Continuous Detection of Diurnal Sodium Fluorescent Lidar over Beijing in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diurnal Sodium Fluorescence Lidar System
3. Research and Improvement on Key Techniques of Daytime Detection
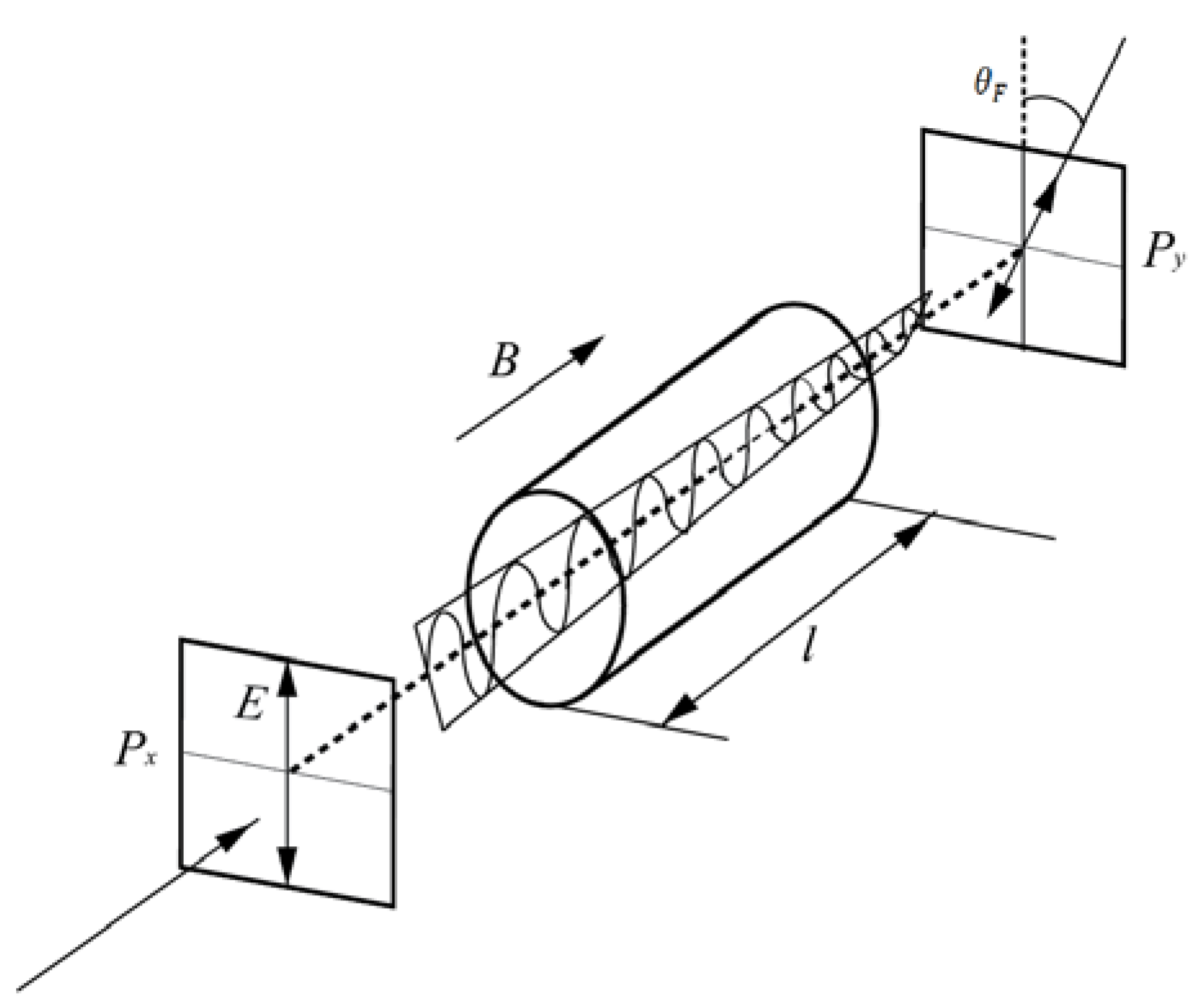
3.1. Daytime Detection Lidar Technology and Working Principle of FADOF
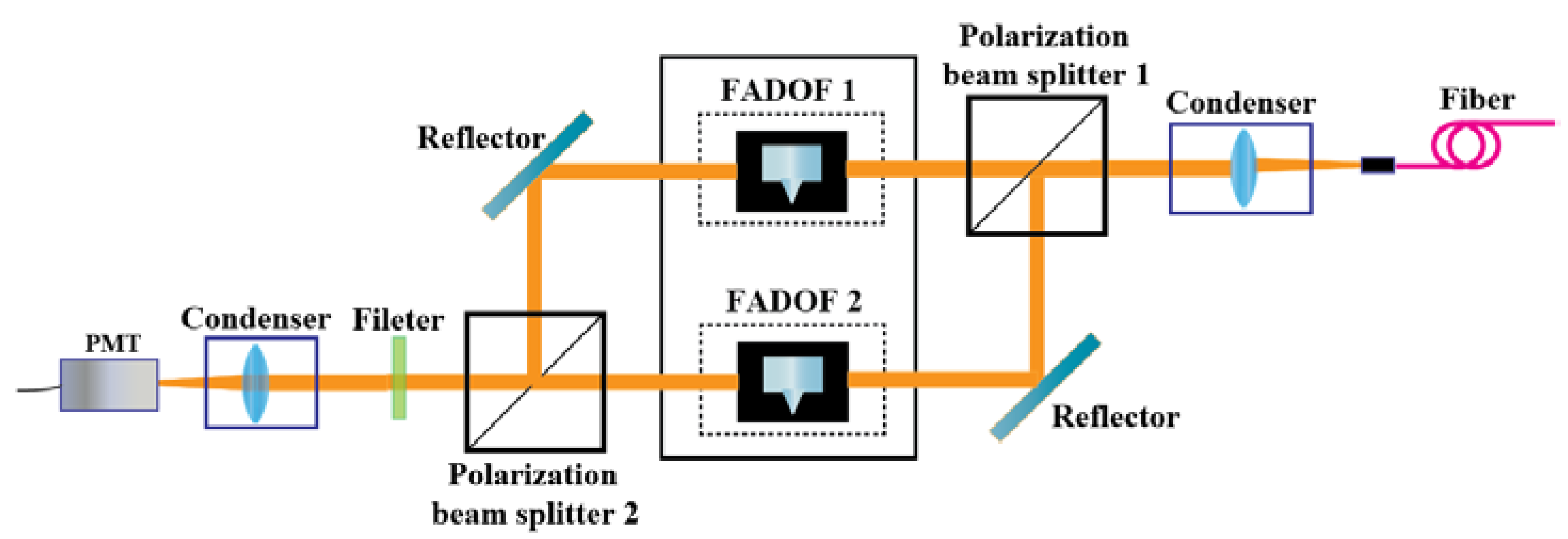
3.2. Improved Optical Path Technology for Daytime Detection of Atomic Filters
3.3. Research and Improvement of Other Key Technologies
4. Analysis of Daytime Observations
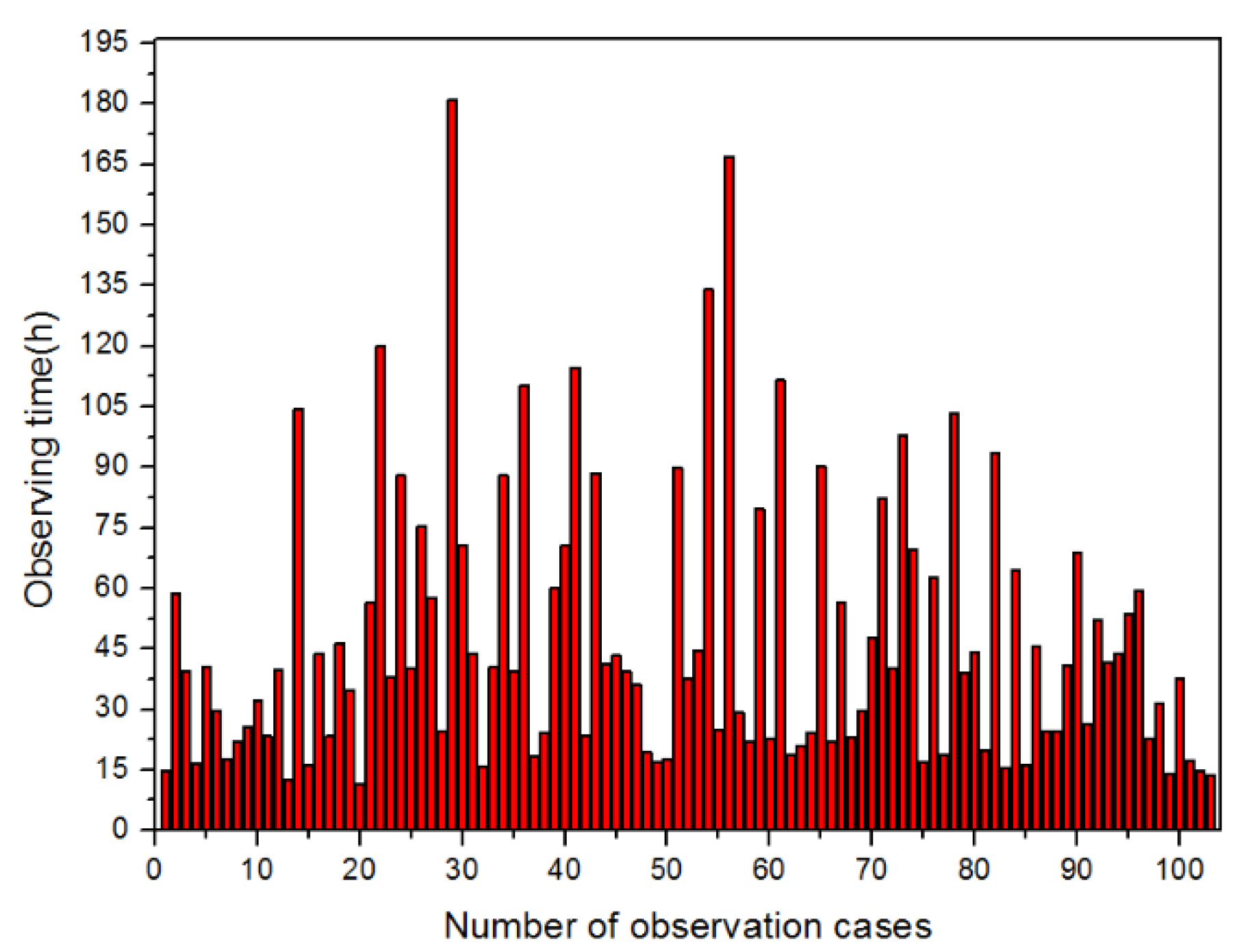
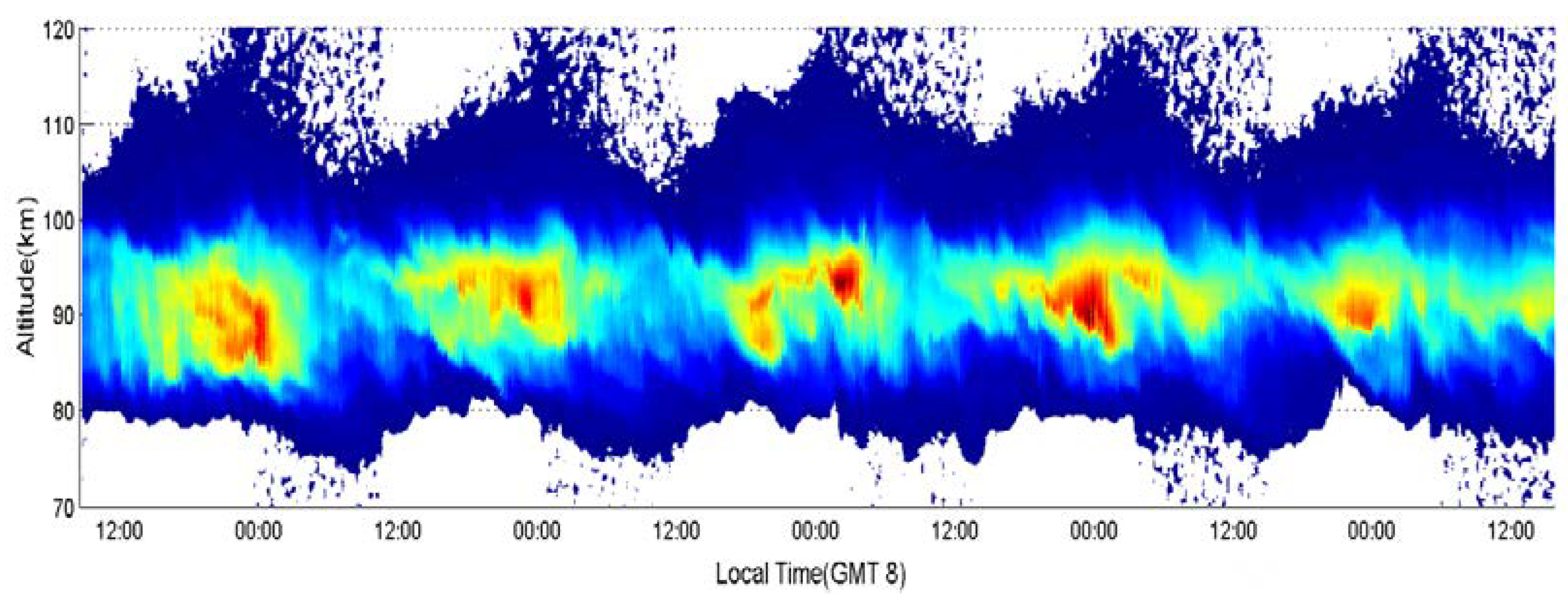
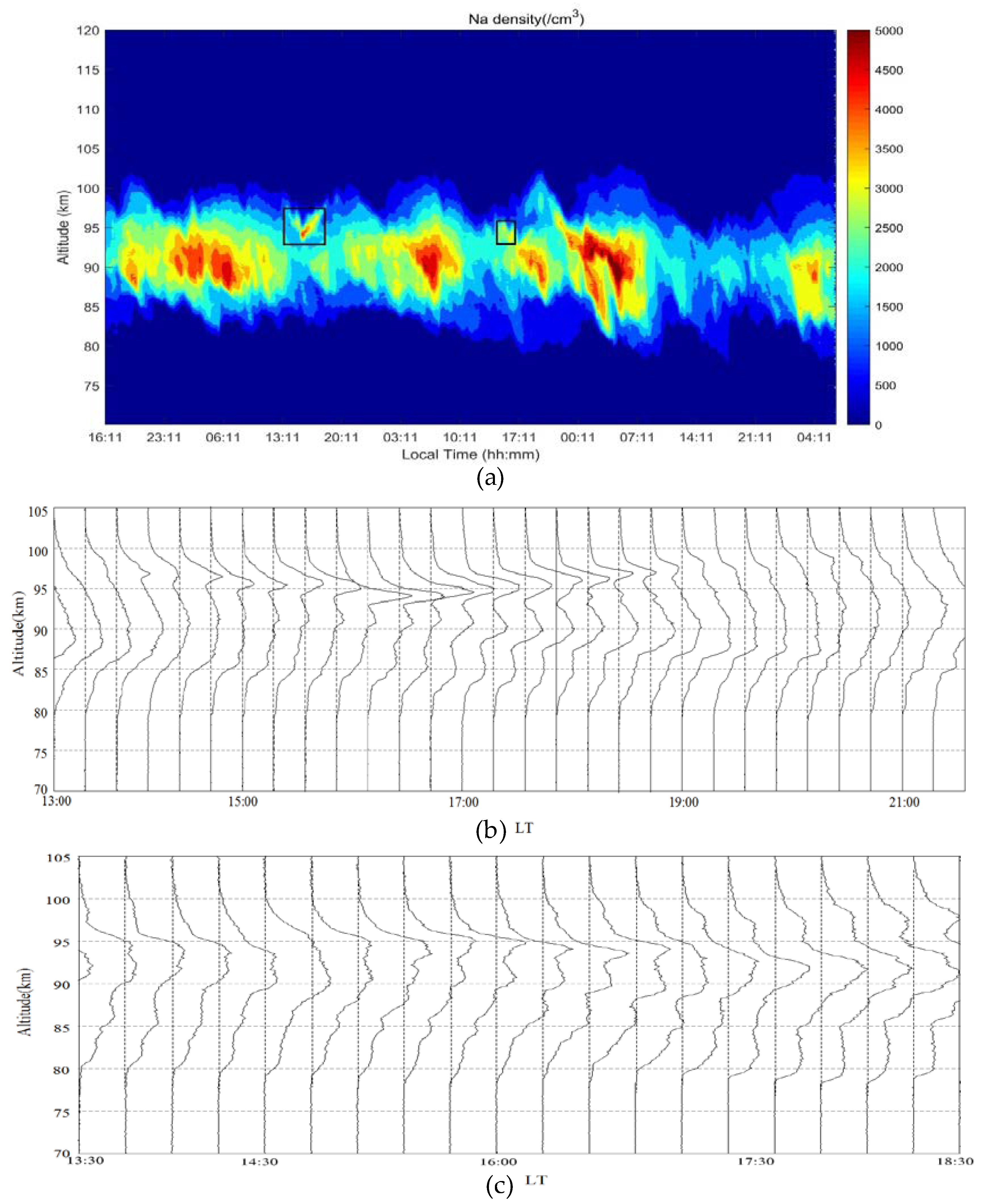
4.1. Statistics of Continuous Observation Duration
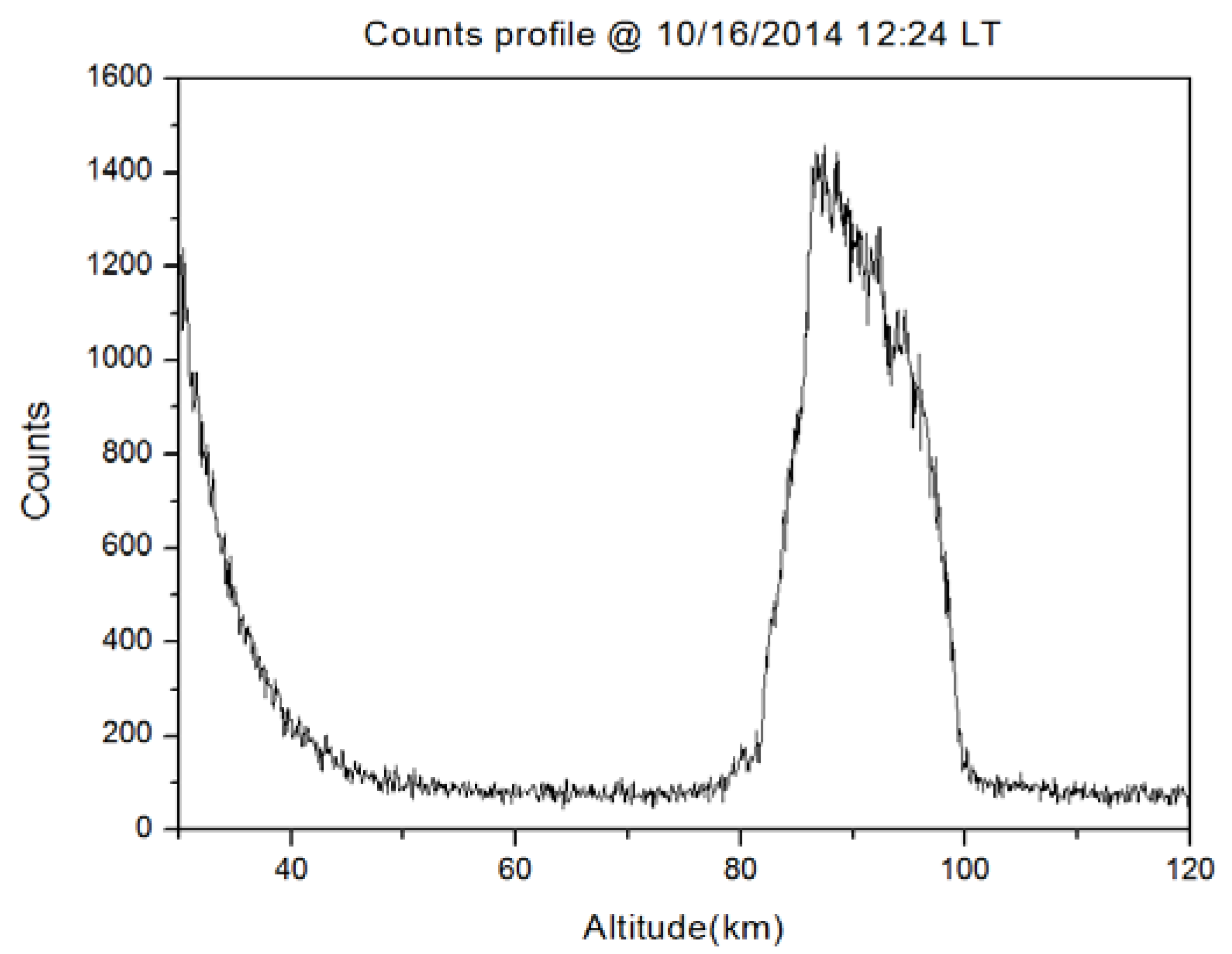
4.2. Detection Results
4.3. Sporadic Sodium Layer During the Daytime
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clemesha, B.R.; Batista, P.P.; Simonich, D.M.; Batista, I.S. Sporadic structures in the atmospheric sodium layer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.S. Sodium resonance fluorescence lidar applications in atmospheric science and astronomy. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plane, J.M.; Gardner, C.S.; Yu, J.; She, C.Y.; Garcia, R.R.; Pumphrey, H.C. Mesospheric Na layer at 40 °N: Modeling and observations. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 3773–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, T.J.; Hostetler, C.A.; Gardner, C.S. Horizonal and vertical structure of the major sporadic sodium layer events observed during ALOHA-90. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Y.; Plane, J.M.; Gumbel, J. On the global distribution of sporadic sodium layers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 030542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Papen, G.C. Resonance fluorescence lidar for measurements of the middle and upper atmosphere. Laser Remote Sens. 2005, 97, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Ejiri, M.K.; Nakamura, T.; Kawahara, T.D. Seasonal variation of nocturnal temperature and sodium density in the mesopause region observed by a resonance scatter lidar over Uji, Japan. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D18126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozawa, S.; Kawahara, T.D.; Saito, N.; Hall, C.M.; Tsuda, T.T.; Kawabata, T.; Wada, S.; Brekke, A.; Takahashi, T.; Fujiwara, H.; et al. Variations of the neutral temperature and sodium density between 80 and 107 km above Tromsø during the winter of 2010–2011 by a new solid-state sodium lidar. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; She, C.Y.; Hagan, M.E.; Williams, B.P.; Li, T.; Arnold, K.; Kawahara, T.D.; Acott, P.E.; Vance, J.D.; Krueger, D.; et al. Roble. Seasonal variation of diurnal perturbations in mesopause region temperature, zonal, and meridional winds above fort collins, colorado (40.6°N, 105°W). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D06103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; She, C.Y.; Krueger, D.A.; Sassi, F.; Garcia, R.; Roble, R.G.; Liu, H.L.; Schmidt, H. Climatology of mesopause region temperature, zonal wind, and meridional wind over Fort Collins, Colorado (41° N, 105° W), and comparison with model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D03105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, D.A.; She, C.Y.; Yuan, T. Retrieving mesopause temperature and line-of-sight wind from full-diurnal-cycle Na lidar observations. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 9469–9489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemesha, B.R.; Simonich, D.M.; Batista, P.P.; Takahashi, H. Seasonal variation in the solar diurnal tide and its possible influence on the atmospheric sodium layer. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemesha, B.R.; Simonich, D.M.; Batista, P.P.; Kirchhoff, V.W.J.H. The Diurnal Variation of Atmospheric Sodium. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.H.; Gardner, C.S.; Senf, D.C. Daytime Lidar Measurements of Tidal Winds in the Mesospheric Sodium Layer at Urbana, Illinois. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 8781–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbwachs, J.A. Atomic resonance filter. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1988, 24, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.; Shay, T.M. Theoretical model for a Faraday anomalous dispersion optical filter. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; White, M.A.; Krueger, D.A.; She, C.Y. Daytime mesopause temperature measurements with a sodium-vapor dispersive Faraday filter in a lidar receiver. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, Z.; White, M.A.; Chen, H.; Krueger, D.A.; She, C.Y. Lidar observations of seasonal variation of diurnal mean temperature in the mesopause region over Fort Collins, Colorado (41°N, 105°W). J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 12371–12379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.Y.; Sherman, J.; Yuan, T.; Williams, B.P.; Arnold, K.; Kawahara, T.D.; Li, T.; Xu, L.F.; Vance, J.D.; Acott, P.; et al. The first 80-hour continuous lidar campaign for simultaneous observation of mesopause region temperature and wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; She, C.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Leblanc, T.; McDermid, I.S. Sodium lidar–observed strong inertia-gravity wave activities in the mesopause region over Fort Collins, Colorado (41° N, 105° W). J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Schmidt, H.; She, C.Y.; Krueger, D.A.; Reising, S. Seasonal variations of semidiurnal tidal perturbations in mesopause region temperature and zonal and meridional winds above Fort Collins, Colorado (40.6° N, 105.1° W). J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; She, C.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Yue, J.; Nakamura, T.; Krueger, D.A.; Wu, Q.; Dou, X.; Wang, S. Observation of local tidal variability and instability, along with dissipation of diurnal tidal harmonics in the mesopause region over Fort Collins, Colorado (41° N, 105° W). J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D06106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Zhao, Y.; Pautet, P.D.; Taylor, M.J.; Pendleton, W.R., Jr. A coordinated investigation of the gravity wave breaking and the associated dynamical instability by a Na lidar and an Advanced Mesosphere Temperature Mapper over Logan, UT (41.7° N, 111.8° W). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 6852–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Yang, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J. Applications of Atomic Spectra Filtering and Atomic Frequency Discrimination in Optoelectronic Systems. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2010, 47, 42301–42307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, L.; Zeng, X. Temperature properties of Na dispersive Faraday optical filter at D1 and D2 line. Opt. Commun. 1998, 156, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lin, X.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, K.; Gong, S. A Doppler lidar with atomic Faraday devices frequency stabilization and discrimination. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2013, 30, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Dou, X.; Gong, J.; Rao, C.; Xiong, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Lin, X.; et al. Hyperspectral solar observation based on the sodium atomic filter. Sci. Sin. 2016, 46, 69602–69606. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Atomic Frequency Discriminator and its Application in Solar Observation. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan, China, 5 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Yang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Gong, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Lin, X.; et al. Joint observation results of Na layer and ionosphere in Wuhan during the Total Solar Eclipse. Sci. China 2015, 45, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Gong, S.; Li, F. Daytime Observation Technology of Lidar by Using Atomic Optical Filer. Chin. J. Lasers 2007, 34, 406–410. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Gong, S.; Li, F.; Dai, Y.; Song, J.; Wang, J.; Li, F. 24 h continuous observation of sodium layer over Wuhan by lidar. Sci. Ser. G 2007, 50, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Yue, C.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Du, L.; Cheng, X.; Chi, W. Seasonal variations of meteoric potassium layer over Beijing (40.41° N, 116.01° E). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2016, 122, 23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, S.D.; She, C.Y.; Yuan, T.; Krueger, D.A.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.S.; Hu, Z.L. Sodium and potassium vapor Faraday filters revisited: Theory and applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 2009, 26, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.W.; Li, F.Q.; Lin, Z.X. Properties and applications of Faraday Anomalous Dispersion Optical Filter. Opt. Optoelectron. Technol. 2003, 1, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Yang, G.; Cheng, X.; Gong, S.; Xu, J.; Li, F.; Gong, W.; Wang, J. Lidar observation campaigns on diurnal variations of the sodium layer in Beijing and Wuhan, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- States, R.; Gardner, C.S. Structure of the mesospheric Na layer at 40°N latitude: Seasonal and diurnal variations. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 3881–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.Y.; Li, T.; Collins, R.L.; Yuan, T.; Williams, B.P.; Kawahara, T.D.; Vance, J.D.; Acott, P.; Krueger, D.A.; Liu, H.L.; et al. Tidal perturbations and variability in mesopause region over Fort Collins, CO (41° N, 105° W): Continuous multi-day temperature and wind lidar observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L24111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Smith, A.K.; Collins, R.L.; She, C.Y. Signature of an overturning gravity wave in the mesospheric sodium layer: Comparison of a nonlinear photochemical-dynamical model and lidar observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; She, C.Y.; Kawahara, T.D.; Krueger, D.A. Variations of midlatitude mesospheric Na layer and their tidal period perturbations based on full diurnal cycle Na lidar observations of 2002–2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Eccles, J.V. A numerical investigation on tidal and gravity wave contributions to the summer time Na variations in the midlatitude E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 10577–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Sojka, J.; Rice, D.; Oberheide, J.; Criddle, N. Investigation of the seasonal and local time variations of the high-altitude sporadic Na layer (Nas) formation and the associated midlatitude descending E layer (Es) in lower E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 5985–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Eccles, J.V.; Raizada, S. Investigation on the distinct nocturnal secondary sodium layer behavior above 95 km in winter and summer over Logan, UT (41.7° N, 112° W) and Arecibo Observatory, PR (18.3° N, 67° W). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2019, 124, 9610–9625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, G.; Song, S.; Gong, S. Double sodium layers observation over Beijing, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Yang, G.; Zou, X.; Gong, S.; Wang, J.; Tian, D.; Cheng, X. Joint observations of sporadic sodium and sporadic E layers at middle and low latitudes in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Du, L.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lin, X.; Xun, Y.; Gong, S.; et al. Development of a solid-state sodium Doppler lidar using an all-fiber-coupled injection seeding unit for simultaneous temperature and wind measurements in the mesopause region. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 5264–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, Z.; Du, L.; Yan, C.; et al. First report of sporadic K layers and comparison with sporadic Na layers at Beijing, China (40.6° N, 116.2° E). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 5214–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Laser Emission System | Nd:YAG Laser | Na Channel |
| Wavelength | 532 nm | 589.158 nm |
| Pulse energy | 230 mJ | 46 mJ |
| Repetition rate | 30 Hz | 30 Hz |
| Pulse width | 10 ns | 10 ns |
| Beam divergence | <0.5 mrad | <0.5 mrad |
| Linewidth | --- | 1.5 GHz |
| Signal Receiving System | ||
| Telescope aperture | 1 m | |
| Focal length | 2 m | |
| Fiber diameter | 1.5 mm | |
| Signal Detection System | ||
| Optical filter FWHM | 1.0 ± 0.2 nm | |
| Out-of-band suppression | OD8 (200–1200 nm) | |
| Peak transmittance | >75% | |
| Quantum efficiency of PMT | <40% | |
| Atomic filter transmittance | >80% | |
| Operating temperature of atomic filter | >160 °C | |
| Atomic filter single peak half linewidth | 0.6 GHz | |
| Data Acquisition and Timing Control System | ||
| Count rate | 150 MHz | |
| Bin width | 640 ns | |
| Bin number | 2048 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xun, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, F.; Gong, S.; Zheng, H.; Cheng, X.; Yang, G.; et al. Continuous Detection of Diurnal Sodium Fluorescent Lidar over Beijing in China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010118
Du L, Wang J, Yang Y, Xun Y, Li F, Wu F, Gong S, Zheng H, Cheng X, Yang G, et al. Continuous Detection of Diurnal Sodium Fluorescent Lidar over Beijing in China. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010118
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Lifang, Jihong Wang, Yong Yang, Yuchang Xun, Faquan Li, Fuju Wu, Shunsheng Gong, Haoran Zheng, Xuewu Cheng, Guotao Yang, and et al. 2020. "Continuous Detection of Diurnal Sodium Fluorescent Lidar over Beijing in China" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010118
APA StyleDu, L., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Xun, Y., Li, F., Wu, F., Gong, S., Zheng, H., Cheng, X., Yang, G., & Lu, Z. (2020). Continuous Detection of Diurnal Sodium Fluorescent Lidar over Beijing in China. Atmosphere, 11(1), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010118





