrates that daily sunshine duration estimates using the proposed method closely correspond with daily sunshine duration measurements. Combined with data for maximum possible sunshine duration, these equations can also estimate regional-scale sunshine on a seasonal basis with higher precision than traditional methods. This was demonstrated over the entire Three-River Headwaters study region by comparing the spatial distribution of sunshine duration estimated from season-based equations with results from three different interpolation methods based on ground observations. The point-scale verification with daily observation data and the regional scale comparison with traditional interpolation methods show that the proposed method can capture the spatial variation of sunshine duration with a high degree of accuracy and precision. The study demonstrates that total cloud amount data from a geostationary satellite can be used successfully to estimate sunshine duration. This has significant application potential in the study of atmospheric energy balance and climate change from the local to the global scale.
Author Contributions
W.Z. designed and conducted the experiment and wrote the manuscript. N.Y. and B.W. revised the manuscript. J.X., W.L., Z.M., L.W., and Q.X. provided some useful advice for the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2016YFA0600303, 2016YFC0501601), part by Advanced Science Foundation Research Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No: QYZDY-SSW-DQC014), part by Science and Technology Service Network Initiative (KFJ_STS-ZDTP-013-02), part by the National Natural Scientific Foundations of China (Grant Nos. 41601463, 41701403), and the director of the Foundation of the Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. Y6SJ2000CX), and part by Qinghai Science and Technology Plan (Grant No. 2019-SF-155).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Chinese Meteorological Data Sharing Service System for providing daily sunshine duration data from meteorological stations and the National Satellite Meteorological Centre for providing the Fengyuan-2G geostationary meteorological satellite (FY-2G) hourly total cloud amount data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhu, X.C.; Qiu, X.F.; Zeng, Y.; Gao, J.Q.; He, Y.J. A remote sensing model to estimate sunshine duration in the Ningxia Hui autonomous region, China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angstrom, A. Solar and terrestrial radiation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1924, 50, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.M. Studies on Radiation Climate of China; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, J.; Selten, J.P.; Chant, D. Long-term trends in sunshine duration and its association with schizophrenia birth rates and age at first registration-data from Australia and the Netherlands. Schizophr. Res. 2002, 54, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothe, S.; Good, E.; Obregón, A.; Ahrens, B.; Nitsche, H. Satellite-based sunshine duration for Europe. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2943–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaa, S. Evaluation of sunshine duration from cloud data in Egypt. Energy 2008, 33, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H. Study on the Measurement Method of Direct Radiation Sunshine Hour. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszko, D.A. Comparison of sunshine duration records from the Campbell-stokes sunshine recorder and CSD3 sunshine duration sensor. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, M.; Yan, N.; Xing, Q. A Method to Estimate Sunshine Duration Using Cloud Classification Data from a Geostationary Meteorological Satellite (FY-2D) over the Heihe River Basin. Sensors 2016, 16, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. The spatial distribution of sunshine hours under undulating terrain of China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2003, 13, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Canada, J. Solar radiation prediction from sunshine in eastern Spain. Renew. Energy 1992, 3, 219–221. [Google Scholar]
- Halouani, N.; Nguyen, C.T.; Vo-Ngoc, D. Calculation of monthly average global solar radiation on horizontal surfaces using daily hours of bright sunshine. Sol. Energy 1993, 50, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, E. Estimating daily sunshine duration over the UK from geostationary satellite data. Weather 2010, 65, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandirmaz, H.M.; Kaba, K. Estimation of daily sunshine duration from Terra and aqua MODIS data. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 613267, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.K. Studies on Radiation in the Epigedsphere; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Q. Refine project model of sunshine resources in China considering terrain masking. J. Agrometeorol. 2011, 32, 273–278. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barbaro, S.; Coppolino, S.; Leone, C.; Sinagra, E. Global solar radiation in Italy. Sol. Energy 1978, 20, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q. The magnitude of the effect of air pollution on sunshine hours in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, M.; Badescu, V.; Dumitrescu, A.; Paulescu, M. A new point of view on the relationship between global solar irradiation and sunshine quantifiers. Sol. Energy 2016, 126, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jervase, J.A.; Al-Lawati, A.; Dorvlo, A.S.S. Contour maps for sunshine ratio for Oman using radial basis function generated data. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Q.; Li, S.M. Estimating of sunshine percentage using the cloud classification data from FY2C. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 1, 1295–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, D.; Monget, J.M.; Albuisson, M.; Guillard, H.; Regas, N.; Wald, L. A method for the determination of the global solar radiation from meteorological satellite data. Sol. Energy 1986, 37, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olseth, J.A.; Skartveit, A. Solar irradiance, sunshine duration and daylight illuminance derived from METEOSAT data from some European sites. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2001, 69, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.; Ineichen, P.; Moore, K.; Kmiecik, M.; Chain, C.; George, R.; Vigonla, F. A new operational model for satellite derived irradiances: Description and validation. Sol. Energy 2002, 73, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandirmaz, H.M. A model for the estimation of daily global sunshine duration from meteorological geostationary satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5061–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, M.A.; Remesan, R.; Han, D.W.; Ejaz, N.; Elahi, A. An improved technique for global daily sunshine duration estimation using satellite imagery. J. Zhujiang Univ. Sci. A (Appl. Phys. Eng.) 2012, 13, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shao, X.; Qin, N. Temporal trends and variability of daily maximum and minimum, extreme temperature events, and growing season length over the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau during 1961–2003. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 16, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D. The system of physic-geographical regions of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau. Sci. China (Ser. D) 1996, 19, 410–417. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D. Changes in spring phenology in the Three-Rivers Headwater Region from 1999 to 2013. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9130–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Shao, Q.Q. Grassland degradation in the “Three-River Headwaters” region, Qinghai Province. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Xu, X.L.; Fu, Y.; Li, S. Wetland changes and their responses to climate change in the “Theree-River Headwater” region of China since the 1990s. Energies 2014, 7, 2515–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P. Practical Manual for Satellite Service Products and Satellite Data Formats for Chinese Geostationary Meteorological; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Cui, P.; Xiao, M. The bia analysis of FY-2G cloud fraction in summer and winter. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2017, 28, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Duffie, J.A.; Beckman, W.A. Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J. Some comments on the evaluation of model performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Lei, T.; Pereira, L.S. Estimating reference evapotranspiration with the FAO Penman–Monteith equation using daily weather forecast messages. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2007, 145, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaizzi, P.D.; Evett, S.R.; Howell, T.A.; Tolk, J.A. Comparison of five models to scale daily evapotranspiration from one-time-of-day measurements. Trans. ASAE 2006, 49, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Hafeez, M.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Vote, C. A novel method to convert daytime evapotranspiration into daily evapotranspiration based on variable canopy resistance. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).