Long-Term Aerosol Trends and Variability over Central Saudi Arabia Using Optical Characteristics from Solar Village AERONET Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
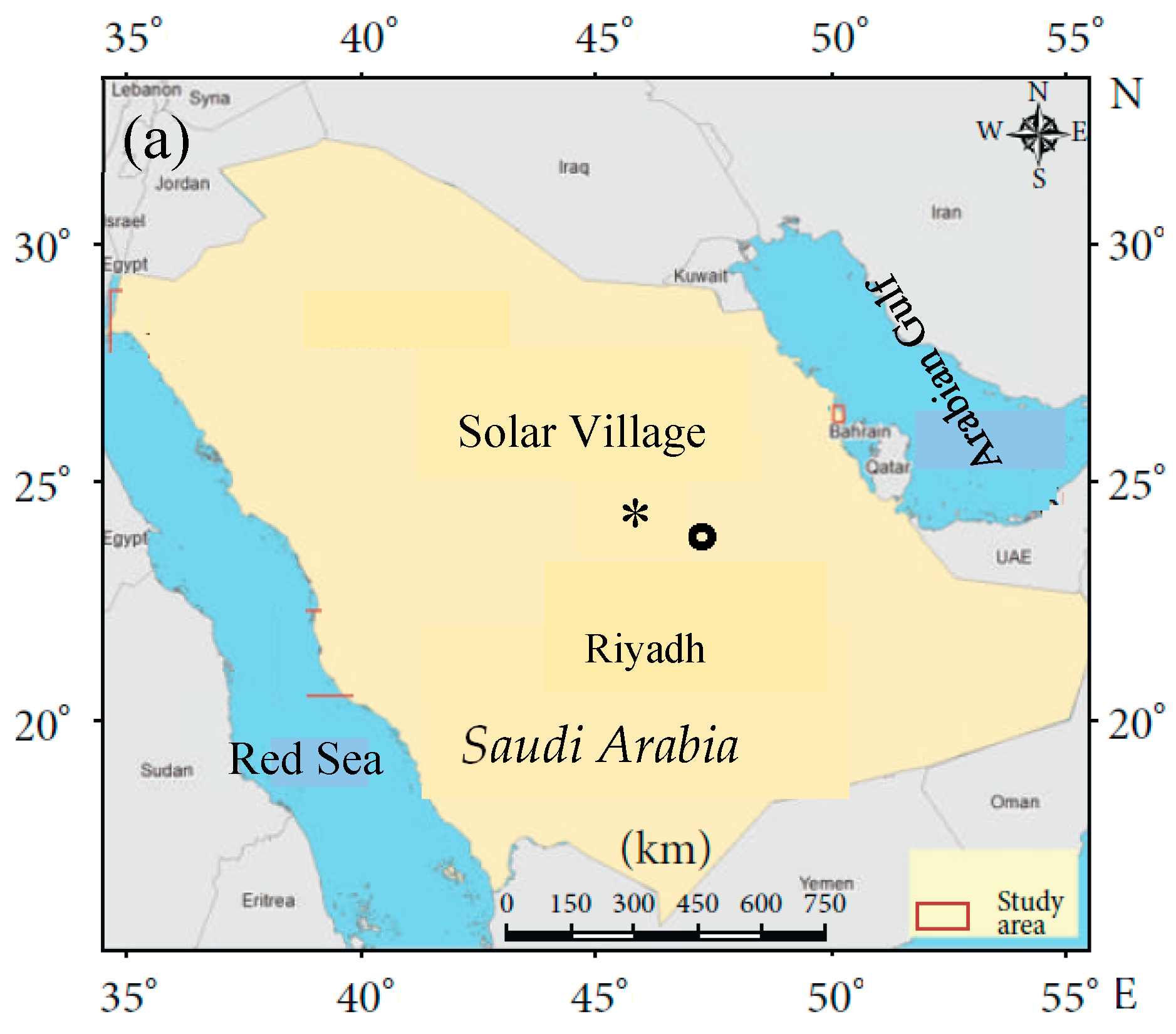
2.1. Study Area
2.2. AERONET
2.3. MODIS
2.4. HYSPLIT Model
2.5. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
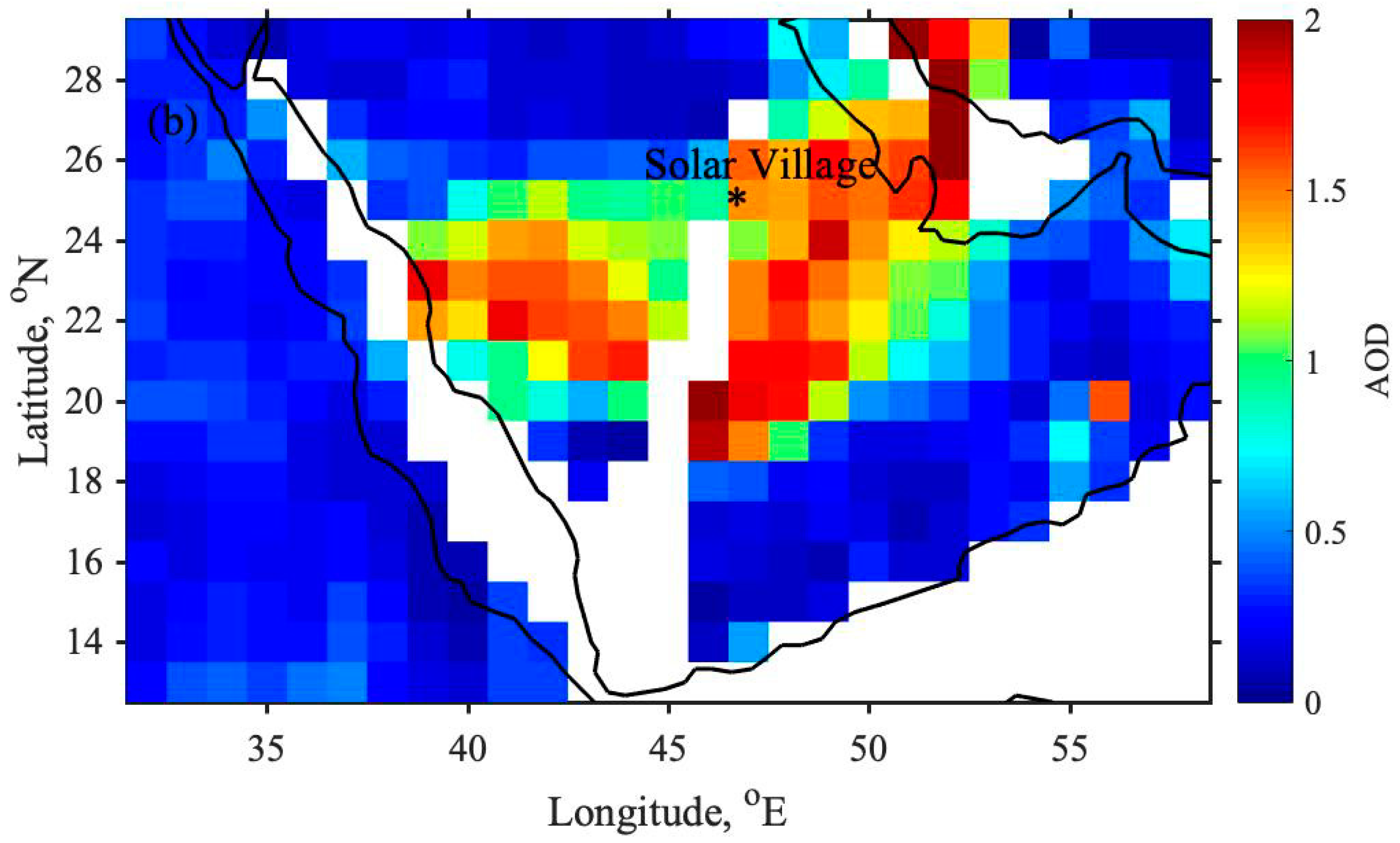
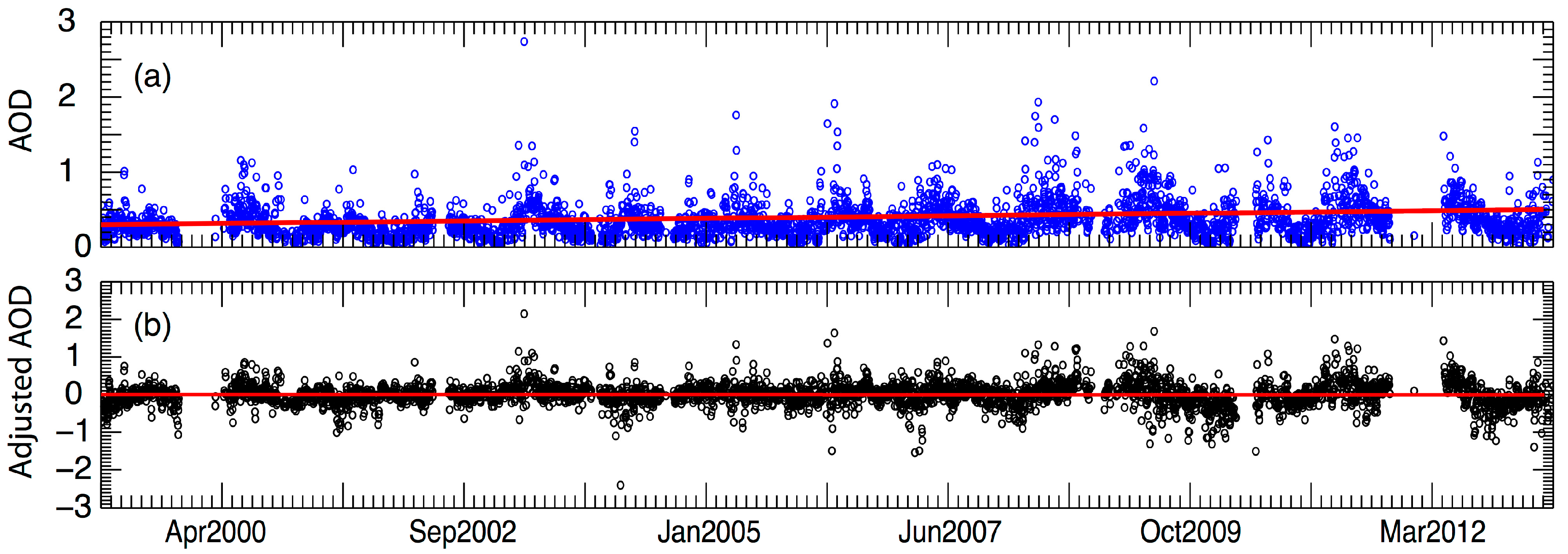
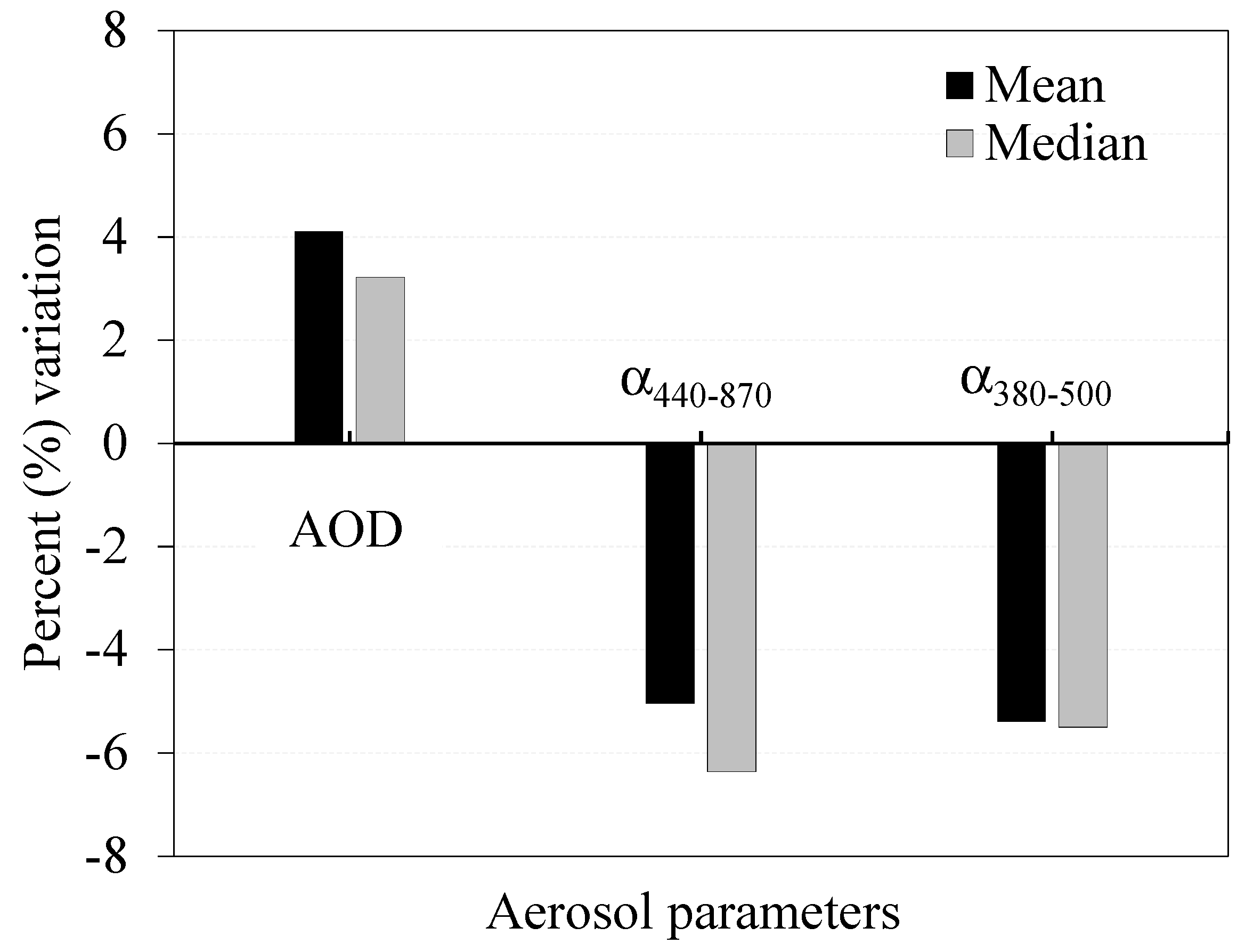
3.1. Variability of Aerosol Parameters During 1999–2013
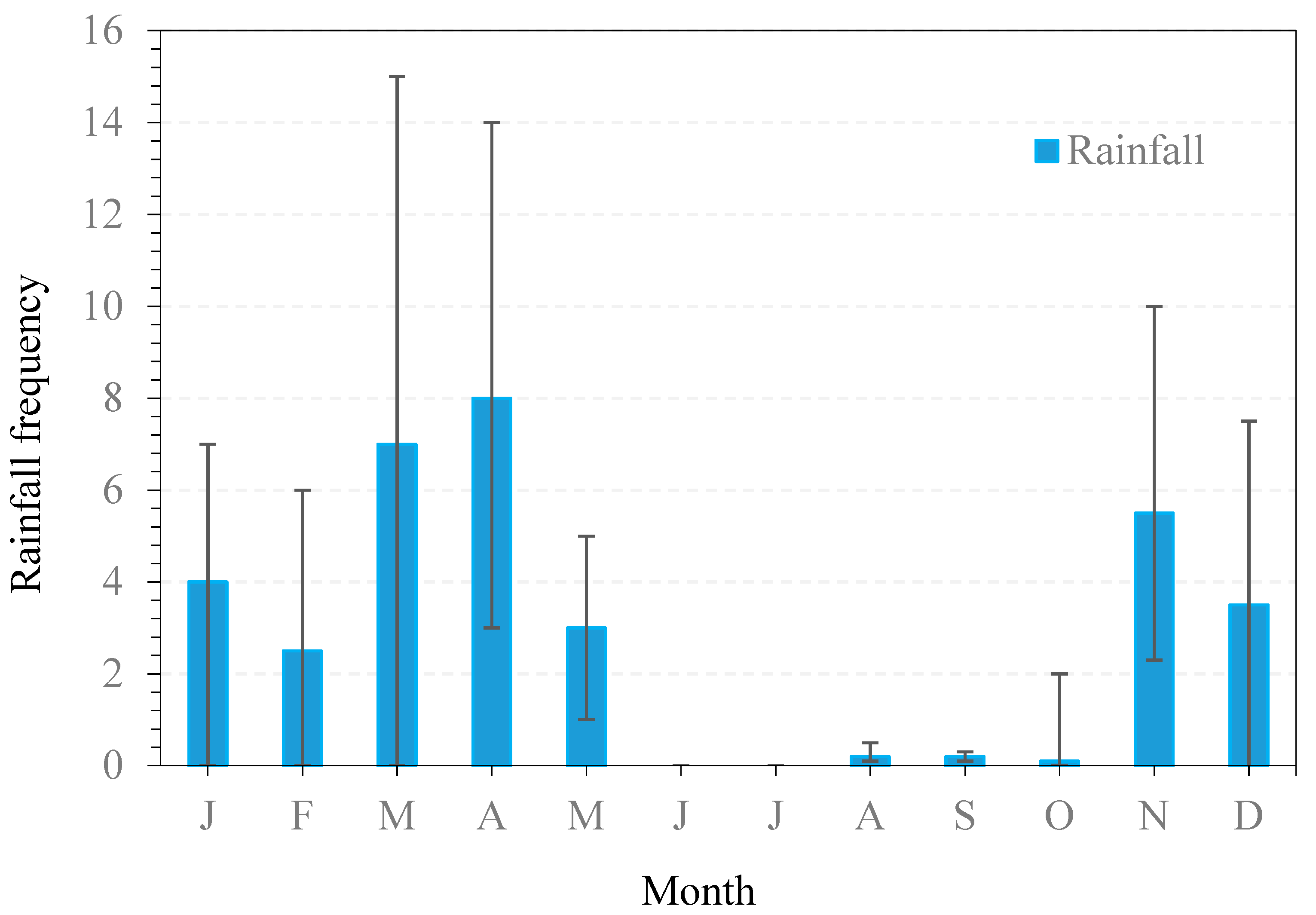
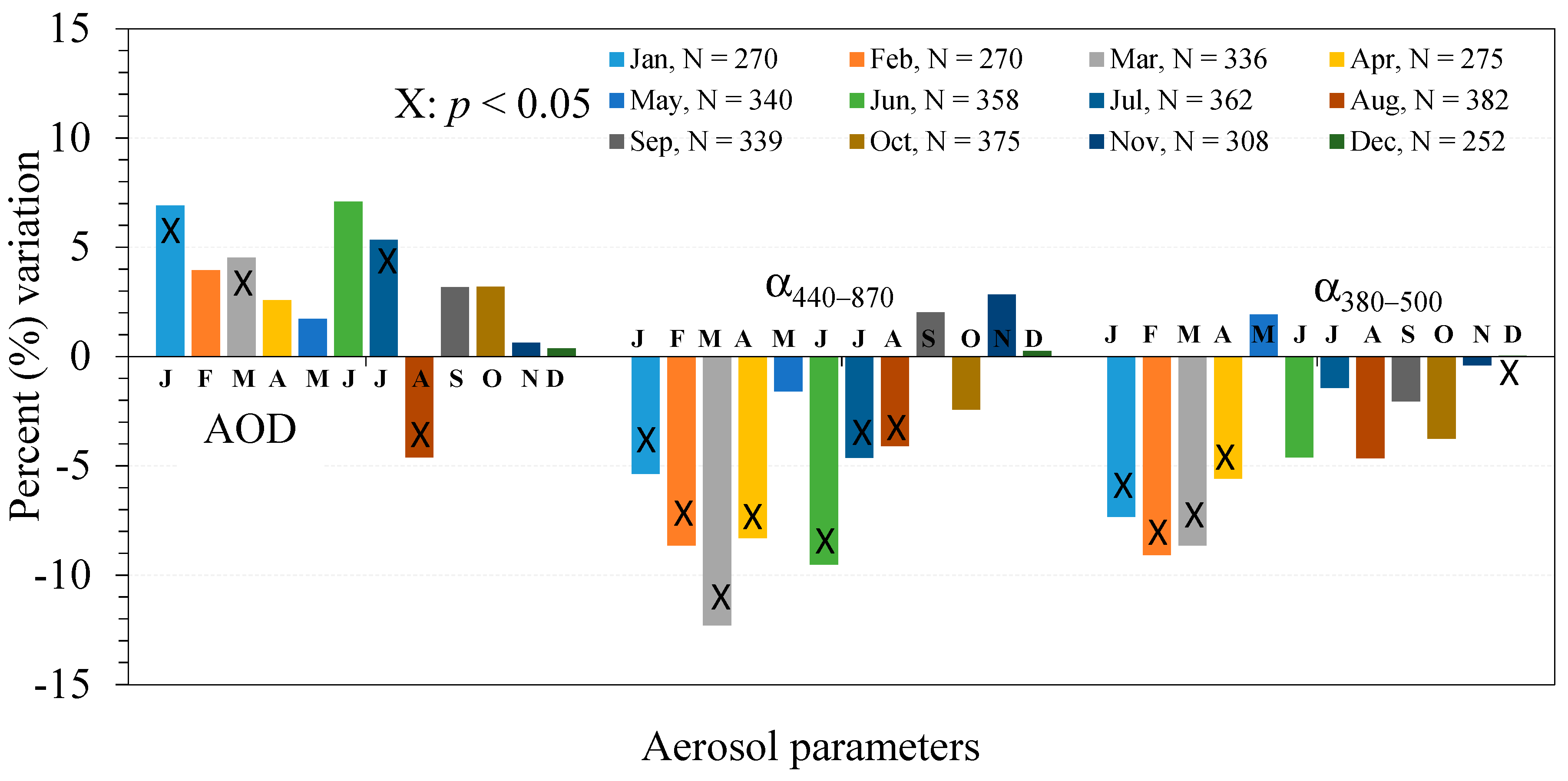
3.2. Monthly and Seasonal Trends
3.2.1. Monthly Trends
3.2.2. Seasonal Trends
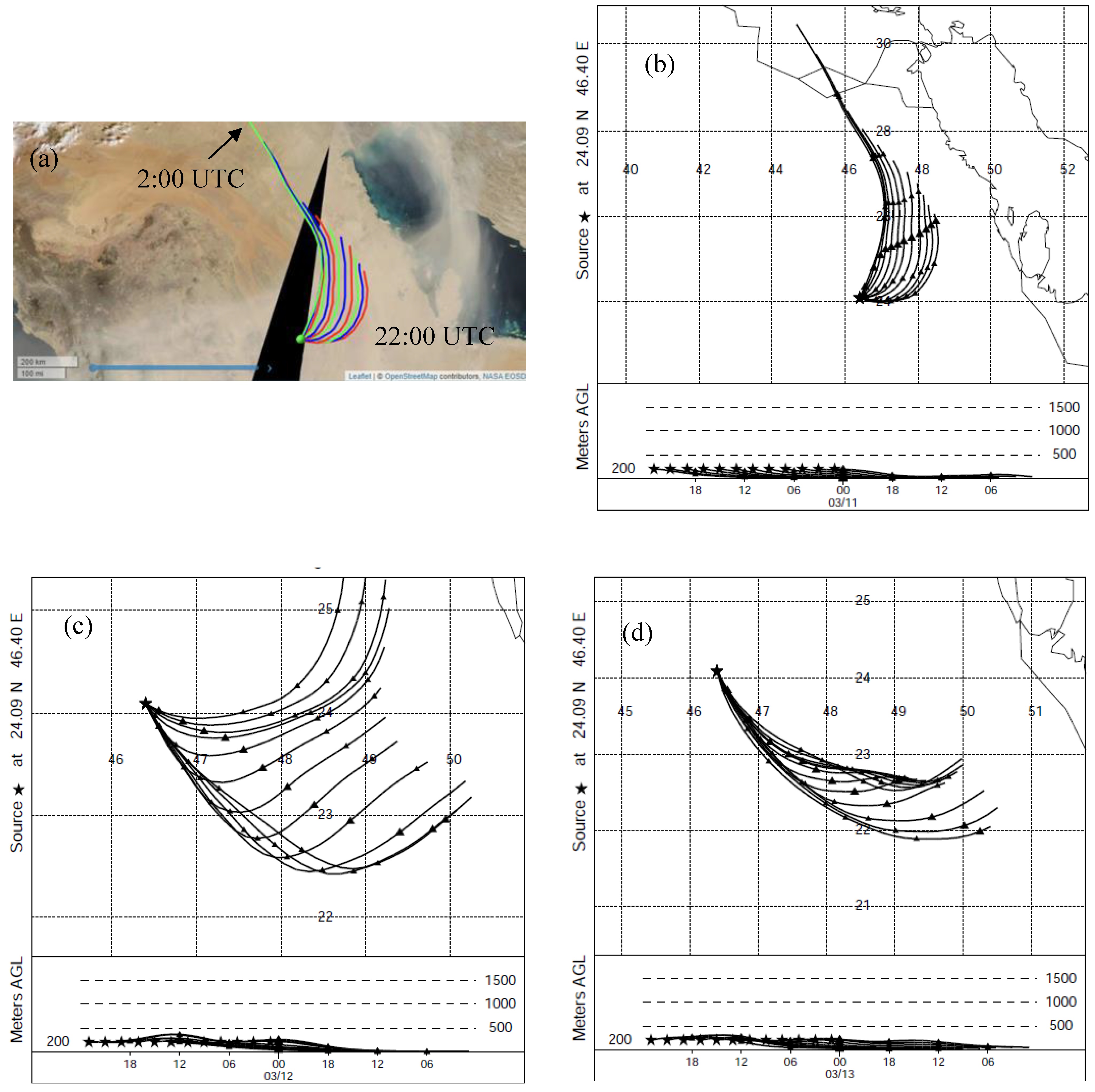
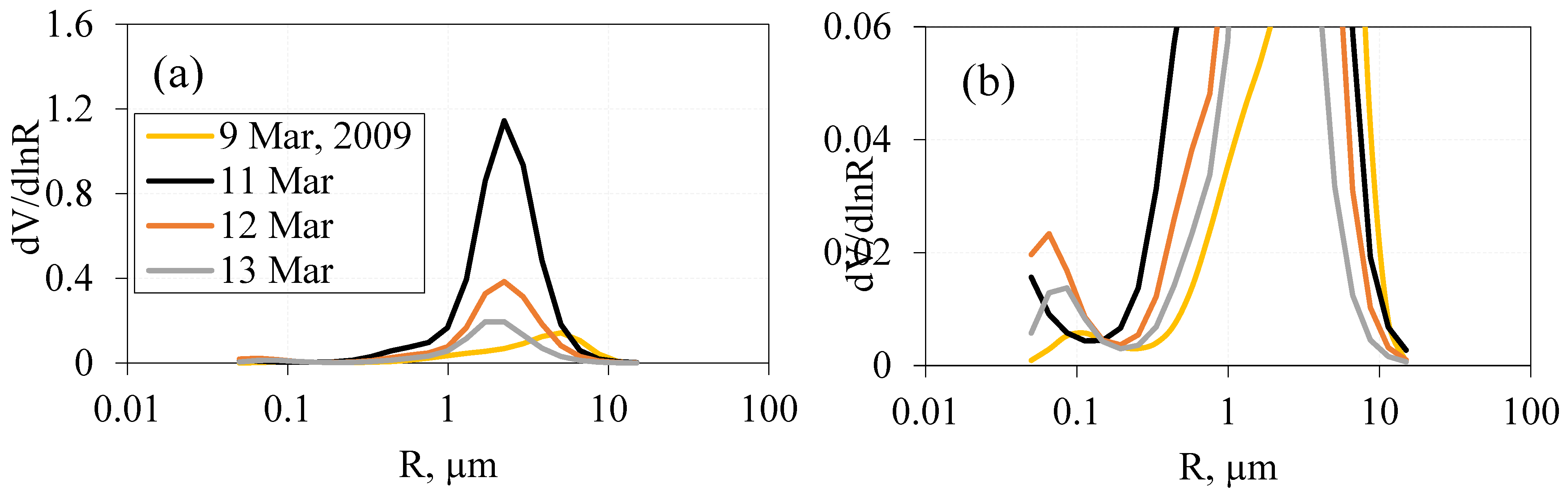
3.3. Effect of Air Mass Transport During Dust Events
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwartz, S.E.; Arnold, F.; Blanchet, J.-P.; Durkee, P.A.; Hofmann, D.J.; Hoppel, W.A.; King, M.D.; Lacis, A.A.; Nakajima, T.; Ogren, J.A.; et al. Group Report: Connections between Aerosol Properties and Forcing of Climate in Aerosol Forcing of Climate; Charlson, R.J., Heintzenberg, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 251–280. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld, D.; Woodley, W.L.; Axisa, D.; Freud, E.; Hudson, J.G.; Givati, A. Aircraft measurements of the impacts of pollution aerosols on clouds and precipitation over the Sierra Nevada. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D15203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A. Air pollution in the Arabian Peninsula (Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman): Causes, effects, and aerosol categorization. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, H.; Pasha, M.; Tapper, N. Assessment of ambient air quality in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia. Curr. World Environ. 2014, 9, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.; Assiri, M.; Ali, M. Assessment of AOD variability over Saudi Arabia using MODIS Deep Blue products. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A.; El-Askary, H.; Adetokunbo, P.; Fuad, A. Analysis of aerosol absorption properties and transport over North Africa and the Middle East using AERONET data. Ann. Geophys. 2016, 34, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.; Kadry, H. Generation of representative weather—Year data for Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 1994, 48, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory analysis of Saudi Arabian dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Singh, B.; Gera, B.S.; Srivastava, M.K.; Dutta, H.N.; Garg, S.C.; Singh, R.A. Study of aerosol optical depth in the central Indian region (During ISRO-GBP Field Campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 6494–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalapureddy, M.C.R.; Devara, P.C.S. Pre-Monsoon aerosol optical properties and spatial distribution over the Arabian Sea during 2006. Atmos. Res. 2010, 95, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedia, S.; Ramachandran, S. Variability in aerosol optical and physical characteristics over the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea deduced from Ångström Exponents. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D14207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghan, S.J.; Schwartz, S.E. Aerosol Properties and Processes: A path from field and laboratory measurements to Global Climate Models. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1059–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment, Water and Agriculture, Saudi Arabia Electricity: Consumption. Available online: https://www.ceicdata.com/en/saudi-arabia/electricity-statistics/electricity-consumption (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Nada, N. Desalination in Saudi Arabia: An overview. Available online: http://www.sawea.org/pdf/waterarabia2013/Session_A/Desalination_In_Saudi_Arabia_An_Overview1_Dr_Nada.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2019).
- Saudi Arabia Population (LIVE). Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/saudi-arabia-population (accessed on 15 November 2019).
- Industry in Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.sidf.gov.sa/en/IndustryinSaudiArabia/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 8 November 2019).
- Alyemeni, M.N.; Almohisen, I.A. Traffic and industrial activities around Riyadh cause the accumulation of heavy metals in legumes: A. case study. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prospero, J.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.; Gill, T. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the NIMBUS 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET: A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Ward, D.E.; Dubovik, O.; Reid, J.S.; Smirnov, A.; Mukelavi, M.M.; Hsu, N.C.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I. Characterization of the optical properties of biomass burning aerosols in Zambia during the 1997 ZIBBEE Field Campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 3425–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.; King, M.; Kaufman, Y.; Eck, T.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol properties retrieved from aerosol robotic network (AERONET) sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, D.M.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Sinyuk, A.; Smirnov, A.; Slutsker, I.; Dickerson, R.R.; Thompson, A.M.; Schafer, J.S. An analysis of AERONET aerosol absorption properties and classifications representative of aerosol source regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D17203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Dubovik, O.; O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Westphal, D.L.; Goroch, A.K.; Pietras, C.; Slutsker, I. Atmospheric aerosol optical properties in the Persian Gulf. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobelspiesse, K.D.; Pietras, C.; Fargion, G.S.; Wang, M.; Frouin, R.; Miller, M.A.; Subramaniam, A.; Balch, W.M. Maritime aerosol optical thickness measured by handheld sun photometers. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamano, M.; Shiobara, M.; Arao, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Aerosol optical characteristics in the yellow sand events observed in May, 1982 in Nagasaki. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 67, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Ångström exponent derived aerosol optical depth over the Ganga basin, India. Ann. and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D07207. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.S.; Eck, T.F.; Christopher, S.A.; Hobbs, P.V.; Holben, B.N. Use of the Ångström exponent to estimate the variability of optical and physical properties of aging smoke particles in Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 27473–27489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.; Strabala, K.; Menzel, W.; Frey, R.; Moeller, C.; Gumley, L. Discriminating clear sky from clouds with MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 32141–32157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S.; Ichoku, C.; Kahn, R.; Eck, T.F. Global evaluation of the Collection 5 MODIS dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.; Rolph, G.; Stunder, B.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. 2015: NOAA’s HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.; Yan, F.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Mahowald, N.; Schultz, M.; Wild, M.; Wu, Y.; Yu, C. Anthropogenic and natural contributions to regional trends in aerosol optical depth, 1980–2006. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, 148–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D.; Li, R.; Raghavan, S.; Liong, S. Investigating the relationship between aerosol optical depth and precipitation over Southeast Asia with relative humidity as an influencing factor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, A. Dust Storms over Saudi Arabia: Temporal and Spatial Characteristics, Climatology and Synoptic Case Studies. Ph.D. Thesis, RMIT University, Melbourne, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
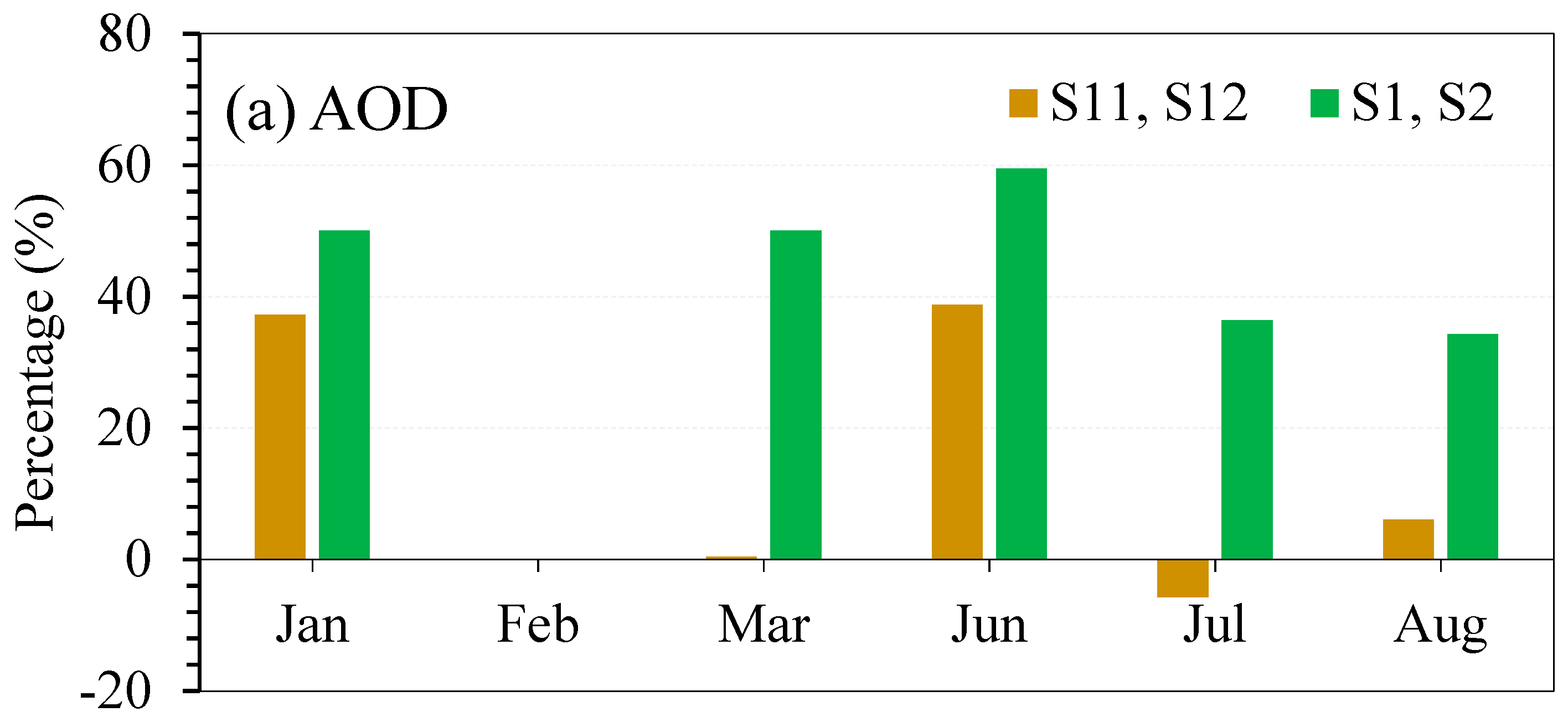
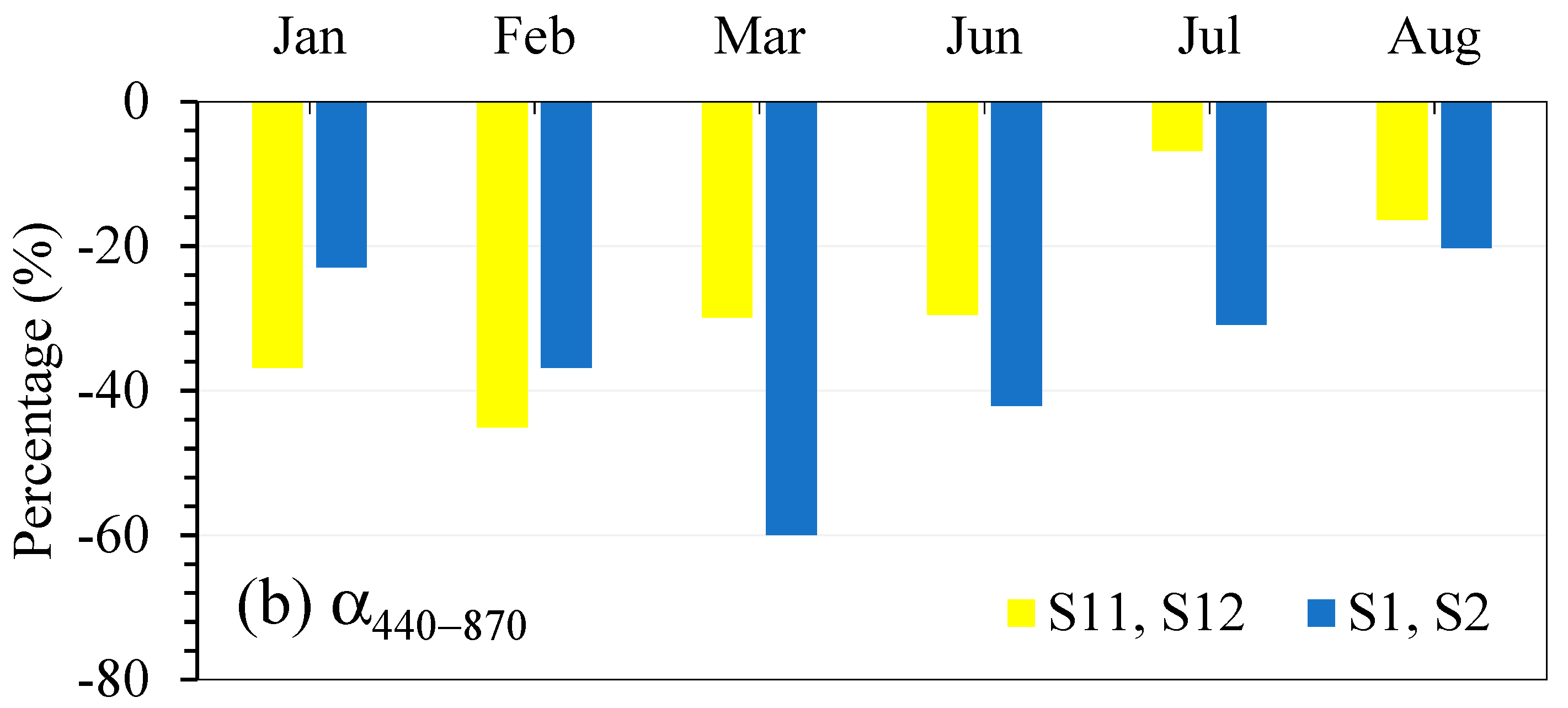
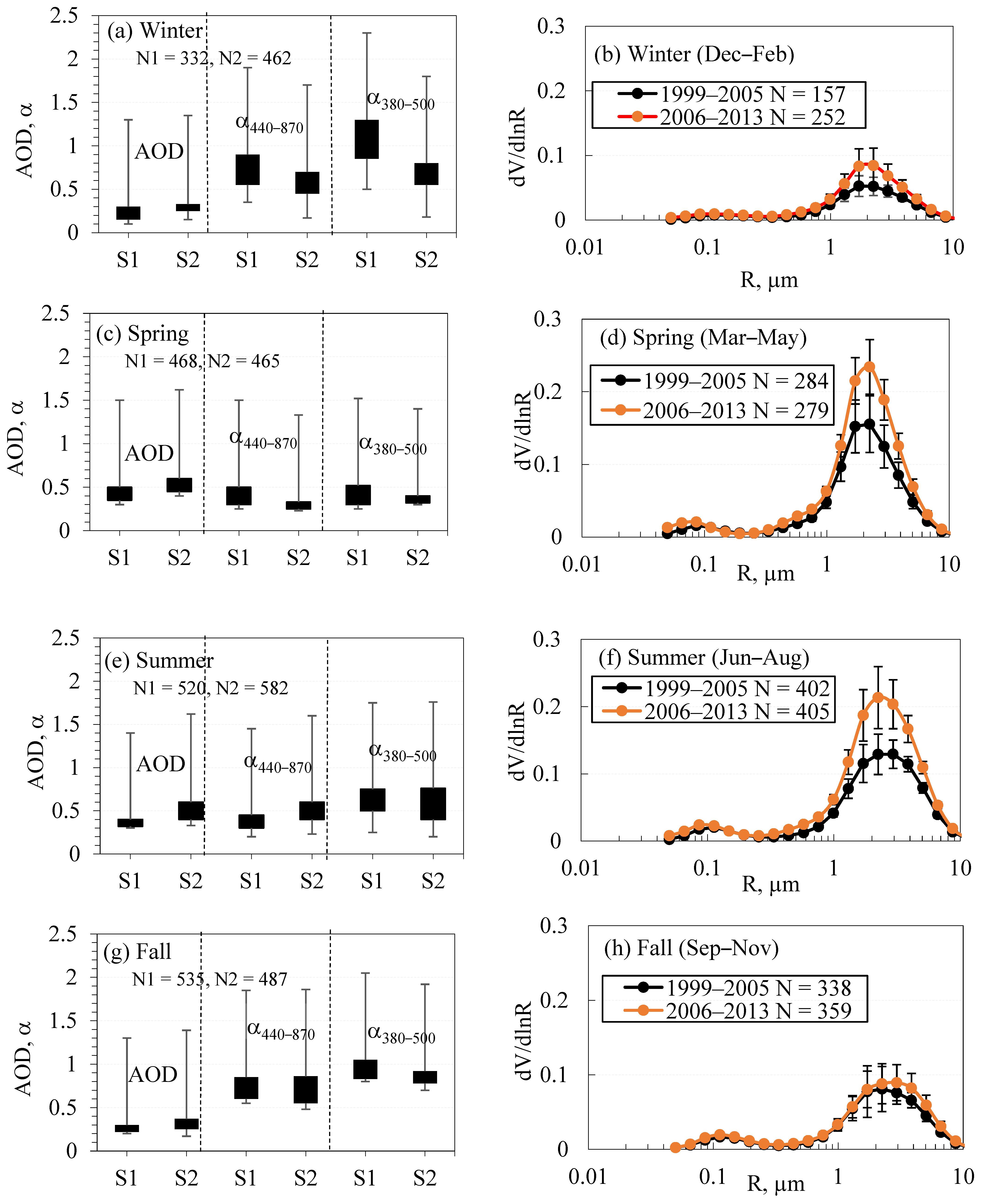
| M | S1 | S2 | p | t | M | S1 | S2 | p | t | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Jan | 112 | 158 | Mar | 183 | 153 | ||||
| AOD | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 1.81 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.01 | 1.89 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 2.01 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 2.35 | ||
| α380–500 | 1.19 | 0.78 | 0.02 | 2.01 | 0.56 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 2.13 | ||
| N | Feb | 115 | 157 | Apr | 140 | 135 | ||||
| AOD | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.05 | 1.79 | 0.42 | 0.54 | 0.10 | 2.13 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.57 | 0.36 | 0.03 | 1.89 | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 2.35 | ||
| α380–500 | 0.84 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 1.85 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 1.94 | ||
| N | May | 163 | 177 | Jul | 158 | 204 | ||||
| AOD | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.14 | 2.02 | 0.33 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 1.83 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.38 | 2.01 | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 1.94 | ||
| α380–500 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 1.89 | 0.68 | 0.58 | 0.15 | 1.94 | ||
| N | Jun | 171 | 187 | Aug | 191 | 191 | ||||
| AOD | 0.37 | 0.59 | 0.01 | 1.85 | 0.35 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 1.83 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 2.01 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.08 | 2.13 | ||
| α380–500 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 1.85 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.29 | 1.89 | ||
| N | Sep | 162 | 177 | Nov | 170 | 138 | ||||
| AOD | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.01 | 1.89 | 0.23 | 0.219 | 0.40 | 2.13 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.65 | 0.57 | 0.26 | 2.35 | 0.66 | 0.88 | 0.02 | 2.02 | ||
| α380–500 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.10 | 1.94 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.43 | 2.35 | ||
| N | Oct | 203 | 172 | Dec | 105 | 147 | ||||
| AOD | 0.23 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 1.89 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 2.35 | ||
| α440–870 | 0.83 | 0.69 | 0.01 | 1.89 | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.08 | 1.94 | ||
| α380–500 | 1.10 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 2.13 | 1.17 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 2.91 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Otaibi, M.; Farahat, A.; Tawabini, B.; Omar, M.H.; Ramadan, E.; Abuelgasim, A.; P. Singh, R. Long-Term Aerosol Trends and Variability over Central Saudi Arabia Using Optical Characteristics from Solar Village AERONET Measurements. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120752
Al Otaibi M, Farahat A, Tawabini B, Omar MH, Ramadan E, Abuelgasim A, P. Singh R. Long-Term Aerosol Trends and Variability over Central Saudi Arabia Using Optical Characteristics from Solar Village AERONET Measurements. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(12):752. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120752
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Otaibi, Mohammed, Ashraf Farahat, Bassam Tawabini, M. Hafidz Omar, Emad Ramadan, Abdelgadir Abuelgasim, and Ramesh P. Singh. 2019. "Long-Term Aerosol Trends and Variability over Central Saudi Arabia Using Optical Characteristics from Solar Village AERONET Measurements" Atmosphere 10, no. 12: 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120752
APA StyleAl Otaibi, M., Farahat, A., Tawabini, B., Omar, M. H., Ramadan, E., Abuelgasim, A., & P. Singh, R. (2019). Long-Term Aerosol Trends and Variability over Central Saudi Arabia Using Optical Characteristics from Solar Village AERONET Measurements. Atmosphere, 10(12), 752. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10120752







